A Novel Synthesis of Highly Efficient Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Pyridine Resin and Its Application in Drinking Water Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Antibacterial Poly(4-vinylpyridine) Resins
2.3. Determination of Surficial N+ Charge Density
2.4. Determination of Strong-Base Group Exchange Capacity
2.5. Antibacterial Testing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Analysis and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Poly(4-vinylpyridine) Resins
3.2. Optimal Antibacterial Alkyl Chain Length of Poly(4-vinylpyridine) Resins
3.3. Rational Design and Preparation of Highly Efficient Antibacterial Poly(4-vinylpyridine) Resin Py-61
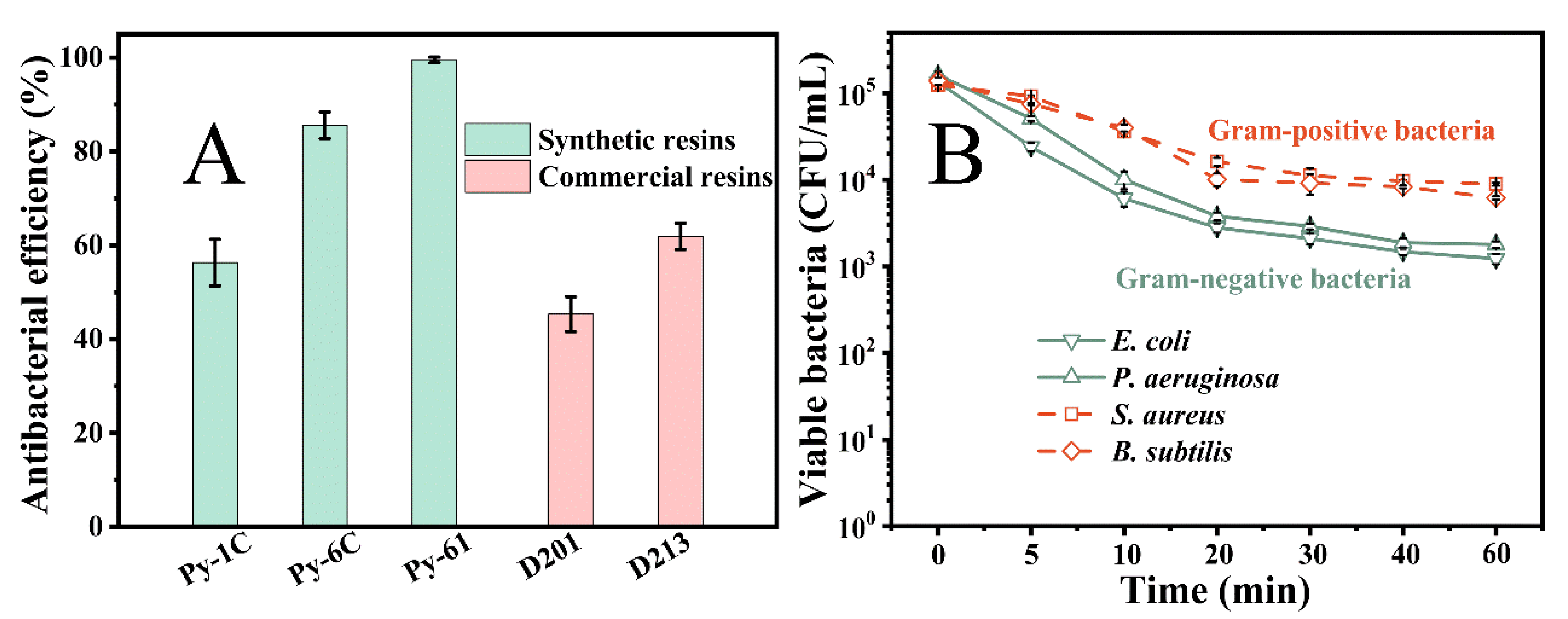
3.4. Antibacterial Performance of Resin Py-61 in Simulated Water
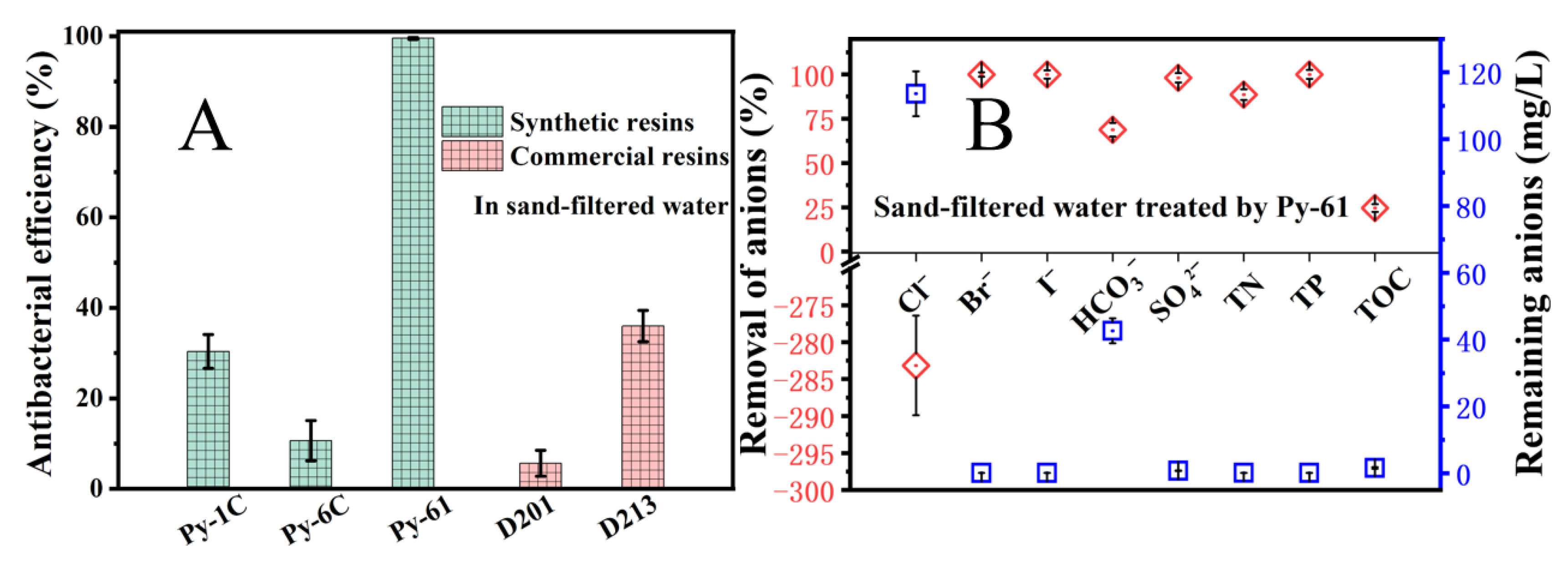
3.5. Disinfection and Purification Performance of Resin Py-61 in Sand-Filtered Water
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pichel, N.; Vivar, M.; Fuentes, M. The problem of drinking water access: A review of disinfection technologies with an emphasis on solar treatment methods. Chemosphere 2018, 218, 1014–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-F.; Mitch, W.A. Drinking water disinfection byproducts (DBPs) and human health effects: Multidisciplinary challenges and opportunities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashau, F.; Ncube, E.J.; Voyi, K. Drinking water disinfection by-products exposure and health effects on pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review. J. Water Health 2018, 16, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrand, V.; Guinamant, J.L.; Bruchet, A.; Brosse, C.; Noij, T.H.M.; Brandt, A.; Sacher, F.; McLeod, C.; Elwaer, A.; Croué, J.; et al. Determination of bromate in drinking water: Development of laboratory and field methods. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Deng, X.; Wan, Q.; Xu, X.; Huang, T. Photoreactivation of fungal spores in water following UV disinfection and their control using UV-based advanced oxidation processes. Water Res. 2018, 148, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.Q.; Wang, W.L.; Huo, Z.Y.; Lu, Y.; Hu, H.Y. Comparison of UV-LED and low pressure UV for water disinfection: Photoreactivation and dark repair of Escherichia coli. Water Res. 2017, 126, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.K.; Ghosh, M. Chlorine resistant bacteria isolated from drinking water treatment plants in West Bengal. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 79, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Shi, P.; Hu, Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.X. Bacterial community shift drives antibiotic resistance promotion during drinking water chlorination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12271–12279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Jia, S.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, S.; Li, A. Metagenomic insights into chlorination effects on microbial antibiotic resistance in drinking water. Water Res. 2013, 47, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.R.E.; Fonseca, A.C.; Mendonça, P.V.; Branco, R.; Serra, A.C.; Morais, P.V.; Coelho, J.F.J. Recent developments in antimicrobial polymers: A review. Materials 2016, 9, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Y. Antimicrobial polymeric materials with quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3626–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chang, F.; Shi, P.; Ye, L.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, Y.; Li, A. Antibiotic resistome alteration by different disinfection strategies in a full-scale drinking water treatment plant deciphered by metagenomic assembly. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.; Shen, S.; Shi, P.; Zhang, H.; Ye, L.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, Y.; Li, A. Antimicrobial resins with quaternary ammonium salts as a supplement to combat the antibiotic resistome in drinking water treatment plants. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibay-Alvarado, J.A.; Garcia-Zamarron, D.J.; Silva-Holguín, P.N.; Donohue-Cornejo, A.; Cuevas-González, J.C.; Espinosa-Cristóbal, L.F.; Ruíz-Baltazar, Á.d.J.; Reyes-López, S.Y. Polymer-based hydroxyapatite–silver composite resin with enhanced antibacterial activity for dental applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.S.; Alhamdan, Y.; Alibrahim, H.; Almulhim, K.S.; Nawaz, M.; Ahmed, S.Z.; Aljuaid, K.; Ateeq, I.S.; Akhtar, S.; Ansari, M.A.; et al. Analyses of experimental dental adhesives based on zirconia/silver phosphate nanoparticles. Polymers 2023, 15, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukdar, M.I.; Ahamad, I.; Iqbal, S.; Malik, M.A.; Dar, O.A.; Akram, M.K.; Fatma, T.; Hashmi, A.A. Fabrication of metal incorporated polymer composite: An excellent antibacterial agent. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1225, 129091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Ilić, K.; Juganson, K.; Ivask, A.; Ahonen, M.; Vrček, I.V.; Kahru, A. Potential ecotoxicological effects of antimicrobial surface coatings: A literature survey backed up by analysis of market reports. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.H. Drinking Water Disinfection By-Products: Toxicological Impacts and Biological Mechanisms Induced by Individual Compounds or as Complex Mixtures; University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign: Champaign, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Chen, M.; Wei, D.; Du, Y. Research progress of disinfection and disinfection by-products in China. J. Environ. Sci. China 2019, 81, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jia, D.; Zhang, G.; Ma, H. Long-chained pyridinium N-chloramines: Synthesis and remarkable biocidal efficacies for antibacterial application. Aust. J. Chem. 2021, 74, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Lv, X.; Du, Z. Substituted pyridinium N-chloramines: Chemical synthesis and antibacterial application. ChemistrySelect 2025, 10, e202405582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, A.; Bian, K.; Shen, S.; Tao, M.; Shi, P. Structure-dependent antimicrobial mechanism of quaternary ammonium resins and a novel synthesis of highly efficient antimicrobial resin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, A.S.S.; Marques, M.R.C.; Costa, L.C.; Maria, L.C.S.; Meron, F. Evaluation of bactericidal action of 2-vinylpiridine copolymers containing quaternary ammonium groups and their charge transfer complexes. Polímeros 2013, 23, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Qian, J.; Pan, B. Fabrication of novel magnetic nanoparticles of multifunctionality for water decontamination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, A.; Bian, K.; Shen, S.; Shi, P. Surficial N+ charge density indicating antibacterial capacity of quaternary ammonium resins in water environment. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsal, E.; Camli, S.T.; Teksen, T.; Tuncel, M.; Tuncel, A. Hydroxyl functionalized uniform-porous beads, synthesis and chromatographic use. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2005, A42, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T11992-2008; Determination of Exchange Capacity of Strong Basic Anion Exchange Resins in Chloride Form. The Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Yin, T.; Wu, Y.; Shi, P.; Li, A.; Xu, B.; Chu, W.; Pan, Y. Anion-exchange resin adsorption followed by electrolysis: A new disinfection approach to control halogenated disinfection byproducts in drinking water. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwakeel, K.Z.; El-Liethy, M.A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Ezzat, S.M.; Kamel, M.M. Facile synthesis of magnetic disinfectant immobilized with silver ions for water pathogenic microorganism’s deactivation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22797–22809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiller, J.C.; Liao, C.J.; Lewis, K.; Klibanov, A.M. Designing surfaces that kill bacteria on contact. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5981–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondrzyk, A.; Fischer, J.; Ritter, H. Antibacterial materials: Structure-bioactivity relationship of epoxy-amine resins containing quaternary ammonium compounds covalently attached. Polym. Int. 2013, 63, 1192–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xia, Q.; Xiao, H. Cationic polymers with tailored structures for rendering polysaccharide-based materials antimicrobial: An overview. Polymers 2019, 11, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ng, A.K.; Xu, R.; Wei, J.; Tan, C.M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial action of dispersed single-walled carbon nanotubes on Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis investigated by atomic force microscopy. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2744–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almousa, R.; Wen, X.; Anderson, G.G.; Xie, D. An improved dental composite with potent antibacterial function. Saudi Dent. J. 2019, 31, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB5749-2022; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. The National Standardization Management Committee of the State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Suzuki, T.; Fujii, Y.; Mitsugashira, T. Adsorption behaviors of f-Elements on quaternary pyridinium resin. J. Ion Exch. 2018, 29, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, K.; Jose Farre, M.; Knight, N. Comparing three Australian natural organic matter isolates to the Suwannee river standard: Reactivity, disinfection by-product yield, and removal by drinking water treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilamová, Z.; Šimonová, Z.; Bednář, J.; Mikeš, P.; Cieslar, M.; Svoboda, L.; Dvorský, R.; Rosenbergová, K.; Kratošová, G. Silver-loaded poly(vinyl alcohol)/polycaprolactone polymer scaffold as a biocompatible antibacterial system. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Bian, C.; Guo, F.; Xiao, X.; Hu, R.; Lin, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Dong, X. In-situ supramolecular self-assembly strategy to fabricate carbon-doped g-C3N4 microtubes: Efficient photocatalytic removal of antibiotics and bacterial inactivation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Ma, C.; Cao, L.; Kong, D.; Feng, H.; Li, W.; Chen, S. Synthesis of MXene/COF/Cu2O heterojunction for photocatalytic bactericidal activity and mechanism evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraugi, S.S.; Asare, F.; Gazo, R.; Routray, W. Advances in sustainable production of biochar and biochar-based nanocomposites: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 514, 145752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
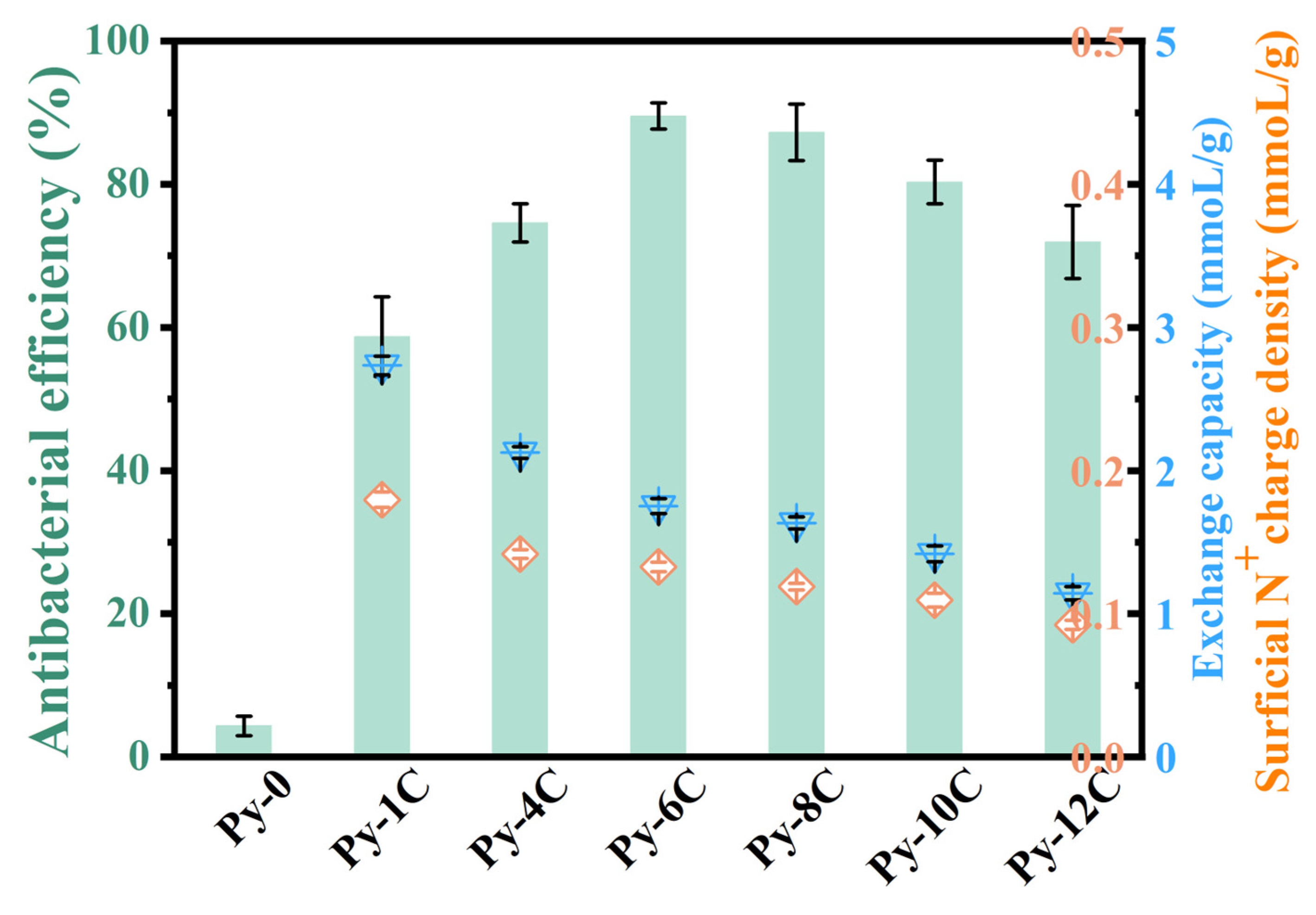
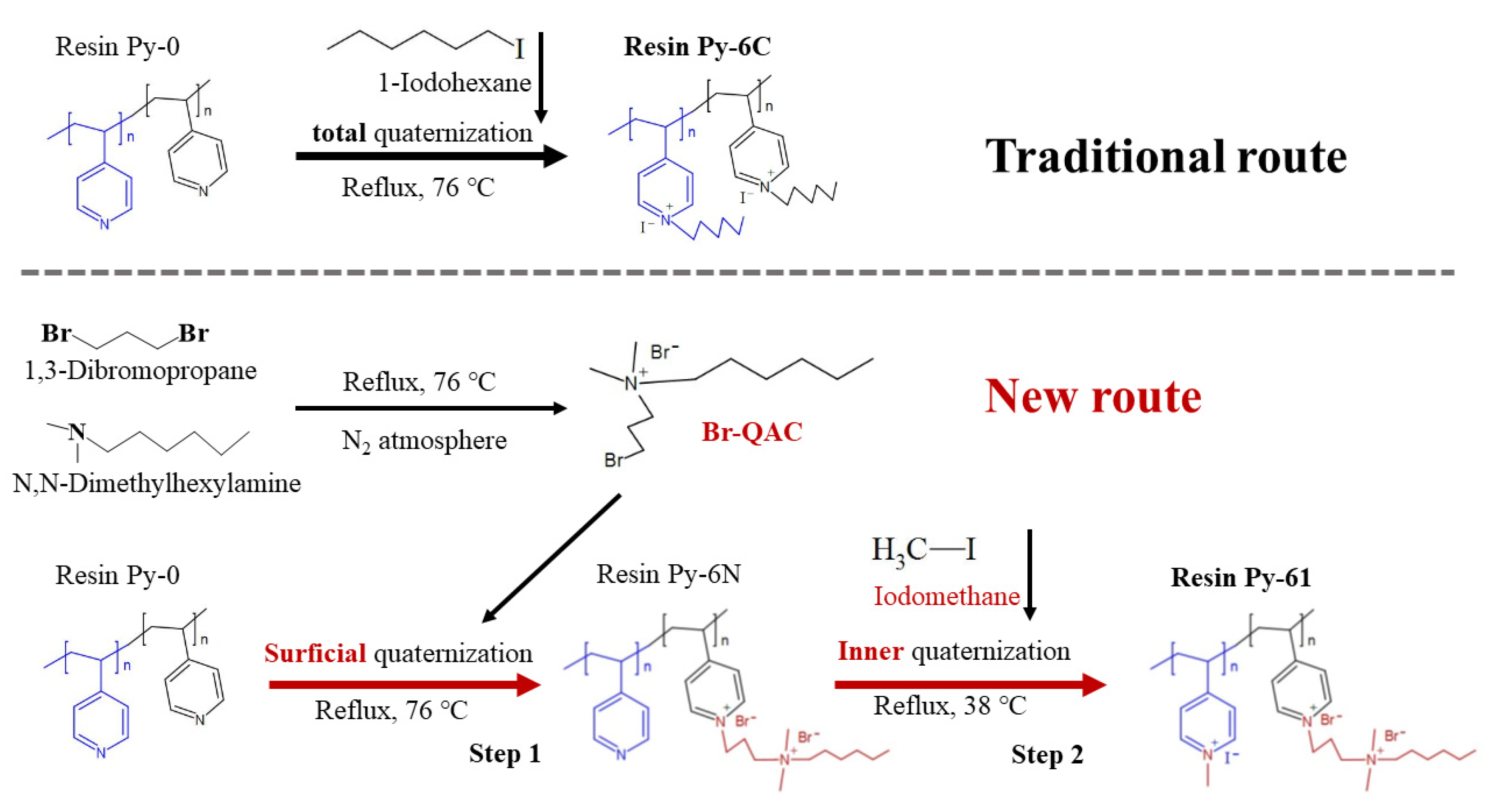
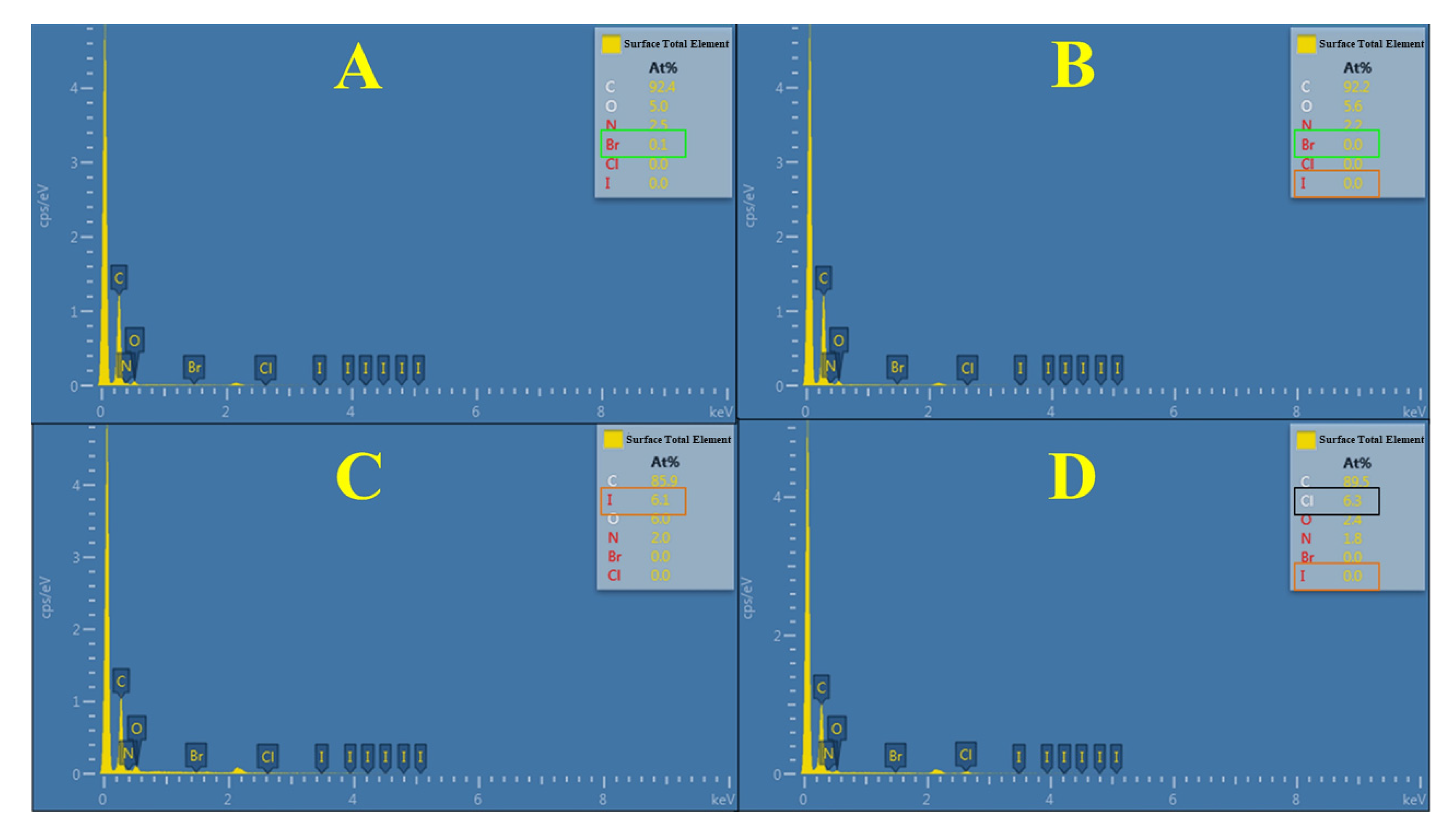
| Resins | Alkyl Chain Length | Cross Linkage | Size (μm) | Average Pore Size (nm) | Strong-Base Group Exchange Capacity (mmol/g) | Surficial N+ Charge Density (mmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Py-0 | None | 25% | 50~80 Mesh/275 μm | 16.06 | None | None |
| Py-1C | C1/methyl | 25% | 50~80 Mesh/275 μm | 16.01 | 2.7350 | 0.1797 ± 2.94% |
| Py-4C | C4/butyl | 25% | 50~80 Mesh/275 μm | 16.01 | 2.1264 | 0.1418 ± 2.18% |
| Py-6C | C6/hexyl | 25% | 50~80 Mesh/275 μm | 15.42 | 1.7522 | 0.1327 ± 2.53% |
| Py-8C | C8/ octyl | 25% | 50~80 Mesh/275 μm | 15.39 | 1.6350 | 0.1191 ± 1.93% |
| Py-10C | C10/ decyl | 25% | 50~80 Mesh/275 μm | 15.27 | 1.4190 | 0.1095 ± 4.29% |
| Py-12C | C12/dodecyl | 25% | 50~80 Mesh/275 μm | 15.24 | 1.1435 | 0.0923 ± 3.57% |
| Py-61 | C6 + C1 | 25% | 50~80 Mesh/275 μm | 15.87 | 2.5251 | 0.1832 ± 2.19% |
| D201 | C1/methyl | 20% | 50~80 Mesh/261 μm | 17.45 | 3.5107 | 0.1811 ± 1.62% |
| D213 | C1/methyl | 20% | 50~80 Mesh/270 μm | 18.26 | 3.4435 | 0.1753 ± 1.55% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Dong, F.; Zuo, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, D.; Wu, J.; Cheng, S.; Li, A. A Novel Synthesis of Highly Efficient Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Pyridine Resin and Its Application in Drinking Water Treatment. Polymers 2025, 17, 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131885
Zhang H, Liu H, Wang W, Dong F, Zuo Y, Huang S, Zhang D, Wu J, Cheng S, Li A. A Novel Synthesis of Highly Efficient Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Pyridine Resin and Its Application in Drinking Water Treatment. Polymers. 2025; 17(13):1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131885
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huaicheng, Haolin Liu, Wei Wang, Fengxia Dong, Yanting Zuo, Shouqiang Huang, Daqian Zhang, Ji Wu, Shi Cheng, and Aimin Li. 2025. "A Novel Synthesis of Highly Efficient Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Pyridine Resin and Its Application in Drinking Water Treatment" Polymers 17, no. 13: 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131885
APA StyleZhang, H., Liu, H., Wang, W., Dong, F., Zuo, Y., Huang, S., Zhang, D., Wu, J., Cheng, S., & Li, A. (2025). A Novel Synthesis of Highly Efficient Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Pyridine Resin and Its Application in Drinking Water Treatment. Polymers, 17(13), 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131885






