Bionic Bovine Achilles Tendon Collagen Composite Membrane Loaded with Anti-Inflammatory Kukoamine B Promotes Skin Wound Healing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the BATC Composite Membrane
2.2. Characterisation of the BATC Composite Membrane
2.2.1. Morphology Observations
2.2.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Spectral Analysis
2.2.3. Thermal Stability Measurement
2.2.4. DPPH Radical-Scavenging Activity
2.2.5. Absorbency and Retention Capacity
2.2.6. Kukoamine B Release In Vitro
2.3. In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Cytocompatibility
2.3.1. Human Skin Fibroblast Cell Culture for In Vitro Models
2.3.2. Preparation of BATC Composite Membrane Extracts
2.3.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.3.4. Cytocompatibility Assay
2.4. In Vivo Study of BATC Composite Membrane Designed to Promote Skin Wound Healing
2.4.1. Establishment of a Mouse Wound Model
2.4.2. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.4.3. Expression Levels of Key Genes Involved in Wound Healing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Characterisation of BATC Composite Membrane
3.1.1. BATC Composite Membrane Structure
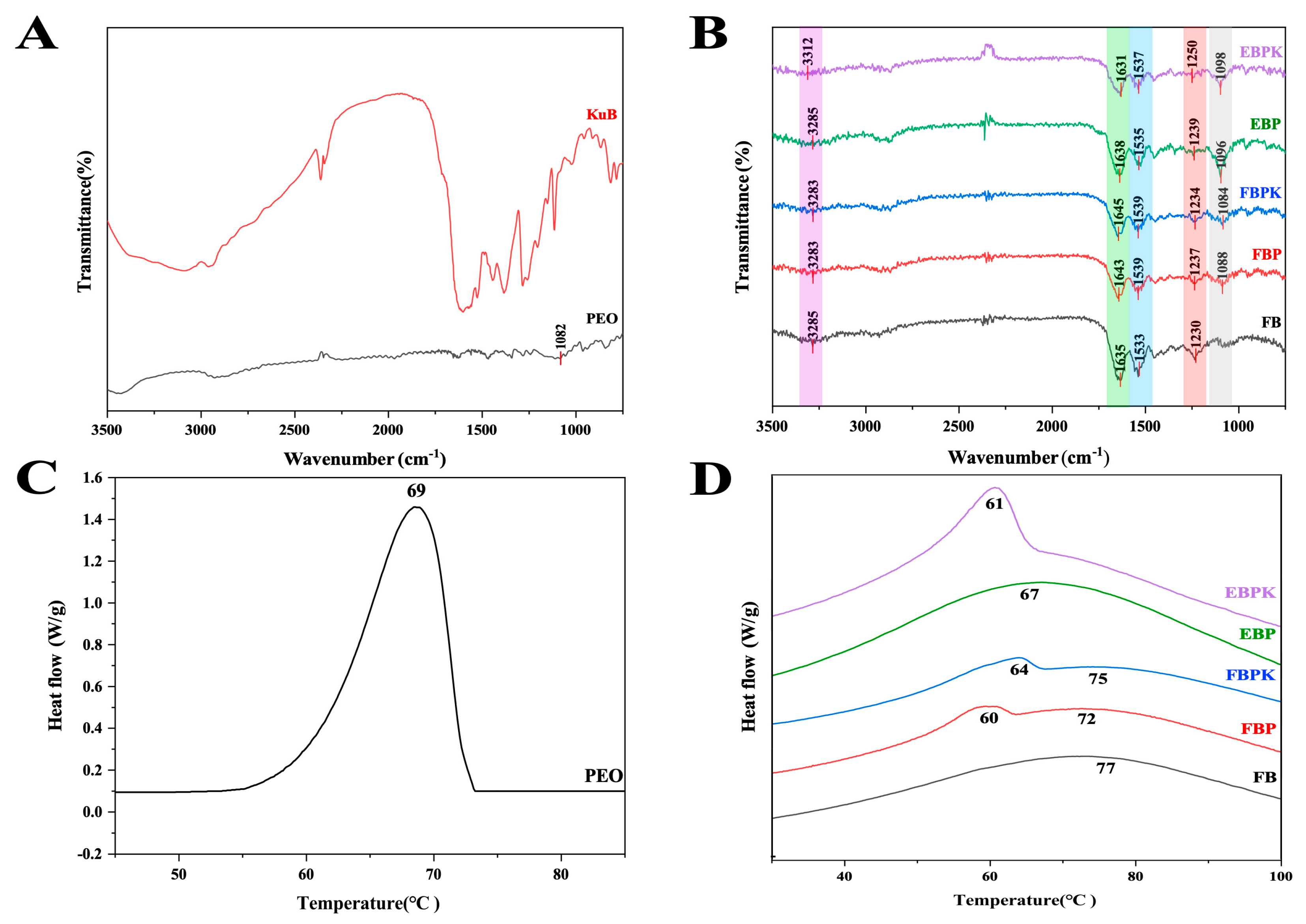
3.1.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
3.1.3. Thermal Stability Analysis
3.1.4. Antioxidant Activity
3.1.5. Absorbency and Retention Capacity
3.1.6. Kukoamine B Release In Vitro
3.2. Cytotoxicity and Cytocompatibility
3.3. Evaluation of Wound-Healing Ability
3.3.1. Wound Area Evaluation
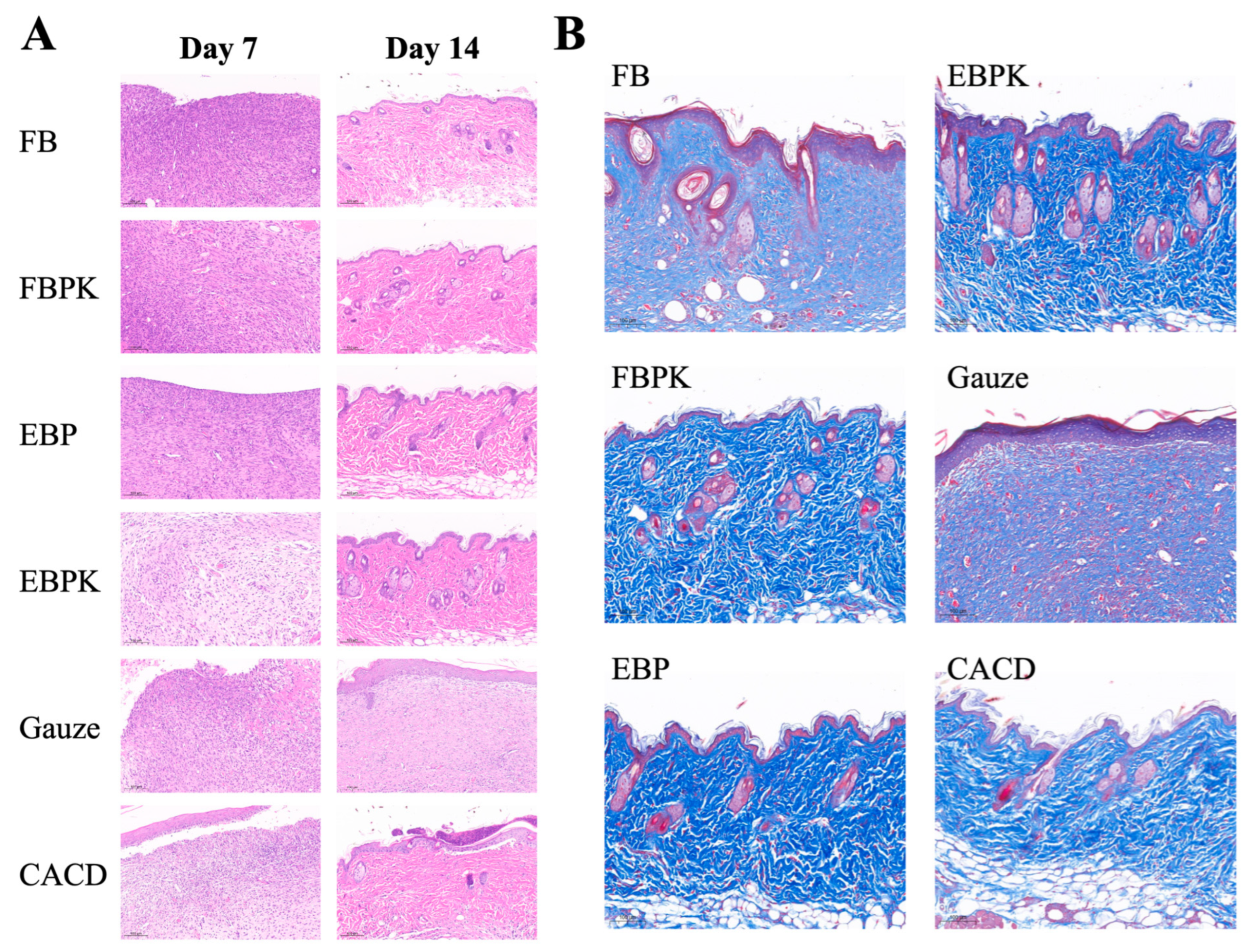
3.3.2. Histological Observation of the Wounds
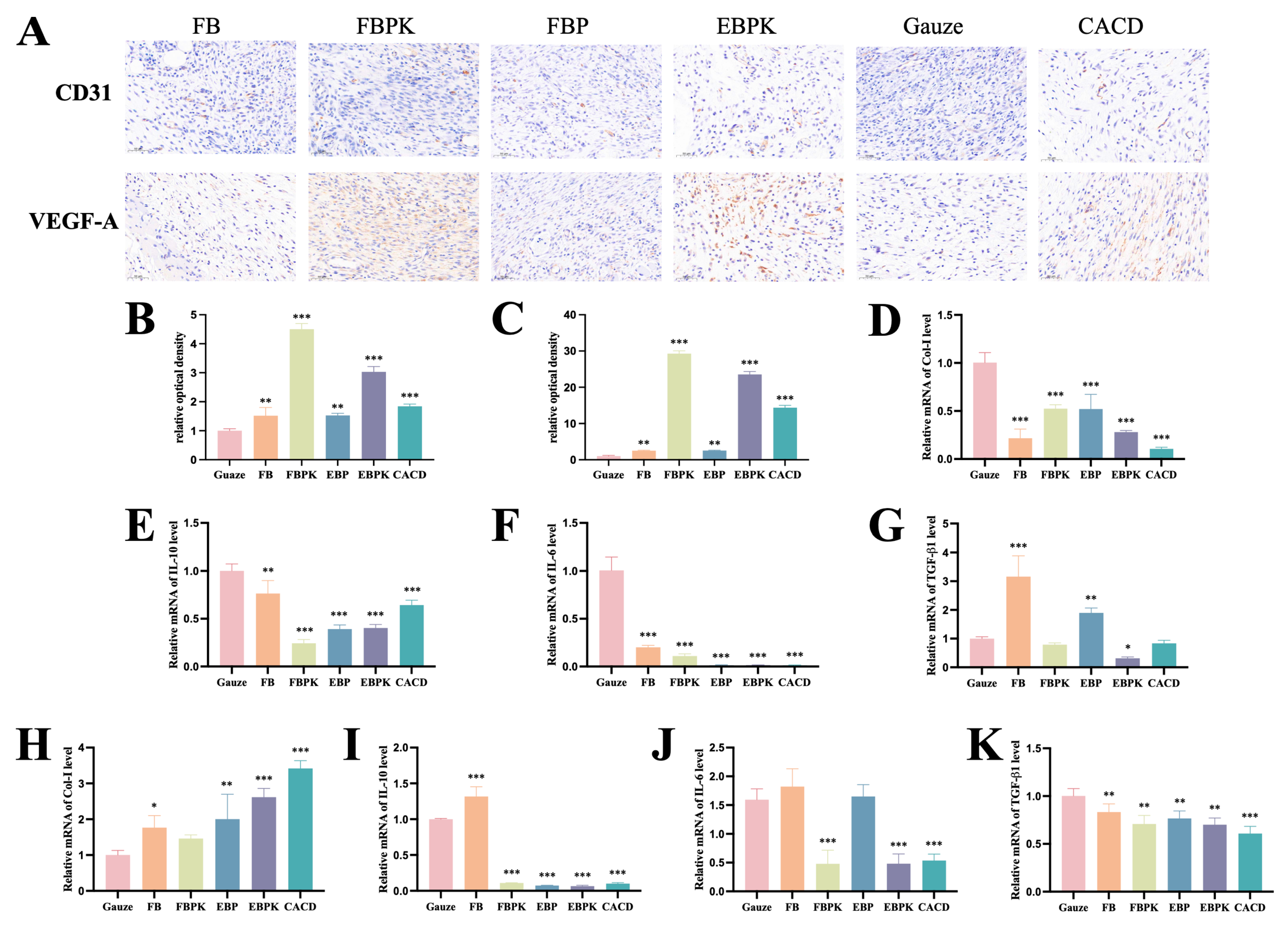
3.3.3. Immunohistochemical Evaluation
3.3.4. Expression Levels of Key Genes Involved in Wound Healing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dąbrowska, A.K.; Spano, F.; Derler, S.; Adlhart, C.; Spencer, N.D.; Rossi, R.M. The Relationship between Skin Function, Barrier Properties, and Body-dependent Factors. Skin Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasra, S.; Pramanik, S.; Oza, V.; Kansara, K.; Kumar, A. Advancements in Wound Management: Integrating Nanotechnology and Smart Materials for Enhanced Therapeutic Interventions. Discov. Nano 2024, 19, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Ni, J.; Lin, Y.; Ge, H.; Zheng, D.; Chen, G.; Sun, X.; et al. Electrospinning in Promoting Chronic Wound Healing: Materials, Process, and Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2025, 13, 1550553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.G.; Tan, T.-W.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Bus, S.A. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. JAMA 2023, 330, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, G.A.; Swogger, E.; Wolcott, R.; deLancey Pulcini, E.; Secor, P.; Sestrich, J.; Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S. Biofilms in Chronic Wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2008, 16, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, A.; Goswami, L.; Kim, B.S. Nanomaterial-Based Therapy for Wound Healing. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumeeruddy-Elalfi, Z.; Gurib-Fakim, A.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Chemical Composition, Antimicrobial and Antibiotic Potentiating Activity of Essential Oils from 10 Tropical Medicinal Plants from Mauritius. J. Herb. Med. 2016, 6, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, J.S.; Matthews, K.H.; Stevens, H.N.E.; Eccleston, G.M. Wound Healing Dressings and Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2892–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Sun, B.; Ni, D.; Wu, J.; Peng, X. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing via Macrophage Modulation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Ren, J. Controlled Release of Silver Ions from AgNPs Using a Hydrogel Based on Konjac Glucomannan and Chitosan for Infected Wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Liu, K.; Jiang, T.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, W.; Tan, R.; Wei, W.; Yang, X.; et al. GelMA/PEGDA Microneedles Patch Loaded with HUVECs-Derived Exosomes and Tazarotene Promote Diabetic Wound Healing. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhakeem, E.; Monir, S.; Teaima, M.H.M.; Rashwan, K.O.; El-Nabarawi, M. State-of-the-Art Review of Advanced Electrospun Nanofiber Composites for Enhanced Wound Healing. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hu, J.; Hong, Z.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Huang, J.; Wu, X.; Ren, J. Multifunctional Electrospun Textiles for Wound Healing. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2022, 18, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Yang, N.; Ling, L.; Zhang, M.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Y. Electrospun Collagen Nanofibers Reduce Inflammation, Inhibit Fibrosis, and Promote Wound Healing on the Ocular Surface. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 20267–20278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackstone, B.N.; Gallentine, S.C.; Powell, H.M. Collagen-Based Electrospun Materials for Tissue Engineering: A Systematic Review. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q. Greener Synthesis of Electrospun Collagen/Hydroxyapatite Composite Fibers with an Excellent Microstructure for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowbhagya, R.; Muktha, H.; Ramakrishnaiah, T.N.; Surendra, A.S.; Sushma, S.M.; Tejaswini, C.; Roopini, K.; Rajashekara, S. Collagen as the Extracellular Matrix Biomaterials in the Arena of Medical Sciences. Tissue Cell 2024, 90, 102497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matinong, A.M.E.; Chisti, Y.; Pickering, K.L.; Haverkamp, R.G. Collagen Extraction from Animal Skin. Biology 2022, 11, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, H.; Wang, J.; Qiu, H.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Song, L.; Ramshaw, J.; et al. Characterization of Recombinant Humanized Collagen Type III and Its Influence on Cell Behavior and Phenotype. J. Leather Sci. Eng. 2022, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zheng, X.; Wang, N.; Fan, S.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J. Kukoamine B Promotes TLR4-Independent Lipopolysaccharide Uptake in Murine Hepatocytes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57498–57513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, D.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Olatunji, O.J.; Wan, P.; Gong, K. Kukoamine B Ameliorate Insulin Resistance, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Other Metabolic Abnormalities in High-Fat/High-Fructose-Fed Rats. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chou, Y.-C.; Yu, P.-C.; Huang, C.-T.; Liu, S.-J. Anti-Adhesive Resorbable Indomethacin/Bupivacaine-Eluting Nanofibers for Tendon Rupture Repair: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 1688.12-2017; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine. Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Madhan, B.; Subramanian, V.; Rao, J.R.; Nair, B.U.; Ramasami, T. Stabilization of Collagen Using Plant Polyphenol: Role of Catechin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2005, 37, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasin, S.N.N.; Said, Z.; Halib, N.; Rahman, Z.A.; Mokhzani, N.I. Polymer-Based Hydrogel Loaded with Honey in Drug Delivery System for Wound Healing Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.-H.; Shen, S.-J.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chou, Y.-C.; Yu, P.-C.; Liu, S.-J. Tri-Layered Doxycycline-, Collagen- and Bupivacaine-Loaded Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Tendon Rupture Repair. Polymers 2022, 14, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ma, L. Therapeutic Effects of Chitosan/β-Glycerophosphate/Collagen Hydrogel Combined with MSCs on Chronic Achilles Tendon Injury via the Akt/GSK-3β Pathway. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2025, 20, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, P.; Sun, J. Endowing Improved Osteogenic Activities with Collagen Membrane by Incorporating Biocompatible Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1259904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darshan, T.G.; Chen, C.-H.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Shalumon, K.T.; Chien, Y.-M.; Kao, H.-H.; Chen, J.-P. Development of High Resilience Spiral Wound Suture-Embedded Gelatin/PCL/Heparin Nanofiber Membrane Scaffolds for Tendon Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 314–333. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, S.K.; Yoo, I.H.; Park, H.Y.; Kang, C.; Han, S.Y.; Moon, J.H.; Park, W.H.; Yeo, Y.H.; Jun, S.; Yi, Y.-S.; et al. An Atelocollagen Injection Enhances the Healing of Nonoperatively Treated Achilles Tendon Tears: An Experimental Study in Rats. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2023, 11, 23259671231200933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, K.; Toyoda, H.; Manaka, T.; Orita, K.; Hirakawa, Y.; Saito, K.; Iio, R.; Shimatani, A.; Ban, Y.; Yao, H.; et al. In Vivo Study on the Repair of Rat Achilles Tendon Injury Treated with Non-Thermal Atmospheric-Pressure Helium Microplasma Jet. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301216. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chou, Y.-C.; Hong, B.-K.; Huang, C.-T.; Liu, S.-J. Novel CO2-Encapsulated Pluronic F127 Hydrogel for the Treatment of Achilles Tendon Injury. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ding, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zou, J. Magnesium Ion/Gallic Acid MOF-Laden Multifunctional Acellular Matrix Hydrogels for Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2025, 8, 3811–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, J.; Li, Y.-Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.-N.; Song, M. Non-Coding RNAs in Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes: Mechanisms, Therapeutic Potential, and Challenges in Wound Healing. World J. Stem Cells 2025, 17, 102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liao, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. The Role of Vascular and Lymphatic Networks in Bone and Joint Homeostasis and Pathology. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1465816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Xu, M.-Z.; Ma, L.; Chen, Q.-D.; He, B.-B.; Ji-De, A. Progress and Perspectives on BMP9-ID1 Activation of HIF-1α and VEGFA to Promote Angiogenesis in Hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1480683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanga, V.; Isseroff, R.R.; Soulika, A.M.; Romanelli, M.; Margolis, D.; Kapp, S.; Granick, M.; Harding, K. Chronic Wounds. Nat. Rev. Dis Primers 2022, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, N.; Phillips, C.J.; Harding, K. A Narrative Review of the Epidemiology and Economics of Chronic Wounds. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 187, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Las Heras, K.; Igartua, M.; Santos-Vizcaino, E.; Hernandez, R.M. Chronic Wounds: Current Status, Available Strategies and Emerging Therapeutic Solutions. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, Q.; Yao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Topham, P.D.; Yue, K.; Ren, L.; Wang, L. Superhydrophobic Hierarchical Fiber/Bead Composite Membranes for Efficient Treatment of Burns. Acta Biomater. 2019, 92, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, S.; Solouk, A.; Mirzadeh, H.; Mazinani, S.; Lagaron, J.M.; Sharifi, S.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review of Key Challenges of Electrospun Scaffolds for Tissue-Engineering Applications: Challenges Regarding Electrospun Scaffolds: A Review. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, 715–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskitoros-Togay, Ş.M.; Bulbul, Y.E.; Dilsiz, N. Combination of Nano-Hydroxyapatite and Curcumin in a Biopolymer Blend Matrix: Characteristics and Drug Release Performance of Fibrous Composite Material Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 590, 119933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pati, F.; Adhikari, B.; Dhara, S. Isolation and Characterization of Fish Scale Collagen of Higher Thermal Stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3737–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Raines, R.T. Collagen-based Biomaterials for Wound Healing. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, J.R.; Zhang, Y.; Ramakrishna, S. In Vitro Culture of Human Dermal Fibroblasts on Electrospun Polycaprolactone Collagen Nanofibrous Membrane. Artif. Organs 2006, 30, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Xiong, X.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, X. Comparison of Collagens Extracted from Swim Bladder and Bovine Achilles Tendon. Mater. Res. Express 2023, 10, 055403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.K.; Taga, Y.; Takagi, Y.K.; Masuda, R.; Hattori, S.; Koide, T. The Thermal Stability of the Collagen Triple Helix Is Tuned According to the Environmental Temperature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, B.; Homer, W.J.A.; Leslie, L.J.; Kyriakou, G.; Rosal, R.; Topham, P.D.; Theodosiou, E. Chemically Cross-linked Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Electrospun Fibrous Mats as Wound Dressing Materials. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Pandit, S.; Balusamy, S.R.; Madhusudanan, M.; Singh, H.; Amsath Haseef, H.M.; Mijakovic, I. Advanced Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy: Gold, Silver, and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Oncological Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2403059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Koh, Y.G.; Lee, W.G.; Seok, J.; Park, K.Y. The Use of Epidermal Growth Factor in Dermatological Practice. Int. Wound J. 2023, 20, 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; He, G.; Tao, X.; Gao, S.; Zhou, M.; Tang, Y.; Tang, K.; Guo, L.; Chen, W. An Aligned-to-Random PLGA/Col1-PLGA/nHA Bilayer Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane Enhances Tendon-to-Bone Healing in a Murine Model. Am. J. Sports Med. 2025, 53, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yun, X.; Guan, Y.; Cao, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Meng, H.; Liu, Y.; Quan, Q.; Wei, M. Wnt3a-Modified Nanofiber Scaffolds Facilitate Tendon Healing by Driving Macrophage Polarization during Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 9010–9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Meng, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Su, W.; Xu, J.; Hou, J.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Z.; et al. Coaxial Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes as Dual-Functional Biomimetic Tendon Sheath for Tendon Repair and Anti-Peritendinous Adhesion. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2402074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieber, J.; Meier-Bürgisser, G.; Miescher, I.; Weber, F.E.; Wolint, P.; Yao, Y.; Ongini, E.; Milionis, A.; Snedeker, J.G.; Calcagni, M.; et al. Bioactive and Elastic Emulsion Electrospun DegraPol Tubes Delivering IGF-1 for Tendon Rupture Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Biodegradable Polymer Electrospinning for Tendon Repairment. Polymers 2023, 15, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wu, G.; Cai, P.; Ding, Y.; Cui, J.; Wu, J.; Shen, Y.; Song, J.; Yuan, Z.; EL-Newehy, M.; et al. Carbon Fiber-Mediated Electrospinning Scaffolds Can Conduct Electricity for Repairing Defective Tendon. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 52104–52115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Primer | Primer Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | Forward | CAAGCTCATTTCCTGGTATGACAAT |
| Reverse | GTTGGGATAGGGCCTCTCTTG | |
| Col-I | Forward | TCCTGACGCATGGCCAAGAAGACA |
| Reverse | TCCGGGCAGAAAGCACAGCACTC | |
| IL-10 | Forward | GCTCCAAGACCAAGGTGTCTACAA |
| Reverse | CCGTTAGCTAAGATCCCTGGATCA | |
| IL-6 | Forward | TCCAGTTGCCTTCTTGGGAC |
| Reverse | GCCATTGCACAACTCTTTTCTCA | |
| TGF-β1 | Forward | CAACAATTCCTGGCGTTACCTTGG |
| Reverse | GAAAGCCCTGTATTCCGTCTCCTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, R.; Mu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Hua, J.; Cao, L.; Chen, D.; Li, K.; Jin, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. Bionic Bovine Achilles Tendon Collagen Composite Membrane Loaded with Anti-Inflammatory Kukoamine B Promotes Skin Wound Healing. Polymers 2025, 17, 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131874
Luo R, Mu Y, Zhao L, Hua J, Cao L, Chen D, Li K, Jin Z, Guo Y, Zhang B, et al. Bionic Bovine Achilles Tendon Collagen Composite Membrane Loaded with Anti-Inflammatory Kukoamine B Promotes Skin Wound Healing. Polymers. 2025; 17(13):1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131874
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Ruting, Yujie Mu, Le Zhao, Jinglin Hua, Lixin Cao, Danting Chen, Kun Li, Zhenkai Jin, Yanchuan Guo, Bing Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Bionic Bovine Achilles Tendon Collagen Composite Membrane Loaded with Anti-Inflammatory Kukoamine B Promotes Skin Wound Healing" Polymers 17, no. 13: 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131874
APA StyleLuo, R., Mu, Y., Zhao, L., Hua, J., Cao, L., Chen, D., Li, K., Jin, Z., Guo, Y., Zhang, B., & Wang, M. (2025). Bionic Bovine Achilles Tendon Collagen Composite Membrane Loaded with Anti-Inflammatory Kukoamine B Promotes Skin Wound Healing. Polymers, 17(13), 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131874






