Block and Statistical Copolymers of Methacrylate Monomers with Dimethylamino and Diisopropylamino Groups on the Side Chains: Synthesis, Chemical Modification and Self-Assembly in Aqueous Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization Methods
2.2.1. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
2.2.2. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H-NMR)
2.2.3. Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR)
2.2.4. Fluorescence Spectroscopy (FS)
2.2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.2.6. Electrophoretic Light Scattering (ELS)
2.3. Polymer Synthesis via RAFT Polymerization
2.3.1. Synthesis of PDMAEMA Homopolymer
2.3.2. Synthesis of PDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA Copolymers
2.3.3. Synthesis of P(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) Copolymers
2.4. Synthesis of Chemically Modified Copolymers
2.4.1. Synthesis of QPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA and QP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA)
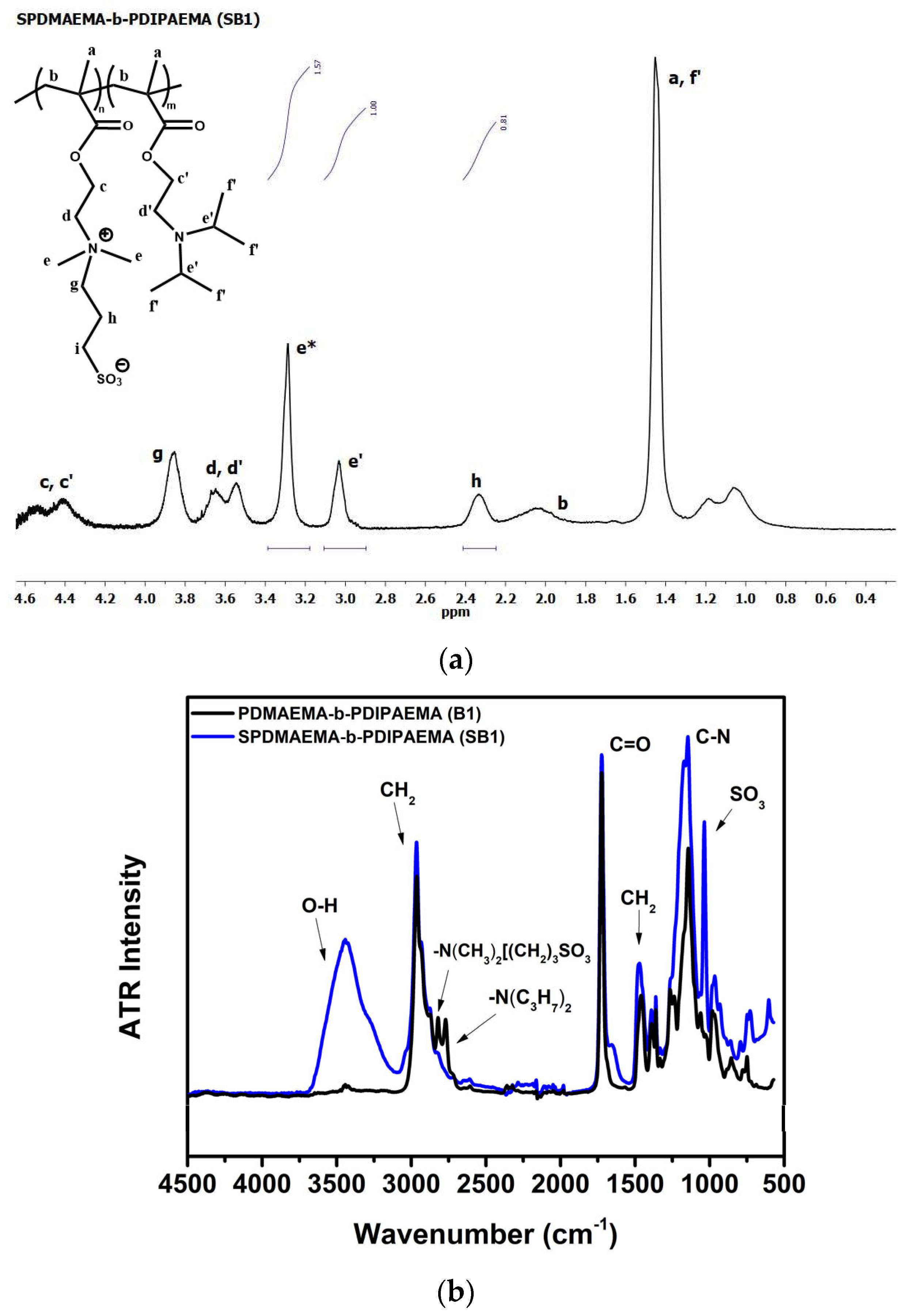
2.4.2. Synthesis of SPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA and SP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA)
2.5. Self-Assembly of Block, Random Precursors and Chemically Modified Copolymers in Aqueous Media
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Molecular Characterization of Block and Random Copolymers
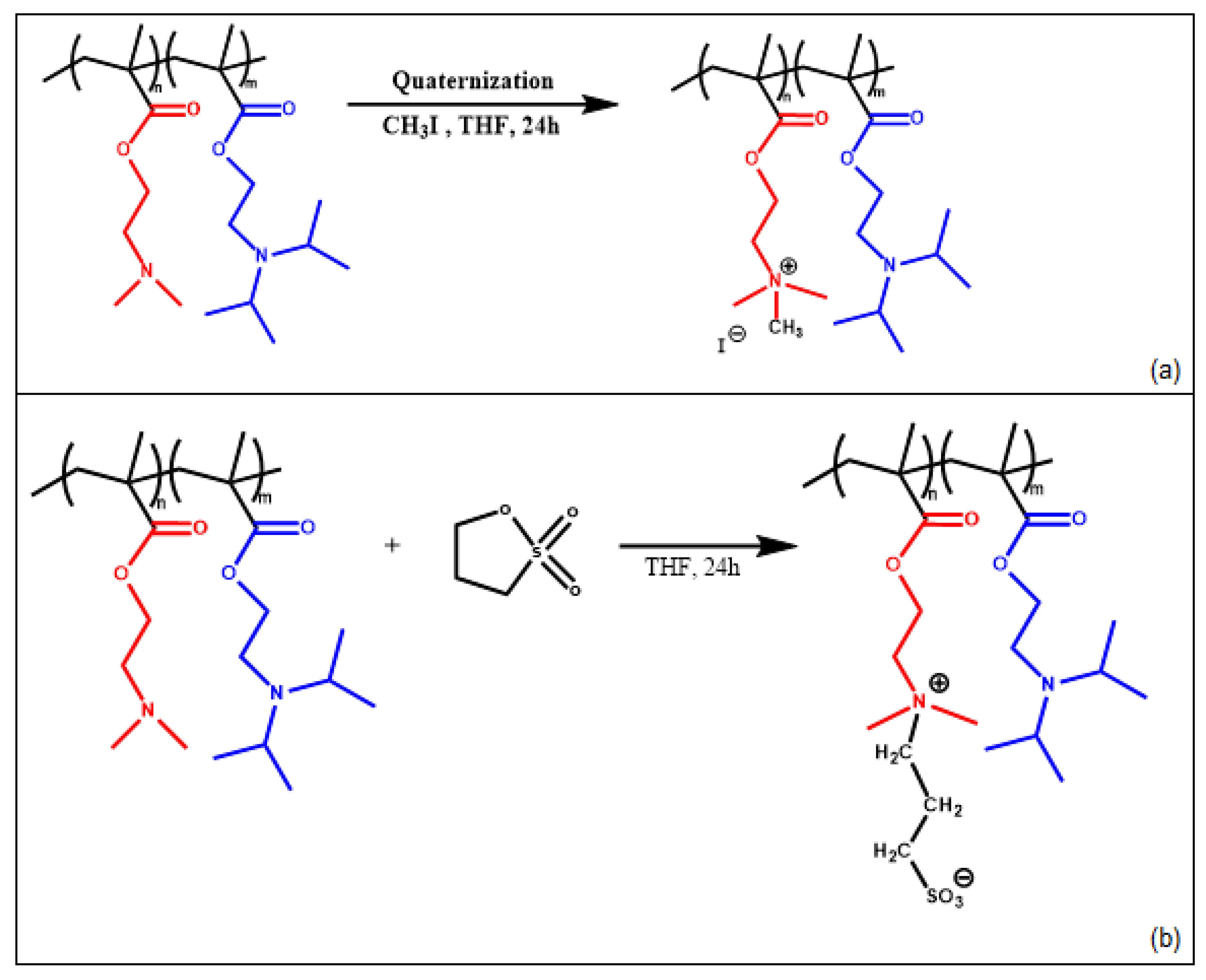
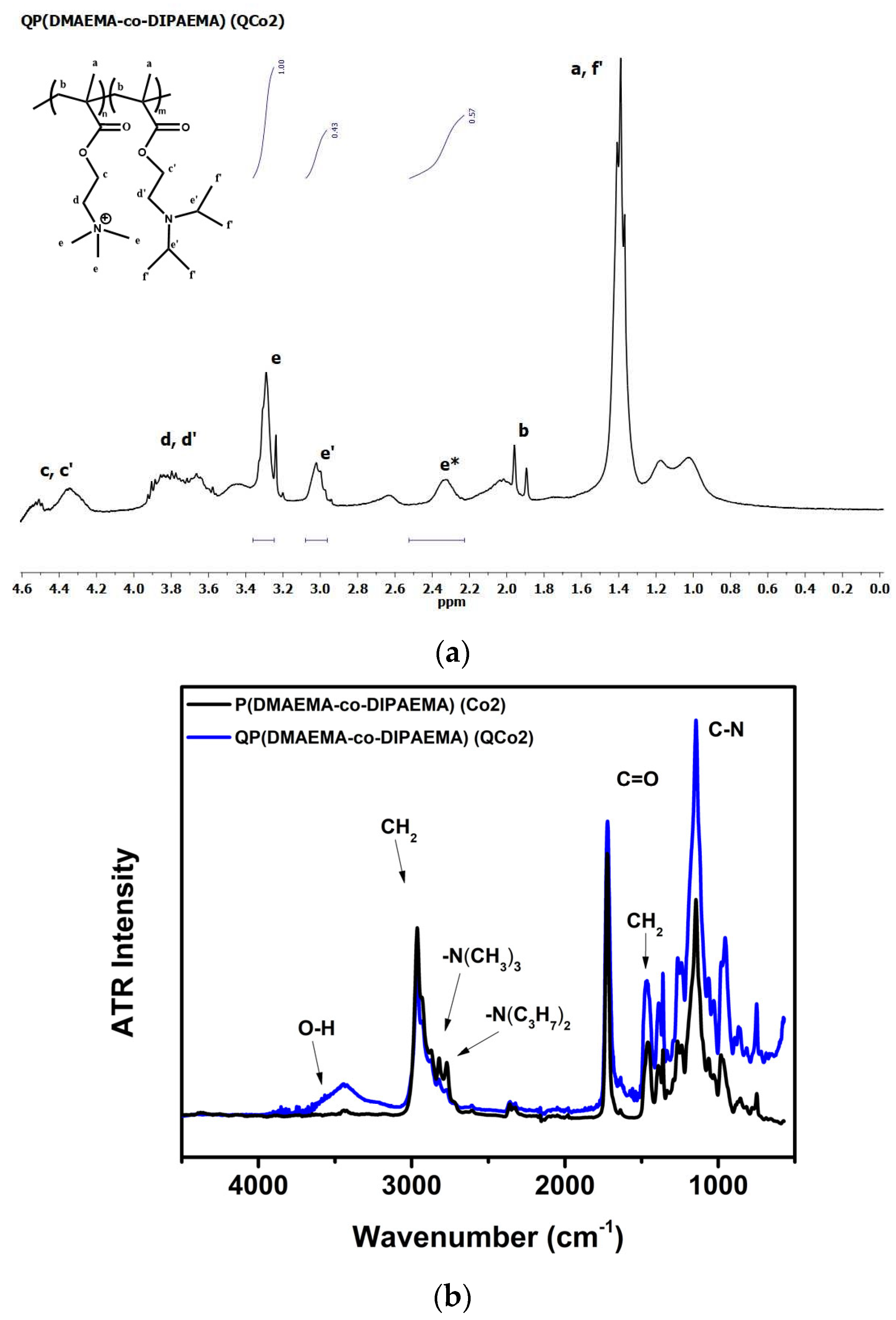
3.2. Synthesis and Molecular Characterization of Chemically Modified Copolymers
3.3. Determination of CMC/CAC of Block and Random Copolymers
3.4. pH Responsiveness of Block and Random Copolymers
3.5. Thermo-Responsiveness of Block and Random Copolymers
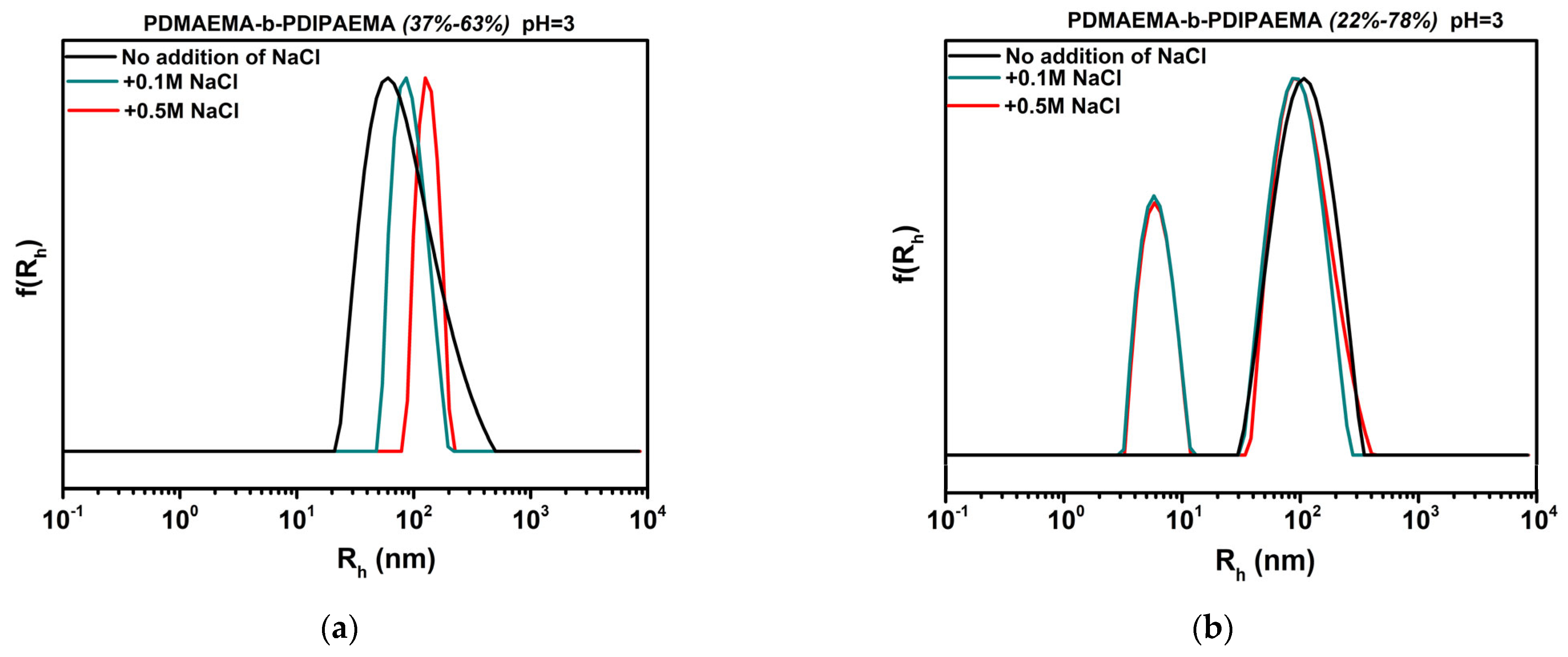
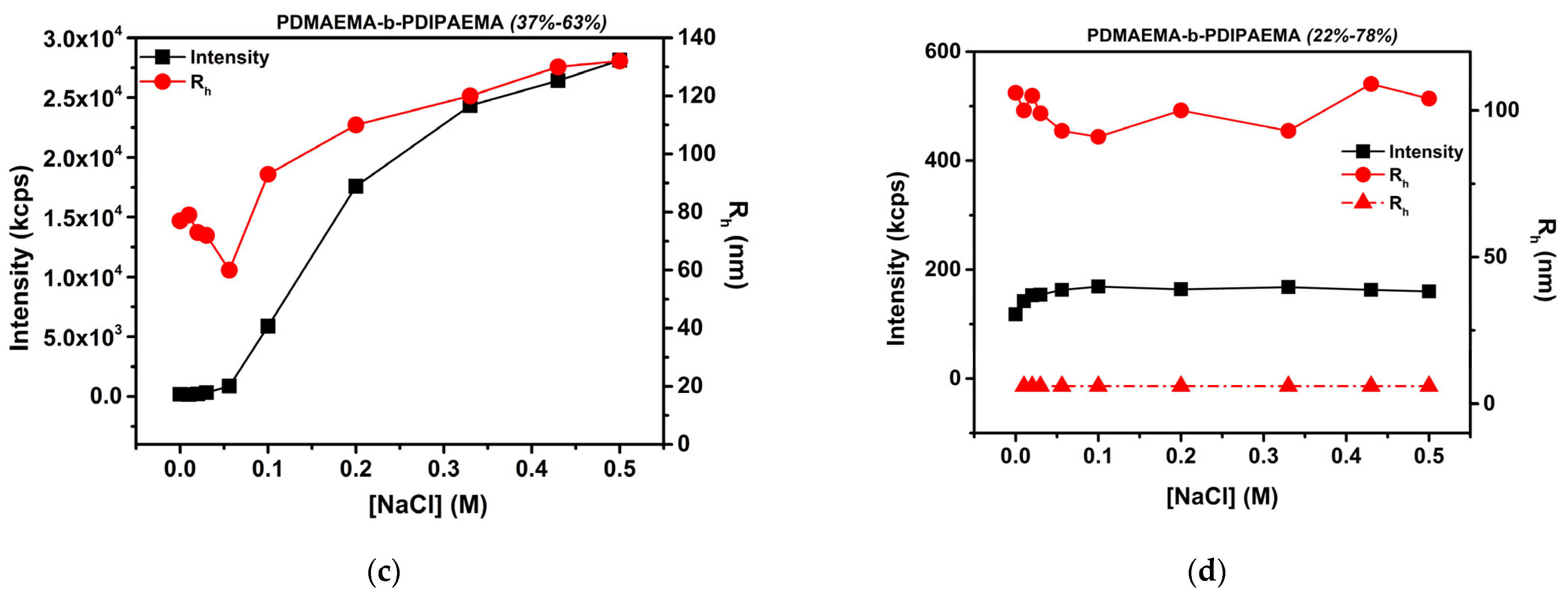
3.6. Effect of Solution Ionic Strength
3.7. Determination of CMC/CAC of Chemically Modified Copolymers
3.8. pH Responsiveness of Chemically Modified Copolymers
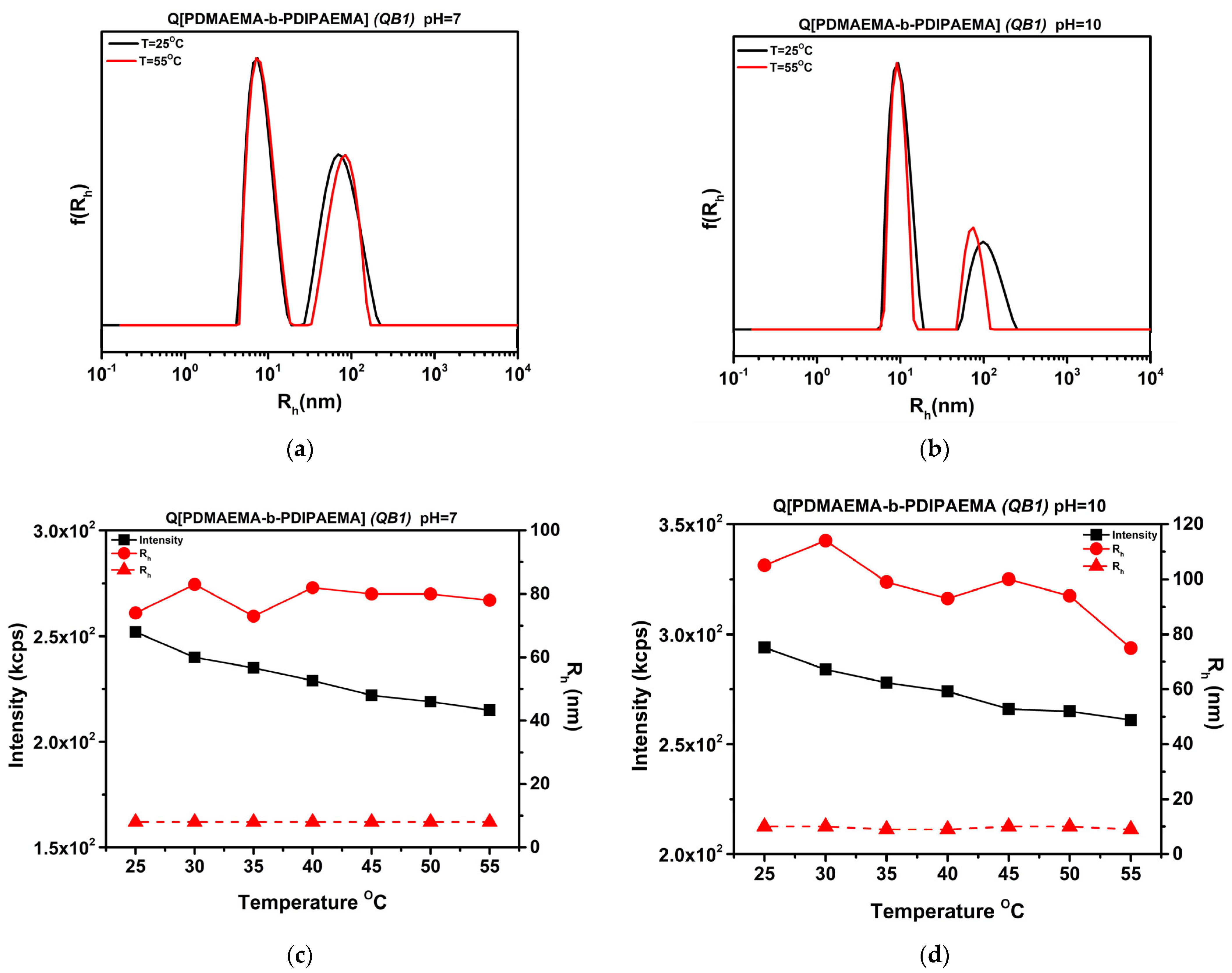
3.9. Thermo-Responsiveness of Chemically Modified Copolymers
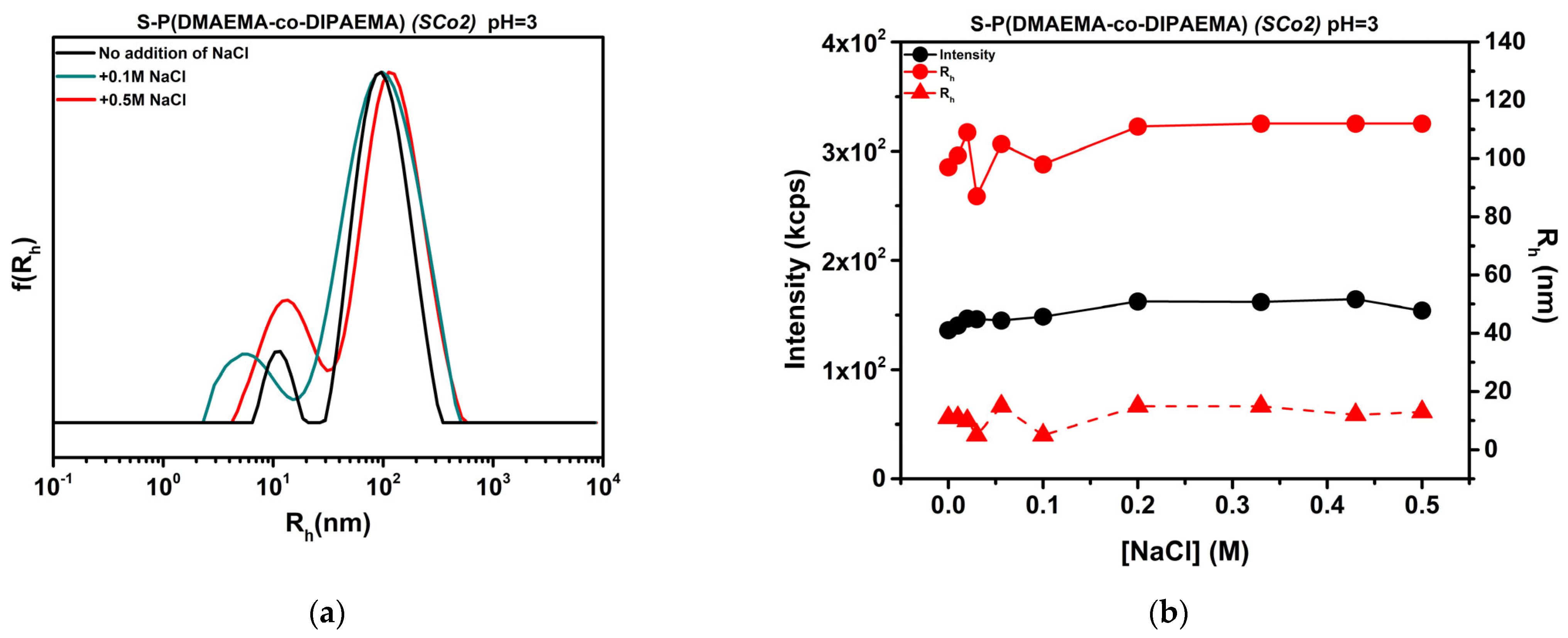
3.10. Effect of Ionic Strength on Chemically Modified Copolymers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perrier, S. 50th Anniversary Perspective: RAFT Polymerization—A User Guide. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7433–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, C.; Bulmus, V.; Davis, T.P.; Ladmiral, V.; Liu, J.; Perrier, S. Bioapplications of RAFT Polymerization. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 5402–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moad, G. RAFT Polymerization to Form Stimuli-Responsive Polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 177–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moad, G.; Rizzardo, E.; Thang, S.H. Radical Addition–Fragmentation Chemistry in Polymer Synthesis. Polymer 2008, 49, 1079–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barner-Kowollik, C.; Davis, T.P.; Heuts, J.P.A.; Stenzel, M.H.; Vana, P.; Whittaker, M.R. RAFTing down Under: Tales of Missing Radicals, Fancy Architectures, and Mysterious Holes. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2003, 41, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, C.L.; Lowe, A.J. Aqueous RAFT Polymerization: Recent Developments in Synthesis of Functional Water-Soluble (Co)Polymers with Controlled Structures. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Tan, Y.B.; Du, X. Preparation and Self-Assembly Behavior of Polystyrene-Block-Poly (Dimethylaminoethyl Methacrylate) Amphiphilic Block Copolymer Using Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Express Polym. Lett. 2008, 2, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Renker, S.; Simon, P.F.W.; Gutmann, J.S.; Jain, A.; Gruner, S.M.; Fetters, L.J.; Coates, G.W.; Wiesner, U. Synthesis and Characterization of Amphiphilic Poly(Ethylene Oxide)-Block-Poly(Hexyl Methacrylate) Copolymers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2003, 204, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsilianis, C.; Gotzamanis, G.; Iatridi, Z. Design of “Smart” Segmented Polymers by Incorporating Random Copolymers as Building Blocks. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Raghupathi, K.; Song, C.; Prasad, P.; Thayumanavan, S. Self-Assembly of Random Copolymers. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13417–13432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R. The Dawning Era of Polymer Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmaljohann, D. Thermo- and pH-responsive polymers in drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seuring, J.; Agarwal, S. Polymers with Upper Critical Solution Temperature in Aqueous Solution. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1898–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Bizmark, N.; Christie, K.S.S.; Datta, S.S.; Ren, Z.J.; Priestley, R.D. Thermoresponsive Polymers for Water Treatment and Collection. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 1894–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, G.; Tuncer, C.; Bütün, V. PH-Responsive Polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cremer, P. Interactions between Macromolecules and Ions: The Hofmeister Series. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrysostomou, V.; Pispas, S. Stimuli-Responsive Amphiphilic PDMAEMA-B -PLMA Copolymers and Their Cationic and Zwitterionic Analogs. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017, 56, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, Y.; Dai, G. Advances in Amphiphilic Hyperbranched Copolymers with an Aliphatic Hyperbranched 2,2-Bis(Methylol)Propionic Acid-Based Polyester Core. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selianitis, D.; Pispas, S. PDEGMA-B-PDIPAEMA Copolymers via RAFT Polymerization and Their PH and Thermoresponsive Schizophrenic Self-Assembly in Aqueous Media. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 1867–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentoukas, T.; Pispas, S. Poly(Dimethylaminoethyl Methacrylate)-B -Poly(Hydroxypropyl Methacrylate) Copolymers: Synthesis and PH/Thermo-Responsive Behavior in Aqueous Solutions. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2018, 56, 1962–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.Q.; Zhang, P.Y. Synthesis of Copper Complexes of Poly [2-(Dimethylamino Ethyl Methacrylate)-B-Poly (Oligo (Ethylene Glycol) Monomethylether Methacrylate-B-Poly [2-(Dimethylamino Ethyl Methacrylate). Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 668, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, L.; Karjalainen, E.; Aseyev, V.; Tenhu, H. Phase Separation of Aqueous Poly(Diisopropylaminoethyl Methacrylate) upon Heating. Langmuir 2021, 38, 5135–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaouzi, D.; Pispas, S. Synthesis and Self-Assembly of Thermoresponsive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-b-Poly(Oligo Ethylene Glycol Methyl Ether Acrylate) Double Hydrophilic Block Copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2019, 57, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billingham, N.; Armes, S.; Butun, V. Selective Quaternisation of 2-(Dimethylamino)Ethyl Methacrylate Residues in Tertiary Amine Methacrylate Diblock Copolymers. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bütün, V. Selective Betainization of 2-(Dimethylamino)Ethyl Methacrylate Residues in Tertiary Amine Methacrylate Diblock Copolymers and Their Aqueous Solution Properties. Polymer 2003, 44, 7321–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colthup, N.B.; Daly, L.H.; Wiberley, S.E. Introduction to Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Available online: https://shop.elsevier.com/books/introduction-to-infrared-and-raman-spectroscopy/colthup/978-0-08-091740-5 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Koromilas, N.D.; Lainioti, G.C.; Oikonomou, E.K.; Bokias, G.; Kallitsis, J.K. Synthesis and Self-Association in Dilute Aqueous Solution of Hydrophobically Modified Polycations and Polyampholytes Based on 4-Vinylbenzyl Chloride. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 54, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodfield, P.; Zhu, Y.-C.; Pei, Y.; Roth, P.M. Hydrophobically Modified Sulfobetaine Copolymers with Tunable Aqueous UCST through Postpolymerization Modification of Poly(Pentafluorophenyl Acrylate). Macromolecules 2014, 47, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, Y.; Terashima, T.; Takenaka, M.; Sawamoto, M. Precision Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Random Copolymers into Uniform and Self-Sorting Nanocompartments in Water. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 5084–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Seymour, B.T.; Lewoczko, E.M.; Kent, E.W.; Chen, M.-L.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhao, B. Zwitterionic Poly(Sulfobetaine Methacrylate)S in Water: From Upper Critical Solution Temperature (UCST) to Lower Critical Solution Temperature (LCST) with Increasing Length of One Alkyl Substituent on the Nitrogen Atom. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 5257–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

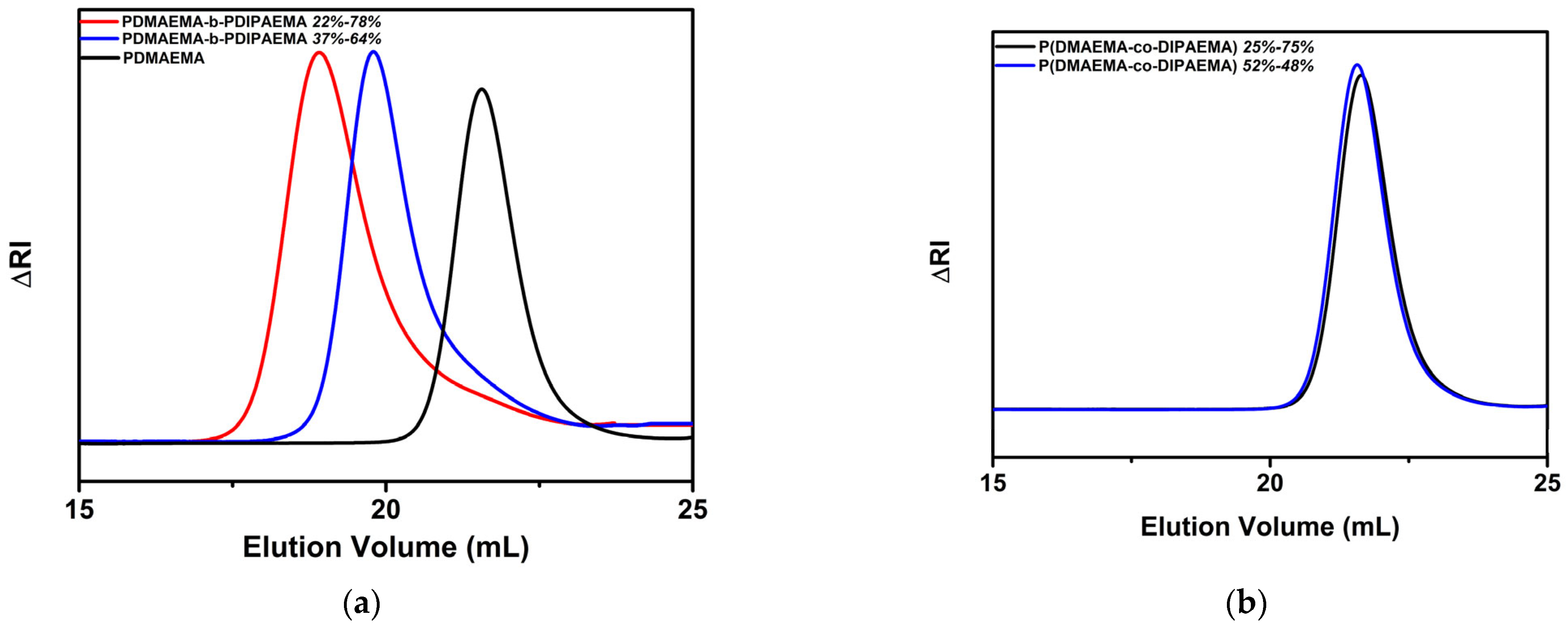
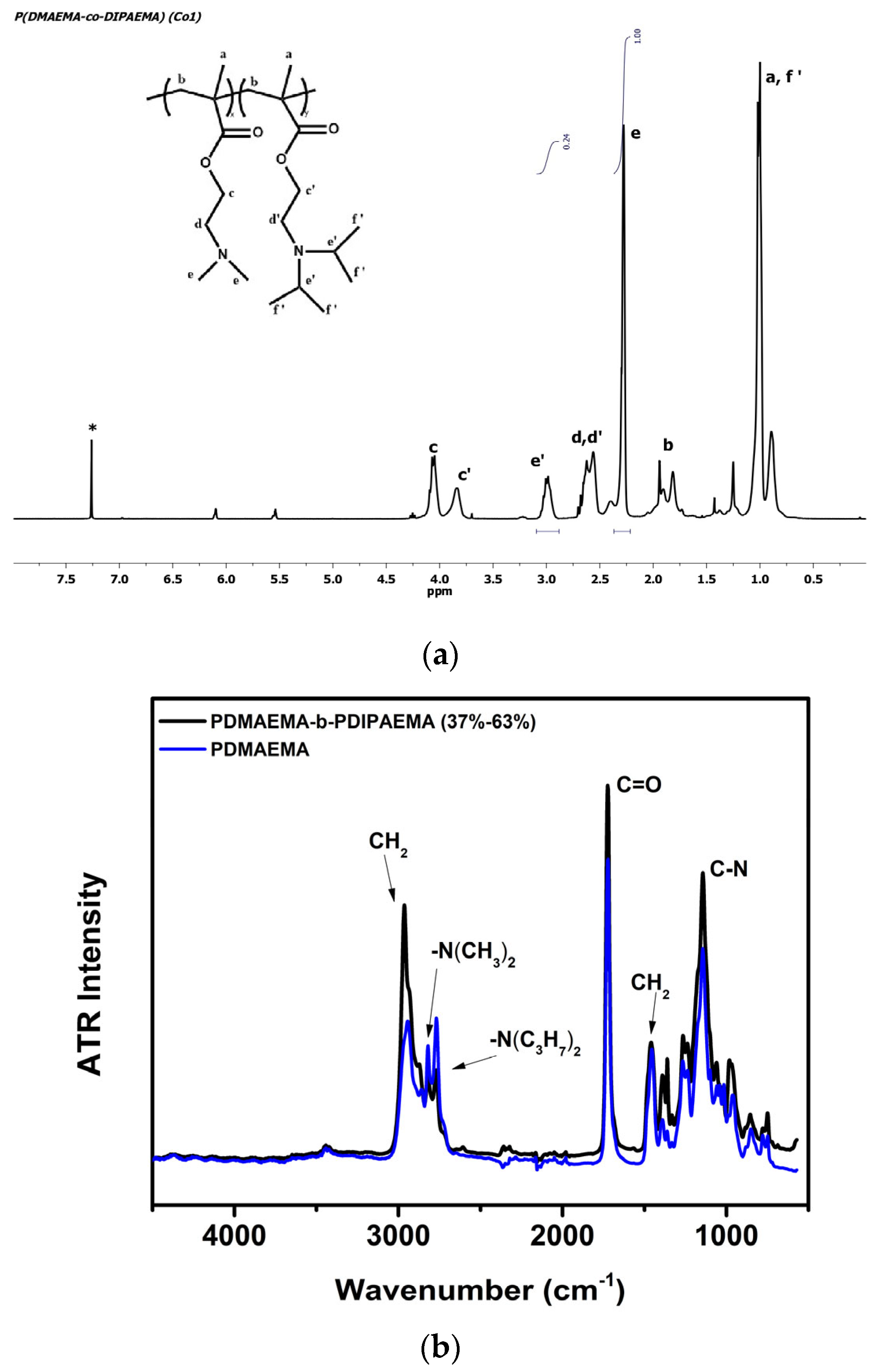






| Copolymer | Mw (×103 g/mol) 1 | Mw/Mn 1 | wt% PDMAEMA 2 (mole%) | wt% PDIPAEMA 2 (mole%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (B1) | 16 | 1.22 | 37 (43) | 63 (57) |
| PDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (B2) | 30.5 | 1.21 | 22 (28) | 78 (72) |
| P(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (Co1) | 8.2 | 1.18 | 52 (60) | 48 (40) |
| P(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (Co2) | 7.8 | 1.17 | 25 (31) | 75 (69) |
| Copolymer | Mw (×103 g/mol) | wt% QPDMAEMAth | wt% PDIPAEMAth | wt% QPDMAEMAexp (mole%) 1 | wt% PDIPAEMAexp (mole%) 1 | wt% PDMAEMAexp (mole%) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (QB1) | 21.1 | 52 | 48 | 48 (53) | 52 (47) | - |
| QPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (QB2) | 36.4 | 35 | 65 | 31 (36) | 69 (64) | - |
| QP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (QCo1) | 12 | 67 | 33 | 51 (54) | 38 (32) | 11 (13) |
| QP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (QCo2) | 9.5 | 38 | 62 | 35 (38) | 49 (43) | 16 (19) |
| SPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (SB1) | 20.4 | 51 | 49 | 44 (36) | 42 (44) | 14 (20) |
| SPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (SB2) | 35.5 | 33 | 67 | 27 (21) | 60 (61) | 13 (18) |
| SP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (SCo1) | 11.5 | 65 | 35 | 45 (37) | 36 (38) | 19 (25) |
| SP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (SCo2) | 9.2 | 36 | 64 | 35 (28) | 51 (53) | 14 (19) |
| Copolymer | CMC/CAC pH = 7 (g/mL) | CMC/CAC pH = 10 (g/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| PDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (B1) | 1 × 10−6 (a) | 9 × 10−7 (a) |
| PDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (B2) | 1 × 10−6 (a) | 1 × 10−6 (a) |
| P(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (Co1) | - | 1 × 10−6 (b) |
| P(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (Co2) | 1.1 × 10−6 (b) | 1.2 × 10−6 (b) |
| Copolymer | Zeta Potential (mV) (pH = 3) | Zeta Potential (mV) (pH = 7) | Zeta Potential (mV) (pH = 10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (B1) | +42.3 | +17.4 | −22.8 |
| PDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (B2) | +46.6 | +27.4 | −8.53 |
| P(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (Co1) | +7.25 | +5.95 | −10 |
| P(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (Co2) | +68.4 | +35.4 | −70.4 |
| Copolymer | pH = 7 | pH = 10 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T = 25 °C | T = 55 °C | T = 25 °C | T = 55 °C | |||||
| Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | |
| PDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA [B1] | 1935 | 33 | 1903 | 32 | 2167 | 78 | 1864 | 75 |
| PDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA [B2] | 3620 | 89 | 2454 | 52 | 1122 | 417 | 827 | 413 |
| P(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) [Co1] | 226 | 90 | 201 | 111 | 5430 | 81 | 4032 | 67 |
| P(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) [Co2] | 470 | 87 | 568 | 98 | 32,000 | 103 | 28,000 | 104 |
| Copolymer | pH = 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No NaCl | 0.5 M NaCl | |||
| Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | |
| PDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA [B1] | 183 | 77 | 289 | 132 |
| PDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA [B2] | 118 | 106 | 160 | 104 |
| P(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) [Co1] | 118 | 89 | 236 | 119 |
| P(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) [Co2] | 580 | 77 | 848 | 93 |
| Copolymer | CMC/CAC pH = 7 (g/mL) | CMC/CAC pH = 10 (g/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| QPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (QB1) | 1 × 10−5 (a) | 2.3 × 10−6 (a) |
| QPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (QB2) | 1.6 × 10−6 (a) | 7.9 × 10−7 (a) |
| QP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (QCo1) | 3.3 × 10−5 (b) | 7 × 10−5 (b) |
| QP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (QCo2) | 4.2 × 10−6 (b) | 3.8 × 10−6 (b) |
| SPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (SB1) | 1.5 × 10−6 (a) | 1 × 10−6 (a) |
| SPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (SB2) | 7.9 × 10−7 (a) | 5.4 × 10−7 (a) |
| SP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (SCo1) | 1.1 × 10−4 (b) | 1 × 10−4 (b) |
| SP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (SCo2) | 2 × 10−5 (b) | 6.2 × 10−6 (b) |
| Copolymer | Zeta Potential (mV) pH = 3 | Zeta Potential (mV) pH = 7 | Zeta Potential (mV) pH = 10 |
|---|---|---|---|
| QPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (QB1) | +37.8 | +27.8 | +21.6 |
| QPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (QB2) | +39.4 | +35.2 | +32.4 |
| QP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (QCo1) | +59.1 | +31.4 | +28.2 |
| QP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (QCo2) | +50.5 | +31.2 | +24.2 |
| SPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (SB1) | +40.1 | +0.72 | −25.6 |
| SPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (SB2) | +53.5 | +37.7 | −29.0 |
| SP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (SCo1) | +51.8 | +16.5 | −27.8 |
| SP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (SCo2) | +48.1 | +29.9 | −38.3 |
| Copolymer | pH = 7 | pH = 10 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T = 25 °C | T = 55 °C | T = 25 °C | T = 55 °C | |||||
| Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | |
| QPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA [QB1] | 252 | 74 | 215 | 78 | 294 | 105 | 261 | 75 |
| QPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA [QB2] | 618 | 83 | 630 | 93 | 669 | 89 | 806 | 95 |
| QP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) [QCo1] | 99 | 112 | 101 | 115 | 329 | 106 | 152 | 102 |
| QP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) [QCo2] | 496 | 61 | 240 | 90 | 600 | 82 | 589 | 85 |
| SPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA [SB1] | 32,200 | 66 | 22,451 | 58 | 32,400 | 66 | 26,400 | 88 |
| SPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA [SB2] | 85,500 | 90 | 84,800 | 75 | 54,300 | 70 | 58,800 | 94 |
| SP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) [SCo1] | 178 | 82 | 167 | 67 | 174 | 76 | 164 | 65 |
| SP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) [SCo2] | 446 | 290 | 430 | 238 | 525 | 68 | 547 | 82 |
| Copolymer | pH = 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No NaCl | 0.5 M NaCl | |||
| Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | Int (kcps) | Rhcum (nm) | |
| QPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (QB1) | 328 | 84 | 250 | 96 |
| QPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (QB2) | 330 | 103 | 304 | 110 |
| QP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (QCo1) | 262 | 62 | 200 | 65 |
| QP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (QCo2) | 100 | 73 | 80 | 68 |
| SPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (SB1) | 808 | 91 | 570 | 94 |
| SPDMAEMA-b-PDIPAEMA (SB2) | 284 | 108 | 290 | 113 |
| SP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (SCo1) | 367 | 94 | 232 | 80 |
| SP(DMAEMA-co-DIPAEMA) (SCo2) | 136 | 97 | 154 | 112 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makri, K.; Pispas, S. Block and Statistical Copolymers of Methacrylate Monomers with Dimethylamino and Diisopropylamino Groups on the Side Chains: Synthesis, Chemical Modification and Self-Assembly in Aqueous Media. Polymers 2024, 16, 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091284
Makri K, Pispas S. Block and Statistical Copolymers of Methacrylate Monomers with Dimethylamino and Diisopropylamino Groups on the Side Chains: Synthesis, Chemical Modification and Self-Assembly in Aqueous Media. Polymers. 2024; 16(9):1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091284
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakri, Kalliopi, and Stergios Pispas. 2024. "Block and Statistical Copolymers of Methacrylate Monomers with Dimethylamino and Diisopropylamino Groups on the Side Chains: Synthesis, Chemical Modification and Self-Assembly in Aqueous Media" Polymers 16, no. 9: 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091284
APA StyleMakri, K., & Pispas, S. (2024). Block and Statistical Copolymers of Methacrylate Monomers with Dimethylamino and Diisopropylamino Groups on the Side Chains: Synthesis, Chemical Modification and Self-Assembly in Aqueous Media. Polymers, 16(9), 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091284








