Dual-Surface-Modified Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Polymer Microcone Array and Its Application to Impact Visual and Voice Warning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
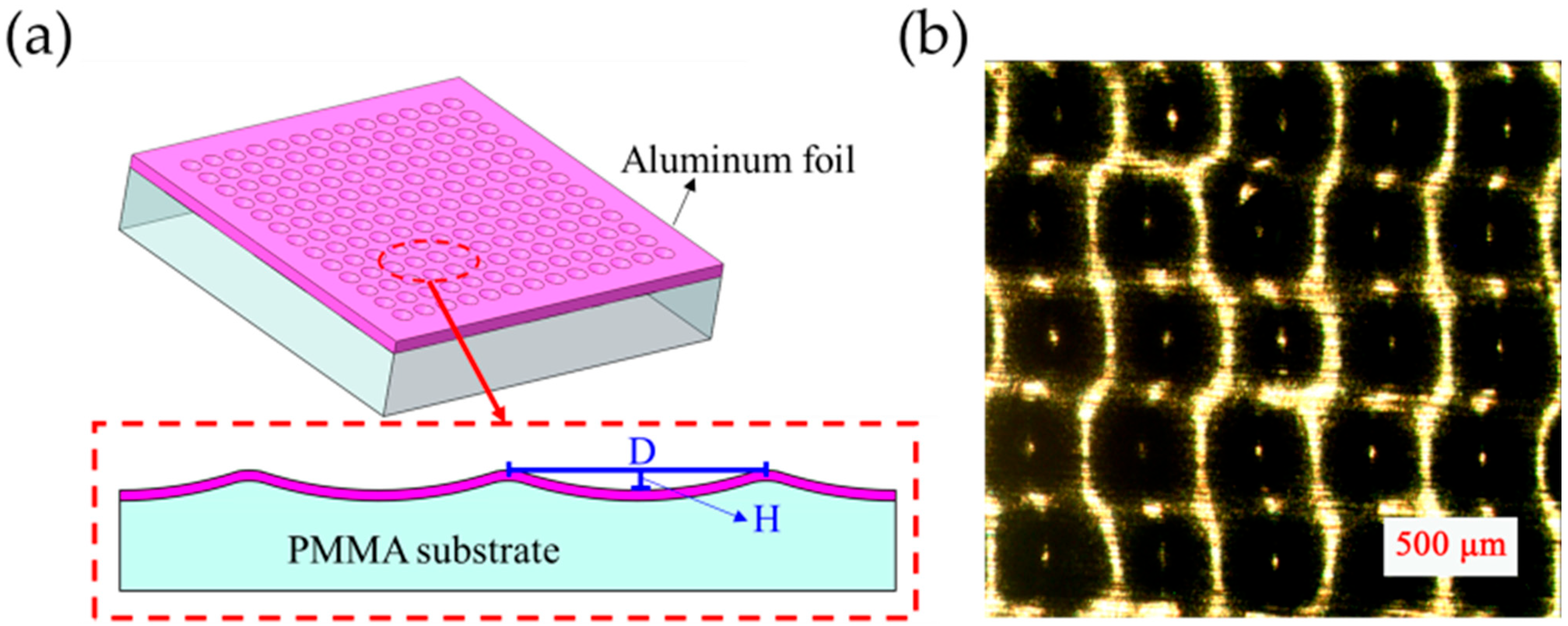
2.1. Fabrication of Tribo-Pairs
2.2. Performance Characterization of the MW-MC-TENG
2.3. Characterization of Materials
3. Results
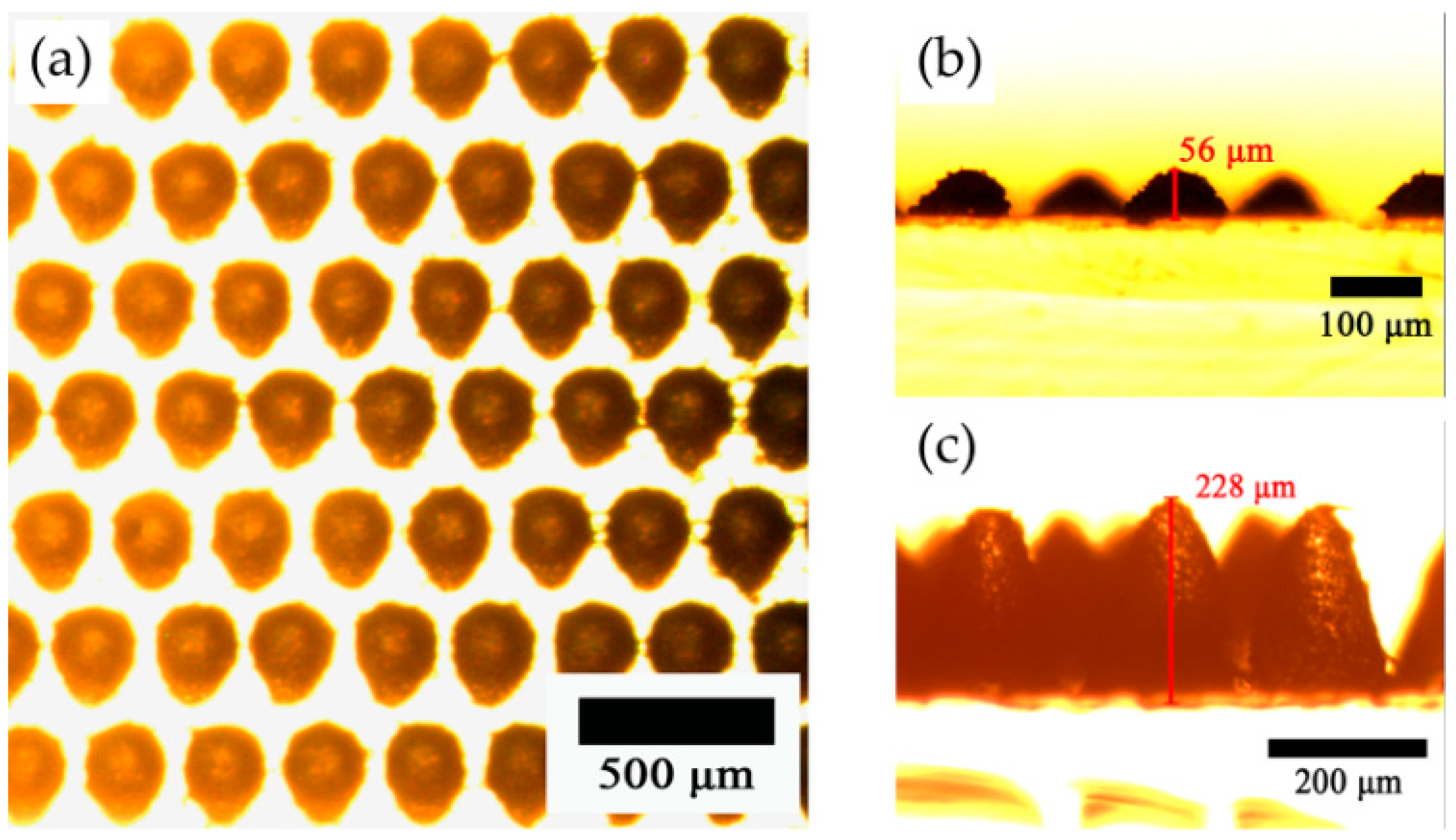
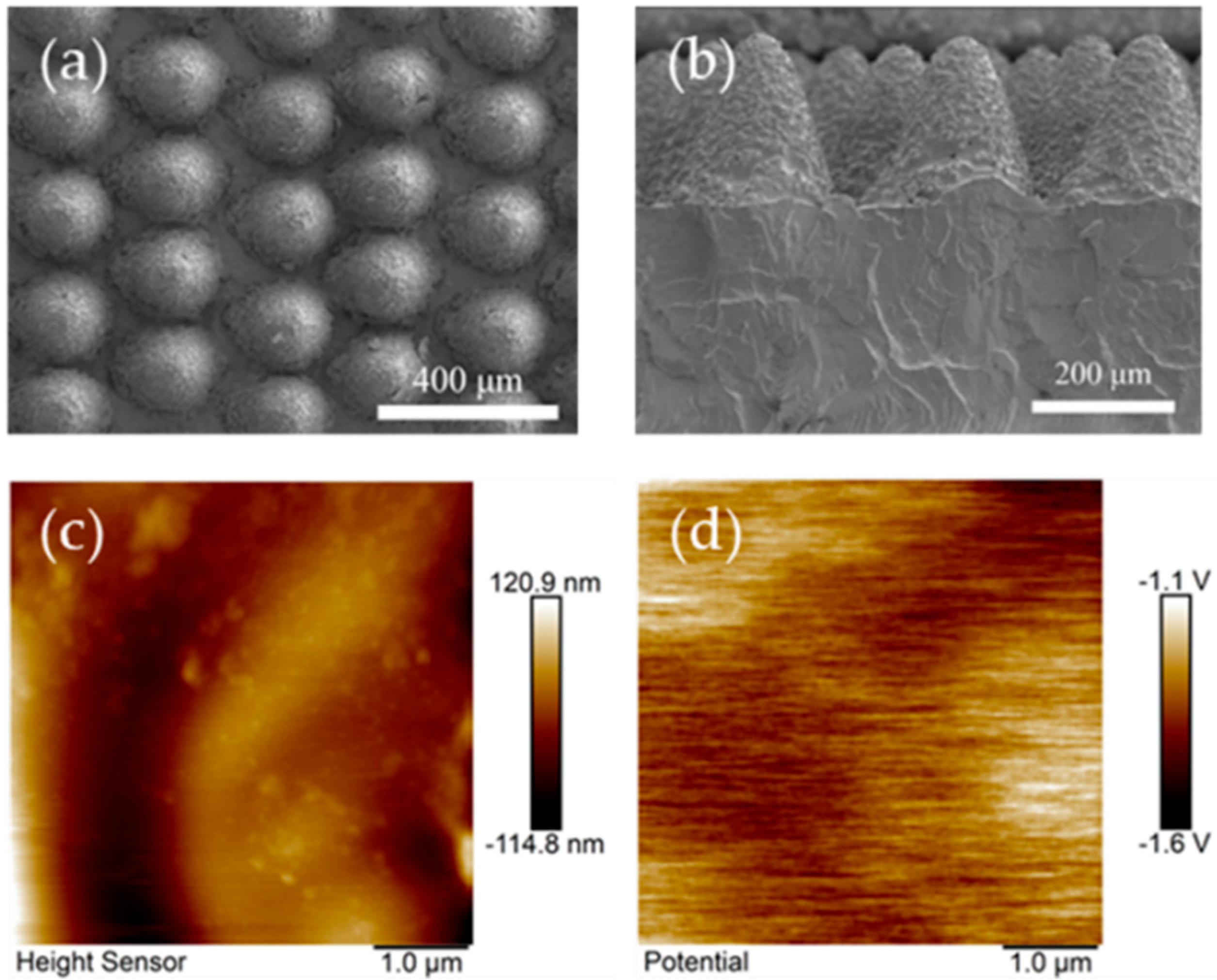
3.1. The Micromorphology Structure of the Samples
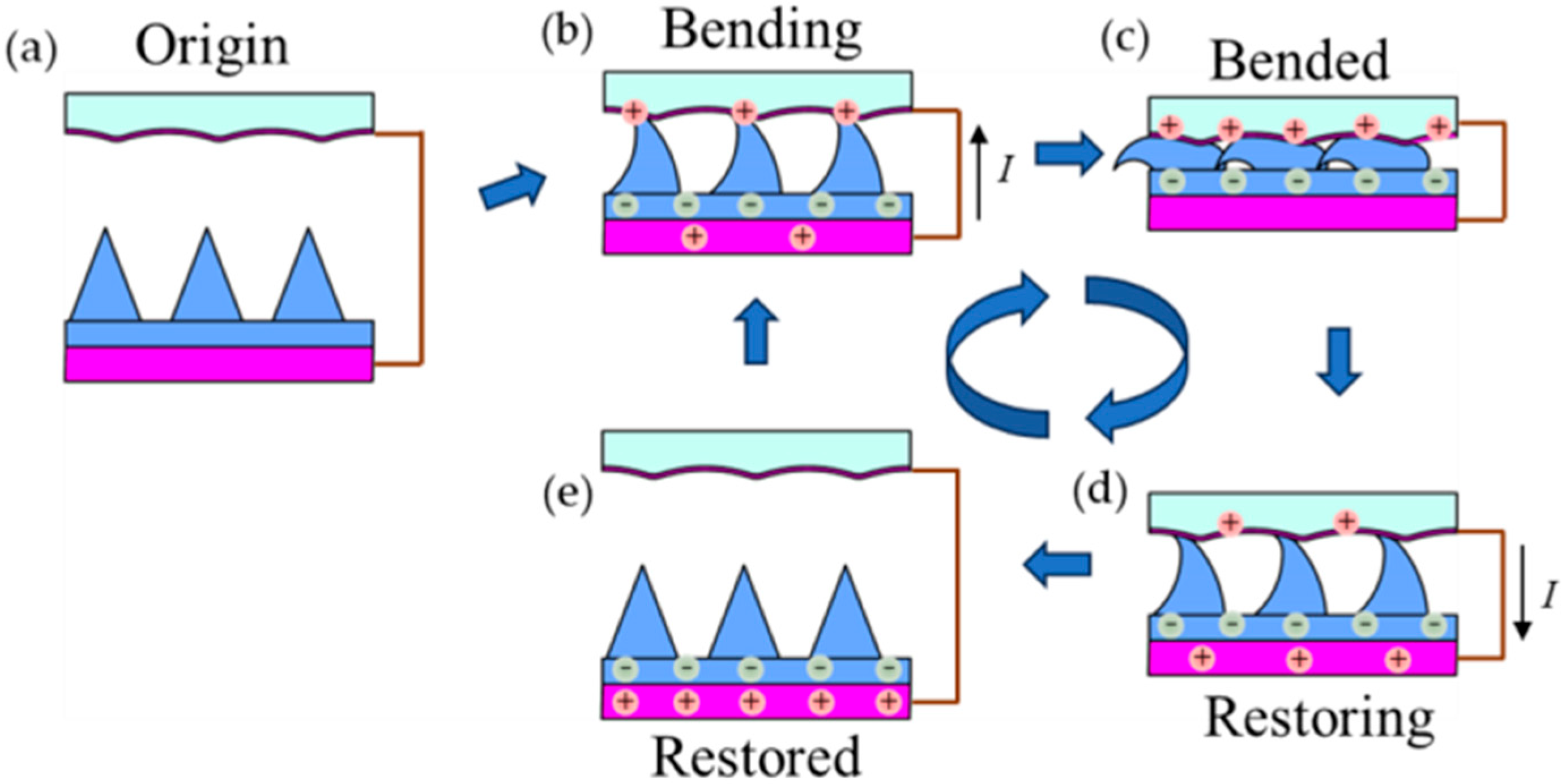
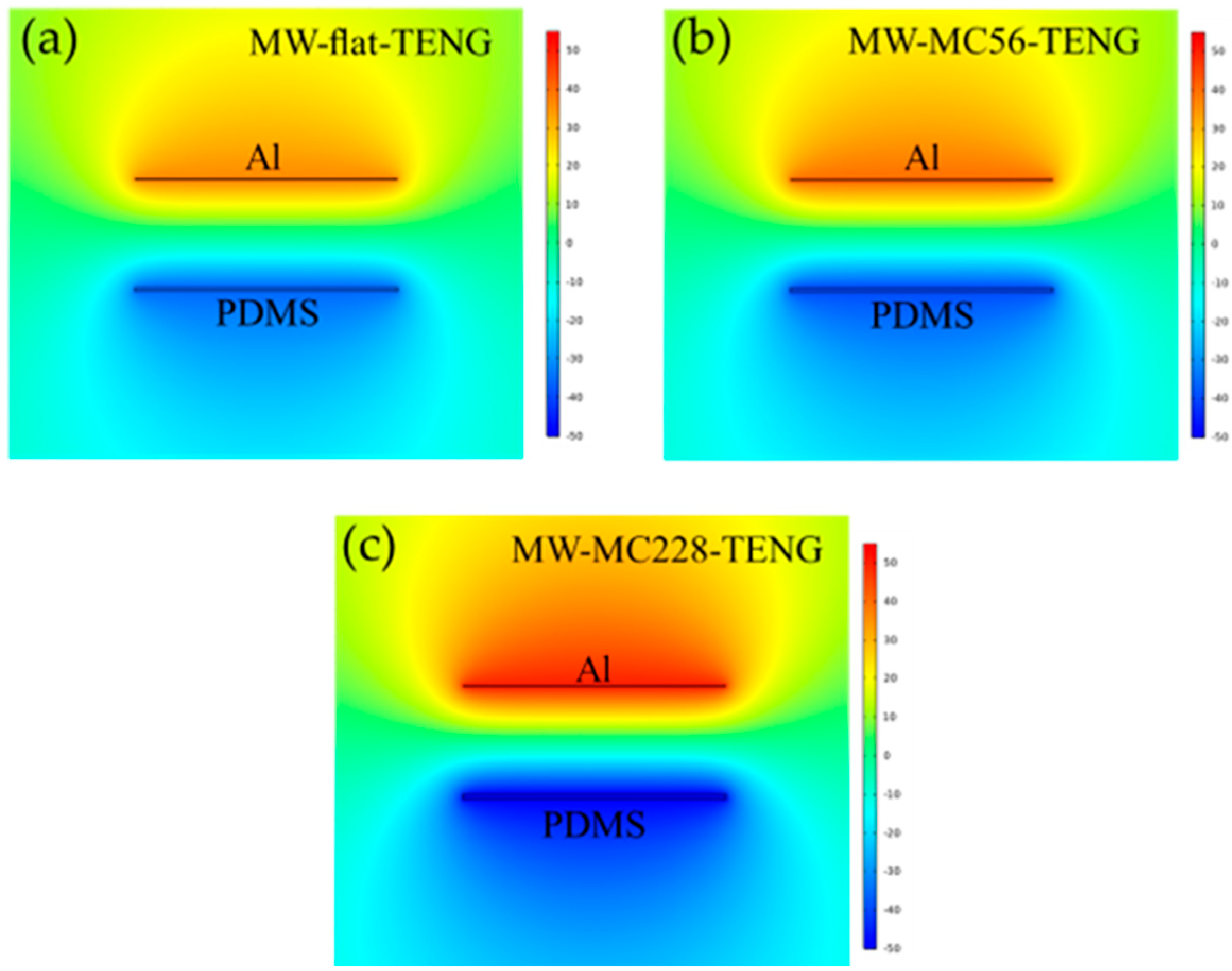
3.2. Working Principle of TENG
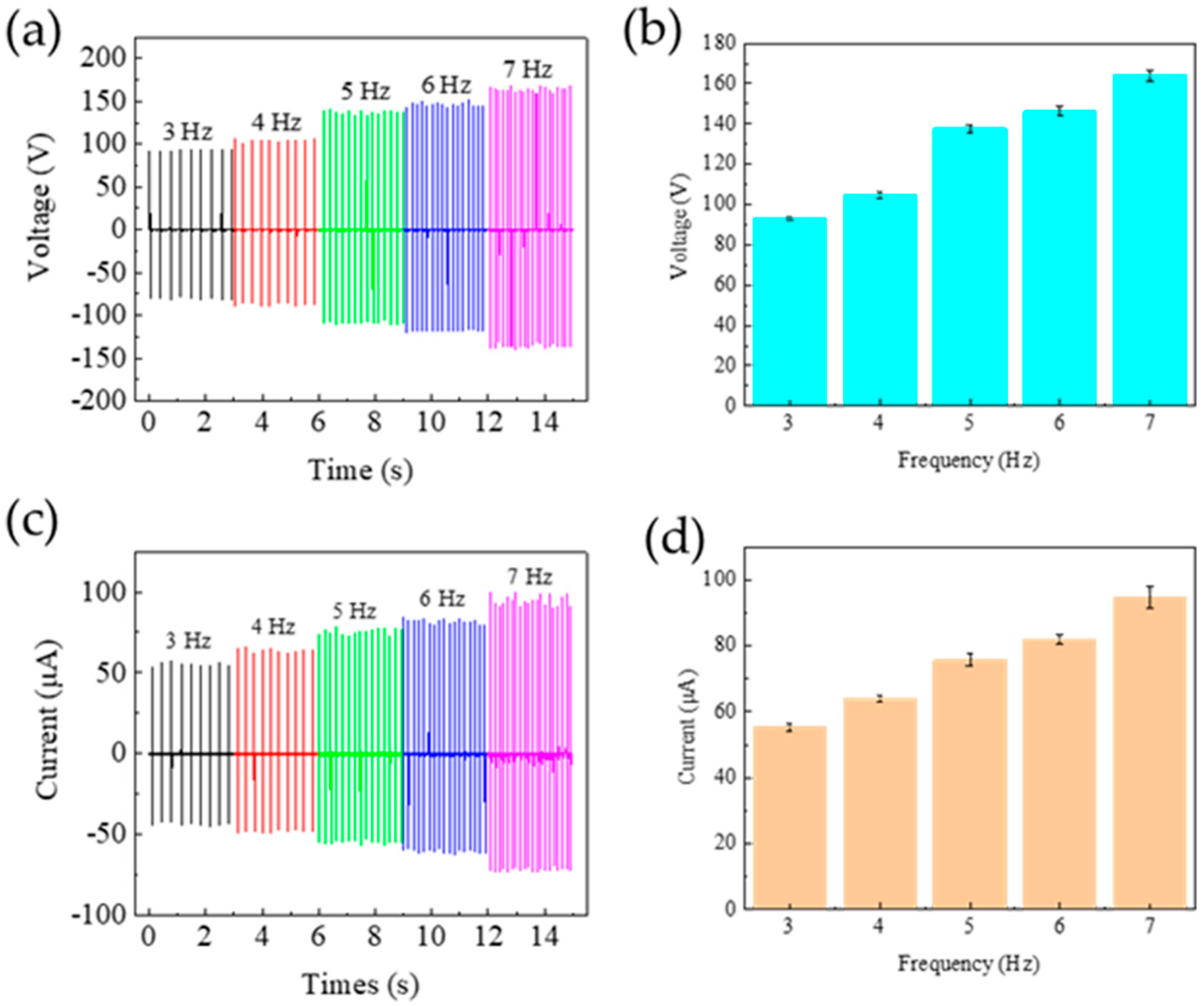
3.3. Output Performance of the TENG
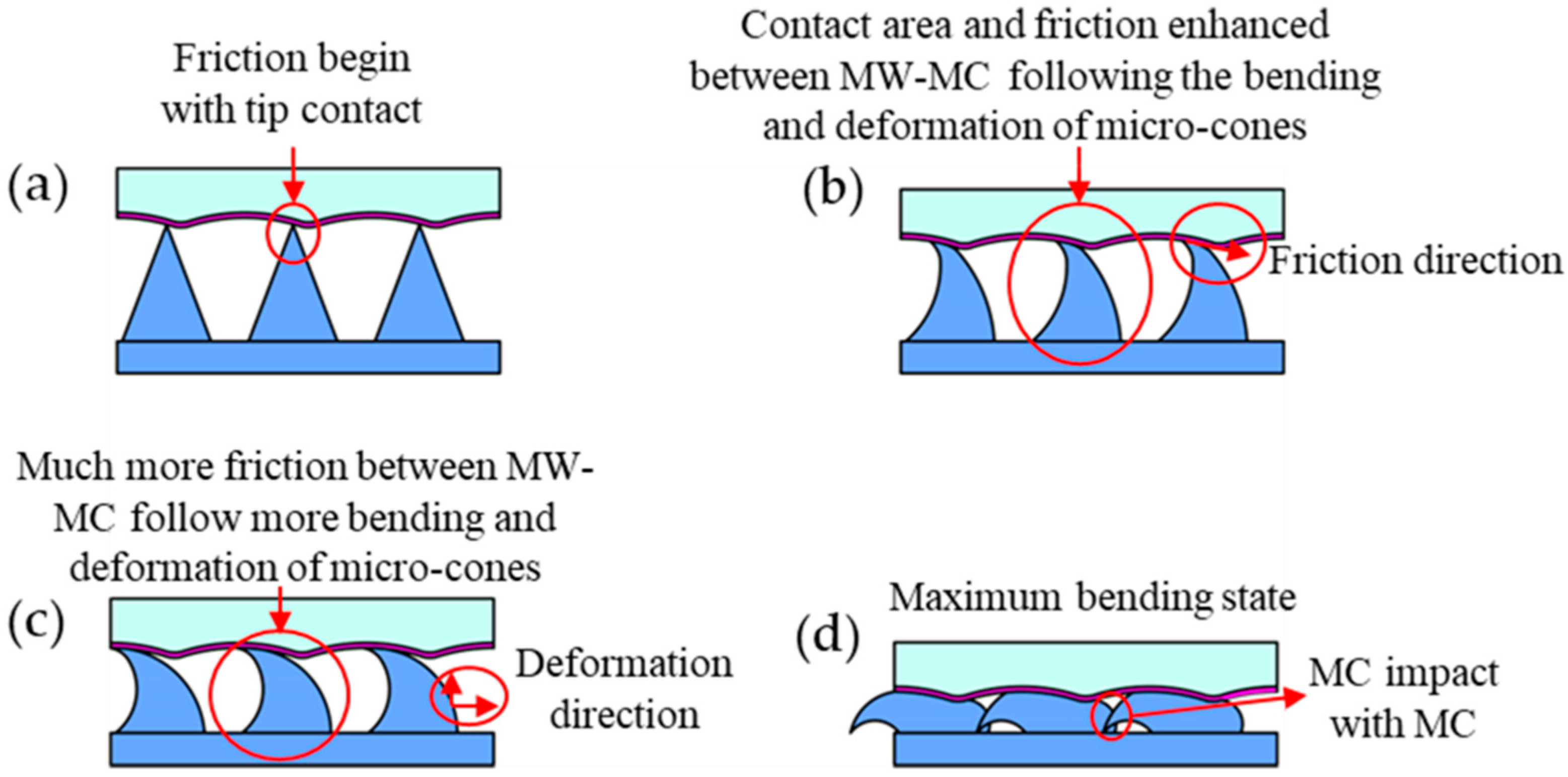
3.4. Improvement Mechanism of the TENG
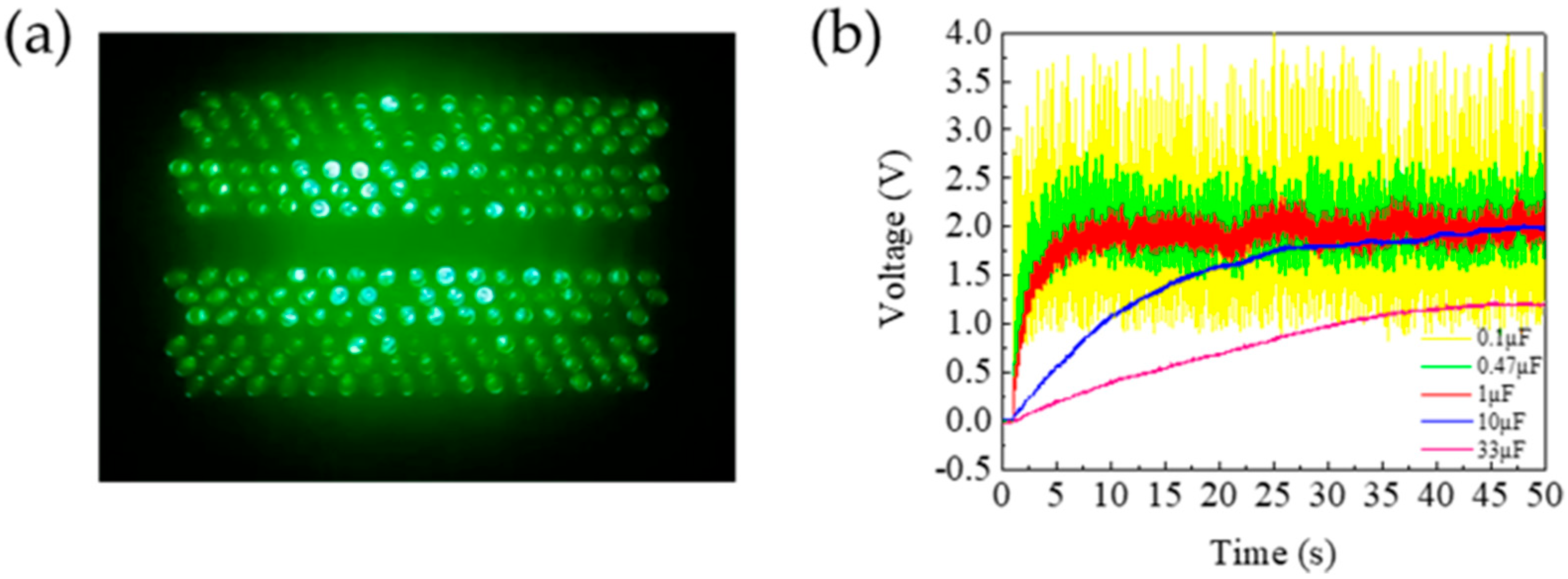
3.5. Power, Charging Capability, and Durability
3.6. Force Sensitive and Flexoelectric Effect
3.7. Impact Warning System Combined with MW-MC-TENG
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dang, V.A.; Vu Khanh, Q.; Nguyen, V.H.; Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, D.C. Intelligent Healthcare: Integration of Emerging Technologies and Internet of Things for Humanity. Sensors 2023, 23, 4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehan, H. Internet of Things (IoT) in Smart Cities: Enhancing Urban Living Through Technology. J. Eng. Technol. 2023, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, J.; Xie, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Multidiscipline Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for the Intelligent Era of Internet of Things. Nanomicro Lett. 2022, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parashakti, R.D.; Perkasa, D.H.; Aprillita, D.; Elvaresia, M.; Rizky, M.A. Human Resource Competency Development to Support the Development of Blue Economy-Based Marine Energy. Ilomata Int. J. Manag. 2024, 5, 524–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Wang, Q.; Su, H.; Li, J.; Xie, B.; Wang, P.; Qiu, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X. Progress in recent research on the design and use of triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting wind energy. Nano Energy 2023, 116, 108789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourasl, H.H.; Barenji, R.V.; Khojastehnezhad, V.M. Solar energy status in the world: A comprehensive review. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 3474–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohit, R.; Kiplangat, D.C.; Veena, R.; Jose, R.; Pradeepkumar, A.; Kumar, K.S. Tracing the evolution and charting the future of geothermal energy research and development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 184, 113531. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Cao, X. From Triboelectric Nanogenerator to Hybrid Energy Harvesters: A Review on the Integration Strategy toward High Efficiency and Multifunctionality. Materials 2023, 16, 6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, R.; Du, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Z.; Lin, Z.; Tan, T. Broadband omnidirectional piezoelectric–electromagnetic hybrid energy harvester for self-charged environmental and biometric sensing from human motion. Nano Energy 2023, 113, 108526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, C.H.; Yuan, H.Z.; Ji, X.P.; Yu, G.X.; Jia, X.D. Size effect of piezoelectric energy harvester for road with high efficiency electrical properties. Appl. Energy 2023, 330, 120379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Lin, P.S.; Hong, S.H.; Tung, S.H.; Liu, C.L. Enhanced Electrical Conductivity and Mechanical Properties of Stretchable Thermoelectric Generators Formed by Doped Semiconducting Polymer/Elastomer Blends. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 3764–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Wang, J.; Xing, Y.; Song, W.; Li, N.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, C. A self-powered lantern based on a triboelectric–photovoltaic hybrid nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.H.; Pan, C.F. Progress in nanogenerators for portable electronics. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hong, K.; Hao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Qin, Y.; Su, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, X. Triboelectric nanogenerators with machine learning for internet of things. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 10, 2400554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Yang, X.; Huang, R.; Zheng, D.; Yuan, J.; Hong, H.; Duan, J.; Zi, Y.; Tang, Q. Universal Energy Solution for Triboelectric Sensors Toward the 5G Era and Internet of Things. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2302009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, H.; Xu, N.; Barbosa, B.H.G.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Khajepour, A.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.L. Intelligent systems using triboelectric, piezoelectric, and pyroelectric nanogenerators. Mater. Today 2022, 52, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawy, K.; Sharma, R.; Yoon, H.-J.; Khan, U.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, T.T.-H. A triboelectric nanogenerator energy harvesting system based on load-aware control for input power from 2.4 μW to 15.6 μW. Nano Energy 2020, 74, 104839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, M.; Cui, X.; Shao, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Triboelectric nanogenerator based self-powered sensor for artificial intelligence. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D.M.; Ryu, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Yoon, H.J.; Kang, M.; Kwak, S.S.; Kim, S.W. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Battery-Free Wireless Sensor System Using Multi-Degree of Freedom Vibration. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2301427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lv, X.; Wang, K. Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerators in Medical Recovery: A Review. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2024, 6, 5465–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Xi, G.; Mao, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D.; Tang, M.; Xu, Z.; Luan, H. Ultrastretchable, Self-Healing Conductive Hydrogel-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Human-Computer Interaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 5128–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, J.H.; Duan, R.G.; Zhang, M.L.; Liu, X.M. Recent Progress Regarding Materials and Structures of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for AR and VR. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Deng, W.L.; Xu, J.; Chen, J. Engineering Materials at the Nanoscale for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2020, 1, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lee, Y.; Lin, Z.H.; Cho, S.; Kim, M.; Ao, C.K.; Soh, S.; Sohn, C.; Jeong, C.K.; Lee, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators: From Technological Progress to Commercial Applications. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 11087–11219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Gao, D.G.; Lyu, B.; Zhang, C.G.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Li, N.; Ma, J.Z. A triboelectric sensor with highly sensitive and durable: Dual regulation strategy based on surface morphology and functional groups on negative/positive tribolayers. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.X.; Yang, S.Q.; Sun, Z.; Chen, P.; Qiao, X.X. Regulating the electrical performance of contact-separation mode triboelectric nanogenerators based on double-sided groove textures. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2024, 34, 035010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Sha, J.; Xu, Y.L.; Chen, S.; Xu, F. All-cellulose nanofiber-based sustainable triboelectric nanogenerators for enhanced energy harvesting. Polymers 2024, 16, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajula, P.; Muhammad, F.M.; Reza, M.S.; Jaisankar, S.N.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, H.D. Fabrication of a silicon elastomer-based self-powered flexible triboelectric sensor for wearable energy harvesting and biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2023, 5, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.H.; Ullah, Z.; Zheng, S.R.; Yang, Z.R.; Yu, S.W.; Zhu, S.P.; Liu, L.W.; He, A.H.; Wang, C.G.; Li, Q. Ultrahigh current output from triboelectric nanogenerators based on UIO-66 materials for electrochemical cathodic protection. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Jun, J.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, H. High-performance triboelectric nanogenerators with artificially well-tailored interlocked interfaces. Nano Energy 2016, 27, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.Y.; Chung, C.K. High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Double-Side Patterned Surfaces Prepared by CO2 Laser for Human Motion Energy Harvesting. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.H.; Chung, C.K. High-Performance Al/PDMS TENG with Novel Complex Morphology of Two-Height Microneedles Array for High-Sensitivity Force-Sensor and Self-Powered Application. Small 2020, 16, e2001209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, K.-H.; Lin, L.; Chung, C.-K. Low-cost micro-graphite doped polydimethylsiloxane composite film for enhancement of mechanical-to-electrical energy conversion with aluminum and its application. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 135, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chung, C.K. PDMS Microfabrication and Design for Microfluidics and Sustainable Energy Application: Review. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.; Ke, K. High contact surface area enhanced Al/PDMS triboelectric nanogenerator using novel overlapped microneedle arrays and its application to lighting and self-powered devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 508, 145310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.K.; Huang, Y.J.; Wang, T.K.; Lo, Y.L. Fiber-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Mechanical Energy Harvesting and Its Application to a Human-Machine Interface. Sensors 2022, 22, 9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Jing, Q.S.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Su, Y.J.; Ma, J.S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.L. Membrane-Based Self-Powered Triboelectric Sensors for Pressure Change Detection and Its Uses in Security Surveillance and Healthcare Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5807–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcho, I.W.; Kim, W.G.; Jeon, S.B.; Park, S.J.; Lee, B.J.; Bae, H.K.; Kim, D.; Choi, Y.K. Surface structural analysis of a friction layer for a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2017, 42, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Xu, L.; Cheng, X.W.; Li, Y.Y.; Huang, X.; Guo, W.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, H. Bioinspired Triboelectric Nanogenerators as Self-Powered Electronic Skin for Robotic Tactile Sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasel, M.S.; Maharjan, P.; Salauddin, M.; Rahman, M.T.; Cho, H.O.; Kim, J.W.; Park, J.Y. An impedance tunable and highly efficient triboelectric nanogenerator for large-scale, ultra-sensitive pressure sensing applications. Nano Energy 2018, 49, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.S.; Ye, B.U.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, D.; Kang, C.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Baik, J.M. Boosted output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator via electric double layer effect. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, G.B.; Xu, Y.; Cochran, P.; Gadegaard, N.; Mulvihill, D.M.; Dahiya, R. Origin of the contact force-dependent response of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.M.; Zhao, P.; Kwon, O.; Sohn, A.; Zhuo, F.P.; Lee, D.M.; Sun, C.; Seol, D.; Lee, D.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Mixed Triboelectric and Flexoelectric Charge Transfer at the Nanoscale. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Morphology | Material | Fabrication Method | Operation Condition | Electrical Characteristics | Ref | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voc (V) | Isc (µA) | Power Density (mW/cm2) | |||||
| Nanoporous-scale morphology | GPA@Nylon -MSF@MXene | Vacuum filtration, etching stripping, and freeze drying | 2 kPa, 1 Hz | 30 | - | - | [25] |
| Microgroove-microgroove | Cu-PDMS | Oxidation, magnetron sputtering, lithography, and etching | 0.5 Mpa, 0.5 Hz | ~50 | - | - | [26] |
| Nanofiber-nanofiber | CNT@PDMS-PDMS | Electrospinning, deacetylation, and impregnating | 15 N, 10 Hz | 94 | 8.5 | 0.015 | [27] |
| Sandpapermorphology-nanofiber | ECF-TPUnw | Ecoflex casting | 4.4 N 5 Hz | 139 | 4.6 | 0.16 | [28] |
| Nanoporous-nanoporous | PVDF-UIO@PVDF | Chemistry functionalization, spin coating | 9 Hz | - | ~50 | ~0.1225 | [29] |
| Nanopillar-nanopillar | Ni-PDMS | Spin coating, electrodeposition | 10 kgf, 3 Hz | ~100 | ~23 | - | [30] |
| Microwave-microcone 180 | Al-PDMS | CO2 laser ablation and cold imprinting | 30 N 6 Hz | 141 | 71.5 | 1.4 | [31] |
| Microwave-microcone 228 | Al-PDMS | CO2 laser ablation and cold imprinting | 30 N 6 Hz | 157 | 78.5 | 1.64 | ours |
| Combination | Symbol | MW-Flat | MW-MC56 | MW-MC228 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patterning Type | Single-Sided | Double-Sided | Double-Sided | |
| Microstructure of Al | microwave (MW) | microwave (MW) | microwave (MW) | |
| Microstructure of PDMS | flat | microcone (MC) | microcone (MC) | |
| Size (cm2) | 5 × 5 | 5 × 5 | 5 × 5 | |
| Power of laser (mW) | 60 | 600 | ||
| Velocity of scanning (mm/s) | 11.4 | 11.4 | ||
| Ablation pitch (µm) | 250 | 250 | ||
| Grain density (number of MCs/cm2) | 1600 | 1600 | ||
| Average MC center depth (µm) | H | flat | 56 | 228 |
| Average MC bottom diameter (µm) | D | - | 118.6 | 174.3 |
| Average MC estimated volume (µm3) | V | - | 205,377.1 | 1,814,089.9 |
| Average MC estimated surface area (µm2) | S | - | 15,161.6 | 66,846.1 |
| Voltage (V) | Voc | 114 | 127 | 157 |
| Current (μA) | Isc | 56.5 | 66 | 78.5 |
| Current density (µA/cm2) | Jsc | 2.26 | 2.64 | 3.14 |
| Device | Patterning Type | Triboelectric Material | Fabrication Method | Voltage | Sensitivity | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-TES | One-side | Latex/FEP-Cu/Acrylic | Multilayer assembly etching | ~15 V | 0.04 V/kPa | [37] |
| DP-TENG | One-side | Au/PDMS-Au | ICP etching, Thermal oxidation | ~65 V | 0.414 V/N | [38] |
| TENG e-skin sensor | Dual-side | PDMS@AgNWs-PDMS@ PTFE tiny burrs | Replication and molding, spray coating, evaporation and reactive ion etching | 3.14 V | 0.127 V/kPa | [39] |
| LU-TEPS | Dual-side | PDMS-PDMS@CNT | Spin coating & curing, evaporation | 120 V | 0.51 V/kPa | [40] |
| Two-layer TENG | Dual-side | Al/porous PDMS-Al@Au NPs | Spin coating and curing | 40 V | <2.13 V/N | [41] |
| MW-MC180-TENG | Dual-side | Al-PDMS/Al | CO2 laser ablation, cold imprinting | 141 | 3.01 V/N | [31] |
| MW-MC228-TENG | Dual-side | Al-PDMS/Al | CO2 laser ablation, cold imprinting | 155 V | 3.91 V/N | Ours |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, D.-Y.; Chung, C.-K. Dual-Surface-Modified Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Polymer Microcone Array and Its Application to Impact Visual and Voice Warning. Polymers 2025, 17, 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111569
Lin D-Y, Chung C-K. Dual-Surface-Modified Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Polymer Microcone Array and Its Application to Impact Visual and Voice Warning. Polymers. 2025; 17(11):1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111569
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Dong-Yi, and Chen-Kuei Chung. 2025. "Dual-Surface-Modified Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Polymer Microcone Array and Its Application to Impact Visual and Voice Warning" Polymers 17, no. 11: 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111569
APA StyleLin, D.-Y., & Chung, C.-K. (2025). Dual-Surface-Modified Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Polymer Microcone Array and Its Application to Impact Visual and Voice Warning. Polymers, 17(11), 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111569







