A Modular and Cost-Effective Droplet Microfluidic Device for Controlled Emulsion Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
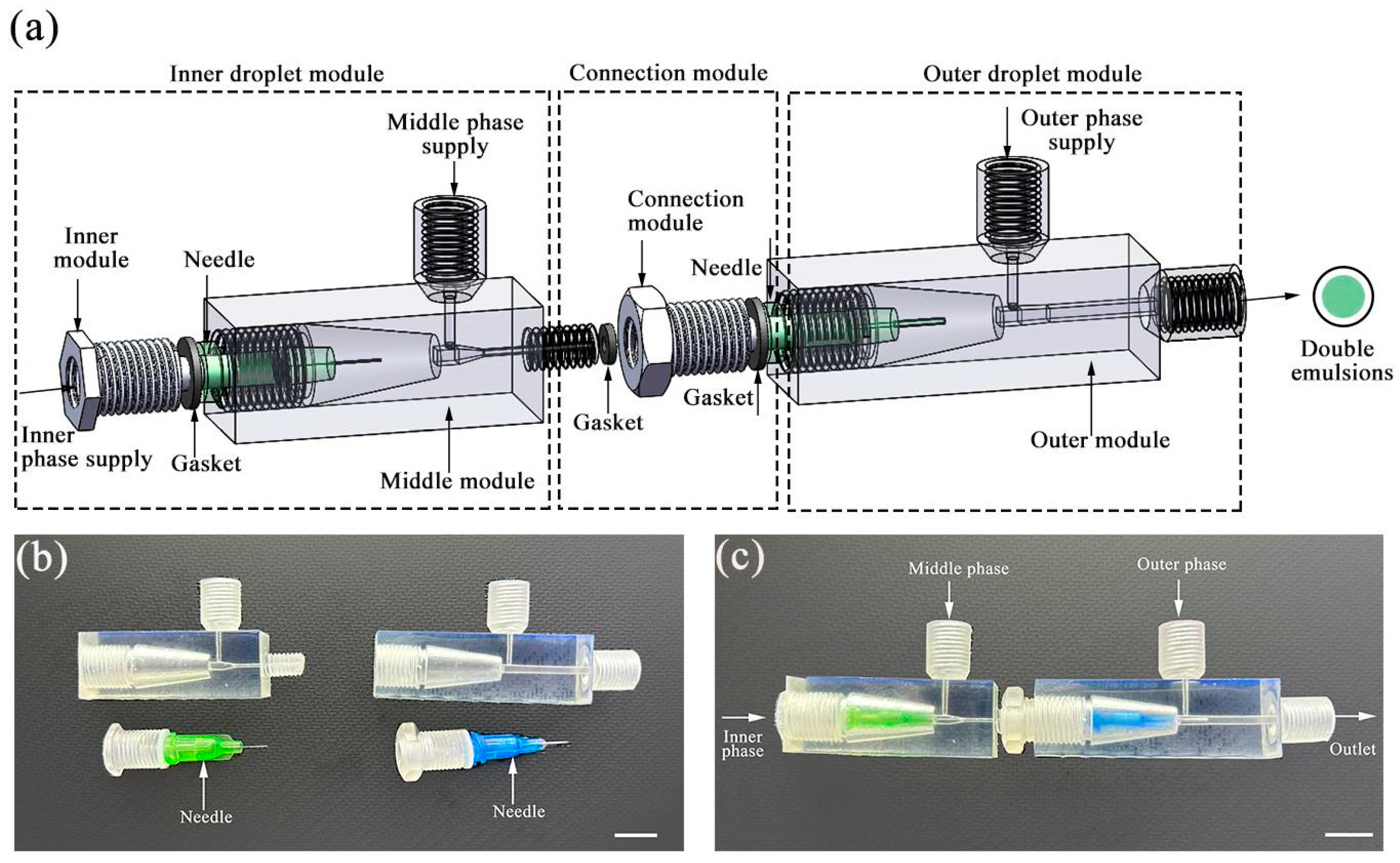
2.1. Fabrication of Plug-and-Play Droplet Microfluidic Device
2.2. General Equipment and Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
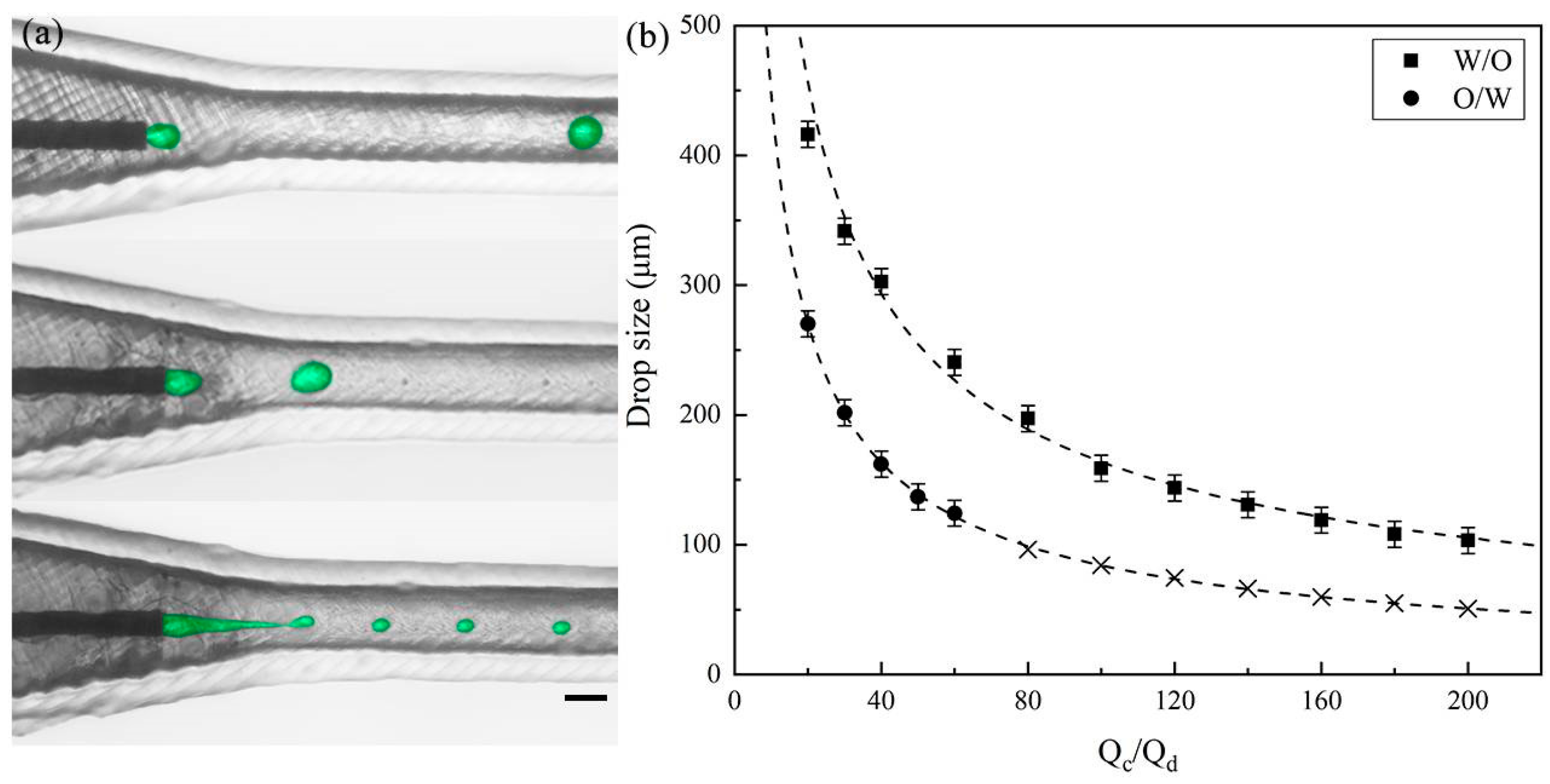
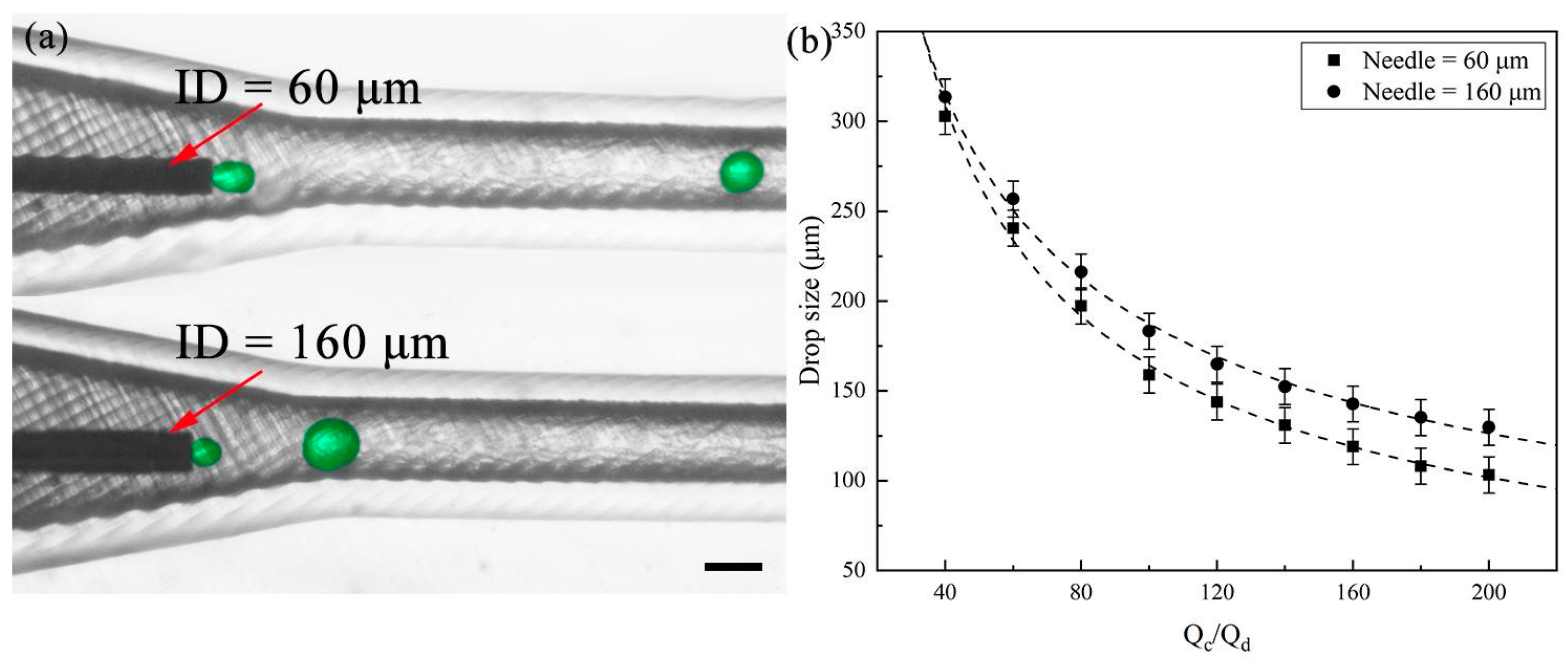
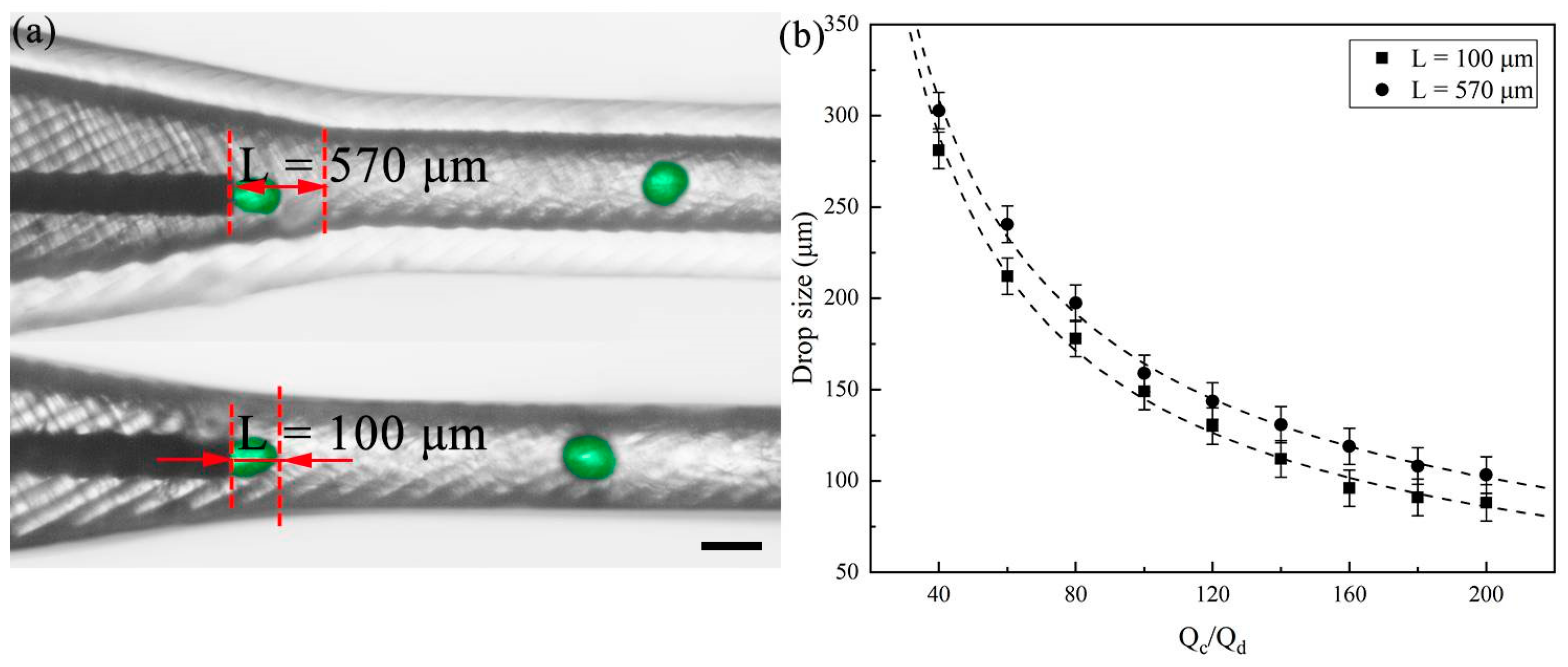
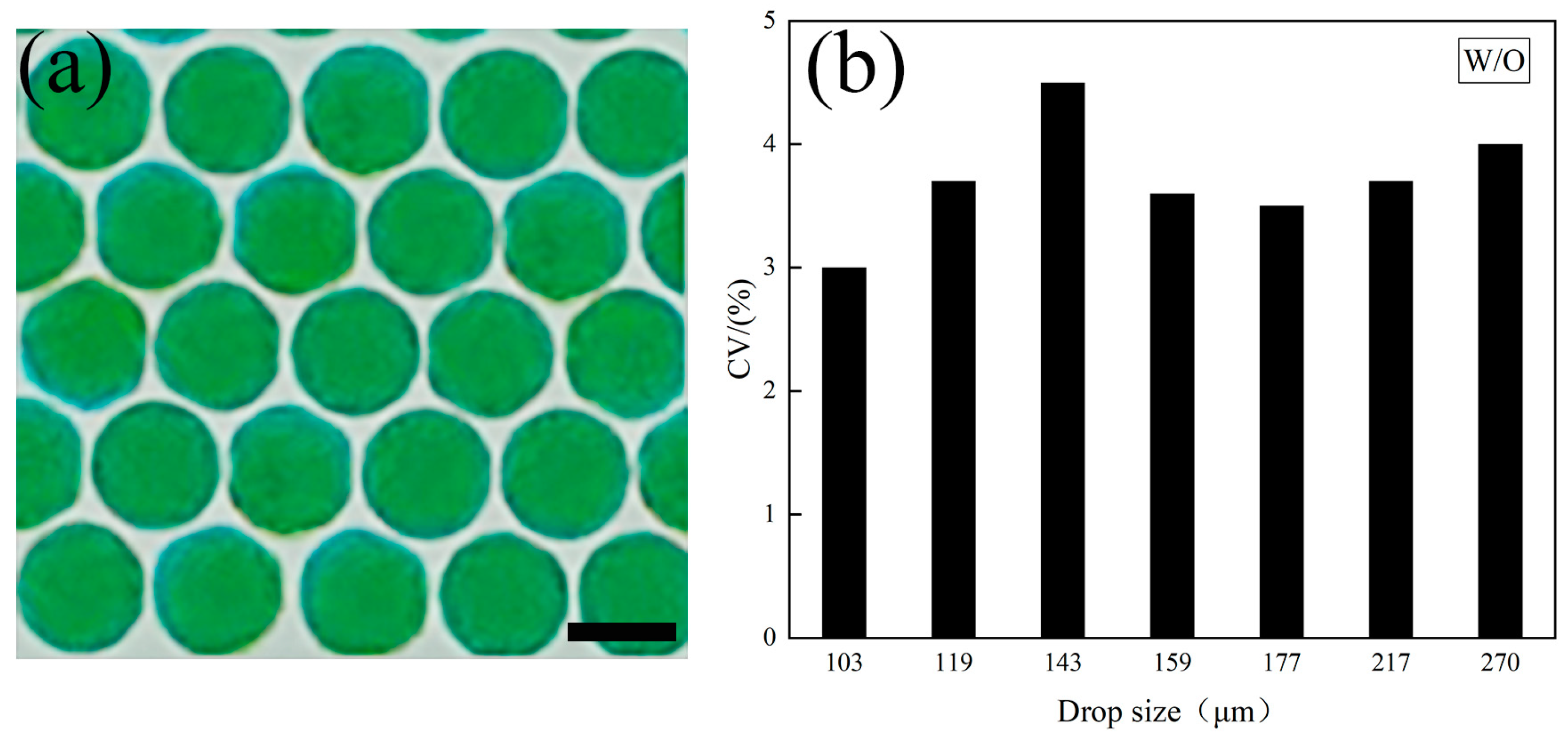
3.1. Single Emulsion Generation
3.2. Double Emulsion Generation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, D.H.; Song, R.; Sun, Q.; Park, W.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Pang, C.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Cho, J.H. Crack-Enhanced Microfluidic Stretchable E-Skin Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 44678–44686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuso, J.M.; Virumbrales-Muñoz, M.; Lang, J.M.; Beebe, D.J. A role for microfluidic systems in precision medicine. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, W.; He, X.H.; Yang, X.L.; Li, M.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.J.; Liu, Z.; Chu, L.Y. Controllable Multicompartmental Capsules with Distinct Cores and Shells for Synergistic Release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8743–8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, J.K.; Tsai, S.S.; Wan, J.; Stone, H.A. Dripping and jetting in microfluidic multiphase flows applied to particle and fiber synthesis. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Emerging Droplet Microfluidics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7964–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kricka, L.J. Microchips, Microarrays, Biochips and Nanochips—Personal Laboratories for the 21st Century. EJIFCC 2000, 12, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, H.; Gärtner, C. Polymer microfabrication methods for microfluidic analytical applications. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, F.; Shinohara, S.; Tabata, O.; Yamaoka, Y.; Kurokawa, M.; Shinohara, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Baba, Y. Replica multichannel polymer chips with a network of sacrificial channels sealed by adhesive printing method. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Gärtner, C. Polymer microfabrication technologies for microfluidic systems. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, U.N.; Su, X.; Guckenberger, D.J.; Dostie, A.M.; Zhang, T.; Berthier, E.; Theberge, A.B. Fundamentals of rapid injection molding for microfluidic cell-based assays. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, U.M.; Marson, S.; Alcock, J.R. Micro-injection moulding of polymer microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2009, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Yue, C.Y.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Ma, L.L. Fabrication of smart COC chips: Advantages of N-vinylpyrrolidone (NVP) monomer over other hydrophilic monomers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 178, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, A.; Khan, S.; Jarad, N.A.; Didar, T.F. The Fabrication and Bonding of Thermoplastic Microfluidics: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guckenberger, D.J.; Groot, T.E.; Wan, A.M.; Beebe, D.J.; Young, E.W. Micromilling: A method for ultra-rapid prototyping of plastic microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2364–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurich, J.C.; Reichenbach, I.G.; Schüler, G. Manufacture and application of ultra-small micro end mills. CIRP Ann. 2012, 61, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; Li, E.Q.; Aguirre-Pablo, A.A.; Thoroddsen, S.T. A simple and low-cost fully 3D-printed non-planar emulsion generator. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 2793–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qi, F.; Mao, H.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Gong, J.; Wang, L.; Malmstadt, N.; Chen, Y. In-situ transfer vat photopolymerization for transparent microfluidic device fabrication. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.M.; Ji, Q.; Duan, H. Three-Dimensional Printed Devices in Droplet Microfluidics. Micromachines 2019, 10, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Kiyosawa, M.; Takeuchi, S. Three-dimensional printed microfluidic modules for design changeable coaxial microfluidic devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 274, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Macdonald, N.P.; Guijt, R.M.; Breadmore, M.C. Increasing the functionalities of 3D printed microchemical devices by single material, multimaterial, and print-pause-print 3D printing. Lab Chip 2018, 19, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, S.L. Droplets and Bubbles in Microfluidic Devices. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2016, 48, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, C.A.; Hinnen, H.S.; Avery, S.; Cate, R.J.; Nordin, G.P.; Pitt, W.G. 3D-Printed Microfluidic Droplet Generator with Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Polymers. Micromachines 2021, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.Q.; Zhang, J.M.; Thoroddsen, S.T. Simple and inexpensive microfluidic devices for the generation of monodisperse multiple emulsions. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 24, 015019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, A.G.; Chircov, C.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Fabrication and Applications of Microfluidic Devices: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, Y.J.; Chiu, Y.J. Fabrication of Polymer Microfluidics: An Overview. Polymers 2022, 14, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Ren, Y.; He, J.; Chen, G.Z.; Koh, K.S. Microfluidic fabrication of porous polydimethylsiloxane microparticles for the treatment of toluene-contaminated water. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2018, 22, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, W. Passive Micropump for Highly Stable, Long-Termed, and Large Volume of Droplet Generation/Transport Inside 3D Microchannels Capable of Surfactant-Free and Droplet-Based Thermocycled Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reactions Based on a Single Thermostatic Heater. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11925–11932. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan, S.; Hashimoto, M. 3D printed fittings and fluidic modules for customizable droplet generators. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2822–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, A.; Cai, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Eaglesham, A. Droplet characteristics in the multi-staged high speed disperser with single inlet. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Phase | W/O | O/W | W/O/W |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inner | DI water | Silicone oil 1 cSt | DI water |
| Middle | — | — | Silicone oil 50 cSt |
| Outer | Silicone oil 50 cSt | DI water/Glycerin 50 cP | DI water/Glycerin 220 cP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Liu, Z.; Tang, F.; Cheng, Y.; Tian, W.; Shi, W.; Zhang, J.M.; Zhang, Y. A Modular and Cost-Effective Droplet Microfluidic Device for Controlled Emulsion Production. Polymers 2024, 16, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060765
Jiang H, Liu Z, Tang F, Cheng Y, Tian W, Shi W, Zhang JM, Zhang Y. A Modular and Cost-Effective Droplet Microfluidic Device for Controlled Emulsion Production. Polymers. 2024; 16(6):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060765
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Hao, Zhaoyue Liu, Fengwei Tang, Yimin Cheng, Wei Tian, Woda Shi, Jia Ming Zhang, and Yajun Zhang. 2024. "A Modular and Cost-Effective Droplet Microfluidic Device for Controlled Emulsion Production" Polymers 16, no. 6: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060765
APA StyleJiang, H., Liu, Z., Tang, F., Cheng, Y., Tian, W., Shi, W., Zhang, J. M., & Zhang, Y. (2024). A Modular and Cost-Effective Droplet Microfluidic Device for Controlled Emulsion Production. Polymers, 16(6), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060765








