Manifestation of Donor–Acceptor Properties of N-Doped Polymer Carbon Dots During Hydrogen Bonds Formation in Different Solvents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of PCD and Preparation of Samples
2.2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussions
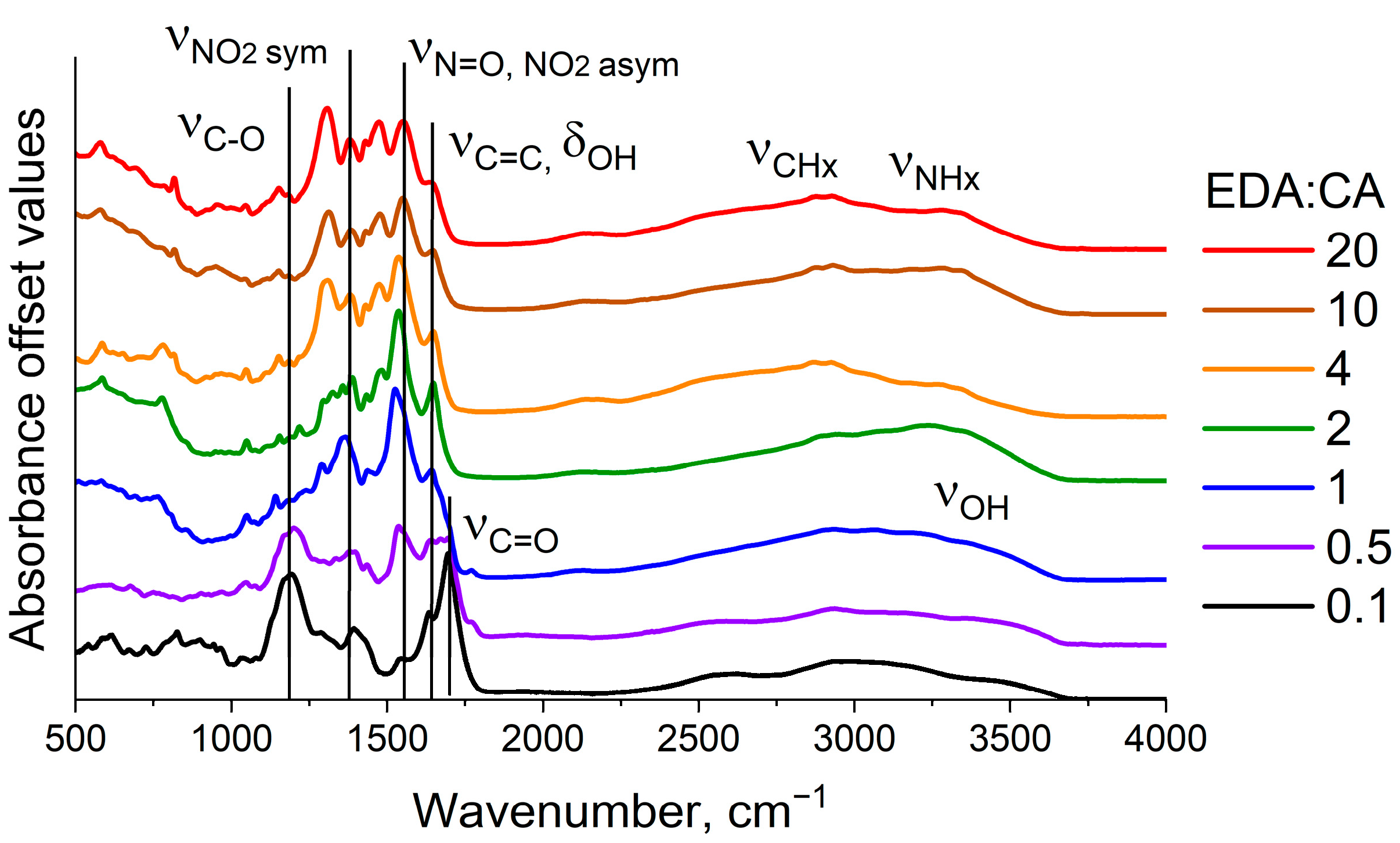
3.1. FTIR Absorption Spectroscopy of Synthesized Polymer Carbon Dots
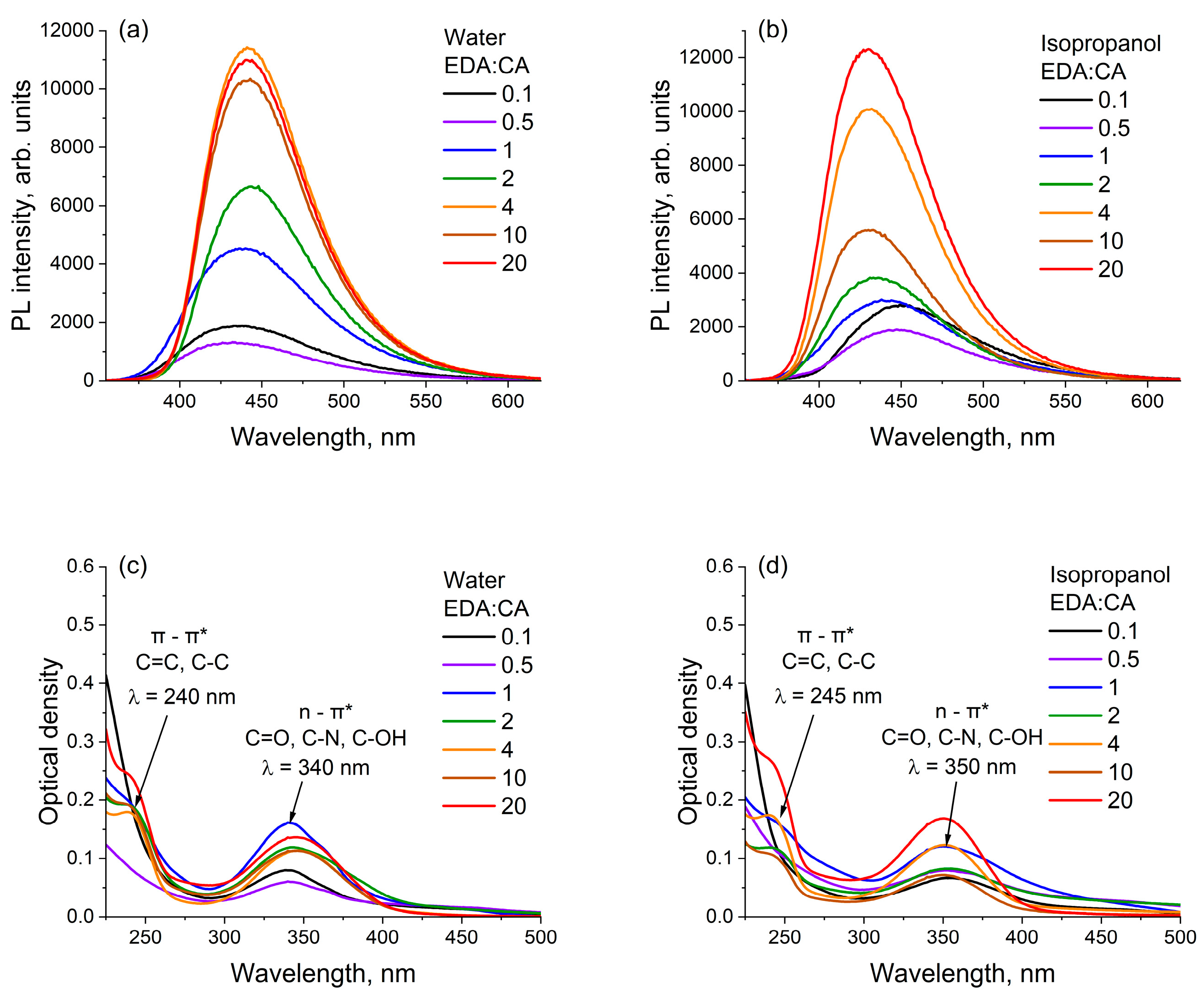
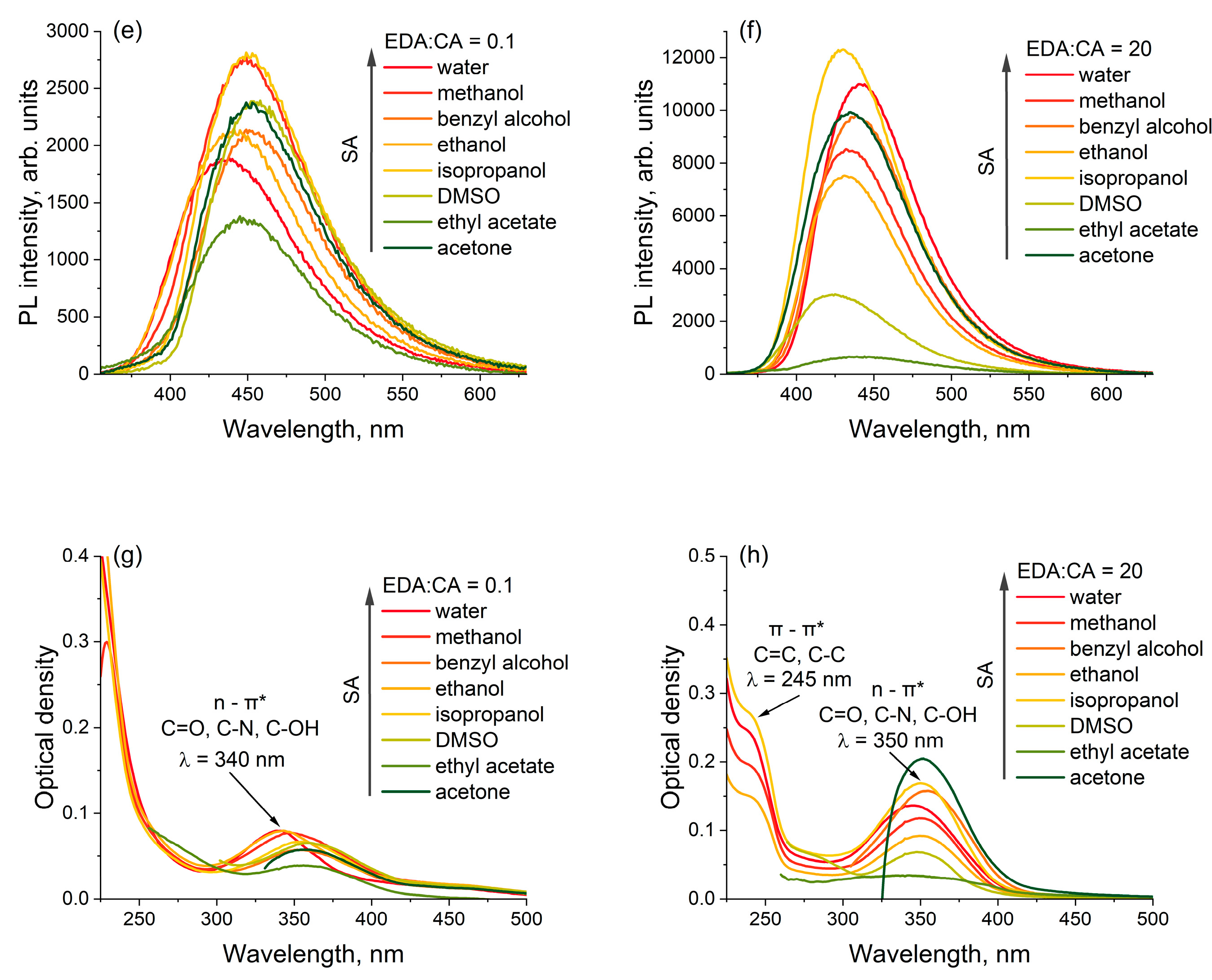
3.2. Optical Absorption and Photoluminescence Spectroscopy of Polymer Carbon Dots in Different Solvents
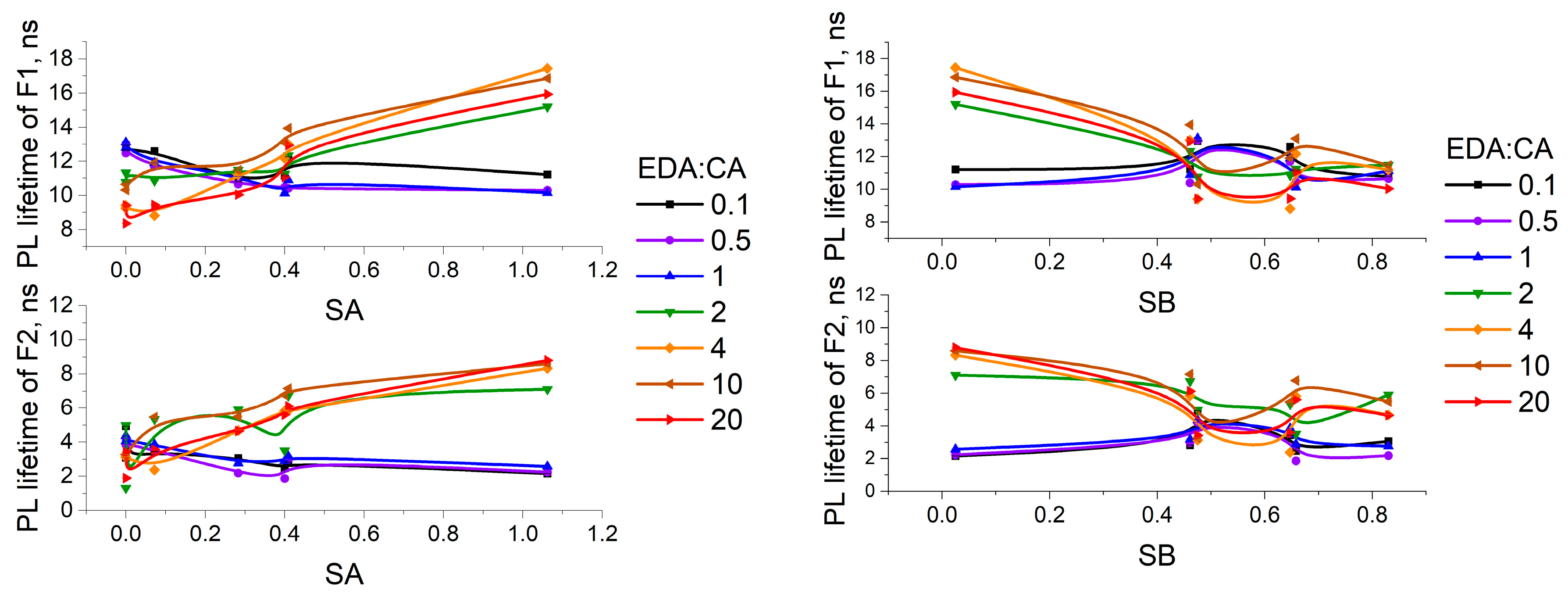
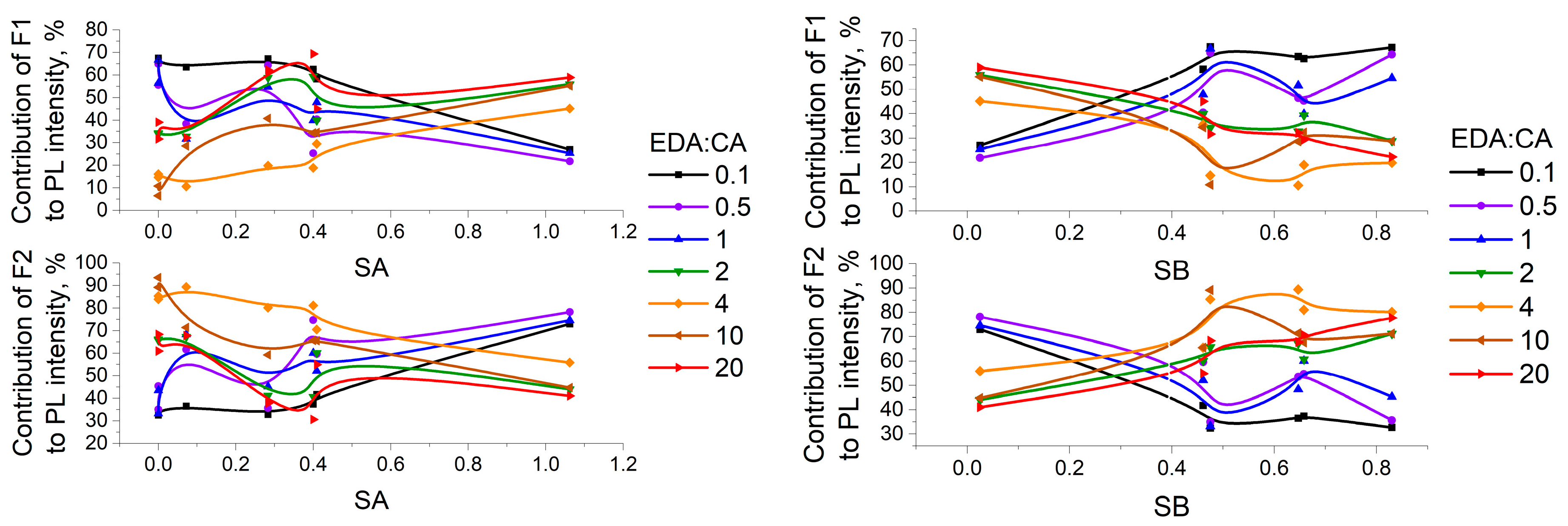
3.3. Study of PCD Photoluminescence Lifetimes in Different Solvents
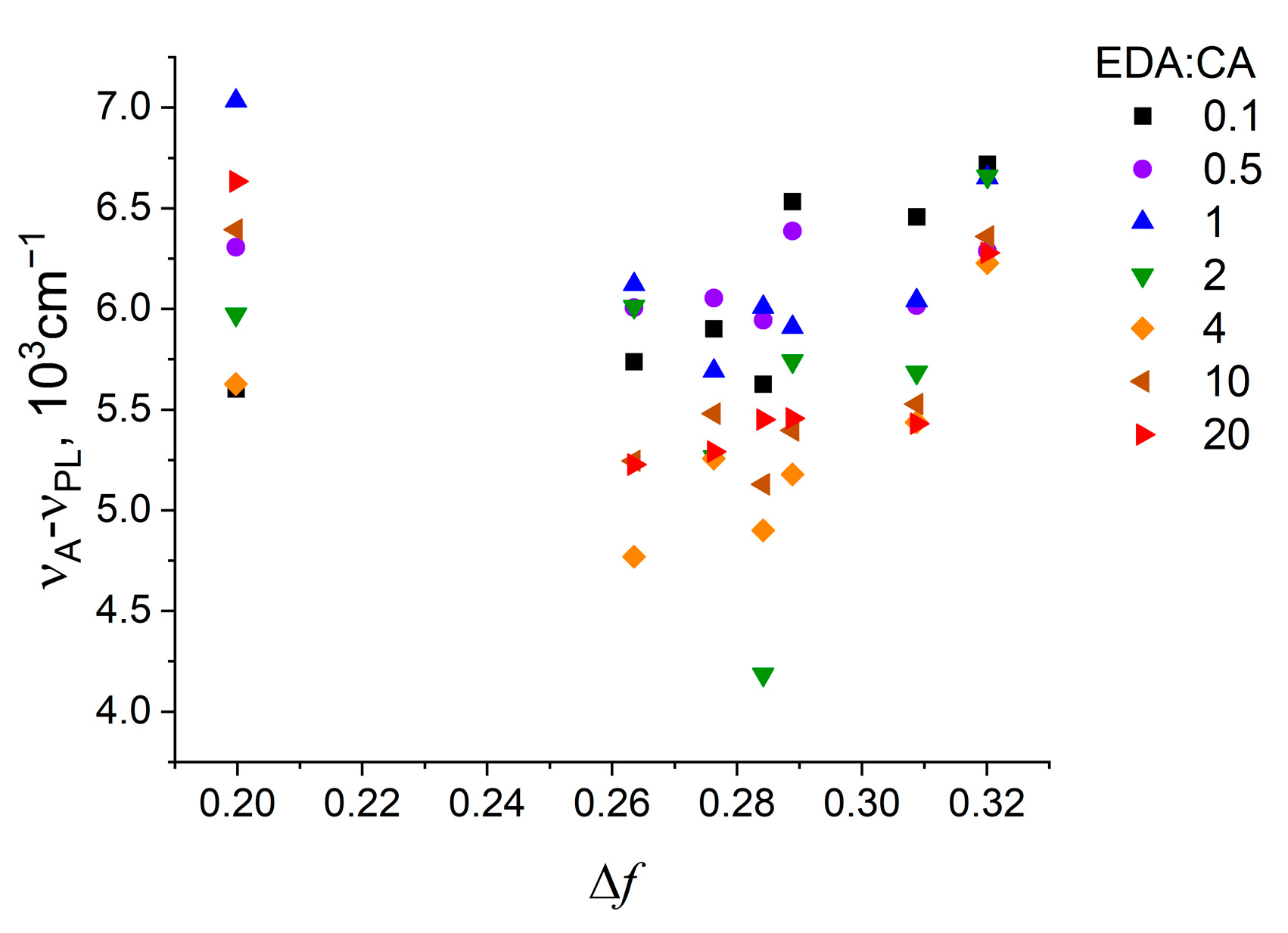
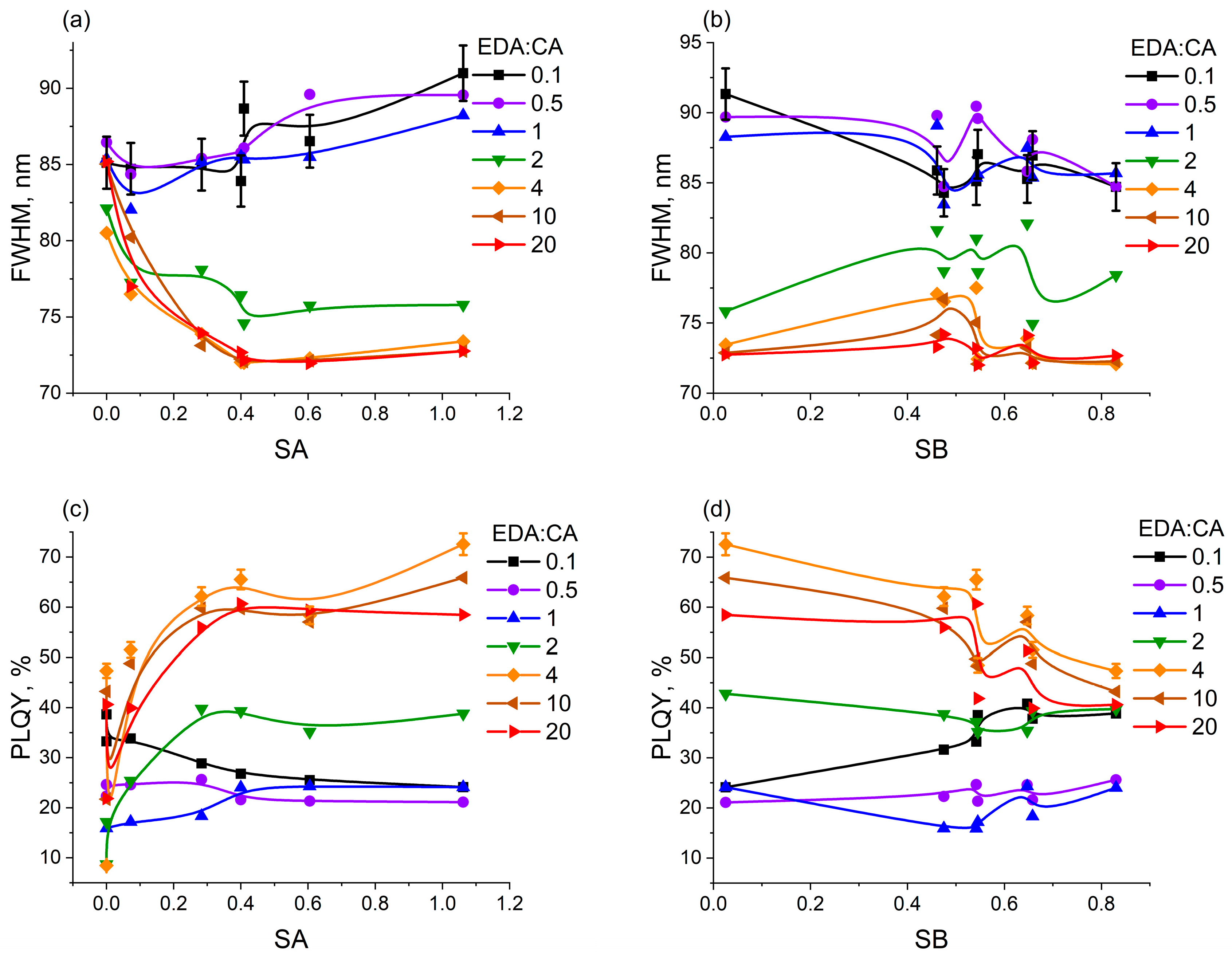
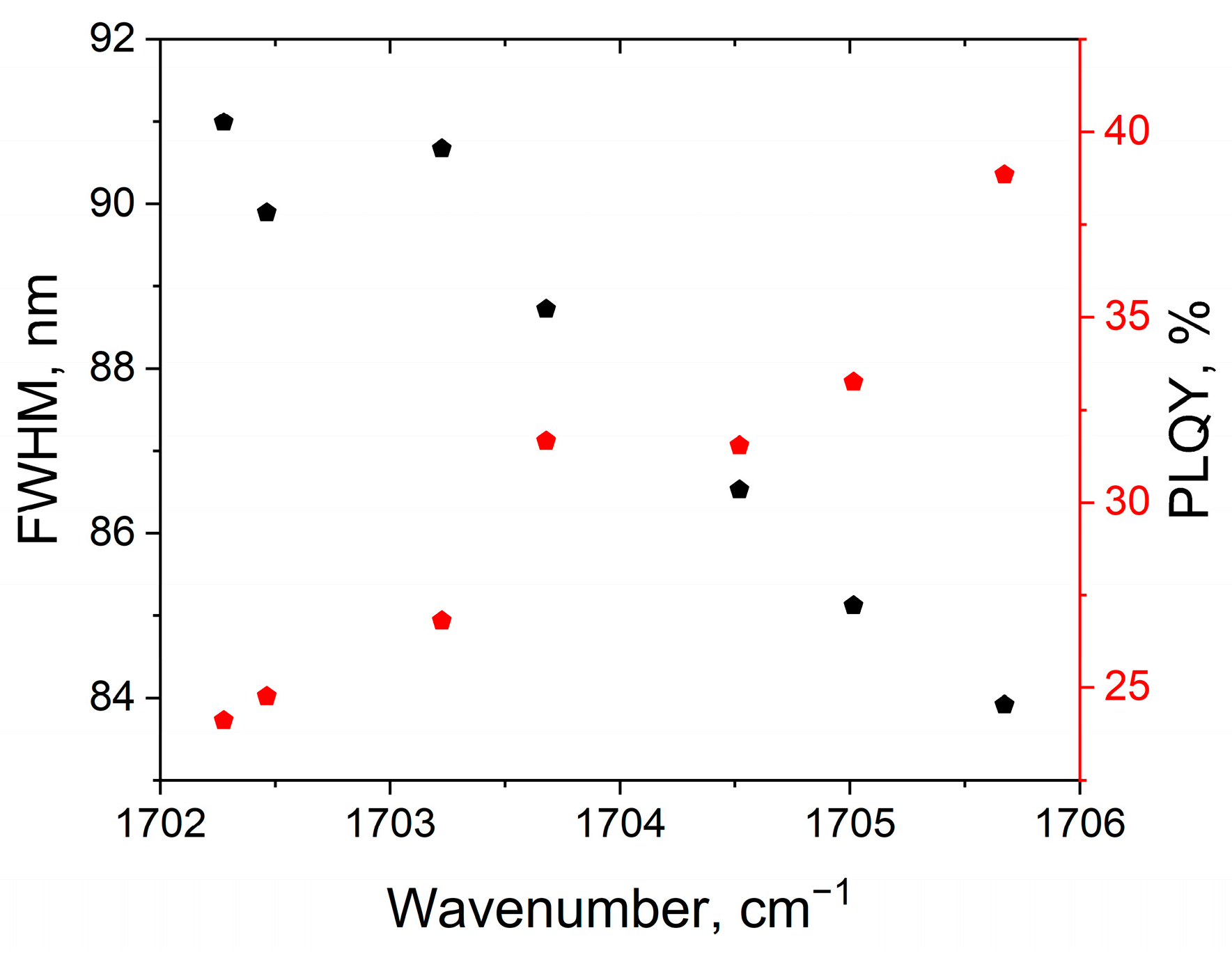
3.4. Correlations Between the Change in PCD Optical Properties in Different Solvents
3.5. Hydrogen Bonds Formation Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ozyurt, D.; Kobaisi, M.A.; Hocking, R.K.; Fox, B. Properties, Synthesis, and Applications of Carbon Dots: A Review. Carbon Trends 2023, 12, 100276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, S. The Light of Carbon Dots: From Mechanism to Applications. Matter 2022, 5, 110–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundi, A.; Chang, C.J. Recent Advances in Synthesis, Modification, Characterization, and Applications of Carbon Dots. Polymers 2022, 14, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, R.; Kumar, J.; Singh, M. Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Sensing Applications: A Review. Anal. Sci. 2024, 40, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhong, X.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; Zou, G.; Hou, H.; Ji, X. A Review of Carbon Dots in Synthesis Strategy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 498, 215468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, M.A.; Abdelrahman, H.H.; Fahmy, M.A.; Ebrahim, D.G.; Moustafa, A.H.E. Pure and Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as Fluorescent Probes for the Detection of Phenol Compounds and Antibiotics in Aquariums. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmanova, O.E.; Laptinskiy, K.A.; Burikov, S.A.; Chugreeva, G.N.; Dolenko, T.A. Implementing Neural Network Approach to Create Carbon-Based Optical Nanosensor of Heavy Metal Ions in Liquid Media. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 286, 122003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmanova, O.E.; Chugreeva, G.N.; Laptinskiy, K.A.; Burikov, S.A.; Dolenko, S.A.; Dolenko, T.A. Decoding Fluorescence Excitation-Emission Matrices of Carbon Dots Aqueous Solutions with Convolutional Neural Networks to Create Multimodal Nanosensor of Metal Ions. Mosc. Univ. Phys. Bull. 2023, 78, S202–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmeleva, M.Y.; Laptinskiy, K.A.; Dolenko, T.A. The Influence of pH on the Properties of Carbon Dots with Different Surface Functionalization: Sizes and Photoluminescence Quantum Yield. Opt. Spectrosc. 2023, 131, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.; Li, L.; Guo, J.; Jin, L.; Lu, J.; Huang, P.; Zhang, S.; Jiao, L. Highly Efficient Red-Emitting Carbon Dots as a “Turn-on” Temperature Probe in Living Cells. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 280, 121538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.; Yan, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Su, W. Orange-Red to NIR Emissive Carbon Dots for Antimicrobial, Bioimaging and Bacteria Diagnosis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 1250–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Luo, Z.; Wang, M. Novel Fluorescent Nanocellulose Hydrogel Based on Nanocellulose and Carbon Dots for Detection and Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Water. Foods 2022, 11, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espina-Casado, J.; Fontanil, T.; Fernández-González, A.; Cal, S.; Obaya, Á.J.; Díaz-García, M.E.; Badía-Laíño, R. Carbon Dots as Multifunctional Platform for Intracellular pH Sensing and Bioimaging. In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 346, 130555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Nitrogen and Chlorine Co-Doped Carbon Dots as a Highly Selective and Sensitive Fluorescent Probe for Sensing of pH, Tetracycline Detection and Cell Imaging. J. Fluoresc. 2024, 34, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Qu, Z.; Sharma, A.; Singh, M.; Tse, B.; Ostrikov, K.; Popat, A.; Sonar, P.; Kumeria, T. Ultra-Bright Green Carbon Dots with Excitation-Independent Fluorescence for Bioimaging. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2023, 13, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, F.; Moukham, H.; Olia, F.; Piras, D.; Ledda, S.; Salis, A.; Stagi, L.; Malfatti, L.; Innocenzi, P. Highly Photostable Carbon Dots from Citric Acid for Bioimaging. Materials 2022, 15, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervald, A.M.; Laptinskiy, K.A.; Chugreeva, G.N.; Burikov, S.A.; Dolenko, T.A. Quenching of Photoluminescence of Carbon Dots by Metal Cations in Water: Estimation of Contributions of Different Mechanisms. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 21617–21628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafeef, M.; Srivastava, I.; Aditya, T.; Pan, D. Carbon Dots: From Synthesis to Unraveling the Fluorescence Mechanism. Small 2024, 20, 2303937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demchenko, A.P.; Dekaliuk, M.O. The Origin of Emissive States of Carbon Nanoparticles Derived from Ensemble-Averaged and Single-Molecular Studies. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14057–14069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Li, X.H.; Chen, X.B.; Wei, J.S.; Li, X.B.; Xiong, H.M. Surface States of Carbon Dots and Their Influences on Luminescence. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 231101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Weber, F.; Weigert, F.; Wang, Y.; Choudhury, S.; Xiao, J.; Lauermann, I.; Resch-Genger, U.; Bande, A.; Petit, T. Influence of Surface Chemistry on Optical, Chemical and Electronic Properties of Blue Luminescent Carbon Dots. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 2056–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolenko, T.; Burikov, S.; Laptinskiy, K.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Shenderova, O.; Vlasov, I. Evidence of Carbon Nanoparticle–Solvent Molecule Interactions in Raman and Fluorescence Spectra. Phys. Status Solidi A Appl. Mater. Sci. 2015, 212, 2512–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, T.; Puskar, L.; Dolenko, T.; Choudhury, S.; Ritter, E.; Burikov, S.; Laptinskiy, K.; Brustowski, Q.; Schade, U.; Yuzawa, H.; et al. Unusual Water Hydrogen Bond Network around Hydrogenated Nanodiamonds. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 5185–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laptinskiy, K.A.; Bokarev, A.N.; Dolenko, S.A.; Plastun, I.L.; Sarmanova, O.E.; Shenderova, O.A.; Dolenko, T.A. The Energy of Hydrogen Bonds in Aqueous Suspensions of Nanodiamonds with Different Surface Functionalization. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2019, 50, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, P.; Vats, B.G.; Pulhani, V. Origin of Solvent and Excitation Dependent Emission in Newly Synthesized Amphiphilic Carbon Dots. J. Lumin. 2022, 244, 118742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fang, X.; He, F.; Bai, J.; Cheng, Y.; Weerasinghe, K.; Meng, X.; Xu, H.; Ding, T. Insights into Fluorophores of Dual-Emissive Carbon Dots Derived by Naphthalenediol Solvothermal Synthesis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 5207–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Neumann, C.; Scholtz, L.; Turchanin, A.; Resch-Genger, U.; Eigler, S. Polarity, Intramolecular Charge Transfer, and Hydrogen Bond Co-Mediated Solvent Effects on the Optical Properties of Graphene Quantum Dots. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengottuvelu, D.; Shaik, A.K.; Mishra, S.; Ahmad, H.; Abbaszadeh, M.; Hammer, N.I.; Kundu, S. Multicolor Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Environment-Dependent Emission Tuning. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 27742–27754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, J. Handbook of Solvents; Wypych, G., Ed.; ChemTech Publishing: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2001; pp. 583–616. ISBN 1-895198-24-0. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, R.T.; Boyd, R.N. Organic Chemistry, 4th ed.; Allyn and Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 1983; ISBN ISBN-10 0205058388. [Google Scholar]
- Hemdan, S.S. The Shift in the Behavior of Methylene Blue Toward the Sensitivity of Medium: Solvatochromism, Solvent Parameters, Regression Analysis and Investigation of Cosolvent on the Acidity Constants. J. Fluoresc. 2023, 33, 2489–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinar-Barranco, L.; Luque-Navarro, P.; Strnad, M.A.; Herrero-Foncubierta, P.; Crovetto, L.; Miguel, D.; Giron, M.D.; Orte, A.; Cuerva, J.M.; Salto, R.; et al. A Solvatofluorochromic Silicon-Substituted Xanthene Dye Useful in Bioimaging. Dyes Pigm. 2019, 168, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sıdır, İ.; Sarı, T.; Gülseven Sıdır, Y.; Berber, H. Synthesis, Solvatochromism and Dipole Moment in the Ground and Excited States of Substitute Phenol Derivative Fluorescent Schiff Base Compounds. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 346, 117075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.M.; Abelt, C.J. Dual-Sensor Fluorescent Probes of Surfactant-Induced Unfolding of Human Serum Albumin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 3912–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mera-Adasme, R.; Moraga, D.; Medina, R.; Domínguez, M. Mapping the Solute–Solvent Interactions for the Interpretation of the Three Types of Solvatochromism Exhibited by Phenolate-Based Dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 359, 119302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, X.; Ma, M. Preparation and Performance Study of Dye-Based Carbon Quantum Dots. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 150, 110541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonia, A.; Minervini, G.; Terracina, A.; Pramanik, A.; Martorana, V.; Sciortino, A.; Carbonaro, C.M.; Olla, C.; Sibillano, T.; Giannini, C.; et al. Dye-Derived Red-Emitting Carbon Dots for Lasing and Solid-State Lighting. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 21274–21286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Long, X.; Ma, Y.; Wu, S. Re-Discussion on the Essence of the Ultra-Bright Fluorescent Carbon Dots Synthesized by Citric Acid and Ethylenediamine. Opt. Mater. 2023, 135, 113311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles in fluorescence spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-387-31278-1. [Google Scholar]
- Vervald, A.M.; Laptinskiy, K.A.; Khmeleva, M.Y.; Dolenko, T.A. IR absorption spectroscopy of carbon dots from citric acid and ethylenediamine: The relationship between their photoluminescence and structure. Opt. Spectrosc. 2024, 132, 193–198. Available online: https://journals.ioffe.ru/articles/58740 (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Sundaraganesan, N.; Saleem, H.; Mohan, S.; Ramalingam, M.; Sethuraman, V. FTIR, FT-Raman Spectra and Ab Initio DFT Vibrational Analysis of 2-Bromo-4-Methyl-Phenylamine. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 62, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Ahmad, A.; Mohamed, N. Characterization of Novel Castor Oil-Based Polyurethane Polymer Electrolytes. Polymers 2015, 7, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, R.W.; Brill, T.B. Vibrational Behavior of the −NO2 Group in Energetic Compounds. Appl. Spectrosc. 2005, 59, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talone, C.J.; Gao, J.; Lynch, J.R.; Tanu, R.M.; Deyrup, S.T. Determination of the Ground- and Excited-State Dipole Moments of Bromocresol Purple in Protic and Aprotic Solvents. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 156, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.; Xu, W.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S. Surface-State Triggered Solvatochromism of Carbonized Polymer Dot and Its Two-Photon Luminescence. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 2567–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Jafarieh, P.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Salamat-Ahangari, R.; Pourhassan-Moghaddam, M.; Jamshidi-Ghaleh, K. Solvent Effect on the Absorption and Emission Spectra of Carbon Dots: Evaluation of Ground and Excited State Dipole Moment. BMC Chem. 2021, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Malfatti, L.; Innocenzi, P. Citric Acid Derived Carbon Dots, the Challenge of Understanding the Synthesis-Structure Relationship. C 2020, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.-W.; Lee, S.; Chang, C.-J.; Liu, L. Recent Progress of Carbon Dot Precursors and Photocatalysis Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Hanif, M.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Hu, D.; et al. Synergistic Effects of Hydrogen Bonds and the Hybridized Excited State Observed for High-Efficiency, Deep-Blue Fluorescent Emitters with Narrow Emission in OLED Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naka, K.; Sato, H.; Higashi, M. Theoretical Study of the Mechanism of the Solvent Dependency of ESIPT in HBT. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 20080–20085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Xiao, L.; Aryee, A.A.; Sun, Y.; Yang, R.; Meng, H.; Qu, L.; Lin, Y.; et al. Hydrogen-Bond-Induced Emission of Carbon Dots for Wash-Free Nucleus Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 9259–9265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.B.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.L.; Zhang, X.X.; Wen, S.Y.; Yi, H.B.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.B. Enhancing the Anti-Solvatochromic Two-Photon Fluorescence for Cirrhosis Imaging by Forming a Hydrogen-Bond Network. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7473–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall Bishen, S.; Adhikari, M.; Pokharia, S.; Mishra, H. The Effect of Polarity and Hydrogen Bonding on the Electronic and Vibrational Structure of the Salicylate Anion in Acetonitrile and Water: Implicit and Explicit Solvation Approaches. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 29569–29587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buisson, R.; Vial, J.C. Transfer Inside Pairs of Pr3+ in LaF3 Studied by Up-Conversion Fluorescence. J. Phys. Lett.-Paris 1981, 42, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Felipe, A.; Cook, A.G.; Abberley, J.P.; Walker, R.; Storey, J.M.D.; Imrie, C.T. An FT-IR Spectroscopic Study of the Role of Hydrogen Bonding in the Formation of Liquid Crystallinity for Mixtures Containing Bipyridines and 4-Pentoxybenzoic Acid. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 108164–108179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, I.S.; Liu, X.; Jin, Y.; Sun, J.; Lee, Y.J. Stoichiometric Analysis of Competing Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonds Using Infrared Spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 23481–23488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Bai, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, R.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z. DNA Tweezer-Assembled, Regenerated Nanosensor for One-Step and Sustainable Detection of Viral RNA and Hg2+. Microchem. J. 2024, 204, 111157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algharagholy, L.A.; García-Suárez, V.M.; Dhahi, H.A. Stable and Robust Discriminative Sensing of Illicit Drug Molecules Utilizing a Specific Geometry of Nanotubes. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2024, 39, 101281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Chiang, W.-H.; Ilhami, F.B.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Cheng, C.-C. Water-Soluble Graphene Quantum Dot-based Polymer Nanoparticles with Internal Donor/Acceptor Heterojunctions for Efficient and Selective Detection of Cancer Cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 637, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh Hoang, N.; Thi Bich Ngoc, N.; Thi Lan Huong, P.; Dao, Q.-D.; Nam Anh, T.; Thi Hai Linh, D.; Nguyen, V.; Tuan Tu, L.; Xuan Nang, H.; Dao, V.-D. Hydrogen Bonding Effect on pH-Sensing Mechanism of Carbon Dots. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 160, 111944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Xu, Y. Hydrogen Bonding-Mediated Assembly of Carbon dot@Zr-Based Metal Organic Framework as a Multifunctional Fluorescence Sensor for Chlortetracycline, pH and Temperature Detection. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 13021–13029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Solvent | SA | SB | Δf |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water—H2O | 1.062 | 0.025 | 0.32 |
| Methanol—CH4O | 0.605 | 0.545 | 0.31 |
| Benzyl alcohol—C7H8O | 0.409 | 0.461 | 0.21 |
| Ethanol—C2H6O | 0.400 | 0.658 | 0.29 |
| Isopropanol—C3H8O | 0.283 | 0.830 | 0.28 |
| DMSO—C2H6OS | 0.072 | 0.647 | 0.26 |
| Ethyl acetate—C4H8O2 | 0 | 0.542 | 0.20 |
| Acetone—C3H6O | 0 | 0.475 | 0.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korepanova, A.; Laptinskiy, K.; Dolenko, T. Manifestation of Donor–Acceptor Properties of N-Doped Polymer Carbon Dots During Hydrogen Bonds Formation in Different Solvents. Polymers 2024, 16, 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243585
Korepanova A, Laptinskiy K, Dolenko T. Manifestation of Donor–Acceptor Properties of N-Doped Polymer Carbon Dots During Hydrogen Bonds Formation in Different Solvents. Polymers. 2024; 16(24):3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243585
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorepanova, Anisiya, Kirill Laptinskiy, and Tatiana Dolenko. 2024. "Manifestation of Donor–Acceptor Properties of N-Doped Polymer Carbon Dots During Hydrogen Bonds Formation in Different Solvents" Polymers 16, no. 24: 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243585
APA StyleKorepanova, A., Laptinskiy, K., & Dolenko, T. (2024). Manifestation of Donor–Acceptor Properties of N-Doped Polymer Carbon Dots During Hydrogen Bonds Formation in Different Solvents. Polymers, 16(24), 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243585






