Effect of Application of a Homogeneous Magnetic Field During Chemical Crosslinking of Magnetic Collagen-Based Hydrogels with Genipin on Their Essential Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Experimental Systems Generating a Homogeneous Magnetic Field
2.2. Preparation of Magnetic Hydrogels
2.3. Gel Fraction
2.4. Microstructure (STEM)
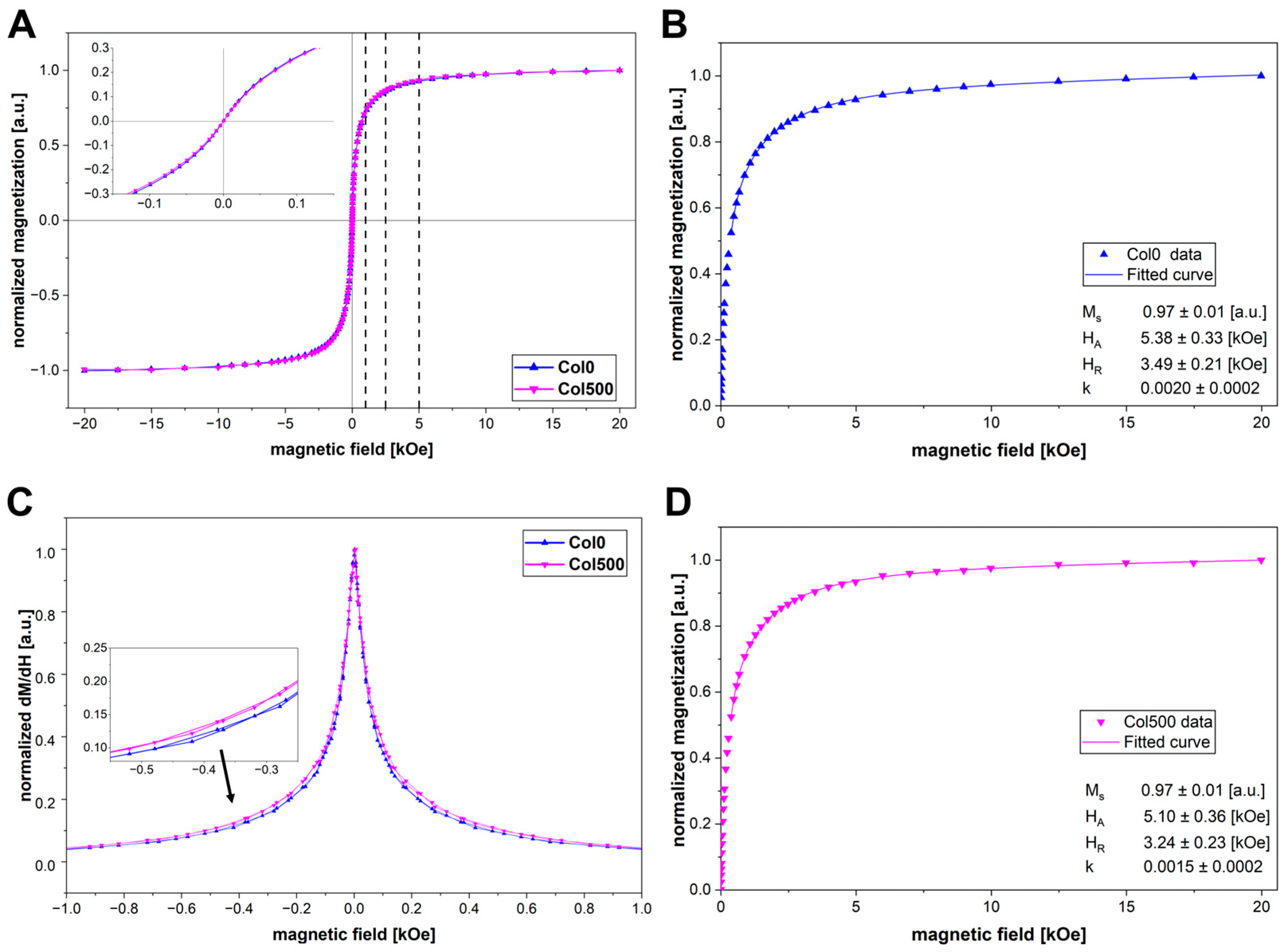
2.5. Magnetic Properties (VSM)
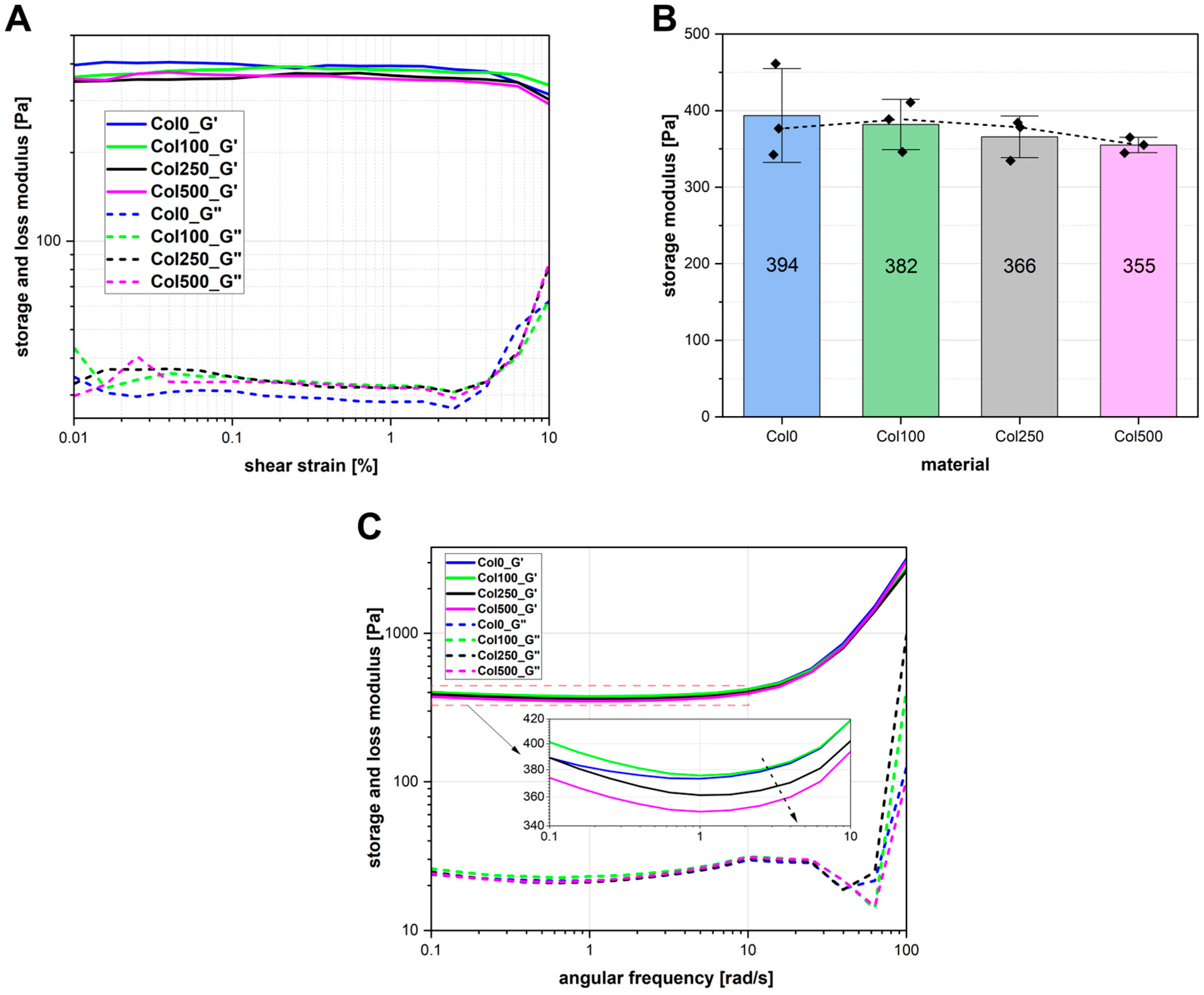
2.6. Rheological Properties
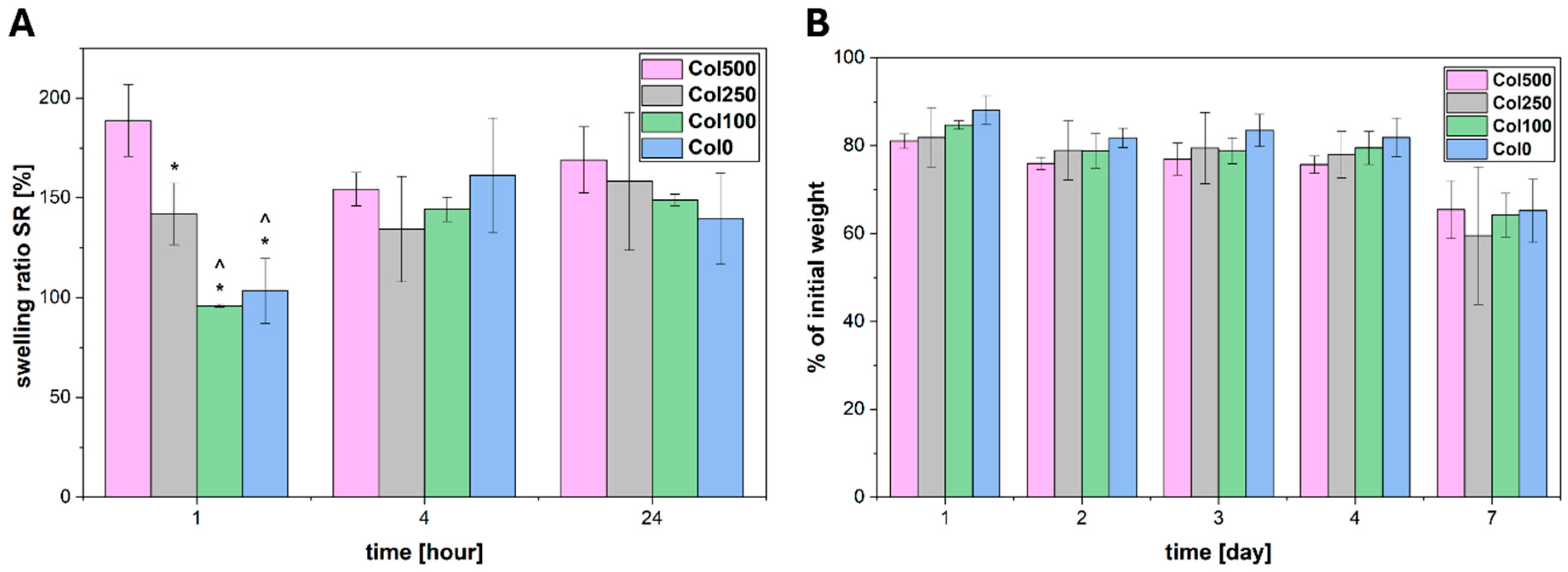
2.7. Swelling and Degradation
3. Summary and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Systems Generating a Static, Homogeneous Magnetic Field
4.3. Details of Preparation of Magnetic Hydrogels
4.4. Gel Fraction Determination
4.5. Microstructure Imaging
4.6. Vibrating Sample Magnetometry (VSM)
4.7. Rheological Characterisation
4.8. Swelling Properties
4.9. Degradation Studies
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rezvani Ghomi, E.; Nourbakhsh, N.; Akbari Kenari, M.; Zare, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Collagen-based biomaterials for biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 1986–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Pei, Y.; Tang, K.; Albu-Kaya, M.G. Structure, extraction, processing, and applications of collagen as an ideal component for biomaterials-a review. Collagen Leather 2023, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wosicka-Frąckowiak, H.; Poniedziałek, K.; Woźny, S.; Kuprianowicz, M.; Nyga, M.; Jadach, B.; Milanowski, B. Collagen and its derivatives serving biomedical purposes: A review. Polymers 2024, 16, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geahchan, S.; Baharlouei, P.; Rahman, A. Marine collagen: A promising biomaterial for wound healing, skin anti-aging, and bone regeneration. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pien, N.; Pezzoli, D.; Van Hoorick, J.; Copes, F.; Vansteenland, M.; Albu, M.; De Meulenaer, B.; Mantovani, D.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P. Development of photo-crosslinkable collagen hydrogel building blocks for vascular tissue engineering applications: A superior alternative to methacrylated gelatin? Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 130, 112460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamán-Díez, P.; García-Gareta, E.; Arruebo, M.; Pérez, M.Á. A bone-on-a-chip collagen hydrogel-based model using pre-differentiated adipose-derived stem cells for personalized bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2023, 111, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, A.; Etxeberria, A.E.; Naffa, R.; Zidan, G.; Seyfoddin, A. 3D-Printed hybrid collagen/GelMA hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Biology 2022, 11, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; AbuSamra, D.B.; Chivu, A.; Argüeso, P.; Dohlman, C.H.; Patra, H.K.; Chodosh, J.; González-Andrades, M. Optimization of collagen chemical crosslinking to restore biocompatibility of tissue-engineered scaffolds. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowska-Łańcucka, J.; Gilarska, A.; Buła, A.; Horak, W.; Łatkiewicz, A.; Nowakowska, M. Genipin crosslinked bioactive collagen/chitosan/hyaluronic acid injectable hydrogels structurally amended via covalent attachment of surface-modified silica particles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; He, Z.; Han, F.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, B. Preparation of collagen/hydroxyapatite/alendronate hybrid hydrogels as potential scaffolds for bone regeneration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A.; Grabska, S. Preparation and characterization of 3D collagen materials with magnetic properties. Polym. Test. 2017, 62, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiorgis, S.; Tsamis, A.; Voutouri, C.; Turcu, R.; Porav, S.A.; Socoliuc, V.; Vekas, L.; Louca, M.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Vavourakis, V.; et al. Engineered magnetoactive collagen hydrogels with tunable and predictable mechanical response. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 114, 111089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettini, S.; Bonfrate, V.; Syrgiannis, Z.; Sannino, A.; Salvatore, L.; Madaghiele, M.; Valli, L.; Giancane, G. Biocompatible collagen paramagnetic scaffold for controlled drug release. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Srinivasan, S.; Rajabzadeh, A.R.; Tang, X.S.; Margel, S. Superparamagnetic amine-functionalized maghemite nanoparticles as a thixotropy promoter for hydrogels and magnetic field-driven diffusion-controlled drug release. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 5272–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, M.; Choi, J.H.; Choi, J.W. Magnetic-assisted cell alignment within a magnetic nanoparticle-decorated reduced graphene oxide/collagen 3D nanocomposite hydrogel. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londhe, P.V.; Londhe, M.V.; Salunkhe, A.B.; Laha, S.S.; Mefford, O.T.; Thorat, N.D.; Khot, V.M. Magnetic hydrogel (MagGel): An evolutionary pedestal for anticancer therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 522, 216228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Margel, S. Design of magnetic hydrogels for hyperthermia and drug delivery. Polymers 2021, 13, 4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, M.; Opiła, G.; Hinz, A.; Stankiewicz, S.; Bzowska, M.; Wolski, K.; Dulińska-Litewka, J.; Przewoźnik, J.; Kapusta, C.; Karewicz, A. Hyaluronic acid-coated SPIONs with attached folic acid as potential T2 MRI contrasts for anticancer therapies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 9059–9073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Mao, H. Magnetically anisotropic hydrogels for tissue engineering. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 6384–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tan, Z.; Guo, B.; Yu, C.; Yao, M.; Liang, L.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yao, F.; Zhang, H.; et al. Magnet-oriented hydrogels with mechanical–electrical anisotropy and photothermal antibacterial properties for wound repair and monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Coradin, T. Magnetically-oriented type I collagen-SiO2@ Fe3O4 rods composite hydrogels tuning skin cell growth. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antman-Passig, M.; Shefi, O. Remote magnetic orientation of 3D collagen hydrogels for directed neuronal regeneration. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2567–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.L.; Righelli, L.; Broomhall, T.J.; Lamont, H.C.; El Haj, A.J. Magnetic nanoparticle-mediated orientation of collagen hydrogels for engineering of tendon-mimetic constructs. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 797437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, T.; Zhang, N.; Dong, L.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, M.; Li, B. The effects of different crossing-linking conditions of genipin on type I collagen scaffolds: An in vitro evaluation. Cell Tissue Bank. 2014, 15, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, B.; Rigó, M.; Guba, S.; Szalai, I.; Barabás, R. Magnetic field response of aqueous hydroxyapatite based magnetic suspensions. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marycz, K.; Kornicka, K.; Röcken, M. Static magnetic field (SMF) as a regulator of stem cell fate–new perspectives in regenerative medicine arising from an underestimated tool. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2018, 14, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Song, C.; Guo, R.; Zhang, X. Static magnetic fields in regenerative medicine. APL Bioeng. 2024, 8, 011503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpak, A.; Kania, G.; Skórka, T.; Tokarz, W.; Zapotoczny, S.; Nowakowska, M. Stable aqueous dispersion of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles protected by charged chitosan derivatives. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiejdasz, S.; Gilarska, A.; Horak, W.; Radziszewska, A.; Strączek, T.; Szuwarzyński, M.; Nowakowska, M.; Kapusta, C. Structurally stable hybrid magnetic materials based on natural polymers–preparation and characterization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 3149–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Du, J. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümler, P. Magnetic guiding with permanent magnets: Concept, realization and applications to nanoparticles and cells. Cells 2021, 10, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpak, A.; Fiejdasz, S.; Prendota, W.; Strączek, T.; Kapusta, C.; Szmyd, J.; Nowakowska, M.; Zapotoczny, S. T1–T2 Dual-modal MRI contrast agents based on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with surface attached gadolinium complexes. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strączek, T.; Fiejdasz, S.; Rybicki, D.; Goc, K.; Przewoźnik, J.; Mazur, W.; Nowakowska, M.; Zapotoczny, S.; Rumian, S.; Kapusta, C. Dynamics of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with various polymeric coatings. Materials 2019, 12, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronov, A.P.; Beketov, I.V.; Komogortsev, S.V.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Medvedev, A.I.; Leiman, D.V.; Larrañaga, A.; Bhagat, S.M. Spherical magnetic nanoparticles fabricated by laser target evaporation. AIP Adv. 2013, 3, 052135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiejdasz, S.; Gilarska, A.; Strączek, T.; Nowakowska, M.; Kapusta, C. Magnetic properties of collagen–chitosan hybrid materials with immobilized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (Spions). Materials 2021, 14, 7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Kumar, P. Insights into structural and magnetic properties of Manganite Perovskite La0.7Ca0.3Mn0.6Co0.4O3 nanoparticles prepared by sol gel auto combustion route. Phys. Open 2025, 24, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R.; Harun-Ur-Rashid, M.; Imran, A.B. Effect of sizes of vinyl modified narrow-dispersed silica cross-linker on the mechanical properties of acrylamide based hydrogel. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, K.A.; Lee, D.; Composto, R.J. pH-Mediated nanoparticle dynamics in hydrogel nanocomposites. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 2765–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Kohane, D.S. Hybrid nanoparticle–hydrogel systems for drug delivery depots and other biomedical applications. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 22780–22792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, P.O.; Herbert, E.G.; Tartivel, L.; Behl, M.; Lendlein, A.; Huber, N.; Lilleodden, E.T. Mechanical characterization of oligo (ethylene glycol)-based hydrogels by dynamic nanoindentation experiments. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H. Hydrogels for colon-specific drug delivery: Swelling kinetics and mechanism of degradation in vitro. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 3128–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulwan, M.; Zapotoczny, S.; Nowakowska, M. Robust “one-component” chitosan-based ultrathin films fabricated using layer-by-layer technique. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 4726–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvinen, J.; Ihalainen, T.O.; Calejo, M.T.; Jönkkäri, I.; Kellomäki, M. Characterization of the microstructure of hydrazone crosslinked polysaccharide-based hydrogels through rheological and diffusion studies. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Target Value of Magnetic Field Induction B [mT] | Measured Value of Magnetic Field Induction B with Standard Deviation [mT] | |
|---|---|---|
| system 1 | 100 | 109 ± 2 |
| system 2 | 250 | 253 ± 17 |
| system 3 | 500 | 486 ± 33 |
| Material | Gel Fraction [%] |
|---|---|
| Col500 | 93.4 ± 4.0 |
| Col250 | 94.6 ± 3.0 |
| Col100 | 87.6 ± 6.1 |
| Col0 | 92.5 ± 5.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gilarska, A.; Horak, W.; Radziszewska, A.; Rybicki, D.; Kapusta, C. Effect of Application of a Homogeneous Magnetic Field During Chemical Crosslinking of Magnetic Collagen-Based Hydrogels with Genipin on Their Essential Properties. Polymers 2025, 17, 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182437
Gilarska A, Horak W, Radziszewska A, Rybicki D, Kapusta C. Effect of Application of a Homogeneous Magnetic Field During Chemical Crosslinking of Magnetic Collagen-Based Hydrogels with Genipin on Their Essential Properties. Polymers. 2025; 17(18):2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182437
Chicago/Turabian StyleGilarska, Adriana, Wojciech Horak, Agnieszka Radziszewska, Damian Rybicki, and Czesław Kapusta. 2025. "Effect of Application of a Homogeneous Magnetic Field During Chemical Crosslinking of Magnetic Collagen-Based Hydrogels with Genipin on Their Essential Properties" Polymers 17, no. 18: 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182437
APA StyleGilarska, A., Horak, W., Radziszewska, A., Rybicki, D., & Kapusta, C. (2025). Effect of Application of a Homogeneous Magnetic Field During Chemical Crosslinking of Magnetic Collagen-Based Hydrogels with Genipin on Their Essential Properties. Polymers, 17(18), 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182437







