Chitosan: A Green Approach to Metallic Nanoparticle/Nanocomposite Synthesis and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Properties of Chitosan
2.1. Degree of Deacetylation (DD)
2.2. Molecular Weight (Mw)
2.3. Solubility
2.4. Viscosity
2.5. Biocompatibility and Thermal Stability
2.6. Relationship between Degree of Deacetylation, Molecular Weight, and Nanoparticles
3. Chitosan’s Effects on Metal Nanoparticle Formation and Functionalization
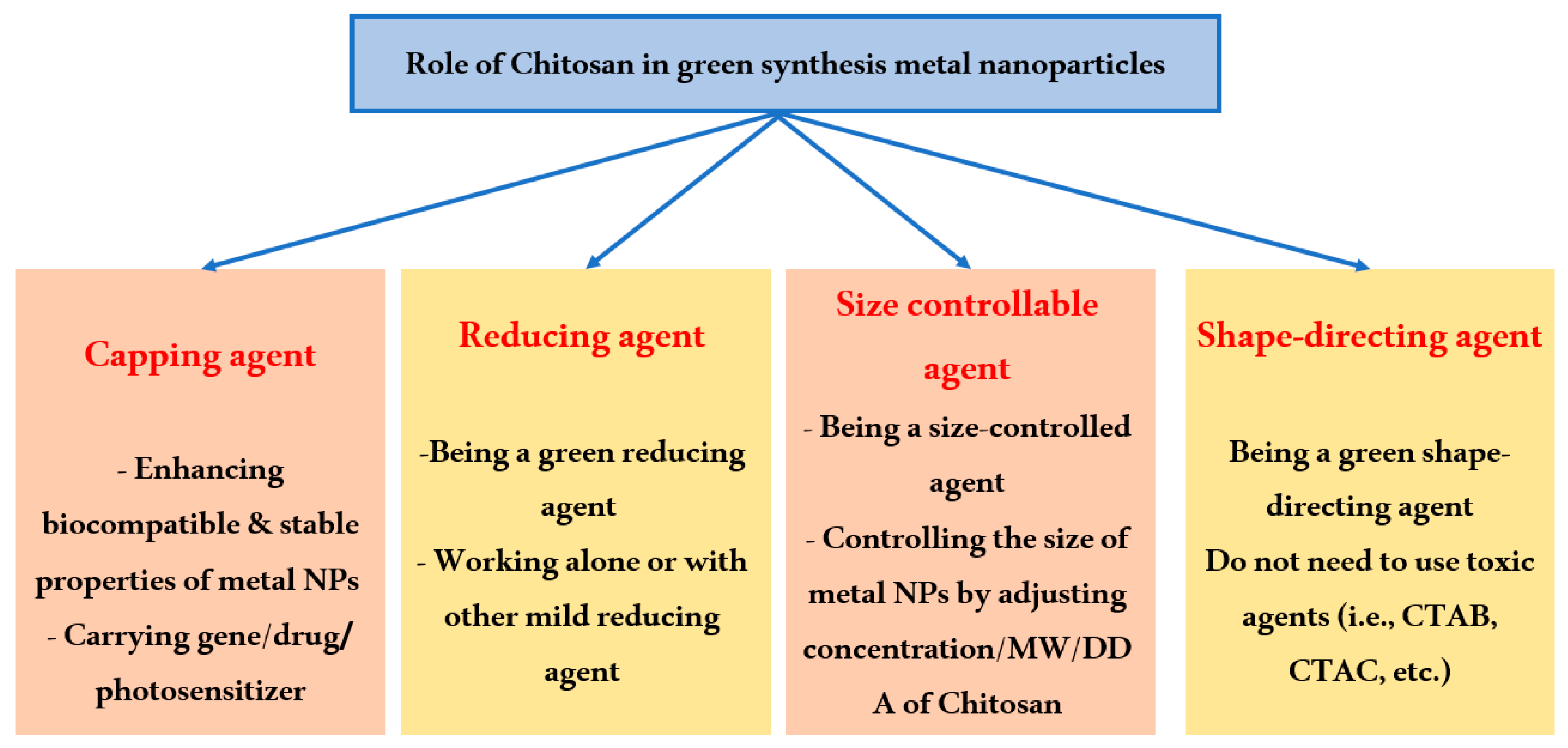
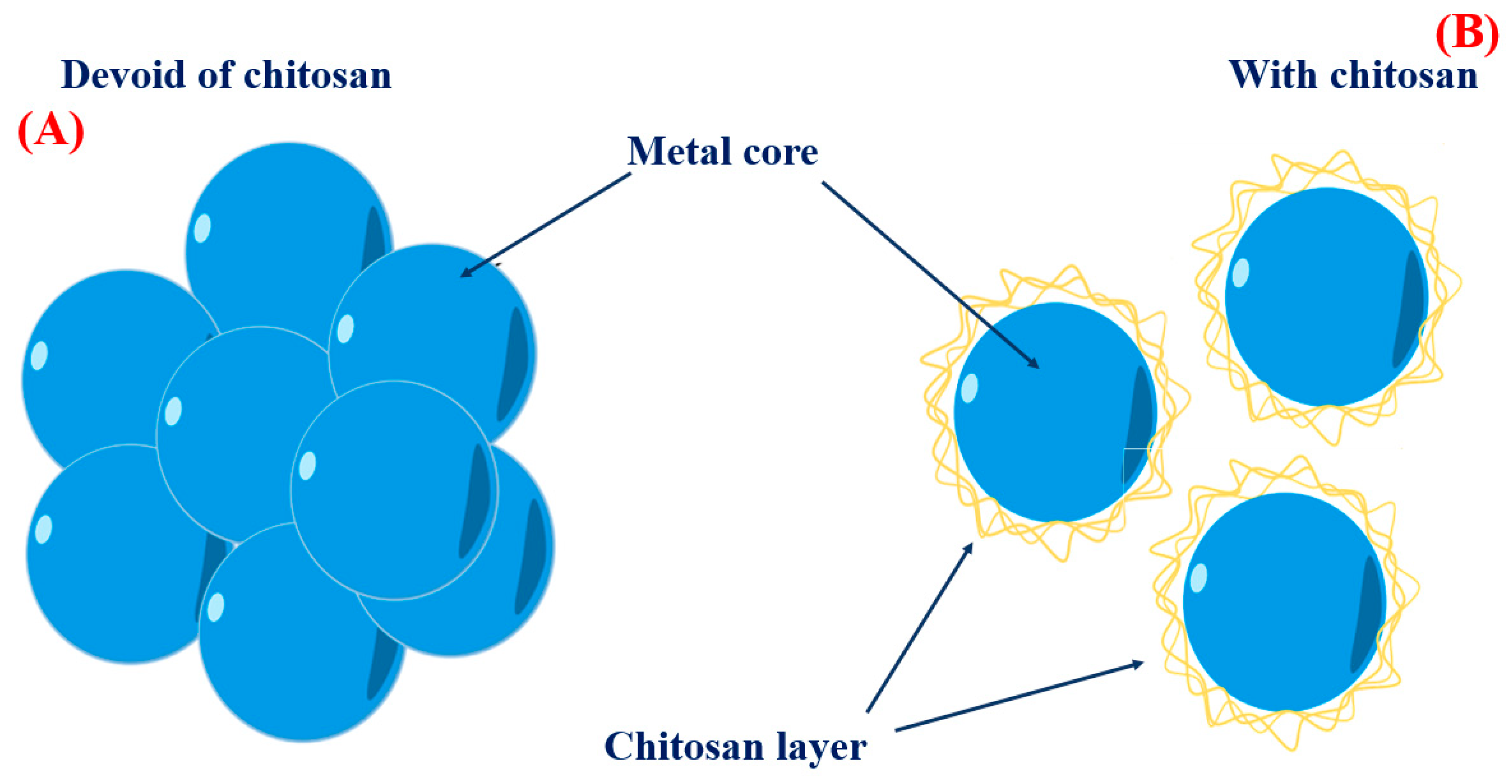
3.1. Chitosan as a Stabilizer
3.2. Chitosan as an Environmentally Friendly Reducing Agent
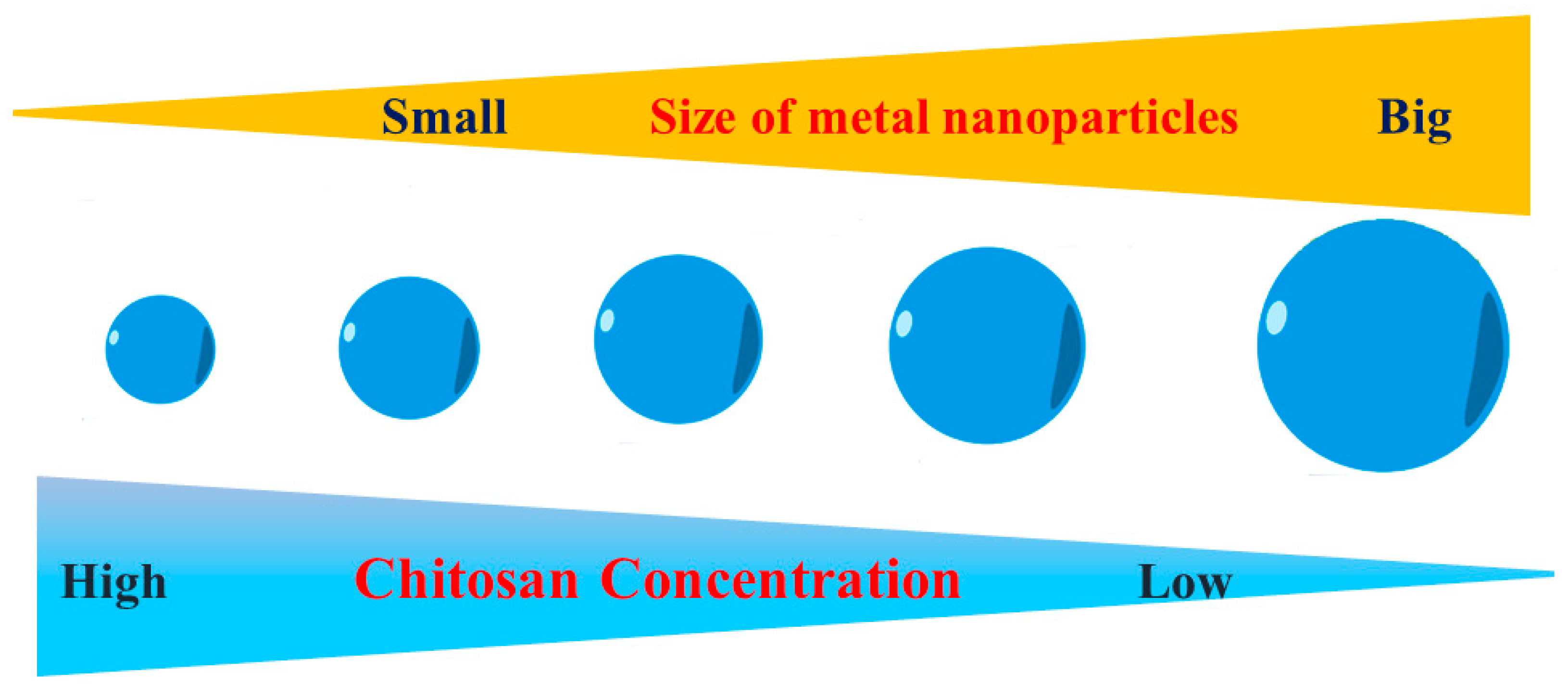
3.3. Chitosan as a Size-Controlling Agent
3.4. Chitosan as a Shape Orientation Agent
3.5. Chitosan as a Multifunctional Tool for Metal Nanoparticle Preparation
4. Preparation of Nanocomposites—Metallic Nanoparticles from CS
| Ref. | Size (nm) | Characterization | Metal |
|---|---|---|---|
| [28] | 20–30 | UV–Vis, FTIR, TEM, EDS, and XRD | Copper–Chitosan Nanoparticle |
| [64] | 25 | UV–Vis, EDX, STEM, and XRD | Chitosan-Stabilized Copper Nanoparticles |
| [65] | 10 | TEM, SEM, X XRD, and UV–Vis, infrared and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopies | CS–AgNPs |
| [66] | 3.5–6.0 | XRD, FE-SEM, UV–Vis, EDAX, FTIR, and TEM | Chitosan–copper oxide nanocomposite |
| [66] | CuO NPs (29.07 nm) and MgO NPs (14.55 nm) | UV–Vis, FTIR, and XRD | Chitosan–CuO-MgO Polymer Nanocomposites |
| [67] | 10–25 | SEM, XRD, and FTIR | Chitosan–CuO bio-nanocomposite |
| [29] | 195.2 | Zeta potential | Fe-loaded chitosan nanoparticles |
| [68] | / | UV–Vis and TEM | AuNPs |
| [37] | 10 ± 60 | UV–Vis, FTIR, TEM, XRD, and AFM | AgNPs |
| [69] | 10 | UV–Vis, EDS, XRD, DLS, FTIR, XPS, and TEM | CS–AuNPs |
| [70] | 75.97 | SEM, XRD, VSM, and FTIR | Fe3O4–CuO–Chitosan Nanocomposites |
| [71] | 5–10 | SEM, UV–Vis, FTIR, TEM, and XRD | Chitosan–Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles |
| [72] | 20 | UV–Vis spectroscopy, XRD, FFT-IR, TGA, DSC, FE-SEM, EDX, AFM, HR-TEM, XPS, and zeta potential analyser | Chitosan–silver nanocomposite |
| [73] | 6–11 | FTIR, FESEM, and EDX | Chitosan–MgO nanocomposite |
| [74] | 15–20 | FTIR, SEM, and XRD | Chitosan–MgO nanocomposite |
| [75] | 44.80 | XRD, FTIR, EDS, TEM, and FESEM | Chitosan–AgNPs |
| [76] | - | TEM, FTIR, UV–Vis, and TEM | AgNPs |
| [76] | 17 | SEM, XRD, and FT-IR | Chi–CuO |
| [40] | 124.3 | / | Chitosan–tripolyphosphate nanoparticles |
| [77] | 20 | UV–Vis, FTIR, XRD, AFM, and TEM | CS–Ag nanocomposites |
| [78] | 6 to 18 | FTIR, XRD, SEM, and TEM | Chitosan–silver nanocomposites |
| [79] | 80 | SEM, Zeta potential, and XRD | AgNPs |
| [80] | 2.1 ± 0.3 | FTIR, UV–vis, Zeta potentials, TEM, XPS, and XRD | PtNPs |
| [81] | 130 | FTIR, XRD, and FESEM | Chitosan–ZnO nanoparticles |
| [82] | 22 | XRD, Zeta potential, TEM, and TGA | Chitosan–zinc oxide Nanocomposites |
| [83] | 40 | SEM | ZnO–chitosan Nanoparticles |
| [84] | - | FT-IR, XRD, SEM, and WDX | Chitosan–zinc oxide nanoparticle |
| [85] | 58 | FT-IR, XRD, and SEM | Chitosan–ZnO nanoparticles |
| [86] | 55 | FT-IR, SEM, and WCA | Chitosan–zinc oxide (ZnO) nanocomposite |
| [87] | MgO NPs: 17 nm, and ZnO NPs: 29 nm | DRX, FT-IR, UV–vis, and SEM | ZnO NPs and MgO NPs |
| [88] | 3–8 | XRD, FTIR, and TEM | Chitosan–Ag nanoparticle |
| [60] | 26.51 | FE-SEM, EDX, XRD and FTIR | Chitosan–TiO2 |
| [27] | 3–15 | UV–vis, FT-IR, and TEM | Chitosan–gold nanoparticle |
| [89] | 60 | XRD, FE-SEM, UV–DRS, and XPES | ZnO |
| [41] | 20–80 | DRX, FT-IR, UV–vis, and SEM | ZnO NPs |
| [90] | 34.5 | XPS XRD, FTIR, TGA, and TEM | Au NPs |
| [91] | - | XRD, BET, FTIR, and SEM | Chitosan–Fe2O3nano composite |
| [92] | - | DRX, FT-IR, TEM, and TGA | Chitosan–zinc oxide hybrid composite |
| [93] | 20 | TEM and SEM-EDX | CuO–chitosan nanocomposite |
| [94] | 17.8 | UV–vis, FT-IR, and TEM | CS–AuNPs |
5. Factors Affecting the Synthesis to Control the Properties of Nanoparticles
5.1. pH
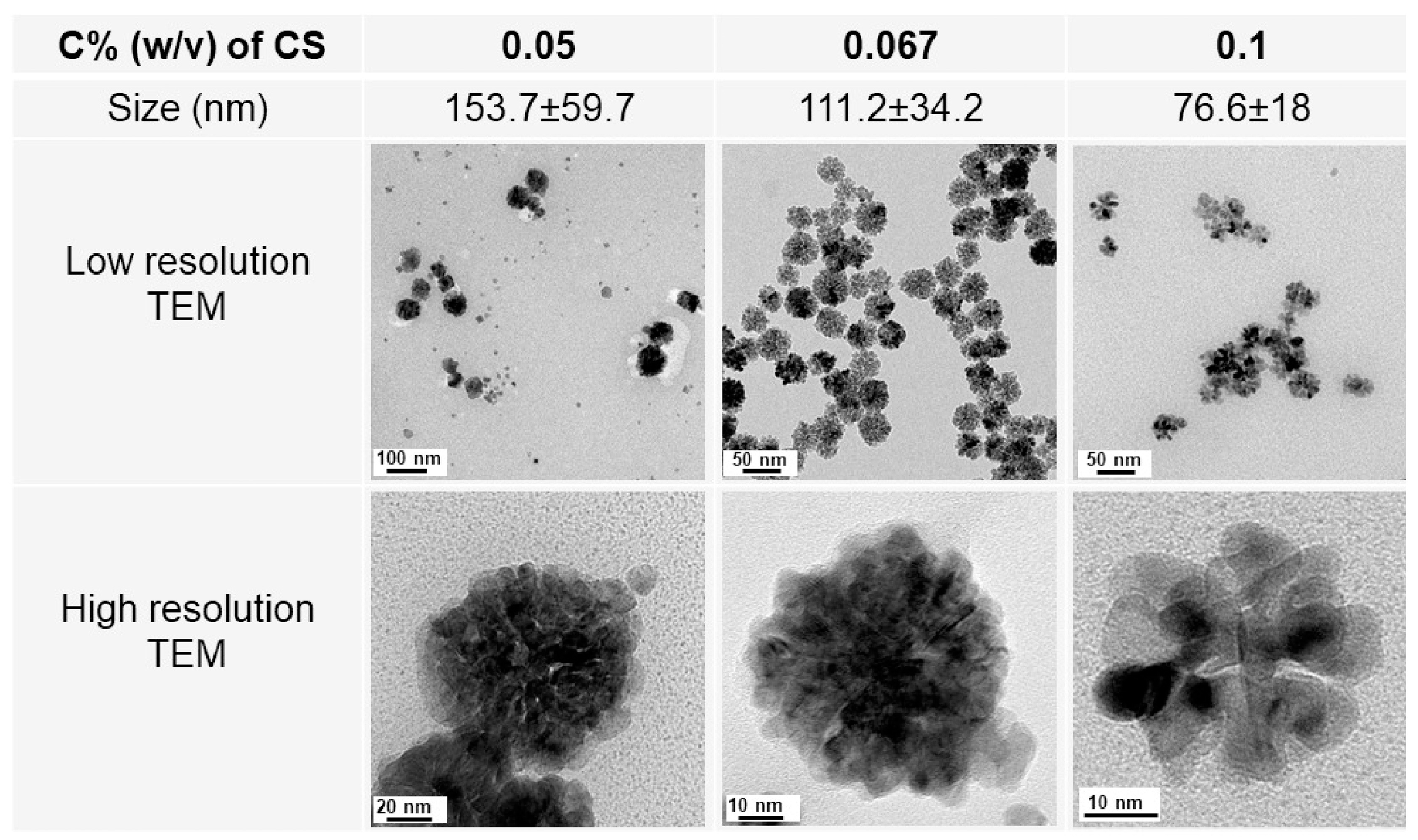
5.2. Chitosan Concentration
5.3. Temperature
5.4. Impact of Ionic Strength
5.5. Cross-Linking Agents
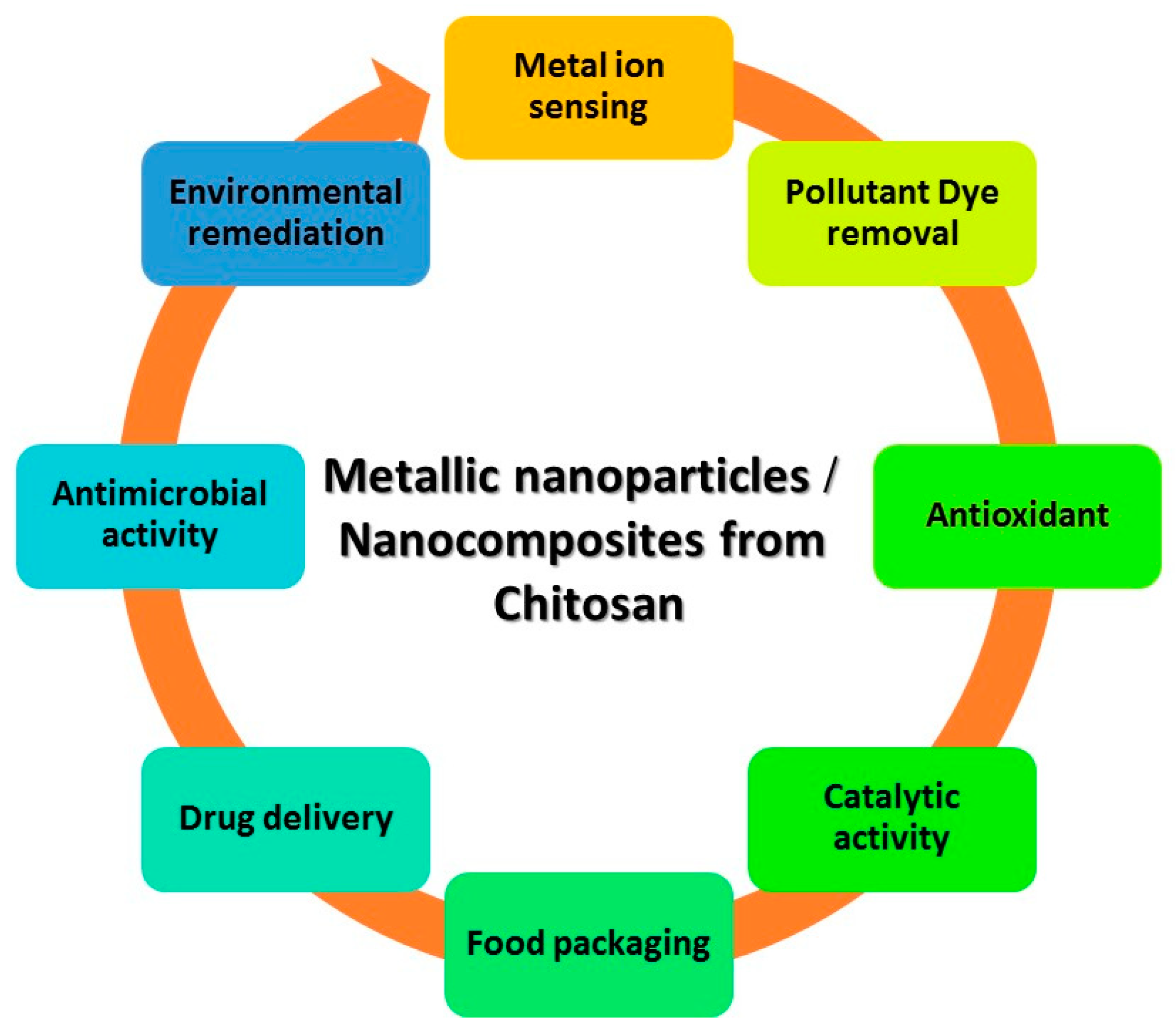
6. Uses for Chitosan-Based Nanocomposites
6.1. Purification of Water
| Nanocomposite Based on Chitosan | Metal/Dye | pH | Extraction Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS/MoO3/TiO2 | Methyl orange | No data | Degradation of photocatalysis under solar light | [108] |
| CS/Ag3PO4/CdS | Methyl orange | 3–8 | Catalytic photo-decolorization | [109] |
| CS/AgNPs | Methyl orange | 3–11 | Photocatalytic decolourization | [72] |
| CS/TiO2 | Congo red, Rhodamine-B | 3–11 | Photocatalytic degradation in the presence of visible light | [110] |
| Palladium/CS | 4-Nitrophenol | No data | Catalytic hydrogenation | [111] |
| CS/PVA/ZnO | Acid Black-1 | No data | Adsorption | [112] |
| Bio-silica/CS | Acid Red 88 | 1–12 | Adsorption | [113] |
| CS/AuNPs | 4-Nitrophenol | No data | Catalytic reduction | [114] |
| CS/lignin/titania | Brilliant Black | No data | Adsorption | [115] |
6.2. Metal Removal Using Metal Nanoparticles from Chitosan
| Chitosan/Metal | Metal Removal | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| MnFe2O4–Chitosan | Adsorption of Cu2+ | [92] |
| Chitosan–Fe3O4 | Pb(II) | [123] |
| Chitosan–FeS | Cu(II) | [124] |
| Chitosan–Fe | Rare-earth metal ions | [119] |
| Fe2O3–Chitosan | Thorium (IV) | [108] |
| PEI@AC@Fe3O4–CS/PVA | Cr(VI) | [125] |
| Fe3O4–Chitosan | Cobalt and nickel | [126] |
| Chitosan–TiO2 | Cr(VI) | [127] |
6.3. Application of Photoacoustic Therapy
6.4. Application of Photothermal Therapy
6.5. Application of Antibacterial Therapy
6.6. Application of Photodynamic Therapy
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamkhande, P.G.; Ghule, N.W.; Bamer, A.H.; Kalaskar, M.G. Metal nanoparticles synthesis: An overview on methods of preparation, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnoudeh, A.J.; Hamad, I.; Abdo, R.W.; Qadumii, L.; Jaber, A.Y.; Surchi, H.S.; Alkelany, S.Z. Synthesis, characterization, and applications of metal nanoparticles. In Biomaterials and Bionanotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 527–612. [Google Scholar]
- Tufani, A.; Qureshi, A.; Niazi, J.H. Iron oxide nanoparticles based magnetic luminescent quantum dots (MQDs) synthesis and biomedical/biological applications: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhamad, A.A.; Zeghoud, S.; Amor, I.B.; Hemmami, H. Chitosan-based hydrogels for wound healing: Correspondence. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 1821–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupusoru, R.V.; Simion, L.; Sandu, I.; Pricop, D.A.; Chiriac, A.; Poroch, V. Aging study of gold nanoparticles functionalized with chitosan in aqueous solutions. Rev. Chi. 2017, 68, 2385–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedri, B.; Shahanipour, K.; Fatahian, S.; Jafary, F. Preparation of chitosan-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles and assessment of their effects on enzymatic antioxidant system as well as high-density lipoprotein/low-density lipoprotein lipoproteins on wistar rat. Biomed. Biotechnol. Res. J. (BBRJ) 2018, 2, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari-Sharbaf, A.; Ezugwu, S.; Ahmed, M.S.; Cottam, M.G.; Fanchini, G. Doping graphene thin films with metallic nanoparticles: Experiment and theory. Carbon 2015, 95, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, I.; Alcántara, A.R.; Civera, M.C.; Arias, C.; Elorza, B.; Heras Caballero, A.; Acosta, N. Chitosan: An overview of its properties and applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heux, L.; Brugnerotto, J.; Desbrieres, J.; Versali, M.-F.; Rinaudo, M. Solid state NMR for determination of degree of acetylation of chitin and chitosan. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L. Determining the deacetylation degree of chitosan: Opportunities to learn instrumental techniques. J. Chem. Educ. 2018, 95, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, M.; Chiellini, F.; Ottenbrite, R.M.; Chiellini, E. Chitosan—A versatile semi-synthetic polymer in biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 981–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.; Daum, G.; Köster, M.; Kulicke, W.-M.; Meyer-Rammes, H.; Bisping, B.; Meinhardt, F. Genetic improvement of Bacillus licheniformis strains for efficient deproteinization of shrimp shells and production of high-molecular-mass chitin and chitosan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 8211–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, M.; Baran, T.; Erdoğan, S.; Menteş, A.; Özüsağlam, M.A.; Çakmak, Y.S. Physicochemical comparison of chitin and chitosan obtained from larvae and adult Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata). Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 45, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Dunn, E.; Grandmaison, E.; Goosen, M.F. Applications and properties of chitosan. In Applications of Chitan and Chitosan; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 3–29. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Ghosh, S.; Pramanik, N. Chitosan biopolymer and its composites: Processing, properties and applications-A comprehensive review. Hybrid Adv. 2024, 6, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofuji, K.; Qian, C.-J.; Nishimura, M.; Sugiyama, I.; Murata, Y.; Kawashima, S. Relationship between physicochemical characteristics and functional properties of chitosan. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, M. Synthesis of Nano-Particles by Miniemulsion Polymerization. Aριστοτέλειο Πανεπιστήμιο Θεσσαλονίκης (AΠΘ). Σχολή Πολυτεχνική. Τμήμα. 2009. Available online: https://www.didaktorika.gr/eadd/handle/10442/19891?locale=en (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Kamath, P.R.; Sunil, D. Nano-chitosan particles in anticancer drug delivery: An up-to-date review. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1457–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abioye, A.O.; Tangyie Chi, G.; T Kola-Mustapha, A.; Ruparelia, K.; Beresford, K.; Arroo, R. Polymer-drug nanoconjugate–an innovative nanomedicine: Challenges and recent advancements in rational formulation design for effective delivery of poorly soluble drugs. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2016, 4, 38–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Germershaus, O.; Lühmann, T.; Rybak, J.-C.; Ritzer, J.; Meinel, L. Application of natural and semi-synthetic polymers for the delivery of sensitive drugs. Int. Mater. Rev. 2015, 60, 101–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado-González, M.; Montalbán, M.G.; Peña-García, J.; Pérez-Sánchez, H.; Víllora, G.; Baños, F.G.D. Chitosan as stabilizing agent for negatively charged nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 161, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L.; Onzi, G.; Morawski, A.; Pohlmann, A.; Guterres, S.; Contri, R. Chitosan as a coating material for nanoparticles intended for biomedical applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 147, 104459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinteza, L.O.; Scomoroscenco, C.; Voicu, S.N.; Nistor, C.L.; Nitu, S.G.; Trica, B.; Jecu, M.-L.; Petcu, C. Chitosan-stabilized Ag nanoparticles with superior biocompatibility and their synergistic antibacterial effect in mixtures with essential oils. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esther, J.; Sridevi, V. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-stabilized gold nanoparticles through a facile and green approach. Gold Bull. 2017, 50, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathiraja, S.; Bui, N.Q.; Manivasagan, P.; Moorthy, M.S.; Mondal, S.; Seo, H.; Phuoc, N.T.; Vy Phan, T.T.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.D. Multimodal tumor-homing chitosan oligosaccharide-coated biocompatible palladium nanoparticles for photo-based imaging and therapy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrica-González, P.; Zamora-Justo, J.A.; Sotelo-López, A.; Vázquez-Martínez, G.R.; Balderas-López, J.A.; Muñoz-Diosdado, A.; Ibáñez-Hernández, M. Gold nanoparticles with chitosan, N-acylated chitosan, and chitosan oligosaccharide as DNA carriers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, A.; Sathiyabama, M. Green synthesis of copper-chitosan nanoparticles and study of its antibacterial activity. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Pan, C.; Liang, C. Antimicrobial activity of Fe-loaded chitosan nanoparticles. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Qian, W. Facile synthesis of Ag and Au nanoparticles utilizing chitosan as a mediator agent. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 62, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesham, M.; Ayodhya, D.; Madhusudhan, A.; Veera Babu, N.; Veerabhadram, G. A novel green one-step synthesis of silver nanoparticles using chitosan: Catalytic activity and antimicrobial studies. Appl. Nanosci. 2014, 4, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapeto, A.P.; Ferraria, A.M.; do Rego, A.M.B. Unraveling the reaction mechanism of silver ions reduction by chitosan from so far neglected spectroscopic features. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhumkar, D.R.; Joshi, H.M.; Sastry, M.; Pokharkar, V.B. Chitosan reduced gold nanoparticles as novel carriers for transmucosal delivery of insulin. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongpreecha, J.; Polpanich, D.; Suteewong, T.; Kaewsaneha, C.; Tangboriboonrat, P. One-pot, large-scale green synthesis of silver nanoparticles-chitosan with enhanced antibacterial activity and low cytotoxicity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Ding, X.; Niu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. Green preparation of core-shell Cu@Pd nanoparticles with chitosan for glucose detection. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, M.; Ahmadvand, D.; Sabouri, Z.; Darroudi, M. Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles by chitosan polymer and assessment of their photocatalytic activity and cytotoxicity influences. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 301, 127649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaivani, R.; Maruthupandy, M.; Muneeswaran, T.; Beevi, A.H.; Anand, M.; Ramakritinan, C.; Kumaraguru, A. Synthesis of chitosan mediated silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) for potential antimicrobial applications. Front. Lab. Med. 2018, 2, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.V.; Hoang, G.; Nguyen, T.P.; Kim, H.H.; Mondal, S.; Manivasagan, P.; Moorthy, M.S.; Lee, K.D.; Junghwan, O. Chitosan as a stabilizer and size-control agent for synthesis of porous flower-shaped palladium nanoparticles and their applications on photo-based therapies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.V.; Ahn, S.-H.; Oh, J. Chitosan-mediated facile green synthesis of size-controllable gold nanostars for effective photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 118, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Rahimi, Z.; Rahimi, M. Chitosan/tripolyphosphate nanoparticles in active and passive microchannels. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Amor, I.; Hemmami, H.; Laouini, S.E.; Mahboub, M.S.; Barhoum, A. Sol-gel synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using different chitosan sources: Effects on antibacterial activity and photocatalytic degradation of AZO Dye. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Shao, D.; Ji, W.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Song, J. The nanotoxicity investigation of optical nanoparticles to cultured cells in vitro. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Jiang, D.; Cai, Y.; Ji, X.; Xie, R.; Yang, W. Tuning the size of gold nanoparticles in the citrate reduction by chloride ions. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5071–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, S.; Sangaranarayanan, M. Shape-controlled electrodeposition of silver using chitosan as structure-directing agent on disposable pencil graphite electrodes: Low-cost electrocatalysts for the detection of hydrogen peroxide and hydrazine hydrate. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2020, 24, 2773–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Gu, G.; Xia, X.-H.; Huo, Q. Cysteine-grafted chitosan-mediated gold nanoparticle assembly: From nanochains to microcubes. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizaki, K.-Y.; Kishioka, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Kobayashi, A.; Yamada, N.; Kataoka, S.; Imai, T.; Kasuno, M. Roles of aromatic side chains and template effects of the hydrophobic cavity of a self-assembled peptide nanoarchitecture for anisotropic growth of gold nanocrystals. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 7282–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luesakul, U.; Komenek, S.; Puthong, S.; Muangsin, N. Shape-controlled synthesis of cubic-like selenium nanoparticles via the self-assembly method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, A.; Huang, L.; Zhu, J.; Chen, L. Synthesis of dextran/Se nanocomposites for nanomedicine application. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 109, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.S.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Shameli, K.; Zainuddin, N.; Yunus, W.M.Z.W. Copper nanoparticles mediated by chitosan: Synthesis and characterization via chemical methods. Molecules 2012, 17, 14928–14936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, F.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; N Al-Haque, H. Chitosan-mediated fabrication of metal nanocomposites for enhanced biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2017, 8, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.S. Greener approach to nanomaterials and their sustainable applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 1, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, B.; Kuiken, T.; Otto, M. Nanotechnology and in situ remediation: A review of the benefits and potential risks. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1813–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, A.A. Bioinspired Nanocomposites for Adsorptive and Photo-assisted Decontamination of Wastewater. In Nanotechnology in Environmental Science; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2018; pp. 685–710. [Google Scholar]
- Lone, M.N.; Wani, I.A. Nanocomposites in Environmental Engineering. In Composites for Environmental Engineering; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 263–318. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Rehman, F.; Rafeeq, H.; Waqas, M.; Asghar, A.; Afsheen, N.; Rahdar, A.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M. In-situ, Ex-situ, and nano-remediation strategies to treat polluted soil, water, and air—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, B.; Zhang, K.; Hoye, R.L.; Torrente-Murciano, L. Importance of Monitoring the Synthesis of Light-Interacting Nanoparticles–A Review on In Situ, Ex Situ, and Online Time-Resolved Studies. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2200524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, K.D.N.; Guillon, E.; Dupont, L.; Kowandy, C.; Coqueret, X. Influence of Au (III) interactions with chitosan on gold nanoparticle formation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 4465–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanpui, P.; Murugadoss, A.; Prasad, P.D.; Ghosh, S.S.; Chattopadhyay, A. The antibacterial properties of a novel chitosan–Ag-nanoparticle composite. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 124, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Qiu, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Sakai, E.; Wei, Y. Preparation of magnetic chitosan nanoparticles as support for cellulase immobilization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3448–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Khan, S.B.; Kamal, T.; Alamry, K.A.; Asiri, A.M. Chitosan-titanium oxide fibers supported zero-valent nanoparticles: Highly efficient and easily retrievable catalyst for the removal of organic pollutants. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, R.C.; Kumaraswamy, R.; Kumari, S.; Sharma, S.; Pal, A.; Raliya, R.; Biswas, P.; Saharan, V. Zinc encapsulated chitosan nanoparticle to promote maize crop yield. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, T.; Khan, S.B.; Asiri, A.M. Nickel nanoparticles-chitosan composite coated cellulose filter paper: An efficient and easily recoverable dip-catalyst for pollutants degradation. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Dash, S.K.; Kar Mahapatra, S.; Tripathy, S.; Ghosh, T.; Das, B.; Das, D.; Pramanik, P.; Roy, S. Chitosan-modified cobalt oxide nanoparticles stimulate TNF-α-mediated apoptosis in human leukemic cells. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 19, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarek, K.; Hueso, J.L.; Kuśtrowski, P.; Stochel, G.; Kyzioł, A. Green synthesis of chitosan-stabilized copper nanoparticles. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 4940–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar-Krishnan, S.; Prokhorov, E.; Hernández-Iturriaga, M.; Mota-Morales, J.D.; Vázquez-Lepe, M.; Kovalenko, Y.; Sanchez, I.C.; Luna-Bárcenas, G. Chitosan/silver nanocomposites: Synergistic antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles and silver ions. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praffulla, S.; Bubbly, S. Synthesis and characterization of Chitosan-CuO-MgO polymer nanocomposites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1953, 030168. [Google Scholar]
- Farhoudian, S.; Yadollahi, M.; Namazi, H. Facile synthesis of antibacterial chitosan/CuO bio-nanocomposite hydrogel beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Li, J.; Cai, J.; Zhong, L.; Ren, G.; Ma, Q. One pot synthesis of gold nanoparticles using chitosan with varying degree of deacetylation and molecular weight. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 178, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xia, Y. Facile synthesis of chitosan-gold nanocomposite and its application for exclusively sensitive detection of Ag+ ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 226, 115290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Huong, N.; Thi Mai Huong, P.; Thi Kim Giang, N.; Thi Lan, P.; Thanh Dong, V.; Tien Dung, C. Fe3O4/CuO/Chitosan Nanocomposites: An Ultrasound-Assisted Green Approach for Antibacterial and Photocatalytic Properties. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 42429–42439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdElhady, M. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/zinc oxide nanoparticles for imparting antimicrobial and UV protection to cotton fabric. Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2012, 2012, 840591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, A.; JeevaKumari, H.L.; Rokesh, K.; Ruckmani, K.; Jeganathan, K.; Jothivenkatachalam, K. A versatile effect of chitosan-silver nanocomposite for surface plasmonic photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 153, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyadh, S.M.; Khalil, K.D.; Aljuhani, A. Chitosan-MgO nanocomposite: One pot preparation and its utility as an ecofriendly biocatalyst in the synthesis of thiazoles and [1, 3, 4] thiadiazoles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, K.D.; Bashal, A.H.; Khalafalla, M.; Zaki, A.A. Synthesis, structural, dielectric and optical properties of chitosan-MgO nanocomposite. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2020, 14, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, P.; Yaswant, G.; Kavitha, S.; Chandramohan, E.; Kowsalya, G.; Vijay, R.; Sudhagar, B.; Kumar, D.R.S. Preparation and characterization of hybrid chitosan-silver nanoparticles (Chi-Ag NPs); A potential antibacterial agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logpriya, S.; Bhuvaneshwari, V.; Vaidehi, D.; SenthilKumar, R.; Nithya Malar, R.; Pavithra Sheetal, B.; Amsaveni, R.; Kalaiselvi, M. Preparation and characterization of ascorbic acid-mediated chitosan–copper oxide nanocomposite for anti-microbial, sporicidal and biofilm-inhibitory activity. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2018, 8, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjunan, N.; Kumari, H.L.J.; Singaravelu, C.M.; Kandasamy, R.; Kandasamy, J. Physicochemical investigations of biogenic chitosan-silver nanocomposite as antimicrobial and anticancer agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruthupandy, M.; Rajivgandhi, G.; Muneeswaran, T.; Vennila, T.; Quero, F.; Song, J.-M. Chitosan/silver nanocomposites for colorimetric detection of glucose molecules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawy, M.E.; Lotfy, T.M.; Shawir, S. Preparation and antibacterial activity of chitosan-silver nanoparticles for application in preservation of minced meat. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.-H.; Lin, X.-L.; Liu, Y.-H.; Li, K.-L.; Zhuang, Q.-Q.; Peng, H.-P.; Liu, A.-L.; Xia, X.-H.; Chen, W. Chitosan-stabilized platinum nanoparticles as effective oxidase mimics for colorimetric detection of acid phosphatase. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10292–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.A.A.; Zain, N.M.; Pauzi, N. Synthesis of chitosan/zinc oxide nanoparticles stabilized by chitosan via microwave heating. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal 2019, 14, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiya, S.; Okram, G.; Dhivya, S.M.; Manivannan, G.; Rajan, M.J. Interaction of chitosan/zinc oxide nanocomposites and their antibacterial activities with Escherichia coli. Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, 3855–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, A.; Moussa, S.; Ulbricht, M.; Textor, T. ZnO nanoparticles-chitosan composite as antibacterial finish for textiles. Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2012, 2012, 693629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, R.; Arami, M.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Bahrami, H.; Khorramfar, S. Novel biocompatible composite (chitosan–zinc oxide nanoparticle): Preparation, characterization and dye adsorption properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 80, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaghi, S.M.; Rahmanifar, B.; Moradi, A.M.; Azar, P.A. Removal of permethrin pesticide from water by chitosan–zinc oxide nanoparticles composite as an adsorbent. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naamani, L.; Dobretsov, S.; Dutta, J. Chitosan-zinc oxide nanoparticle composite coating for active food packaging applications. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 38, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, I.B.; Hemmami, H.; Laouini, S.E.; Temam, H.B.; Zaoui, H.; Barhoum, A. Biosynthesis MgO and ZnO nanoparticles using chitosan extracted from Pimelia Payraudi Latreille for antibacterial applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akmaz, S.; Dilaver Adıgüzel, E.; Yasar, M.; Erguven, O. The Effect of Ag Content of the Chitosan-Silver Nanoparticle Composite Material on the Structure and Antibacterial Activity. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 690918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, A.; Jothivenkatachalam, K. Chitosan assisted synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: An efficient solar light driven photocatalyst and evaluation of antibacterial activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 10207–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zuo, F.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ding, X. Green and facile synthesis of gold nanoparticles stabilized by chitosan. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2014, 51, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broujeni, B.R.; Nilchi, A.; Hassani, A.; Saberi, R. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/Fe2O3 nano composite for the adsorption of thorium (IV) ion from aqueous solution. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldorai, Y.; Shim, J.-J. Chitosan-zinc oxide hybrid composite for enhanced dye degradation and antibacterial activity. Compos. Interfaces 2013, 20, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, M.; Hebeish, A. Preparation and evaluation of CuO/chitosan nanocomposite for antibacterial finishing cotton fabric. J. Ind. Text. 2010, 39, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanayutsiri, T.; Patrojanasophon, P.; Opanasopit, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Plianwong, S.; Rojanarata, T. Rapid synthesis of chitosan-capped gold nanoparticles for analytical application and facile recovery of gold from laboratory waste. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.H.; Shehabeldine, A.M.; Ali, O.M.; Salem, S.S. Synthesis of chitosan-based gold nanoparticles: Antimicrobial and wound-healing activities. Polymers 2022, 14, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Lapitsky, Y. Biomolecular uptake effects on chitosan/tripolyphosphate micro-and nanoparticle stability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 193, 111081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, C.O.; Gunasekaran, S.; Ravishankar, C. Chitosan-capped gold nanoparticles for indicating temperature abuse in frozen stored products. npj Sci. Food 2019, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Alves, D.C.; Healy, B.; Pinto, L.A.d.A.; Cadaval, T.R.S.A., Jr.; Breslin, C.B. Recent developments in chitosan-based adsorbents for the removal of pollutants from aqueous environments. Molecules 2021, 26, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picola, I.P.D.; Busson, K.A.N.; Casé, A.H.; Nasário, F.D.; Tiera, V.A.d.O.; Taboga, S.R.; Neto, J.R.; Tiera, M.J. Effect of ionic strength solution on the stability of chitosan–DNA nanoparticles. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2013, 8, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prado-Audelo, M.L.; Caballero-Florán, I.H.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Mendoza-Muñoz, N.; González-Torres, M.; Urbán-Morlán, Z.; Florán, B.; Cortes, H.; Leyva-Gómez, G. Chitosan-decorated nanoparticles for drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogugbue, C.J.; Sawidis, T. Bioremediation and detoxification of synthetic wastewater containing triarylmethane dyes by Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from industrial effluent. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 967925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüschweiler, B.J. Toxicity of non-regulated aromatic amines from azo dyes in textiles: Knowns and unknowns. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 221, S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.K.; Rahayu, F.; Ben Amor, I.; Quadir, M.; Murianingrum, M.; Parnidi, P.; Ayub, A.; Supriyadi, S.; Sakiroh, S.; Saefudin, S. Environmental resilience through artificial intelligence: Innovations in monitoring and management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 18379–18395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, S. Removal of various pollutants from water and wastewater by modified chitosan adsorbents. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 2331–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Shen, Y.; Wen, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, W. Fast and highly efficient removal of dyes under alkaline conditions using magnetic chitosan-Fe (III) hydrogel. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5200–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Khan, S.B.; Kamal, T.; Anwar, Y.; Alamry, K.A.; Asiri, A.M. Anti-bacterial chitosan/zinc phthalocyanine fibers supported metallic and bimetallic nanoparticles for the removal of organic pollutants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
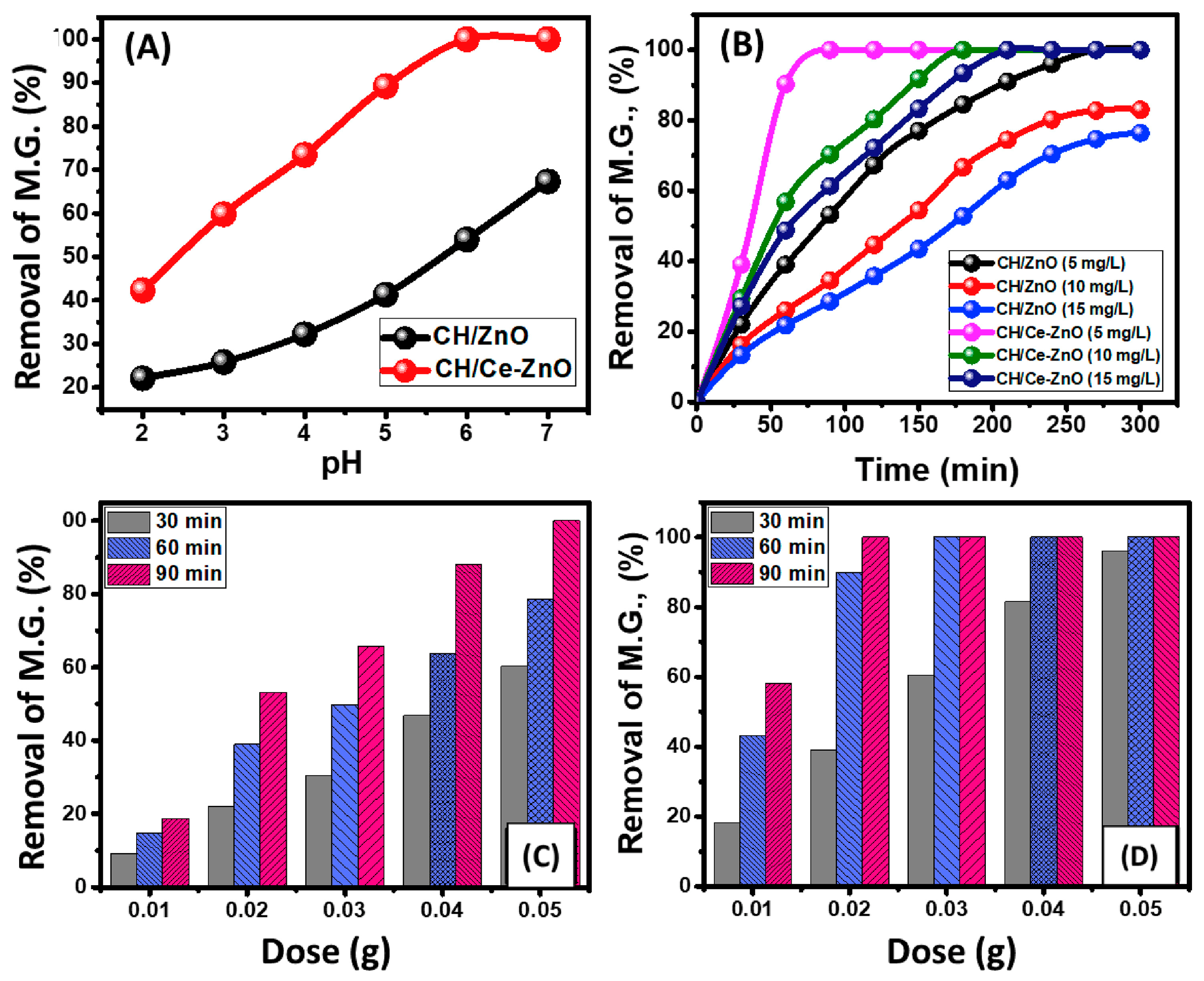
- Saad, A.M.; Abukhadra, M.R.; Ahmed, S.A.-K.; Elzanaty, A.M.; Mady, A.H.; Betiha, M.A.; Shim, J.-J.; Rabie, A.M. Photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye using chitosan supported ZnO and Ce–ZnO nano-flowers under visible light. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 258, 110043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanocomposite of chitosan/SiO2/carbon nanotubes and its application for dyes removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 145, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Xiao, L.; Zeng, L.; Cao, C.; Wang, J. Ag3PO4/chitosan/CdS nanocomposites exhibiting high photocatalytic activities under visible-light illumination. Powder Technol. 2017, 321, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Nithya, A.; Jothivenkatachalam, K. Photocatalytic and antimicrobial activities of chitosan-TiO2 nanocomposite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1762–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanavel, S.; Manivannan, N.; Mathivanan, N.; Gupta, V.K.; Narayanan, V.; Stephen, A. Preparation and characterization of cross-linked chitosan/palladium nanocomposites for catalytic and antibacterial activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 257, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Krishnakumar, B.; Sobral, A.J.; Koh, J. Bio-based (chitosan/PVA/ZnO) nanocomposites film: Thermally stable and photoluminescence material for removal of organic dye. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.D.C.; Khataee, A.; Safari, M.; Joo, S. Preparation of bio-silica/chitosan nanocomposite for adsorption of a textile dye in aqueous solutions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, O.; Bonardd, S.; Saldías, C.; Radic, D.; Leiva, Á. Biobased chitosan nanocomposite films containing gold nanoparticles: Obtainment, characterization, and catalytic activity assessment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16561–16570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masilompane, T.M.; Chaukura, N.; Mishra, S.B.; Mishra, A.K. Chitosan-lignin-titania nanocomposites for the removal of brilliant black dye from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhakeem, M.A.; Ramadan, M.M.; Basaad, F.S. Removing of heavymetals from water by chitosan nanoparticles. J. Adv. Chem. 2015, 11, 3765–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A.C.; Mecabô, A.; Fagundes, T.; Rodrigues, C.A. Adsorption of Cr (VI) using Fe-crosslinked chitosan complex (Ch-Fe). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sherbini, A.-S.A.; Ghannam, H.E.; El-Ghanam, G.M.; El-Ella, A.A.; Youssef, A.M. Utilization of chitosan/Ag bionanocomposites as eco-friendly photocatalytic reactor for Bactericidal effect and heavy metals removal. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Zheng, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, E.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Yan, Y. Preparation of diethylenetriamine-modified magnetic chitosan nanoparticles for adsorption of rare-earth metal ions. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 7739–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Chen, D.; Sun, Y.; Jiao, D.; Zeng, D.; Liu, Z. Adsorption of Cu2+ ions using chitosan-modified magnetic Mn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 324, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Deliyanni, E.A. Mercury (II) removal with modified magnetic chitosan adsorbents. Molecules 2013, 18, 6193–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, I.B.; Hemmami, H.; Laouini, S.E.; Ahmed, S.; Mohammed, H.A.; Abdullah, J.A.A.; Azooz, E.A.; Al-Mulla, E.A.J.; Alharthi, F. Enhancing oxidant and dye scavenging through MgO-based chitosan nanoparticles for potential antioxidant coatings and efficient photocatalysts. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, P.; Xiao, W.; Li, G.; Yi, J.; He, Y.; Chen, C.; Ding, P.; Duan, Y. Efficient removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution by a novel ion imprinted magnetic biosorbent: Adsorption kinetics and mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, J.; Shen, C.; Li, H.; Liu, W. Carbonaceous sulfur-containing chitosan–Fe (III): A novel adsorbent for efficient removal of copper (II) from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Arputharaj, E.; Dahms, H.-U.; Patel, A.K.; Huang, Y.-L. Chitosan-based nanocomposites for removal of Cr (VI) and synthetic food colorants from wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 127018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, M.J.; Nouralishahi, A.; Hallajisani, A. Fe3O4-chitosan nanocomposite as a magnetic biosorbent for removal of nickel and cobalt heavy metals from polluted water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Obaidi, N.S.; Sadeq, Z.E.; Mahmoud, Z.H.; Abd, A.N.; Al-Mahdawi, A.S.; Ali, F.K. Synthesis of chitosan-TiO2 nanocomposite for efficient Cr (VI) removal from contaminated wastewater sorption kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism. J. Oleo Sci. 2023, 72, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Jeon, M.; Kim, C. Photoacoustic imaging in nanomedicine. In Applications of Nanoscience in Photomedicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, A.B.E.; Balasundaram, G.; Moothanchery, M.; Dinish, U.; Bi, R.; Ntziachristos, V.; Olivo, M. A review of clinical photoacoustic imaging: Current and future trends. Photoacoustics 2019, 16, 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khot, M.I.; Andrew, H.; Svavarsdottir, H.S.; Armstrong, G.; Quyn, A.J.; Jayne, D.G. A review on the scope of photothermal therapy–based nanomedicines in preclinical models of colorectal cancer. Clin. Color. Cancer 2019, 18, e200–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margheri, G.; Trigari, S.; Berti, M.; Muniz Miranda, M.; Traversi, R. Chitosan-Capped Au Nanoparticles for Laser Photothermal Ablation Therapy: UV-Vis Characterization and Optothermal Performances. J. Spectrosc. 2018, 2018, 8271254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Sun, X.; Jasinski, J.; Patel, D.; Gobin, A.M. Gold/chitosan nanocomposites with specific near infrared absorption for photothermal therapy applications. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 853416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ning, C.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Tan, G.; Mao, C. Nanomaterials as photothermal therapeutic agents. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 99, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Wang, H.; He, B.; Zeng, L.; Tan, T.; Cao, H.; He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, Y. Current approaches of photothermal therapy in treating cancer metastasis with nanotherapeutics. Theranostics 2016, 6, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.W.; Manivasagan, P.; Kwon, J.; Mondal, S.; Ly, C.D.; Lee, J.; Kang, Y.-H.; Kim, C.-S.; Oh, J. Folic acid–conjugated chitosan-functionalized graphene oxide for highly efficient photoacoustic imaging-guided tumor-targeted photothermal therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, M.; Montalbán, M.; Carissimi, G.; Lima, B.; Feresin, G.E.; Cano, M.; Giner-Casares, J.; López-Cascales, J.; Enriz, R.D.; Víllora, G. Antibacterial effect of chitosan–gold nanoparticles and computational modeling of the interaction between chitosan and a lipid bilayer model. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, G.; Regiel-Futyra, A.; Andreu, V.; Sebastian, V.; Kyzioł, A.; Stochel, G.y.; Arruebo, M. Bactericidal effect of gold–chitosan nanocomposites in coculture models of pathogenic bacteria and human macrophages. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17693–17701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S. Enhanced antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles immobilized in a chitosan nanocarrier. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari, K.; Pichaimani, A.; Kumpati, P. Acridine orange tethered chitosan reduced gold nanoparticles: A dual functional probe for combined photodynamic and photothermal therapy. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 20471–20479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, M.; Lv, J.; Li, H.; Yuan, Z. Chemiluminescence in combination with organic photosensitizers: Beyond the light penetration depth limit of photodynamic therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefflova, K.; Chen, J.; Zheng, G. Killer beacons for combined cancer imaging and therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 2110–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Amor, I.; Hemmami, H.; Grara, N.; Aidat, O.; Ben Amor, A.; Zeghoud, S.; Bellucci, S. Chitosan: A Green Approach to Metallic Nanoparticle/Nanocomposite Synthesis and Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182662
Ben Amor I, Hemmami H, Grara N, Aidat O, Ben Amor A, Zeghoud S, Bellucci S. Chitosan: A Green Approach to Metallic Nanoparticle/Nanocomposite Synthesis and Applications. Polymers. 2024; 16(18):2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182662
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Amor, Ilham, Hadia Hemmami, Nedjoud Grara, Omaima Aidat, Asma Ben Amor, Soumeia Zeghoud, and Stefano Bellucci. 2024. "Chitosan: A Green Approach to Metallic Nanoparticle/Nanocomposite Synthesis and Applications" Polymers 16, no. 18: 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182662
APA StyleBen Amor, I., Hemmami, H., Grara, N., Aidat, O., Ben Amor, A., Zeghoud, S., & Bellucci, S. (2024). Chitosan: A Green Approach to Metallic Nanoparticle/Nanocomposite Synthesis and Applications. Polymers, 16(18), 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182662









