Effect of Water Absorption and Stacking Sequences on the Tensile Properties and Damage Mechanisms of Hybrid Polyester/Glass/Jute Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
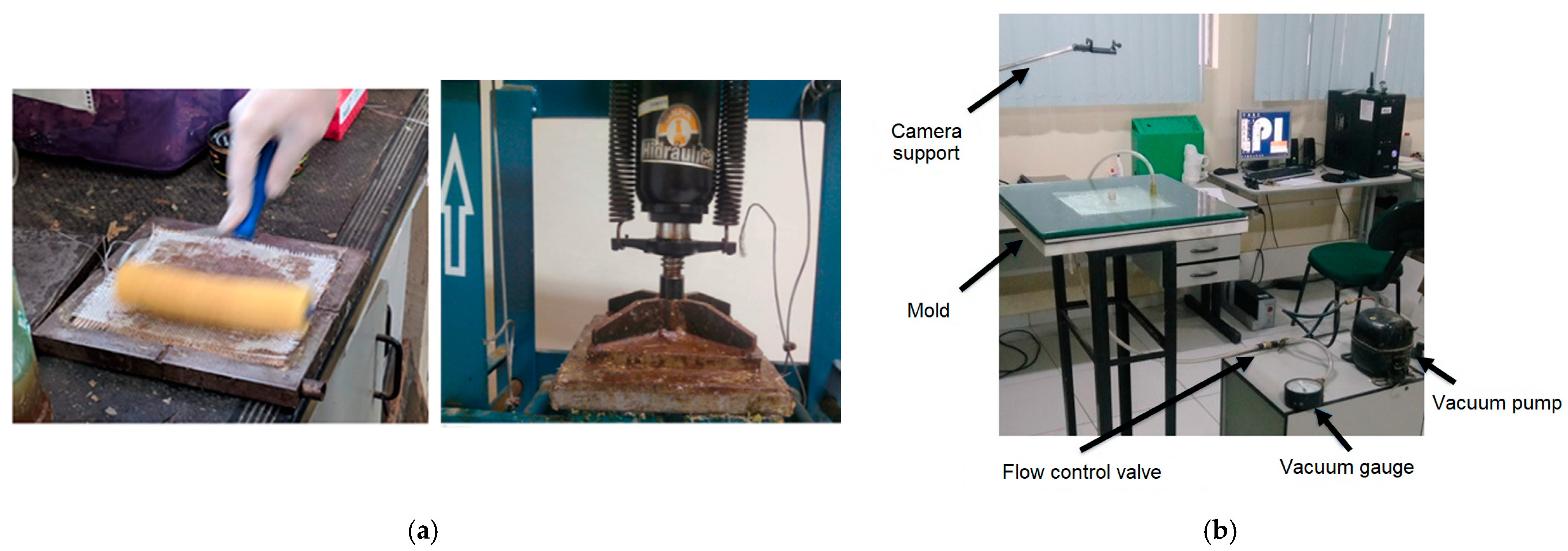
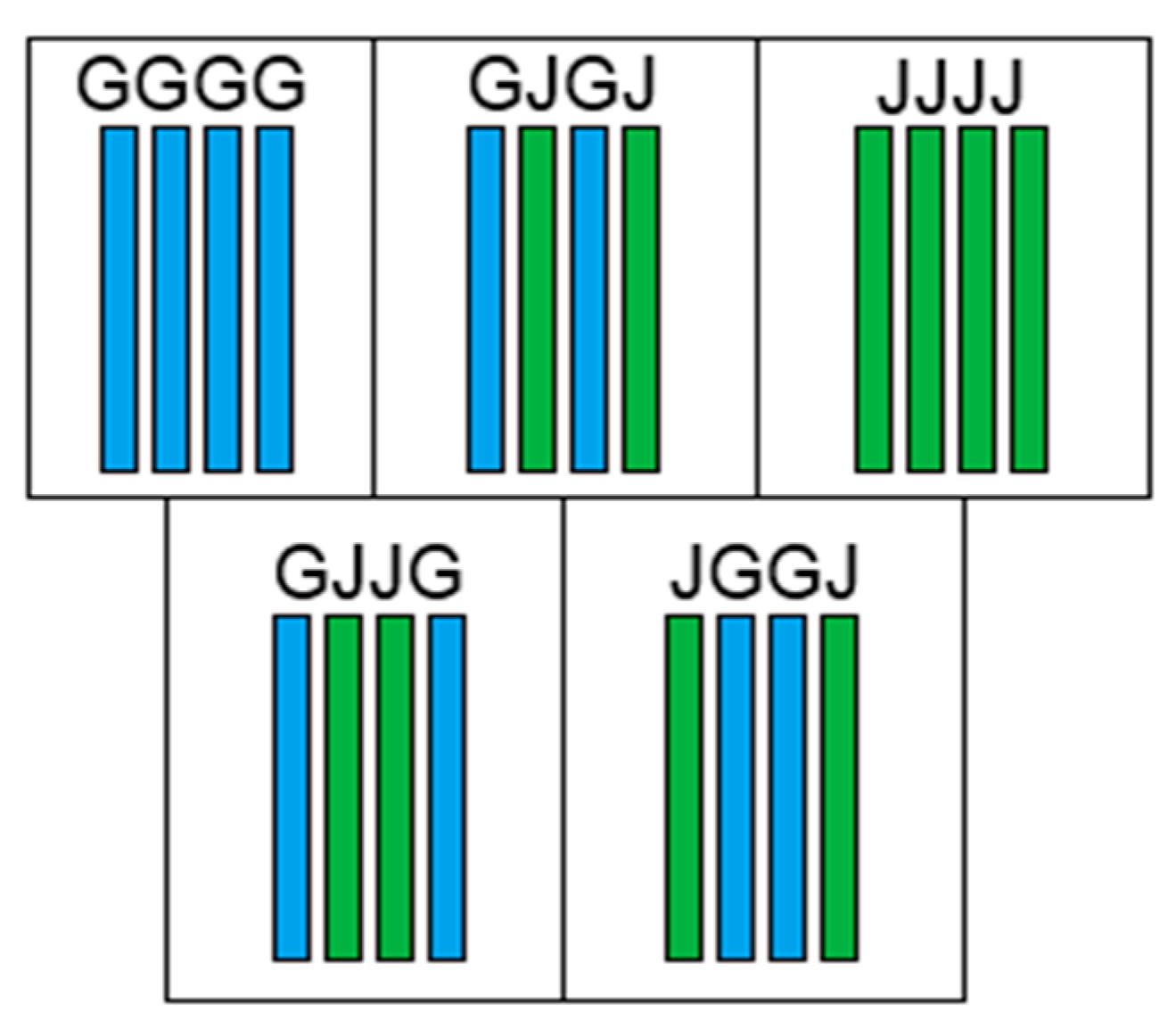
2.2. Manufacturing of Composites
2.3. Tensile Tests
2.4. Hybrid Effect Methodology
2.5. Scanning Eletron Microscope (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Volumetric Fraction of Fibers
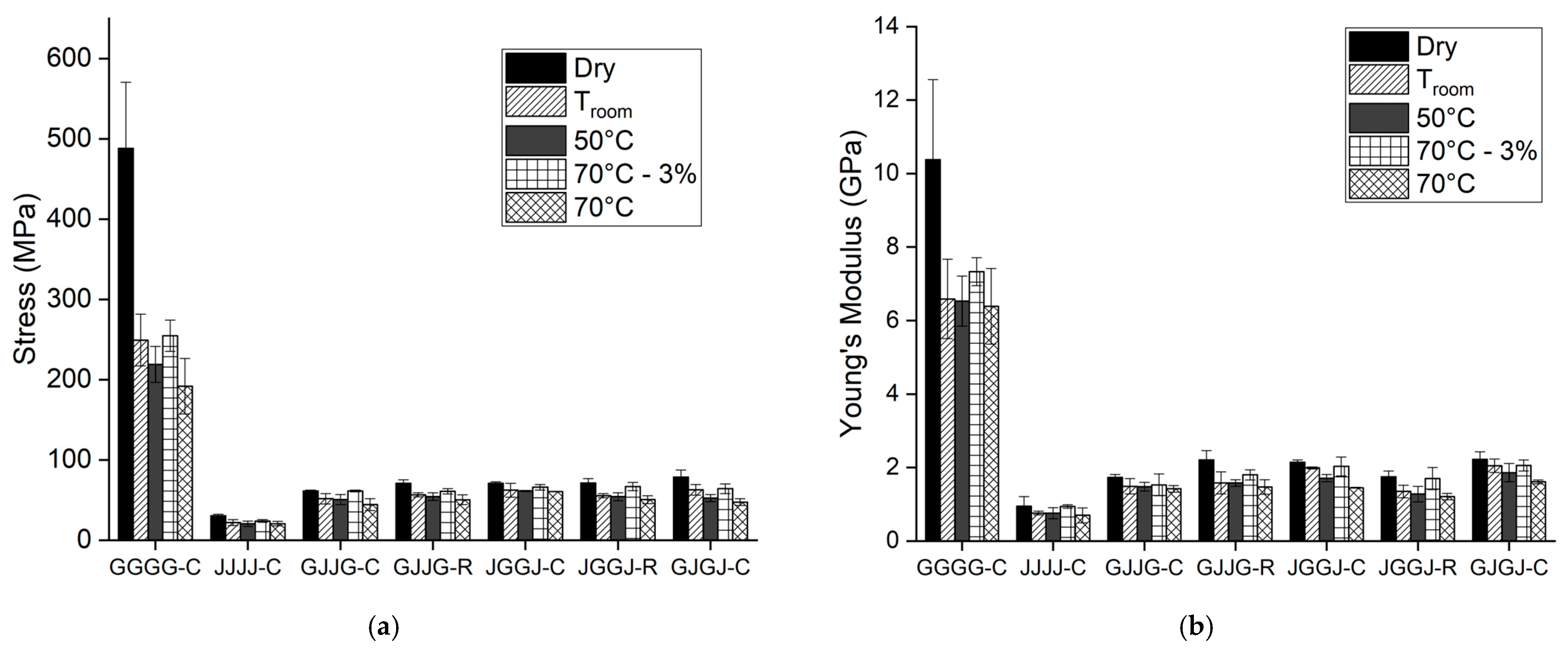
3.2. Tensile Tests Results
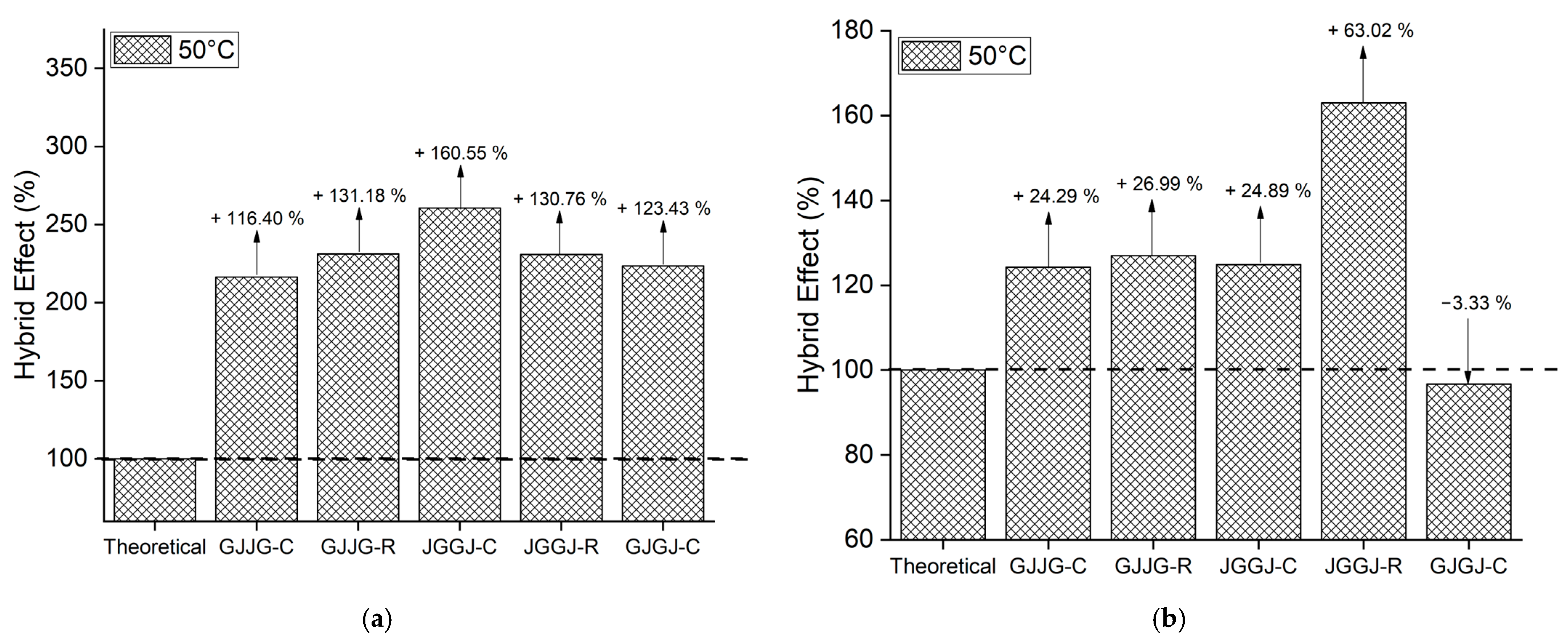
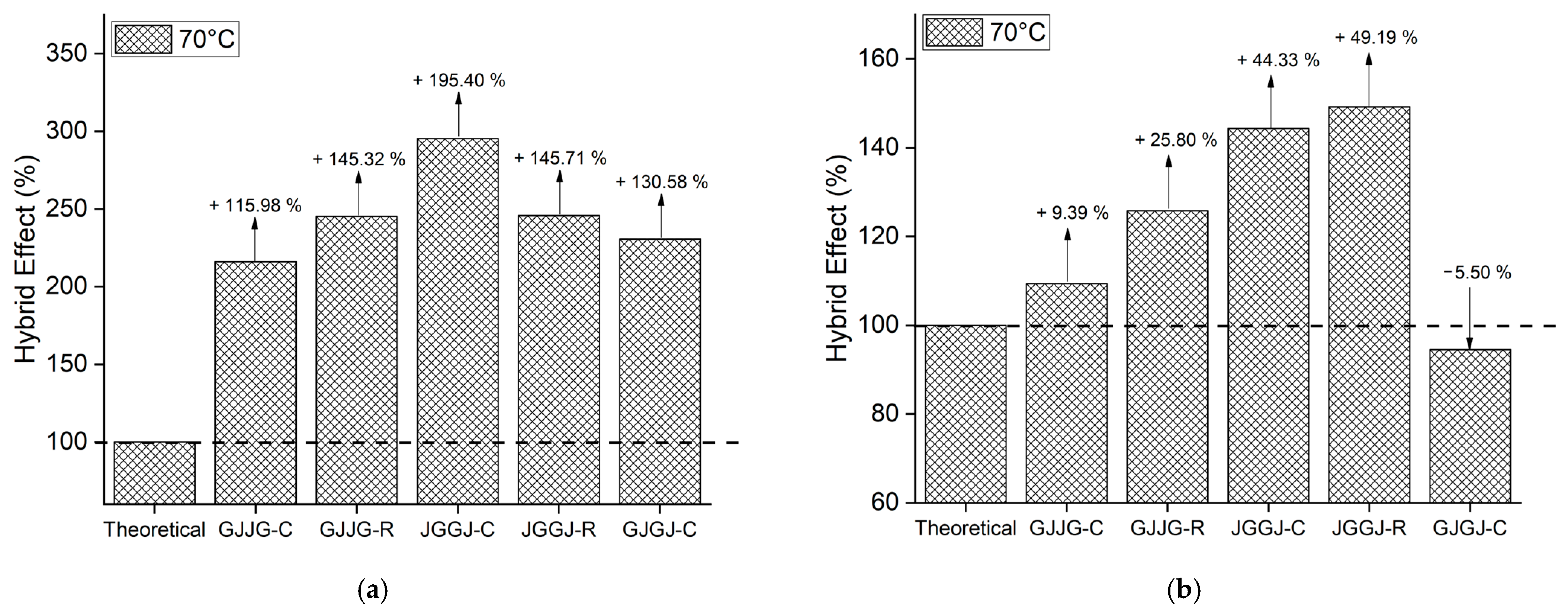
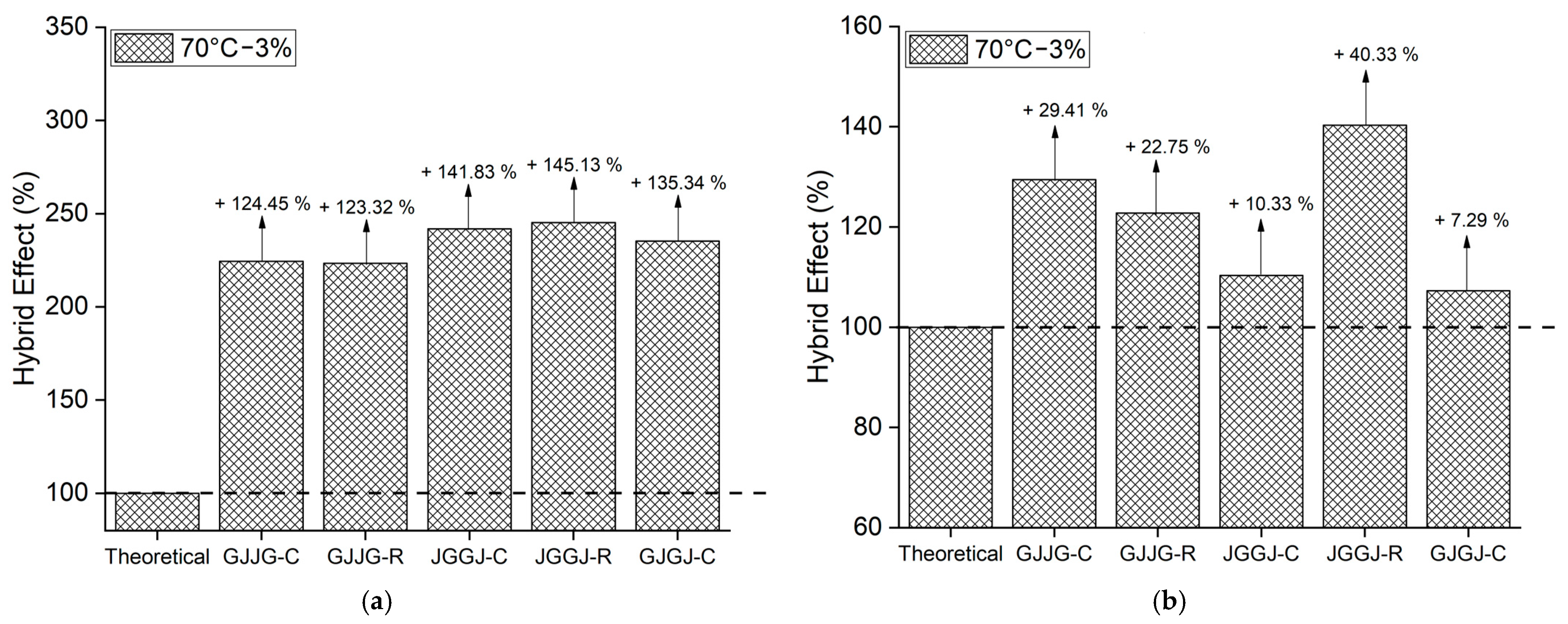
3.3. Hybrid Effect
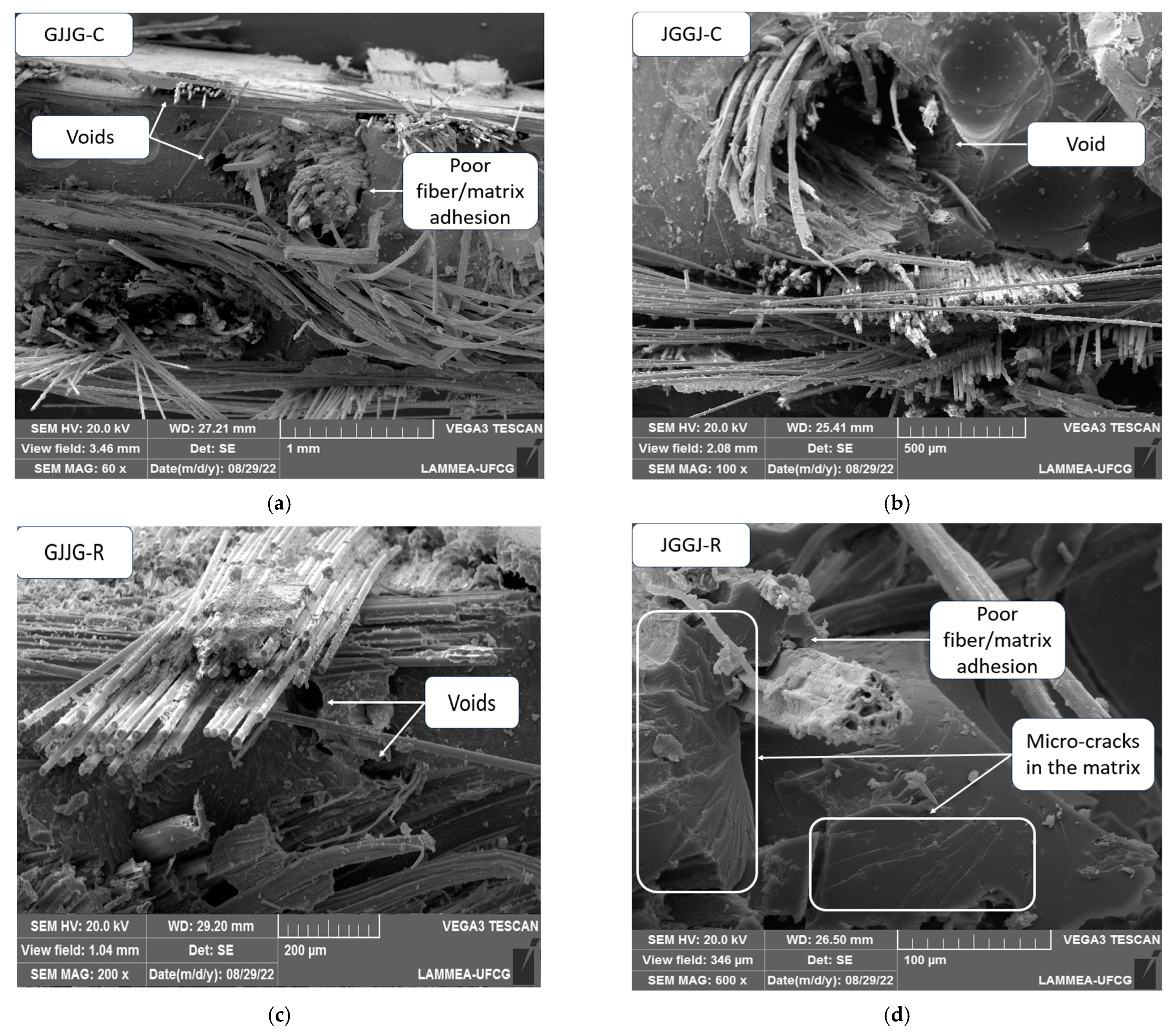
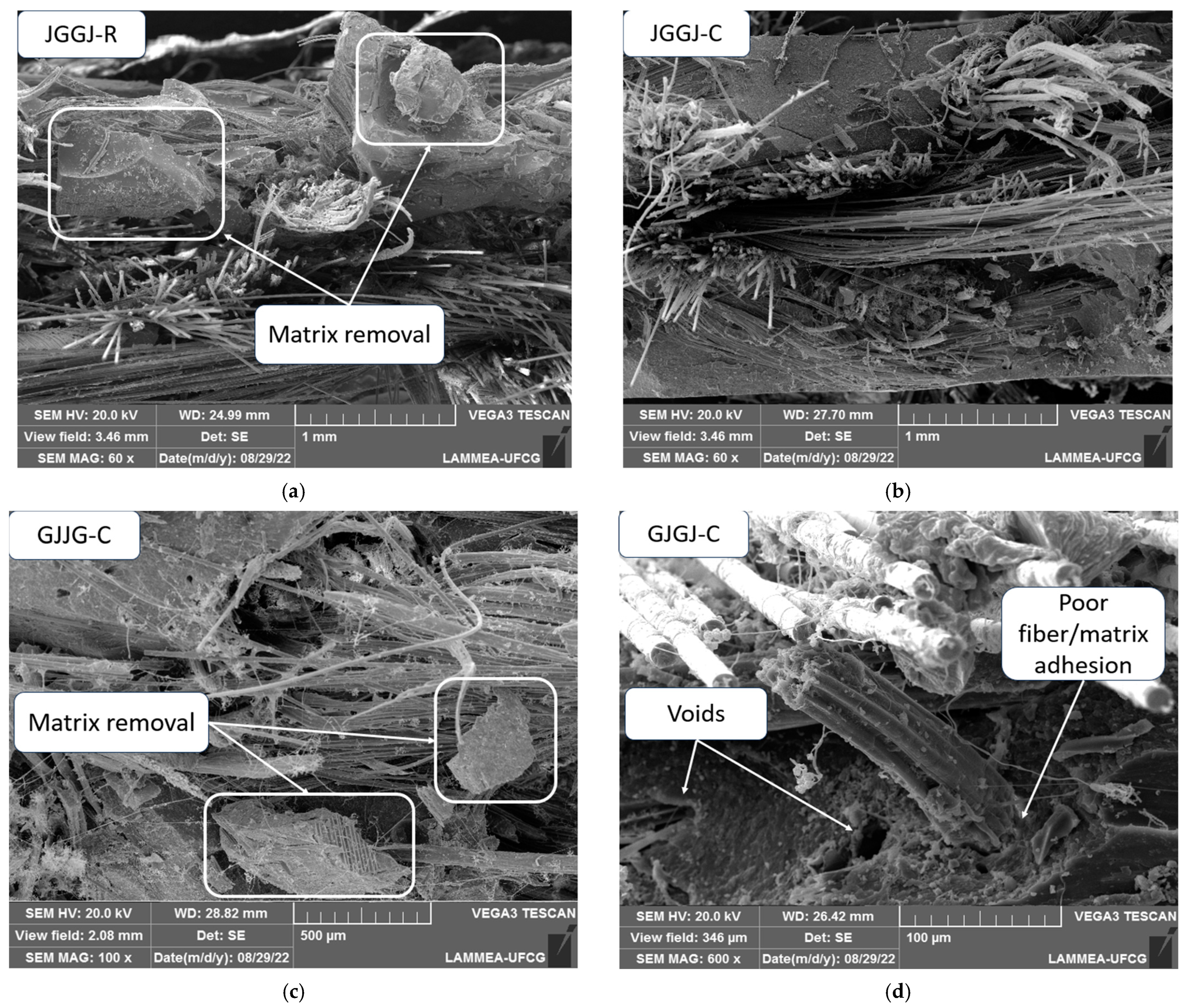
3.4. Damage Mechanism of Dry and Wet Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, J.R. Polymer ageing: Physics, chemistry or engineering? Time to reflect. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2006, 9, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, P.V.; Rabello, M.S.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Joseph, K.; Thomas, S. Environmental effects on the degradation behaviour of sisal fibre reinforced polypropylene composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 1357–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreopoulos, A.G.; Tarantili, P.A. Water sorption characteristics of epoxy resin–UHMPE fibers composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 70, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcovich, N.E.; Reboredo, M.M.; Aranguren, M.I. Moisture diffusion in polyester–Woodflour composites. Polymer 1999, 40, 7313–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scida, D.; Assarar, M.; Poilâne, C.; Ayad, R. Influence of hygrothermal ageing on the damage mechanisms of flax-fibre reinforced epoxy composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 48, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.A.; Smith, P.A. Modeling the Transport of Low-Molecular-Weight Penetrants Within Polymer Matrix Composites. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafodya, I.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Durability study of pultruded CFRP plates immersed in water and seawater under sustained bending: Water uptake and effects on the mechanical properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 70, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hachem, Z.; Célino, A.; Challita, G.; Moya, M.-J.; Fréour, S. Hygroscopic multi-scale behavior of polypropylene matrix reinforced with flax fibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 140, 111634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esleman, E.A.; Önal, G. Effect of saltwater on the mechanical properties of basalt/carbon/glass-epoxy hybrid composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2022, 56, 3783–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lang, A.W.; Li, X.; Nutt, S.R. Hygrothermal aging effects on fatigue of glass fiber/polydicyclopentadiene composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 110, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Li, H.; Su, X. Effects of immersion and sustained bending on water absorption and thermomechanical properties of ultraviolet cured glass fiber-reinforced acylate polymer composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 2275–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Lang, A.W.; Zhang, Y.; Nutt, S.R. Water immersion aging of polydicyclopentadiene resin and glass fiber composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 124, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekielski, A.; Żelaziński, T.; Mishra, P.K.; Skudlarski, J. Properties of Biocomposites Produced with Thermoplastic Starch and Digestate: Physicochemical and Mechanical Characteristics. Materials 2021, 14, 6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangar, S.P.; Whiteside, W.S. Nano-cellulose reinforced starch bio composite films- A review on green composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbelaiz, A.; Cantero, G.; Fernández, B.; Mondragon, I.; Gañán, P.; Kenny, J.M. Flax fiber surface modifications: Effects on fiber physico mechanical and flax/polypropylene interface properties. Polym. Compos. 2005, 26, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F. Chemical treatments on plant-based natural fibre reinforced polymer composites: An overview. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, S.; Kumaran, P.; Mohanamurugan, S.; Vijay, R.; Singaravelu, D.L.; Vinod, A.; Sanjay, M.R.; Siengchin, S.; Bhat, K.S. Influence of wood dust fillers on the mechanical, thermal, water absorption and biodegradation characteristics of jute fiber epoxy composites. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 27, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeevi, S.; Shanmugam, V.; Kumar, S.; Ganesan, V.; Sas, G.; Johnson, D.J.; Shanmugam, M.; Ayyanar, A.; Naresh, K.; Neisiany, R.E.; et al. Effects of water absorption on the mechanical properties of hybrid natural fibre/phenol formaldehyde composites. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubari, S.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ishak, M.R.; Ilyas, R.A.; Asyraf, M.R.M. Potential of Natural Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites in Sandwich Structures: A Review on Its Mechanical Properties. Polymers 2021, 13, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.P.L.; Xing, X.S.; Li, R.K.Y. Moisture absorption studies of sisal fibre reinforced polypropylene composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Miao, M.; Ding, X. Influence of moisture absorption on the interfacial strength of bamboo/vinyl ester composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, H.N.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Richardson, M.O.W. Effect of water absorption on the mechanical properties of hemp fibre reinforced unsaturated polyester composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollino, F.; Giannella, V.; Armentani, E.; Sepe, R. Mechanical behavior of chemically-treated hemp fibers reinforced composites subjected to moisture absorption. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akil, H.M.; Cheng, L.W.; Mohd Ishak, Z.A.; Abu Bakar, A.; Abd Rahman, M.A. Water absorption study on pultruded jute fibre reinforced unsaturated polyester composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, M.R.; Yogesha, B. Studies on Natural/Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Hybrid Composites: An Evolution. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Rejab, M.R.M.; Siregar, J.P.; Mohamad, Z.; Quanjin, M.; Mohammed, A.A. Mechanical properties of hybrid glass fiber/rice husk reinforced polymer composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 27, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujon, M.A.S.; Habib, M.A.; Abedin, M.Z. Experimental investigation of the mechanical and water absorption properties on fiber stacking sequence and orientation of jute/carbon epoxy hybrid composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10970–10981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Inder Preet Singh, J.; Singh, S.; Dhawan, V.; Kumar Tiwari, S. A Brief Review of Jute Fibre and Its Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 28427–28437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretsis, G. A review of the tensile, compressive, flexural and shear properties of hybrid fibre-reinforced plastics. Composites 1987, 18, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, R.; Manikandan, V. Mechanical properties of palmyra/glass fiber hybrid composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 2216–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swolfs, Y.; Gorbatikh, L.; Verpoest, I. Fibre hybridisation in polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 67, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshwaran, N.; ElayaPerumal, A.; Alavudeen, A.; Thiruchitrambalam, M. Mechanical and water absorption behaviour of banana/sisal reinforced hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4017–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Thomas, S. Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Longana, M.L.; Jalalvand, M.; Wisnom, M.R.; Potter, K.D. Pseudo-ductility in intermingled carbon/glass hybrid composites with highly aligned discontinuous fibres. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 73, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swolfs, Y.; Verpoest, I.; Gorbatikh, L. Recent advances in fibre-hybrid composites: Materials selection, opportunities and applications. Int. Mater. Rev. 2019, 64, 181–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpurohit, A.; Joannès, S.; Singery, V.; Sanial, P.; Laiarinandrasana, L. Hybrid Effect in In-Plane Loading of Carbon/Glass Fibre Based Inter- and Intraply Hybrid Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marom, G.; Fischer, S.; Tuler, F.R.; Wagner, H.D. Hybrid effects in composites: Conditions for positive or negative effects versus rule-of-mixtures behaviour. J. Mater. Sci. 1978, 13, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T. On the improvement of mechanical properties of composites by hybrid composition. In Proceedings of the 8th International Reinforced Plastics Conference, London, UK, 10–12 October 1972; pp. 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Bunsell, A.R.; Harris, B. Hybrid carbon and glass fibre composites. Composites 1974, 5, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweben, C. Tensile strength of hybrid composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1977, 12, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerscales, J.; Short, D. Carbon fibre and glass fibre hybrid reinforced plastics. Composites 1978, 9, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manders, P.W.; Bader, M.G. The strength of hybrid glass/carbon fibre composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1981, 16, 2233–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, M.; Hsieh, K. Fatigue fracture of embedded copper conductors in multifunctional composite structures. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Sui, X.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Liu, Y.; Qian, X. Optimization of interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy composites via carbon nanotube sizing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 347, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paran, S.M.R.; Abdorahimi, M.; Shekarabi, A.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Jafari, S.H.; Saeb, M.R. Modeling and analysis of nonlinear elastoplastic behavior of compatibilized polyolefin/polyester/clay nanocomposites with emphasis on interfacial interaction exploration. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 154, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.S.; Vijayarangan, S. Tensile, flexural and interlaminar shear properties of woven jute and jute-glass fabric reinforced polyester composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 207, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, K.; Thomas, S.; Pavithran, C. Effect of chemical treatment on the tensile properties of short sisal fibre-reinforced polyethylene composites. Polymer 1996, 37, 5139–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devireddy, S.B.R.; Biswas, S. Physical and thermal properties of unidirectional banana–jute hybrid fiber-reinforced epoxy composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2016, 35, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, P.S.; Rao, M.V.; Kumar, V.K.; Raghavendra, G.; Ojha, S.; Inala, R. Evaluation of mechanical and tribological properties of bamboo–glass hybrid fiber reinforced polymer composite. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 46, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriranga, B.K.; Kirthan, L.J.; G, A. The mechanical properties of hybrid laminates composites on epoxy resin with natural jute fiber and S-glass fibers. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 8927–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, C.; Ranjan Deo, C.; Baskey, S. Influence of moisture absorption on mechanical properties of kenaf/glass reinforced polyester hybrid composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 2596–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, R.A.; Magalhaes, P.A.A. Analysis of the mechanical and thermal properties of jute and glass fiber as reinforcement epoxy hybrid composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaddami, H.; Arrakhiz, F.-e.; Hafs, O.; Assimi, T.E.; Boulafrouh, L.; Ablouh, E.-H.; Mansori, M.; Banouni, H.; Bouzit, S.; Erchiqui, F.; et al. Implementation and Characterization of a Laminate Hybrid Composite Based on Palm Tree and Glass Fibers. Polymers 2021, 13, 3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, S.; Muralidhar, M.; Singh, T.J.; Sarkar, S. Characterization of Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Bamboo/GFRP and Jute/GFRP Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.; Hejda, M.; Young, R.J.; Eichhorn, S.J. Deformation micromechanics of a model cellulose/glass fibre hybrid composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 2218–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthi, N.; Kumaresan, K.; Sathish, S.; Prabhu, L.; Gokulkumar, S.; Balaji, D.; Vigneshkumar, N.; Rohinth, S.; Rafiq, S.; Muniyaraj, S.; et al. Effect of weight fraction on the mechanical properties of flax and jute fibers reinforced epoxy hybrid composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 8006–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, C.; Ranjan Deo, C.; Kumar Das, S. Performance studies of polyester-based hybrid composites reinforced with palmyra-palm leaf stalk and glass fibers. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 2671–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komai, K.; Minoshima, K.; Shiroshita, S. Hygrothermal degradation and fracture process of advanced fibre-reinforced plastics. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 143, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Seo, D.W. Effect of water absorption fatigue on mechanical properties of sisal textile-reinforced composites. Int. J. Fatigue 2006, 28, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezgani, L.; Madani, K.; Feaugas, X.; Touzain, S.; Cohendoz, S.; Valette, J. Influence of water ingress onto the crack propagation rate in a AA2024-T3 plate repaired by a carbon/epoxy patch. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 55, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranha, R.; Filho, M.A.A.; de Lima Santos, C.; Fonseca, V.M.; Rivera, J.L.V.; de Lima, A.G.B.; de Amorim, W.F.; Carvalho, L.H. Water Sorption in Hybrid Polyester/Glass/Jute Composites Processed via Compression Molding and Vacuum-Assisted Resin Transfer Molding. Polymers 2023, 15, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3039; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. American Society for Testing Materials (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Yu, T. Tensile and interfacial properties of unidirectional flax/glass fiber reinforced hybrid composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 88, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, S.C.; Koczak, M.J. Thick-section AS4-graphite/E-glass/PPS hybrid composites: Part I. Tensile behavior. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1996, 56, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, S.; Michael, D.P.; Bensely, A.; Lal, D.M.; Rajadurai, A. Mechanical property evaluation of natural fiber coir composite. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, E.; García-Manrique, J.A. Water Absorption Behaviour and Its Effect on the Mechanical Properties of Flax Fibre Reinforced Bioepoxy Composites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 390275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbehera, S.; Acharya, S. Effect of cenosphere addition on the mechanical properties of jute-glass fiber hybrid epoxy composites. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 46, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Brookfield viscosity at 25 °C sp3: 60 rpm (CP) | 250–350 |
| Thixotropy index | 1.30–2.10 |
| Solid content—Reichhold method (%) | 55–63 |
| Density at 25 °C (g/cm3) | 1.07–1.11 |
| Acidity index (mgKOH/g) | 30 maximum |
| Exothermic curve at 25 °C | |
| 5–7 8–14 140–180 |
| Post-cure | 60 °C |
| Composites | Glass Fiber Weight Fraction (%) | Jute Fiber Weight Fraction (%) | Total Fiber Weight Fraction of Composites (%) | Fiber Volume Fraction of Composites (%) | Total Fiber Volume Fraction of Jute (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GGGG-C 1 | 59.70 ± 3.27 | 0 | 59.70 ± 3.27 | 39.35 ± 3.21 | 0 |
| JJJJ-C | 0 | 44.10 ± 2.10 | 44.10 ± 2.10 | 36.87 ± 1.97 | 36.87 ± 1.97 |
| GJGJ-C | 15.23 ± 0.43 | 26.10 ± 0.74 | 41.33 ± 1.17 | 30.68 ± 1.02 | 24.77 ± 0.90 |
| GJJG-C | 15.23 ± 1.06 | 26.11 ± 1.82 | 41.34 ± 2.89 | 30.72 ± 2.55 | 24.81 ± 2.24 |
| GJJG-R 1 | 17.77 ± 1.77 | 30.46 ± 3.04 | 48.23 ± 4.82 | 36.99 ± 4.48 | 30.42 ± 4.06 |
| JGGJ-C | 15.28 ± 1.16 | 26.19 ± 2.00 | 41.47 ± 3.16 | 30.83 ± 2.76 | 24.91 ± 2.42 |
| JGGJ-R | 18.15 ± 1.18 | 31.12 ± 2.02 | 49.28 ± 3.20 | 37.94 ± 3.00 | 31.27 ± 2.73 |
| Fracture Stress (MPa) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composites | Dry | Room | 50 °C | 70 °C | 70 °C–3% |
| GGGG-C | 488.22 ± 82.21 | 249.29 ± 32.28 | 219.01 ± 22.36 | 191.78 ± 34.61 | 254.60 ± 19.43 |
| JJJJ-C | 30.36 ± 1.87 | 21.89 ± 3.67 | 20.65 ± 3.28 | 20.53 ± 2.74 | 23.83 ± 1.66 |
| GJJG-C | 61.39 ± 0.88 | 51.61 ± 6.46 | 50.78 ± 6.29 | 44.38 ± 7.44 | 61.23 ± 1.21 |
| GJJG-R | 70.72 ± 0.53 | 56.54 ± 2.67 | 54.25 ± 4.80 | 50.41 ± 6.20 | 60.92 ± 3.44 |
| JGGJ-C | 70.72 ± 2.04 | 62.23 ± 8.47 | 61.14 ± 0.72 | 60.70 ± 0.18 | 65.97 ± 3.39 |
| JGGJ-R | 71.09 ± 5.73 | 55.34 ± 2.64 | 54.15 ± 4.84 | 50.49 ± 4.92 | 66.87 ± 5.23 |
| GJGJ-C | 78.69 ± 8.76 | 62.90 ± 6.67 | 52.43 ± 4.37 | 47.38 ± 4.26 | 64.20 ± 6.03 |
| Elastic Modulus (GPa) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composites | Dry | Room | 50 °C | 70 °C | 70 °C–3% |
| GGGG-C | 10.38 ± 2.18 | 6.59 ± 1.08 | 6.53 ± 0.68 | 6.39 ± 1.03 | 7.33 ± 0.38 |
| JJJJ-C | 0.95 ± 0.26 | 0.76 ± 0.05 | 0.76 ± 0.15 | 0.70 ± 0.20 | 0.94 ± 0.05 |
| GJJG-C | 1.73 ± 0.08 | 1.49 ± 0.21 | 1.48 ± 0.12 | 1.42 ± 0.09 | 1.53 ± 0.30 |
| GJJG-R | 2.21 ± 0.25 | 1.58 ± 0.30 | 1.58 ± 0.09 | 1.47 ± 0.20 | 1.80 ± 0.14 |
| JGGJ-C | 2.14 ± 0.07 | 1.99 ± 0.03 | 1.71 ± 0.10 | 1.45 ± 0.01 | 2.03 ± 0.26 |
| JGGJ-R | 1.75 ± 0.16 | 1.35 ± 0.17 | 1.28 ± 0.21 | 1.21 ± 0.09 | 1.70 ± 0.30 |
| GJGJ-C | 2.22 ± 0.21 | 2.05 ± 0.18 | 1.86 ± 0.25 | 1.61 ± 0.05 | 2.06 ± 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aranha, R.; Filho, M.A.A.; Santos, C.d.L.; de Andrade, T.H.F.; Fonseca, V.M.; Rivera, J.L.V.; dos Santos, M.A.; de Lima, A.G.B.; de Amorim, W.F., Jr.; de Carvalho, L.H. Effect of Water Absorption and Stacking Sequences on the Tensile Properties and Damage Mechanisms of Hybrid Polyester/Glass/Jute Composites. Polymers 2024, 16, 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070925
Aranha R, Filho MAA, Santos CdL, de Andrade THF, Fonseca VM, Rivera JLV, dos Santos MA, de Lima AGB, de Amorim WF Jr., de Carvalho LH. Effect of Water Absorption and Stacking Sequences on the Tensile Properties and Damage Mechanisms of Hybrid Polyester/Glass/Jute Composites. Polymers. 2024; 16(7):925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070925
Chicago/Turabian StyleAranha, Rudá, Mario A. Albuquerque Filho, Cícero de L. Santos, Tony Herbert F. de Andrade, Viviane M. Fonseca, Jose Luis Valin Rivera, Marco A. dos Santos, Antonio G. B. de Lima, Wanderley F. de Amorim, Jr., and Laura H. de Carvalho. 2024. "Effect of Water Absorption and Stacking Sequences on the Tensile Properties and Damage Mechanisms of Hybrid Polyester/Glass/Jute Composites" Polymers 16, no. 7: 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070925
APA StyleAranha, R., Filho, M. A. A., Santos, C. d. L., de Andrade, T. H. F., Fonseca, V. M., Rivera, J. L. V., dos Santos, M. A., de Lima, A. G. B., de Amorim, W. F., Jr., & de Carvalho, L. H. (2024). Effect of Water Absorption and Stacking Sequences on the Tensile Properties and Damage Mechanisms of Hybrid Polyester/Glass/Jute Composites. Polymers, 16(7), 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070925






