Chitosan-Polyaniline (Bio)Polymer Hybrids by Two Pathways: A Tale of Two Biocomposites
Abstract
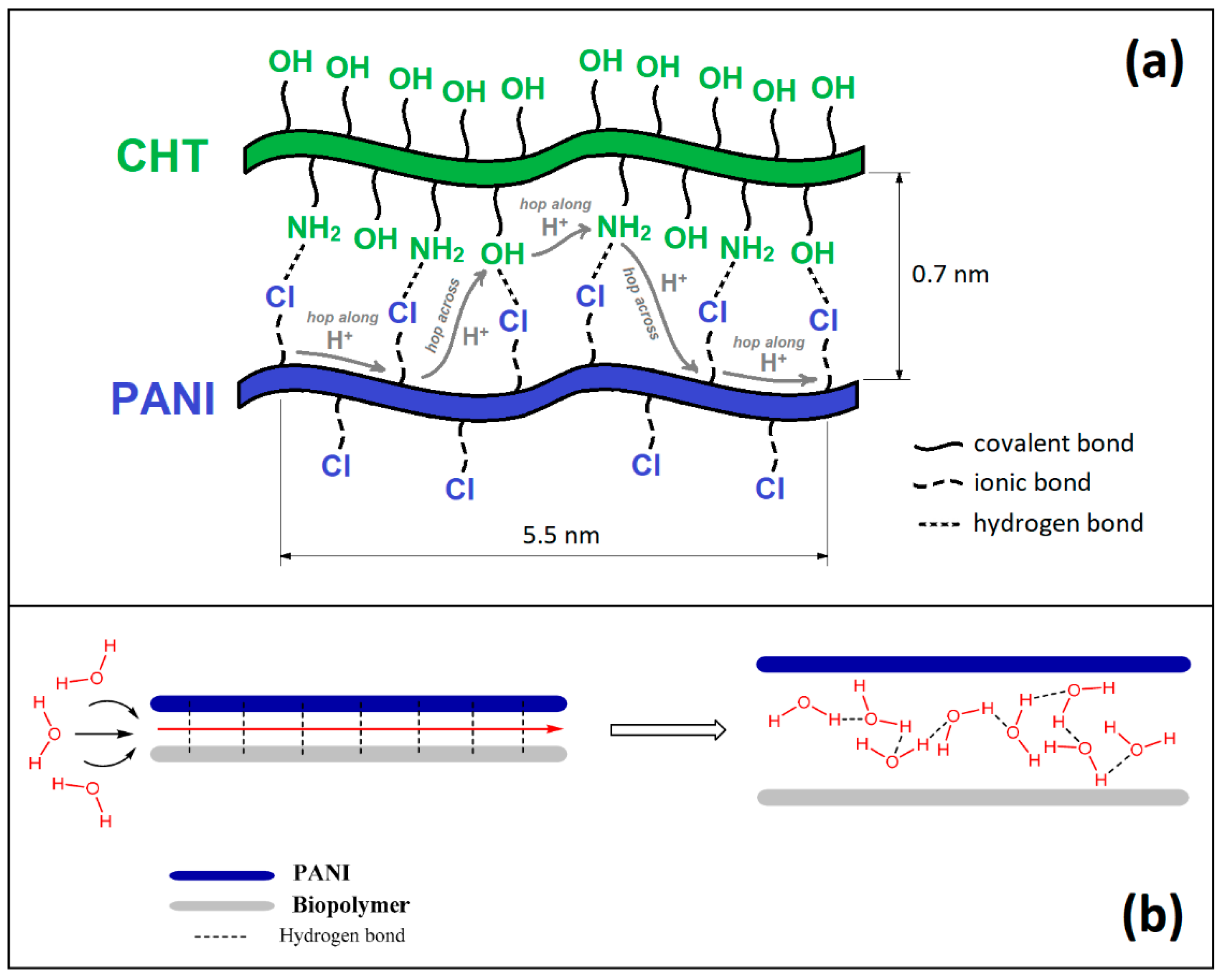
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Shorthand Notations
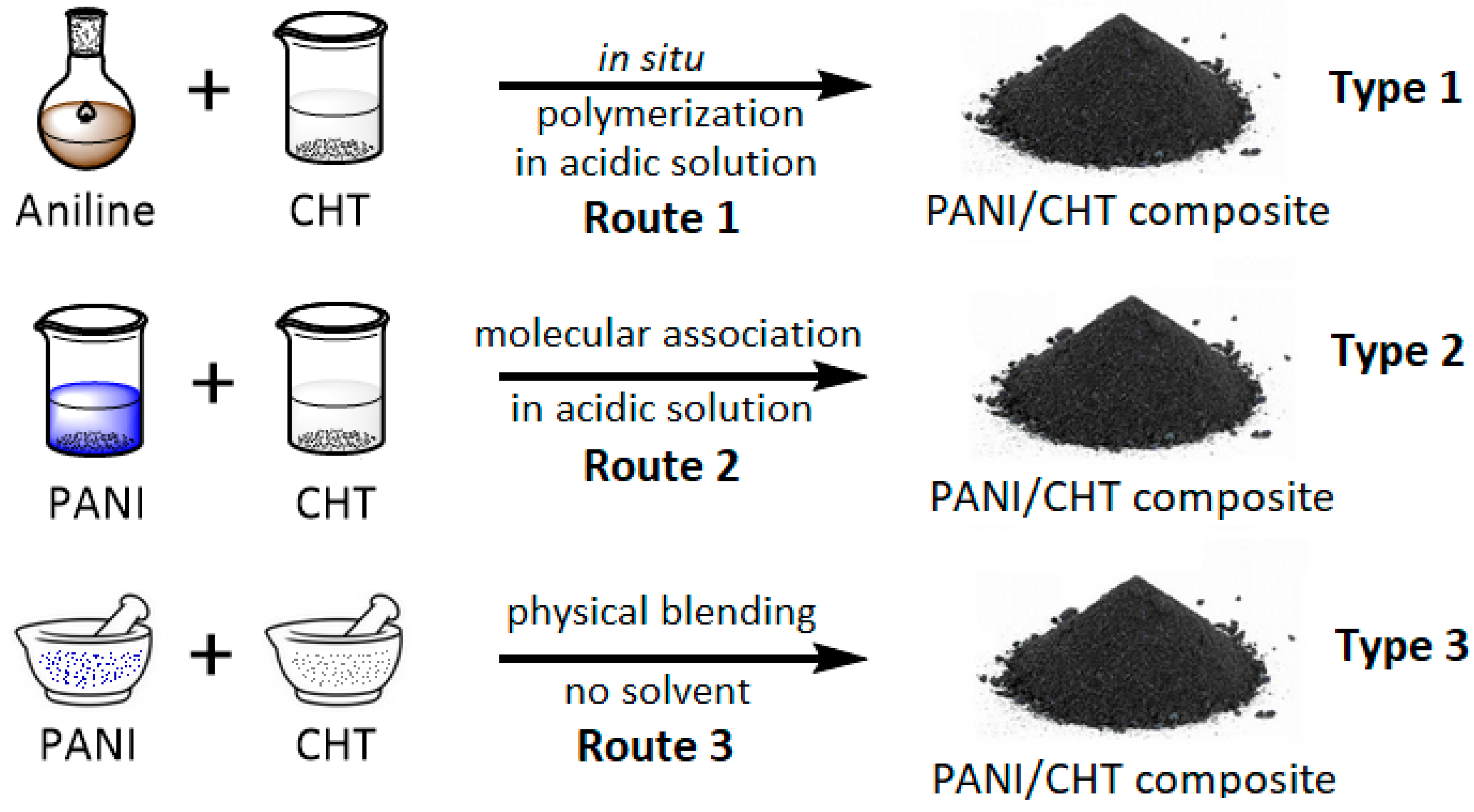
2.3. Preparation of Polymer Composites via Three Different Routes
2.4. Synthesis of Composites
2.4.1. In Situ Polymerized Composites—Route 1
2.4.2. Molecularly Associated Composites—Route 2
2.4.3. Physically Blended Samples—Route 3
2.5. Materials Characterization
2.5.1. 13C Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy
2.5.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.5.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5.4. Solvent Swelling Tests
2.5.5. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.5.6. Raman Spectroscopy
2.5.7. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD) Analysis
2.5.8. Equilibrium Dye Adsorption
2.5.9. Solubility Tests
2.5.10. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR) Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Characterization
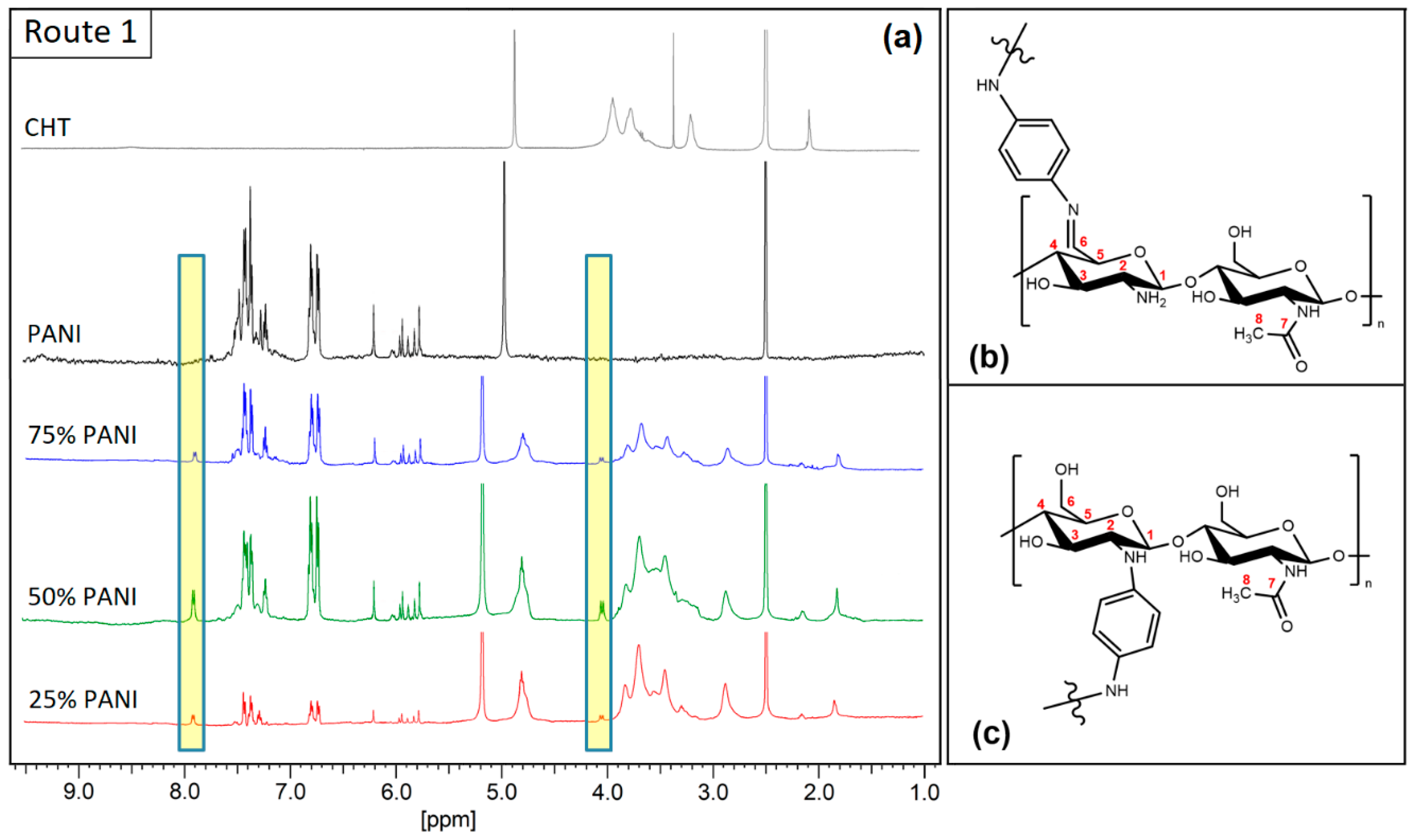
3.1.1. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR) Spectroscopy
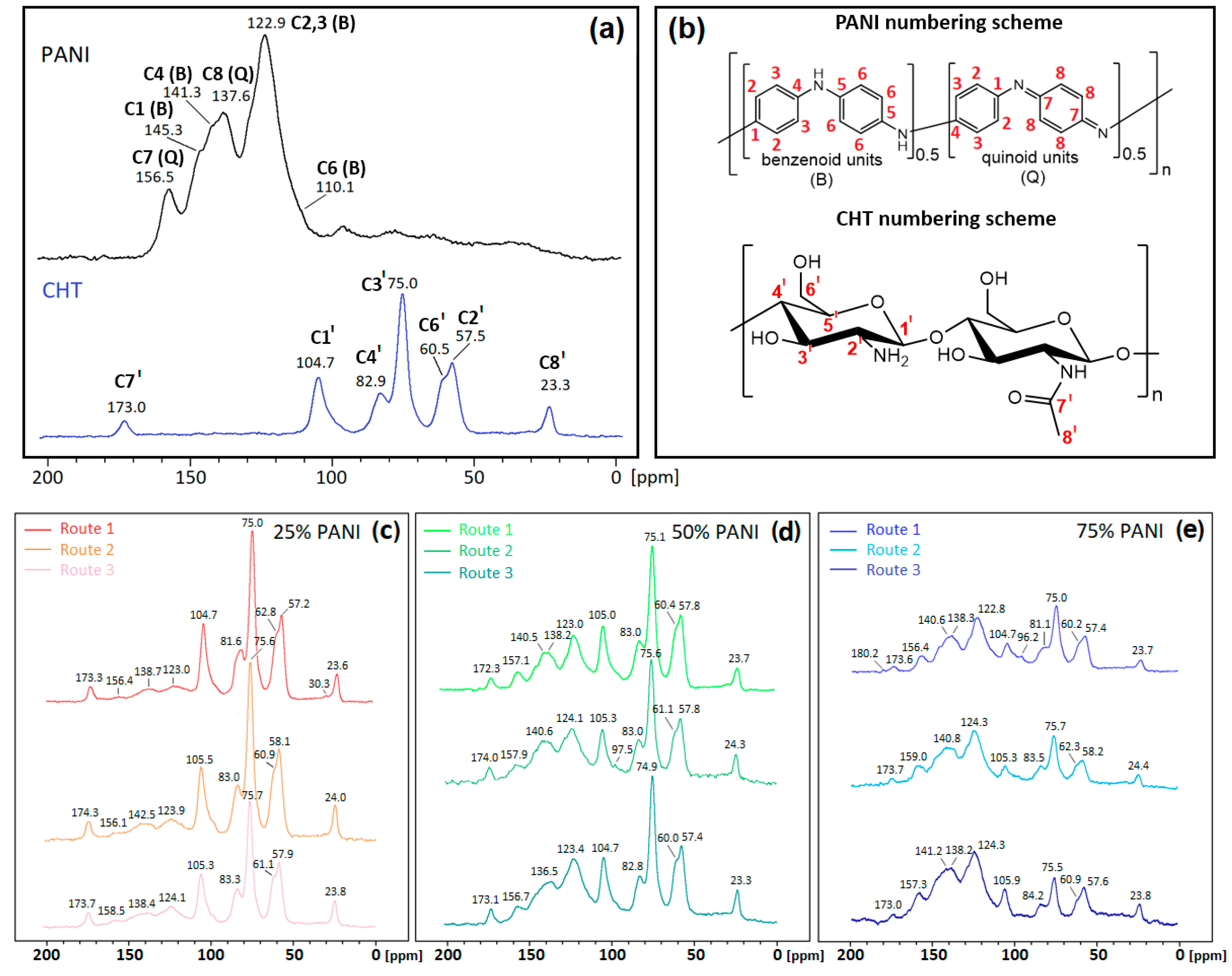
3.1.2. 13C Solid State NMR Spectroscopy
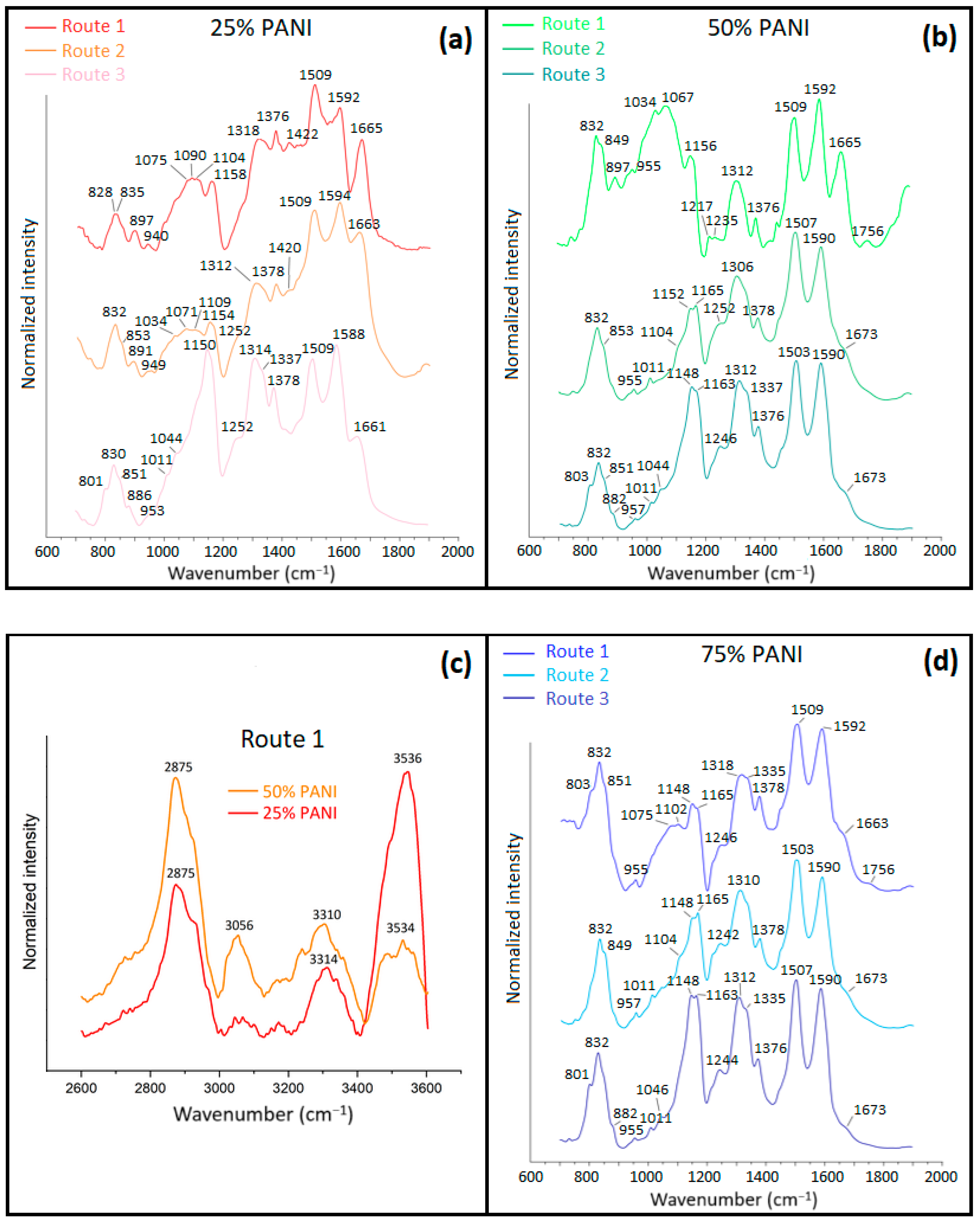
3.1.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
3.1.4. Raman Spectroscopy
3.2. Physical Characterization
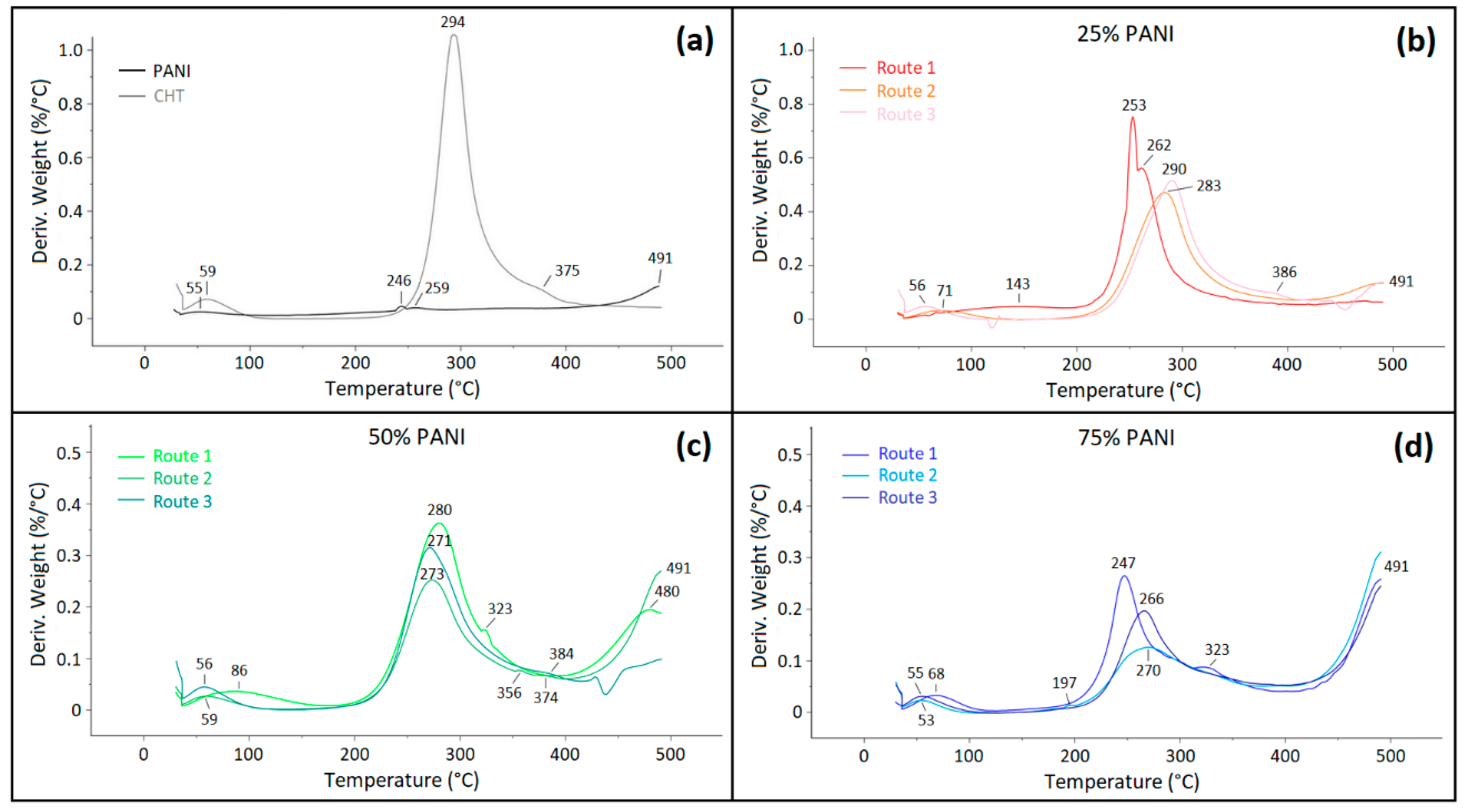
3.2.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
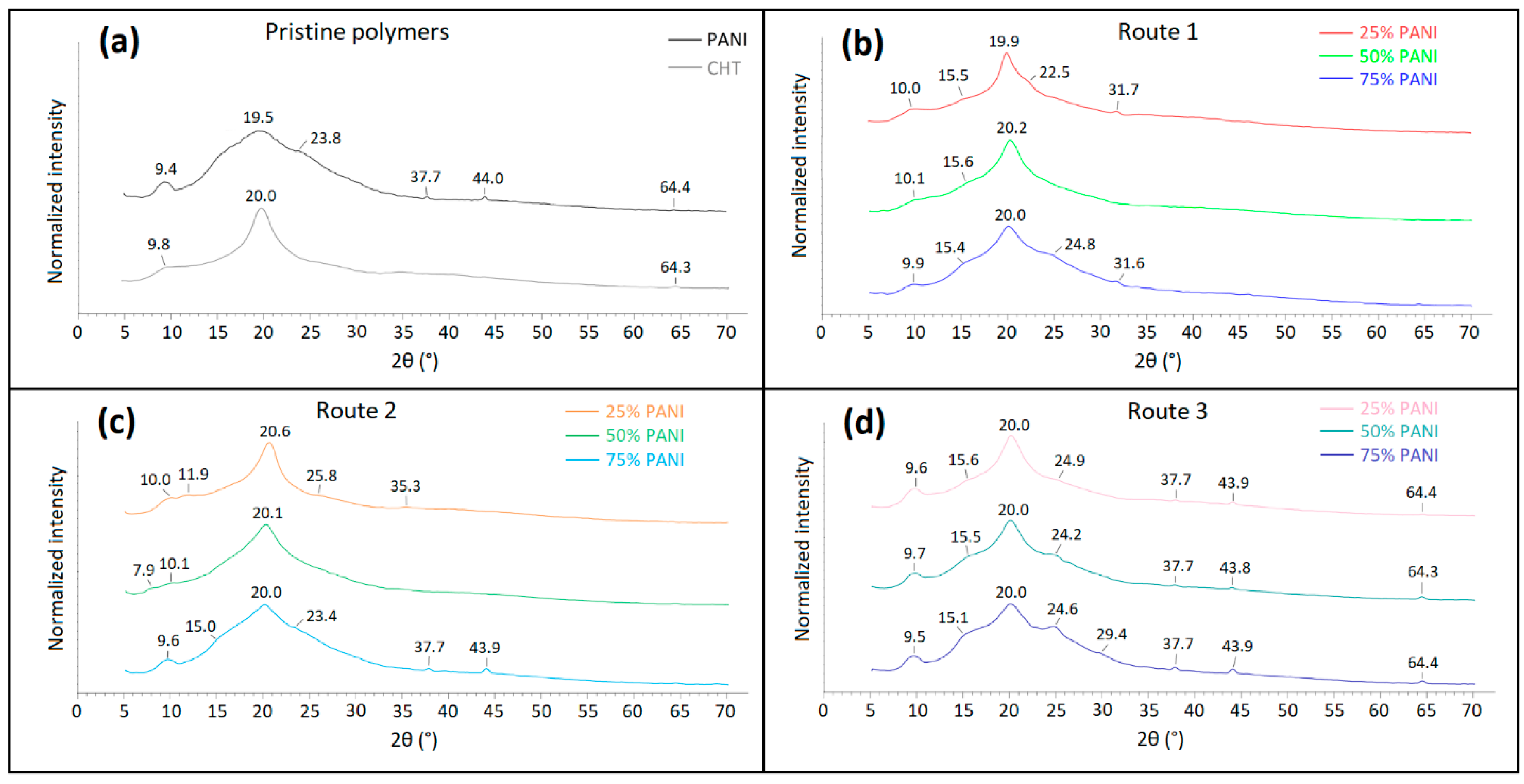
3.2.3. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
3.2.4. Solvent Swelling Tests
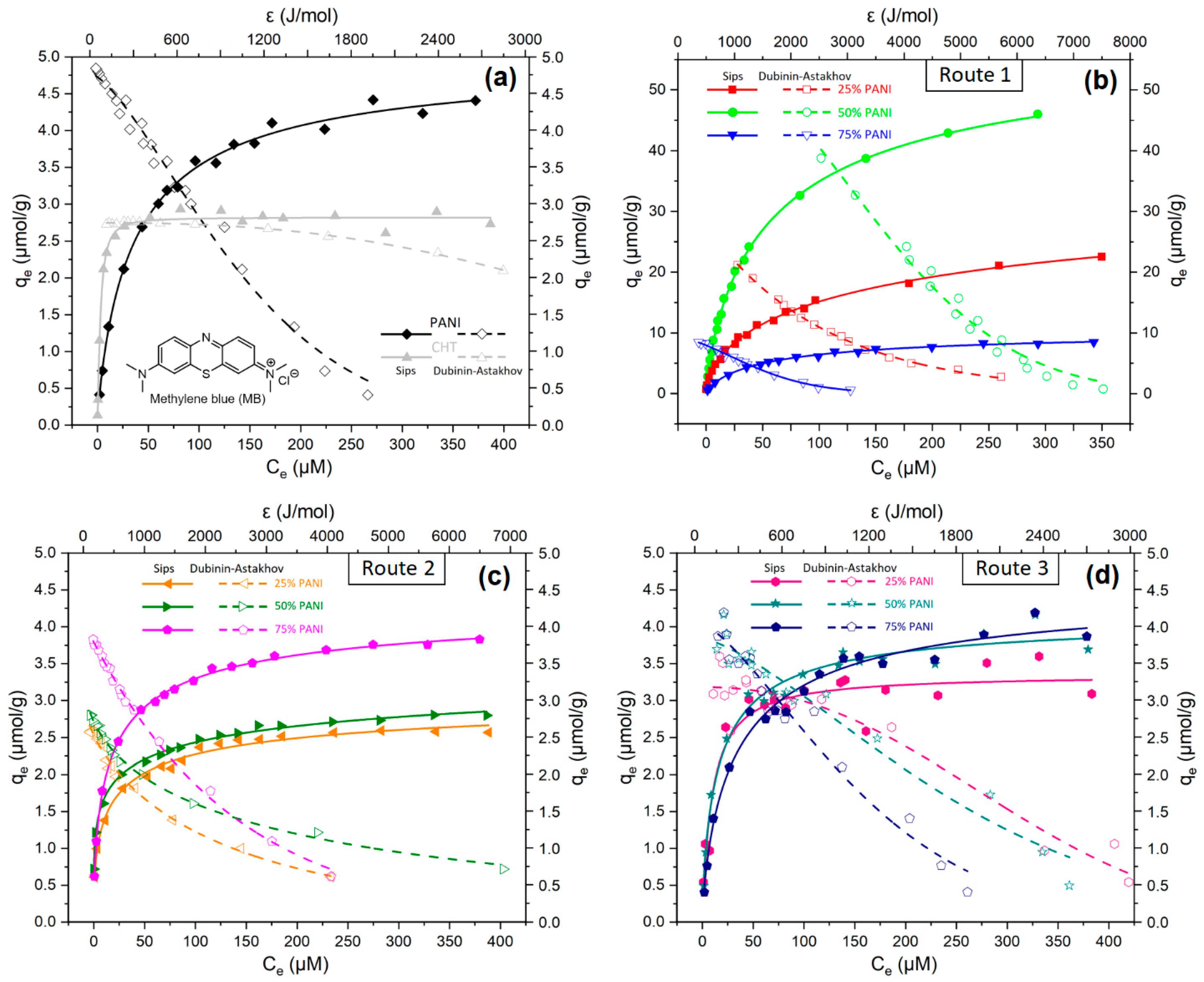
3.2.5. Equilibrium Dye Adsorption
3.2.6. Solubility Tests
3.3. Chemistry of Formation of PANI/CHT Type 1 Composite
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.; Tirmizi, S.A.; Burns, A.; Barney, A.A.; Risen, W.M. Chitaline Materials: Soluble Chitosan-Polyaniline Copolymers and Their Conductive Doped Forms. Synth. Met. 1989, 32, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, Y.A.; Evitts, R.W.; Cree, D.E.; Wilson, L.D. Polyaniline/Biopolymer Composite Systems for Humidity Sensor Applications: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatkhah, A.; Jani, P.; Wilson, L.D. Redox-Responsive Polymer Template as an Advanced Multifunctional Catalyst Support for Silver Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10560–10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.H.; Dolatkhah, A.; Aboumourad, T.; Dehabadi, L.; Wilson, L.D. Investigation of Templated and Supported Polyaniline Adsorbent Materials. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 6976–6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanpitcha, T.; Sirivat, A.; Jamieson, A.M.; Rujiravanit, R. Preparation and Characterization of Polyaniline/Chitosan Blend Film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 64, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kabbi, A.S.; Abbas, S.J. Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel Nanocomposite Polymer. Ukr. J. Phys. 2023, 68, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasvandian, S.; Shahgholi, M.; Karimipour, A. Investigating the Effects of Chitosan Atomic Ratio and Drug Type on Mechanical Properties of Silica Aerogel/Chitosan Nanocomposites Using Molecular Dynamics Approach. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 401, 124639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDiarmid, A.G.; Chiang, J.C.; Halpern, M.; Huang, W.S.; Mu, S.L.; Nanaxakkara, L.D.; Wu, S.W.; Stuart, I.; Yaniger, S.I. “Polyaniline”: Interconversion of Metallic and Insulating Forms. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1985, 121, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geniès, E.M.; Boyle, A.; Lapkowski, M.; Tsintavis, C. Polyaniline: A Historical Survey. Synth. Met. 1990, 36, 139–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapurina, I.; Stejskal, J. The Mechanism of the Oxidative Polymerization of Aniline and the Formation of Supramolecular Polyaniline Structures. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 1295–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Riede, A.; Hlavatá, D.; Prokeš, J.; Helmstedt, M.; Holler, P. The Effect of Polymerization Temperature on Molecular Weight, Crystallinity, and Electrical Conductivity of Polyaniline. Synth. Met. 1998, 96, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechtschein, M.; Santier, C.; Travers, J.P.; Chroboczek, J.; Alix, A.; Ripert, M. Water Effects in Polyaniline: NMR and Transport Properties. Synth. Met. 1987, 18, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, Y.A.; Cree, D.E.; Wilson, L.D. Preparation of Multi-Component Biocomposites and Characterization of Their Physicochemical and Mechanical Properties. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, S.; Machappa, T.; Ravikiran, Y.T.; Chethan, B.; Revanasiddappa, M. Room Temperature Humidity Sensing Performance of Polyaniline–Holmium Oxide Composite. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, V.; Grinberg, N.; Moldoveanu, S.C. Advances in Chromatography; Grushka, E., Grinberg, N., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Yang, L. The Adsorption of Basic Dyes from Aqueous Solution on Modified Peat–Resin Particle. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sips, R. On the Structure of a Catalyst Surface. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinin, M.M.; Radushkevich, L.V. Equation of the Characteristic Curve of Activated Charcoal. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1947, 55, 331–333. [Google Scholar]
- Kleineidam, S.; Schüth, C.; Grathwohl, P. Solubility-Normalized Combined Adsorption-Partitioning Sorption Isotherms for Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4689–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.T.; Teng, H. Langmuir and Dubinin–Radushkevich Analyses on Equilibrium Adsorption of Activated Carbon Fabrics in Aqueous Solutions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2000, 75, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bembnowska, A.; Pełech, R.; Milchert, E. Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions of Chlorinated Organic Compounds onto Activated Carbons. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 265, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M.F.; Hemat, M.D.; Elboray, E.E.; Aly, M.F. Novel Crystalline and Thermally Stable Chitosan-Chromone Based Polymers: Synthesis and Characterization. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1241, 130625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaparekar, P.S.; Poddar, N.; Anandasadagopan, S.K. Fabrication and Characterization of Chrysin—A Plant Polyphenol Loaded Alginate-Chitosan Composite for Wound Healing Application. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 206, 111922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinin, M.M.; Astakhov, V.A.; Radushkevich, L.V. Physical Adsorption of Gases and Vapors in Micropores; Cadenhead, D.A., Danielli, J.F., Rosenberg, M.D., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Inglezakis, V.J. Solubility-Normalized Dubinin–Astakhov Adsorption Isotherm for Ion-Exchange Systems. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2007, 103, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naar, N.; Lamouri, S.; Jeacomine, I.; Pron, A.; Rinaudo, M. A Comprehensive Study and Characterization of Colloidal Emeraldine Base. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2012, 49, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashiwa, H.; Shigemasa, Y.; Roy, R. Dissolution of Chitosan in Dimethyl Sulfoxide by Salt Formation. Chem. Lett. 2000, 29, 596–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaid, N.; Jackson, T.L.; Elsaid, Z.; Alqathama, A.; Somavarapu, S. PLGA Microparticles Entrapping Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles for the Ocular Delivery of Ranibizumab. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2923–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafin, A.G.; Latypova, L.R.; Andriianova, A.N. Synthesis and Polymerization of 2-(1-Methylbut-2-en-1-yl)Aniline and Its Products Modification. Polym. Test. 2021, 104, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafin, A.G.; Latypova, L.R.; Andriianova, A.N.; Mullagaliev, I.N.; Salikhov, S.M.; Salikhov, R.B.; Usmanova, G.S. Polymerization of New Aniline Derivatives: Synthesis, Characterization and Application as Sensors. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 21006–21016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venancio, E.C.; Wang, P.C.; MacDiarmid, A.G. The Azanes: A Class of Material Incorporating Nano/Micro Self-Assembled Hollow Spheres Obtained by Aqueous Oxidative Polymerization of Aniline. Synth. Met. 2006, 156, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, J.; Tan, W.; Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Dong, F.; Guo, Z. Antifungal Activity of Double Schiff Bases of Chitosan Derivatives Bearing Active Halogeno-Benzenes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 179, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Aotegen, B.; Zhong, Z. Preparation and Antibacterial Activity of C2-Benzaldehyde-C6-Aniline Double Schiff Base Derivatives of Chitosan. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2018, 67, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.T.; Win, Y.F. Total Assignment of NMR Spectral Lines of Schiff Base Derivatives with Pyridine Core. World Appl. Sci. J. 2010, 8, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Sarı, N.; Gürkan, P. Some Novel Amino Acid—Schiff Bases and Their Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization, Solid State Conductivity Behaviors and Potentiometric Studies. Naturforsch. B 2004, 59, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Wu, H.T.; Mao, C.F.; Liao, W.T. Conductive Chitosan-Graft-Polyaniline Copolymer: Synthesis and Characterization. Polym. Bull. 2021, 79, 6259–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, C.S.; Singh, P.; Abbas, N.S.; Shukla, S.K. Structurally Functionalized Cupric Oxide Encapsulated Chitosan Grafted Polyaniline Composite for Potentiometric Sensing of Methyl Parathion. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2021, 222, 2100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zujovic, Z.D.; Bowmaker, G.A.; Tran, H.D.; Kaner, R.B. Solid-State NMR of Polyaniline Nanofibers. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcasuzaa, P.; Reynaud, S.; Ehrenfeld, F.; Khoukh, A.; Desbrieres, J. Chitosan-graft-Polyaniline-Based Hydrogels: Elaboration and Properties. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento, G.M. Spectroscopy of Polyaniline Nanofibers; Kumar, A., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2010; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/8652 (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Trchova, M.; Stejskal, J. Polyaniline: The Infrared Spectroscopy of Conducting Polymer Nanotubes (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 1803–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trchová, M.; Morávková, Z.; Bláha, M.; Stejskal, J. Raman Spectroscopy of Polyaniline and Oligoaniline Thin Films. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 122, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zając, A.; Hanuza, J.; Wandas, M.; Dymińska, L. Determination of N-Acetylation Degree in Chitosan Using Raman Spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 134, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bláha, M.; Marek, F.; Morávková, Z.; Svoboda, J.; Brus, J.; Dybal, J.; Prokeš, J.; Varga, M.; Stejskal, J. Role of p-Benzoquinone in the Synthesis of a Conducting Polymer, Polyaniline. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 7128–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Rashidimoghadam, S. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro bioactivity study of glutaraldehyde crosslinked chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol)/ascorbic acid-MWCNTs bionanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guan, J.; Zhou, W.; Tan, S.; Cai, Z. From individuals to families: Design and application of self-similar chiral nanomaterials. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 11, 3975–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, S.; Khastgir, D. Determination of Crystal Structure of Polyaniline and Substituted Polyanilines through Powder X-ray Diffraction Analysis. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehabadi, L. Development of Biopolymers and Their Modified Forms as Sustainable Sorbent Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, M.N.; Agnely, F.; Yagoubi, N.; Grossiord, J.L.; Couarraze, G. Water state characterization, swelling behavior, thermal and mechanical properties of chitosan based networks. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 15, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, I.Y.; Vlasov, P.V.; Lebedeva, M.F.; Gofman, I.V.; Elokhovsky, V.Y.; Popova, E.N.; Lozhkin, M.S.; Vlasova, E.N.; Kuryndin, I.S.; Smirnov, M.A.; et al. Mechanical Response and Network Characterization of Conductive Polyaniline/Polyacrylamide Gels. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 187, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, B.G.K.; Udoetok, I.A.; Faye, O.; Wilson, L.D. Counterion Effects in Metal Hybrid Biopolymer Materials for Sulfate Adsorption: An Experimental and Computational Study. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 4595–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Yang, S.C. Controlling the pKa for Protonic Doping of Polyaniline by Non-Covalent Complexation. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2006, 965, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Z.; Chen, X.G.; Liu, N.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, C.S.; Meng, X.H.; Liu, C.G. Protonation Constants of Chitosan with Different Molecular Weight and Degree of Deacetylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzevari, M.; Cree, D.E.; Wilson, L.D. Graphene Oxide−Chitosan Composite Material for Treatment of a Model Dye Effluent. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 13045–13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Mohamed, A.A. The use of chitosan-based composites for environmental remediation: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242 Pt 2, 124787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, G.R. Optimum Isotherm Equation and Thermodynamic Interpretation for Aqueous 1,1,2-Trichloroethene Adsorption Isotherms on Three Adsorbents. Adsorption 1995, 1, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Grange, P. Application of the Dubinin-Radushkevich and Dubinin-Astakhov Equations in the Characterization of Microporous Solids. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1996, 113, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatkhah, A. Investigation of Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Nanocomposites for Dye Treatment in Aqueous Solution. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Perween, S.; Ranjan, A. Dramatic Enhancement in Adsorption of Congo Red Dye in Polymer-Nanoparticle Composite of Polyaniline-Zinc Titanate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, M.; Akbari, A. Facile Fabrication of Magnetic Chitosan Hydrogel Beads and Modified by Interfacial Polymerization Method and Study of Adsorption of Cationic/Anionic Dyes from Aqueous Solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, S.; Foo, K.Y.; Md Yusof, E.N.; Jawad, A.H.; Wilson, L.D.; Sabar, S. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Phosphorylated Chitosan and Its Adsorption Performance Towards Acid Red 88 Dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabar, S.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusof, N.H.; Subramaniam, S.; Foo, K.Y.; Wilson, L.D.; Lee, H.K. Preparation of Sulfonated Chitosan for Enhanced Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 151, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, K.K.; Kim, E.; Nam, J.; Lee, S.; Mun, J.; Kim, T.H. Chitosan-Grafted-Polyaniline Copolymer as an Electrically Conductive and Mechanically Stable Binder for High-Performance Si Anodes in Li-Ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 333, 135532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, F. A Novel Sensing Platform Based on Periodate-Oxidized Chitosan. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshk, S.M.A.S.; Ramadan, A.M.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Irfan, A.; Bondock, S. An Unexpected Reactivity During Periodate Oxidation of Chitosan and the Affinity of Its 2, 3-Di-Aldehyde Toward Sulfa Drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Shukla, S.K. Advances in Polyaniline-Based Nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 1331–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Assignment | δ, ppm * | Multiplicity | Integration ** | Number of H Atoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PANI signatures | ||||
| Benzenoid rings (B) | 7.2–7.6 | multiplet | 4.00 | 4 |
| Quinoid rings (Q) | 6.7–6.9 | multiplet | 5.90 | 4 |
| CHT signatures | ||||
| C1 *** proton | 4.7–4.9 | broad peak | 1.14 | 1 |
| C6 protons | 3.8–4.0 | broad peak | 2.36 | 2 |
| C4, C5 protons | 3.5–3.7 | broad peak | 1.90 | 2 |
| C3 proton | 3.3 | multiplet | 0.924 | 1 |
| C2 proton | 3.2 | broad peak | 1.25 | 1 |
| C8 (–CH3) protons | 1.8–1.9 | singlet | 0.573 | 3 |
| Binary composite (50% PANI) signatures ** | ||||
| –C6H=N– | 7.93 | doublet | 0.192 | 1 |
| –C5H– | 4.05 | multiplet | 0.170 | 1 |
| Sample Preparation Route | Sample | Experimental Swelling in Water (%) | Theoretical Swelling * (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Composite (In situ polymerization) | 25% PANI | 60 ± 26 | 360 |
| 50% PANI | 111 ± 31 | 380 | |
| 75% PANI | 155 ± 31 | 390 | |
| Type 2 Composite (Association in water) | 25% PANI | 180 ± 9 | 360 |
| 50% PANI | 237 ± 17 | 380 | |
| 75% PANI | 284 ± 9 | 390 | |
| Type 3 Composite (Physical mixing of solids) | 25% PANI | 379 ± 30 | 360 |
| 50% PANI | 405 ± 13 | 380 | |
| 75% PANI | 422 ± 8 | 390 | |
| Pristine polymer Pristine biopolymer | PANI | 398 ± 42 | 398 |
| CHT | 346 ± 24 | 346 |
| Sample Preparation Route | Sample | (µmol/g) | Heterogeneity Parameter | b (kJ/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Sips | b DA | b ns | |||
| Type 1 Composite (in situ polymerization) | 25% PANI | 39.6 | 35.2 | 0.98 | 2.13 |
| 50% PANI | 59.3 | 57.9 | 2.05 | 4.21 | |
| 75% PANI | 10.5 | 9.14 | 1.66 | 1.61 | |
| Type 2 Composite (Association in water) | 25% PANI | 3.23 | 2.98 | 0.72 | 2.17 |
| 50% PANI | 4.09 | 3.37 | 0.52 | 3.25 | |
| 75% PANI | 4.42 | 4.07 | 1.01 | 2.30 | |
| Type 3 Composite (Physical mixing of solids) | 25% PANI | 3.35 | 3.18 | 2.34 | 2.43 |
| 50% PANI | 4.15 | 3.86 | 1.49 | 2.02 | |
| 75% PANI | 4.58 | 4.08 | 1.48 | 1.28 | |
| Pristine polymer | PANI | 4.99 | 4.77 | 1.47 | 4.82 |
| Pristine biopolymer | CHT | 2.82 | 2.75 | 2.58 | 1.14 |
| Sample | Formula of Complex | Solubility, mg/g |
|---|---|---|
| 25% PANI (Type 1) | (PANI/CHT)·2⅖DMSO | 0.820 |
| 50% PANI (Type 1) | (PANI/CHT)·2DMSO | 0.107 |
| 75% PANI (Type 1) | (PANI/CHT)·5¾DMSO | 1.62 |
| PANI | PANI·2DMSO | 2.09 |
| CHT (non-ionized form) | CHT·⅛DMSO | 0.00119 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anisimov, Y.A.; Yang, H.; Kwon, J.; Cree, D.E.; Wilson, L.D. Chitosan-Polyaniline (Bio)Polymer Hybrids by Two Pathways: A Tale of Two Biocomposites. Polymers 2024, 16, 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182663
Anisimov YA, Yang H, Kwon J, Cree DE, Wilson LD. Chitosan-Polyaniline (Bio)Polymer Hybrids by Two Pathways: A Tale of Two Biocomposites. Polymers. 2024; 16(18):2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182663
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnisimov, Yuriy A., Heng Yang, Johnny Kwon, Duncan E. Cree, and Lee D. Wilson. 2024. "Chitosan-Polyaniline (Bio)Polymer Hybrids by Two Pathways: A Tale of Two Biocomposites" Polymers 16, no. 18: 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182663
APA StyleAnisimov, Y. A., Yang, H., Kwon, J., Cree, D. E., & Wilson, L. D. (2024). Chitosan-Polyaniline (Bio)Polymer Hybrids by Two Pathways: A Tale of Two Biocomposites. Polymers, 16(18), 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182663









