Preliminary Study on the Development of a Biodegradable Functional Nasal Packing Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
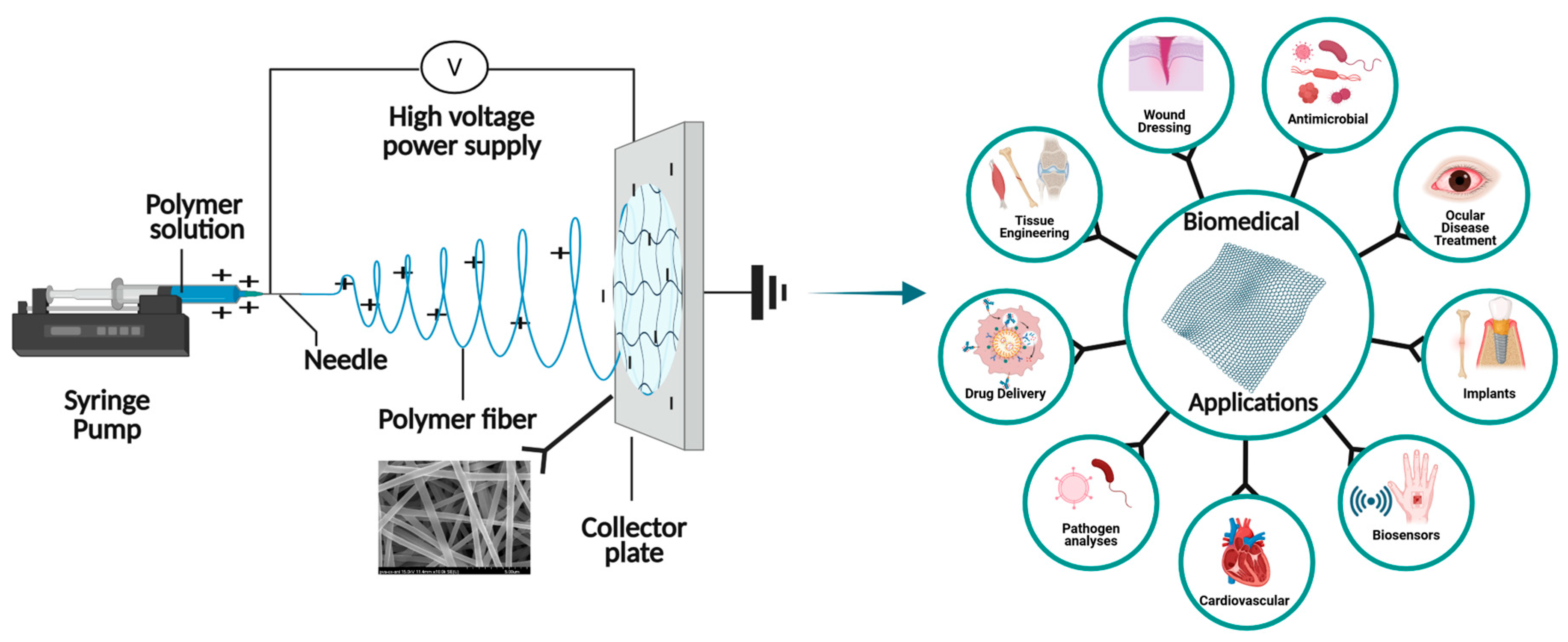
2.1. Fabrication of Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes
2.1.1. Materials
2.1.2. Preparation of CDs
2.1.3. Polymer Solution Preparation for Electrospinning
2.1.4. Electrospinning of Nanofiber Membranes
2.1.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Analysis
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
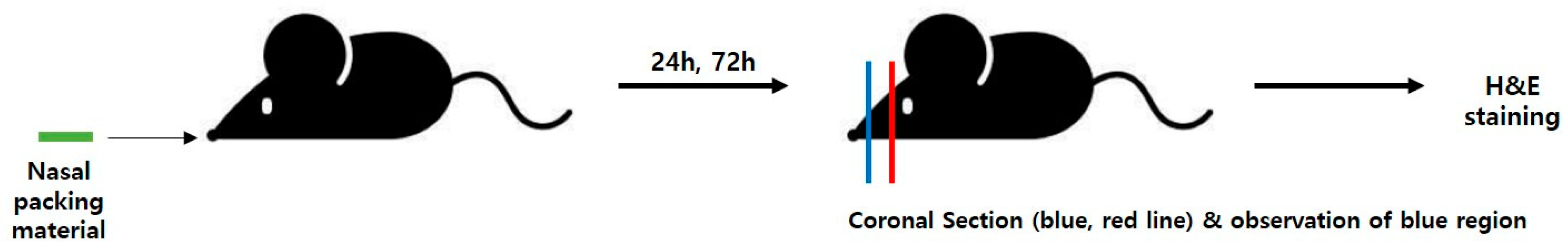
2.3. Animal Experiment
2.3.1. Mouse Model and Packing Procedure
2.3.2. Histological Analysis
3. Results
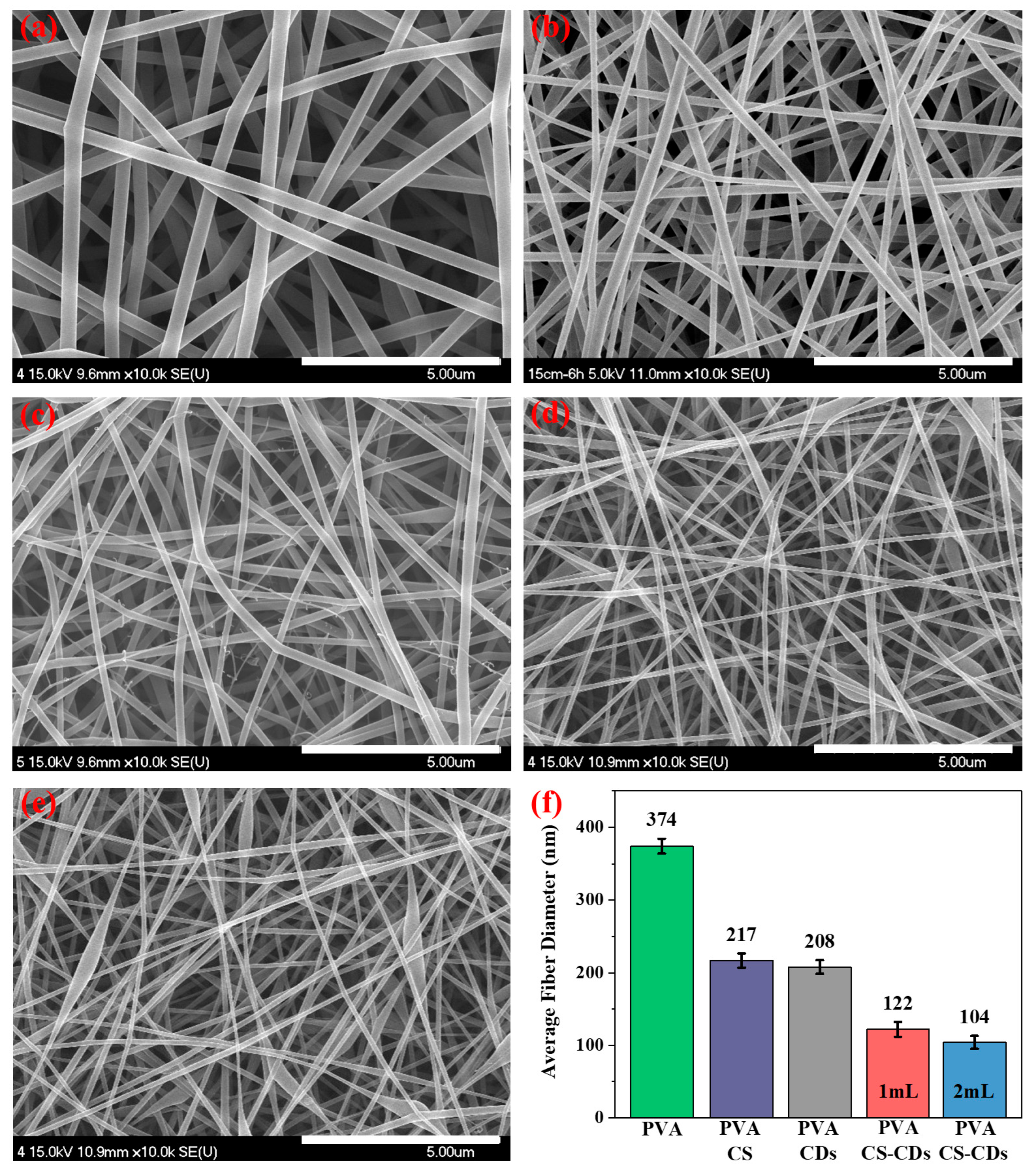
3.1. SEM Analysis
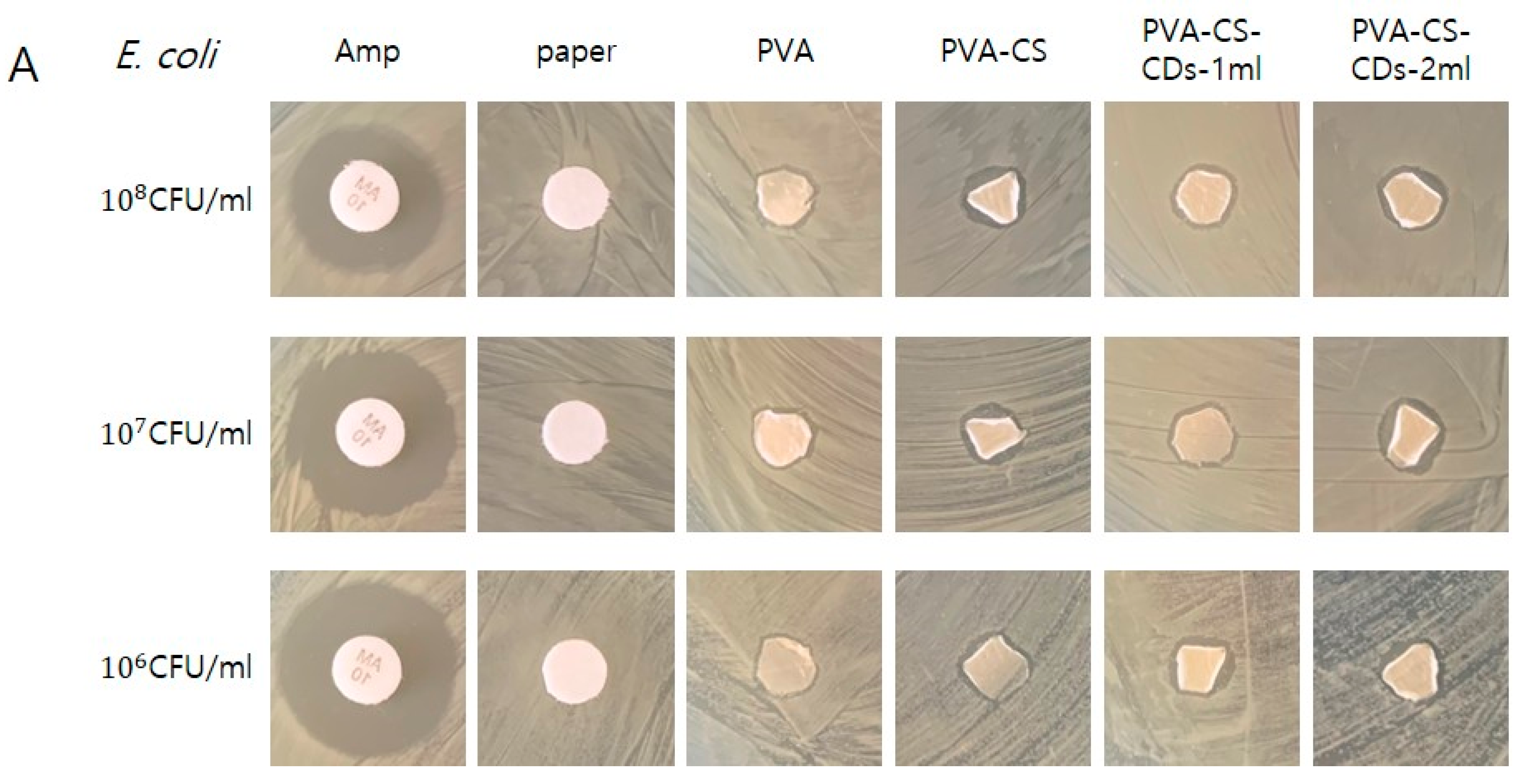
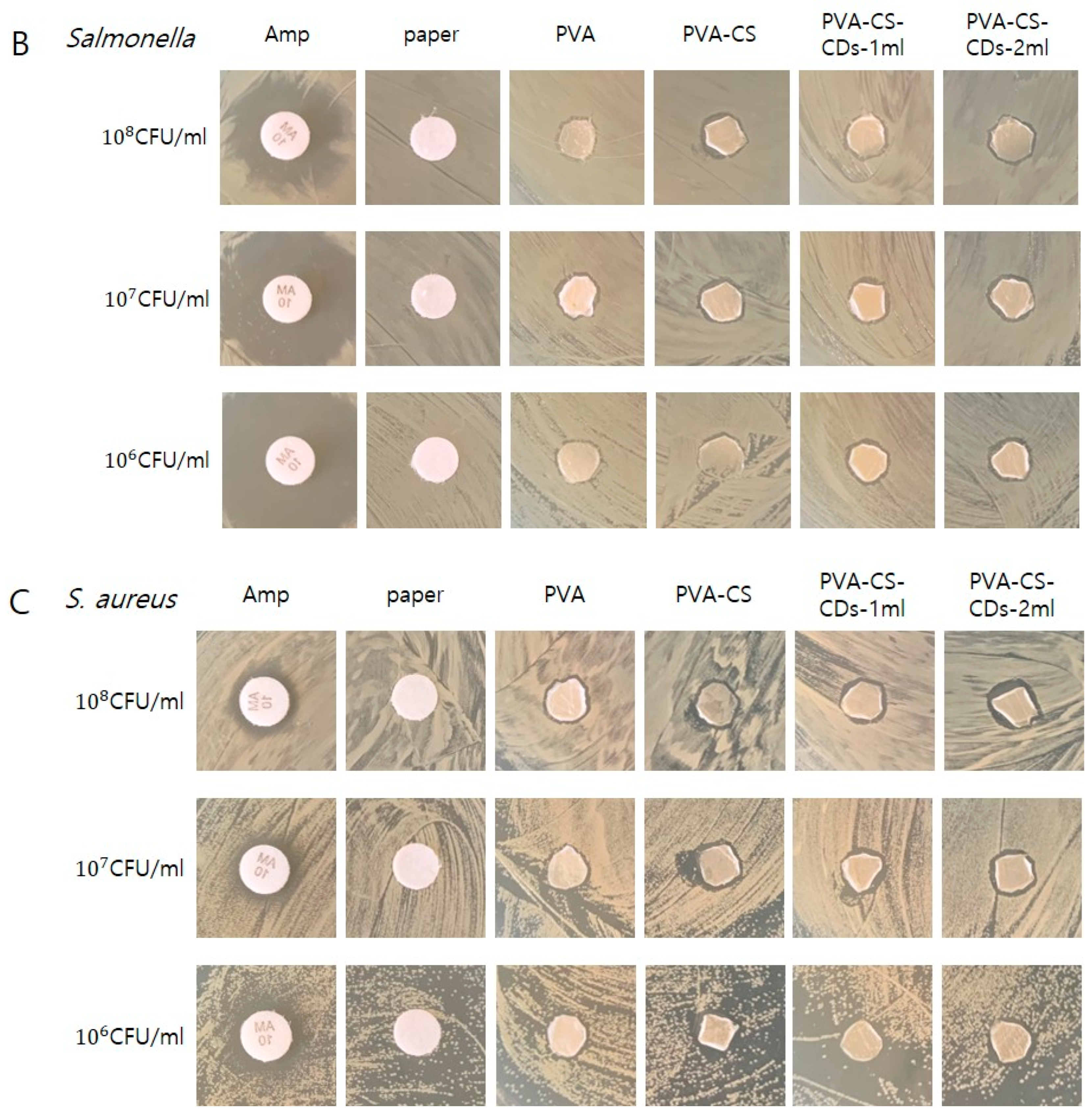
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
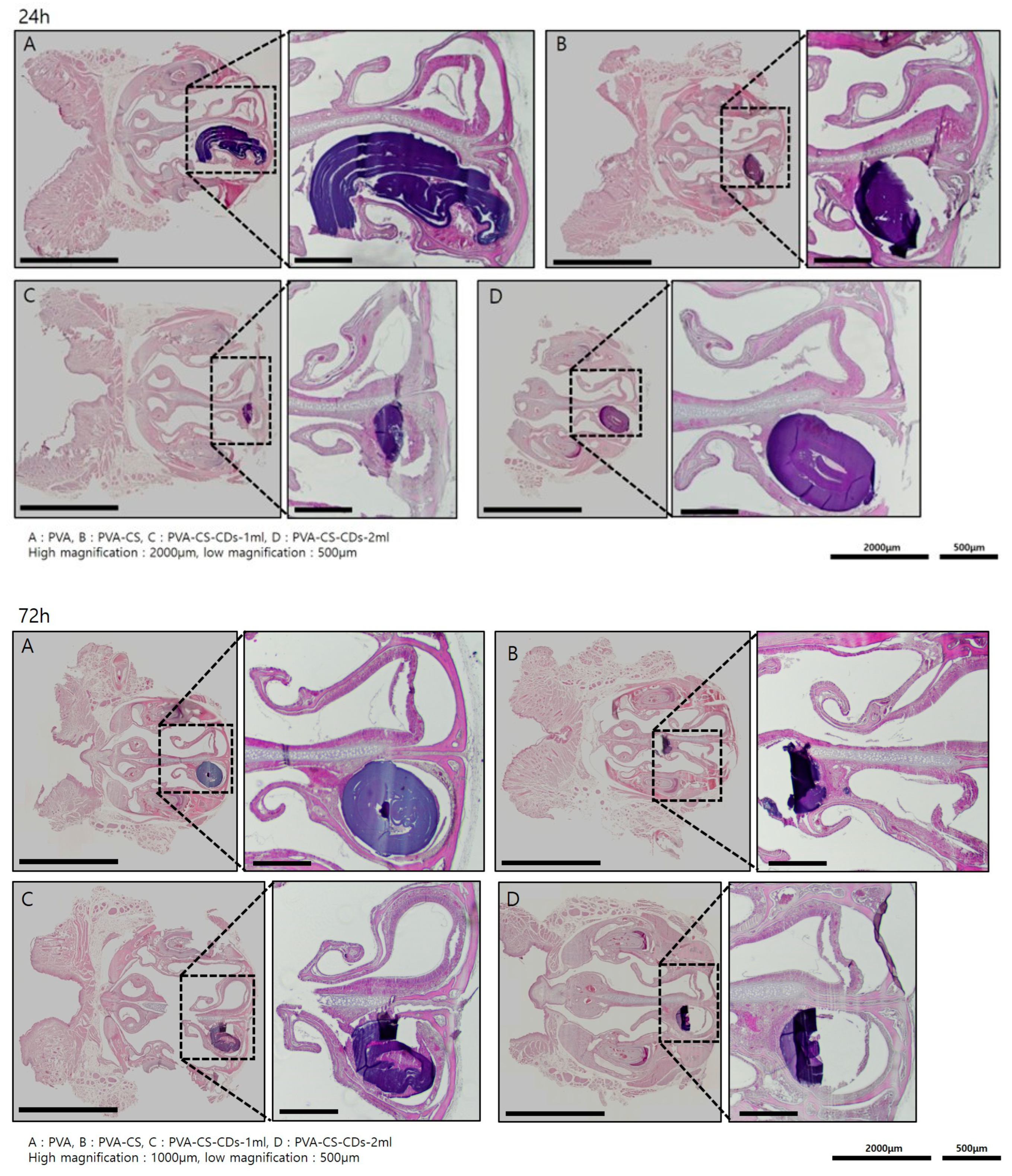
3.3. Animal Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melis, A.; Karligkiotis, A.; Bozzo, C.; Machouchas, N.; Volpi, L.; Castiglia, P.; Castelnuovo, P.; Meloni, F. Comparison of three different polyvinyl alcohol packs following functional endoscopic Nasal surgery. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Cong, W.; Liu, Y.; Song, C.; Mi, H.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Shen, C. Antibacterial polyurethane foams with quaternized-chitosan as a chain extender for nasal packing and hemostasis. Acta Biomater. 2024, 181, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, R.; Sharma, R.; Malhotra, V.; Rathore, P.K. Comparison of Trans-septal Suturing Technique With Polyvinyl Alcohol Sponge-Based Nasal Packing for Hemostasis in Septoplasty. Cureus 2022, 14, e25161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, M. A robust carbon dot-based antibacterial CDs-PVA film as a wound dressing for antibiosis and wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 1940–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, E.; Abboud, H.; Nagy, N.; Hofmeister, B.; Ostorházi, E.; Tóth, B.; Pinke, B.; Mészáros, L.; Zelkó, R.; Kazsoki, A. Formulation and Development of Nanofiber-Based Ophthalmic Insert for the Treatment of Bacterial Conjunctivitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, M.; Youssef, A.; Baseer, R.A. Fabrication of multifunctional ZnO@tannic acid nanoparticles embedded in chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol blend packaging film. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, R.; Lai, J.; Mai, D.; Li, L.; Dai, L.; Lu, Y.; Lin, J. Construction of chitosan/carboxylated polyvinyl alcohol/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) composite antibacterial hydrogel for rapid wound healing. Biomater. Adv. 2025, 166, 214041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parın, F.N.; El-Ghazali, S.; Yeşilyurt, A.; Parın, U.; Ullah, A.; Khatri, M.; Kim, I.S. PVA/Inulin-Based Sustainable Films Reinforced with Pickering Emulsion of Niaouli Essential Oil for Potential Wound Healing Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Ge-Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Mu, P.; Cui, J. Excellent Antibacterial Properties of Silver/Silica-Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol Transparent Film. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimirad, S.; Khaki, M.; Ghaznavi-Rad, E.; Abtahi, H. Investigation of a novel bilayered PCL/PVA electrospun nanofiber incorporated Chitosan-LL37 and Chitosan-VEGF nanoparticles as an advanced antibacterial cell growth-promoting wound dressing. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 661, 124341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Yang, L.; Ma, R.; Xiang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Ren, J.; Xu, B.B.; El-Bahy, Z.M.; Thabet, H.K.; Huang, Z.; et al. Amoxicillin-laded sodium alginate/cellulose nanocrystals/polyvinyl alcohol composite nanonetwork sponges with enhanced wound healing and antibacterial performance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280 Pt 1, 135701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badgujar, P.; Malik, A.K.; Mehata, A.K.; Setia, A.; Verma, N.; Randhave, N.; Shukla, V.N.; Kande, V.; Singh, P.; Tiwari, P.; et al. Polyvinyl alcohol-chitosan based oleanolic acid nanofibers against bacterial infection: In vitro studies and in vivo evaluation by optical and laser Doppler imaging modalities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279 Pt 4, 135532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenawy, E.R.; Kamoun, E.A.; Elsigeny, S.M.; Heikal, S.; El-Shehawy, A.A.; Mahmoud, Y.A. Vanillin loaded-physically crosslinked PVA/chitosan/itaconic membranes for topical wound healing applications. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2024, 22, 22808000241281273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Rehman, S.R.; Ahmed, R.; Zahid, A.A.; Sharifi, M.; Falahati, M.; Hasan, A. Electrospun chitosan membranes containing bioactive and therapeutic agents for enhanced wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Structural and functional design of electrospun nanofibers for hemostasis and wound healing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 1027–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lee, B.K. Incorporation of biomass-derived carbon dots and hydrochar into electrospun polylactic acid membranes: A sustainable zero-waste approach to highly efficient methylene blue, malachite green and neutral red dye removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282 Pt 4, 137160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, W.J.; Yu, Y.; He, C.; Li, X.Q. Green synthesis of biomass-derived carbon dots as an efficient corrosion inhibitor. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Su, Z.; Zhang, K.; Ren, J.; Sun, R.; Wang, X. All-Biomass Fluorescent Hydrogels Based on Biomass Carbon Dots and Alginate/Nanocellulose for Biosensing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Xiong, J.; Lei, S.; Wang, L.; Qin, X. Diameter Refinement of Electrospun Nanofibers: From Mechanism, Strategies to Applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, D.; Kalita, N.K.; Hakkarainen, M. Carbon Dot-Modified Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Mats: Increased Susceptibility to Degradation under Soil Burial and UV Irradiation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailley, D.; Hébraud, A.; Schlatter, G. A Review on the Impact of Humidity during Electrospinning: From the Nanofiber Structure Engineering to the Applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.H.; So, E.; Mustafa, F.E.; Jeong, J.-h.; Lee, B.-K. Preliminary Study on the Development of a Biodegradable Functional Nasal Packing Material. Polymers 2025, 17, 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131878
Lee DH, So E, Mustafa FE, Jeong J-h, Lee B-K. Preliminary Study on the Development of a Biodegradable Functional Nasal Packing Material. Polymers. 2025; 17(13):1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131878
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dong Hoon, EunA So, Faizan E Mustafa, Jae-ho Jeong, and Bong-Kee Lee. 2025. "Preliminary Study on the Development of a Biodegradable Functional Nasal Packing Material" Polymers 17, no. 13: 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131878
APA StyleLee, D. H., So, E., Mustafa, F. E., Jeong, J.-h., & Lee, B.-K. (2025). Preliminary Study on the Development of a Biodegradable Functional Nasal Packing Material. Polymers, 17(13), 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131878






