Thermoplastics for Clear Aligners: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Thermoplastics
3. General Requirements of Thermoplastics for Clear Aligners
4. Optical Properties
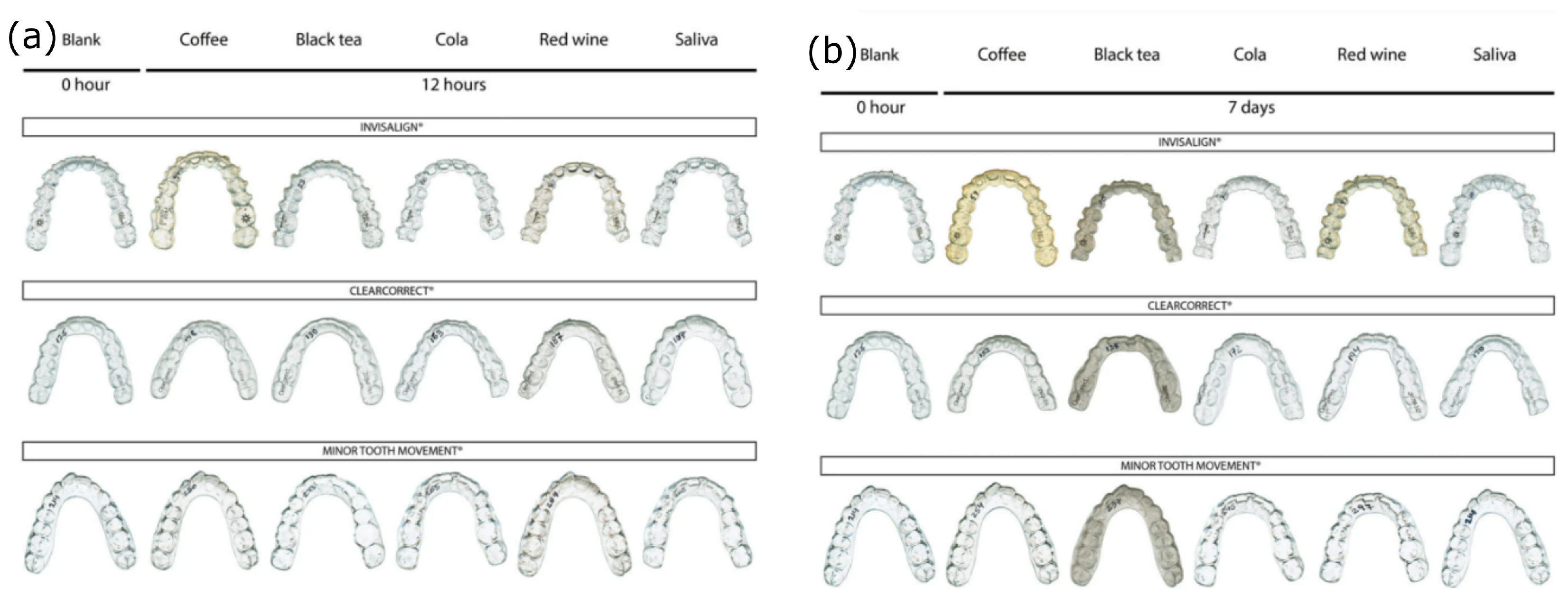
5. Aging and Chemical Resistance
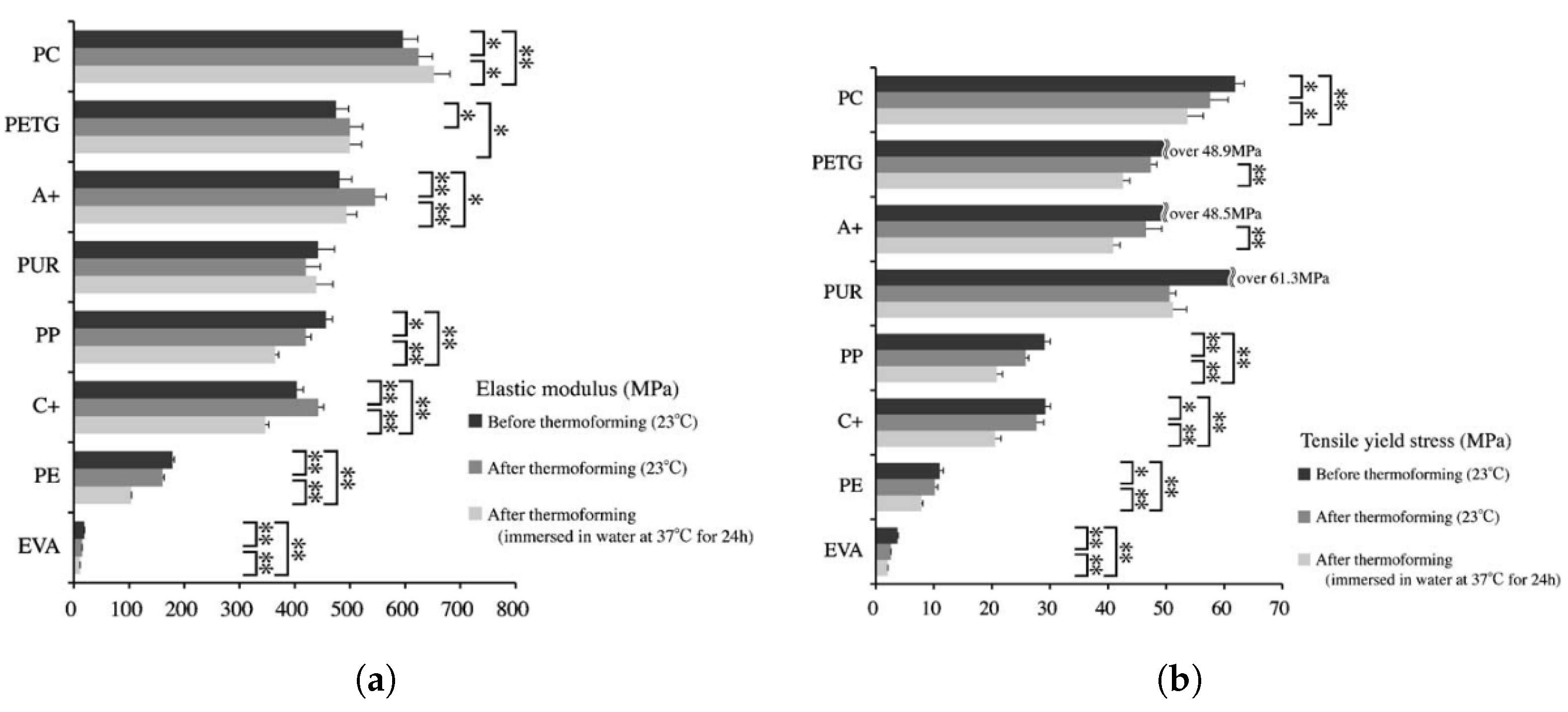
6. Mechanical Properties
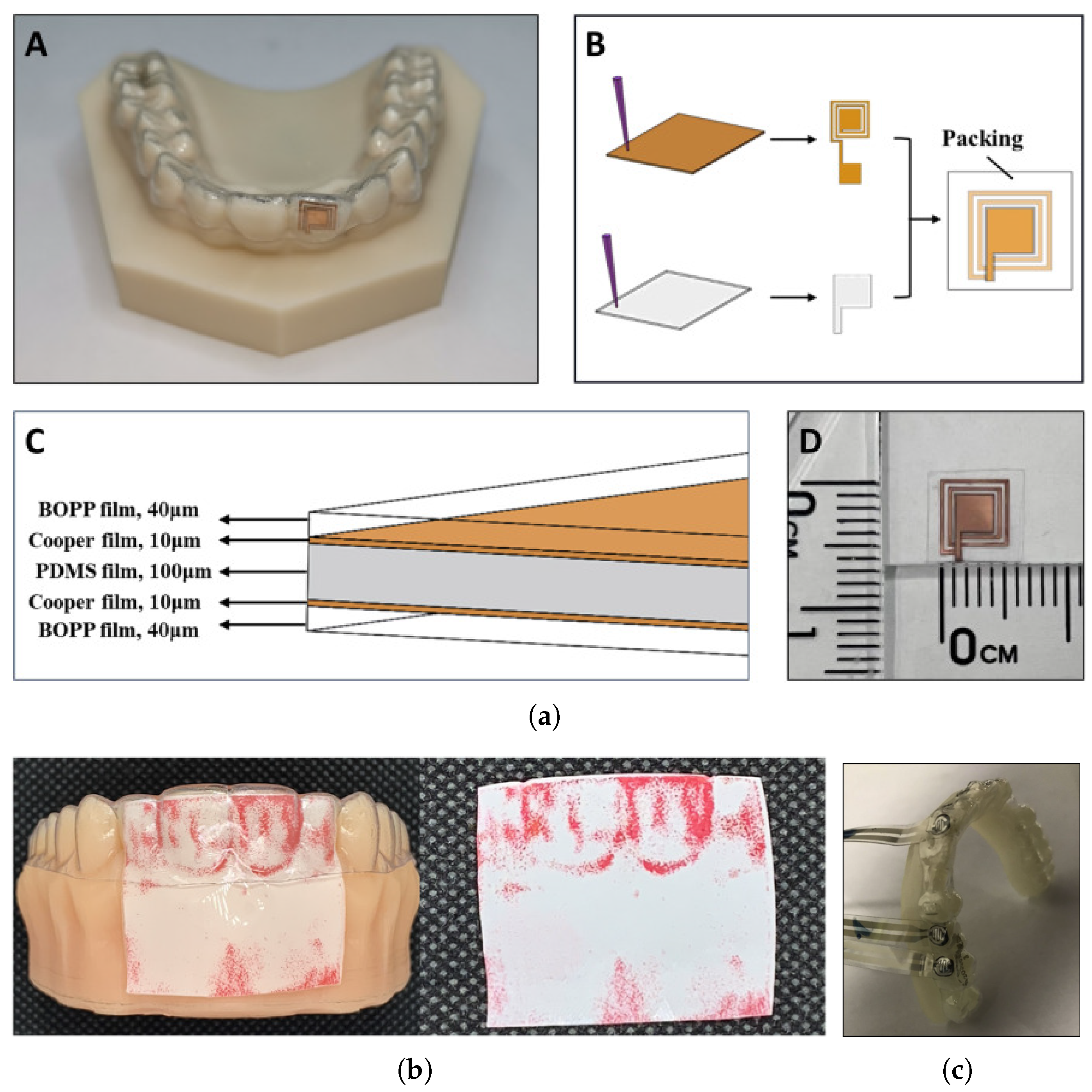
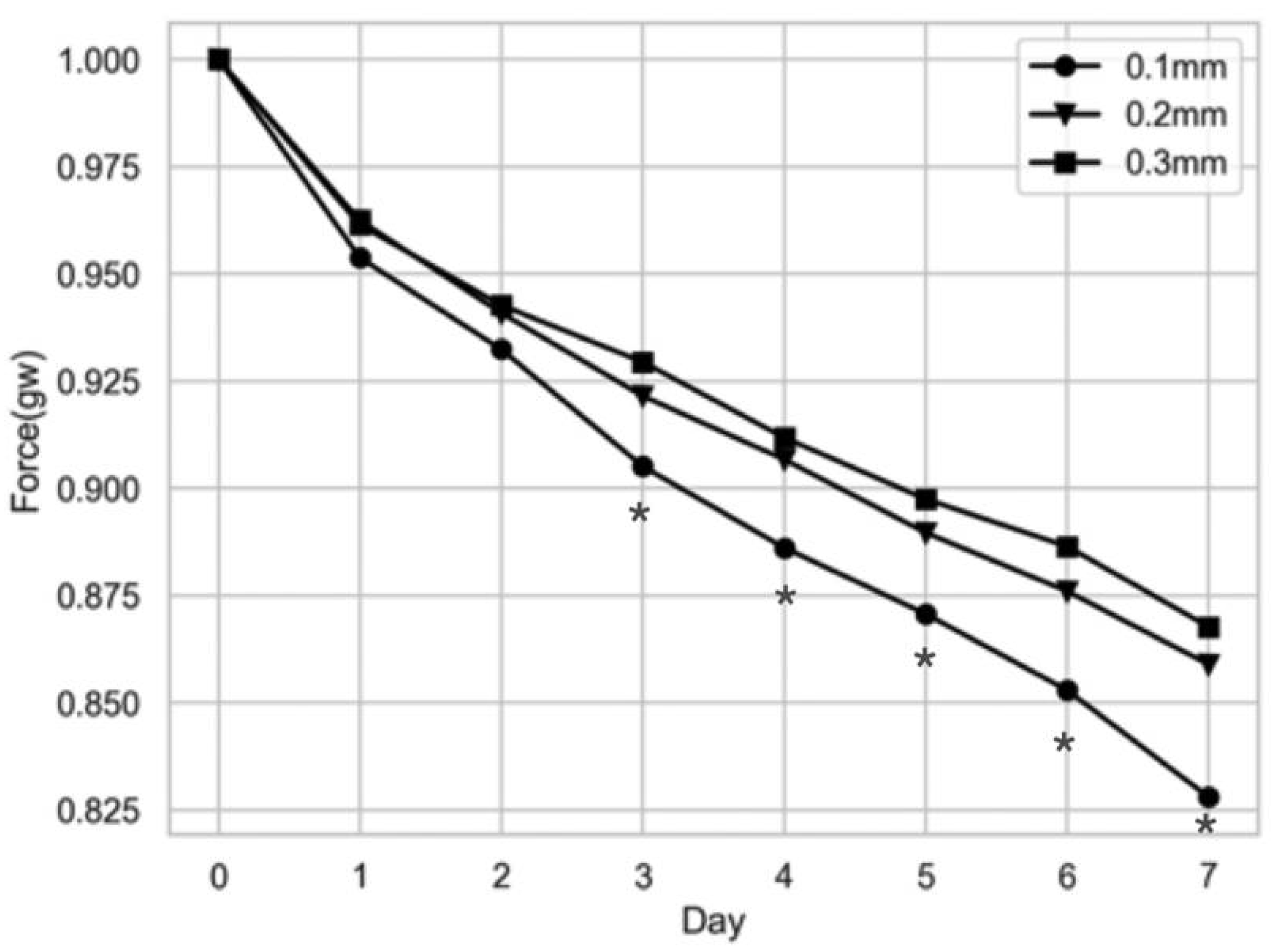
6.1. Orthodontic Force and Strain Measurements
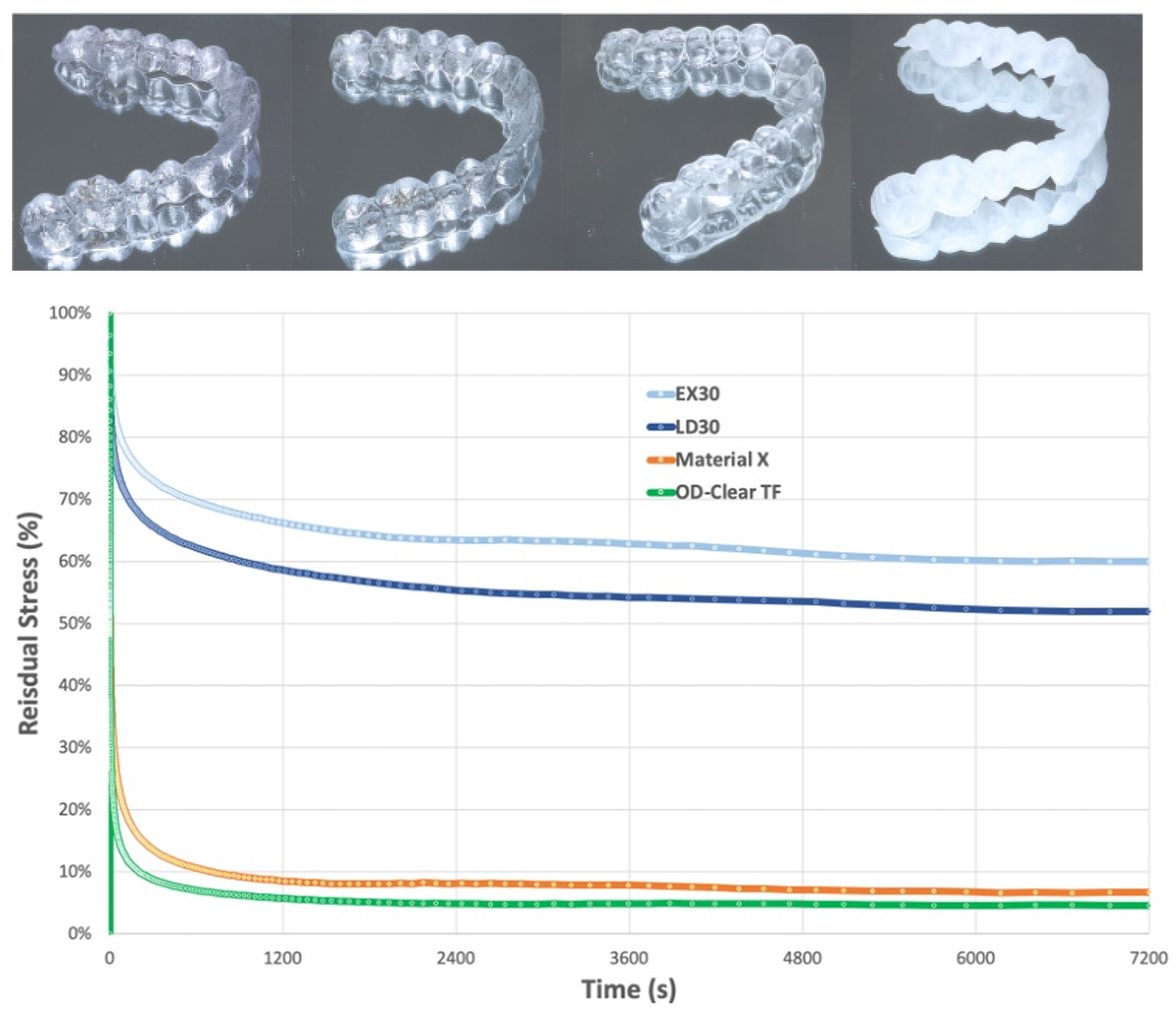
6.2. Stress Relaxation and Creep
7. Thermal Properties
8. Biocompatibility
8.1. In Vitro Testing
8.2. In Vivo Testing
9. Environmental Effects and Recyclability of Clear Aligners
- Polymer manufacturing and processing to either flat sheets for thermoforming or resin for 3D printing;
- The aligner manufacturing process, including the energy consumption of the machinery used for thermoforming, 3D printer, and cleaning;
- Secondary materials, such as the 3D printed molds in the case of thermoformed aligners, manufacturing errors and wastes, cleaning agents, packaging, etc.;
- Shipment;
- The final disposal of the aligner.
10. Perspectives and Research Directions of Clear Aligner Thermoplastics
- The use of different plastics for each stage of treatment or for each type of movement.
- Implementing the material properties in the tooth movement software.
- The treatment efficiency and biocompatibility of 3D printed and SMP clear aligners.
- Prescription duration and activation distance.
- The use of aiders to speed up the treatment.
- Extend the literature on the biocompatibility effects of 3D resins and SMP, as well as on their effects on treatment and long-term exposure to this type of material, including variables such as the curing time and cleaning process in the case of 3D printed aligners and the release of noxious chemicals (BPA, BPF, BPS, phthalates, …).
- Extend the literature on estrogenic-active substances that may be released from medical-grade plastics, 3D resins, and SMPs, as claimed in [72]. This may include the following:
- –
- Standardized methods to measure the estrogenic activity of a chemical that leaches from a plastic.
- –
- The short and long-term effects on the human body of the estrogenic active chemical and the body uptake of the substance, all for different life stages, focusing on fetuses and children.
- –
- Define, if possible, health risk thresholds for that chemical.
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAT | Clear aligner technique |
| NiTi | Nickel-Titanium superelastic alloy |
| CAM | Computer-aided manufacturing |
| SMP | Shape memory polymers |
| PET | Polyethene terephthalate |
| PETG | Polyethene terephthalate glycol-modified |
| TPU | Generic thermoplastic polyurethane |
| hTPU | High hardness thermoplastic polyurethane |
| mTPU | Middle hardness thermoplastic polyurethane |
| sTPU | Soft hardness thermoplastic polyurethane |
| PCTG | Poly cyclohexylenedimethylene terephthalate glycol-modified Copolyester |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| EVA | Ethylene vinyl acetate resin |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PC | Polycarbonate |
| Tg | Glass transition |
| Tm | Melting point |
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| BPF | Bisphenol F |
| BPS | Bisphenol S |
| DMTA | Dynamic mechanical thermal analysis |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| 3PB | Three-point bending |
| OMSS | Orthodontic measurement and simulation system |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| DIC | Digital image correlation |
| LCA | Life-cycle assessment |
| E | Elastic modulus |
References
- Wash, N. Orthodontics in 3 millennia. Chapter 9: Functional appliances to midcentury. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 129, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbell, M.B. A brief history of orthodontics. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1990, 98, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, N. Orthodontics in 3 millennia. Chapter 1: Antiquity to the mid-19th century. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2005, 127, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, J.I.J. The origins and evolution of fixed orthodontic appliances. Dent. Nurs. 2014, 10, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remensnyder, O. Dental Massage Device. 1928. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US1691785A/en (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Kau, C.H.; Soh, J.; Christou, T.; Mangal, A. Orthodontic Aligners: Current Perspectives for the Modern Orthodontic Office. Medicina 2023, 59, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesling, H.D. Coordinating the predetermined pattern and tooth positioner with conventional treatment. Am. J. Orthod. Oral Surg. 1946, 32, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponitz, R.J. Invisible retainers. Am. J. Orthod. 1971, 59, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, S.; De Felice, M.E.; Valenti, C.; Pagano, S.; Caruso, S.; Gatto, R.; Lombardo, G. An evaluation of the Invisalign® Aligner Technique and consideration of the force system: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2024, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, B.; Siva, S.; Duraisamy, S.; Idaayath, A.; Kannan, R. Properties of Orthodontic Clear Aligner Materials—A Review. J. Evol. Med Dent. Sci. 2021, 10, 3288–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshazly, T.; Salvatori, D.; Bourauel, C.; Elattar, H.; Alkabani, Y. Effect of Thickness and Material Type of Orthodontic Aligners on Force Transmission: An in Vitro Study Using Pressure-Sensitive Films. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 28, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmann, L.; Gerngro, M. Effect of Dental Thermoplastic Materials on the Clinical Effectiveness of Clear Aligner. Austin J. Dent. 2021, 8, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, A.; Rochman, A. Characterization of TPU-elastomers by thermal analysis (DSC). Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichu, Y.M.; Alwafi, A.; Liu, X.; Andrews, J.; Ludwig, B.; Bichu, A.Y.; Zou, B. Advances in orthodontic clear aligner materials. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 22, 384–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harandi, M.T.; Abu Arqub, S.; Warren, E.; Kuo, C.L.; Da Cunha Godoy, L.; Mehta, S.; Feldman, J.; Upadhyay, M.; Yadav, S. Assessment of clear aligner accuracy of 2 clear aligners systems. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2023, 164, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.W.; Kim, K.A.; Kim, S.H. A new type of clear orthodontic retainer incorporating multi-layer hybrid materials. Korean J. Orthod. 2015, 45, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, Z.A. The Effect of Attachment Flash on Clear Aligner Force Delivery. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, B.E. Effect of Gingival Margin Design on Clear Aligner Material Strain and Force Delivery. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Bai, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and characterization of thermoplastic materials for invisible orthodontics. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.S.; Fang, D.Y.; Zhang, N.; Ding, X.J.; Zhang, K.Y.; Bai, Y.X. Mechanical Properties of Orthodontic Thermoplastics PETG/ PC2858 after Blending. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 19, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, A.; Serra, F.G.; Deregibus, A.; Castroflorio, T. Shape-Memory Polymers in Dentistry: Systematic Review and Patent Landscape Report. Materials 2019, 12, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönfeld, D.; Koss, S.; Vohl, N.; Friess, F.; Drescher, D.; Pretsch, T. Dual Stimuli-Responsive Orthodontic Aligners: An In Vitro Study. Materials 2023, 16, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshazly, T.M.; Keilig, L.; Alkabani, Y.; Ghoneima, A.; Abuzayda, M.; Talaat, S.; Bourauel, C.P. Primary Evaluation of Shape Recovery of Orthodontic Aligners Fabricated from Shape Memory Polymer (A Typodont Study). Dent. J. 2021, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.K. Orthodontic Appliance by Using a Shape Memory Polymer. US Patent 2005/0003318 A1, 6 January 2005. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20050003318A1/en (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Elshazly, T.M.; Keilig, L.; Alkabani, Y.; Ghoneima, A.; Abuzayda, M.; Talaat, W.; Talaat, S.; Bourauel, C.P. Potential Application of 4D Technology in Fabrication of Orthodontic Aligners. Front. Mater. 2022, 8, 794536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClearX Aligners. Available online: https://clearxaligners.com/products (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Koenig, N.; Choi, J.Y.; McCray, J.; Hayes, A.; Schneider, P.; Kim, K.B. Comparison of dimensional accuracy between direct-printed and thermoformed aligners. Korean J. Orthod. 2022, 52, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremonini, F.; Vianello, M.; Bianchi, A.; Lombardo, L. A Spectrophotometry Evaluation of Clear Aligners Transparency: Comparison of 3D-Printers and Thermoforming Disks in Different Combinations. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, S. The optimal orthodontic displacement of clear aligner for mild, moderate and severe periodontal conditions: An in vitro study in a periodontally compromised individual using the finite element model. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.P.; Peña, F.M.; Martínez, V.; Giraldo, D.C.; Cardona, C.I. Initial force systems during bodily tooth movement with plastic aligners and composite attachments: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortona, A.; Rossini, G.; Parrini, S.; Deregibus, A.; Castroflorio, T. Clear aligner orthodontic therapy of rotated mandibular round-shaped teeth: A finite element study. Angle Orthod. 2020, 90, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Wang, R.; Zheng, L.; Wang, C.; Aversa, R.; Fan, Y. Effects of different designs of orthodontic clear aligners on the maxillary central incisors in the tooth extraction cases: A biomechanical study. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laohachaiaroon, P.; Samruajbenjakun, B.; Chaichanasiri, E. Initial Displacement and Stress Distribution of Upper Central Incisor Extrusion with Clear Aligners and Various Shapes of Composite Attachments Using the Finite Element Method. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunta, O.; Festila, D.; Muresan, V.; Coloși, T.; Stan, O.P.; Baciut, M. Mathematical Modeling and Digital Simulation of Teeth Dynamics for the Approximation of Orthodontic Treatment Duration. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, M.; Roslly, M.N.; Ismail, Z.; Jaafar, N.A.; Shafie, S.; Mokhtar, N. Mathematical Modelling and Simulation of Periodontal Ligament Using COMSOL Multiphysics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mathematical Sciences and Statistics 2022 (ICMSS 2022), Wuhan, China, 7–9 January 2022; Wahi, N., Mohd Safari, M.A., Hasni, R., Abdul Razak, F., Gafurjan, I., Fitrianto, A., Eds.; Atlantis Press International BV: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Maltha, J.C.; Van ’t Hof, M.A.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. Optimum force magnitude for orthodontic tooth movement: A mathematic model. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2004, 125, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, V.; Macera, L.; Taglieri, G.; Spera, L.; Marzo, G.; Quinzi, V. Color Stability, Chemico-Physical and Optical Features of the Most Common PETG and PU Based Orthodontic Aligners for Clear Aligner Therapy. Polymers 2022, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniele, V.; Macera, L.; Taglieri, G.; Di Giambattista, A.; Spagnoli, G.; Massaria, A.; Messori, M.; Quagliarini, E.; Chiappini, G.; Campanella, V.; et al. Thermoplastic Disks Used for Commercial Orthodontic Aligners: Complete Physicochemical and Mechanical Characterization. Materials 2020, 13, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macrì, M.; Murmura, G.; Varvara, G.; Traini, T.; Festa, F. Clinical Performances and Biological Features of Clear Aligners Materials in Orthodontics. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 819121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Sun, W.T.; Liao, W.; Lu, W.X.; Li, Q.W.; Jeong, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.H. Colour stabilities of three types of orthodontic clear aligners exposed to staining agents. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 8, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, G.; Rompré, P.; Tavares, J.R.; Montpetit, A. Colorimetric and spectrophotometric measurements of orthodontic thermoplastic aligners exposed to various staining sources and cleaning methods. Head Face Med. 2020, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porojan, L.; Vasiliu, R.D.; Porojan, S.D.; Bîrdeanu, M.I. Surface Quality Evaluation of Removable Thermoplastic Dental Appliances Related to Staining Beverages and Cleaning Agents. Polymers 2020, 12, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, M.H.; Porto, B.; Mohebi, S.; Zhu, L.; Hans, M. Physical and chemical properties of five different clear thermoplastic materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T. Quantitative Evaluation Criteria for the Mechanical Properties of Orthodontic Clear Aligners. Ph.D. Thesis, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ryokawa, H.; Miyazaki, Y.; Fujishima, A.; Miyazaki, T.; Maki, K. The mechanical properties of dental thermoplastic materials in a simulated intraoral environment. Orthod. Waves 2006, 65, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.; Eliades, G.; Zinelis, S.; Eliades, T.; Bradley, T.G. Structural conformation and leaching from in vitro aged and retrieved Invisalign appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2004, 126, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F. A Standardized Characterization of the Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Orthodontic Clear Aligners. Ph.D. Thesis, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Albertini, P.; Mazzanti, V.; Mollica, F.; Pellitteri, F.; Palone, M.; Lombardo, L. Stress Relaxation Properties of Five Orthodontic Aligner Materials: A 14-Day In-Vitro Study. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.J. Stress Relaxation in Orthodontic Aligner Plastics; An In Vitro Comparison Study. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, A.L.; Beeman, C.S.; Hicks, E.P.; Bush, H.M.; Mitchell, R.J. The Essential Work of Fracture of Thermoplastic Orthodontic Retainer Materials. Angle Orthod. 2010, 80, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wu, B.M. Changes in mechanical properties, surface morphology, structure, and composition of Invisalign material in the oral environment. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 157, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, A.K.; Cantele, A.; Polychronis, G.; Zinelis, S.; Eliades, T. Changes in Roughness and Mechanical Properties of Invisalign® Appliances after One- and Two-Weeks Use. Materials 2019, 12, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerard Bradley, T.; Teske, L.; Eliades, G.; Zinelis, S.; Eliades, T. Do the mechanical and chemical properties of Invisalign TM appliances change after use? A retrieval analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2016, 38, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, E.; Panayi, N.; Polychronis, G.; Papageorgiou, S.N.; Zinelis, S.; Eliades, G.; Eliades, T. In-house 3D-printed aligners: Effect of in vivo ageing on mechanical properties. Eur. J. Orthod. 2022, 44, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohda, N.; Iijima, M.; Muguruma, T.; Brantley, W.A.; Ahluwalia, K.S.; Mizoguchi, I. Effects of mechanical properties of thermoplastic materials on the initial force of thermoplastic appliances. Angle Orthod. 2013, 83, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendura Dental Webpage. Available online: https://www.zenduradental.com/pages/zendura-a-properties (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Leyona Pushpa Femina, I.; Chandrashekar, B.S.; Arun, A.V.; Raju, A.S.; Ramesh Kumar, P.C.; Shetty, B. Effects of Carbonated Drinks on Mechanical Properties of Three Types of Thermoplastic Aligner Materials: An In vitro Study. J. Indian Orthod. Soc. 2020, 54, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teske, L. Mechanical Properties and Patient Perceptions of Commonly Used Clear Aligner Systems As-Received and After Clinical Use. Master’s Thesis, Marquette University, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cintora-López, P.; Arrieta-Blanco, P.; Martin-Vacas, A.; Paz-Cortés, M.M.; Gil, J.; Aragoneses, J.M. In vitro analysis of the influence of the thermocycling and the applied force on orthodontic clear aligners. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1321495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburrino, F.; D’Antò, V.; Bucci, R.; Alessandri-Bonetti, G.; Barone, S.; Razionale, A.V. Mechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Polymers for Aligner Manufacturing: In Vitro Study. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, P.; Juneja, M.; Siena, F.L.; Bajaj, D.; Breedon, P. Mechanical and geometric properties of thermoformed and 3D printed clear dental aligners. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 156, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albilali, A.T.; Baras, B.H.; Aldosari, M.A. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Different Thermoplastic Orthodontic Retainer Materials after Thermoforming and Thermocycling. Polymers 2023, 15, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupaix, R.B.; Boyce, M.C. Finite strain behavior of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) and poly(ethylene terephthalate)-glycol (PETG). Polymer 2005, 46, 4827–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.J.; Chung, C.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.J.; Cha, J.Y. Thermo-mechanical properties of 3D printed photocurable shape memory resin for clear aligners. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jindal, P.; Worcester, F.; Siena, F.L.; Forbes, C.; Juneja, M.; Breedon, P. Mechanical behaviour of 3D printed vs thermoformed clear dental aligner materials under non-linear compressive loading using FEM. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 112, 104045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirey, N.; Mendonca, G.; Groth, C.; Kim-Berman, H. Comparison of mechanical properties of 3-dimensional printed and thermoformed orthodontic aligners. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2023, 163, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanović, A.; Sedmak, A.; Golubović, Z.; Mihajlović, K.Z.; Žurkić, A.; Trajković, I.; Milošević, M. The effect of time on mechanical properties of biocompatible photopolymer resins used for fabrication of clear dental aligners. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 119, 104494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, S.; Rongo, R.; Bucci, R.; Razionale, A.V.; Valletta, R.; D’Antò, V. In vitro cytotoxicity of different thermoplastic materials for clear aligners. Angle Orthod. 2019, 89, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Hao, W.; Li, Y.z.; Chen, J.; Yao, J.r.; Shao, Z.z.; Li, H.; Yang, J.j.; Chen, S.y. Biocompatibility evaluation of polyethylene terephthalate artificial ligament coating hydroxyapatite by fibroblasts cells in vitro. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 2012, 17, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, D.; Cianci, C.; Laurenziello, M.; Troiano, G.; De Cillis, F.; Tepedino, M.; Montaruli, G.; Grassia, V.; Lo Muzio, L.; Pappalettere, C. Comparison of the Stress Strain Capacity between Different Clear Aligners. Open Dent. J. 2019, 13, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravuri, P.; Kubavat, A.K.; Rathi, V.; Luke John, T.; Varma, P.K.; Mujoo, S.; Somaraj, V. Effectiveness and Biocompatibility of Tooth Aligners Made from Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PeT-G), Polypropylene (PP), Polycarbonate (PC), Thermoplastic Polyurethanes (TPUs), and Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA): A Systematic Review. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16, S93–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, G.D.; Yang, C.Z.; Stoner, M.A. Estrogenic chemicals often leach from BPA-free plastic products that are replacements for BPA-containing polycarbonate products. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Mahmud, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Shen, Z.; Liu, X. Biobased Amorphous Polyesters with High Tg: Trade-Off between Rigid and Flexible Cyclic Diols. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6401–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gupta, N. Determining elastic modulus from dynamic mechanical analysis: A general model based on loss modulus data. Materialia 2018, 4, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemelmanns, P.; Pfeiffer, P. Shock absorption capacities of mouthguards in different types and thicknesses. Int. J. Sport. Med. 2001, 22, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar Singh, R.; Kumar Singh, S.; Kumar Mahto, S.; Misra, N. In vitro biocompatibility analysis of functionalized poly(vinyl chloride)/layered double hydroxide nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 40611–40620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercoli, F.; Tepedino, M.; Parziale, V.; Luzi, C. A comparative study of two different clear aligner systems. Prog. Orthod. 2014, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, I.; Bourauel, C.; Alkabani, Y.; Mohamed, N.; Kim, H.; Alhotan, A.; Ghoneima, A.; Elshazly, T. Physiochemical and mechanical characterisation of orthodontic 3D printed aligner material made of shape memory polymers (4D aligner material). J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 150, 106337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, G.M.; Mapelli, A.; Maspero, C.; Santaniello, T.; Serafin, M.; Farronato, M.; Caprioglio, A. Direct 3D Printing of Clear Orthodontic Aligners: Current State and Future Possibilities. Materials 2021, 14, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Kwon, J.S.; Jiang, H.B.; Cha, J.Y.; Kwang-Mahn, K. Effects of thermoforming on the physical and mechanical properties of thermoplastic materials for transparent orthodontic aligners. Korean J. Orthod. 2018, 48, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golkhani, B.; Weber, A.; Keilig, L.; Reimann, S.; Bourauel, C. Variation of the modulus of elasticity of aligner foil sheet materials due to thermoforming. J. Orofac. Orthop./Fortschritte Kieferorthopädie 2021, 83, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlandingham, M.; Villarrubia, J.; Guthrie, W.; Meyers, G. Nanoindentation of Polymers: An Overview. In Macromolecular Symposia; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2001; Volume 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppolu, P.; Sirisha, S.; Penala, S.; Reddy, P.K.; Alotaibi, D.H.; Abusalim, G.S.; Lingam, A.S.; Mukhtar, A.H.; Barakat, A.; AlMokhatieb, A.A. Correlation of Blood and Salivary pH Levels in Healthy, Gingivitis, and Periodontitis Patients before and after Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourauel, C.; Drescher, D.; Thier, M. An experimental apparatus for the simulation of three-dimensional movements in orthodontics. J. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 14, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, D.; Bourauel, C.; Thier, M. Application of the orthodontic measurement and simulation system (OMSS) in orthodontics. Eur. J. Orthod. 1991, 13, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsabti, N.; Bourauel, C.; Talic, N. Comparison of force loss during sliding of low friction and conventional TMA orthodontic archwires. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2021, 82, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshazly, T.M.; Nang, D.; Golkhani, B.; Elattar, H.; Bourauel, C. Effect of Aging of Orthodontic Aligners in Different Storage Media on Force and Torque Generation: An In Vitro Study. Oral 2023, 3, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandil, A.; Al Kordy, S.A.; Boghdady, D.E.; Labib, A.; Harzer, W.; Bourauel, C. Evaluation of SARDAC Technique During En-Masse Retraction in Lingual Orthodontics. Semin. Orthod. 2023, 29, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholy, F.; Panchaphongsaphak, T.; Kilic, F.; Schmidt, F.; Lapatki, B. Forces and moments delivered by PET-G aligners to an upper central incisor for labial and palatal translation. J. Orofac. Orthop./Fortschritte Kieferorthopädie 2015, 76, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.; Foley, P.; Bankhead, B.; Miranda, G.; Adel, S.M.; Kim, K.B. Forces and moments generated by 3D direct printed clear aligners of varying labial and lingual thicknesses during lingual movement of maxillary central incisor: An in vitro study. Prog. Orthod. 2023, 24, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Brown, B.E.; Mantell, S.C.; Heo, Y.C.; Larson, B.E.; Fok, A.S. Validation of finite element models for orthodontic aligners. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 134, 105404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawamura, M.; Nakano, H.; Shiogama, M.; Takano, N.; Maki, K. Using digital image correlation to measure displacement and strain during involving distal movement of anterior teeth with clear aligner. Dent. Mater. J. 2023, 42, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göllner, M.; Holst, A.; Berthold, C.; Schmitt, J.; Wichmann, M.; Holst, S. Noncontact intraoral measurement of force-related tooth mobility. Clin. Oral Investig. 2010, 14, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshazly, T.M.; Keilig, L.; Salvatori, D.; Chavanne, P.; Aldesoki, M.; Bourauel, C. Effect of trimming line design and edge extension of orthodontic aligners on force transmission: An in vitro study. J. Dent. 2022, 125, 104276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervinara, F.; Cianci, C.; De Cillis, F.; Pappalettera, G.; Pappalettere, C.; Siciliani, G.; Lombardo, L. Experimental Study of the Pressures and Points of Application of the Forces Exerted between Aligner and Tooth. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshazly, T.M.; Bourauel, C.; Ismail, A.M.; Ghoraba, O.; Chavanne, P.; Elattar, H.; Alhotan, A. Effect of thermomechanical ageing on force transmission by orthodontic aligners made of different thermoformed materials: An experimental study. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2024, 27, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, A.; McCray, J.; Bankhead, B.; Lee, M.M.; Miranda, G.; Adel, S.M.; Kim, K.B. Forces and moments generated during extrusion of a maxillary central incisor with clear aligners: An in vitro study. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ning, S.; Zhao, G.; Ye, Z.; Kong, Y.; Yang, D. Prospects for 3D-printing of clear aligners—A narrative review. Front. Mater. 2024, 11, 1438660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Wang, X.; Wu, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q. The force effects of two types of polyethylene terephthalate glyc-olmodified clear aligners immersed in artificial saliva. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaik, A.; Wei, X.L.; Abusamak, I.; Iddi, I. Effects of time and clear aligner removal frequency on the force delivered by different polyethylene terephthalate glycol-modified materials determined with thin-film pressure sensors. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 155, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; He, B.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, L.; Lv, A. Force measurement system for invisalign based on thin film single force sensor. Measurement 2017, 97, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, P.; Wang, H.; Bai, Y. Changes in force associated with the amount of aligner activation and lingual bodily movement of the maxillary central incisor. Korean J. Orthod. 2016, 46, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ren, C.; Hao, W.; Zhang, M.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Z. An Ultra-Thin Piezoresistive Stress Sensor for Measurement of Tooth Orthodontic Force in Invisible Aligners. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Y.; Weiting, L.; Xiaoying, C.; Xin, F. Sensors | Free Full-Text | Flexible Piezoelectric Tactile Sensor Array for Dynamic Three-Axis Force Measurement. Sensors 2016, 16, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Ho, C.T.; Huang, T.H.; Kao, C.T. An in vitro evaluation of aligner force decay in artificial saliva. J. Dent. Sci. 2023, 18, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Pu, B.; Chen, G.; Han, J.; Xiao, S.; Fan, Y.; Li, J. Wireless measurement of orthodontic forces in invisible aligners. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2024, 21, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suha, A.A.A.; Akram, F.A.; Hayder, F.S. Effect of Orthodontic Force on Salivary Levels of Lactate Dehydrogenase Enzyme. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2024, 10, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaqeeh, S.A.; Anil, S. Lactate Dehydrogenase Activity in Gingival Crevicular Fluid as a Marker in Orthodontic Tooth Movement. Open Dent. J. 2011, 5, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, M.; Arqub, S.A. Biomechanics of clear aligners: Hidden truths & first principles. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2022, 11, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, H.Y. Comparison of the Properties of Copolyester, Polypropylene, and Polyurethane Based Aligners. Ph.D. Thesis, Boston University, Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo, L.; Martines, E.; Mazzanti, V.; Arreghini, A.; Mollica, F.; Siciliani, G. Stress relaxation properties of four orthodontic aligner materials: A 24-hour in vitro study. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggy, F.; Zinelis, S.; Polychronis, G.; Patcas, R.; Schätzle, M.; Eliades, G.; Eliades, T. ATR-FTIR Analysis and One-Week Stress Relaxation of Four Orthodontic Aligner Materials. Materials 2020, 13, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Huang, F.; Chen, W.; Cai, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, Z. The thickness and gap width of aligners made of three types of thermoforming materials: An in-vitro study. Semin. Orthod. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeras, I.M. Glass-Transition Phenomena in Polymer Blends. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Blends; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalaie, K.; Fatemi, S.M.; Ghaffari, S. Dynamic mechanical and thermal properties of clear aligners after thermoforming and aging. Prog. Orthod. 2021, 22, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenger, L. Thermal Properties of Commonly Used Clear Aligner Systems As-Received and After Clinical Use. Master’s Thesis, Marquette University, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Eliades, T.; Pratsinis, H.; Athanasiou, A.E.; Eliades, G.; Kletsas, D. Cytotoxicity and estrogenicity of Invisalign appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 136, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Mangal, U.; Yu, J.H.; Kim, G.T.; Kim, H.; Seo, J.Y.; Cha, J.Y.; Lee, K.J.; Kwon, J.S.; Choi, S.H. Evaluation of the effects of temperature and centrifugation time on elimination of uncured resin from 3D-printed dental aligners. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhamees, A. The new additive era of orthodontics: 3D-printed aligners and shape memory polymers—The latest trend—And their environmental implications. J. Orthod. Sci. 2024, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayi, N.; Cha, J.Y.; Kim, K.B. 3D Printed Aligners: Material Science, Workflow and Clinical Applications. Semin. Orthod. 2023, 29, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinzi, V.; Orilisi, G.; Vitiello, F.; Notarstefano, V.; Marzo, G.; Orsini, G. A spectroscopic study on orthodontic aligners: First evidence of secondary microplastic detachment after seven days of artificial saliva exposure. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 866, 161356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, A. Potential health risks of aligners and retainers. Br. Dent. J. 2024, 236, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Dayeh, A.A.; Tipton, D. Bisphenol A Release from Orthodontic Clear Aligners: An In-Vitro Study. Recent Prog. Mater. 2021, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çifçi Özkan, E.; Dumanlı Gök, G. Evaluation of bisphenol release of different clear aligner materials using the liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry method. Angle Orthod. 2023, 93, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhendi, A.; Khounganian, R.; Almudhi, A.; Ahamad, S.R. Leaching of Different Clear Aligner Systems: An In Vitro Study. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Spirito, F.; Amato, A.; Di Palo, M.P.; Ferraro, R.; Cannatà, D.; Galdi, M.; Sacco, E.; Amato, M. Oral and Extra-Oral Manifestations of Hypersensitivity Reactions in Orthodontics: A Comprehensive Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, N.; Surendranath, A.R.; Pathak, J.L.; Yu, S.; Chung, C.Y. Bisphenol A (BPA) the mighty and the mutagenic. Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 5, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straková, J.; Valeriya, G.; Brosché, S.; Karlsson, T.; Buonsante, V. A Call to Action: Free Children from BPA’s Toxic Legacy. Int. Pollut. Elimin. Netw. (IPEN) 2022, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, H. Phthalates and Their Impacts on Human Health. Healthcare 2021, 9, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grindler, N.M.; Vanderlinden, L.; Karthikraj, R.; Kannan, K.; Teal, S.; Polotsky, A.J.; Powell, T.L.; Yang, I.V.; Jansson, T. Exposure to Phthalate, an Endocrine Disrupting Chemical, Alters the First Trimester Placental Methylome and Transcriptome in Women. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sax, L. Polyethylene Terephthalate May Yield Endocrine Disruptors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osimitz, T.G.; Eldridge, M.L.; Sloter, E.; Welsh, W.; Ai, N.; Sayler, G.S.; Menn, F.; Toole, C. Lack of androgenicity and estrogenicity of the three monomers used in Eastman’s Tritan™ copolyesters. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2196–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, F.; Khalib, K.; Conlon, N. PEG That Reaction: A Case Series of Allergy to Polyethylene Glycol. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 61, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.B.; Bundy, V. Hypersensitivity to different polyethylene glycol–containing products. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 734–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaturay, P.; Nasser, S.; Ewan, P. Polyethylene Glycol–Induced Systemic Allergic Reactions (Anaphylaxis). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, V.; Singh, S.; Anil, A.G.; Sunil Kumar Naik, T.S.; Garg, S.; Samuel, J.; Kumar, M.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Singh, J. Occurrence, toxicity and remediation of polyethylene terephthalate plastics. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1777–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uter, W.; Werfel, T.; White, I.R.; Johansen, J.D. Contact Allergy: A Review of Current Problems from a Clinical Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awosika, O.; Kao, S.; Rengifo-Pardo, M.; Ehrlich, A. Angioedema, Stomatitis, and Urticaria Caused by Contact Allergy to Invisalign. Dermat. Contact Atopic Occup. Drug 2017, 28, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allareddy, V.; Nalliah, R.; Lee, M.K.; Rampa, S.; Allareddy, V. Adverse clinical events reported during Invisalign treatment: Analysis of the MAUDE database. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 152, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, L.; Novara, F.; Margherini, S.; Tenconi, C.; Raspanti, M. Scanning electron microscopy analysis of the growth of dental plaque on the surfaces of removable orthodontic aligners after the use of different cleaning methods. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2015, 7, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levrini, L.; Mangano, A.; Margherini, S.; Tenconi, C.; Vigetti, D.; Muollo, R.; Marco Abbate, G. ATP Bioluminometers Analysis on the Surfaces of Removable Orthodontic Aligners after the Use of Different Cleaning Methods. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016, 5926941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektas, S.; Thurnheer, T.; Eliades, T.; Attin, T.; Karygianni, L. Initial Bacterial Adhesion and Biofilm Formation on Aligner Materials. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charavet, C.; Gourdain, Z.; Graveline, L.; Lupi, L. Cleaning and Disinfection Protocols for Clear Orthodontic Aligners: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2022, 10, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X.; Lin, J. Biological Safe Gold Nanoparticle-Modified Dental Aligner Prevents the Porphyromonas gingivalis Biofilm Formation. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 18685–18692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raszewski, Z.; Kulbacka, J.; Nowakowska-Toporowska, A. Mechanical Properties, Cytotoxicity, and Fluoride Ion Release Capacity of Bioactive Glass-Modified Methacrylate Resin Used in Three-Dimensional Printing Technology. Materials 2022, 15, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, M.; Hopkins, A.; Duong, E.; Kelly, K.S.; Esfandi, J.; Shokeen, B.; Wu, T.; Lux, R. The Effect of Initial Orthodontic Therapy with Clear Aligners and Fixed Appliances on Microbial Profiles and Clinical Parameters. J. Calif. Dent. Assoc. 2024, 52, 2409957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenzato, N.; Di Iasio, G.; Martìn Carreras-Presas, C.; Caprioglio, A.; Del Fabbro, M. Materials for Clear Aligners—A Comprehensive Exploration of Characteristics and Innovations: A Scoping Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairallah, M.K.; Mohamed, K.M.; Refai, W.M.; Abdelhamid, A.N. PET-G versus TPU Aligner Materials in Achieving Torque Movement Using Ellipsoid Attachment. Egypt. Orthod. J. 2025, 67, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairallah, M.K.A.; Mohamed, K.M.; Refai, W.M. Comparison between the effect of PETG and TPU aligner materials on attachment surface wear. Egypt. Orthod. J. 2024, 66, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobrega, C.; Nunes, G.P.; de Paiva Buischi, Y.; Kajimoto, N.d.C.; Delbem, A.C.B. In vitro assessment of dental erosion caused by clear aligners. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 152, 106390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, B.; James, J.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Recycling of medical plastics. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2021, 4, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.P.M. Aligners, Environmental Contamination, and The Role of Orthodontics. Angle Orthod. 2021, 92, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veseli, E.; Veseli, K.; Behluli, E. The carbon emissions of clear aligner therapy: A critical review. APOS Trends Orthod. 2024, 14, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesté, A.G. Evaluación del impacto ambiental de los alineadores ortodónticos transparentes: Una perspectiva de la huella de carbono. Rev. Ilustre Cons. Gen. Colegios Odontól. Estomatól. (RCOE) 2023, 28, 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Lancen, L. Exploring the Recyclability of Invisalign Plastic: How to Properly Dispose of Used Aligners and Reduce Plastic Waste—Climate of Our Future. 2023. Available online: https://www.climateofourfuture.org/exploring-the-recyclability-of-invisalign-plastic-how-to-properly-dispose-of-used-aligners-and-reduce-plastic-waste/ (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Peter, E.; J, M.; Ani George, S. Are clear aligners environment friendly? Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 161, 619–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marya, A.; Viet, H. Biodegradable clear aligners. Br. Dent. J. 2024, 236, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacey, S. Aligner sustainability: No clear fit: Align Technology responds. BDJ Pract. 2023, 36, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunca, M. The Environmental Impact of Clear Aligners: Is Recycling and Waste Management Controlled? Eur. J. Ther. 2024, 30, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GT Flex Material. Available online: https://goodfit.com/clear-aligners-and-retainers/gt-flex-clear-aligner-materials/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Paszkiewicz, S.; Irska, I.; Piesowicz, E. Environmentally Friendly Polymer Blends Based on Post-Consumer Glycol-Modified Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) (PET-G) Foils and Poly(Ethylene 2,5-Furanoate) (PEF): Preparation and Characterization. Materials 2020, 13, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerhart, A.J.J.E.; Faaij, A.P.C.; Patel, M.K. Replacing fossil based PET with biobased PEF; Process analysis, energy and GHG balance. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6407–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, R. Replacing all petroleum-based chemical products with natural biomass-based chemical products: A tutorial review. RSC Sustain. 2023, 1, 179–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temoor, A.; Muhammad, S.; Farrukh, A. Biodegradation of plastics: Current scenario and future prospects for environmental safety | Environmental Science and Pollution Research. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7287–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, T.; de Freitas, K.M.S.; Ohira, E.T.B.; de Souza, J.E.P.; de Oliveira, R.C.G.; de Oliveira, R.C.G.; Valarelli, F.P.; Pinzan-Vercelino, C.R.M.; Cotrin, P. Comparison of the efficiency of initial dental alignment with Invisalign® aligners changed every 7 or 14 days in mature adults: Randomized clinical trial. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2024, 27, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Mei, l.; Long, H.; Jian, F.; Lai, W. Changing clear aligners every 10 days or 14 days? A randomised controlled trial. Australas. Orthod. J. 2023, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levrini, L.; Carganico, A.; Deppieri, A.; Saran, S.; Bocchieri, S.; Zecca, P.A.; Bertini, S.; D’Apote, A.; Segù, M. Predictability of Invisalign® Clear Aligners Using OrthoPulse®: A Retrospective Study. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadirian, H.; Yazarloo, S.; Heidari, S.; Gholamrezayi, E. Mechanical vibration as an adjunct to clear aligner treatment for accelerating tooth movement: A review. Dent. Res. J. 2022, 19, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Alansari, S.; Atique, M.I.; Gomez, J.P.; Hamidaddin, M.; Thirumoorthy, S.N.; Sangsuwon, C.; Khoo, E.; Nervina, J.M. The effects of brief daily vibration on clear aligner orthodontic treatment. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2018, 7, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojima, K.; Kau, C.H. A perspective in accelerated orthodontics with aligner treatment. Semin. Orthod. 2017, 23, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani-Hani, M.; Amin Karami, M. Piezoelectric Tooth Aligner for Accelerated Orthodontic Tooth Movement. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; Volume 2018, pp. 4265–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, B.; Ding, T.; Wan, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, L.; Liu, X. Piezoelectric stimulation enhances bone regeneration in alveolar bone defects through metabolic reprogramming of macrophages. Exploration 2024, 4, 20230149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Hu, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, P. A colorimetric paper sensor for lactate assay using a cellulose-Binding recombinant enzyme. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, L.; Wen, J.; Ma, Y.; Dai, G.; Mo, F.; Wang, J. A Comprehensive Review of Advanced Lactate Biosensor Materials, Methods, and Applications in Modern Healthcare. Sensors 2025, 25, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material | E (MPa) | Tg (°C) | Tm (°C) | Transparency | Aging | Chemical Resistance | Biocompatibility (Grade) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PETG | 2000–2200 | 80 | - | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Excellent (4–5) | [14,39,46,60,68] |
| PET | 2000–3100 | 80 | 260 | Good | Good | Excellent | Excellent (4–5) | [60,63,68,69,70] |
| hTPU | 2200–2500 | 90–120 | 150–220 | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Good (4) | [47,60,62,68] |
| PC | 2000–2500 | 145 | 297 | Excellent | Poor | Good | Poor (3–4) | [12,20,62,71] |
| PCTG | 1300–2300 | 100–120 | - | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent (4–5) | [72,73] |
| EVA | 5–100 | 20 | 90 | Excellent | Good | Good | Excellent (4–5) | [12,71,74] |
| PP | 600 | −18 | 175 | Poor | Good | Excellent | Good (4) | [12,71] |
| PE | 200 | −90 | 137 | Poor | Good | Excellent | Good (4) | [12,71] |
| PVC | 2500–3000 | 90 | 200 | Excellent | Poor | Poor | Poor (3–4) | [75,76,77] |
| Invisalign | 700–900 | 120 | 220 | Excellent | Good | Good | Good (4) | [39,41,52,58] |
| Generic multilayer | 700–900 | 120 | 220 | Excellent | Good | Good | Good (4) | [17,18,78] |
| TC-85 3d resin | 2000–2500 | 75 | - | Poor | No data | No data | Poor (3–4) | [22,64,78,79] |
| Dental LT 3D resin | 2000–2500 | 75 | - | Poor | No data | Poor | Poor (3–4) | [64,79] |
| Accura 60 SLA | 2700–3000 | 60 | - | Good | No data | No data | Toxic (1) | [79] |
| E-Guard Envisiontec 3D | 2000–2200 | No data | No data | No data | No data | No data | Poor (3–4) | [66,79] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delgado, J.I.; Kehyaian, P.; Fernández-Blázquez, J.P. Thermoplastics for Clear Aligners: A Review. Polymers 2025, 17, 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121681
Delgado JI, Kehyaian P, Fernández-Blázquez JP. Thermoplastics for Clear Aligners: A Review. Polymers. 2025; 17(12):1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121681
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelgado, José Ignacio, Pablo Kehyaian, and Juan P. Fernández-Blázquez. 2025. "Thermoplastics for Clear Aligners: A Review" Polymers 17, no. 12: 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121681
APA StyleDelgado, J. I., Kehyaian, P., & Fernández-Blázquez, J. P. (2025). Thermoplastics for Clear Aligners: A Review. Polymers, 17(12), 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121681








