The Multi-Challenges of the Multi-Ion-Imprinted Polymer Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Multi-Ion-Imprinted Polymers Utilized in Multiple Scenarios
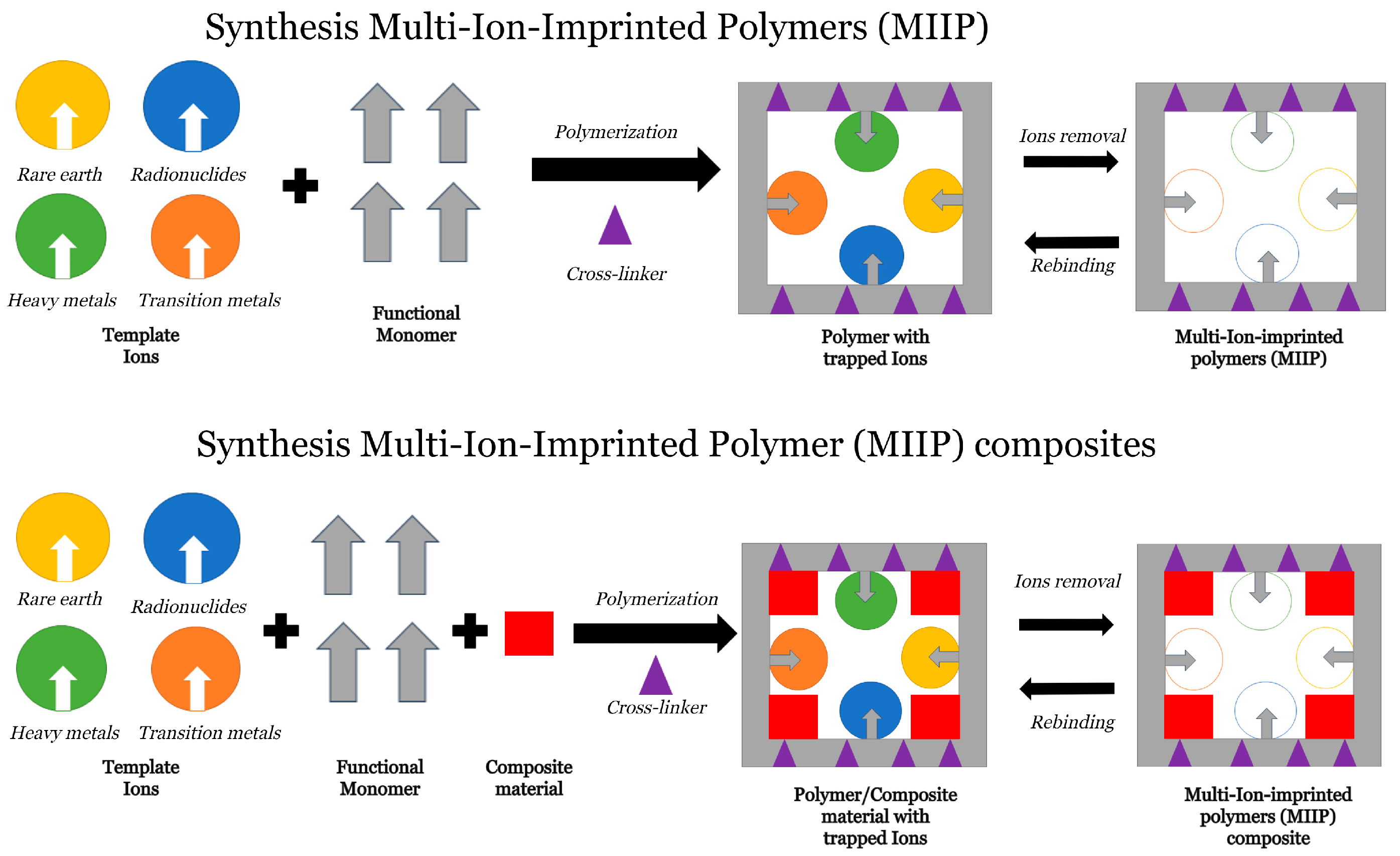
3. Classification, Mechanisms, and Synthesis of MIIPs
4. Multi-Ion-Imprinted Composites, Synthesis, Materials and Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.; Turner, S.R. Hypercrosslinked Polymers: A Review. Polym. Rev. 2018, 58, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumughan, V.; Nypelö, T.; Hasani, M.; Larsson, A. Fundamental aspects of the non-covalent modification of cellulose via polymer adsorption. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 298, 102529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekwagep, P.M.S.; Crapnell, R.D.; Banks, C.E.; Betlem, K.; Rinner, U.; Canfarotta, F.; Lowdon, J.W.; Eersels, K.; van Grinsven, B.; Peeters, M.; et al. A Critical Review on the Use of Molecular Imprinting for Trace Heavy Metal and Micropollutant Detection. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Zakaria, E.; Khalil, M.; El-Tantawy, A.; El-Saied, F. Synthesis of ion-imprinted polymers based on chitosan for high selectivity of La(III), Ce(III) and Sm(III) via solid phase extraction. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 356, 119058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, D.; Cheng, L.; Ahmed, R.; Romanovski, V.; et al. Multi-templates molecularly imprinted polymers for simultaneous recognition of multiple targets: From academy to application. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 166, 117173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakavula, S.; Biata, N.R.; Dimpe, K.M.; Pakade, V.E.; Nomngongo, P.N. Multi-ion imprinted polymers (MIIPs) for simultaneous extraction and preconcentration of Sb(III), Te(IV), Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from drinking water sources. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdaya, N.; Triadenda, A.L.; Rahayu, D.; Hasanah, A.N. A Review: Using Multiple Templates for Molecular Imprinted Polymer: Is It Good? Polymers 2022, 14, 4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, E.A.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Al-Sahari, M.; Mohamed, R.M.S.R.; Crane, R.; Ab Aziz, N.A.; Govarthanan, M. Challenges and opportunities in the application of bioinspired engineered nanomaterials for the recovery of metal ions from mining industry wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-G.; He, X.-L.; Huang, J.-H.; Luo, R.; Ge, H.-Z.; Wołowicz, A.; Wawrzkiewicz, M.; Gładysz-Płaska, A.; Li, B.; Yu, Q.-X.; et al. Impacts of heavy metals and medicinal crops on ecological systems, environmental pollution, cultivation, and production processes in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 219, 112336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzak, S.A.; Faruque, M.O.; Alsheikh, Z.; Alsheikhmohamad, L.; Alkuroud, D.; Alfayez, A.; Hossain, S.M.Z.; Hossain, M.M. A comprehensive review on conventional and biological-driven heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kandasubramanian, B. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Selective Recognition and Extraction of Heavy Metal Ions and Toxic Dyes. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 396–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Preparation of nanocellulose grafted molecularly imprinted polymer for selective adsorption Pb(II) and Hg(II). Chemosphere 2023, 316, 137832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z. Cadmium ion-imprinted polymers for adsorption and detection of cadmium ions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebolledo-Perales, L.E.; Ibarra, I.; Guzmán, M.F.; Islas, G.; Romero, G.A. A novel ion-imprinted polymer based on pyrrole as functional monomer for the voltammetric determination of Hg(II) in water samples. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 434, 141258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Huang, X.; Wei, S.; Xiao, C.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z. Novel dual-template magnetic ion imprinted polymer for separation and analysis of Cd2+ and Pb2+ in soil and food. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Ding, Y.; Chen, L. Synthesis of multi-ion imprinted polymers based on dithizone chelation for simultaneous removal of Hg2+, Cd2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+ from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 44087–44095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiri, E.; Arabkhani, P.; Haddadi, H.; Asfaram, A.; Varma, R.S. A silanized magnetic amino-functionalized carbon nanotube-based multi-ion imprinted polymer for the selective aqueous decontamination of heavy metal ions. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 21704–21716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, N.; Mishra, S. A review on the recovery and separation of rare earths and transition metals from secondary resources. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 884–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çıtlakoğlu, M.; Yolcu, Z. Synthesis and characterization of zinc(II) methacrylate monomer complex and adsorption properties of zinc(II) ion-imprinted polymer. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2023, 555, 121605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, S.; Taghizadeh, M.; Yamini, Y. Magnetic Cr(VI) Ion Imprinted Polymer for the Fast Selective Adsorption of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivián-Castro, E.Y.; Zepeda-Navarro, A.; Guzmán-Mar, J.L.; Flores-Alamo, M.; Mata-Ortega, B. Ion-Imprinted Polymer Structurally Preorganized Using a Phenanthroline-Divinylbenzoate Complex with the Cu(II) Ion as Template and Some Adsorption Results. Polymers 2023, 15, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.; Batlokwa, B. Selective and Simultaneous Removal of Ni (II) and Cu (II) Ions from Industrial Wastewater Employing a Double Ni-Cu-Ion Imprinted Polymer. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2018, 5, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yusoff, M.M.; Mostapa, N.R.N.; Sarkar, S.; Biswas, T.K.; Rahman, L.; Arshad, S.E.; Sarjadi, M.S.; Kulkarni, A.D. Synthesis of ion imprinted polymers for selective recognition and separation of rare earth metals. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nik Mustapa, N.R.; Malek, N.F.A.; Yusoff, M.M.; Rahman, M.L. Ion imprinted polymers for selective recognition and separation of lanthanum and cerium ions from other lanthanide. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2762–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, F.; Sarabadani, P.; Khorrami, A.R. Synthesis, characterization and application of a new nano-structured samarium(III) ion-imprinted polymer. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 5499–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Liu, Q.; Ren, Z.; Hu, H.; Sun, B.; Liu, C.; Shao, P.; Yang, L.; Pavlostathis, S.G.; Luo, X. Selective removal and recovery of La(III) using a phosphonic-based ion imprinted polymer: Adsorption performance, regeneration, and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.B.; Jauhari, D. Double-ion imprinted polymer @magnetic nanoparticles modified screen printed carbon electrode for simultaneous analysis of cerium and gadolinium ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 875, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Tang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Wang, S.; Yang, H.; et al. Advanced porous adsorbents for radionuclides elimination. EnergyChem 2023, 5, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumkar, V.V.; Galamboš, M.; Viglašová, E.; Daňo, M.; Šmelková, J. Ion-Imprinted Polymers: Synthesis, Characterization, and Adsorption of Radionuclides. Materials 2021, 14, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, X.; Su, C.; Li, Z.; Xue, J.; Hu, N.; Peng, P.; Liao, L.; Wang, H. A highly sensitive and selective sensor for trace uranyl (VI) ion based on a graphene-coated carbon paste electrode modified with ion imprinted polymer. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.A.F.; Selambakkannu, S.; Azian, H.; Ratnam, C.T.; Yamanobe, T.; Hoshina, H.; Seko, N. Synthesis of surface ion-imprinted polymer for specific detection of thorium under acidic conditions. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yang, S.; He, W.; Zhao, T.; Li, C.; Hua, D. Biogene-derived aerogels for simultaneously selective adsorption of uranium(VI) and strontium(II) by co-imprinting method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 271, 118849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, Z.; Liu, P. An all-solid-state NO3- ion-selective electrode with gold nanoparticles solid contact layer and molecularly imprinted polymer membrane. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkütük, E.B.; Özalp, E.; Özcan, A.A.; Diltemiz, S.E. Selective Separation of Thiocyanate Ion by Ion-Imprinted Polymer. Hacet. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 37, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, B.; Shamsipur, M.; Seyedzadeh, Z. Preparation of a K+-imprinted polymer for the selective recognition of K+ in food samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 2006–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budnicka, M.; Sobiech, M.; Sieczko, K.; Luliński, P. Ion-Imprinted Layers as Calcium-Ion Carriers: An Impact of a Functional Monomer on Physicochemical Properties, Composition, and Surface Morphology. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 5666–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; Abdel-Latif, D. Fabrication of Au(III) ion-imprinted polymer based on thiol-modified chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Kim, D. Synthesis and Selective Sorption Behavior of Pt(IV) Ion-Imprinted Polymer Particles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 13340–13347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Guo, B.; Luo, J.; Deng, F.; Zhang, S.; Luo, S.; Crittenden, J. Recovery of Lithium from Wastewater Using Development of Li Ion-Imprinted Polymers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, X.; Luo, M.; Meng, M.; Ni, L.; Qiu, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhong, G.; Liu, Z.; et al. Synthesis of hydrophilic surface ion-imprinted polymer based on graphene oxide for removal of strontium from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.G.F.; Batlokwa, B.S. Multi-templated Pb-Zn-Hg Ion Imprinted Polymer for the Selective and Simultaneous Removal of Toxic Metallic Ions from Wastewater. Int. J. Chem. 2017, 9, 58114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, D.; Türkmen, M.; Akgönüllü, S.; Denizli, A. Development of ion imprinted based magnetic nanoparticles for selective removal of arsenic (III) and arsenic (V) from wastewater. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, E.; Renani, S.B.; Zahedi, P. A dual template ion-imprinted polymer based on acrylamide monomer/modified graphene oxide for simultaneous adsorption of Ni(ii) and Cd(ii). New J. Chem. 2024, 48, 9794–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Liu, S.; Shao, N.; Tian, Z.; Zhu, X. Synthesis of a novel magnetic chitosan-mediated GO dual-template imprinted polymer for the simultaneous and selective removal of Cd(II) and Ni(II) from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 676, 132266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Balouch, A.; Alveroglu, E.; Ullah, R.; Shah, M.T.; Jagirani, M.S.; Mahar, A.M.; Chang, S.A. Synthesis of amine-functionalized ultrasonic assisted dual metal imprinted polymer: A real magnetic sorbent for simultaneous removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from water samples. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, M.; Ezzatzadeh, E.; Jalilian, R.; Taheri, A. Micro solid phase extraction of cadmium and lead on a new ion-imprinted hierarchical mesoporous polymer via dual-template method in river water and fish muscles: Optimization by experimental design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.B.; Jauhari, D.; Verma, A. A dual-ion imprinted polymer embedded in sol–gel matrix for the ultra trace simultaneous analysis of cadmium and copper. Talanta 2014, 120, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashami, Z.S.; Taheri, A.; Alikarami, M. Synthesis of a magnetic SBA-15-NH2@Dual-Template Imprinted Polymer for solid phase extraction and determination of Pb and Cd in vegetables; Box Behnken design. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1204, 339262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolmohammad-Zadeh, H.; Rahimpour, E.; Pasandideh, Y. Utilizing a Nanocomposite Based on Ion-Imprinted Polydopamine-Coated Magnetic Graphene Oxide for Extraction of Cd(II) and Ni(II) from Water Samples. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 75, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Xu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Li, F.; Bi, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, X.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, J. Application Prospect of Ion-Imprinted Polymers in Harmless Treatment of Heavy Metal Wastewater. Molecules 2024, 29, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lin, G.; Liu, C.; Chu, S.; Mo, C.; Liu, X. Progress and challenges in molecularly imprinted polymers for adsorption of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 36, e00178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branger, C.; Meouche, W.; Margaillan, A. Recent advances on ion-imprinted polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 859–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.; Ashraf, S.; Mueller, A. The binding of metal ions to molecularly-imprinted polymers. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Cao, H.; Mai, D.; Ye, T.; Wu, X.; Yuan, M.; Yu, J.; Xu, F. A novel morphological ion imprinted polymers for selective solid phase extraction of Cd(II): Preparation, adsorption properties and binding mechanism to Cd(II). React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 151, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surapong, N.; Pongpinyo, P.; Santaladchaiyakit, Y.; Burakham, R. A biobased magnetic dual-dummy-template molecularly imprinted polymer using a deep eutectic solvent as a coporogen for highly selective enrichment of organophosphates. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 136045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçük, M.; Osman, B.; Özer, E.T. Dummy molecularly imprinted polymer-based solid-phase extraction method for the determination of some phthalate monoesters in urine by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1713, 464532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariani, M.D.; Zuhrotun, A.; Manesiotis, P.; Hasanah, A.N. Dummy template molecularly imprinted polymers as potential sorbents in the separation and purification of active compounds in natural products. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakavula, S.; Biata, N.R.; Dimpe, K.M.; Pakade, V.E.; Nomngongo, P.N. A Critical Review on the Synthesis and Application of Ion-Imprinted Polymers for Selective Preconcentration, Speciation, Removal and Determination of Trace and Essential Metals from Different Matrices. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajini, T.; Mathew, B. A brief overview of molecularly imprinted polymers: Highlighting computational design, nano and photo-responsive imprinting. Talanta Open 2021, 4, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, M.G.; Benhawy, A.H.; Khalifa, R.M.; El Nashar, R.M.; Trojanowicz, M. Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in the Analysis of Waters and Wastewaters. Molecules 2021, 26, 6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardeshi, S.; Singh, S.K. Precipitation polymerization: A versatile tool for preparing molecularly imprinted polymer beads for chromatography applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 23525–23536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, R.; Shahmari, M.; Taheri, A.; Gholami, K. Ultrasonic-assisted micro solid phase extraction of arsenic on a new ion-imprinted polymer synthesized from chitosan-stabilized pickering emulsion in water, rice and vegetable samples. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 61, 104802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamaoui, A.; García-Guzmán, J.J.; Amine, A.; Palacios-Santander, J.M.; Cubillana-Aguilera, L. Synthesis techniques of molecularly imprinted polymer composites. In Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 49–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Miao, P.; Liu, S.; Gao, J.; Han, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, T. Preparation and Application Progress of Imprinted Polymers. Polymers 2023, 15, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yang, L.; Teng, Y.; Zhong, M.; Lu, X.; Kan, X. Preparation and Application of Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on Dopamine Self-Polymerization. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, B312–B316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanvase, B.; Sonawane, S. Ultrasound assisted in situ emulsion polymerization for polymer nanocomposite: A review. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2014, 85, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.N.A.; Hasbullah, N.A.; Rosdi, M.R.H.; Musa, M.S.; Rusli, A.; Ariffin, A.; Shafiq, M.D. Polymerization and Applications of Poly(methyl methacrylate)–Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites: A Review. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 47490–47503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Kukkar, D.; Brown, R.J.C.; Kim, K.-H. Recent advances in the synthesis of and sensing applications for metal-organic framework-molecularly imprinted polymer (MOF-MIP) composites. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 258–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Lamb, D.; Chen, Z.; Lesniewski, P.J.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Simultaneously determining multi-metal ions using an ion selective electrode array system. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 6, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, J.C.; Silveyra, J.; Ureña, M. Multi-ion and pH sensitivity of AgGeSe ion selective electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2016, 89, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shang, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X. Synthesis and application of ion imprinting polymer coated magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective adsorption of nickel ion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 428, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Wu, S.; Sun, C. Ion-Imprinted Polymer Modified with Carbon Quantum Dots as a Highly Sensitive Copper(II) Ion Probe. Polymers 2021, 13, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Gan, Q.; Feng, C. Preparation and application of Ni(ii) ion-imprinted silica gel polymer for selective separation of Ni(ii) from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15102–15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Zhu, Z.; Song, R.; Li, Z.; Chen, C. An ion-imprinted sensor based on chitosan-graphene oxide composite polymer modified glassy carbon electrode for environmental sensing application. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 317, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboufazeli, F.; Zhad, H.R.L.Z.; Sadeghi, O.; Karimi, M.; Najafi, E. Novel ion imprinted polymer magnetic mesoporous silica nano-particles for selective separation and determination of lead ions in food samples. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3459–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A. Molecular imprinting polymers and their composites: A promising material for diverse applications. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Pham-Huy, C.; He, H. Core-shell nanoparticles coated with molecularly imprinted polymers: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2677–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Multi-Ions Imprinted Polymer | Templates | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Type of Ions | Method of Synthesis | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIIP—tetraion | Hg(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), Ni(II) | 105.34, 91.79, 75.03, 63.54 | Transition/heavy metals | Sol–gel | [16] |
| Sb(III), Te(IV), Pb(II), Cd(II) | 57.8, 51.3, 61.9, 65.6 | Heavy metals | Sol–gel | [6] | |
| Hg(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Cd(II) | 7.85, 3.15, 1.56, 3.72 | Transition/heavy metals | Sol–gel | [17] | |
| MIIP—triion | La(III), Ce(III), Sm(III) | 39.34, 38.24, 40.51 | Rare earth | Sol–gel | [4] |
| Pb(II), Zn(II), Hg(II) | - | Transition/heavy metals | Bulk | [41] | |
| MIIP—diion | Cd(II), Pb(II) | 41.69, 76.39 | Heavy metals | Sol–gel | [15] |
| Cu(II), Ni(II) | - | Transition/heavy metals | Bulk | [22] | |
| As(III), As(V) | 91.7, 99 | Heavy metals | Emulsion | [42] | |
| Ni(II), Cd(II) | 153.13, 188.67 | Transition/heavy metals | Surface imprint | [43] | |
| Cd(II), Ni(II) | 33.91, 39.35 | Transition/heavy metals | Surface imprint | [44] | |
| Pb(II), Cd(II) | - | Heavy metals | Ultrasonic-mediated precipitation | [45] | |
| Cd(II), Pb(II) | 18.18, 23.81 | Heavy metals | Precipitation | [46] | |
| Cd(II), Cu(II) | - | Transition/heavy metals | Sol–gel | [47] | |
| Pb(II), Cd(II) | 10.28, 10.38 | Heavy metals | Ultrasonic- precipitation | [48] | |
| Cd(II), Ni(II) | - | Transition/heavy metals | Self-polymerization | [49] | |
| U(VI), Sr(II) | 317, 160 | Radionuclides | Self-polymerization | [32] | |
| Ce(IV), Gd(III) | - | Rare earth | Thermal polymerization/Surface imprinting | [27] |
| Imprinted Polymer Composites | Combine Materials | Method of Synthesis | Application | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIIP | Magnetic | Sol–gel | adsorption | [15] |
| MIIP | Graphene oxide | Surface imprint | adsorption | [43] |
| IIP | Magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes particles | Emulsion | adsorption | [71] |
| IIP | Quantum dots | Surface imprinting | sensors | [72] |
| IIP | Silica | Surface imprinting/Ultrasonic-mediated | adsorption | [73] |
| MIIP | Magnetic | Thermal polymerization | sensors | [27] |
| MIIP | Graphene oxide/magnetic | Surface imprint | adsorption | [44] |
| MIIP | Carbon nanotube /Magnetic | Self-polymerization | adsorption | [49] |
| IIP | Graphene oxide | Surface imprint | sensors | [74] |
| IIP | Magnetic/Silica | Surface imprint | adsorption | [75] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zepeda-Navarro, A.; Segoviano-Garfias, J.J.N.; Bivián-Castro, E.Y. The Multi-Challenges of the Multi-Ion-Imprinted Polymer Synthesis. Polymers 2024, 16, 2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192804
Zepeda-Navarro A, Segoviano-Garfias JJN, Bivián-Castro EY. The Multi-Challenges of the Multi-Ion-Imprinted Polymer Synthesis. Polymers. 2024; 16(19):2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192804
Chicago/Turabian StyleZepeda-Navarro, Abraham, José J. N. Segoviano-Garfias, and Egla Yareth Bivián-Castro. 2024. "The Multi-Challenges of the Multi-Ion-Imprinted Polymer Synthesis" Polymers 16, no. 19: 2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192804
APA StyleZepeda-Navarro, A., Segoviano-Garfias, J. J. N., & Bivián-Castro, E. Y. (2024). The Multi-Challenges of the Multi-Ion-Imprinted Polymer Synthesis. Polymers, 16(19), 2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192804







