Effect of Side Substituent on Comb-like Polysiloxane Membrane Pervaporation Properties During Recovery of Alcohols C2-C4 from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
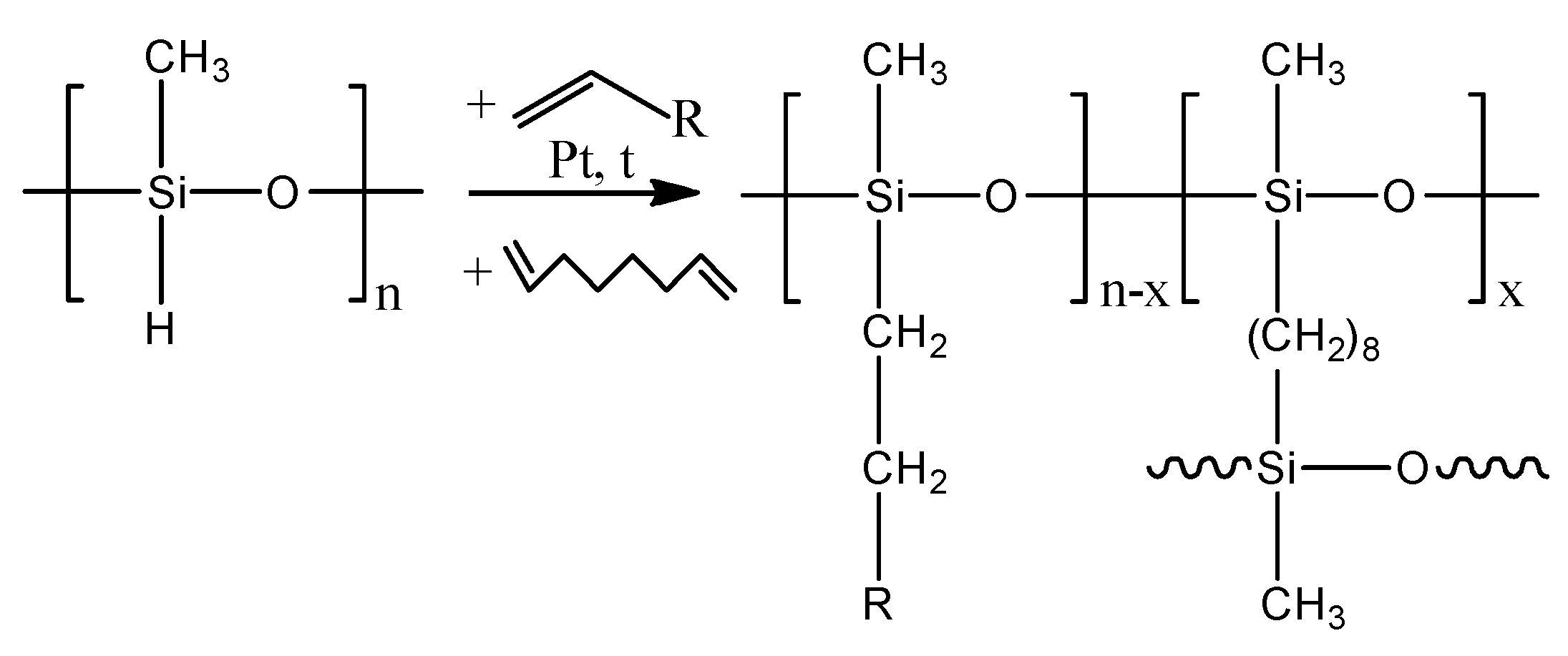
2.2. Synthesis and Production of Membranes
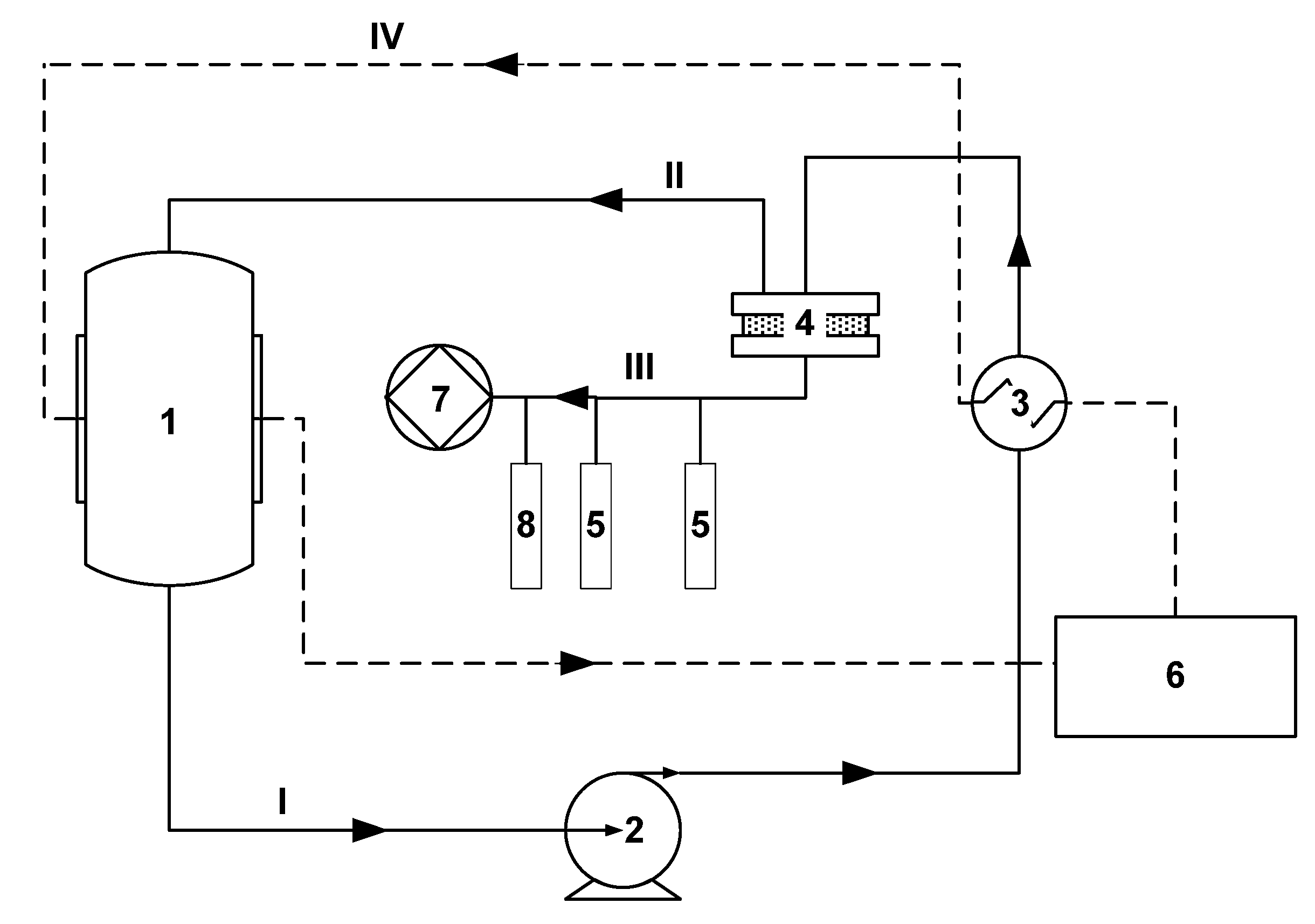
2.3. Vacuum Pervaporation
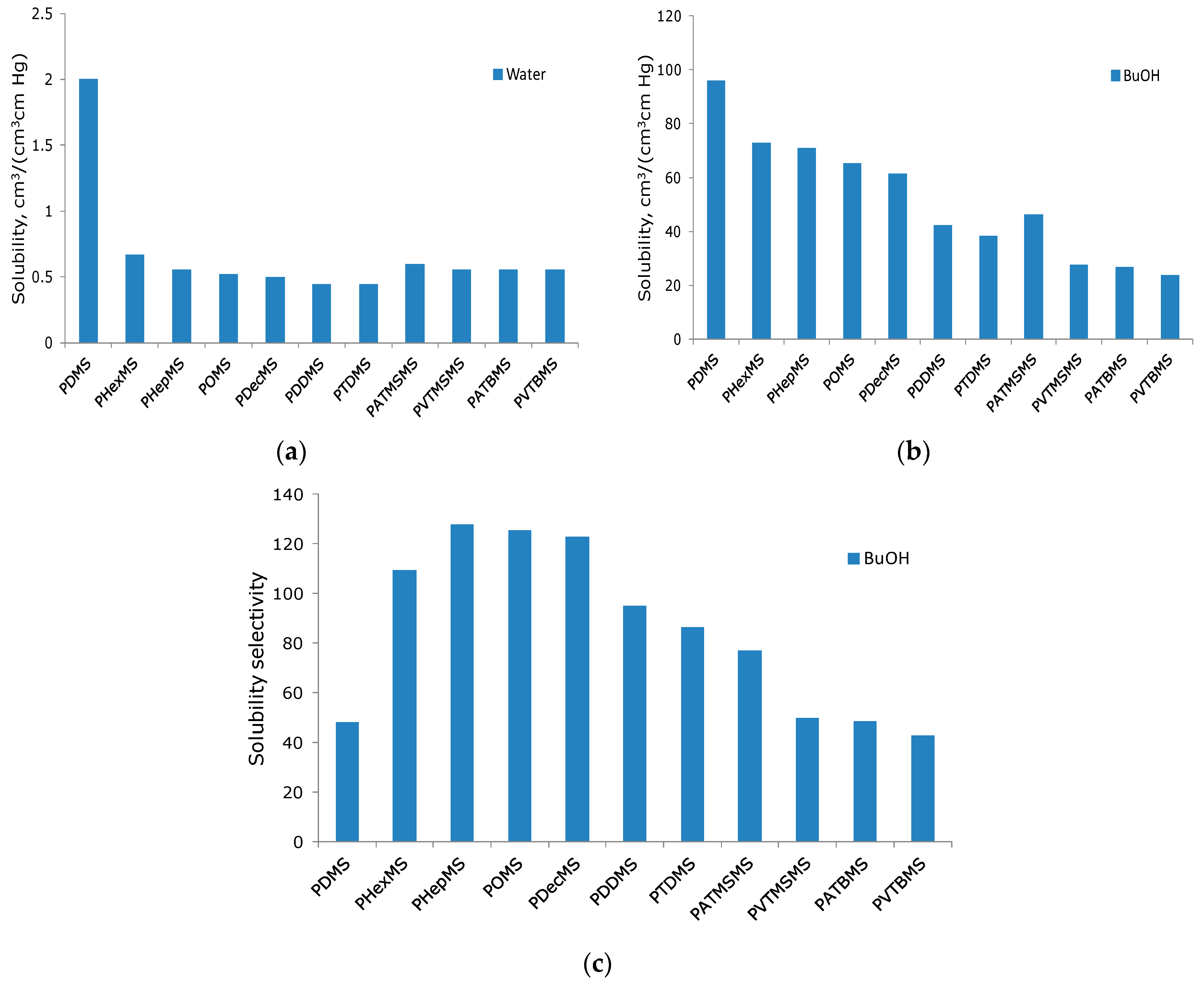
2.4. Determination of Sorption and Solubility Coefficients
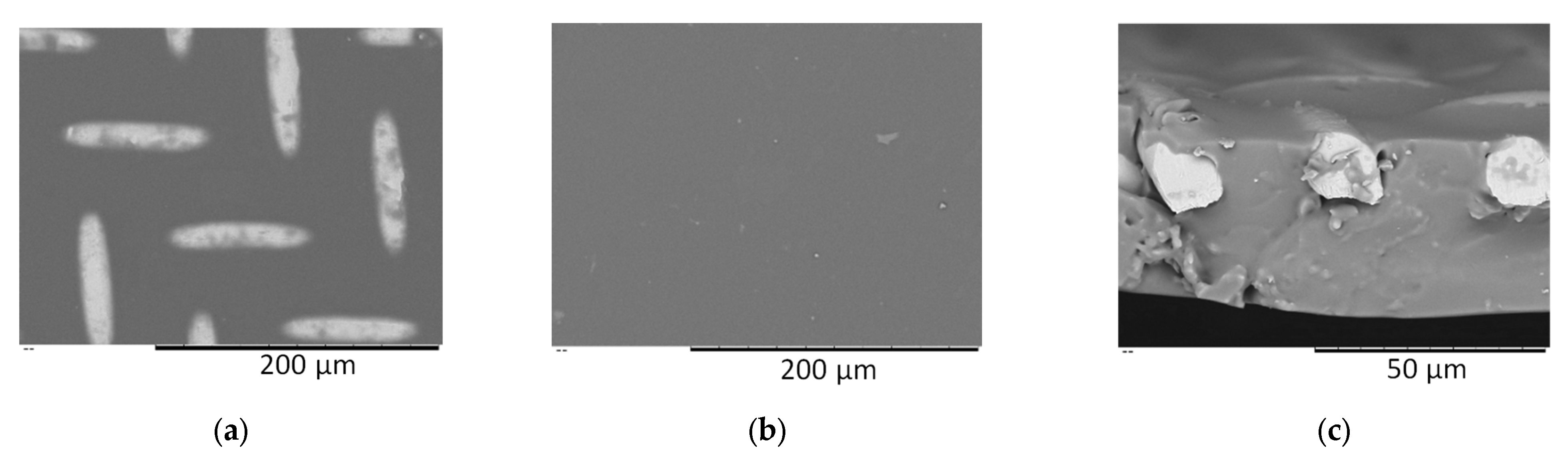
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results and Dicussion
3.1. Synthesis of Membranes from Comb-like Polysiloxane
- -
- The use of the reaction mixture as a molding solution;
- -
- The use of a single catalyst for the modification and cross-linking of the membrane material;
- -
- The absence of stages of polymer recovery and purification (low solvent consumption);
- -
- The simplicity of the modification of the material chemical structure (variability in the use of modifying agents with terminal double bonds);
- -
- Little time spent on membrane production.
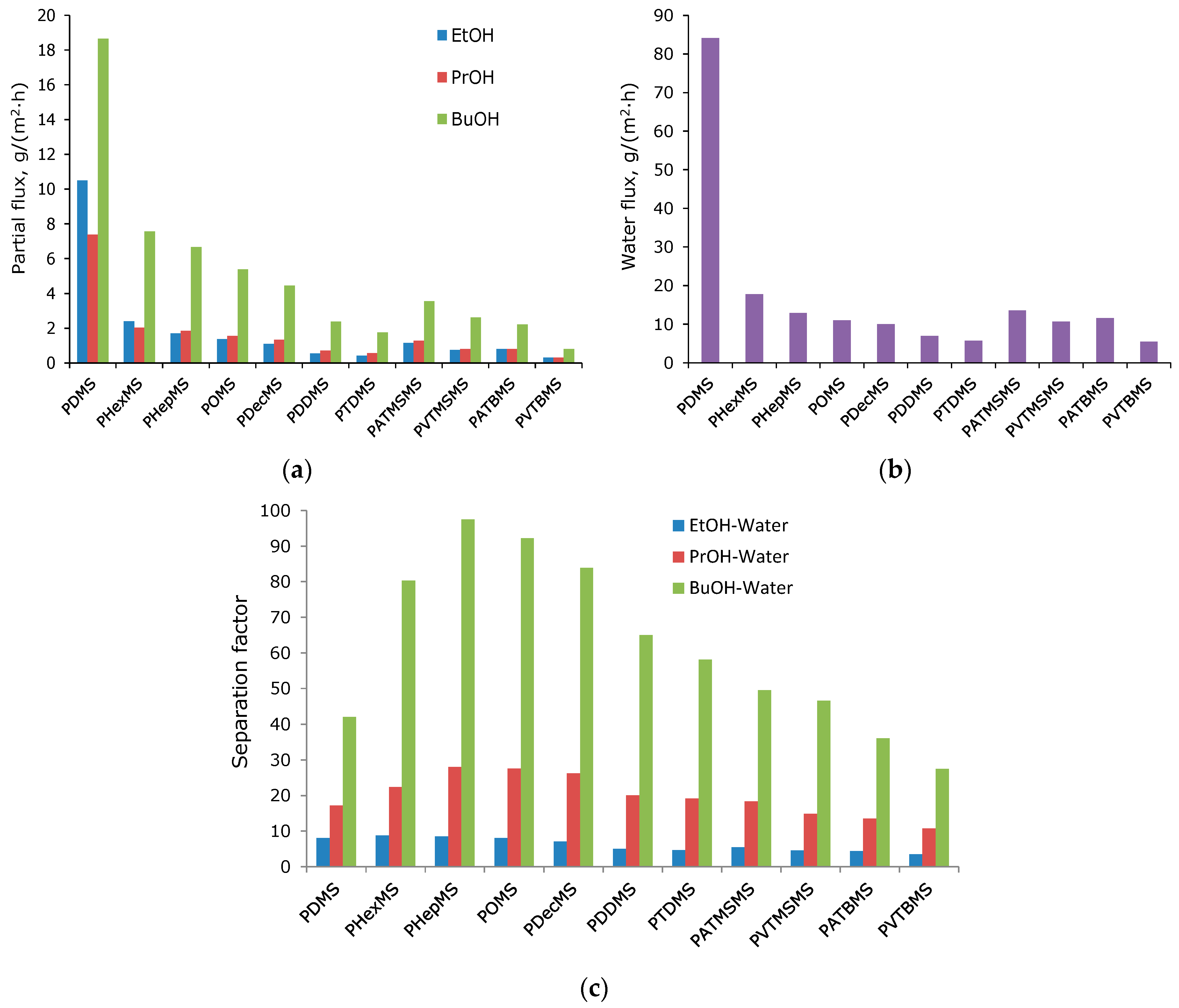
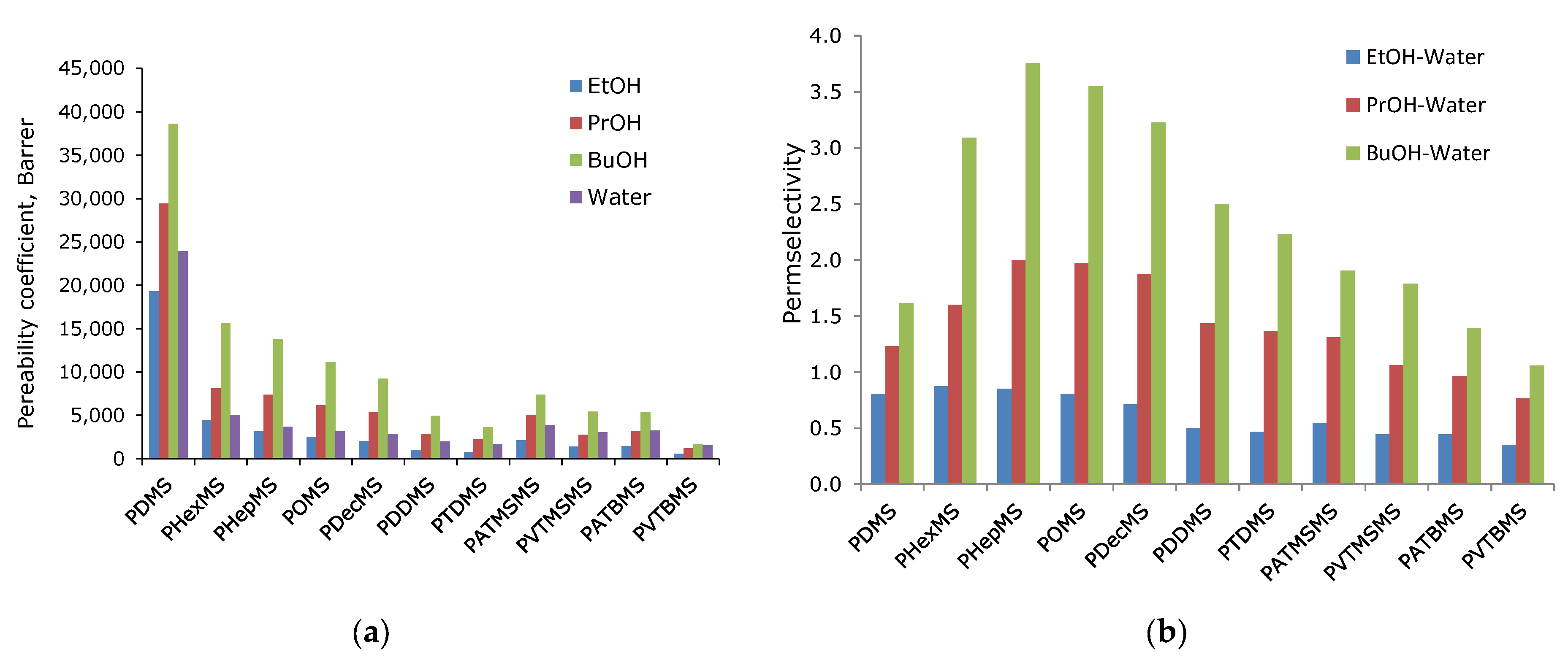
3.2. Transport Properties of the Obtained Membranes Based on Comb-like Polysiloxane
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| yi, xi, wi | the component mass fraction [g ∙ g−1] |
| Ji | component mass permeate flux [kg ∙ m−2 ∙ h−1] |
| l | membrane selective layer thickness [cm] |
| Mi | molar mass of the component [kg ∙ mol−1] |
| Pi | permeability coefficient [Barrer] |
| Si | solubility coefficient [cm3 ∙ cm−3 ∙ cm Hg−1)] |
| αi/j | separation factor alcohol/water [-] |
| ni | amount of substance [mol] |
| mi | mass of component [g] |
| Vi | volume of component [cm3] |
| ρi | density of component [g/m3] |
| BuOH | n-butanol |
| PrOH | n-propanol |
| EtOH | ethanol |
| W | water |
References
- Majone, M.; Aulenta, F.; Dionisi, D.; D’Addario, E.N.; Sbardellati, R.; Bolzonella, D.; Beccari, M. High-rate anaerobic treatment of Fischer–Tropsch wastewater in a packed-bed biofilm reactor. Water. Res. 2010, 44, 2745–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Klerk, A. Fischer–Tropsch Refining; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; 619p. [Google Scholar]
- Krylova, A.Y.; Kryazhev, Y.G.; Kulikova, M.V.; Kurkin, V.I.; Lyadov, A.S.; Sagitov, S.A. Synthesis of Alcohols from CO and H2 on Iron Catalysts Containing Carbon Fiber. Solid Fuel Chem. 2011, 45, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylova, A.Y.; Kurkin, V.I.; Kulikova, M.V.; Lyadov, A.S.; Sagitov, S.A. Synthesis of Monohydric Alcohols from CO and H2 on Fe/Sibunit Catalysts. Solid Fuel Chem. 2011, 45, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölbel, H.; Ralek, M. The Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis in the Liquid Phase. Cat. Rev 1980, 21, 225–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeji, T.C.; Qureshi, N.; Blaschek, H.P. Butanol fermentation research: Upstream and downstream manipulations. Chem. Rec. 2004, 4, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wei, W.; Jin, W. Pervaporation Membranes for Biobutanol Production. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, T.; Yanagishita, H.; Kitamoto, D.; Haraya, K.; Nakane, T.; Matsuda, H.; Koura, N.; Sano, T. Production of highly concentrated ethanol in a coupled fermentation/pervaporation process using silicalite membranes. Biotechnol. Tech. 1997, 11, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozicka, A.; Niemisto, J.; Keiski, R.L.; Kujawski, W. Apparent and intrinsic properties of commercial PDMS based membranes in pervaporative removal of acetone, butanol and ethanol from binary aqueous mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, A.; Friedl, A. Investigation of pervaporation performance of POMS membrane during separation of butanol from water and the effect of added acetone and ethanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 170, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, I.L.; Ushakov, N.V.; Volkov, V.V.; Finkel’shtein, E.S. Polydimethylsilalkylene-Dimethylsiloxanes as Advanced Membrane Materials for Thermopervaporative Recovery of Oxygenates from Aqueous Reaction Media. Petr. Chem. 2016, 56, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zák, M.; Klepic, M.; Štastná, L.C.; Sedláková, Z.; Vychodilová, H.; Hovorka, S.; Friess, K.; Randová, A.; Brozová, L.; Jansen, J.C.; et al. Selective removal of butanol from aqueous solution by pervaporation with a PIM-1 membrane and membrane aging. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, I.L.; Malakhov, A.O.; Khotimsky, V.S.; Litvinova, E.G.; Finkelshtein, E.S.; Ushakov, N.V.; Volkov, V.V. Novel PTMSP-based membranes containing elastomeric fillers: Enhanced 1-butanol/water pervaporation selectivity and permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jang, K.S.; Galebach, P.; Gilbert, C.; Tompsett, G.; Conner, W.C.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Seeded growth, silylation, and organic/water separation properties of MCM-48 membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtin, D.S.; Kulikov, L.A.; Maksimov, A.L.; Volkov, A.V. Stabilization of gas transport properties of composite membranes based on poly [1-trimethylsilyl-1-propine] by introducing porous aromatic frameworks nanoparticles obtained by the Friedel-Crafts reaction. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2020, 93, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtin, D.S.; Kulikov, L.A.; Legkov, S.A.; Khotimskiy, V.S.; Levin, I.S.; Borisov, I.L.; Maksimov, A.L.; Volkov, V.V.; Karakhanov, E.A.; Volkov, A.V. Aging of thin-film composite membranes based on PTMSP loaded with porous aromatic frameworks. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemoto, M.; Negishi, H.; Sakaki, K.; Ikegami, T.; Chohnan, S.; Nitta, Y.; Ohta, H. Efficient butanol recovery from acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation cultures grown on sweet sorghum juice by pervaporation using silicalite-1 membrane. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhmakin, V.V.; Teplyakov, V.V. The evaluation of the C1–C4 hydrocarbon permeability parameters in the thin film composite membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 186, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, I.L.; Grushevenko, E.A.; Podtynnikov, I.A.; Bakhtin, D.S.; Bondarenko, G.N. Novel Membrane Material Based on Polybutadiene and Polydimethylsiloxane for Gas Separation and Hydrophobic Pervaporation. Petr. Chem. 2018, 58, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W.; Wijmans, J.G.; Huang, Y. Permeability, permeance and selectivity: A preferred way of reporting pervaporation performance data. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 348, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawska, A.; Knozowska, K.; Kujawa, J.; Kujawski, W. Influence of downstream pressure on pervaporation properties of PDMS and POMS based membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 159, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, I.L.; Golubev, G.S.; Vasilevsky, V.P.; Volkov, A.V.; Volkov, V.V. Novel hybrid process for bio-butanol recovery: Thermopervaporation with porous condenser assisted by phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelshtein, E.; Makovetskii, K.; Gringolts, M.; Rogan, Y.; Golenko, T.; Starannikova, L.; Yampolskii, Y.; Shantarovich, V.; Suzuki, T. Addition-type polynorbornene with Si(CH3)3 side group: Synthesis, gas permeation and free volume. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 7022–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starannikova, L.; Pilipenko, M.; Belov, N.; Yampolskii, Y.; Gringolts, M.; Finkelshtein, E. Addition-type polynorbornene with Si(CH3)3 side groups: Detailed study of gas permeation and thermodynamic properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 323, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Li, J.; An, V. The potential of the first corporation to produce biofuels as a result of fermentation: In terms of energy consumption. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grushevenko, E.A.; Borisov, I.L.; Volkov, A.V. High-Selectivity Polysiloxane Membranes for Gases and Liquids Separation (A Review). Pet. Chem. 2021, 61, 959–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, R.S.; Raharjo, R.; Toy, L.G.; Lin, H.; Freeman, B.D. Self-Consistent Model of Concentration and Temperature De-pendence of Permeability in Rubbery Polymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Drioli, E.; Golemme, G. Membrane Gas Separation: A Review/State of the Art. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 4638–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, T.C.; Gupta, R.P.; Turk, B.S.; Freeman, B.D. Mixed-Gas Permeation of Syngas Components in Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) and Poly(1-Trimethylsilyl-1-Propyne) at Elevated Temperatures. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 191, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.B. Sorption and Permeation Behaviors of a Series of Olefins and Nitrogen through PDMS Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 299, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.; Ferreira, A.; Mendes, A. Study and Optimization of Aroma Recovery from Beer by Pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 341, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börjesson, J.; Karlsson, H.O.E.; Trägårdh, G. Pervaporation of a model apple juice aroma solution: Comparison of membrane performance. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 119, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, J.; Trägårdh, G.; Lipnizki, F. The Influence of Permeant and Membrane Properties on Mass Transfer in Pervaporation of Volatile Organic Compounds from Dilute Aqueous Solutions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 1199–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, I.; Podtynnikov, I.; Grushevenko, E.; Scharova, O.; Anokhina, T.; Makaev, S.; Volkov, A.; Volkov, V. High Selective Composite Polyalkylmethylsiloxane Membranes for Pervaporative Removal of MTBE from Water: Effect of Polymer Side-Chain. Polymers 2020, 12, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.; Brisdon, B.J.; England, R.; Field, R.W. Performance of PDMS and Organofunctionalised PDMS Membranes for the Pervaporative Recovery of Organics from Aqueous Streams. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 137, 63–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, I.L.; Grushevenko, E.A.; Anokhina, T.S.; Bakhtin, D.S.; Levin, I.S.; Bondarenko, G.N.; Volkov, V.V.; Volkov, A.V. Influence of side chains assembly on the structure and transport properties of comb-like polysiloxanes in hydrocarbon separation. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 22, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grushevenko, E.A.; Borisov, I.L.; Bakhtin, D.S.; Legkov, S.A.; Bondarenko, G.N.; Volkov, A.V. Membrane material based on octyl-substituted polymethylsiloxane for separation of C3/C1 hydrocarbons. Petr. Chem. 2017, 57, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Symbol of Membrane | Polymer |
|---|---|
| PHexMS | Polyhexylmethylsiloxane |
| PHepMS | Polyheptylmethylsiloxane |
| POMS | Polyoctylmethylsiloxane |
| PDecMS | Polydecylmethylsiloxane |
| PDDMS | Polydodecylmethylsiloxane |
| PTDMS | Polytetradecylmethylsiloxane |
| PVTBMS | Poly-3,3-dimethylbutylmethylsiloxane |
| PATBMS | Poly-4,4-dimethylpentene-1methylsiloxane |
| PVTMSMS | Poly-3,3-dimethylsilbutylmethylsiloxane |
| PATMSMS | Poly-4,4-dimethylsilpentylmethylsiloxane |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| Membrane | Partial Flux, g/(m2 h) | Separation Factor (X/Water) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BuOH | PrOH | EtOH | Water | BuOH | PrOH | EtOH | |
| PDMS | 18.7 | 7.4 | 10.5 | 84.1 | 42 | 17.2 | 8.1 |
| PHexMS | 7.6 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 17.8 | 80.4 | 22.4 | 8.7 |
| PHepMS | 6.7 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 12.9 | 97.5 | 28.0 | 8.5 |
| POMS | 5.4 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 11.0 | 92.3 | 27.5 | 8.1 |
| PDecMS | 4.4 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 10.0 | 83.9 | 26.2 | 7.1 |
| PDDMS | 2.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 6.9 | 65.0 | 20.1 | 5.0 |
| PTDMS | 1.8 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 5.7 | 58.1 | 19.1 | 4.7 |
| PATMSMS | 3.6 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 13. 6 | 49.5 | 18.3 | 5.5 |
| PVTMSMS | 2.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 10.7 | 46.5 | 14.9 | 4.5 |
| PATBMS | 2.2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 11.6 | 36.1 | 13.5 | 4.4 |
| PVTBMS | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 5.5 | 27.5 | 10.7 | 3.5 |
| Membrane | Permeability Coefficient, Barrer | Separation Factor (X/Water) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BuOH | PrOH | EtOH | Water | BuOH | PrOH | EtOH | |
| PDMS | 38,700 | 29,450 | 19,330 | 23,930 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| PHexMS | 15,600 | 8100 | 4420 | 5060 | 3.1 | 1.6 | 0.9 |
| PHepMS | 13,800 | 7360 | 3130 | 3680 | 3.8 | 2.0 | 0.9 |
| POMS | 11,140 | 6180 | 2530 | 3140 | 3.5 | 2.0 | 0.8 |
| PDecMS | 9200 | 5340 | 2025 | 2850 | 3.2 | 1.9 | 0.7 |
| PDDMS | 4930 | 2830 | 990 | 1970 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 0.5 |
| PTDMS | 3630 | 2220 | 760 | 1620 | 2.2 | 1.4 | 0.5 |
| PATMSMS | 7360 | 5060 | 2120 | 3870 | 1.9 | 1.3 | 0.5 |
| PVTMSMS | 5430 | 2760 | 1380 | 3040 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 0.5 |
| PATBMS | 5340 | 3190 | 1470 | 3250 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| PVTBMS | 1660 | 1200 | 550 | 1570 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grushevenko, E.; Chechenov, I.; Rokhmanka, T.; Anokhina, T.; Bazhenov, S.; Borisov, I. Effect of Side Substituent on Comb-like Polysiloxane Membrane Pervaporation Properties During Recovery of Alcohols C2-C4 from Water. Polymers 2024, 16, 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243530
Grushevenko E, Chechenov I, Rokhmanka T, Anokhina T, Bazhenov S, Borisov I. Effect of Side Substituent on Comb-like Polysiloxane Membrane Pervaporation Properties During Recovery of Alcohols C2-C4 from Water. Polymers. 2024; 16(24):3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243530
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrushevenko, Evgenia, Islam Chechenov, Tatyana Rokhmanka, Tatiana Anokhina, Stepan Bazhenov, and Ilya Borisov. 2024. "Effect of Side Substituent on Comb-like Polysiloxane Membrane Pervaporation Properties During Recovery of Alcohols C2-C4 from Water" Polymers 16, no. 24: 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243530
APA StyleGrushevenko, E., Chechenov, I., Rokhmanka, T., Anokhina, T., Bazhenov, S., & Borisov, I. (2024). Effect of Side Substituent on Comb-like Polysiloxane Membrane Pervaporation Properties During Recovery of Alcohols C2-C4 from Water. Polymers, 16(24), 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243530











