Antifungal Action of Edible Coating Comprising Artichoke-Mediated Nanosilver and Chitosan Nanoparticles for Biocontrol of Citrus Blue Mold
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Art (Artichoke Extract) Preparation
2.2. Art-Based Biosynthesis of AgNPs
2.3. Nanocomposite (NC) Preparation
2.4. Nanomaterial Characterization
2.4.1. FTIR Spectroscopy
2.4.2. Assessment of Particle Charges and Sizes
2.4.3. Ultrastructure of Nanoparticles
2.5. Blue Mold Isolates
2.6. Evaluation of Blue Mold Antifungal Activity In Vitro
2.6.1. Qualitative WD (Well Diffusion) Method
2.6.2. Quantitative MFCs (Minimum Fungicidal Concentrations)
2.7. Orange Edible Coating (EC) with Antifungal Nanocomposites
2.7.1. EC Preparation
2.7.2. Orange Treatment
2.7.3. Microscopic Optical Observations of Treated Mycelia
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
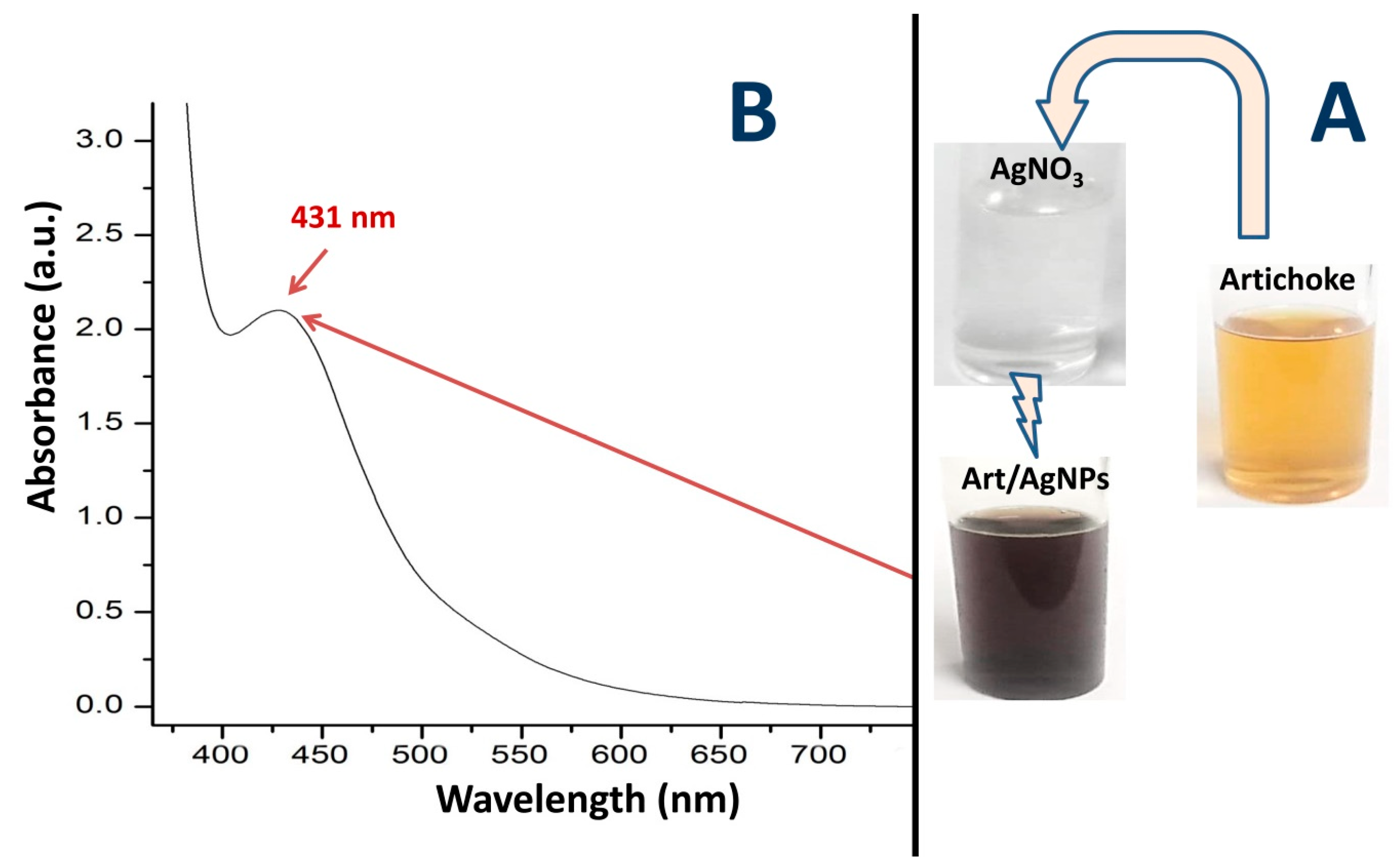
3.1. Appearance of Art-Biosynthesized AgNPs
3.2. FTIR Analysis
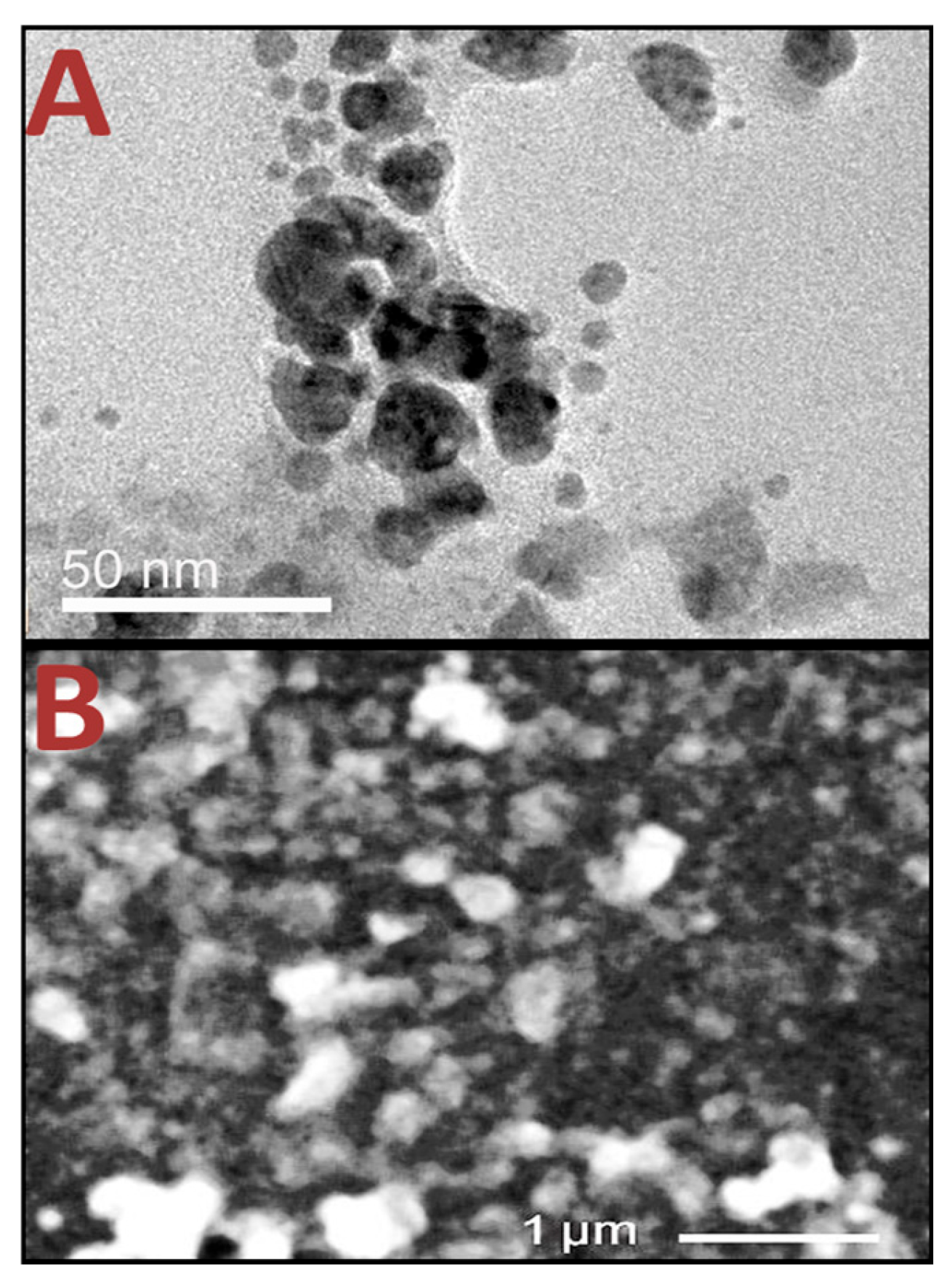
3.3. Structural Analysis of Nanomaterials
3.4. Nanomaterials’ Inhibition Activity Against Penicillium Italicum
3.5. Microscopic Observations of Blue Mold Treated with Nanocomposites
3.6. Cht-Based Edible Coating for Treatment of Oranges
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Art | Artichoke leaf extract |
| Cht | Chitosan nanoparticles |
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| ζ | Zeta potential |
| PDA | Potato dextrose agar |
| PDB | Potato dextrose broth |
| RT | Room temperature |
References
- Wang, Z.; Sui, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, X.; Wang, Q. Biological control of postharvest fungal decays in citrus: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatta, U.K. Alternative management approaches of citrus diseases caused by Penicillium digitatum (green mold) and Penicillium italicum (blue mold). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 833328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strano, M.C.; Altieri, G.; Allegra, M.; Di Renzo, G.C.; Paterna, G.; Matera, A.; Genovese, F. Postharvest technologies of fresh citrus fruit: Advances and recent developments for the loss reduction during handling and storage. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Upadhyay, A.; Shukla, S.; Bajpai, V.K.; Kieliszek, M.; Yadav, A.; Kumaravel, V. Next generation edible nanoformulations for improving post-harvest shelf-life of citrus fruits. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 1825–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, S.; Viana, J.C. Production of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis using artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) aqueous extract and measurement of their electrical conductivity. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. 2018, 9, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wei, R.; Deng, A.; Lei, T. Protective effects of ethanolic extracts from artichoke, an edible herbal medicine, against acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.B.; Affes, H.; Ksouda, K.; Dhouibi, R.; Sahnoun, Z.; Hammami, S.; Zeghal, K.M. Pharmacological studies of artichoke leaf extract and their health benefits. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olas, B. An overview of the versatility of the parts of the globe artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.), its by-products and dietary supplements. Nutrients 2024, 16, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Choudhary, A.; Kaur, H.; Mehta, S.; Husen, A. Metal-based nanoparticles, sensors, and their multifaceted application in food packaging. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeya, J.K.; Ngombe, N.K.; Mutwale, P.K.; Safari, J.B.; Matlou, G.G.; Krause, R.W.; Nkanga, C.I. Antimicrobial capping agents on silver nanoparticles made via green method using natural products from banana plant waste. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2025, 53, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoun, S.; Arif, R.; Jangid, N.K.; Meena, R.K. Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.; Singh, P.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, P.; Bhankar, V.; Kumar, K. Plant-mediated synthesis of nanoparticles and their applications: A review. Mater. Res. Bull. 2023, 163, 112233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.; Luo, J.; Qi, X.; Naz, A.; Khan, I.A.; Liu, H.; Yu, S.; Wei, J. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, structure, properties and applications. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, G.; Aboelkassim, E.; Abd Elhaleem, S.M.; Belal, F. A comprehensive review on silver nanoparticles: Synthesis approaches, characterization techniques, and recent pharmaceutical, environmental, and antimicrobial applications. Microchem. J. 2024, 196, 109615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmana, M.; Mahmood, S.; Hilles, A.R.; Rahman, A.; Arifin, M.A.B.; Ahmed, S. A review on chitosan and chitosan-based bionanocomposites: Promising material for combatting global issues and its applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 832–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, C.; Caroline, D.G.; Pandi Prabha, S. Nanochitosan augmented with essential oils and extracts as an edible antimicrobial coating for the shelf life extension of fresh produce: A review. Polym Bull. 2021, 2021, 8009–8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.A.; Tayel, A.A.; Zidan, N.S.; El Rabey, H.A. Bioactive coatings from nano-biopolymers/plant extract composites for complete protection from mycotoxigenic fungi in dates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4338–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.F.; Abd-Elraoof, W.A.; Tayel, A.A.; Alzuaibr, F.M.; Abonama, O.M. Antifungal application of biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles with pomegranate peels and nanochitosan as edible coatings for citrus green mold protection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygi, K.O.; Bayram, H.M.; Bayram, E. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using artichoke flower petals and application in endodontic dentistry. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 5531–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaggaf, M.S.; Moussa, S.H.; Tayel, A.A. Application of fungal chitosan incorporated with pomegranate peel extract as edible coating for microbiological, chemical and sensorial quality enhancement of Nile tilapia fillets. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghuthaymi, M.A.; Diab, A.M.; Elzahy, A.F.; Mazrou, K.E.; Tayel, A.A.; Moussa, S.H.; Arru, L. Green biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles by cinnamon extract and their antimicrobial activity and application as edible coatings with nano-chitosan. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 670709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, M.M.; El-Hefnawy, M.E.; Tayel, A.A. Innovative anticancer nanocomposites from Corchorus olitorius mucilage/chitosan/selenium nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaldi, S.; Mata-Essayag, S.; Hartung de Capriles, C. Well diffusion for antifungal susceptibility testing. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 8, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, J.H.; Ferraro, M.J. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: A review of general principles and contemporary practices. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharchoufi, S.; Parafati, L.; Licciardello, F.; Muratore, G.; Hamdi, M.; Cirvilleri, G.; Restuccia, C. Edible coatings incorporating pomegranate peel extract and biocontrol yeast to reduce Penicillium digitatum postharvest decay of oranges. Food Microbiol. 2018, 74, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-saggaf, M.S. Formulation of insect chitosan stabilized silver nanoparticles with propolis extract as potent antimicrobial and wound healing composites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 2021, 5578032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyam, A.; Chandran, S.S.; George, B.; Sreelekha, E. Plant mediated synthesis of AgNPs and its applications: An overview. Inorg. Nano Met. Chem. 2021, 51, 1646–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.; Iqbal, M.A.; Iqbal, Y.; Malik, M.; Bakhsh, S.; Irfan, S.; Ahmad, R.; Pham, P.V. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles for biomedical applications: A mini review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 145, 109980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, C.; Ahmad, S.; Ri, C.; Tang, J. Preferential role of distinct phytochemicals in biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. J. Environ. Man. 2023, 344, 118546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaniyah, L.; Fiddaroini, S.; Hayati, E.K.; Rahman, M.F.; Sabarudin, A. Biosynthesis, characterization, and in-vitro anticancer effect of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using Acalypha indica Linn: In-silico approach. OpenNano 2025, 21, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, O.; Abbak, M.; Demirbolat, G.M.; Birtekocak, F.; Aksel, M.; Pasa, S.; Cevik, O. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via Cynara scolymus leaf extracts: The characterization, anticancer potential with photodynamic therapy in MCF7 cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapriya, M.; Sharmili, S.A.; Baskar, R.; Balaji, R.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Alanzi, K.F.; Vaseeharan, B. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Cynara scolymus leaves: Enhanced hemolytic, antimicrobial, antiproliferative, and photocatalytic activity. J. Clus. Sci. 2020, 31, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshref, E.M.; Omar, A.A.E.-D.; Moussa, S.H.; Alabdalall, A.H.; Al-Saggaf, M.S.; Alalawy, A.I.; Almutairi, F.M.; Gad, H.A.; Tayel, A.A. Antimicrobial Nanocomposites from Chitosan and Squash Synthesized Nano-Selenium Eradicate Skin Pathogens. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, 202400881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobish, A.M.; El-Nokrashy, A.M.; Elshafey, A.E.; Tayel, A.A. Investigating the Potential of Chitosan-nanocomposites as a Bio-Based Adsorbent for Sustainable Aflatoxin Eradication from Fish Feed. Egypt. J. Vet. Sci. 2025, 56, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghuthaymi, M.A. Antibacterial action of insect chitosan/gum Arabic nanocomposites encapsulating eugenol and selenium nanoparticles. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, M.M.; Elekhtiar, R.S.; El-Hefnawy, M.; Mahrous, H.; Alhayyani, S.; Al-Goul, S.T.; Orif, M.I.; Tayel, A.A. Fabrication and Assessment of Potent Anticancer Nanoconjugates from Chitosan Nanoparticles, Curcumin and Eugenol. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1030936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elraoof, W.A.; Tayel, A.A.; El-Far, S.W.; Abukhatwah, O.M.W.; Diab, A.M.; Abonama, O.M.; Assas, M.A.; Abdella, A. Characterization and antimicrobial activity of chitosan-selenium nanocomposite biosynthesized using Posidonia oceanica. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 26001–26014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rabey, H.A.; Almassabi, R.F.; Mohammed, G.M.; Abbas, N.H.; Bakry, N.; Althiyabi, A.S.; Alshubayli, I.H.; Tayel, A.A. Potent Antibacterial Nanocomposites from Okra mucilage/Chitosan/Silver Nanoparticles for Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Typhimurium Eradication. Green. Process. Synth. 2024, 13, 20230225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayel, A.A.; Aborabu, A.A.S.; Assas, M.; Ghobashy, M.O.I.; Zayed, M.M.; Omar, A.A. Anticandidal Nanocomposites from Purslane Seed Mucilage Mediated Nanosilver and Nanochitosan. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2025, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikar, S.K.; Giri, D.D.; Pal, D.B.; Mishra, P.K.; Upadhyay, S.N. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: A review. Green. Sustain. Chem. 2016, 6, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.; Baran, M.F.; Keskin, C.; Kandemir, S.I.; Valiyeva, M.; Mehraliyeva, S.; Khalilov, R.; Eftekhari, A. Ecofriendly/rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles using extract of waste parts of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and evaluation of their cytotoxic and antibacterial activities. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 2270472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuso, P.; Quizhpe, J.; Rosell, M.D.L.Á.; Peñalver, R.; Nieto, G. Bioactive compounds, health benefits and food applications of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and artichoke by-products: A review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoglund, S.; Hedberg, J.; Yunda, E.; Godymchuk, A.; Blomberg, E.; Odnevall Wallinder, I. Difficulties and flaws in performing accurate determinations of zeta potentials of metal nanoparticles in complex solutions—Four case studies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0181735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Garrido-Maestu, A.; Jeong, K.C. Application, mode of action, and in vivo activity of chitosan and its micro-and nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Moya, F.; Suarez-Fernandez, M.; Lopez-Llorca, L.V. Molecular mechanisms of chitosan interactions with fungi and plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shallan, M.A.; Ali, M.A.; Meshrf, W.A.; Marrez, D.A. In vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant and anticancer activities of globe artichoke (Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus L.) bracts and receptacles ethanolic extract. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 101774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masci, V.L.; Alicandri, E.; Antonelli, C.; Paolacci, A.R.; Marabottini, R.; Tomassi, W.; Tiezzi, A.; Garzoli, S.; Ovidi, E.; Ciaffi, M.; et al. Cynara cardunculus L. var. scolymus L. Landrace “Carciofo Ortano” as a Source of Bioactive Compounds. Plants 2024, 13, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turksever, C.; Gurel, D.B.; Sahiner, A.; Çağındı, O.; Esmer, O.K. Effects of Green Extraction Methods on Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) Leaves. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2024, 62, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.; Serag, A.; Farag, M.A. Cynara cardunculus L.: Outgoing and Potential Trends of Phytochemical, Industrial, Nutritive and Medicinal Merits. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 69, 103937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Lo, R. Phenolic compounds from the leaf extract of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and their antimicrobial activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7272–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Pan, H.; Deng, L.; Qian, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Zhong, C. The antifungal activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles against four pathogens causing kiwifruit post-harvest rot. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 988633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, M.A.; Ashrafudoulla, M.; Parvez, M.A.K.; Balusamy, S.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Kim, J.H.; Akter, S. Chitosan-coated polymeric silver and gold nanoparticles: Biosynthesis, characterization and potential antibacterial applications: A review. Polymers 2022, 14, 5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, S.H.; Tayel, A.A.; Alsohim, A.S.; Abdallah, R.R. Botryticidal activity of nanosized silver-chitosan composite and its application for the control of gray mold in strawberry. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sani, A.; Hassan, D.; Chanihoon, G.Q.; Melo Máximo, D.V.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, E.P. Green Chemically Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles–Chitosan Coatings for Enhancing Strawberry Shelf-Life. Polymers 2024, 16, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganash, M.; Ghany, T.M.A.; Omar, A.M. Morphological and biomolecules dynamics of phytopathogenic fungi under stress of silver nanoparticles. Bionanoscience 2018, 8, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, K.; Glińska, S.; Gapińska, M.; Ruman, T.; Nowak, A.; Aydin, E.; Gutarowska, B. Silver nanoparticles: A mechanism of action on moulds. Metallomics 2016, 8, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñiguez-Moreno, M.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A.; Calderón-Santoyo, M. An extensive review of natural polymers used as coatings for postharvest shelf-life extension: Trends and challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.L.; Wang, Q.S.; Li, C.L.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, Y.L. Transcriptome sequencing analysis reveals silver nanoparticles antifungal molecular mechanism of the soil fungi Fusarium solani species complex. J. Hazard. 2020, 388, 122063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Tebar, N.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A.; Fernández-López, J.; Viuda-Martos, M. Chitosan edible films and coatings with added bioactive compounds: Antibacterial and antioxidant properties and their application to food products: A review. Polymers 2023, 15, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Somasundram, C.; Razali, Z.; Mourad, A.H.I.; Hamed, F.; Ahmed, Z.F. Aloe vera/chitosan-based edible film with enhanced antioxidant, antimicrobial, thermal, and barrier properties for sustainable food preservation. Polymers 2024, 16, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H. Preparation and Application of Edible Chitosan Coating Incorporating Natamycin. Polymers 2025, 17, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Nanoparticle | Size Range (nm) | Mean Diameter (nm) | ζ Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cht | 46.72–392.51 | 148.67 | +37.5 |
| Art/AgNPs | 3.16–27.49 | 10.35 | −23.8 |
| Cht/Art/AgNPs | 69.44–492.15 | 203.22 | +30.9 |
| Antifungal Compound | Penicillium italicum Isolates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pi A | Pi L | Pi O | ||||
| ZOI ** | MFC | ZOI | MFC | ZOI | MFC | |
| Cht | 19.3 ± 1.4 a | 35.0 | 17.7 ± 1.7 a | 42.5 | 18.9 ± 1.8 a | 37.5 |
| Art | 18.2 ± 2.1 a | 37.5 | 15.8 ± 1.6 b | 37.5 | 17.2 ± 1.6 b | 35.0 |
| Art/AgNPs | 24.2 ± 1.8 b | 27.5 | 22.5 ± 2.2 c | 32.5 | 23.3 ± 2.5 c | 30.0 |
| Cht/Art/AgNPs | 31.1 ± 2.3 c | 17.5 | 27.4 ± 2.6 d | 22.5 | 28.6 ± 2.3 d | 20.0 |
| Enilconazole | 24.8 ± 2.2 b | 25.0 | 22.3 ± 2.0 c | 32.5 | 24.1 ± 1.8 c | 30.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alghuthaymi, M.A. Antifungal Action of Edible Coating Comprising Artichoke-Mediated Nanosilver and Chitosan Nanoparticles for Biocontrol of Citrus Blue Mold. Polymers 2025, 17, 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121671
Alghuthaymi MA. Antifungal Action of Edible Coating Comprising Artichoke-Mediated Nanosilver and Chitosan Nanoparticles for Biocontrol of Citrus Blue Mold. Polymers. 2025; 17(12):1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121671
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlghuthaymi, Mousa Abdullah. 2025. "Antifungal Action of Edible Coating Comprising Artichoke-Mediated Nanosilver and Chitosan Nanoparticles for Biocontrol of Citrus Blue Mold" Polymers 17, no. 12: 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121671
APA StyleAlghuthaymi, M. A. (2025). Antifungal Action of Edible Coating Comprising Artichoke-Mediated Nanosilver and Chitosan Nanoparticles for Biocontrol of Citrus Blue Mold. Polymers, 17(12), 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121671






