Investigation of the Effects of Polymer-Based Grinding Aids on the Surface Chemistry Properties of Cement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterizations of PCEs
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Zeta Potential
2.3.2. Turbidity
2.3.3. Ion Chromatography
2.3.4. Rheology
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mardani-Aghabaglou, A.; Tuyan, M.; Yılmaz, G.; Arıöz, Ö.; Ramyar, K. Effect of different types of superplasticizers on fresh, rheological and strength properties of selfconsolidating concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.M.; Palacios, M.; Puertas, F. Compatibility between polycarboxylate-based admixtures and blended-cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 35, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Nicolás, M.; Duran, A.; Navarro-Blasco, I.; Fernández, J.M.; Sirera, R.; Alvarez, J.I. Study on the effectiveness of PNS and LS superplasticizers in air lime-based mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 82, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Plank, J. Synthesis, and properties of a vinyl ether-based polycarboxylate superplasticizer for concrete possessing clay tolerance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hooton, R.D. Effects of organosilane-modified polycarboxylate superplasticizer on the fluidity and hydration properties of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 132, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, X. Correlations of the dispersing capability of NSF and PCE types of superplasticizers and their impacts on cement hydration with the adsorption in fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Song, F.; Wang, T.; Fan, S.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J. Effect of the different hydrophobic groups of polycarboxylate superplasticizers on the properties in cement mortars. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuhiro, Y.; Tazawa, E.; Kawai, K.; Enohata, T. Adsorption characteristics of superplasticisers on cement component minerals. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar]
- Plank, J.; Hirsch, C. Impact of zeta potential of early cement hydration phases on superplasticizer adsorption. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.J.; Ferraris, C.F. Acoustophoretic characterization of cement suspensions. Mater. Struct. 2002, 35, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninness, B.J.; Bousfield, D.W.; Tripp, C.P. The importance of adsorbed cationic surfactant structure in dictating the subsequent interaction of anionic surfactants and polyelectrolytes with pigment surfaces. Colloid Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 203, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhang, S.; Banthia, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Interpreting the early-age reaction process of alkali-activated slag by using combined embedded ultrasonic measurement, thermal analysis, XRD, FTIR and SEM. Compos. B Eng. 2020, 186, 107840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowke, D.; Gehlen, C. The zeta potential of cement and additions in cementitious suspensions with high solid fraction. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 95, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plassard, C.; Lesniewska, E.; Pochard, I.; Nonat, A. Nanoscale experimental investigation of particle interactions at the origin of the cohesion of cement. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7263–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.J.; Kunjappu, J.T. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gagné, R. Shrinkage-reducing admixtures. In Science and Technology of Concrete Admixtures; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 457–469. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, H.S.; Barakat, R.; Alhilali, A.; Saleh, M.; Cheeseman, C.R. Hydrophobic concrete using wastepaper sludge ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 70, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.Y.; Gauvin, F.; Wang, F.Z.; Liu, G.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Effect of hydrophobicity on autogenous shrinkage and carbonation of alkali activated slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.; Lu, Z.; Hou, S. Effects of the charge characteristics of polycarboxylate superplasticizers on the adsorption and the retardation in cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Wang, S.; Zeng, L.; Peng, X. Effect of styrene-butadiene rubber latex on the rheological behavior and pore structure of cement paste. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 163, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, E.; Ghahari, S.A.; Feng, Y.; Severgnini, F.; Lu, N. Effect of zinc oxide and Al-zinc oxide nanoparticles on the rheological properties of cement paste. Compos. B Eng. 2016, 105, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Du, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, F.; Fang, K.; Yu, J.; Sheng, B. Syntheses of polycarboxylate superplasticizers: Microwave induction versus conventional thermal induction. Compos. B Eng. 2021, 207, 108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y. Study of the air-entraining behavior based on the interactions between cement particles and selected cationic, anionic and nonionic surfactants. Materials 2020, 13, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elakneswaran, Y.; Nawa, T.; Kurumisawa, K. Zeta potential study of paste blends with slag. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Gretz, M. Study on the interaction between anionic and cationic latex particles and Portland cement. Colloid Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 330, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Emmerling, S.; Pakusch, J.; Rueckel, M.; Nieberle, J. Retardation effect of styrene-acrylate copolymer latexes on cement hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 75, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Shang, S.; Yin, F.; Aishah, A.; Salmiah, A.; Ooi, T.L. Adsorptive behavior of surfactants on surface of Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroh, J.; Schlegel, M.C.; Schmidt, W.; Thi, Y.N.; Meng, B.; Emmerling, F. Time-resolved in situ investigation of Portland cement hydration influenced by chemical admixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 197-1; Cement. Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements. British Standard Institution: London, UK, 2011.
- Özcan, E.D.; Çinku, K.; Özdamar, Ş.; Özkan, Ş.G.; Ergin, H. Investigation of the effect of polymer-based novel grinding aids on cement grinding efficiency. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 139, 51870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papo, A.; Piani, L. Effect of various superplasticisers on the rheological properties of Portland cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 2097–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfill, P.F.G. A viscometric study of cement pastes including a note on experimental techniques. Mag. Concr. Res. 1981, 33, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M.; Adams, W.J.; Schennach, R.; Cocke, D.L. A review of cement-superplasticizer interactions and their models. Adv. Cement Res. 2000, 12, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, M.; Puertas, F.; Bowen, P.; Houst, Y.F. Effect of PCs superplasticizers on the rheological properties and hydration process of slag-blended cement pastes. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Ogawa, S.; Hanehara, S. Controlling of the adsorption and dispersing force of polycarboxylate-type superplasticizer by sulfate ion concentration in aqueous phase. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.J.; Zimmermann, J.; Hampel, C.; Kurz, C.; Schober, I.; Frunz, L.; Plassard, C.; Lesniewska, E. The role of adsorption energy in the sulfate-polycarboxylate competition. ACI Int. Conf. Superplast. Other Chem. Admix. 2009, 20, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, M.R.; Berliner, R. Investigation of the structure of ettringite by time-of-flight neutron powder diffraction techniques. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangeon, S.; Claret, F.; Roosz, C.; Sato, T.; Gaboreau, S.; Linard, Y. Structure of nanocrystalline calcium silicate hydrates: Insights from X-ray diffraction, synchrotron X-ray absorption and nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2016, 49, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbez, C.; Jonsson, B.; Pochard, I.; Nonat, A.; Cabane, B. Surface charge density and electrokinetic potential of highly charged minerals: Experiments and Monte Carlo simulations on calcium silicate hydrate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 9219–9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medala, M.; Labbez, C.; Pochard, I.; Nonat, A. Ettringite surface chemistry: Interplay of electrostatic and ion specificity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 354, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönlein, M.; Plank, J. Influence of PCE kind and dosage on ettringite crystallization performed under terrestrial and microgravity conditions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 3575–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Zhu, H.; Zeng, X.; Long, G.; Xie, Y. How nano-bubble water and nano-silica affect the air-voids characteristics and freeze-thaw resistance of air-entrained cementitious materials at low atmospheric pressure. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 69, 106179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Lan, X.; Zhu, H.; Long, G.; Xie, Y. Investigation on air-voids structure and compressive strength of concrete at low atmospheric pressure. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 122, 104139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Lan, X.; Zhu, H.; Liu, H.; Umar, H.A.; Xie, Y.; Long, G.; Ma, C. A review on bubble stability in fresh concrete: Mechanisms and main factors. Materials 2020, 13, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
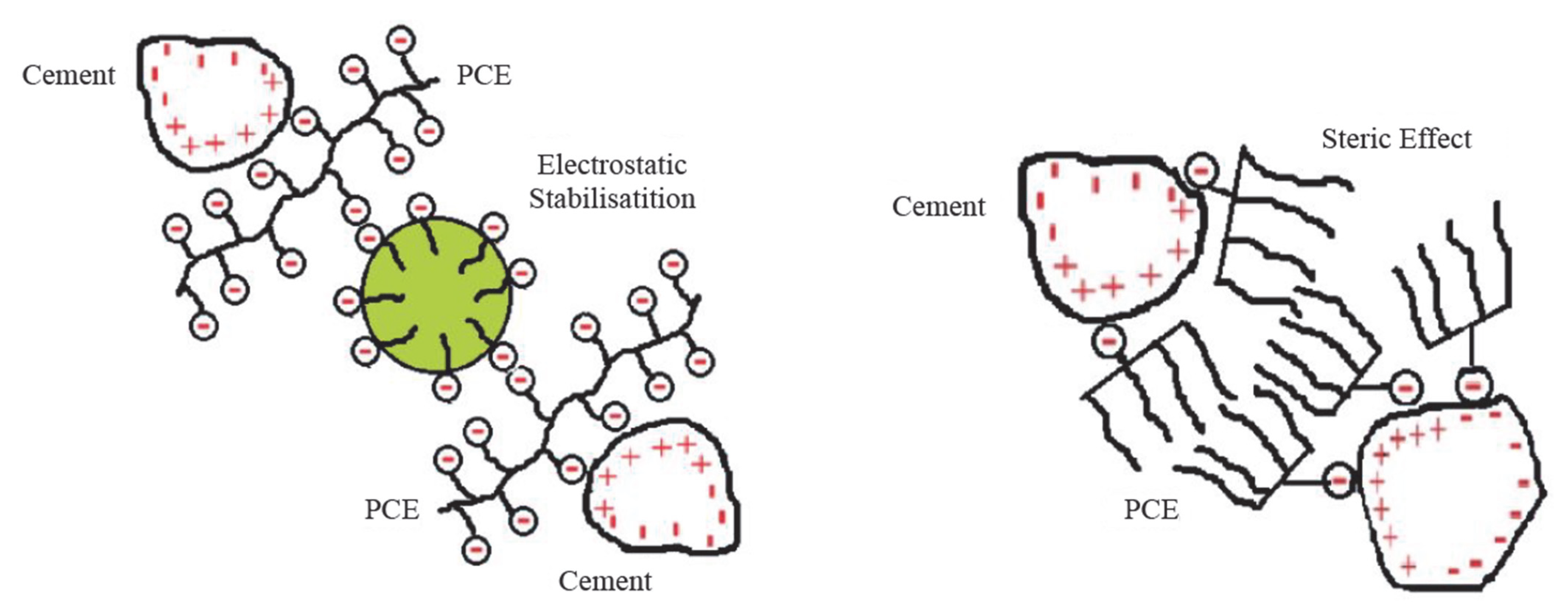
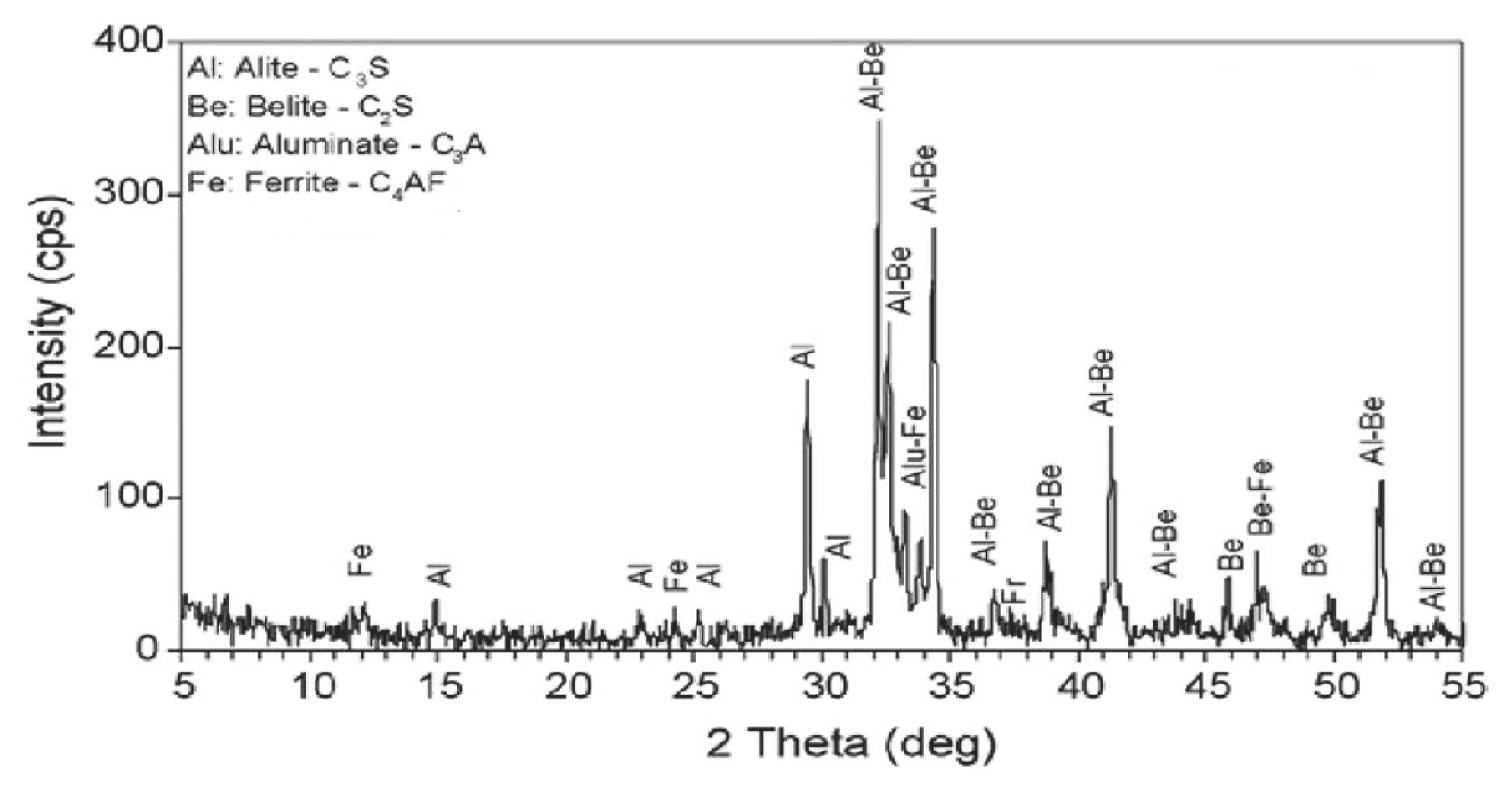
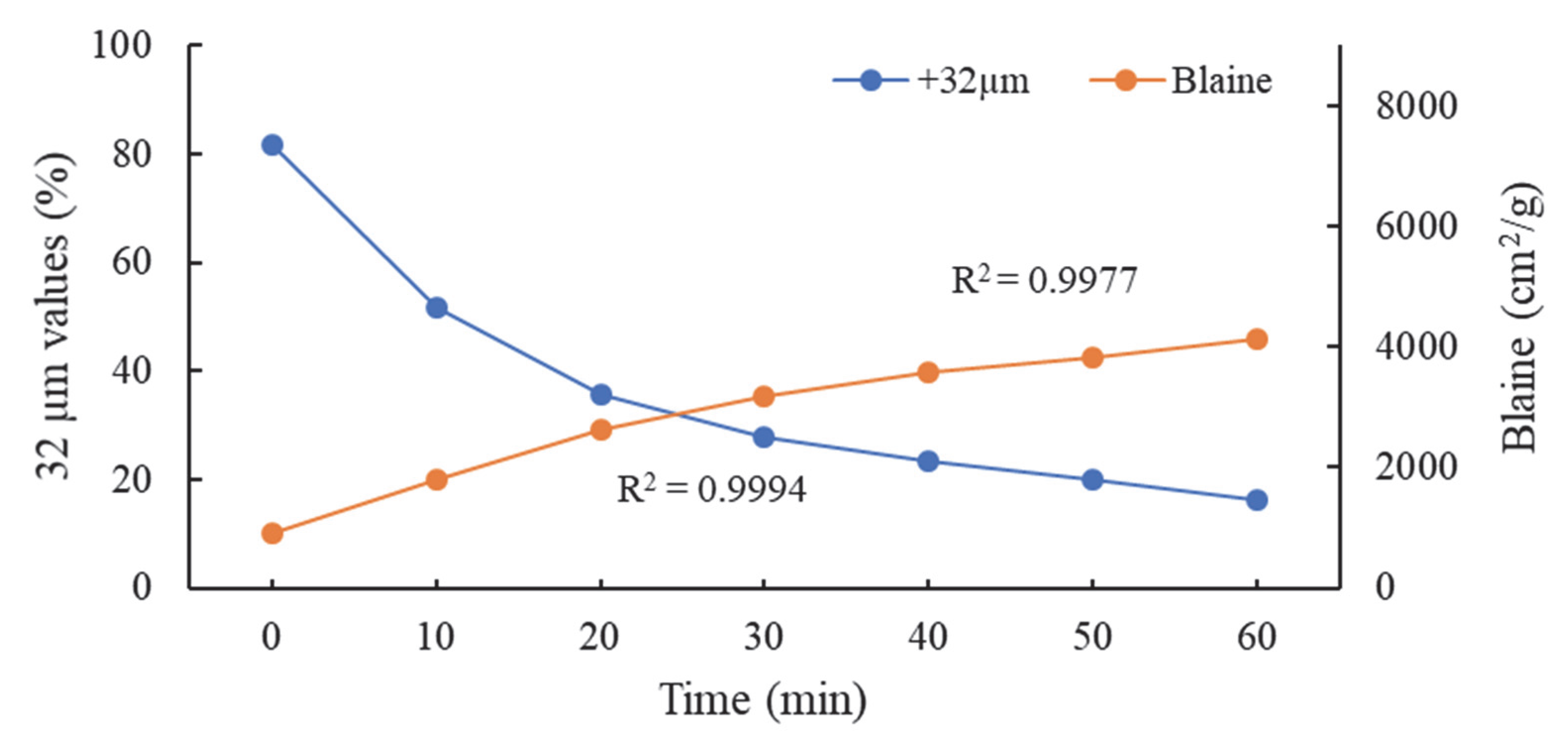
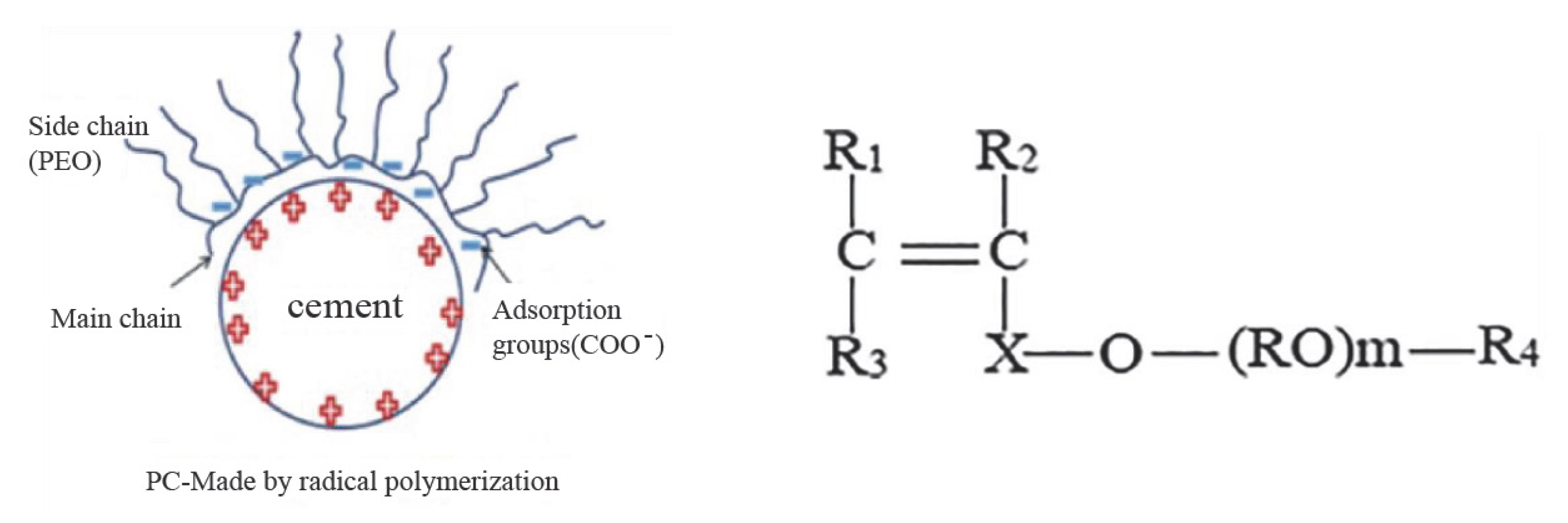
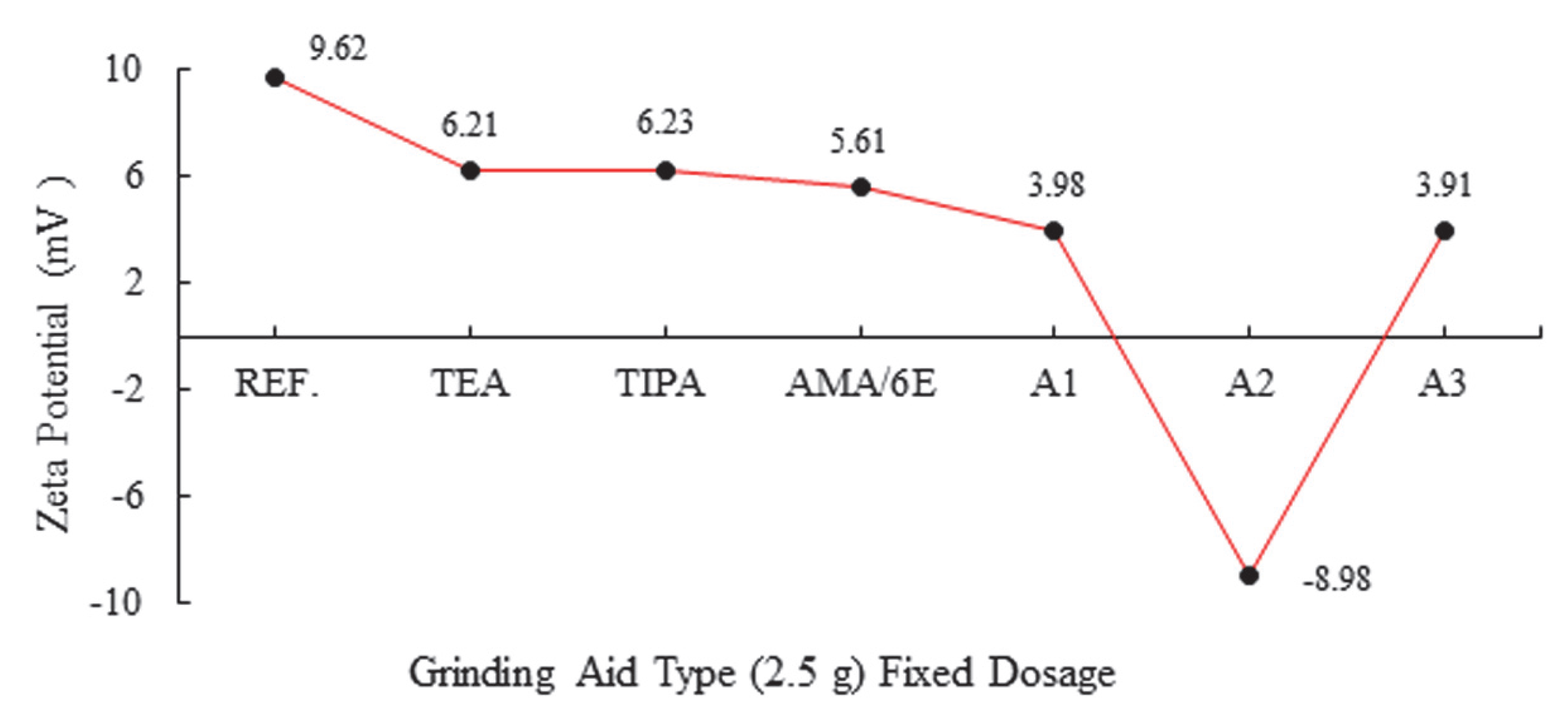
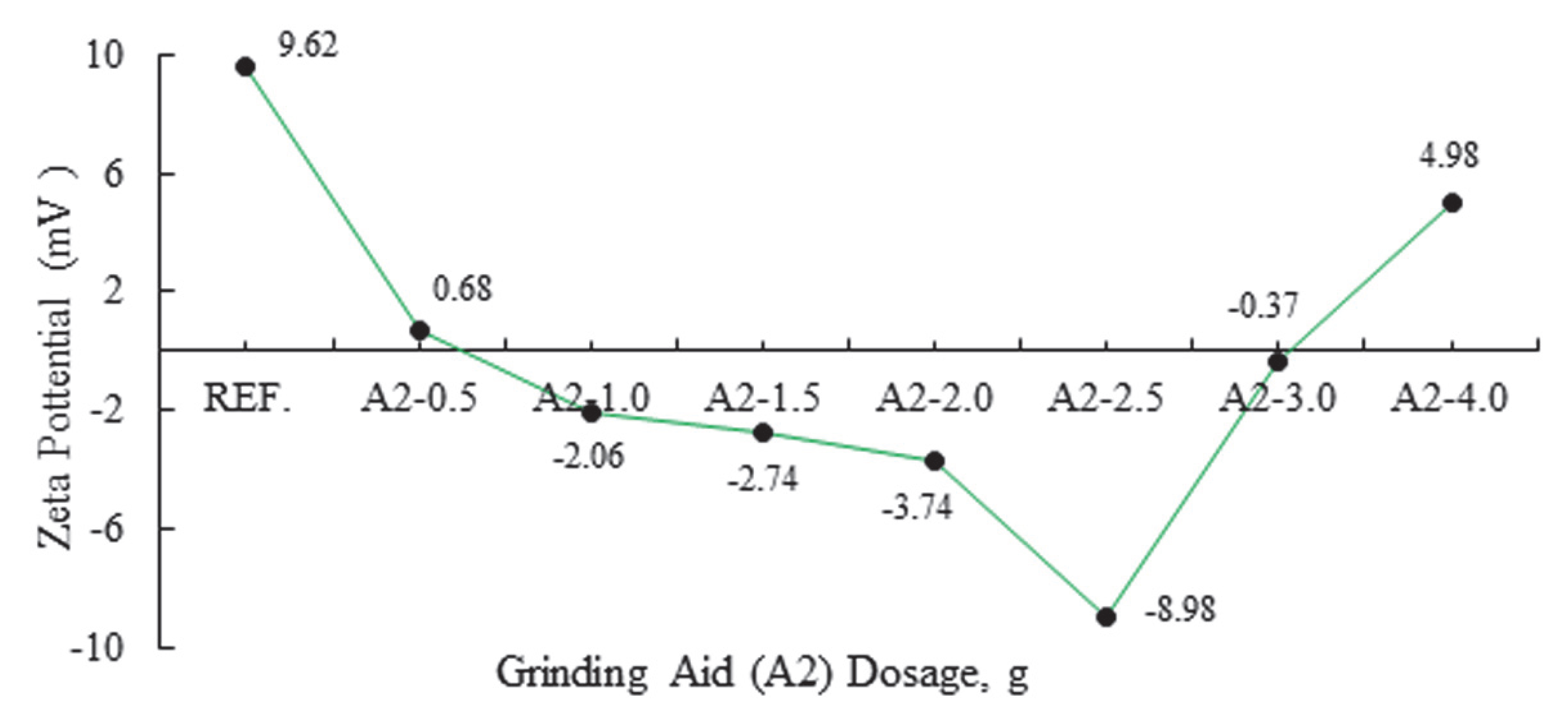
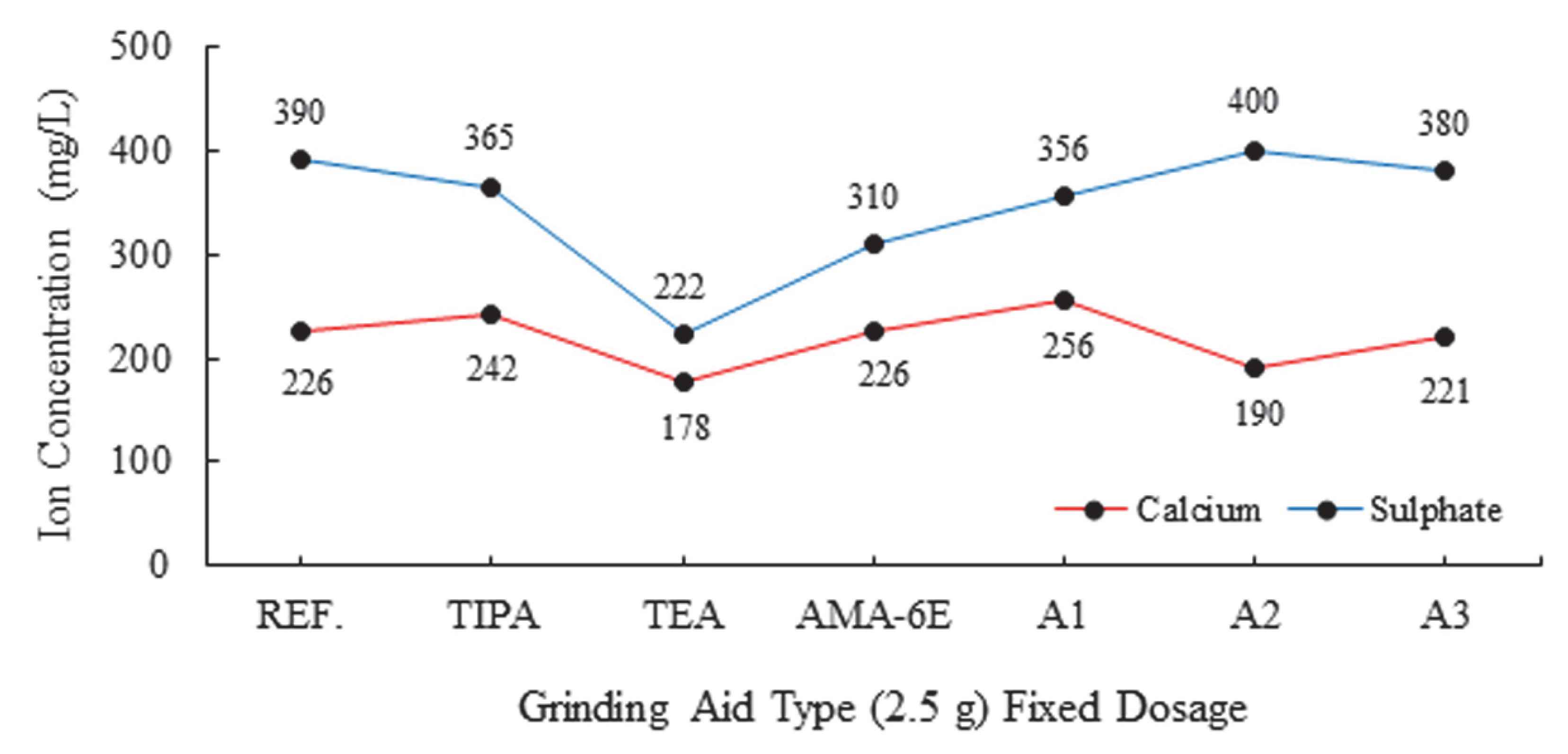
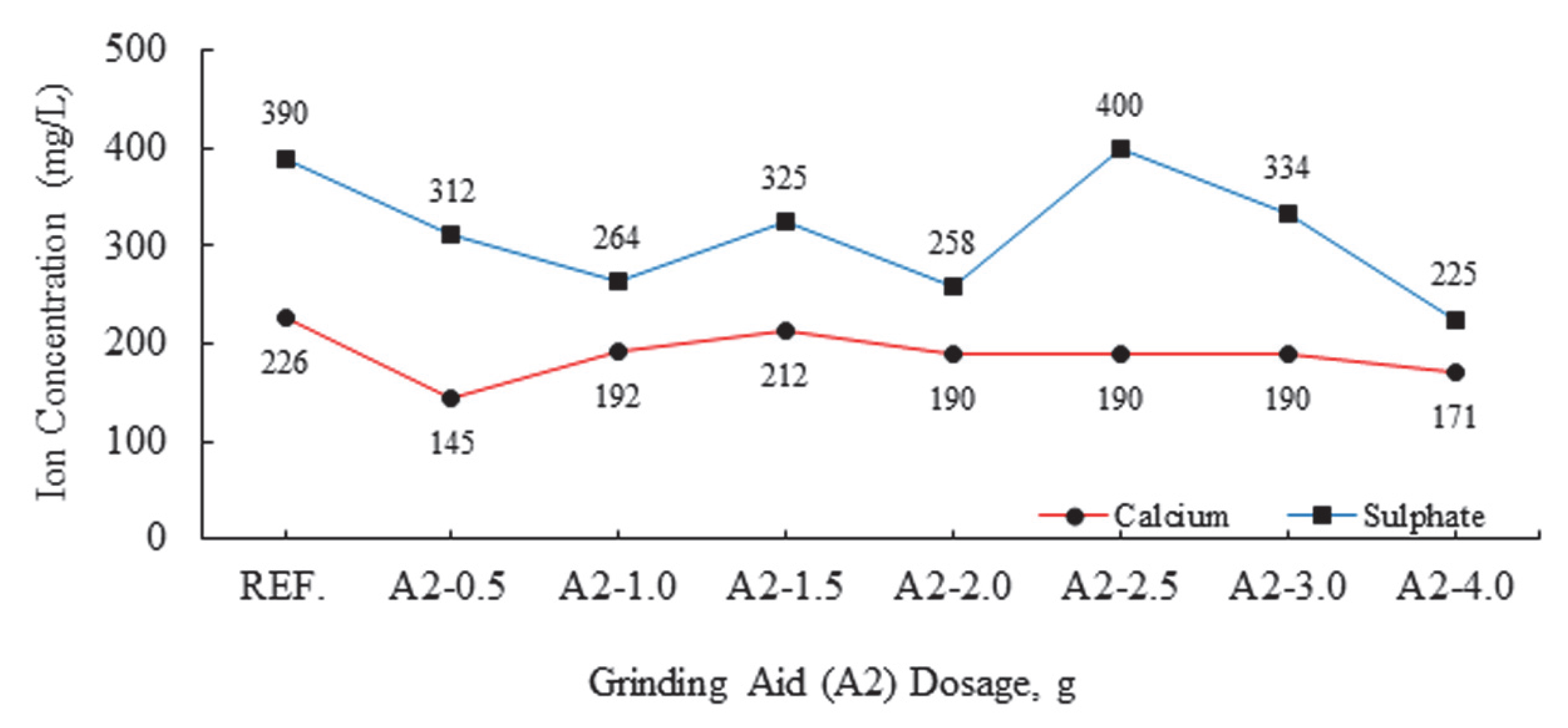
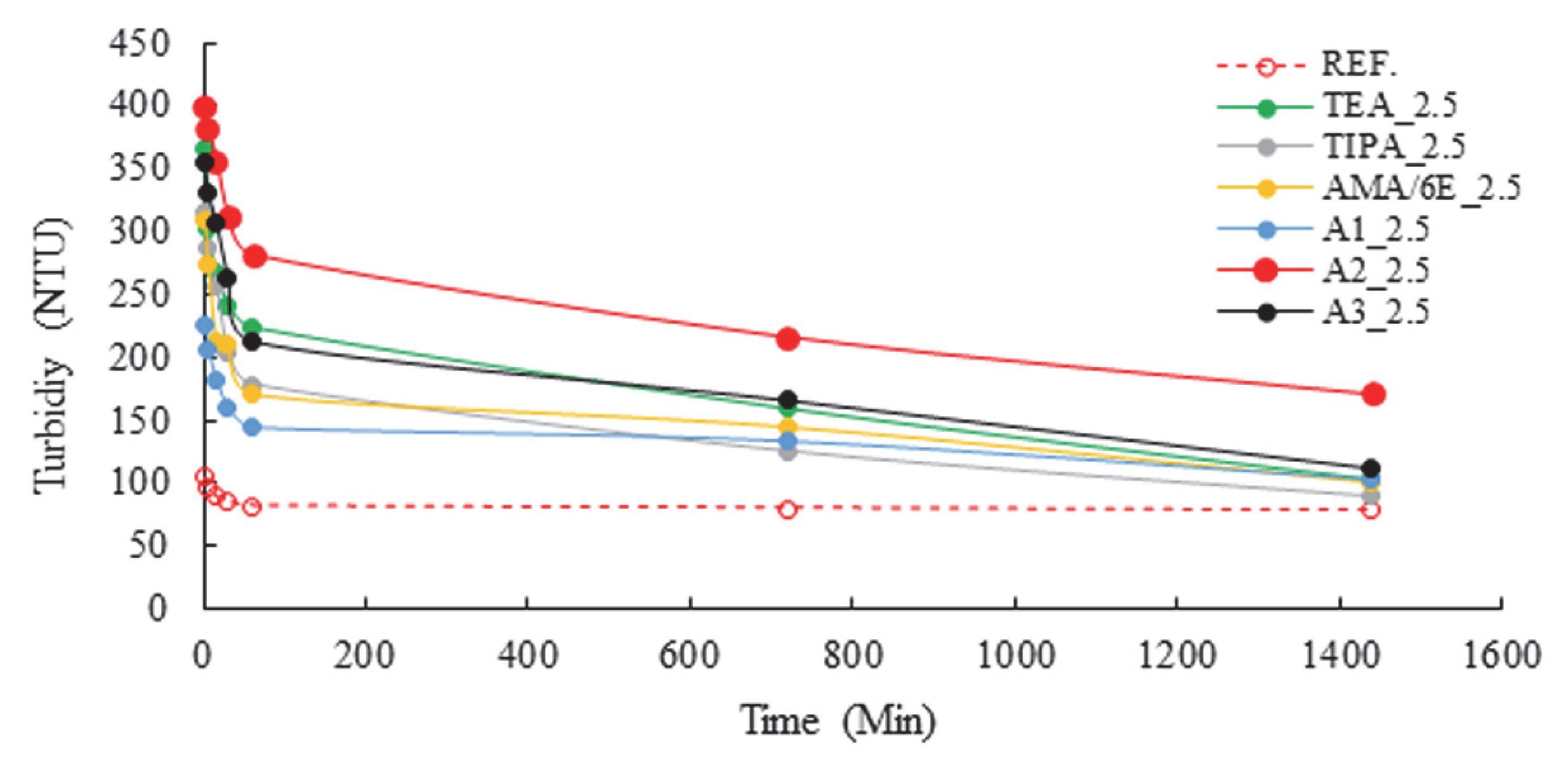
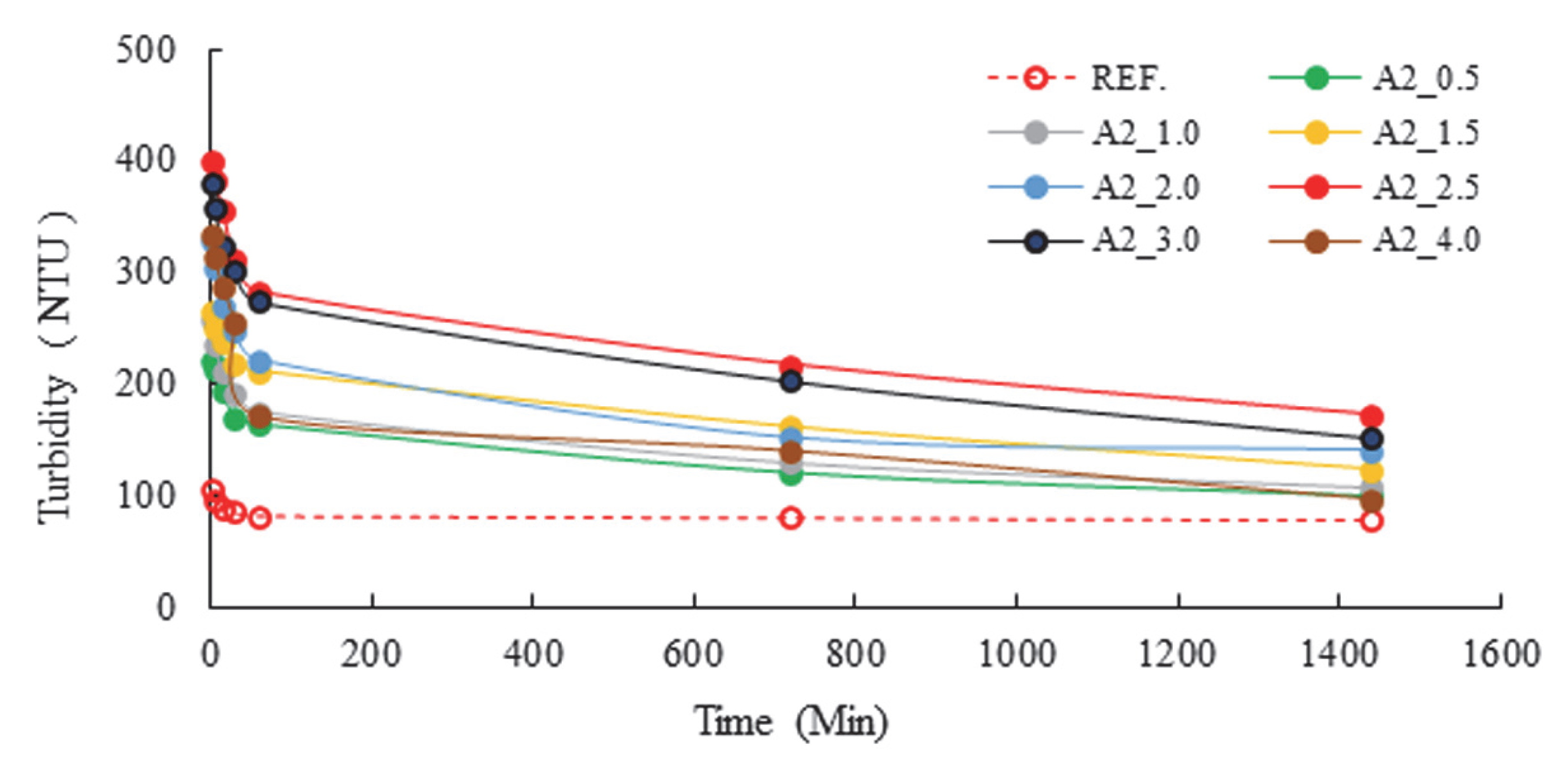
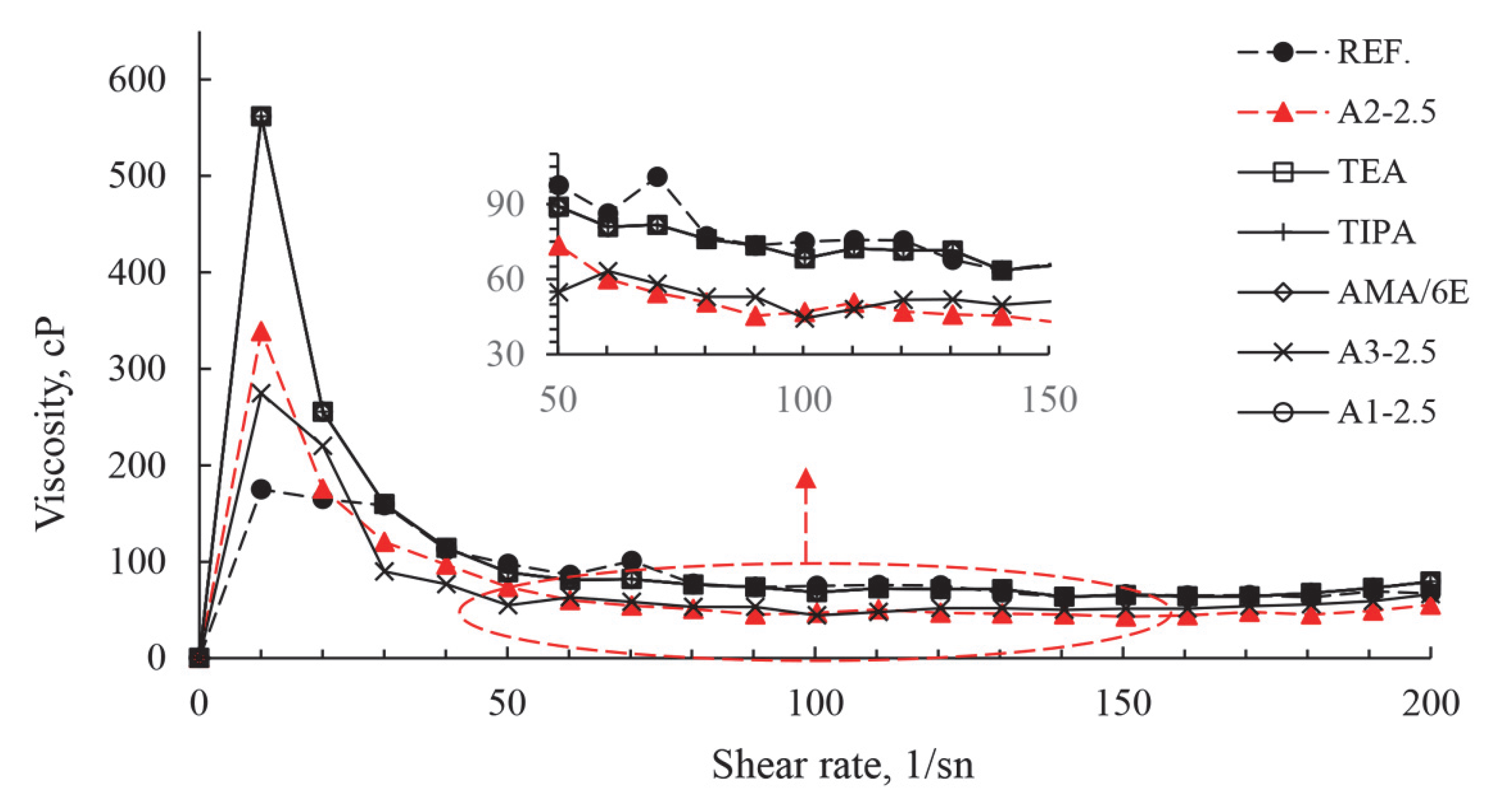
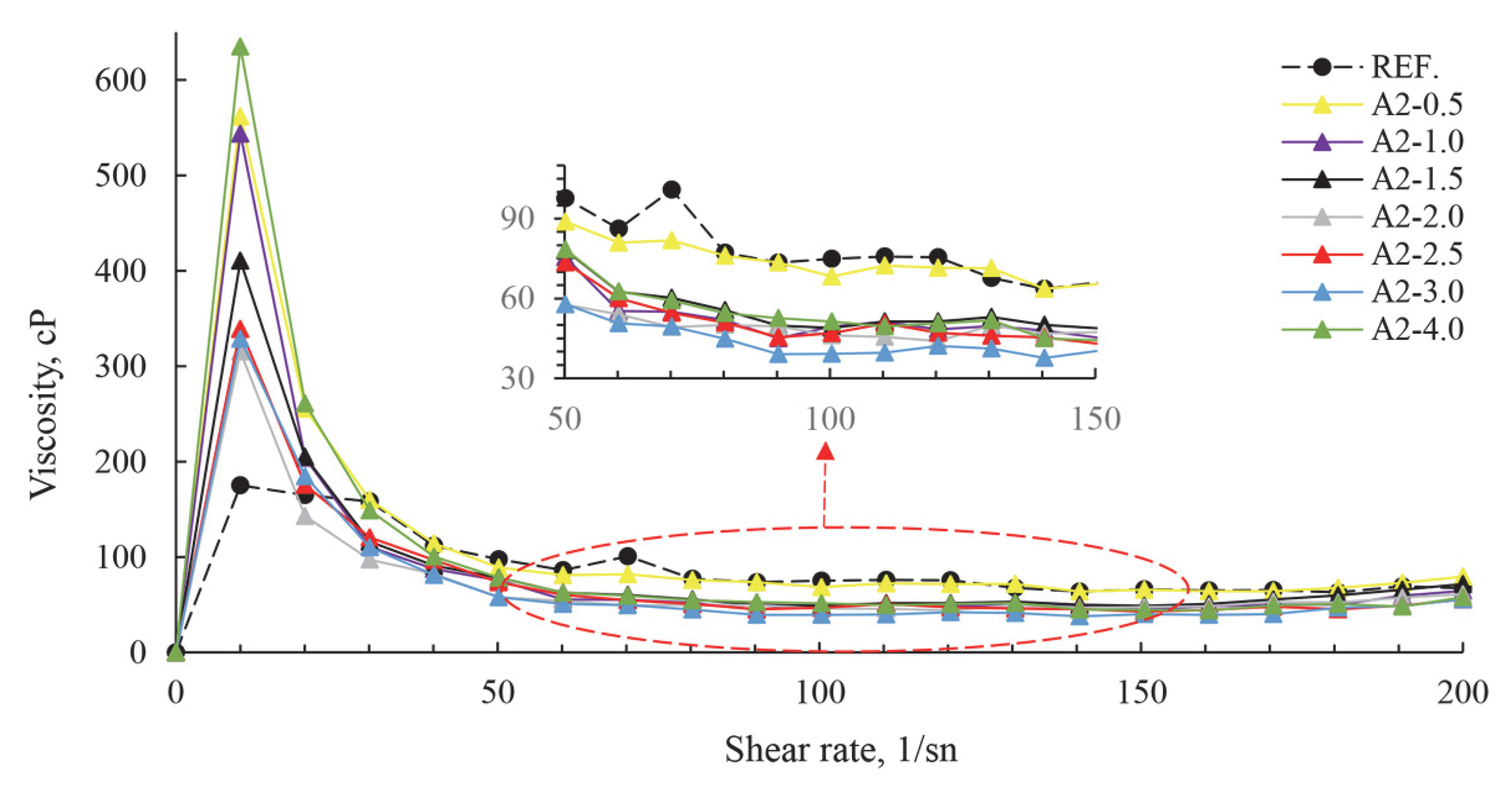
| Major Oxides | Clinker (%) | Gypsum (%) | Limestone (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 20.62 | 1.45 | 0.00 |
| Al2O3 | 4.95 | 0.54 | 0.15 |
| Fe2O3 | 3.87 | 0.25 | 0.10 |
| CaO | 65.41 | 34.27 | 56.25 |
| MgO | 1.93 | 0.33 | 0.47 |
| SO3 | 0.63 | 40.83 | 0.04 |
| LOI | 0.41 | 22.22 | 42.67 |
| Na2O | 0.30 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| K2O | 0.73 | 0.11 | 0.02 |
| TiO2 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Mn3O4 | 0.23 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| Total | 99.38 | 100.03 | 99.74 |
| Polymer | Solid Rate (%) | pH | Color | Density (g/cm3) | Molecular Weight (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEA | 88 | 11.6 | Transparent | 1.12 | 149.19 |
| TIPA | 78 | 7.8 | Transparent | 1.02 | 191.27 |
| AMA-6E | 52 | 5.6 | Brown | 1.07 | 58,700 |
| A1 | 50 | 5.8 | Light Yellow | 1.05–1.15 | 59,000 |
| A2 | 50 | 5.73 | Transparent | 1.05–1.15 | 60,000 |
| A3 | 50 | 6.0 | Transparent | 1.05–1.15 | 58,900 |
| Analyze Name | Instrument |
|---|---|
| Zeta Potential | NanoBrook ZetaPALS |
| Ion Chromatography | Thermo Dionex ICS-1100 |
| Turbidity | Thermo Orion AQUAfast II AQ2010 |
| Viscosity | Brookfıeld R/S Plus Rheometer |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çinku, K.; Dengiz Özcan, E.; Özdamar, Ş.; Ergin, H. Investigation of the Effects of Polymer-Based Grinding Aids on the Surface Chemistry Properties of Cement. Polymers 2025, 17, 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192691
Çinku K, Dengiz Özcan E, Özdamar Ş, Ergin H. Investigation of the Effects of Polymer-Based Grinding Aids on the Surface Chemistry Properties of Cement. Polymers. 2025; 17(19):2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192691
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇinku, Kenan, Ebru Dengiz Özcan, Şenel Özdamar, and Hasan Ergin. 2025. "Investigation of the Effects of Polymer-Based Grinding Aids on the Surface Chemistry Properties of Cement" Polymers 17, no. 19: 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192691
APA StyleÇinku, K., Dengiz Özcan, E., Özdamar, Ş., & Ergin, H. (2025). Investigation of the Effects of Polymer-Based Grinding Aids on the Surface Chemistry Properties of Cement. Polymers, 17(19), 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192691






