Melatonin and Bacterial Cellulose Regulate the Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines, VEGF, PCNA, and Collagen in Cutaneous Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Diabetes Induction
2.3. Melatonin Treatment
2.4. Treatment with Bacterial Cellulose and Commercial Healing
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Evaluation and Quantification of Collagen I and III
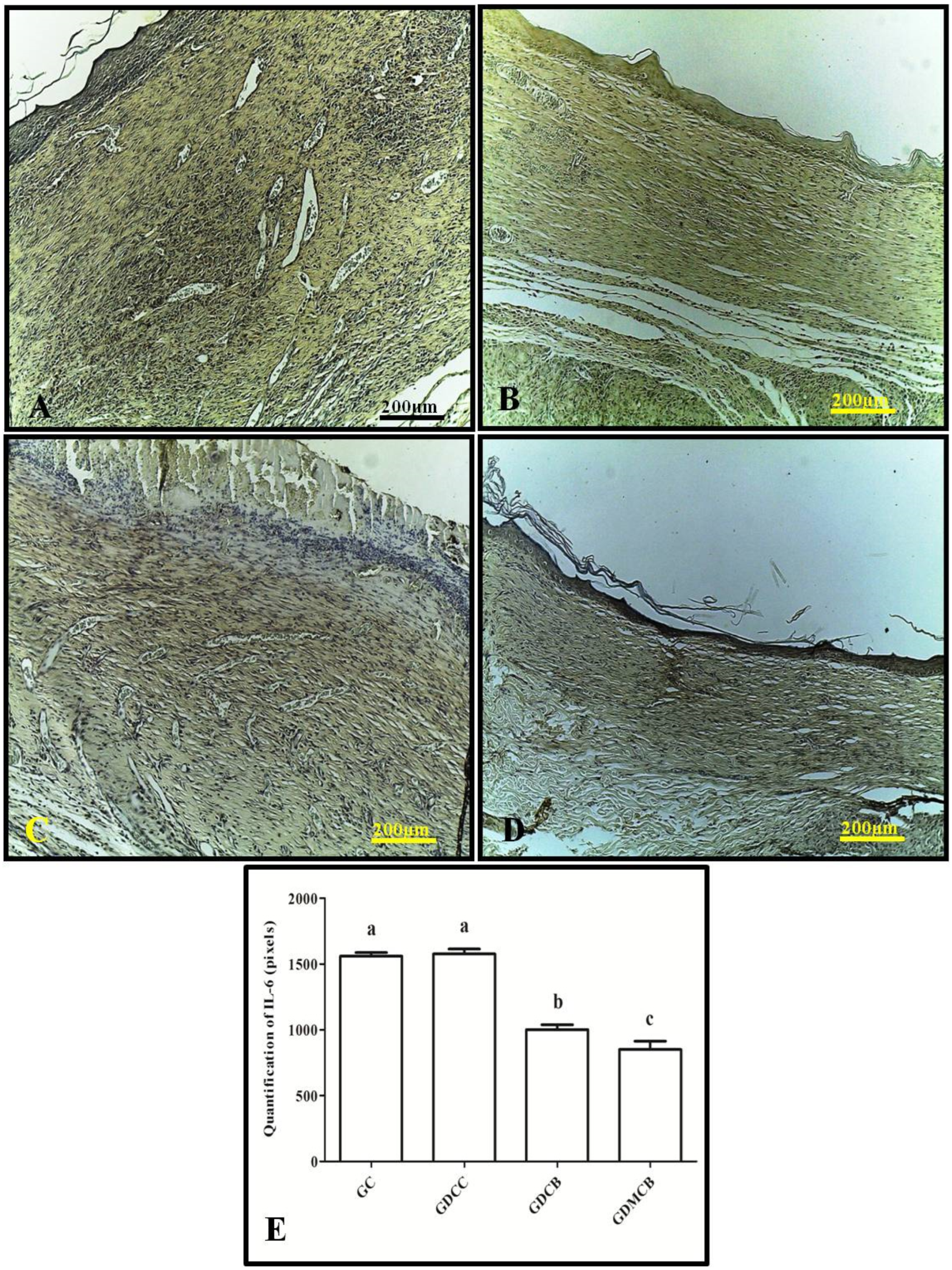
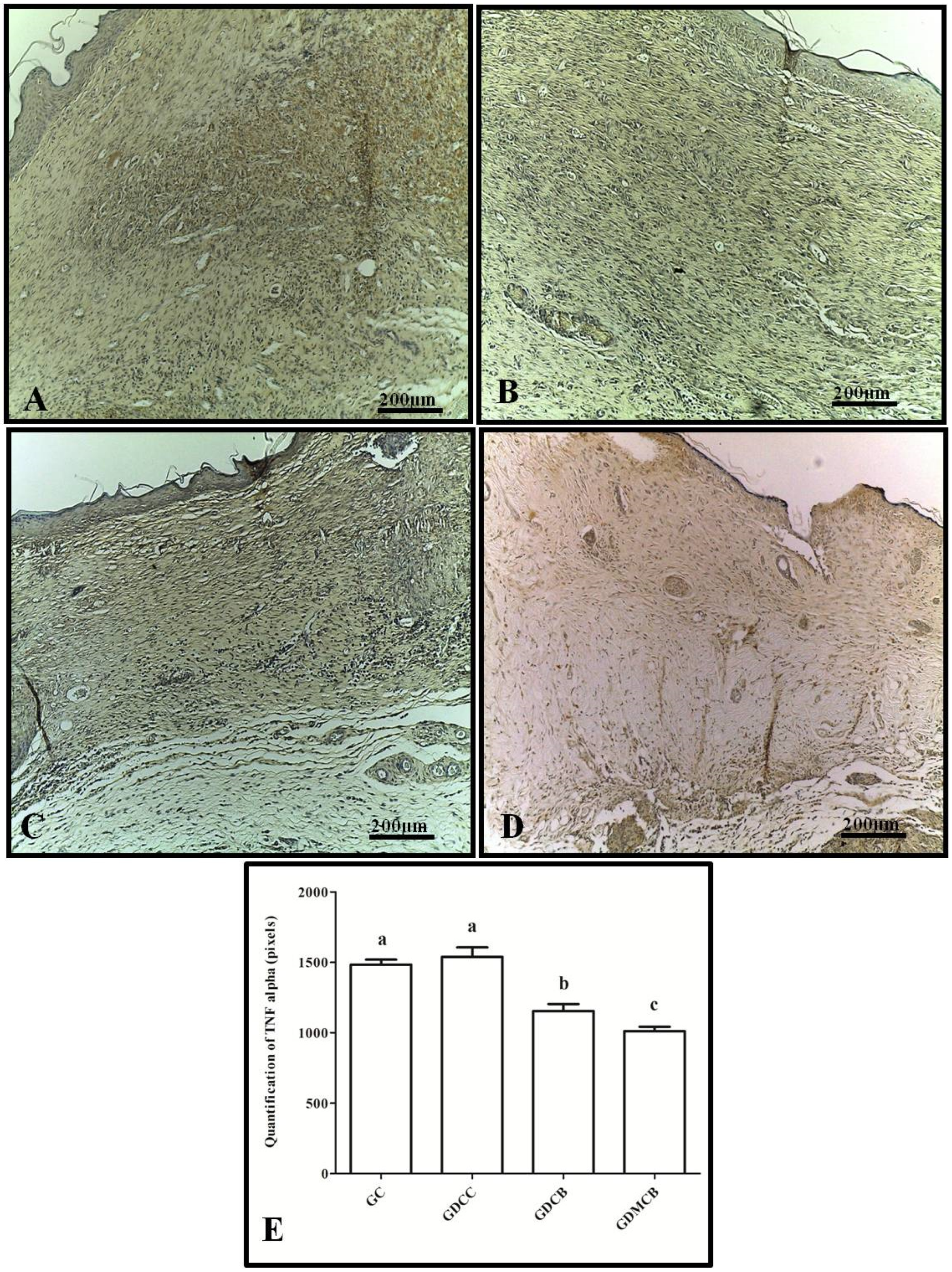
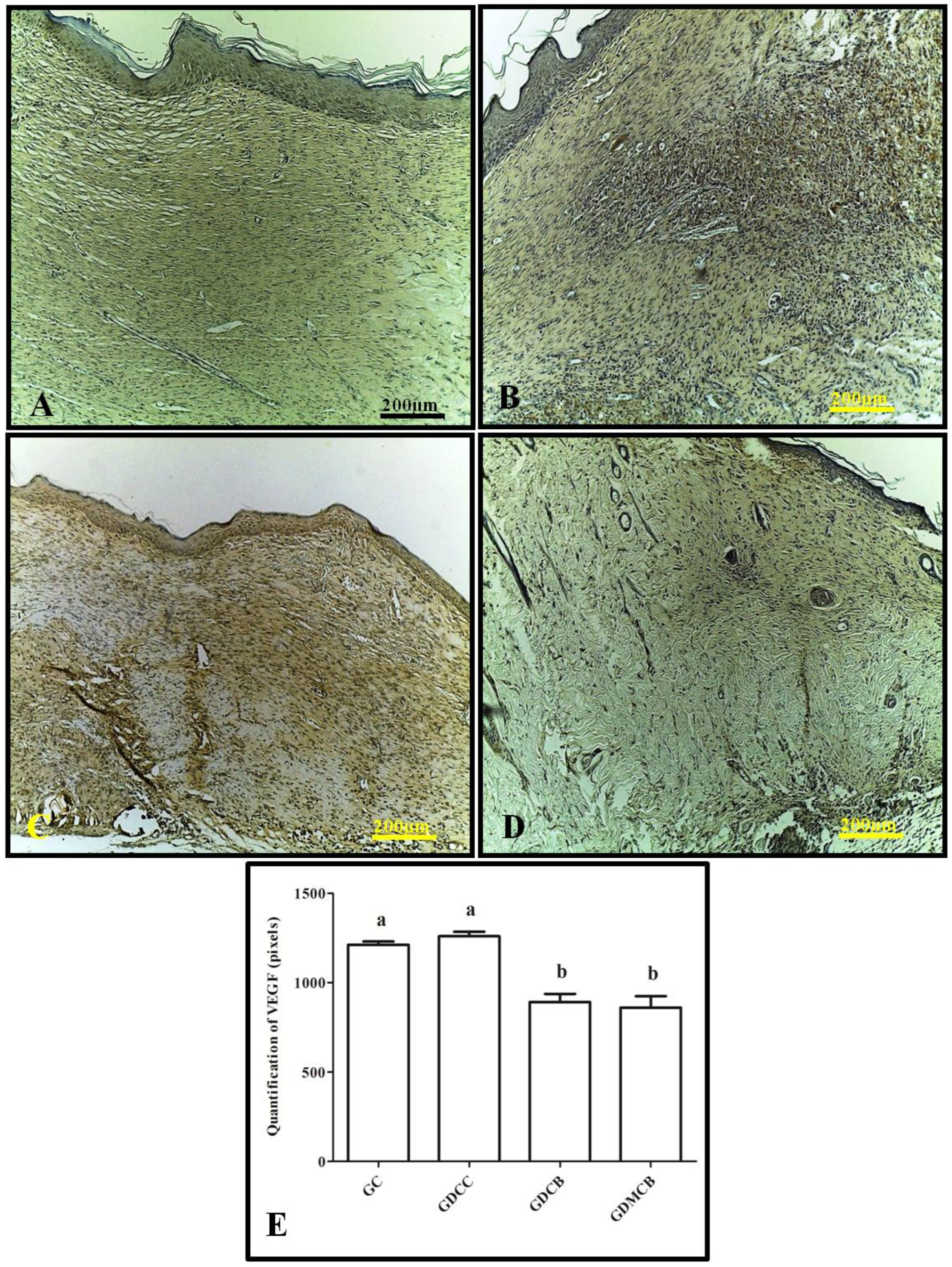
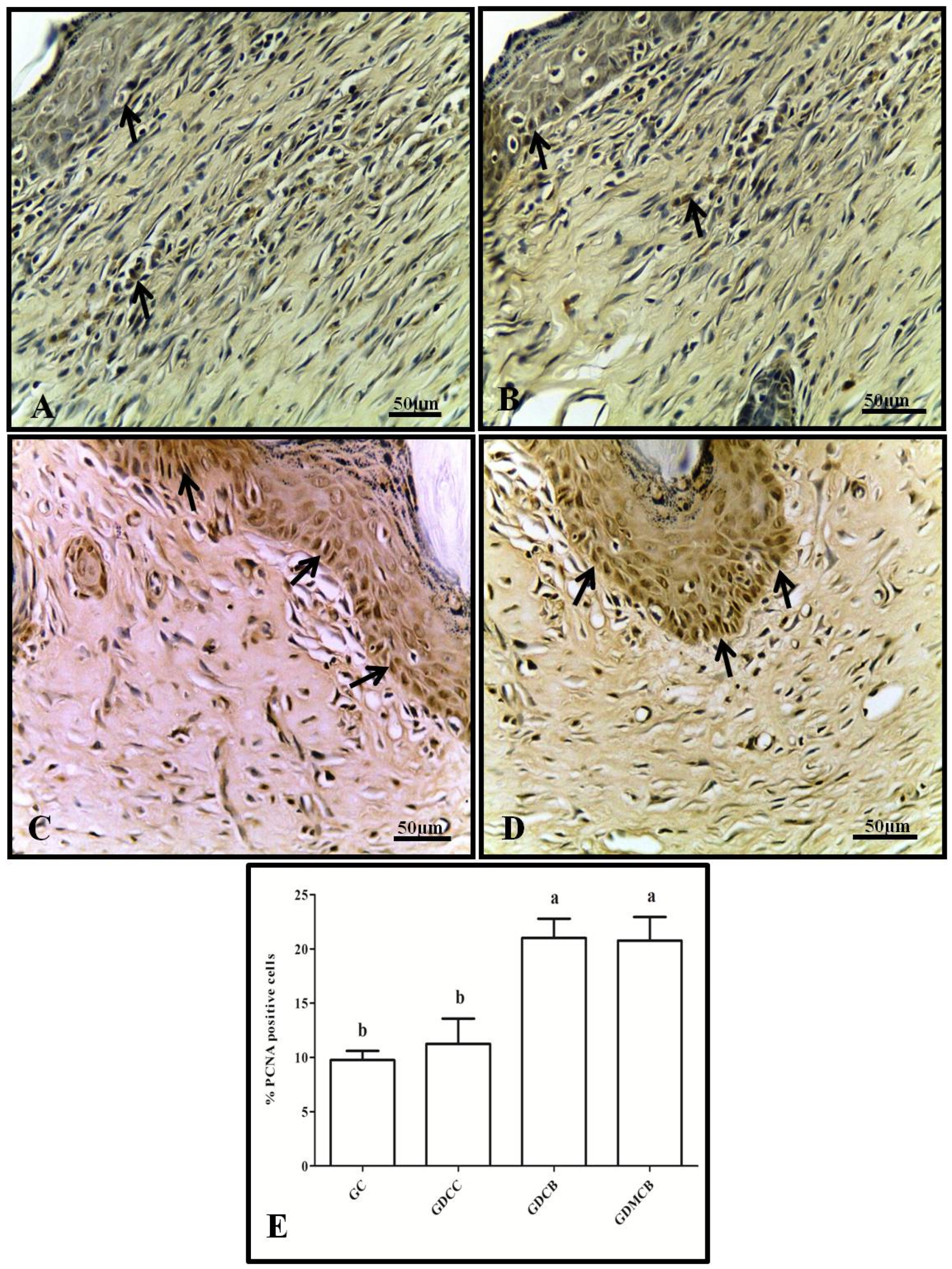
3. Results
3.1. Immunohistochemistry (IL-6, TNF-α, VEGF, and PCNA)
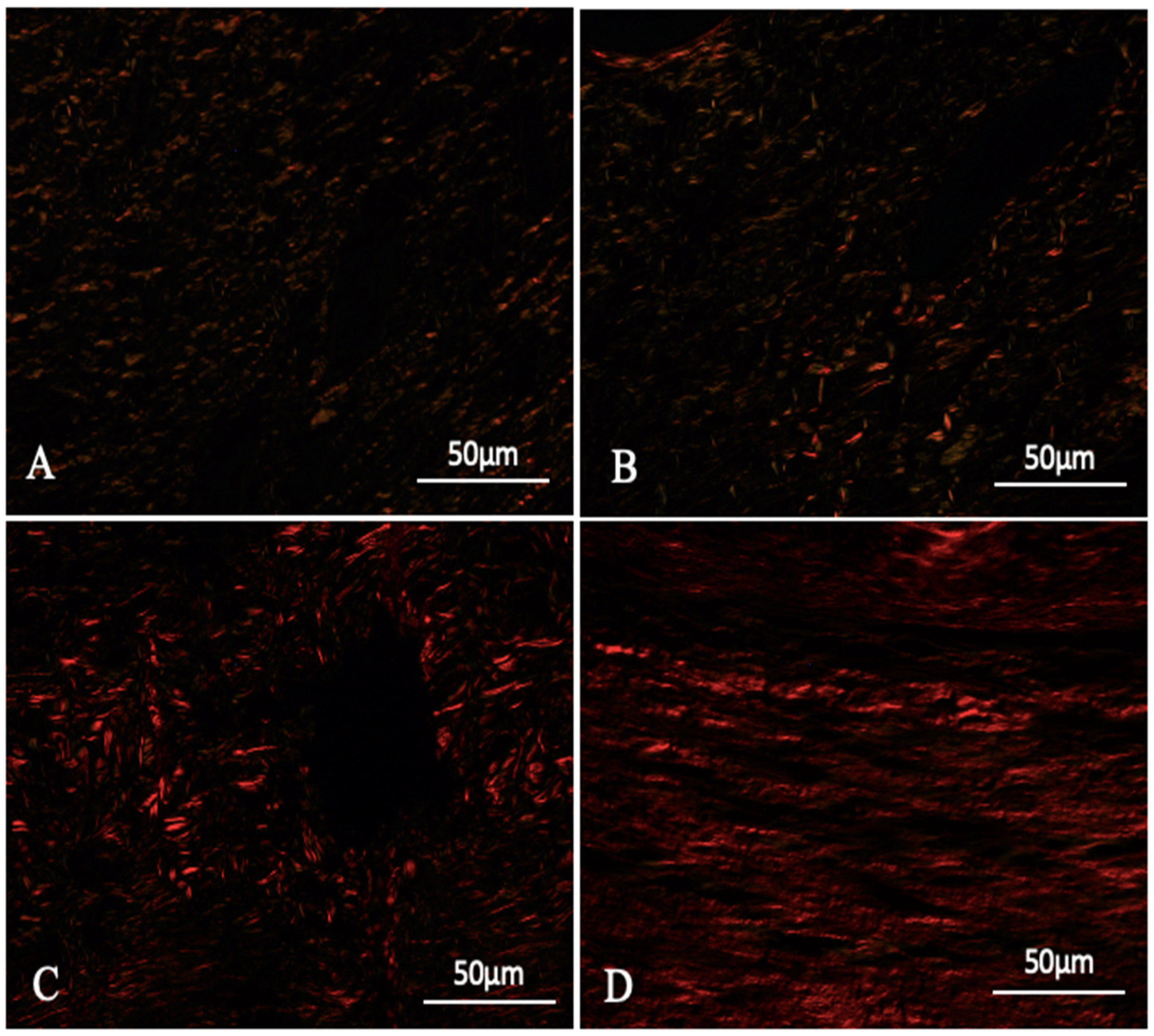
3.2. Evaluation and Quantification of Collagen I and III
4. Discussion
4.1. Bacterial Cellulose in Wound Healing
4.2. Melatonin in Wound Healing
4.3. The Role of Cytokines in Wound Healing
4.4. Cell Proliferation
4.5. The Role of Collagen in Wound Healing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brem, H.; Tomic-Canic, M. Cellular and molecular basis of wound healing in diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Lin, Z.; Liu, W.; Hu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhuang, X.; Guan, S.; Wu, X.; Hu, T.; Quan, S.; et al. Emodin accelerates diabetic wound healing by promoting anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 936, 175329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.G.M.; de Melo, I.M.F.; de Alves, É.R.; de Araújo, A.C.C.; Teixeira, V.W.; Teixeira, Á.A.C. Uso de Melatonina na Cicatrização de Feridas: Uma Revisão. Temas Saúde 2022, 22, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamiya, Y.; Ravi, S.P.; Coyle, A.; Chakrabarti, S.; Paul, A. Engineering nanoparticle therapeutics for impaired wound healing in diabetes. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Bioactive skin-mimicking hydrogel band-aids for diabetic wound healing and infectious skin incision treatment. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 3962–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, O.; Oboh, G.; Adefegha, S.; Osesusi, A. Effect of aqueous extract from root and leaf of Sphenocentrum jollyanum pierre on wounds of diabetic rats: Influence on wound tissue cytokines, vascular endothelial growth factor and microbes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 293, 115266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitto, A.; Minutoli, L.; Altavilla, D.; Polito, F.; Fiumara, T.; Marini, H.; Galeano, M.; Calò, M.; Cascio, P.L.; Bonaiuto, M.; et al. Simvastatin enhances VEGF production and ameliorates impaired wound healing in experimental diabetes. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 57, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorkhabi, R.; hossein Ahoor, M.; Haghjo, A.G.; Tabei, E.; Taheri, N. Assessment of tear inflammatory cytokines concentration in patients with diabetes with varying severity of involvement. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 224, 109233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, A.J.; Abdelhafiz, A.H.; Forbes, A.; Munshi, M. Evidence-based diabetes care for older people with Type 2 diabetes: A critical review. Diabet. Med. 2019, 36, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Wang, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Liu, C.; Xing, H.; Li, X. Efficient delivery of VEGF-A mRNA for promoting diabetic wound healing via ionizable lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 632, 122565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Cardoso Coelho, O.C.; Carrazoni, P.G.; da Cunha Monteiro, V.L.; de Assis Dutra, M.F.; Mota, R.A.; Tenório Filho, F. Biopolímero produzido a partir da cana-de-áçucar para cicatrização cutânea. Acta Cir. Bras. 2002, 17, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, L.M.; Pinto, F.C.; Oliveira, G.M.; Lima, S.V.; Aguiar, J.L.; Lins, E.M. Efficacy of bacterial cellulose membrane for the treatment of lower limbs chronic varicose ulcers: A randomized and controlled trial. Rev. Col. Bras. Cir. 2017, 44, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, G.M.; Vieira, J.M.S.; da Silva, J.G.M.; de Albuquerque, É.L.M.S.; de Albuquerque, A.V.; de Aguiar, J.L.A.; Pinto, F.C. Curativo de celulose bacteriana para o tratamento de lesões por pressão em pacientes hospitalizados. Rev. Enferm. Atual Derme 2019, 87, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.G.M.; Pinto, F.C.M.; de Oliveira, G.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Campos Júnior, O.; da Silva, R.O.; Teixeira, V.W.; de Melo, I.M.; Paumgartten, F.J.; de Souza, T.P.; et al. Non-clinical safety study of a sugarcane bacterial cellulose hydrogel. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, e960997932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Tong, C.; Yang, J.; Cong, P.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zou, R.; Xiao, K.; et al. Injectable melatonin-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCS)-based hydrogel accelerates wound healing by reducing inflammation and promoting angiogenesis and collagen deposition. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Bhutani, S.; Kim, C.H.; Irwin, M.R. Anti-inflammatory effects of melatonin: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 93, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Ren, L.; Ma, H.; Hu, R.; Gao, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J. Melatonin promotes diabetic wound healing in vitro by regulating keratinocyte activity. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 4682–4693. [Google Scholar]
- Pugazhenthi, K.; Kapoor, M.; Clarkson, A.N.; Hall, I.; Appleton, I. Melatonin accelerates the process of wound repair in full-thickness incisional wounds. J. Pineal Res. 2008, 44, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, T.R.; Rocha, V.L.; de Rincon, G.C.N.; de Oliveira Junior, E.R.; Celes, M.R.N.; Lima, E.M.; Amaral, A.C.; Miguel, M.P. Topical application of melatonin accelerates the maturation of skin wounds and increases collagen deposition in a rat model of diabetes. J. Tissue Viability 2022, 31, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira de Melo, I.M.; Martins Ferreira, C.G.; Lima da Silva Souza, E.H.; Almeida, L.L.; Bezerra de Sá, F.; Cavalcanti Lapa Neto, C.J.; de Castro, M.V.; Teixeira, V.W.; Teixeira, Á.A. Melatonin regulates the expression of inflammatory cytokines, VEGF and apoptosis in diabetic retinopathy in rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 327, 109183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberholzer, M.; Östreicher, M.; Christen, H.; Brühlmann, M. Methods in quantitative image analysis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 105, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.-S.; Kim, J.-H.; Im, S.; Lee, K.B.; Sohn, S.; Kang, W.H. Application of computerized image analysis in pigmentary skin diseases. Int. J. Dermatol. 2001, 40, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weibel, E.R. Principles and methods for the morphometric study of the lung and other organs. Lab. Investig. 1963, 12, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dias, F.C.R.; de Gomes, M.L.M.; de Melo, F.C.S.A.; Menezes, T.P.; Martins, A.L.; do Cupertino, M.C.; Otoni, W.C.; da Matta, S.L. Pfaffia glomerata hydroalcoholic extract stimulates penile tissue in adult Swiss mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 261, 113182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbino, C.A.; Pereira, L.M.; Curi, R. Mecanismos envolvidos na cicatrização: Uma revisão. Rev. Bras. Ciências Farm. 2005, 41, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.; Osuna, C.; Gitto, E. Actions of Melatonin in the Reduction of Oxidative Stress. J. Biomed. Sci. 2000, 7, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, M.; Deodato, B.; Altavilla, D.; Cucinotta, D.; Arsic, N.; Marini, H.; Torre, V.; Giacca, M.A.; Squadrito, F. Adeno-associated viral vector-mediated human vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer stimulates angiogenesis and wound healing in the genetically diabetic mouse. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiano, R.D.; Tepper, O.M.; Pelo, C.R.; Bhatt, K.A.; Callaghan, M.; Bastidas, N.; Bunting, S.; Steinmetz, H.G.; Gurtner, G.C. Topical Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Accelerates Diabetic Wound Healing through Increased Angiogenesis and by Mobilizing and Recruiting Bone Marrow-Derived Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1935–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favi, P.M.; Benson, R.S.; Neilsen, N.R.; Hammonds, R.L.; Bates, C.C.; Stephens, C.P.; Dhar, M.S. Cell proliferation, viability, and in vitro differentiation of equine mesenchymal stem cells seeded on bacterial cellulose hydrogel scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, F.D.; Pinto, F.C.; Andrade-da-Costa, B.L.; Silva, J.G.; Campos Júnior, O.; Aguiar, J.L. Biocompatible bacterial cellulose membrane in dural defect repair of rat. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherng, J.-H.; Chou, S.-C.; Chen, C.-L.; Wang, Y.-W.; Chang, S.-J.; Fan, G.-Y.; Leung, F.S.; Meng, E. Bacterial Cellulose as a Potential Bio-Scaffold for Effective Re-Epithelialization Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-C.; Wu, Y.-H.; Hu, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-C. The Antimicrobial Effects of Bacterial Cellulose Produced by Komagataeibacter intermedius in Promoting Wound Healing in Diabetic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, G.M.O.; Gomes Filho, A.O.; Silva, J.G.M.; Silva, A.G.; Lins, E.M.; Oliveira, M.D.L.D.; Andrade, C.A.S. Bacterial cellulose biomaterials for the treatment of lower limb ulcers. Rev. Colégio Bras. Cir. 2023, 50, e20233536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobnik, J. Wound healing and the effect of pineal gland and melatonin. J. Exp. Integr. Med. 2012, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ul-Islam, M.; Ikram, M.; Islam, S.U.; Ullah, M.W.; Israr, M.; Jang, J.H.; Yoon, S.; Park, J.K. Preparation and structural characterization of surface modified microporous bacterial cellulose scaffolds: A potential material for skin regeneration applications in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Loh, E.Y.X.; Fauzi, M.B.; Ng, M.H.; Mohd Amin, M.C.I. In vivo evaluation of bacterial cellulose/acrylic acid wound dressing hydrogel containing keratinocytes and fibroblasts for burn wounds. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorotelyak, E.A.; Malchenko, L.A.; Rogovaya, O.S.; Lazarev, D.S.; Butorina, N.N.; Brodsky, V.Y. Melatonin Stimulates Epithelium Migration in Wound Models In Vitro and In Vivo. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 168, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, C.D.; Verestiuc, L.; Ulea, E.; Lipsa, F.D.; Vulpe, V.; Munteanu, C.; Bulgariu, L.; Pașca, S.; Tamas, C.; Ciuntu, B.M.; et al. Evaluation of Keratin/Bacterial Cellulose Based Scaffolds as Potential Burned Wound Dressing. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Kirsner, R. Pathophysiology of acute wound healing. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.V.C.; Machado, M.R.; Pinto, F.C.M.; de Lira, M.M.M.; de Albuquerque, A.V.; Lustosa, E.S.; Silva, J.G.; Campos, O. A new material to prevent urethral damage after implantation of artificial devices: An experimental study. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2017, 43, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cavalcante, A.R.T.; de Lima, R.P.; de Souza, V.S.B.; Pinto, F.C.M.; Campos Júnior, O.; da Silva, J.G.M.; de Albuquerque, A.V.; de Andrade Aguiar, J.L. Effects of bacterial cellulose gel on the anorectal resting pressures in rats submitted to anal sphincter injury. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragothaman, M.; Kannan Villalan, A.; Dhanasekaran, A.; Palanisamy, T. Bio-hybrid hydrogel comprising collagen-capped silver nanoparticles and melatonin for accelerated tissue regeneration in skin defects. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 128, 112328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva, J.G.M.; de Melo, I.M.F.; Alves, É.R.; de Oliveira, G.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Cavalcanti, I.M.F.; Araujo, D.N.; Pinto, F.C.M.; de Andrade Aguiar, J.L.; Wanderley Teixeira, V.; et al. Melatonin and Bacterial Cellulose Regulate the Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines, VEGF, PCNA, and Collagen in Cutaneous Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats. Polymers 2024, 16, 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182611
da Silva JGM, de Melo IMF, Alves ÉR, de Oliveira GM, da Silva AA, Cavalcanti IMF, Araujo DN, Pinto FCM, de Andrade Aguiar JL, Wanderley Teixeira V, et al. Melatonin and Bacterial Cellulose Regulate the Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines, VEGF, PCNA, and Collagen in Cutaneous Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats. Polymers. 2024; 16(18):2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182611
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva, Jaiurte Gomes Martins, Ismaela Maria Ferreira de Melo, Érique Ricardo Alves, Glícia Maria de Oliveira, Anderson Arnaldo da Silva, Isabela Macário Ferro Cavalcanti, Diego Neves Araujo, Flávia Cristina Morone Pinto, José Lamartine de Andrade Aguiar, Valéria Wanderley Teixeira, and et al. 2024. "Melatonin and Bacterial Cellulose Regulate the Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines, VEGF, PCNA, and Collagen in Cutaneous Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats" Polymers 16, no. 18: 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182611
APA Styleda Silva, J. G. M., de Melo, I. M. F., Alves, É. R., de Oliveira, G. M., da Silva, A. A., Cavalcanti, I. M. F., Araujo, D. N., Pinto, F. C. M., de Andrade Aguiar, J. L., Wanderley Teixeira, V., & Coelho Teixeira, Á. A. (2024). Melatonin and Bacterial Cellulose Regulate the Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines, VEGF, PCNA, and Collagen in Cutaneous Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats. Polymers, 16(18), 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182611








