Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in the Analysis of Explosives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preparation Methods for Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Used in the Analysis of Explosives
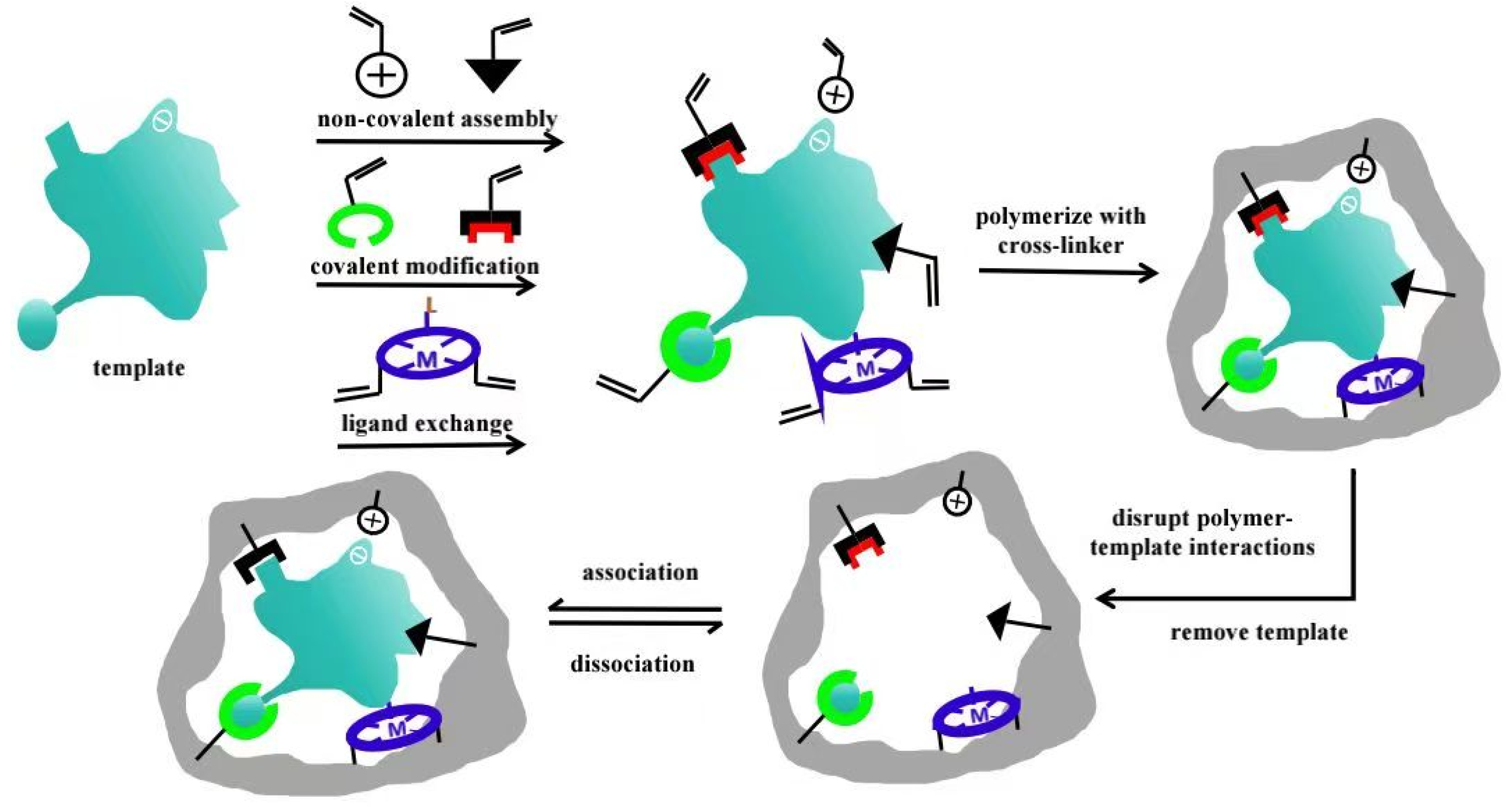
2.1. Preparation Techniques
2.1.1. The Entrapment Method
2.1.2. New Techniques
2.2. Preparation Methods for Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Detection of Different Explosives
2.2.1. Nitroaromatics
2.2.2. Nitrate Esters
2.2.3. Nitramines
2.2.4. Peroxides
3. Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in the Analysis of Explosives
3.1. Sample Pretreatment
3.1.1. Solid-Phase Extraction
3.1.2. Solid-Phase Microextraction
3.1.3. Liquid-Phase Microextraction
3.2. Sensors
3.2.1. Electrochemical Sensors
3.2.2. Photochemical Sensors
3.2.3. Other Sensors
3.3. Other Emerging Applications
4. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MIPs | Molecularly Imprinted Polymers |
| HPLC | High-performance Liquid Chromatography |
| CEC | Capillary Electrochromatography |
| SPE | Solid-Phase Extraction |
| NIPs | Nonimprinted Polymers |
| TNT | Trinitrotoluene |
| IMS | Ion Mobility Spectrometry |
| QDs | Quantum Dots |
| MMA | Methyl Methacrylate |
| NVP | Nvinylpyrrolidone |
| MAA | Methacrylic Acid |
| MA | Methyl Acrylate |
| AA | Acrylic Acid |
| TRIM | Trimethylolpropane Trimethacrylate |
| MMOFs | Microporous Metal–Organic Frameworks |
| MIHSs | Molecularly Imprinted Hollow Spheres |
| NIHSs | Nonimprinted Polymer Hollow Spheres |
| CL-20 | Hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane |
| EGDMA | Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| KPS | Potassium Persulfate |
| APTES | 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane |
| TEOS | Tetraethyl Orthosilicate |
| ACVA | 4,4′-Azobis(4-cyanovaleric Acid) |
| DHEBA | N,N′-(1,2-Dihydroxyethylene)bisacrylamide |
| AAM | Acrylamide |
| FRET | Förster Resonance Energy Transfer |
| RDF | Radial Distribution Function |
| KBI | Kirkwood–Buff Integral |
| MICs | Molecularly Imprinted Colloidal Particles |
| NICs | Nonimprinted Colloidal Particles |
| NC | Nitrocellulose |
| FT-IR | Fourier Transform Infrared |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| RDX | 1,3,5-trinitroperhydro-1,3,5-triazine |
| HMX | Octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine |
| TADB | Tetraacetyldibenzylhexaazaisowurtzitane |
| TATP | Triacetone Triperoxide |
| HMTD | Hexamethylene Triperoxide Diamine |
| Cz | Carbazole |
| TEAP | Tetraethylammonium Perchlorate |
| PBE | Peroxide-Based Explosive |
| PCz | Polycarbazole |
| SPME | Solid-Phase Microextraction |
| LPME | Liquid-Phase Microextraction |
| DLLME | Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction |
| AIBN | Azobisisobutyronitrile |
| LSV | Linear Sweep Voltammetry |
| CV | Cyclic Voltammetry |
| SWV | Square Wave Voltammetry |
| CA | Chronoamperometry |
| PM | Piezoelectric Microgravimetry |
| DFT | Density Functional Theory |
| SERS | Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy |
| CL | Chemiluminescence |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| LSPR | Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| PhC | Photonic Crystal |
| OWS | Optical Waveguide Spectroscopy |
| GNSs | Gold Nanostars |
| POF | Plastic Optical Fiber |
| MICA | Molecularly Imprinted Colloidal Array |
| QCM | Quartz Crystal Microbalance |
| MIPC | Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Crystal |
| NCs | Nanocrystals |
| 3-NT | 3-Nitrotoluene |
| NM | Nitromethane |
| PCL | Polycaprolactone |
| PL | Photoluminescence |
| GOx | Graphene Oxide |
| CNTs | Carbon Nanotubes |
| PETN | Pentaerythritol Tetranitrate |
| FAPA-MS | Flowing Atmospheric Pressure Afterglow Mass Spectrometry |
| RSD | Relative Standard Deviation |
References
- Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Fernández-Calviño, D.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Arenas-Lago, D. Effects of military training, warfare and civilian ammunition debris on the soil organisms: An ecotoxicological review. Biol. Fert. Soils 2024, 60, 813–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galante, N.; Franceschetti, L.; Del Sordo, S.; Casali, M.B.; Genovese, U. Explosion-related deaths: An overview on forensic evaluation and implications. Forensic Sci. Med. Pat. 2021, 17, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebran, A.; Abou Khalil, E.; El Moheb, M.; Albaini, O.; El Warea, M.; Ibrahim, R.; Karam, K.; El Helou, M.O.; Ramly, E.P.; El Hechi, M.; et al. The Beirut port explosion injuries and lessons learned: Results of the Beirut blast assessment for surgical services (BASS) multicenter study. Ann. Surg. 2022, 275, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lyu, X.; Liang, S.; Liu, Z. Application of fluorescence sensing technology in trace detection of explosives. Dyes. Pigment. 2023, 220, 111651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, B.; Gupta, A.K.; Pandey, D. Recent developments of image processing to improve explosive detection methodologies and spectroscopic imaging techniques for explosive and drug detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 6849–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorsone, E.; Manai, R.; Cali, K.; Ricatti, M.J.; Farno, S.; Persaud, K.; Mucignat, C. Biosensor array based on ligand binding proteins for narcotics and explosives detection. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2021, 334, 129587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, I.A.; Golker, K.; Olsson, G.D.; Suriyanarayanan, S.; Wiklander, J.G. The use of computational methods for the development of molecularly imprinted polymers. Polymers 2021, 13, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadi, A.; Youssef, K.; Akhtarian, S.; Tabesh, E.; Kraft, G.; Brar, S.K.; Rezai, P. Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) based core-shell microspheres for bacteria isolation. Polymers 2022, 251, 124917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Garipcan, B.; Patra, H.K.; Uzun, L. Molecular imprinting applications in forensic science. Sensors 2017, 17, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.; Santelli, S.; Giorgetti, A.; Pelletti, G.; Pirani, F.; Fais, P.; Pascali, J.P. The Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Forensic Toxicology: Issues and Perspectives. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrila, A.M.; Diacon, A.; Iordache, T.V.; Rotariu, T.; Ionita, M.; Toader, G. Hazardous Materials from Threats to Safety: Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Versatile Safeguarding Platforms. Polymers 2024, 16, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apak, R.; Üzer, A.; Sağlam, Ş.; Arman, A. Selective electrochemical detection of explosives with nanomaterial based electrodes. Electroanalysis 2023, 35, e202200175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadurmus, L.; Bilge, S.; Sınağ, A.; Ozkan, S.A. Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-Based sensing for detection of explosives: Current perspectives and future applications. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2022, 155, 116694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarejousheghani, M.; Lorenz, W.; Vanninen, P.; Alizadeh, T.; Cämmerer, M.; Borsdorf, H. Molecularly imprinted polymer materials as selective recognition sorbents for explosives: A review. Polymers 2019, 11, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, Z.; Huang, Z.; Li, K.; Lv, Y. Biosensors for explosives: State of art and future trends. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, R. Molecular imprinting technology and its application in explosive detection. J. People’s Public Secur. Univ. China (Sci. Technol.) 2010, 16, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C.; Andersson, H.S.; Andersson, L.I.; Ansell, R.J.; Kirsch, N.; Nicholls, I.A.; O’Mahony, J.; Whitcombe, M.J. Molecular imprinting science and technology: A survey of the literature for the years up to and including 2003. J. Mol. Recognit. 2006, 19, 106–180. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Cormack, P.A.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly imprinted monodisperse microspheres for competitive radioassay. Anal. Commun. 1999, 36, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly imprinted microspheres as antibody binding mimics. React. Funct. Polym. 2001, 48, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Sakakibara, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Kimura, M.; Shirai, H.; Hanabusa, K. Preparation of Porous Polymers by” in Situ Precipitation” Using Low Molecular Weight Gelators. Polym. J. 2002, 34, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Li, H.; Meng, Z.; Liang, X.; Xue, M.; Wang, Q.; Dong, X. Detection of nitrobenzene compounds in surface water by ion mobility spectrometry coupled with molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringer, R.C.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Grant, S.A. Comparison of molecular imprinted particles prepared using precipitation polymerization in water and chloroform for fluorescent detection of nitroaromatics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 703, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerlig, J.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles in chemical sensing–Synthesis, characterisation and application. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2015, 207, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Song, X.; Wang, A.; Chen, L.; Han, S. Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers-capped CdTe quantum dots for the fluorescent sensing of 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8146–8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayes, A.G.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly imprinted polymer beads: Suspension polymerization using a liquid perfluorocarbon as the dispersing phase. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 3769–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X. Progress of the preparation of molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres by seed swelling and suspension polymerization. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2009, 28, 978–981. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Zhang, L.; Fu, C. Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Microspheres Prepared by Seed Swelling and Suspension Polymerization. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2002, 20, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Norrlöw, O.; Glad, M.; Mosbach, K. Acrylic polymer preparations containing recognition sites obtained by imprinting with substrates. J. Chromatogr. A 1984, 299, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Guan, G.; Gao, D.; Liu, J. Surface molecular self-assembly strategy for TNT imprinting of polymer nanowire/nanotube arrays. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8339–8346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y. Study on Novel Molecularly Imprinting Strategy and Its Applications for the Electrochemical Detection of Nitroaromatic Compounds. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Florea, A.; Cristea, C.; Bessueille, F.; Vocanson, F.; Goutaland, F.; Zhang, A.; Săndulescu, R.; Lagarde, F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. 1, 3, 5-Trinitrotoluene detection by a molecularly imprinted polymer sensor based on electropolymerization of a microporous-metal-organic framework. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2015, 207, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Xu, W. Synthesis of Molecular Imprinting Polymers with Silica Gel as a Sacrificial Material. J. Anal. Sci. 2005, 21, 113–114. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chen, H.; Shi, S.; Jia, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, H. Preparation of novel gallic acid-based dummy-template molecularly imprinted polymer adsorbents for rapid adsorption of dibutyl phthalate from water. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 349, 123917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Hou, C.; Lu, W.; Ni, Y. Preparation Method of Fluorescent MolecularImprinting and Its TNT Detection. J. Xi’an Technol. Univ. 2013, 33, 549–553. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z. Study on the Efficient Desensitization of Nitramine Explosives by In-situ Polymerization Coating of Adhesive. In Annual Report on Science and Technology of China Academy of Engineering Physics; CNKI: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Amarh, F.A.; Kangmennaa, A.; Agorku, E.S.; Voegborlo, R.B. A state-of-the-art review of trends in molecularly imprinted polymers in the clean-up of pesticides in environmental samples. Sustain. Environ. 2024, 10, 2298067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, A.I.; Lobato, D.; Gago, S.; Bonifácio, V.D.; Viveiros, R.; Casimiro, T. Enhanced biosensing by green, switchable photochromic molecularly imprinted polymers. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2025, 426, 137122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohle, R.; Jeanty, P.; Stegmeier, S.; Hürttlen, J.; Fleischer, M. Detection of explosives based on the work function read-out of molecularly imprinted polymers. Procedia Eng. 2012, 47, 1370–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xue, M.; Xue, F.; Mu, X.; Xu, Z.; Meng, Z.; Zhu, G.; Shea, K.J. Molecularly imprinted hollow spheres for the solid phase extraction of estrogens. Talanta 2015, 140, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer in the Separation and Determination of Nitramine Explosives. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Cao, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, Z. A robust electrochemical sensor for Gefitinib detection using three-dimensional framework molecularly imprinted polymer-loaded carbon nanotubes. Microchem. J. 2025, 208, 112485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunte, G.; Heil, M.; Röseling, D.; Hürttlen, J.; Pontius, H.; Krause, H. Trace detection of explosives vapours by molecularly imprinted polymers for security measures. Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 2009, 34, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Hu, L. Molecularly Imprinted Piezoelectric Sensor for Detecting Explosives. J. Xi’an Technol. Univ. 2012, 32, 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J. Preparation and Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on INT Detection. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Science & Technology, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Puttasakul, T.; Tancharoen, C.; Sukjee, W.; Pintavirooj, C.; Sangma, C. Detection of 2, 4, 6-Trinitrotoluene by MIP-composite Based Electrochemical Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2021 9th International Electrical Engineering Congress, Pattaya, Thailand, 10–12 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanzadeh, J.; Khataee, A.; Oskoei, Y.M.; Fattahi, H.; Bagheri, N. Selective chemiluminescence method for the determination of trinitrotoluene based on molecularly imprinted polymer-capped ZnO quantum dots. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 10659–10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T. Preparation of magnetic TNT-imprinted polymer nanoparticles and their accumulation onto magnetic carbon paste electrode for TNT determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Wei, T.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, H.; Zhang, P. Detection of TNT by a molecularly imprinted polymer film-based surface plasmon resonance sensor. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2102–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, L.; Herdes, C. The porogen effect on the complexation step of trinitrotoluene–methacrylic acid: Towards efficient imprinted polymer sensors. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2018, 3, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, A.R.; Zafarghandi, R.S. Selective determination of 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene in water samples based on magnetic imprinted nanoparticles via grafting polymerization. J. Brazil. Chem. Soc. 2015, 26, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zeng, L.; Chen, X.; Hao, H. Detection of TNT by surface plasmon resonance based on molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Forensic Sci. Med. 2015, 1, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Stringer, R.C.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Grant, S.A. Detection of nitroaromatic explosives using a fluorescent-labeled imprinted polymer. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4015–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Dong, X.; Fidalgo de Cortalezzi, M. Molecularly imprinted polymers labeled with amino-functionalized carbon dots for fluorescent determination of 2, 4-dinitrotoluene. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancharoen, C.; Sukjee, W.; Yenchitsomanus, P.T.; Panya, A.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Sangma, C. Selectivity enhancement of MIP-composite sensor for explosive detection using DNT-dengue virus template: A co-imprinting approach. Mater. Lett. 2021, 285, 129201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegel, V.I.; Lopatynskyi, A.M.; Lytvyn, V.K.; Demydov, P.V.; Martínez-Pastor, J.P.; Abargues, R.; Gadea, E.; Piletsky, S.A. Localized surface plasmon resonance nanochips with molecularly imprinted polymer coating for explosives sensing. Semicond. Phys. Quant. 2020, 23, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Deng, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Hu, D.; Guo, L.; Li, L.; Wan, S.; et al. Highly sensitive determination of 4-nitrophenol with coumarin-based fluorescent molecularly imprinted poly (ionic liquid). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiripour, F.; Ghasemi, S.; Azizi, S.N. Förster resonance energy transfer-based molecularly imprinted polymer/amine-functionalized metal-organic framework nanocomposite for trace level detection of 4-nitrophenol. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1202, 339638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saloni, J.; Dasary, S.S.; Anjaneyulu, Y.; Yu, H.; Hill, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers for detection of explosives: Computational study on molecular interactions of 2, 6-dinitrotoluene and methacrylic acid complex. Struct. Chem. 2010, 21, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhong, C.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Y. Synthesis of D-A Type Triphenylamine Sulfone/Ketone FluorescentPolymers and Their Application in TNT Detection. J. Southwest Univ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 39, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Fang, H.; Wei, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; He, S. Detection of trinitrotoluene based on fluorescence quenching sensor technology. Chin. J. Quantum Electron. 2024, 41, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Mo, S.; Zhou, M.; Chang, G.; Xu, Y. Preparation and Properties of Novel Isoxazoline-based TNT Adsorbent. J. Southwest Univ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 38, 30–38+95. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Asher, S.A.; Meng, Z.; Yan, Z.; Xue, M.; Qiu, L.; Yi, D. Visual detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrotolune by molecularly imprinted colloidal array photonic crystal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 316, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Meng, X.; Xiao, Z. Synthesis of a surface molecular imprinting polymer based on silica and its application in the identification of nitrocellulose. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 9802–9811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Z. Preparation of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Surface Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Modified Electrode and its Application in Detection of Nitrocellulose. Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 2019, 44, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xiao, Z.; Scott, S.K. Preparation and Application of Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Coated Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Nitrocellulose Detection. Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 2019, 44, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Meng, Z.; Xue, M.; Qiu, L.; Dong, X.; Xu, Z.; He, X.; Liu, X.; Li, J. Simultaneous selective extraction of nitramine explosives using molecularly imprinted polymer hollow spheres from post blast samples. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamo, S.K.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J. Development of a molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensor for the electrochemical determination of triacetone triperoxide (TATP). Sensors 2014, 14, 23269–23282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saglam, S.; Uzer, A.; Apak, R. Direct determination of peroxide explosives on polycarbazole/gold nanoparticle-modified glassy carbon sensor electrodes imprinted for molecular recognition of TATP and HMTD. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 17662–17669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setayeshfar, I.; Najafi, M.; Asadi, S. Improved preconcentration workflow for organic explosive traces in aqueous samples using solvent-assisted dispersive solid-phase extraction. Forensic Sci. Int. 2024, 359, 112025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Butler, B.; Mirza, F.; Habib-Ullah, S.; Fei, D. Smart molecularly imprinted polymers: Recent developments and applications. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2013, 34, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağlam, Ş.; Üzer, A.; Tekdemir, Y.; Erçağ, E.; Apak, R. Electrochemical sensor for nitroaromatic type energetic materials using gold nanoparticles/poly (o-phenylenediamine–aniline) film modified glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 2015, 139, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordel-Madeleine, S.; Eudes, V.; Pichon, V. Identification of the nitroaromatic explosives in post-blast samples by online solid phase extraction using molecularly imprinted silica sorbent coupled with reversed-phase chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5237–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, A. Removal of 2, 4, 6-Trinitrotoluene from “Pink Water” Using Molecularly-Imprinted Absorbent. Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 2012, 37, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordel, S.; Chapuis-Hugon, F.; Eudes, V.; Pichon, V. Selective extraction of nitroaromatic explosives by using molecularly imprinted silica sorbents. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xue, M.; Meng, Z.H.; Xu, Z.B.; Luo, J. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers for the solid-phase extraction of hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane (cl-20) from soil samples. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 4413–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Meng, Z.H.; Xue, M.; Qiu, L.L.; Zhang, C.F. Separation of 1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetraazacyclooctane and 1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazacyclohexane by molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Tao, H.; Tao, H.; Shuai, Q.; Huang, L. Recent progress of covalent organic frameworks as attractive materials for solid-phase microextraction: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2024, 1287, 341953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, J.; Fan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, J.; Yang, X.; Zhu, F.; Ouyang, G. Molecularly imprinted polymer sheathed mesoporous silica tube as SPME fiber coating for determination of tobacco-specific nitrosamines in water. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagirani, M.S.; Soylak, M. Green sorbents for the solid phase extraction of trace species. Curr. Opin. Green Sust. 2024, 47, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.; Giannetto, M.; Mori, G.; D’Agostino, G.; Careri, M.; Mangia, A. Solid-phase microextraction of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene using a molecularly imprinted-based fiber. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2411–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Abedi, H.; Yamini, Y.; Adlnasab, L. Molecular-imprinted polymer extraction combined with dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extractionfor ultra-preconcentration of mononitrotoluene. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 3759–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, Y.; Rahimian, F.; Yousefinejad, S.; Aliasghari, F.; Soleimani, E. Microextraction techniques for occupational biological monitoring: Basic principles, current applications and future perspectives. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2024, 38, e5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, L.A.; Tobiszewski, M.; Kubica, P.; Koronkiewicz, S.; Vakh, C. Polymeric porous membranes as solid support and protective material in microextraction processes: A review. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2024, 173, 117651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, B.K.; Uysal, S.; Uzun, L. Greener approaches/materials for forensic sciences. Essent. Chem. 2025, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Xue, M.; Xu, Z.; Dong, X.; Xue, F.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Meng, Z. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the sensing of explosives and chemical warfare agents. Curr. Org. Chem. 2015, 19, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedborg, E.; Winquist, F.; Lundström, I.; Andersson, L.I.; Mosbach, K. Some studies of molecularly-imprinted polymer membranes in combination with field-effect devices. Sensor. Actuat. A-Phys. 1993, 37, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, X.; Chen, W. Recent advances in electrochemical sensors for the detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 17, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibl, N.; Duma, L.; Gonzato, C.; Haupt, K. Polydopamine-based molecularly imprinted thin films for electro-chemical sensing of nitro-explosives in aqueous solutions. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 135, 107541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağlam, S.; Üzer, A.; Erçağ, E.; Apak, R. Electrochemical determination of TNT, DNT, RDX, and HMX with gold nanoparticles/poly (carbazole-aniline) film–modified glassy carbon sensor electrodes imprinted for molecular recognition of nitroaromatics and nitramines. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7364–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdost-fard, F.; Roushani, M. Impedimetric detection of trinitrotoluene by using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a gold nanoparticle@ fullerene composite and an aptamer-imprinted polydopamine. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3997–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.P.; Sosnowska, M.; Sobczak, J.W.; Kc, C.B.; Nesterov, V.N.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Simultaneous chronoamperometry and piezoelectric microgravimetry determination of nitroaromatic explosives using molecularly imprinted thiophene polymers. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 8361–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riskin, M.; Tel-Vered, R.; Bourenko, T.; Granot, E.; Willner, I. Imprinting of molecular recognition sites through electropolymerization of functionalized Au nanoparticles: Development of an electrochemical TNT sensor based on π-donor−acceptor interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9726–9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trammell, S.A.; Melde, B.J.; Zabetakis, D.; Deschamps, J.R.; Dinderman, M.A.; Johnson, B.J.; Kusterbeck, A.W. Electrochemical detection of TNT with in-line pre-concentration using imprinted diethylbenzene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilicas. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2011, 155, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Hou, A.G.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, Z.F. Electrochemical sensor prepared from molecularly imprinted polymer for recognition of TNT. Polym. Composite. 2015, 36, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, F.B.; Beduk, T.; Sena-Torralba, A.; Beduk, D.; Lahcen, A.A.; Kutner, W.; Kaushik, A. Beyond Single-Analyte Detection: Advancing Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Simultaneous Multi-Target Sensing. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2025, 185, 118177. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, T.; Choudhury, D.R.; Ghosh, D.; Saha, C. Advancements in optical sensors for explosive materials Identification: A comprehensive review. Res. Chem. 2024, 8, 101602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ding, L.; Xie, S.; Liu, P.; Xie, D.; Wang, S.; Cheng, F. Molecularly imprinted polymer photoelectrochemical sensor for the detection of triazophos in water based on carbon quantum dot-modified titanium dioxide. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holthoff, E.L.; Stratis-Cullum, D.N.; Hankus, M.E. Xerogel-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Explosives Detection; SPIE: Orlando, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cennamo, N.; Donà, A.; Pallavicini, P.; D’Agostino, G.; Dacarro, G.; Zeni, L.; Pesavento, M. Sensitive detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene by tridimensional monitoring of molecularly imprinted polymer with optical fiber and five-branched gold nanostars. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2015, 208, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Giustina, G.; Sonato, A.; Gazzola, E.; Ruffato, G.; Brusa, S.; Romanato, F. SPR Enhanced molecular imprinted sol–gel film: A promising tool for gas-phase TNT detection. Mater. Lett. 2016, 162, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.R.; Linman, M.J.; Timmers, M.M.; Dean, S.L.; Burkett, C.M.; Lloyd, J.A.; Keelor, J.D.; Baughman, B.M.; Edmiston, P.L. Selective detection of gas-phase TNT by integrated optical waveguide spectrometry using molecularly imprinted sol–gel sensing films. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 593, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lu, H. Ratiometric fluorescence and mesoporous structure dual signal amplification for sensitive and selective detection of TNT based on MIP@ QD fluorescence sensors. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3200–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lu, H. Mesoporous structured MIPs@ CDs fluorescence sensor for highly sensitive detection of TNT. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.P.; Wojnarowicz, A.; Kelm, A.; Woznicki, P.; Borowicz, P.; Majka, A.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Chemosensor for selective determination of 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol using a custom designed imprinted polymer recognition unit cross-linked to a fluorophore transducer. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, H.; Bunes, B.R.; Wu, N.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Zang, L. Trace detection of RDX, HMX and PETN explosives using a fluorescence spot sensor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Yang, Y.Y.; Han, S. Surface molecular imprinting technology integrated SERS sensing: Emerging trends and future perspectives toward on-site hazardous analysis. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2024, 179, 117866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Meng, Z.; Dong, X.; Xue, M.; Qiu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhong, F.; He, X. Colorimetric screening of nitramine explosives by molecularly imprinted photonic crystal array. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apodaca, D.C.; Pernites, R.B.; Del Mundo, F.R.; Advincula, R.C. Detection of 2, 4-dinitrotoluene (DNT) as a model system for nitroaromatic compounds via molecularly imprinted short-alkyl-chain SAMs. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6768–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinia, A.M.; Sheikholeslami, M. Development of a new solar system integrating photovoltaic and thermoelectric modules with paraffin-based nanomaterials. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Wang, A.; Liu, J.; Khan, I.; Sadiq, S.; Khan, A.; Yaseen, W.; Zaman, S.; Mueed, A.; Miao, Y. Designing MOF-based green nanomaterials for enhanced pathogen resistance and pesticide degradation in tomato plants. Environ. Sci-Nano 2025, 12, 1186–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar-Gadea, E.; Sanchez-Alarcon, I.; Soosaimanickam, A.; Rodriguez-Canto, P.J.; Perez-Pla, F.; Martínez-Pastor, J.P.; Abargues, R. Molecularly imprinted nanocomposites of CsPbBr 3 nanocrystals: An approach towards fast and selective gas sensing of explosive taggants. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 1754–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegłowski, M.; Lusina, A.; Nazim, T.; Otłowski, T.; Gierczyk, B.; Hoogenboom, R. Enhanced detection of explosives: A novel approach using poly (2-oxazoline) s-based molecularly imprinted polymers combined with ambient mass spectrometry. Eur. Polym. J. 2025, 224, 113704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgal, D.; Singh, R.P.; Bharti, T.; Dwivedi, P.; Yadav, N.; Mishra, V. Synergistic catalytic activity of copper doped magnetic carbon aerogel in click chemistry for synthesizing 1, 2, 3-triazole glycoconjugate derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1327, 141102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anumandla, R.; Shanigaram, P.; Samineni, R.; Varukolu, M.; Kokku, P.; Challapalli, S.; Veldurthi, S. Synthesis of highly stable nitrogen doped carbon encapsulated nano Cu2O pom discs (NCENCu2O pom discs) and its click chemistry. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1321, 139798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Malah, T.; El-Bayaa, M.N.; Abdelrahman, M.T.; Awad, H.M.; Soliman, H.A. Synthesis of Some 1, 2, 3-triazole-bridged glycosides with benzoquniline-3-carbonitriles via click chemistry for anticancer, and docking evaluation. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1321, 139681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorakkattu, P.; Awasti, N.; Sajith Babu, K.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Deliephan, A.; Shah, K.; Singh, P.; Pandiselvam, R.; Nirmal, N.P. 3D printing: Trends and approaches toward achieving long-term sustainability in the food industry. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2025, 45, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, D.; Li, Z.; Chen, B. Rheology control of cement paste by in-situ polymerization for 3D printing applications. Cem. Concr. Res. 2025, 187, 107731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Yin, X. Advances in 3D printing combined with tissue engineering for nerve regeneration and repair. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Target | Functional Monomer | Cross-Linking Agent | Porogen | Initiator | Initiation Method | Temperature | Preparation Method | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNT | MAA | Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate (EGDMA) | Chloroform | -- | Thermal Initiation | 50 °C | In situ Polymerization | [34] |
| TNT | Acrylate | EGDMA | Acetonitrile | UV-Starter Irgacure 369 | UV Initiation | Room Temperature | In situ Polymerization | [42] |
| TNT | MAA | EGDMA | Chloroform | -- | Thermal Initiation | 70 °C | Surface Molecular Imprinting Method | [43] |
| TNT | MAA | EGDMA | Acetonitrile | Potassium Persulfate | Thermal Initiation | 50 °C | Emulsion Polymerization | [44] |
| TNT | MAA | EGDMA | Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) | AIBN | -- | -- | Precipitation Polymerization | [45] |
| TNT | APTES | TEOS | Acetonitrile | -- | -- | Room Temperature | Surface Molecular Imprinting Method | [46] |
| TNT | MAA | EGDMA | Acetonitrile | AIBN | Thermal Initiation | 60 °C | Surface Molecular Imprinting Method | [47] |
| TNT | AA | EGDMA | Acetonitrile | AIBN | Thermal Initiation | 60 °C | Surface Molecular Imprinting Method | [48] |
| TNT | MAA | -- | Acetonitrile (ACN), DMSO, Water, and Binary Mixtures of ACN and DMSO with Different Molar Ratios | -- | -- | 25 °C | -- | [49] |
| TNT | 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) | Tetraethyl Orthosilicate (TEOS) | Acetonitrile | -- | -- | -- | Emulsion Polymerization | [24] |
| TNT | MAA | EGDMA | Acetonitrile | AIBN | Thermal Initiation | 60 °C | Precipitation Polymerization | [50] |
| TNT | MAA | EGDMA | ACN and DMSO | AIBN | Thermal Initiation | 65 °C | In situ Polymerization | [51] |
| TNT/DNT | MAA | EGDMA/EGDA | Chloroform | AIBN or 4,4′-Azobis(4-cyanovaleric Acid) (ACVA) | Thermal Initiation | 50 °C | Precipitation Polymerization | [22] |
| TNT/DNT | AAM | EGDMA | ACN | ABVN | UV Initiation | 4 °C | Precipitation Polymerization | [21] |
| TNT/DNT | MAA | EGDMA | Chloroform | 1-Hydroxycyclohexylphenyl Ketone (Photoinitiator) | UV Initiation | -- | Solution Polymerization | [52] |
| DNT | AA and MA | EGDMA | Methanol | AIBN | UV Initiation | Room Temperature | In situ Polymerization | [53] |
| DNT | MAA/NVP/MMA/AAM | N,N′-(1,2-Dihydroxyethylene)bisacrylamide (DHEBA) | DMSO | AIBN | UV Initiation | 65 °C | Template-Virus Coimprinting Method | [54] |
| 4-NP | AAM | -- | -- | -- | UV Initiation | 4 °C | Bulk Polymerization | [55] |
| 4-NP | Coumarin-Based Alkenyl Fluorescent Ionic Liquid (Coumarin-FL-IL) | EGDMA | Methanol and ACN | -- | -- | -- | Precipitation Polymerization | [56] |
| 4-NP | MAA | EGDMA | Methanol | AIBN | -- | -- | Surface Molecular Imprinting Method | [57] |
| Target | Functional Monomer | Cross-Linking Agent | Porogen | Initiator | Initiation Method | Temperature | Preparation Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | MAA | EGDMA | Acetone | AIBN | Thermal Initiation | 50 °C | In situ Polymerization | [63] |
| NC | MAA | EGDMA | Acetone | AIBN | Thermal Initiation | 45 °C | Surface Molecular Imprinting Method | [64] |
| NC | MAA | EGDMA | Acetone | AIBN | Thermal Initiation | 55 °C | Surface Molecular Imprinting Method | [65] |
| Target | Functional Monomer | Cross-Linking Agent | Porogen | Initiator | Initiation Method | Temperature | Preparation Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMX and RDX | MAA/AAM | AIBN | Acetonitrile | AIBN | UV Initiation | 4 °C | Precipitation Polymerization | [40] |
| CL-20 | AAM | EGDMA | Acetonitrile | AIBN | Thermal Initiation | 60 °C | Precipitation Polymerization | [40] |
| CL-20 | AAM | EGDMA | Acetonitrile | -- | UV Initiation | 4 °C | Sacrificial Template Method | [66] |
| Target | Functional Monomer | Cross-Linking Agent | Porogen | Initiator | Initiation Method | Temperature | Preparation Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TATP | Pyrrole | -- | Acetonitrile | -- | -- | -- | Electropolymerization (LiClO4) | [67] |
| TATP/HMTD | Carbazole (Cz) | -- | Acetonitrile | -- | -- | -- | Electropolymerization (TEAP) | [68] |
| Target | LOD | Linear Range | Electrochemical Analysis Technique | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNT | 4.4 × 10−17 mol/L | 4.4 × 10−15–4.4 × 10−8 mol/L | Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV) | [31] |
| TNT | 5 × 10−11 mol/L | 5 × 10−11–1.6 × 10−8 mol/L | Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) | [88] |
| TNT/DNT | 1.1 × 10−7 mol/L/ 1.65 × 10−7 mol/L | 4.4 × 10−7–4.4 × 10−6 mol/L/ 5.49 × 10−7–5.49 × 10−6 mol/L | Square Wave Voltammetry (SWV) | [89] |
| TNT | 3.5 × 10−8 mol/L | 1 × 10−17–1.5 × 10−6 mol/L | CV | [90] |
| DNT | 4.4 × 10−12 mol/L | -- | CV | [54] |
| TNT | 1.32 × 10−12 mol/L | -- | CV | [54] |
| TNT | 5 × 10−10 mol/L | 1 × 10−9–1.3 × 10−7 mol/L | SWV | [47] |
| TNT | 6.2 × 10−4 mol/L/ 7 × 10−5 mol/L | 7 × 10−4–5.6 × 10−3 mol/L | Chronoamperometry (CA) Piezoelectric Microgravimetry (PM) | [91] |
| TNT | 2 × 10−10 mol/L | -- | LSV | [92] |
| TNT | 5.73 × 10−8 mol/L 2.2 × 10−9 mol/L | 8.81 × 10−8–2.20 × 10−6 mol/L 2.20 × 10−9–2.20 × 10−6 mol/L | SWV | [93] |
| PETN | 4.43 × 10−12 mol/L | -- | CV | [54] |
| NC | 3.45 × 10−10 g/L | 0–7 × 10−5 g/L | CV and Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) | [65] |
| RDX | 1 × 10−10 mol/L | 1 × 10−10–1.1 × 10−8 mol/L | CV | [89] |
| RDX/HMX | 4.5 × 10−8 mol/L/ 3.4 × 10−8 mol/L | 2.25 × 10−7–4.5 × 10−6 mol/L/ 1.69 × 10−7–3.38 × 10−6 mol/L | SWV | [90] |
| TATP | 1.2 × 10−7 mol/L | 3.69 × 10−7–2.0 × 10−4 mol/L | CV | [67] |
| TATP | 6.75 × 10−8 mol/L | 4.5 × 10−7–4.5 × 10−6 mol/L | CV and DPV | [68] |
| HMTD | 8.61 × 10−8 mol/L | 5.74 × 10−7–5.74 × 10−6 mol/L | CV and DPV | [68] |
| Target | LOD | Linear Range | Analysis Time | Sensor | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNT | 3 × 10−6 mol/L | -- | -- | Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) | [98] |
| TNT | 3.0 × 10−11 mol/L | 8.8 × 10−11–2.2 × 10−7 mol/L and 2.2 × 10−7–8.8 × 10−7 mol/L | -- | Chemiluminescence (CL) | [46] |
| TNT | 1 × 10−8 mol/L | 1 × 10−8–1 × 10−5 mol/L | -- | Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) | [48] |
| TNT | 4.1 × 10−7 mol/L | -- | -- | Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR) | [99] |
| TNT | 1.15 × 10−12 mol/L | -- | -- | SPR | [100] |
| TNT | 1.03 × 10−6 g | 3 × 10−4–3 × 10−2 mol/L | 120 s | Photonic Crystal (PhC) | [62] |
| TNT | 4.40 × 10−7 mol/L | 2.20 × 10−6–2.20 × 10−4 mol/L | -- | IMS | [21] |
| TNT | Chloroform-based: 1 × 10−7 mol/L Water-based: 1 × 10−4 mol/L | -- | 60 s | Fluorescence | [22] |
| TNT | 4.07 × 10−5 mol/L | 0–5 × 10−4 mol/L | 60 s | Fluorescence | [52] |
| TNT | 3.74 × 10−11 mol/L | 1.76 × 10−11–4.40 × 10−11 mol/L | 100 s | Optical Waveguide Spectroscopy (OWS) | [101] |
| TNT | 2.8 × 10−7 mol/L | 8 × 10−7–3 × 10−5 mol/L | -- | Fluorescence | [24] |
| TNT | 1.5 × 10−8 mol/L | 5 × 10−8–6 × 10−7 mol/L | -- | Fluorescence | [102] |
| TNT | 1.7 × 10−8 mol/L | 5 × 10−4–2 × 10−2 mol/L | -- | Fluorescence | [103] |
| TNT | 1 × 10−10 mol/L | 1 × 10−15–1 × 10−7 mol/L | -- | SPR | [51] |
| DNT | 3.01 × 10−5 mol/L | 0–5 × 10−4 mol/L | 600 s | Fluorescence | [52] |
| DNT | Chloroform-based: 1 × 10−5 mol/L Water-based: 2 × 10−5 mol/L | -- | 300 s | Fluorescence | [22] |
| DNT | 2.75 × 10−7 mol/L | 5.49 × 10−7–5.49 × 10−5 mol/L | -- | IMS | [21] |
| TNP | 8.73 × 10−13 mol/L | 8.73 × 10−13–8.91 × 10−11 mol/L | -- | Fluorescence | [104] |
| DNT | 1.54 × 10−6 mol/L | 5.49 × 10−6–8.24 × 10−5 mol/L | 1800 s | Fluorescence | [53] |
| 4-NP | 5 × 10−10 mol/L | 1 × 10−9–7.5 × 10−6 mol/L | 60 s | Fluorescence | [56] |
| 4-NP | 9 × 10−9 mol/L | 5 × 10−8–5 × 10−5 mol/L | -- | Fluorescence | [57] |
| RDX | 2 × 10−10 g | -- | 20 s | Fluorescence | [105] |
| HMX | 3 × 10−10 g | -- | 20 s | Fluorescence | [105] |
| PETN | 3 × 10−10–3 × 10−9 g | -- | 20 s | Fluorescence | [105] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, C.; Feng, L.; Deng, X.; Li, Y.; Mei, H.; Guo, H.; Zhu, J.; Hu, C. Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in the Analysis of Explosives. Polymers 2025, 17, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101410
Wei C, Feng L, Deng X, Li Y, Mei H, Guo H, Zhu J, Hu C. Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in the Analysis of Explosives. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101410
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Chenjie, Lin Feng, Xianhe Deng, Yajun Li, Hongcheng Mei, Hongling Guo, Jun Zhu, and Can Hu. 2025. "Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in the Analysis of Explosives" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101410
APA StyleWei, C., Feng, L., Deng, X., Li, Y., Mei, H., Guo, H., Zhu, J., & Hu, C. (2025). Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in the Analysis of Explosives. Polymers, 17(10), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101410






