Aging Mechanisms and Performance Degradation of XLPE Submarine Cable Insulation Under Marine Major Anion Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Solution Preparation
2.3. Characterization Methods
2.3.1. Volume Resistivity Testing
2.3.2. Dielectric Property Testing
2.3.3. Breakdown Field Strength Testing
2.3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy Testing
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
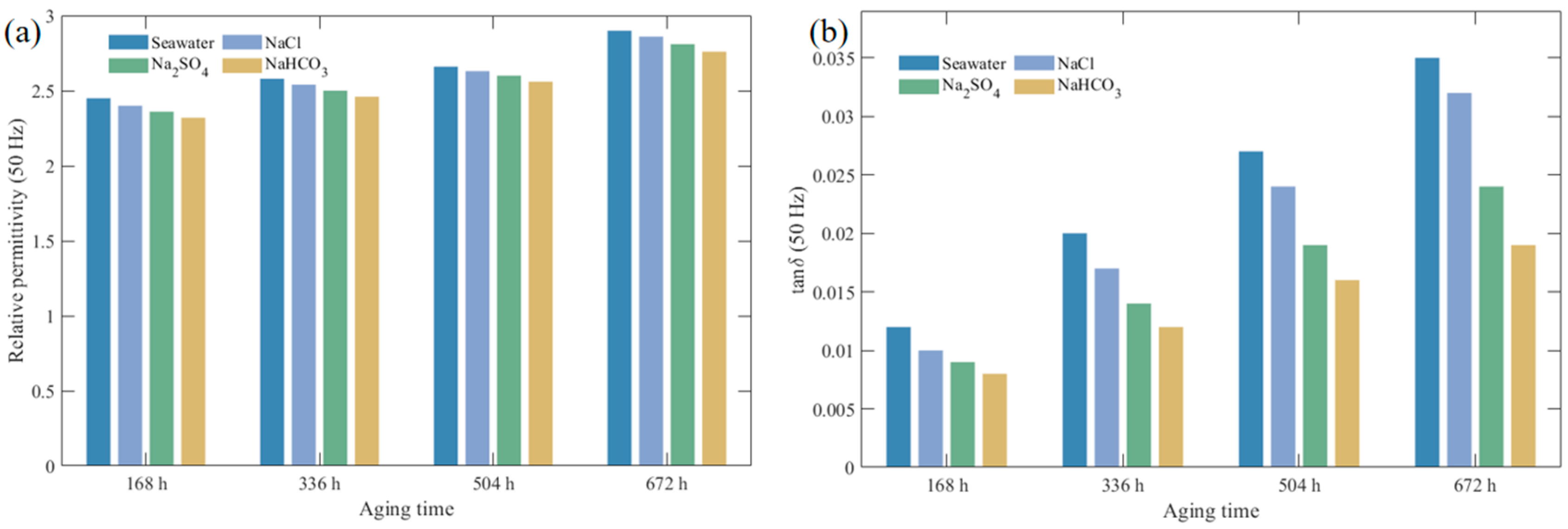
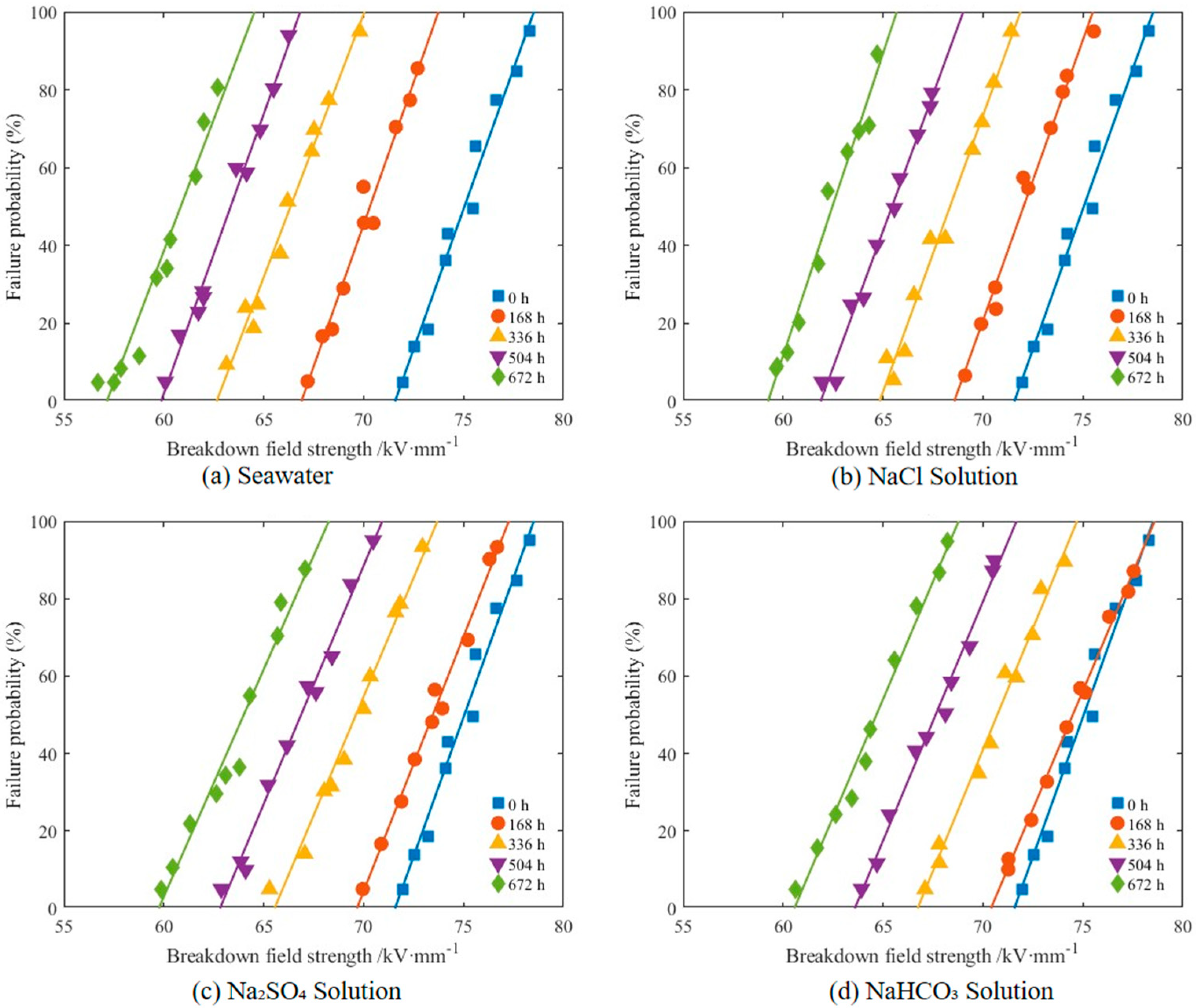
3.1. Electrical Performance Variation Analysis
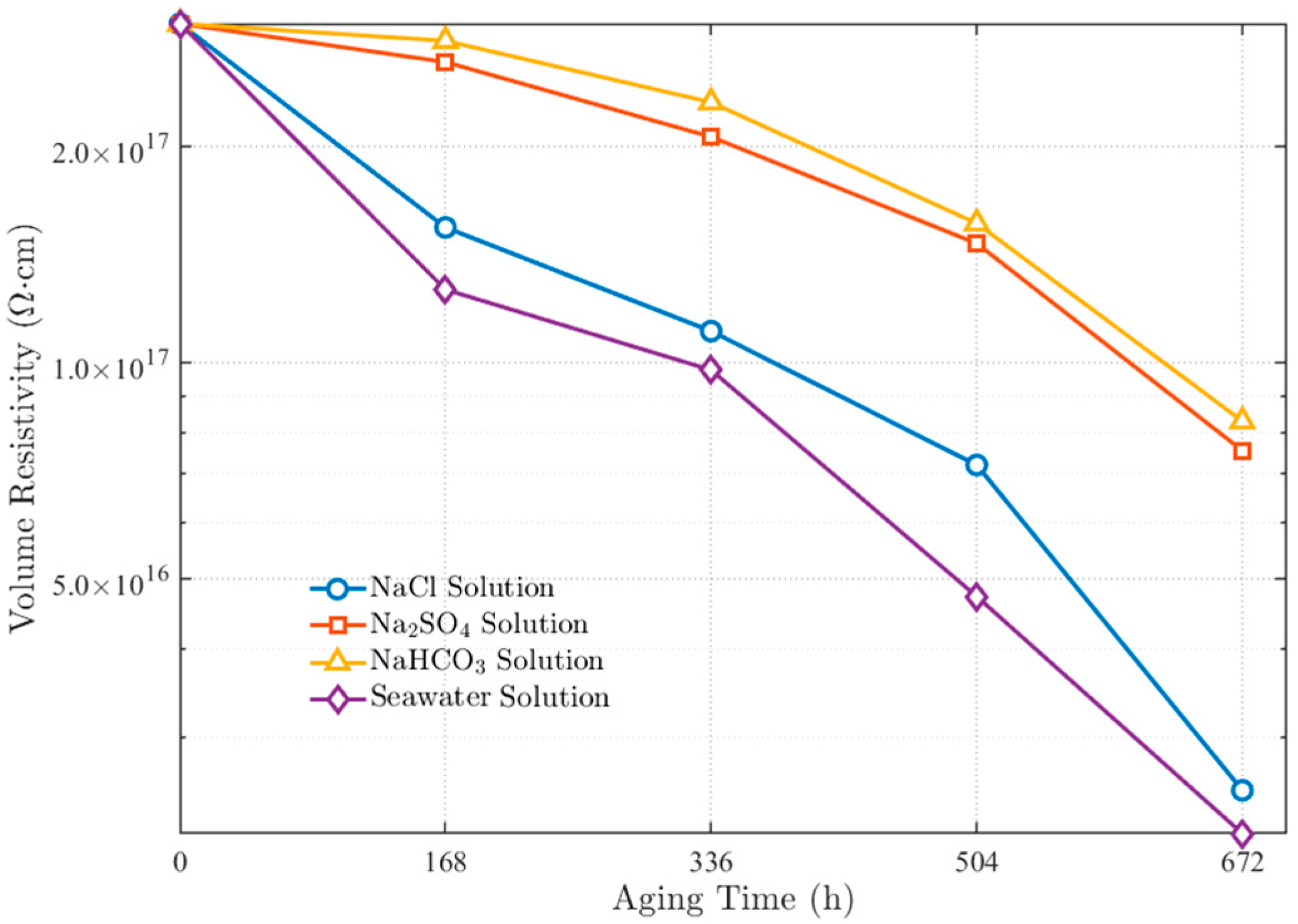
3.1.1. Volume Resistivity Variation Pattern
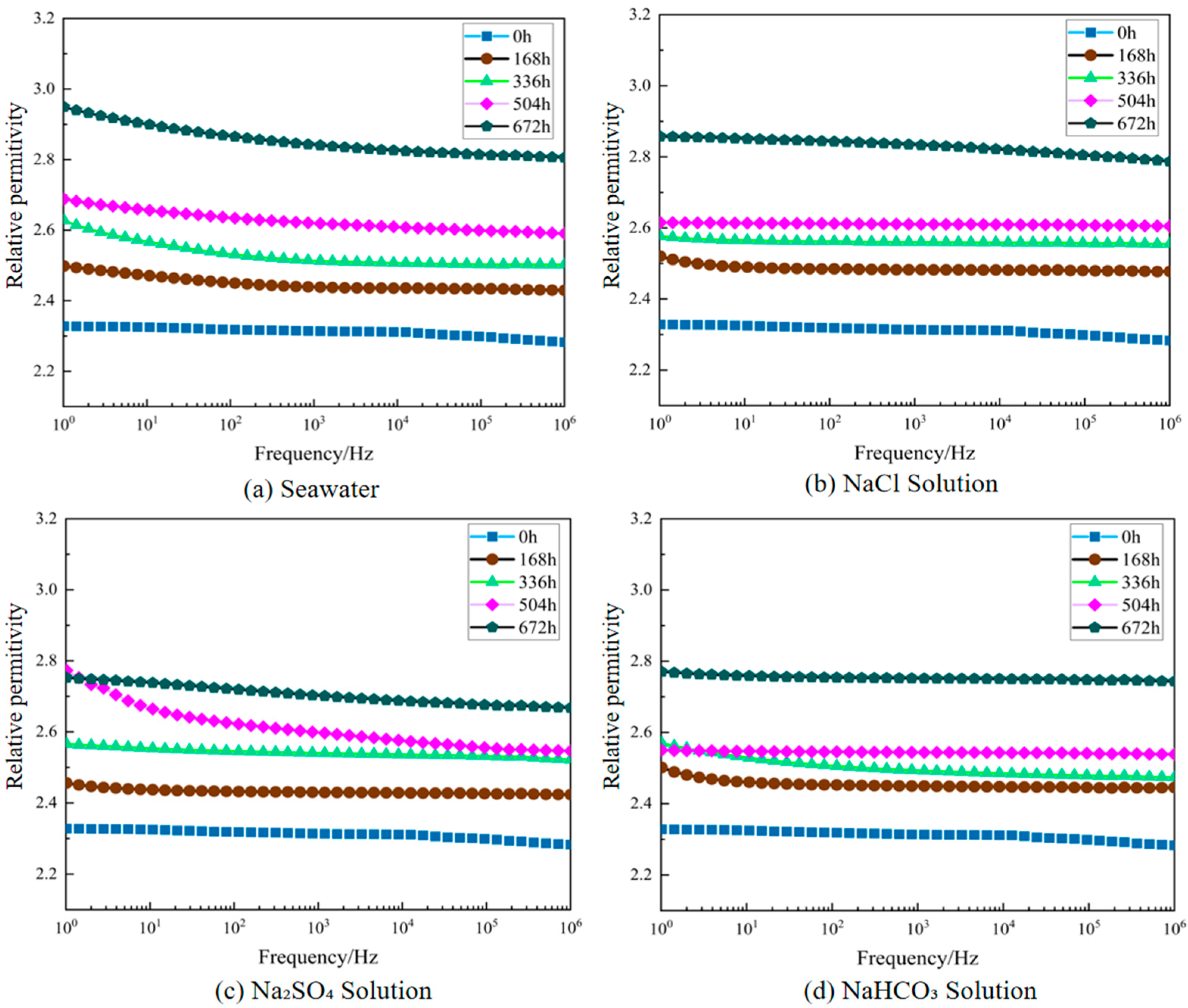
3.1.2. Dielectric Performance Variation
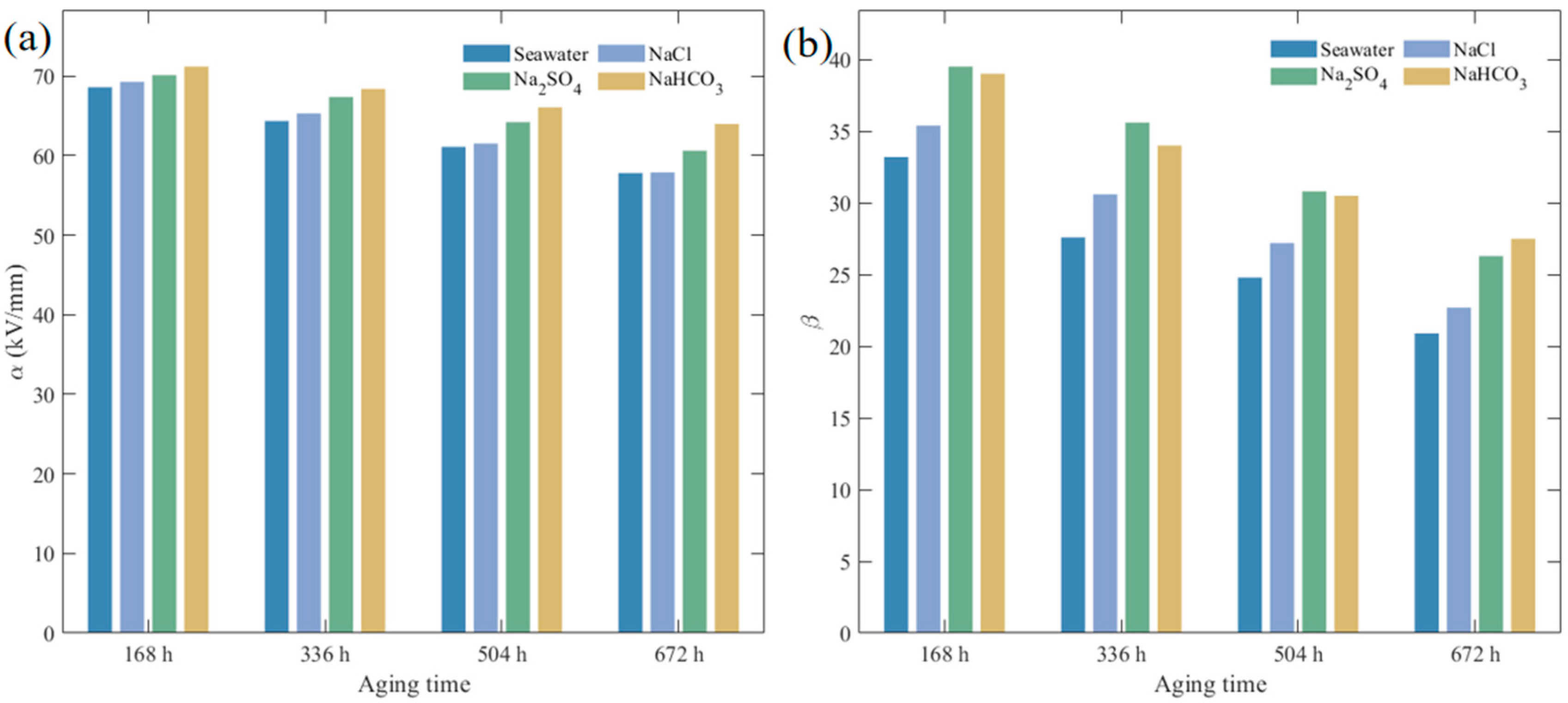
3.1.3. Breakdown Field Strength Degradation Characteristics
3.2. Material Structure Variation Analysis
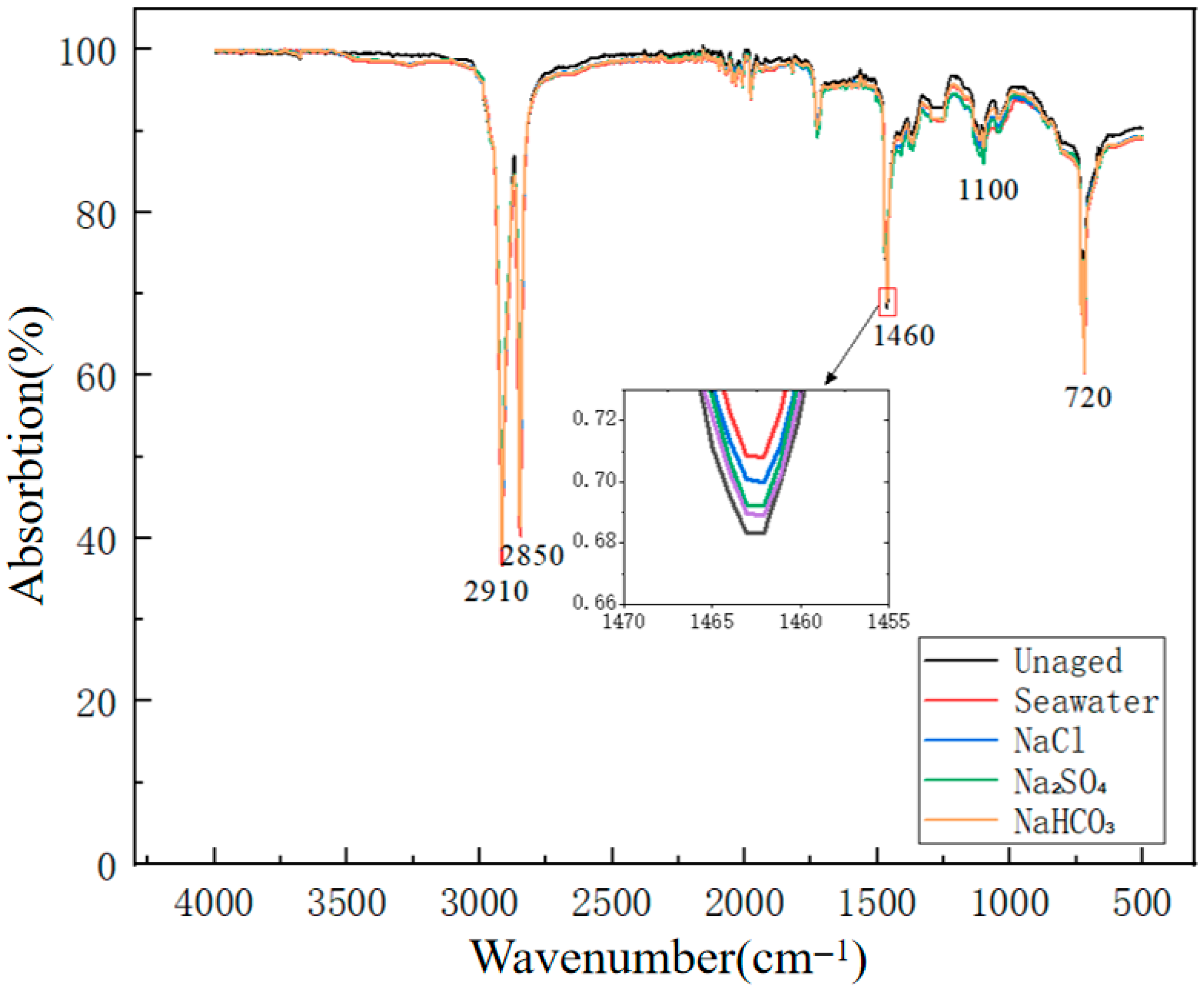
3.2.1. Chemical Structure Evolution (FTIR Analysis)
3.2.2. Microscopic Morphology Changes (SEM Analysis)
3.3. Correlation Between Electrical Degradation and Microstructural Changes
4. Degradation Mechanism Discussion
4.1. Single Anion Degradation Mechanism
4.2. Multi-Ion Synergistic Action Mechanisms
5. Conclusions
- Seawater environments cause the most severe XLPE performance degradation, with volume resistivity decreasing by 93% and breakdown strength declining from 75.37 kV/mm to 57.84 kV/mm (23.2% reduction), significantly exceeding the impact of any single ion environment.
- Microscopic structural analysis confirmed the intrinsic mechanisms underlying macroscopic performance changes—seawater environments resulted in up to 28.3% reduction in the methylene index at 1460 cm−1 and formation of the most severe crack networks and pore structures on surfaces.
- Single anion degradation strength follows the pattern Cl− > SO42− > HCO3−, directly related to their chemical activities and reaction mechanisms.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munro, L.R.; Zou, Q.; Tang, W.; Flynn, D. Prediction Model for Movement and Life Expectancy of Subsea Cables under Wave and Current Action. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Tian, X.; Fang, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, E.; Yang, D. Risk Identification and Safety Evaluation of Offshore Wind Power Submarine Cable Construction. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worzyk, T. Submarine Power Cables: Design, Installation, Repair, Environmental Aspects, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, B.; Bruce, A.; MacGill, I. Impact of shared battery energy storage systems on photovoltaic self-consumption and electricity bills in apartment buildings. Appl. Energy 2019, 245, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauseth, F.; Haugdal, H. Electric field simulations of high voltage DC extruded cable systems. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2017, 33, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Lan, R.; Wei, Y.; Nie, Y.; Li, S. The Lifetime Prediction and Insulation Failure Mechanism of XLPE for High-Voltage Cable. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2023, 30, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, D.; Bailey, C.; Rajaguru, P.; Tang, W.; Yin, C. Prognostics and health management of subsea cables. In Prognostics and Health Management of Electronics: Fundamentals, Machine Learning, and the Internet of Things; Pecht, M., Kang, M., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Chapter 16; pp. 451–478. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Fan, C.; Xu, C.; Dong, H.; Guo, J.; Liang, A.; Zhao, L. Anchor Fault Identification Method for High-Voltage DC Submarine Cable Based on VMD-Volterra-SVM. Energies 2023, 16, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, L.; Burnett, D.; Drew, S.; Marle, G.; Hagadorn, L.; Bartlett-McNeil, D.; Irvine, N. Submarine cables and the oceans: Connecting the world. Mar. Policy 2009, 33, 467–473. [Google Scholar]
- Kroodsma, D.A.; Mayorga, J.; Hochberg, T.; Miller, N.A.; Boerder, K.; Ferretti, F.; Wilson, A.; Bergman, B.; White, T.D.; Block, B.A.; et al. Tracking the global footprint of fisheries. Science 2018, 359, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinmohammadi, F.; Flynn, D.; Bailey, C.; Pecht, M.; Yin, C.; Rajaguru, P.; Robu, V. Predicting Damage and Life Expectancy of Subsea Power Cables in Offshore Renewable Energy Applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54658–54669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissouvanadin, B.; Roy, S.L.; Teyssedre, G.; Laurent, C.; Denizet, I.; Mammeri, M.; Poisson, B. Impact of concentration gradient of antioxidant on polymer dielectric properties. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Du, W.; Li, S.; Tu, Y.; Liang, R.; Liu, B. Study on the Characteristics of Silicone Rubber Aged in Different Environments. Polymers 2020, 12, 3035. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Lan, R.; Zheng, Y.; Long, H.; Hao, C.; Li, S. Aging Characteristics of the Insulation Layer of HVDC Cables and Effect of Space Charge Accumulation on Electric Field Distribution. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2024, 31, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniyi, A.O.; Sutherland, T.; Langa, H. A Comparative Study of the Non-Destructive Diagnostic Tests of 500 Hz Accelerated-Aged XLPE Power Cables. Energies 2025, 18, 3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Ye, X.; Luo, X.; Zhang, H.; He, M.; Li, J.; Li, Q. Prediction Model for Trends in Submarine Cable Burial Depth Variation Considering Dynamic Thermal Resistance Characteristics. Energies 2024, 17, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, Z.; Wu, K.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Li, S. Influence of Oxygen Diffusion on Thermal Ageing of Cross-Linked Polyethylene Cable Insulation. Materials 2020, 13, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosier, I.L.; Praeger, M.; Hilling, J.; Vaughan, A.S.; Swingler, S.G. The effects of water on the dielectric properties of crosslinked polyethylene. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 3298–3307. [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen, S.; Kainulainen, T.; Karttunen, M.; Fagerholm, H. Dielectric properties of crosslinked polyethylene samples from a failed cable. Polymers 2021, 13, 1183. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, X. Corrosion of Copper Armor Caused by Induced Current in a 500 kV Alternating Current Submarine Cable. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 195, 107144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.A.; Wang, S.L.; Chou, W.C.; Sheu, D.D. Carbonate chemistry and projected future changes in pH and CaCO3 saturation state of the South China Sea. Mar. Chem. 2006, 101, 277–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wong, G.T.F. Carbonate Chemistry in the Northern South China Sea Shelf-Sea in June 2010. Deep-Sea Res. II 2015, 117, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, E.G.; Dai, M.; Cao, Z.; Zhai, W.; Guo, L.; Shen, S.S.P.; Du, C. The Carbonate System of the Northern South China Sea: Seasonality and Exchange with the Western North Pacific. Prog. Oceanogr. 2021, 191, 102464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J.; Feistel, R.; Wright, D.G.; McDougall, T.J. The Composition of Standard Seawater and the Definition of the Reference-Composition Salinity Scale. Deep-Sea Res. I 2008, 55, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60216-1:2013; Electrical Insulating Materials—Thermal Endurance Properties—Part 1: Ageing Procedures and Evaluation of Test Results. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Chen, F.; Yang, W.; Liu, F.; Zhu, L.; Sun, Z. Experimental Study of Sediment Incipient Velocity and Scouring in Submarine Cable Burial Areas. Water 2025, 17, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60243-1:2013; Electric Strength of Insulating Materials—Test Methods—Part 1: Tests at Power Frequencies. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Mecheri, Y.; Boukezzi, L.; Boubakeur, A.; Lallouani, M. Dielectric and mechanical behavior of crosslinked polyethylene under thermal aging. In Proceedings of the 2000 Annual Report—Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP); IEEE: Kitchener, ON, Canada, 2000; pp. 560–563. [Google Scholar]
- Fabiani, D.; Montanari, G.C.; Cavallini, A.; Montani, A. Relation between space charge accumulation and partial discharge activity in enameled wires under PWM-like voltage waveforms. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2004, 11, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of Low-Frequency Dielectric Loss of XLPE Cable Insulation Based on Extended Debye Model. Energies 2021, 14, 4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G. Correlation between Microstructural Degradation and Dielectric Response of Thermally Aged XLPE. Materials 2023, 16, 4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Bulinski, A.; Castellon, J.; Frechette, M.; Gubanski, S.; Kindersberger, J.; Montanari, G.C.; Nagao, M.; Morshuis, P.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Dielectric properties of XLPE/SiO2 nanocomposites based on CIGRE WG D1.24 activities. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 1482–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulmine, J.V.; Janissek, P.R.; Heise, H.M.; Akcelrud, L. Polyethylene characterization by FTIR. Polym. Test. 2002, 21, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, A.; Sugimoto, M.; Kudoh, H.; Tamura, K.; Seguchi, T. Degradation mechanisms of silicone rubber (SiR) by accelerated ageing for cables of nuclear power plant. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2013, 20, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hårberg, S.B.; Wenner, S.; Hvidsten, S.; Einarsrud, M.-A. Inception of Vented Water Trees in High Voltage XLPE Cable Insulation: Effect of Inorganic Contaminations inside the Semiconductive Material. J. Appl. Polymers. Sci. 2024, 141, 56136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y.; Meng, P. Water Tree Propagation in a Wide Temperature Range: Insight into the Role of Mechanical Behaviors of Crosslinked Polyethylene (XLPE) Material. Polymers 2021, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvamany, P.; Varadarajan, G.S.; Chillu, N.; Sarathi, R. Investigation of XLPE Cable Insulation Using Electrical, Thermal and Mechanical Properties, and Aging Level Adopting Machine Learning Techniques. Polymers 2022, 14, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Solution Name | Main Chemical Reagent | Dosage (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| NaCl Solution | NaCl | 3.048 × 104 |
| Na2SO4 Solution | Na2SO4 | 3.92 × 103 |
| NaHCO3 Solution | NaHCO3 | 2.0 × 102 |
| Seawater Solution | NaCl | 3.048 × 104 |
| Na2SO4 | 3.92 × 103 | |
| NaHCO3 | 2.0 × 102 |
| Solution | Aging Time (h) | α (kV/mm) | β |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | 0 | 75.37 | 45.0 |
| Seawater | 168 | 68.62 | 33.2 |
| Seawater | 336 | 64.37 | 27.6 |
| Seawater | 504 | 61.12 | 24.8 |
| Seawater | 672 | 57.84 | 20.9 |
| NaCl | 168 | 69.28 | 35.4 |
| NaCl | 336 | 65.31 | 30.6 |
| NaCl | 504 | 61.54 | 27.2 |
| NaCl | 672 | 57.90 | 22.7 |
| Na2SO4 | 168 | 70.14 | 39.5 |
| Na2SO4 | 336 | 67.38 | 35.6 |
| Na2SO4 | 504 | 64.23 | 30.8 |
| Na2SO4 | 672 | 60.65 | 26.3 |
| NaHCO3 | 4.0 | 71.20 | 39.0 |
| NaHCO3 | 1.5 | 68.40 | 34.0 |
| NaHCO3 | 6.0 | 66.10 | 30.5 |
| NaHCO3 | 672 | 64.00 | 27.5 |
| Absorption Peak Position/cm−1 | Unaged | Seawater Solution | NaCl Solution | Na2SO4 Solution | NaHCO3 Solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2910 | 487.32 | 356.85 | 378.94 | 412.67 | 441.28 |
| 2850 | 462.17 | 334.29 | 355.82 | 389.45 | 418.93 |
| 1460 | 198.47 | 142.33 | 151.76 | 167.89 | 179.52 |
| 720 | 234.61 | 172.84 | 184.37 | 203.28 | 218.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, L.; Liu, Z.; Han, Z.; Han, S.; Li, G.; Liu, Q. Aging Mechanisms and Performance Degradation of XLPE Submarine Cable Insulation Under Marine Major Anion Effects. Polymers 2025, 17, 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182450
Zou L, Liu Z, Han Z, Han S, Li G, Liu Q. Aging Mechanisms and Performance Degradation of XLPE Submarine Cable Insulation Under Marine Major Anion Effects. Polymers. 2025; 17(18):2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182450
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Liang, Zheng Liu, Zhiyun Han, Shoushui Han, Guochang Li, and Qingsong Liu. 2025. "Aging Mechanisms and Performance Degradation of XLPE Submarine Cable Insulation Under Marine Major Anion Effects" Polymers 17, no. 18: 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182450
APA StyleZou, L., Liu, Z., Han, Z., Han, S., Li, G., & Liu, Q. (2025). Aging Mechanisms and Performance Degradation of XLPE Submarine Cable Insulation Under Marine Major Anion Effects. Polymers, 17(18), 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182450









