Design Strategies of PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications in Health Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Construction Strategies of PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Hydrogels
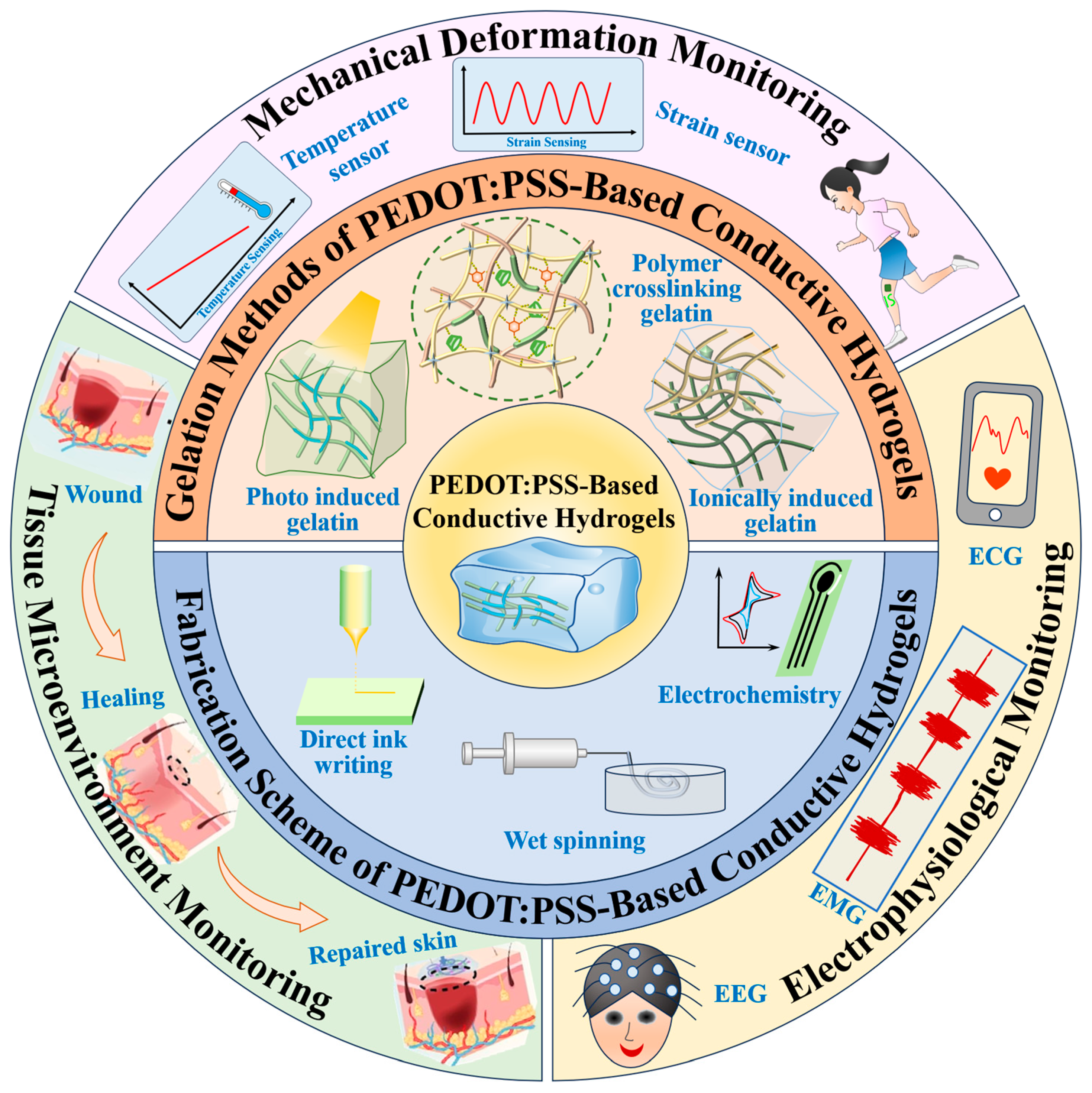
2.1. Gelation Methods of PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Hydrogels
2.1.1. Polymer Crosslink Gelatin
2.1.2. Ionically Induced Gelatin
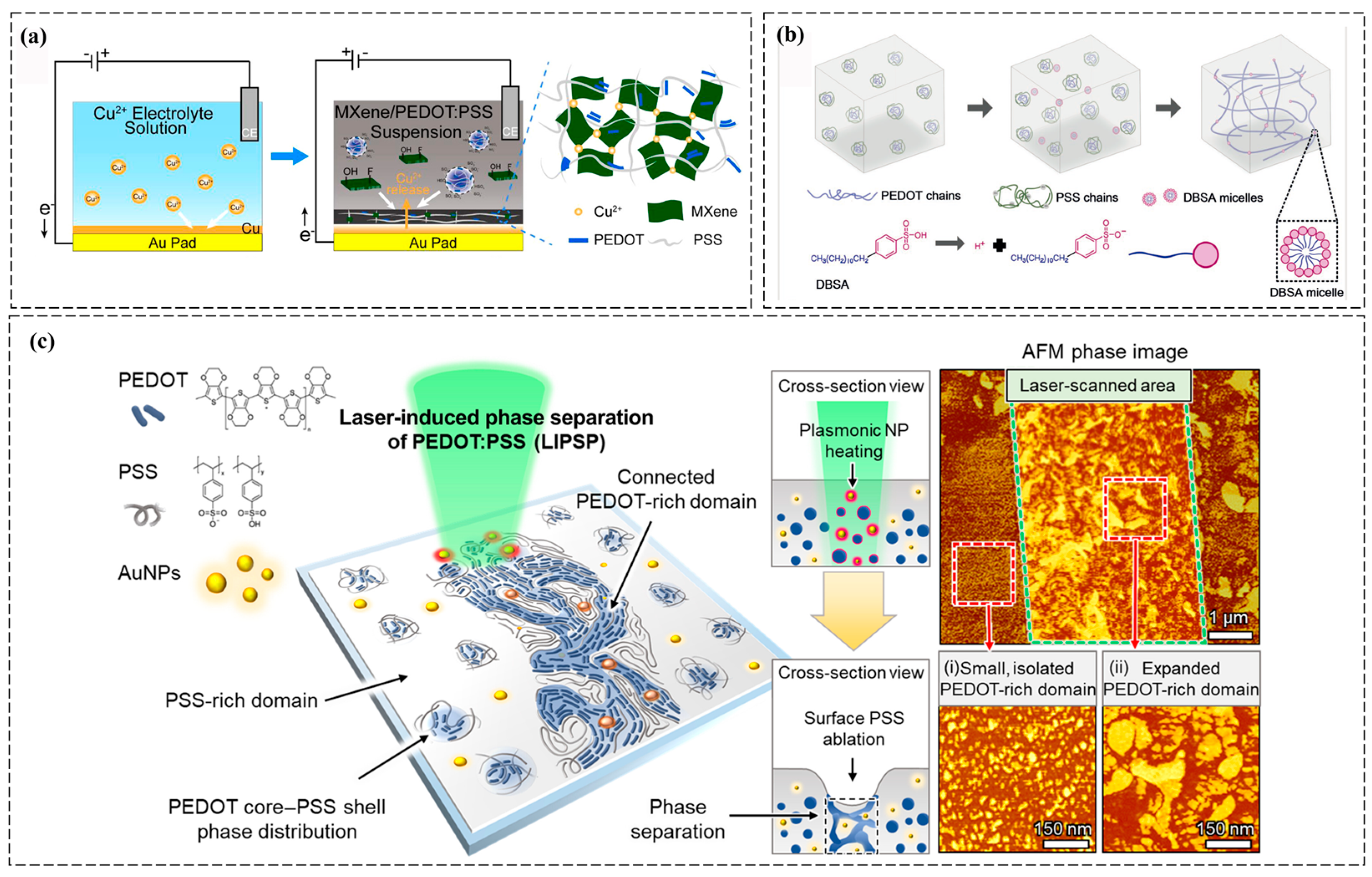
2.1.3. Photo-Induced Gelatin
2.2. Fabrication Technologies of PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Hydrogels
2.2.1. Casting and Molding
2.2.2. Wet Spinning
2.2.3. Electrospinning
2.2.4. Electrochemistry
2.2.5. Inkjet Printing
2.2.6. Direct Ink Writing

2.2.7. Digital Light Processing
3. Application of PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Hydrogels in Wearable Sensors
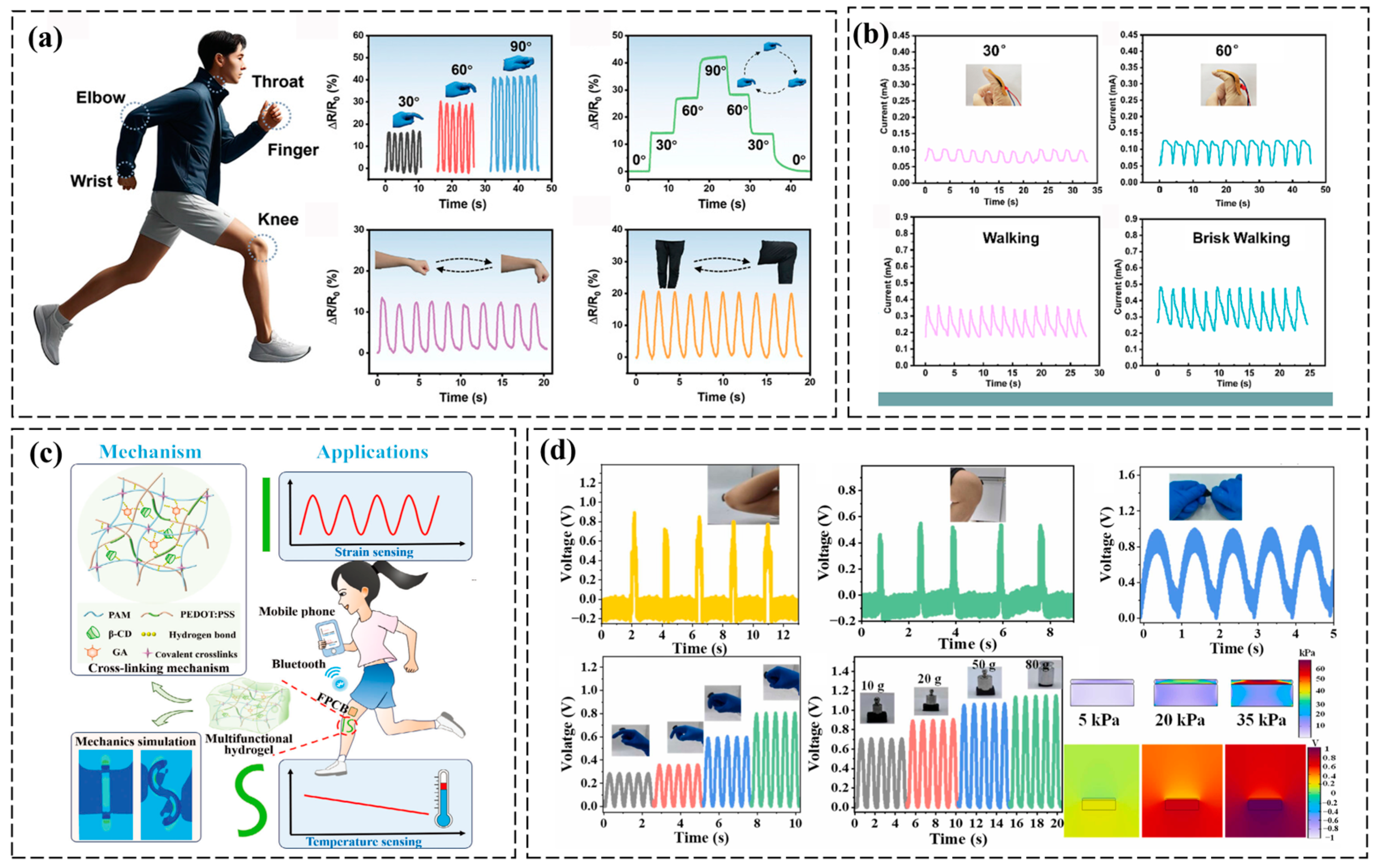
3.1. Mechanical Deformation Monitoring
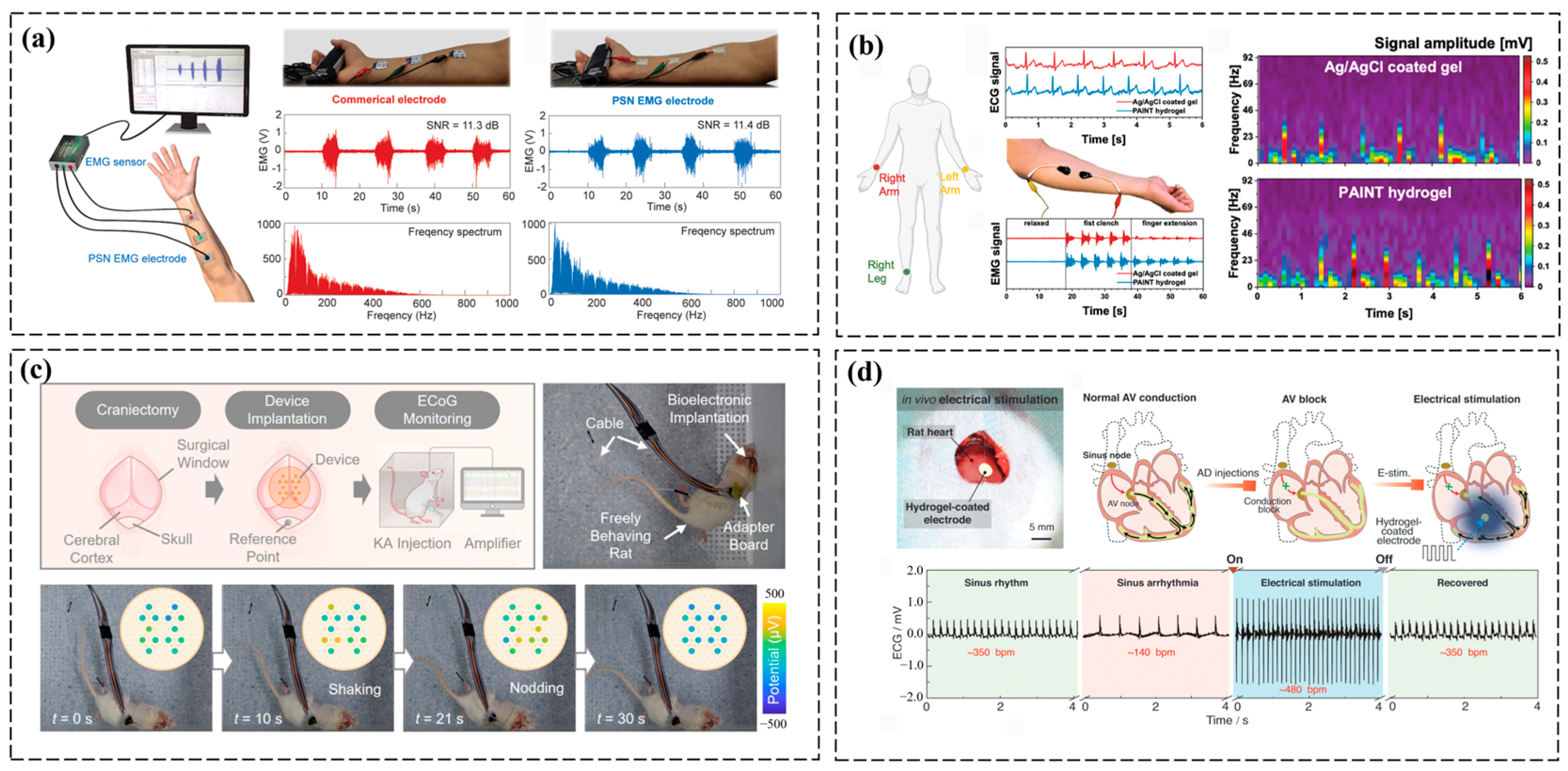
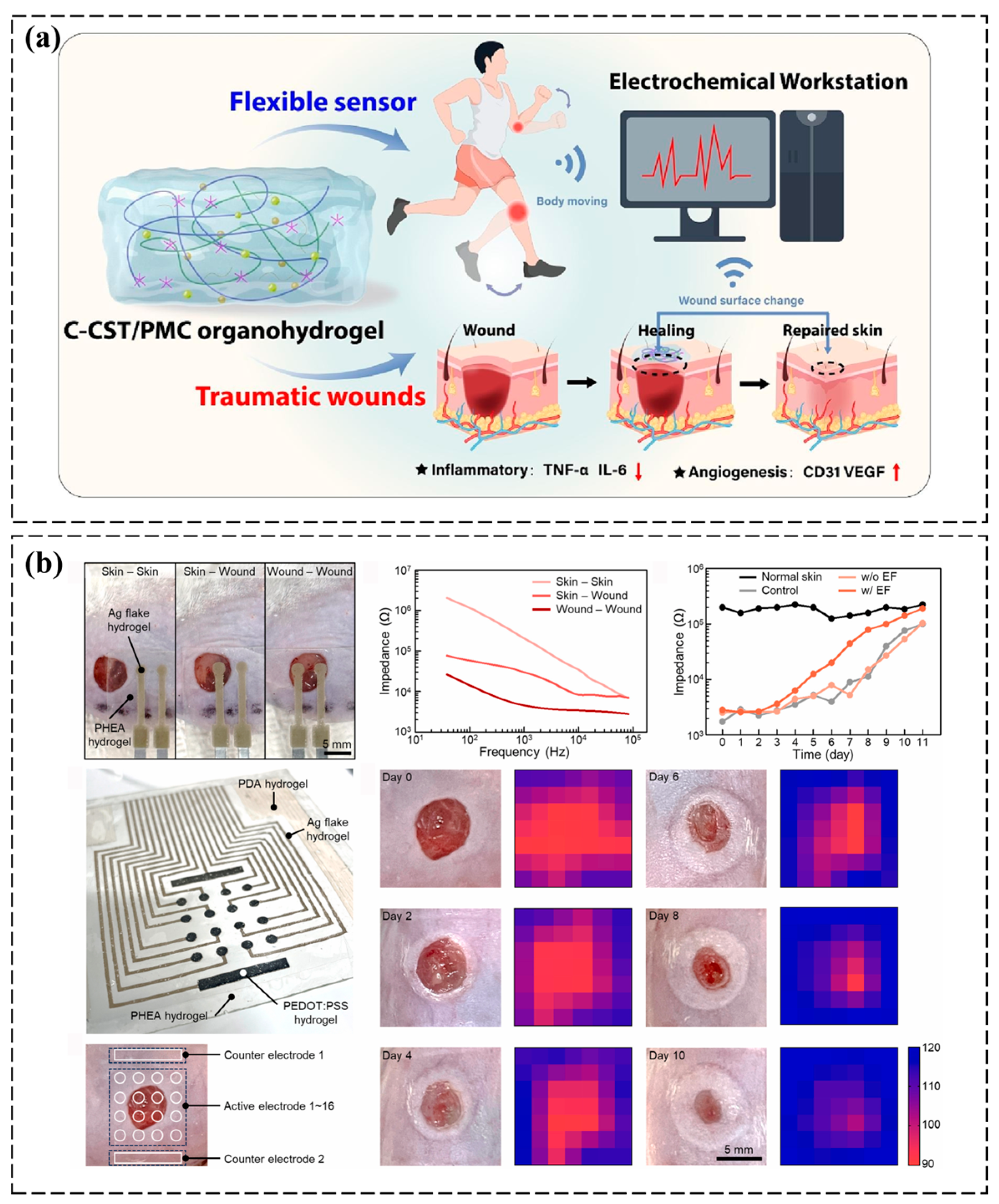
3.2. Tissue Microenvironment Monitoring
3.3. Electrophysiological Monitoring
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Wang, M.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, P.; Sun, B.; Gao, Q.; Gao, C.; Liu, R. Highly adhesive and self-healing γ-PGA/PEDOT:PSS conductive hydrogels enabled by multiple hydrogen bonding for wearable electronics. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.X.; Ni, Y.M.; Biesold, G.M.; Cheng, Y.; Ge, M.Z.; Li, H.Q.; Huang, J.Y.; Lin, Z.Q.; Lai, Y.K. Recent advances in conductive hydrogels: Classifications, properties, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 473–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tan, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Cai, J.; Liu, Y. Design strategies and emerging applications of conductive hydrogels in wearable sensing. Gels 2025, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Z.; Hao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chang, J. Capacitive pressure sensor combining dual dielectric layers with integrated composite electrode for wearable healthcare monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 12974–12985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Zhou, P.; Hu, F.; Rong, Y.; Lu, B.; Gu, Y. High-stretchability, ultralow-hysteresis conductingpolymer hydrogel strain sensors for soft machines. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2203650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wen, F.; Lai, Y.; Li, H. Conductive hydrogel for flexible bioelectronic device: Current progress and future perspective. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2308974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.J.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Chen, C.; Cai, C.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Fu, J. Multifunctional conductive hydrogels and their applications as smart wearable devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2561–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, C.; Liu, S.; Huang, L.; Fang, T.; Li, J.; Xu, F.; Li, F. Smart glove integrated with tunable MWNTs/PDMS fibers made of a one-step extrusion method for finger dexterity, gesture, and temperature recognition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 23764–23773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, S.; Qian, X.; Jiao, J.; Ma, B.; Chen, J.; Cheng, H.; Li, X.; Lin, Y.; et al. Injectable and conductive nanomicelle hydrogel with α-tocopherol encapsulation for enhanced myocardial infarction repair. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 10216–10229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, L.F.; Liu, W.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, Z. Highly-stable, injectable, conductive hydrogel for chronic neuromodulation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Chen, S.M.; Wang, F.; Liu, M.; Li, J.H.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.S.; Zhang, H.Q.; Liu, D.; He, R.Y.; et al. High-conductivity, self-healing, and adhesive ionic hydrogels for health monitoring and human-machine interactions under extreme cold conditions. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2412726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, W.; Fan, X.; Shi, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, L.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Han, L.; Lu, X.; et al. A polyphenol-derived redox-active and conductive nanoparticle-reinforced hydrogel with wet adhesiveness for myocardial infarction repair by simultaneously stimulating anti-inflammation and calcium homeostasis pathways. Nano Today 2024, 55, 102157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.A.; Alegret, N.; Almeida, B.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.; Andrews, A.M.; Ballerini, L.; Barrios-Capuchino, J.J.; Becker, C.; Blick, R.H.; Bonakdar, S.; et al. Interfacing with the brain: How nanotechnology can contribute. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 10630–10717. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.; Lin, X.; Rivnay, J. Organic electrochemical transistors as on-site signal amplifiers for electrochemical aptamer-based sensing. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Wang, T.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Xie, X.; Wei, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, C.; He, Y.; Xu, F. Materials with tunable optical properties for wearable epidermal sensing in health monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, C.; Rao, Q.; Wu, J.; Qi, J.; Jiang, X. A bilayer microfluidics-based elastic encapsulation method of liquid metal circuits with cellular resolution. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 13118–13127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Han, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Shen, J.; Zhang, K.; Mai, S.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Chen, X.; et al. A soft-fiber bioelectronic device with axon-like architecture enables reliable neural recording in vivo under vigorous activities. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2407874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhuang, T.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Dai, X.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Chong, D.; et al. Multifunctional filler-free PEDOT:PSS hydrogels with ultrahigh electrical conductivity induced by lewis-acid-promoted ion exchange. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2302919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Park, J.M.; Park, C.S.; Na, H.; Kang, Y.; Lee, W.; Sun, J.Y. Anisotropically conductive hydrogels with directionally aligned PEDOT:PSS in a PVA matrix. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 4013–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tu, T.; Li, T.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Fang, L.; Ye, X.S.; Liang, B. 3D MXene/PEDOT:PSS composite aerogel with a controllable patterning property for highly sensitive wearable physical monitoring and robotic tactile sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 23877–23887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, M.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Shi, G. Ultrahigh-conductivity polymer hydrogels with arbitrary structures. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.X.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.C.; Lei, T.; Kim, Y.; Niu, S.M.; Wang, H.L.; Wang, X.; Foudeh, A.M.; Tok, J.B.H.; et al. Soft and elastic hydrogel-based microelectronics for localized low-voltage neuromodulation. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, D.N.; Lee, S.J.; Timsina, R.; Qiu, X.Y.; Castro, N.J.; Zhang, L.G. Development of 3D printable conductive hydrogel with crystallized PEDOT:PSS for neural tissue engineering. Mat. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2019, 99, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Shon, A.; Joseph, R.; Pavlov, A.; Stefanov, A.; Namkoong, M.; Guo, H.; Bui, D.; Master, R.; Sharma, A.; et al. Soft, stretchable conductive hydrogels for high-performance electronic implants. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eads4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Gao, C.; Ge, C.; Chen, Z.; Liu, K.; Xu, W.; Su, B.; Fang, J. All-fabric tactile sensors based on sandwich structure design with tunable responsiveness. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 32002–32010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ye, Z.; Cai, Y.; Tu, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.; Fang, L.; Mao, X.; Xu, S.; Ye, X.; et al. Electrode surface rebuilding for electrochemical assembling of conductive PEDOT:PSS hydrogel towards biosensing. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 911, 116183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Nie, W.; Tsai, S.H.; Wang, N.; Huang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Wen, R.; Ma, L.; Yan, F.; Xia, Y. PEDOT:PSS for flexible and stretchable electronics: Modifications, strategies, and applications. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. 3D printing of highly conductive and strongly adhesive PEDOT:PSS hydrogel-based bioelectronic interface for accurate electromyography monitoring. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 677, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, J.; Wan, R.T.; Feig, V.R.; Tringides, C.M.; Xu, J.K.; Yuk, H.; Lu, B.Y. PEDOTs-based conductive hydrogels: Design, fabrications, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2415151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.; Stoy, L.M.; Sun, J.D.; Amponsah, P.E.O.; Li, L.; Soto, M.; Song, S. Fabrication of sodium trimetaphosphate-based PEDOT:PSS conductive hydrogels. Gels 2024, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, M.; Jing, L.; Jia, Q.; Lv, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Cai, X. Enhanced neural activity detection with microelectrode arrays modified by drug-loaded calcium alginate/chitosan hydrogel. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 267, 116837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wu, W.J. Stripping superficial polystyrene sulfonate on PEDOT:PSS via dodecyl benzenesulfonic acid for high-performance double-crosslinked hydrogel in flexible supercapacitor. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 467, 143080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, D. A wireless health monitoring system accomplishing bimodal decoupling based on an "IS"-shaped multifunctional conductive hydrogel. Small 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, X.; Jia, X.T.; Naficy, S.; Shu, K.W.; Forsyth, M.; Wallace, G.G. A cytocompatible robust hybrid conducting polymer hydrogel for use in a magnesium battery. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9349–9355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaf, M.A.; Muthukumar, M. Electrostatic effect on the solution structure and dynamics of PEDOT:PSS. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4286–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, K.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, T.; Yan, J.; Wang, H. Ultra-high electrical conductivity in filler-free polymeric hydrogels toward thermoelectrics and electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Ling, H.; Wang, C.; Ni, J.; Saltik, B.C.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; et al. Room-temperature-formed PEDOT:PSS hydrogels enable injectable, soft, and healable organic bioelectronics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1904752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, D.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.; Han, S.; Ha, I.; Bang, J.; Kim, K.K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, T.S.; et al. Digital selective transformation and patterning of highly conductive hydrogel bioelectronics by laser-induced phase separation. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Gao, C.; Gao, Q. Surface engineering via self-assembly on PEDOT:PSS fibers: Biomimetic fluff-like morphology and sensing application. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Liang, Y.; Ning, N.; Wu, H.; Tian, M. Strain-insensitive stretchable conductive fiber based on helical core with double-network hydrogel. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.Z. Conductive polymer ultrafine fibers via electrospinning: Preparation, physical properties and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 115, 100704. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, C.; Jin, K.; Yan, J.; Qin, Y.; Hong, F.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y. Nanofiber-based stretchable electrodes for oriented culture and mechanotransduction monitoring of smooth muscle cells. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 3248–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Li, Z.; Zheng, L.; Ye, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liang, B.; Li, T.Y. Recent progress in the biomedical application of PEDOT:PSS hydrogels. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, V.R.; Tran, H.; Lee, M.; Liu, K.; Huang, Z.; Beker, L.; Mackanic, D.G.; Bao, Z.N. An electrochemical gelation method for patterning conductive PEDOT:PSS hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Wu, J.; Cho, W.R.; Leach, M.K.; Franz, E.W.; Naim, Y.I.; Gu, Z.; Corey, J.M.; Martin, D.C. Highly aligned poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene) (PEDOT) nano- and microscale fibers and tubes. Polymer 2013, 54, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihar, E.; Roberts, T.; Saadaoui, M.; Herve, T.; De Graaf, J.B.; Malliaras, G.G. Inkjet-printed PEDOT:PSS electrodes on paper for electrocardiography. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, M.Y.; RaviChandran, N.; Kim, N.; Kee, S.; Stuart, L.; Aw, K.C.; Stringer, J. Direct patterning of highly conductive PEDOT:PSS/ionic liquid hydrogel via microreactive inkjet printing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 37069–37076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Xu, Z.; Yu, X.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Feng, W. Liquid-in-liquid printing of 3D and mechanically tunable conductive hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xue, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Shan, L.; Duan, Q.; Xing, J.; Lan, Y.; Lu, B.; Liu, J. 3D printed implantable hydrogel bioelectronics for electrophysiological monitoring and electrical modulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2314471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Garcia, J.; Leahy, L.M.; Song, R.; Mullarkey, D.; Fei, B.; Dervan, A.; Shvets, I.V.; Stamenov, P.; Wang, W.X.; et al. 3D printing of multifunctional conductive polymer composite hydrogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, H.; Lu, B.Y.; Lin, S.; Qu, K.; Xu, J.K.; Luo, J.H.; Zhao, X.H. 3D printing of conducting polymers. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Sun, M.; Lu, X.; Xu, K.; Yu, M.; Yang, H.; Yin, J. A 3D printable gelatin methacryloyl/chitosan hydrogel assembled with conductive PEDOT for neural tissue engineering. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2024, 273, 111241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Zou, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, W.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; You, R. Silk fibroin-based antifreezing and highly conductive hydrogel for sensing at ultralow temperature. ACS Sens. 2025, 10, 2297–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Qu, N.; Sheng, W.; Lin, T.H.; Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, R. tough and strain-sensitive organohydrogels based on MXENE and PEDOT/PSS and their effects on mechanical properties and strain-sensing performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 11914–11929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Wan, R.; Yao, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, B. All 3D-printed high-sensitivity adaptive hydrogel strain sensor for accurate plant growth monitoring. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, H. Bioinspired super-robust conductive hydrogels for machine learning-assisted tactile perception system. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2416275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Xu, T.; Du, H.S.; Si, C.L. Strong, conductive, and freezing-tolerant polyacrylamide/PEDOT:PSS/cellulose nanofibrils hydrogels for wearable strain sensors. Carbohyd. Polym. 2023, 305, 120567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, P.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Li, G.; Chang, Q.; Shi, K.M.; Wang, X.; et al. Fully polymeric conductive hydrogels with low hysteresis and high toughness as multi-responsive and self-powered wearable sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2316346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, B.; Hu, W. PEDOT-molecular bridging foam-hydrogel based wearable triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting and sensing. Nano Energy 2025, 134, 110572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W.; Yang, G.; Jiang, X. Rapid fabrication of self-healing, conductive, and injectable gel as dressings for healing wounds in stretchable parts of the body. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, C.; Ma, X.; Zhu, T.; Ma, W.; Jin, Q.; Du, R.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Kong, D.S.; et al. In situ forming dual-conductive hydrogels enable conformal, self-adhesive and antibacterial epidermal electrodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2302846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Han, B. A multifunctional conductive organohydrogel as a flexible sensor for synchronous real-time monitoring of traumatic wounds and pro-healing process. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 151419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, J.U.; An, Y.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, N.S.; Kim, D.H. Functional-hydrogel-based electronic-skin patch for accelerated healing and monitoring of skin wounds. Biomaterials 2025, 314, 122802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gu, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, Q. Stretchable organic electrochemical transistors for sustained high-fidelity electrophysiology and deep learning-assisted sleep monitoring. Matter 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Yu, J.; Quan, Z.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; Tian, F.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, D.; et al. A reusable, healable, and biocompatible PEDOT:PSS hydrogel-based electrical bioadhesive interface for high-resolution electromyography monitoring and time-frequency analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tian, F.J.; Wang, W.; Wan, R.; Cao, J.; Chen, C.; Zhao, D.; Liu, J.; Zhong, J.; Wang, F.; et al. Design of highly conductive, intrinsically stretchable, and 3D printable PEDOT:PSS hydrogels via PSS-chain engineering for bioelectronics. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 5936–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, W.; Li, W.; Li, T.; Popovic, M.R.; Naguib, H.E. Conductive bio-based hydrogel for wearable electrodes via direct ink writing on skin. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2403721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Geng, B.; Chen, F.; Yuan, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Jia, W.; Hu, W. Triple-network-based conductive polymer hydrogel for soft and elastic bioelectronic interfaces. SmartMat 2024, 5, e1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, J.Z.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Xu, H.Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Ma, Y.J.; Feng, X.; Yu, J. Intrinsically adhesive and conductive hydrogel bridging the bioelectronic-tissue interface for biopotentials recording. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 7755–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Chen, X.M.; Wang, F.C.; Lin, J.S.; Liu, J. Mechanically-compliant bioelectronic interfaces through fatigue-resistant conducting polymer hydrogel coating. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2304095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Li, J.; Xiao, P.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, Z.; He, Y.; Xu, F. Wearable smart contact lenses: A critical comparison of three physiological signals outputs for health monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 257, 116284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Ge, P.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Kang, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, Z.; He, Y. Smart contact Lenses: From rational design strategies to wearable health monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, R.B.; Du, W.; Griggs, S.; Maria, I.P.; McCulloch, I.; Rivnay, J. Ambipolar inverters based on cofacial vertical organic electrochemical transistor pairs for biosignal amplification. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabh1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivnay, J.; Inal, S.; Salleo, A.; Owens, R.M.; Berggren, M.; Malliaras, G.G. Organic electrochemical transistors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, H.; Si, W.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.; Yu, Y.; Lan, S.; Meng, F.; Liu, Y. High-entropy enhanced capacitive energy storage. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
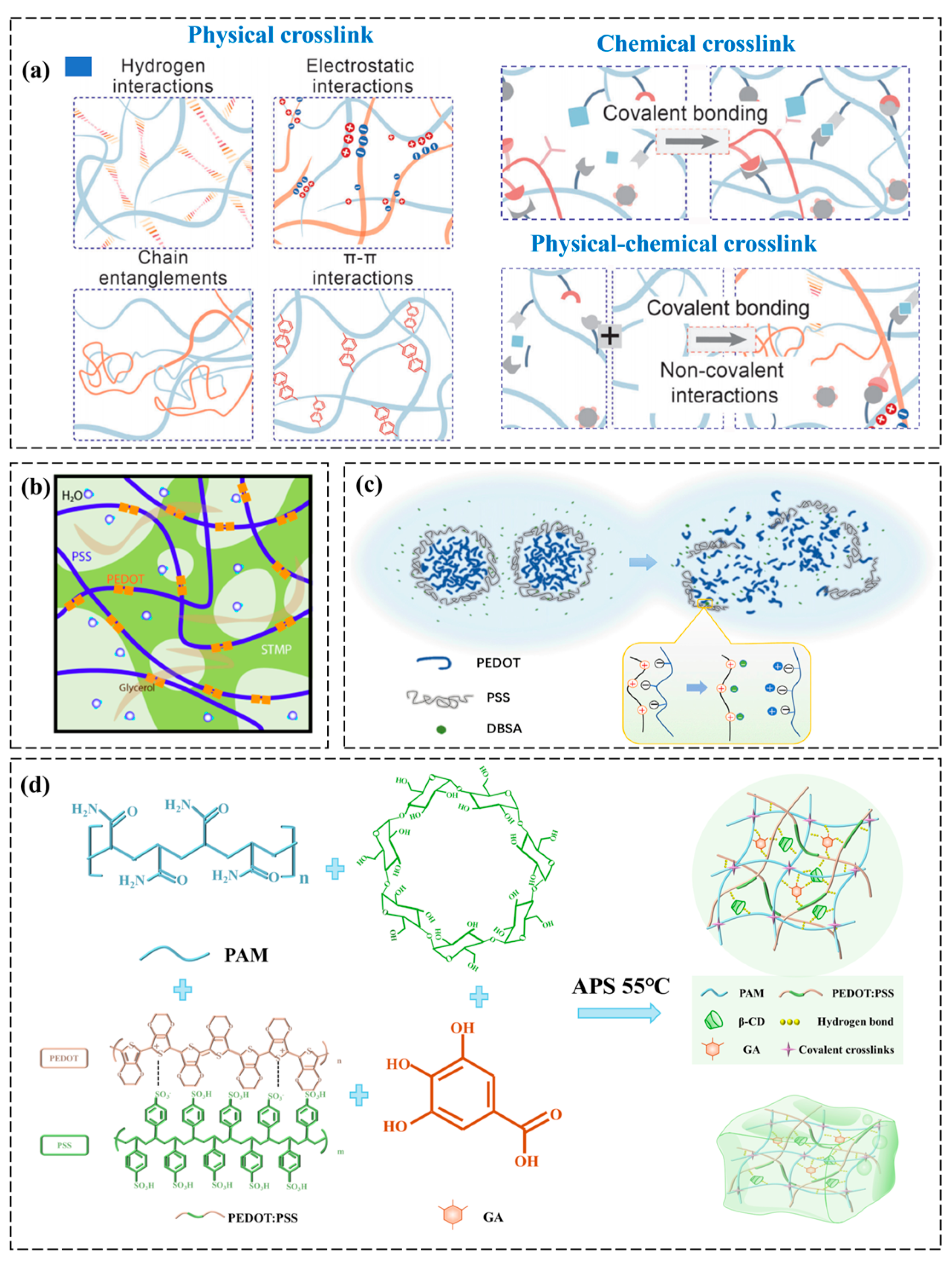
| Criteria | Physical Crosslinking | Chemical Crosslinking | Hybrid Crosslinking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | High (Dynamic ionic networks enable free ion mobility) | Moderate (Rigid networks may restrict ionic transport) | High (Combined ionic/covalent pathways synergize charge transfer) |
| Mechanical Strength | Low-Moderate (Reversible bonds limit stability) | High (Irreversible covalent bonds create robust networks) | Tunable (Balanced covalent rigidity and dynamic adaptability) |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent (No toxic residues; natural polymer compatibility) | Limited (Potential cytotoxicity from residual crosslinkers) | Moderate (Depends on crosslinker type; reversible interactions reduce toxicity risks) |
| Scalability | High (Simple processing; ambient conditions) | Moderate (Requires precise chemical control; post-treatment needed) | Moderate-High (Adaptable to multiple fabrication methods) |
| Key Advantages |
|
|
|
| Key Limitations |
|
|
|
| Typical Applications | Wearable sensors, transient bioelectronics | Structural scaffolds, implantable devices | Multifunctional sensors, adaptive soft robotics |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tan, S.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, Z.; Han, F.; Liu, Y. Design Strategies of PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications in Health Monitoring. Polymers 2025, 17, 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091192
Li Y, Zhang X, Tan S, Li Z, Sun J, Li Y, Xie Z, Li Z, Han F, Liu Y. Design Strategies of PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications in Health Monitoring. Polymers. 2025; 17(9):1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091192
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yingchun, Xuesi Zhang, Shaozhe Tan, Zhenyu Li, Jiachun Sun, Yufeng Li, Zhengwei Xie, Zijin Li, Fei Han, and Yannan Liu. 2025. "Design Strategies of PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications in Health Monitoring" Polymers 17, no. 9: 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091192
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhang, X., Tan, S., Li, Z., Sun, J., Li, Y., Xie, Z., Li, Z., Han, F., & Liu, Y. (2025). Design Strategies of PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications in Health Monitoring. Polymers, 17(9), 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091192







