Relationship Between Filler Type, Thermomechanical Properties, and Aging of RTV Silicone Foams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Manufacturing
2.2. Material Characterization
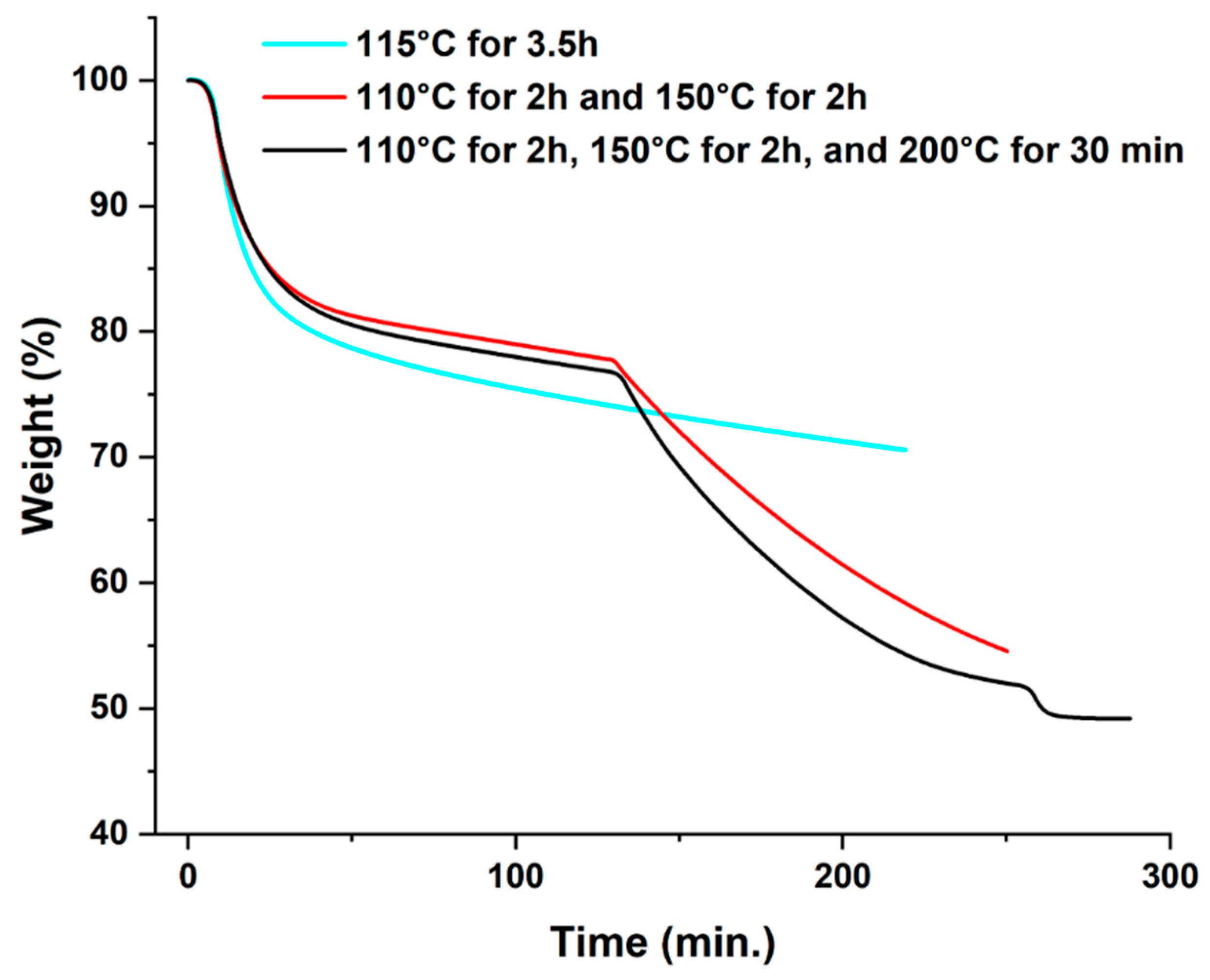
2.3. Accelerated Aging Study
3. Results and Discussion
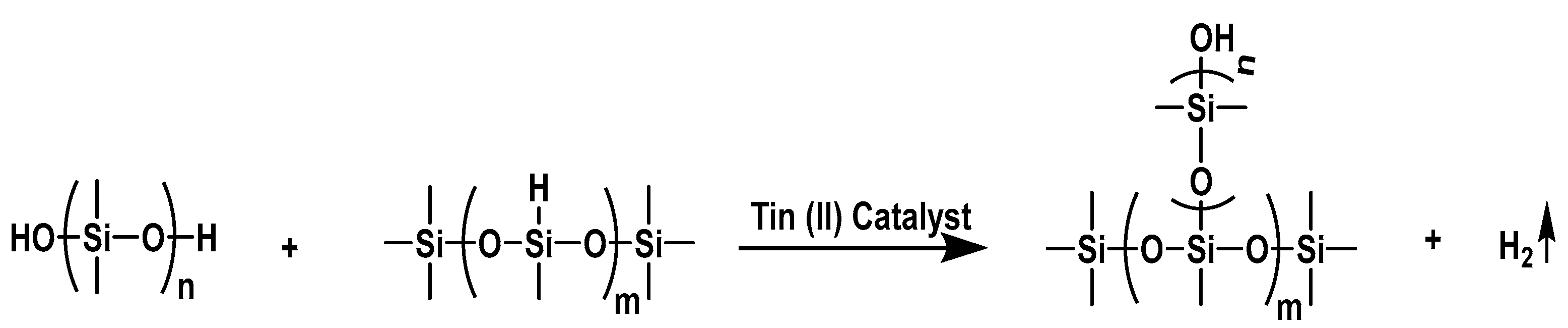
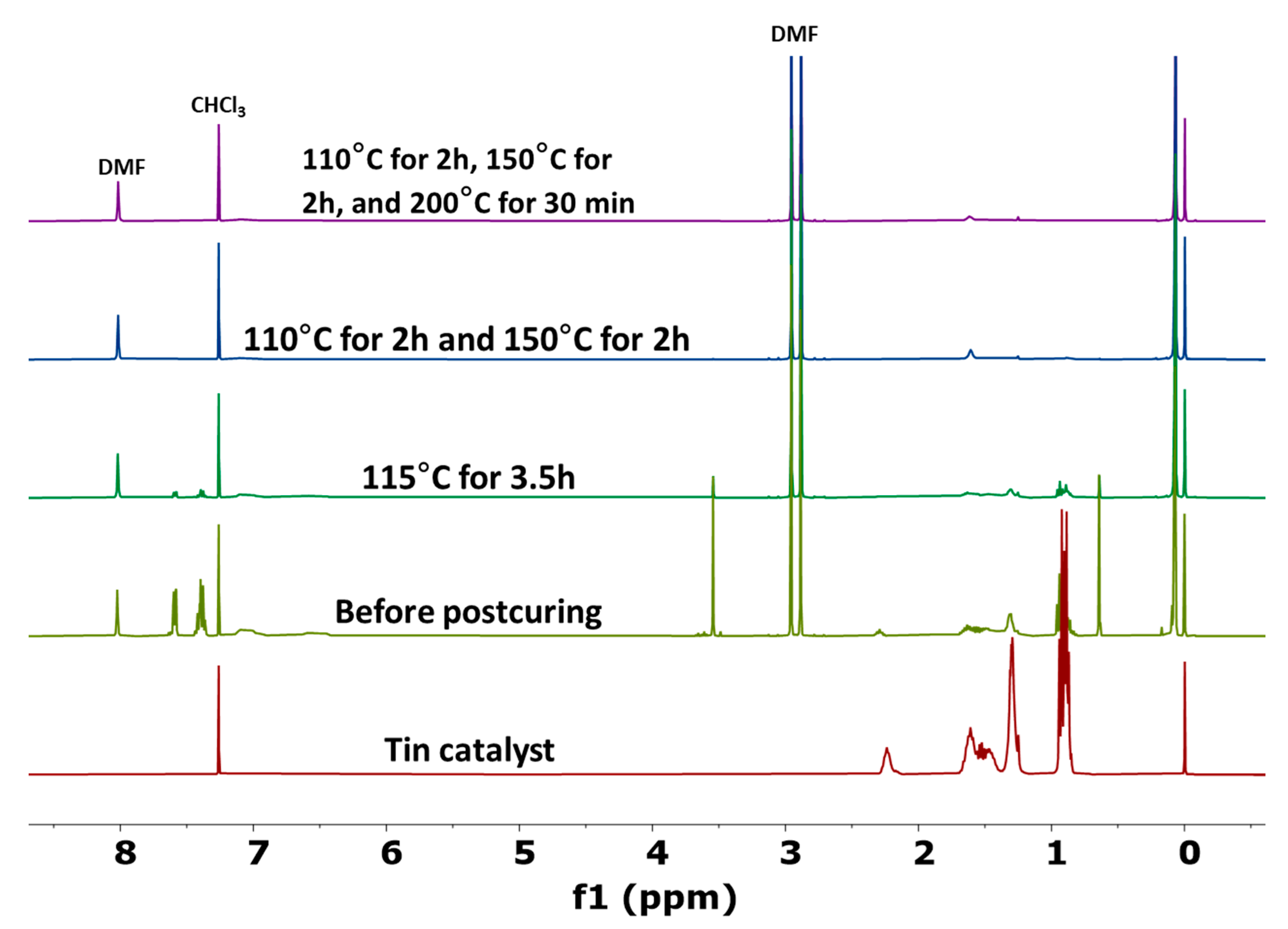
3.1. Thermal Degradation of Tin Catalyst
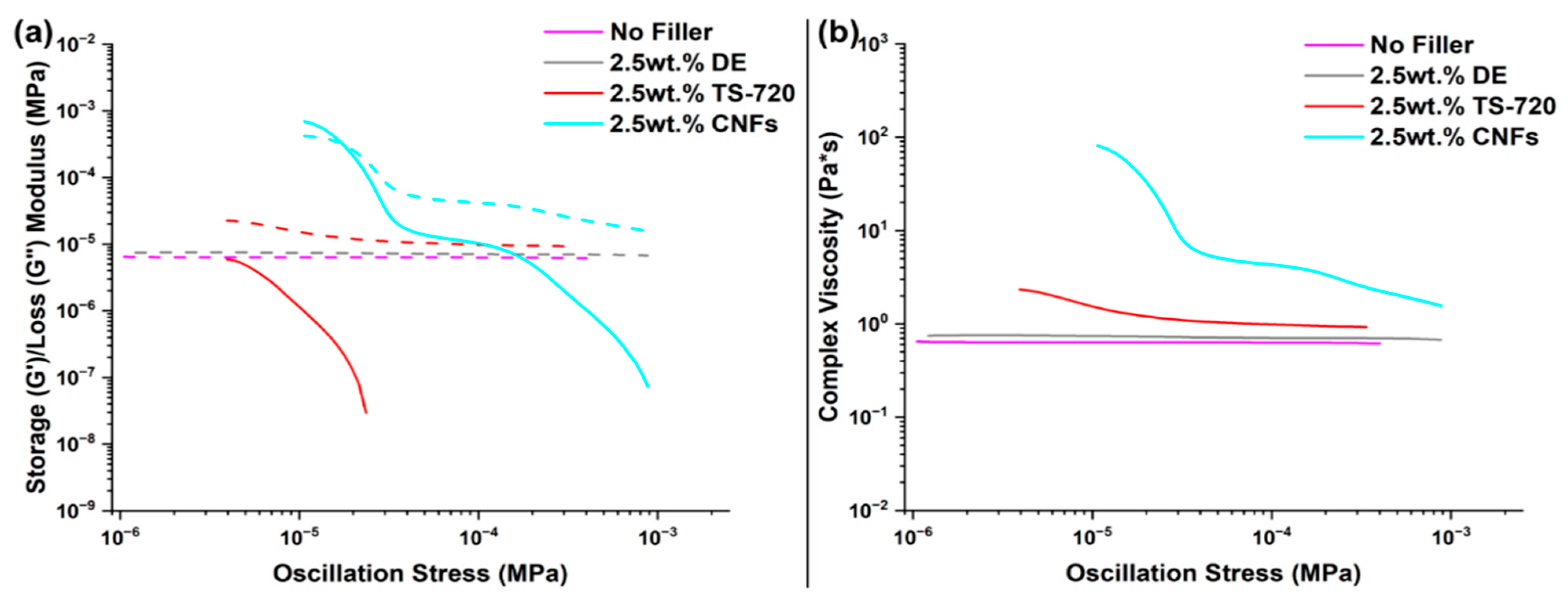
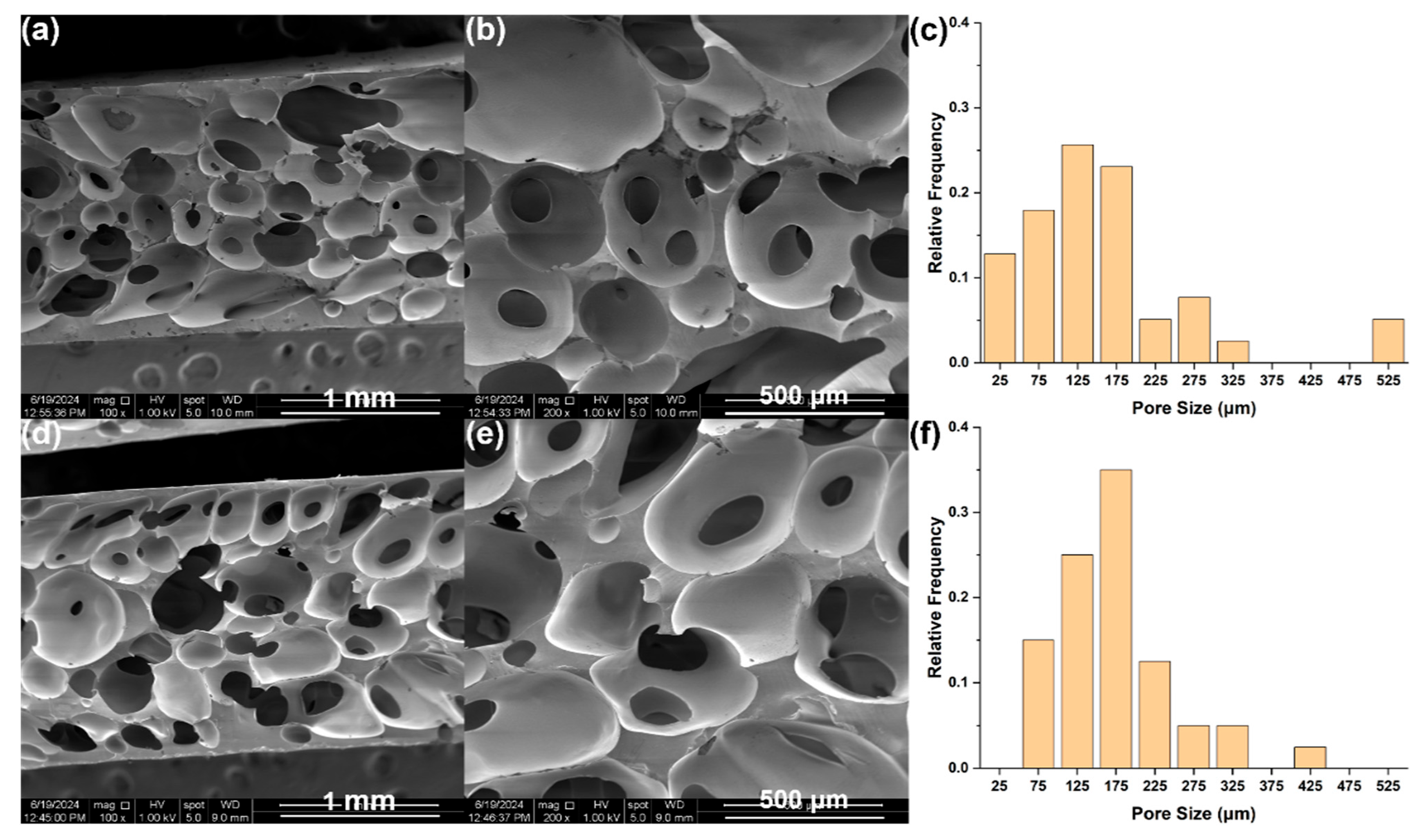
3.2. RTV Foams Containing 2.5 wt.% Fillers
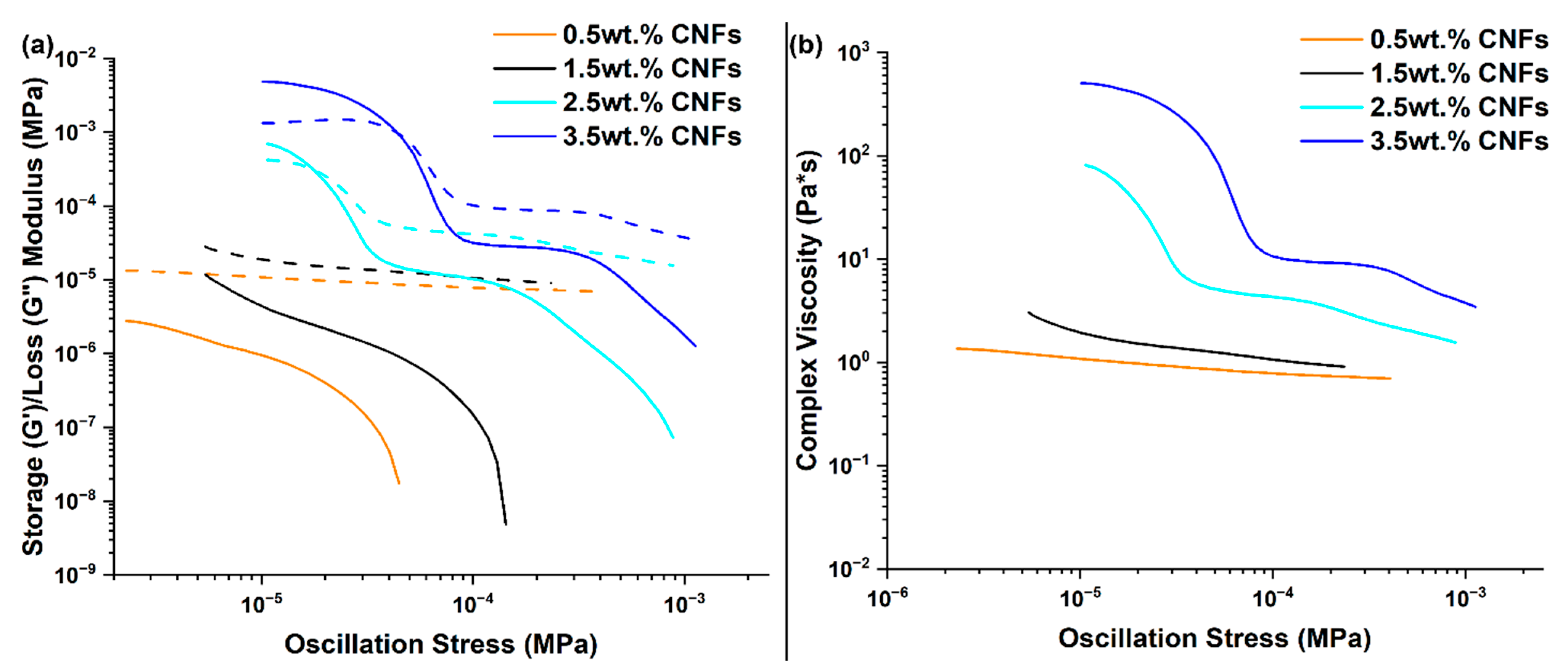
3.3. RTV Foams Containing up to 3.5 wt.% CNFs
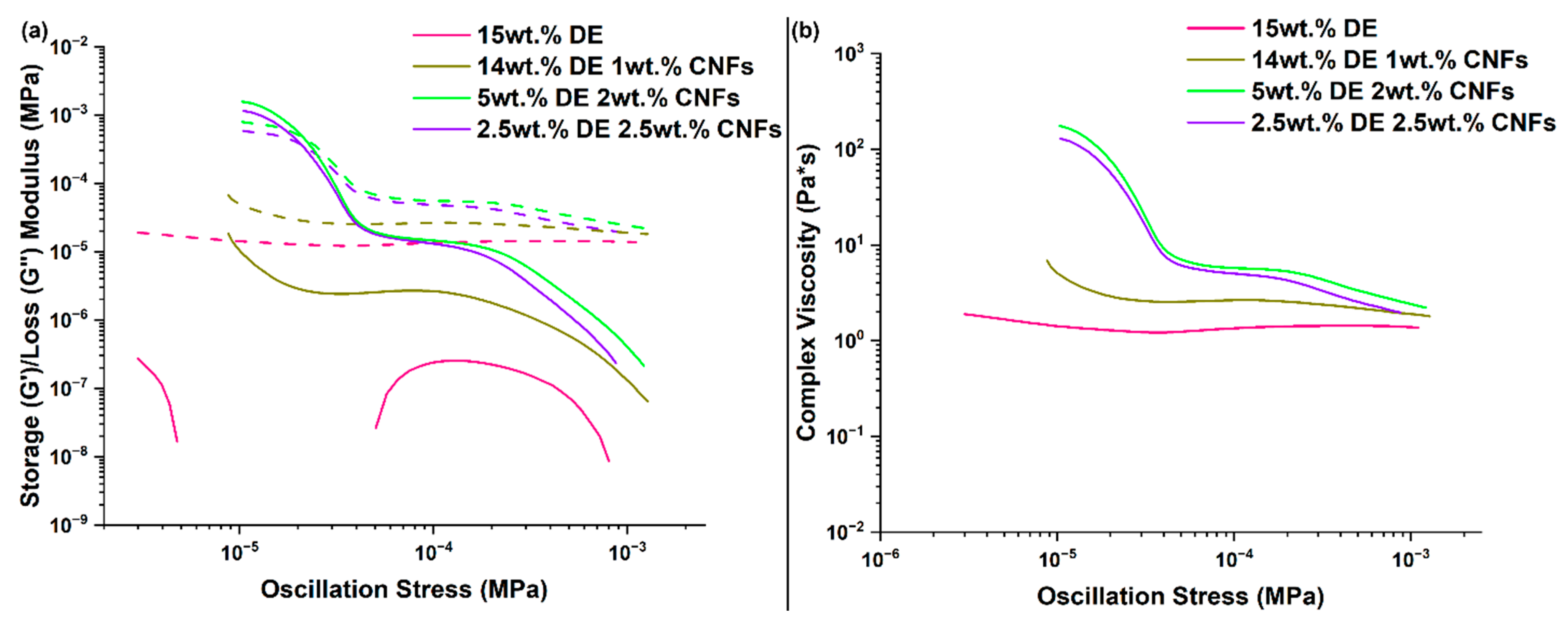
3.4. RTV Foams Containing a Combination of DE and CNFs
3.5. Aging Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Der Weij, F.W. The action of tin compounds in condensation-type RTV silicone rubbers. Die Makromol. Chem. 1980, 181, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, J.; Zárraga, R.; Salazar-Hernández, C. Organotin catalysts in organosilicon chemistry. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2012, 26, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.; Nair, B.N.; Suzuki, T.; Anilkumar, G.M.; Padmanabhan, M.; Hareesh, U.N.S.; Warrier, K.G. Hydrophobic and Metallophobic Surfaces: Highly Stable Non-wetting Inorganic Surfaces Based on Lanthanum Phosphate Nanorods. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oruganti, S.; Mansour, N.N.; Panesi, M.; Panerai, F. Microstructure of pyrolyzing RTV silicone. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 207, 110237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mollah, A.A.; Keshri, A.K.; Kumar, M.; Singh, K.; Rallabhandi, K.D.V.S.; Seelaboyina, R. Development of Macroporous Silicone Rubber for Acoustic Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8751–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbalinia, S.; Katbab, A.; Nazockdast, H.; Katbab, P. Highly compressible piezoresistive strain sensor with a semi-IPN structure based on PU sponge/RTV silicone rubber/MWCNTs. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M.J. Properties and Applications of Silicones. In Advances in Silicones and Silicone-Modified Materials; ACS Symposium Series, Vol. 1051; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labouriau, A.; Robison, T.; Meincke, L.; Wrobleski, D.; Taylor, D.; Gill, J. Aging mechanisms in RTV polysiloxane foams. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 121, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.W.C.; Swain, A.C.; Khan, N.A. Influence of cross-linker and tin (II) bis-2-ethylhexanoate on compression set characteristics of poly(dimethylsiloxane) elastomer networks. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 116, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coons, J.E.; McKay, M.D.; Hamada, M.S. A Bayesian analysis of the compression set and stress-strain behavior in a thermally aged silicone foam. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 1824–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Chinn, S.; Maxwell, R.S.; Wilson, T.S.; Birdsell, S.A. Compression set in gas-blown condensation-cured polysiloxane elastomers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2499–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labouriau, A.; Taylor, D.; Stephens, T.S.; Pasternak, M. Mössbauer and NMR characterization of tin octoate: Neat and residues in RTV foams. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labouriau, A.; Cady, C.; Gill, J.; Taylor, D.; Zocco, A.; Stull, J.; Henderson, K.; Wrobleski, D. The effects of gamma irradiation on RTV polysiloxane foams. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 117, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labouriau, A.; Cox, J.D.; Schoonover, J.R.; Patterson, B.M.; Havrilla, G.J.; Stephens, T.; Taylor, D. Mössbauer, NMR and ATR-FTIR spectroscopic investigation of degradation in RTV siloxane foams. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, S.; Lgaz, H.; Mandal, S.; Adnin, R.J.; Lee, D.-E.; Lee, H.-S.; Mohammad Harmay, N.S.; Al Bakri Abdullah, M.M.; Wang, X.-Y.; Yang, H.-M. Multi-technique investigation on the surface interaction of diatomaceous earth with organic phase change material: Experimental and molecular dynamics aspects. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 391, 123292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallimore, G.R.; Milligan, R.J. Rtv Silicone Foam for Spacecraft Electronic Assemblies. Sampe J. 1982, 18, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Reka, A.A.; Pavlovski, B.; Fazlija, E.; Berisha, A.; Pacarizi, M.; Daghmehchi, M.; Sacalis, C.; Jovanovski, G.; Makreski, P.; Oral, A. Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, thermal modification, and application. Open Chem. 2021, 19, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Skinner, A.R. Thermal ageing studies on room-temperature vulcanised polysiloxane rubbers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 73, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, F.; Jamali, A.R.; Abbasi, M.N.; Mallah, M.A.; Rao, A.A.; Wahocho, S.A.; Anees-ur-Rehman, H.; Chandio, Z.A. A comprehensive review of hydrophobic silica and composite aerogels: Synthesis, properties and recent progress towards environmental remediation and biomedical applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 11226–11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, N.; Alghunaimi, F.I.; Saleh, T.A. Hydrophobic and oleophilic carbon nanofiber impregnated styrofoam for oil and water separation: A green technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, X.M.; Stockdale, J.R.; Adhikari, S.; Legett, S.A.; Pacheco, A.; Guajardo, J.A.; Labouriau, A. Interplay between Shelf Life and Printability of Silica-Filled Suspensions. Polymers 2023, 15, 4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M.; Vittoria, V.; Vertuccio, L.; Lafdi, K.; De Vivo, B.; Lamberti, P.; Spinelli, G.; Tucci, V. The role of carbon nanofiber defects on the electrical and mechanical properties of CNF-based resins. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 305704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askounis, A.; Yamada, Y.; Ikuta, T.; Takahashi, K.; Takata, Y.; Sefiane, K. On the linear dependence of a carbon nanofiber thermal conductivity on wall thickness. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 115119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, T.W.; Kondo, A.; Kozawa, T.; Ohmura, T.; Tuan, W.H.; Naito, M. Effect of fumed silica properties on the thermal insulation performance of fibrous compact. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 9966–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranguren, M.I. Crystallization of polydimethylsiloxane: Effect of silica filler and curing. Polymer 1998, 39, 4897–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frone, A.N.; Berlioz, S.; Chailan, J.F.; Panaitescu, D.M. Morphology and thermal properties of PLA-cellulose nanofibers composites. Carbohyd Polym. 2013, 91, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.; Cho, D. Fiber aspect ratio effect on mechanical and thermal properties of carbon fiber/ABS composites via extrusion and long fiber thermoplastic processes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 80, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diatomaceous Earth. Millipore Sigma. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/search/diatomaceous-earth?focus=products&page=1&perpage=30&sort=relevance&term=Diatomaceous%20earth&type=product (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Carbon Nanofibers. Millipore Sigma. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/search/carbon-nanofibers?focus=products&page=1&perpage=30&sort=relevance&term=carbon%20nanofibers&type=product (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Stein, J.; Prutzman, L.C. Stress-Relaxation Studies of Model Silicone Rtv Networks. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1988, 36, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diani, J.; Fayolle, B.; Gilormini, P. A review on the Mullins effect. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briody, C.; Duignan, B.; Jerrams, S.; Tiernan, J. The implementation of a visco-hyperelastic numerical material model for simulating the behaviour of polymer foam materials. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2012, 64, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, R.W.; Roxburgh, D.G. A pseudo-elastic model for the Mullins effect in filled rubber. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1999, 455, 2861–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| RTV Foam with | Maximum Tensile Stress (MPa) | Compressive Strain at 0.6 MPa (%) | Tear Strength (N/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Filler | 0.039 ± 0.010 | 81.1 ± 5.5 | 23.9 ± 0.1 |
| 2.5 wt.% DE | 0.057 ± 0.001 | 70.5 ± 6.5 | 27.5 ± 5.8 |
| 2.5 wt.% TS-720 | 0.089 ± 0.010 | 61.0 ± 1.2 | 35.8 ± 1.8 |
| 2.5 wt.% CNFs | 0.150 ± 0.020 | 67.9 ± 2.6 | 52.6 ± 1.8 |
| RTV Foam with | Thermal Conductivity at 25 °C (W m−1 K−1) | Td5% (°C) | Derivative Peak (°C) | Glass Transition (°C) | Melting Peak (°C) | Crystallization Peak (°C), % Crystallization (Xc) | Specific Heat at 25 °C (J g−1 C−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No filler | 0.10 | 360 | 401 | −124 | −53 | −96, 19.2 | 1.48–1.65 |
| 2.5 wt.% DE | 0.11 | 362 | 420 | −124 | −54 | −97, 7.3 | 1.45–1.53 |
| 2.5 wt.% TS-720 | 0.10 | 373 | 416 | −123 | N/A | N/A, N/A | 1.22–1.50 |
| 2.5 wt.% CNFs | 0.12 | 375 | 417 | −118 | −51 | −87, 25.8 | 1.43–1.54 |
| RTV Foam with | Maximum Tensile Stress (MPa) | Compressive Strain at 0.6 MPa (%) | Tear Strength (N/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 wt.% CNFs | 0.072 ± 0.009 | 75.9 ± 2.7 | 27.9 ± 5.3 |
| 1.5 wt.% CNFs | 0.089 ± 0.002 | 74.3 ± 2.7 | 30.2 ± 2.9 |
| 2.5 wt.% CNFs | 0.150 ± 0.020 | 67.9 ± 2.6 | 52.6 ± 1.8 |
| RTV Foam with | Thermal Conductivity at 25 °C (W m−1 K−1) | Td5% (°C) | Derivative Peak (°C) | Glass Transition (°C) | Melting Peak (°C) | Crystallization Peak (°C), % Crystallization (Xc) | Specific Heat at 25 °C (J g−1 C−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 wt.% CNFs | 0.10 | 369 | 410 | −120 | −51 | −89, 26.4 | 1.42–1.54 |
| 1.5 wt.% CNFs | 0.10 | 370 | 425 | −119 | −51 | −89, 26.3 | 1.33–1.60 |
| 2.5 wt.% CNFs | 0.12 | 375 | 417 | −118 | −51 | −87, 25.8 | 1.43–1.54 |
| RTV Foam with | Maximum Tensile Stress (MPa) | Compressive Strain at 0.6 MPa (%) | Tear Strength (N/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 wt.% DE | 0.215 ± 0.020 | 63.2 ± 0.8 | 76.8 ± 5.1 |
| 14 wt.% DE + 1 wt.% CNFs | 0.345 ± 0.040 | 68.1 ± 2.6 | 103.1 ± 5.0 |
| 5 wt.% DE +2 wt.% CNFs | 0.311 ± 0.030 | 61.5 ± 4.2 | 73.0 ± 0.1 |
| 2.5 wt.% DE +2.5 wt.% CNFs | 0.155 ± 0.010 | 67.8 ± 2.6 | 63.9 ± 1.8 |
| RTV Foam with | Thermal Conductivity at 25 °C (W m−1 K−1) | Td5% (°C) | Derivative Peak (°C) | Glass Transition (°C) | Melting Peak (°C) | Crystallization Peak (°C), % Crystallization (Xc) | Specific Heat at 25 °C (J g−1 C−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 wt.% DE | 0.10 | 359 | 412 | −120 | −52 | −87, 18.9 | 1.55–1.58 |
| 14 wt.% DE + 1 wt.% CNFs | 0.10 | 363 | 407 | −119 | −51 | −84, 19.9 | 1.42–1.59 |
| 5 wt.% DE +2 wt.% CNFs | 0.11 | 370 | 416 | −120 | −50 | −85, 26.5 | 1.40–1.51 |
| 2.5 wt.% DE +2.5 wt.% CNFs | 0.11 | 371 | 414 | −118 | −50 | −85, 26.4 | 1.20–1.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres, X.M.; Stockdale, J.R.; Pacheco, A.; Legett, S.A.; Bezek, L.B.; Benedikt, B.; Labouriau, A.; Adhikari, S. Relationship Between Filler Type, Thermomechanical Properties, and Aging of RTV Silicone Foams. Polymers 2025, 17, 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141998
Torres XM, Stockdale JR, Pacheco A, Legett SA, Bezek LB, Benedikt B, Labouriau A, Adhikari S. Relationship Between Filler Type, Thermomechanical Properties, and Aging of RTV Silicone Foams. Polymers. 2025; 17(14):1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141998
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres, Xavier M., John R. Stockdale, Adam Pacheco, Shelbie A. Legett, Lindsey B. Bezek, Bart Benedikt, Andrea Labouriau, and Santosh Adhikari. 2025. "Relationship Between Filler Type, Thermomechanical Properties, and Aging of RTV Silicone Foams" Polymers 17, no. 14: 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141998
APA StyleTorres, X. M., Stockdale, J. R., Pacheco, A., Legett, S. A., Bezek, L. B., Benedikt, B., Labouriau, A., & Adhikari, S. (2025). Relationship Between Filler Type, Thermomechanical Properties, and Aging of RTV Silicone Foams. Polymers, 17(14), 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141998






