A New Paradigm on Waste-to-Energy Applying Hydrovoltaic Energy Harvesting Technology to Face Masks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Mask-Based Hydrovoltaic Power Generator (MHPG)
2.3. Electrical Output Performance by Different Features
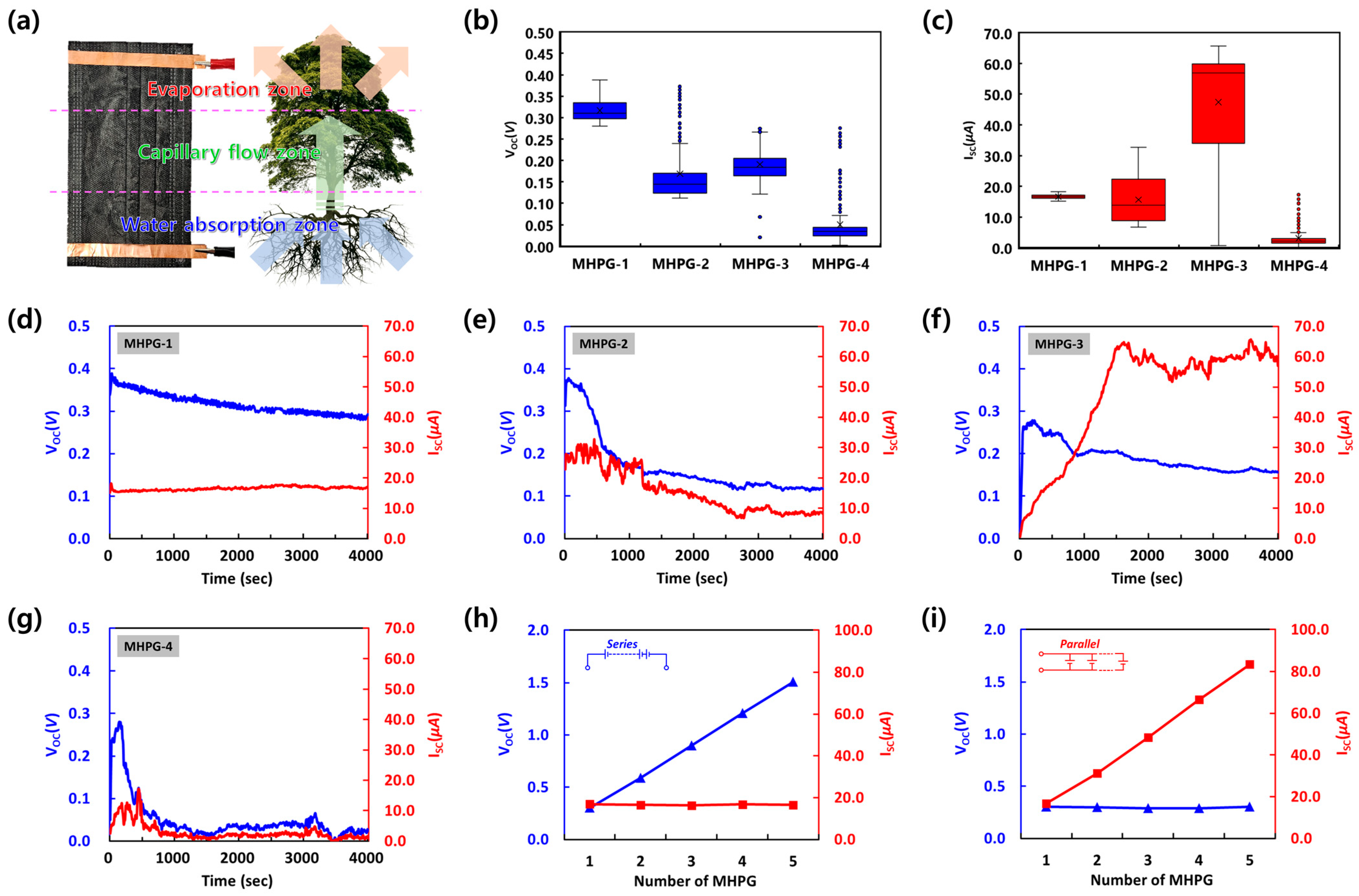
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations of MHPGs
3.2. Electrical Performances by Different Features
3.3. Discussion and Future Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fadare, O.O.; Okoffo, E.D. COVID-19 face masks: A potential source of microplastic fibers in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, N.U.; Fred-Ahmadu, O.H.; Bassey, D.E.; Atayero, A.A. COVID-19 pandemic and emerging plastic-based personal protective equipment waste pollution and management in Africa. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangkham, S. Face mask and medical waste disposal during the novel COVID-19 pandemic in Asia. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2020, 2, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; Lee, H.K.; Huyen, D.T.T.; Chen, S.-S.; Kwon, Y.-N. Microplastics waste in environment: A perspective on recycling issues from PPE kits and face masks during the COVID-19 pandemic. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; An, C.; Chen, X.; Lee, K.; Zhang, B.; Feng, Q. Disposable masks release microplastics to the aqueous environment with exacerbation by natural weathering. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Bagchi, M.; Markoglou, N.; An, C.; Peng, H.; Bi, H.; Yang, X.; Sun, H. Towards environmentally sustainable management: A review on the generation, degradation, and recycling of polypropylene face mask waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 461, 132566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, R.; Tyagi, V.; Pathak, A. Waste-to-energy: A way from renewable energy sources to sustainable development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 3164–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabasová, A.; Kropáč, J.; Kermes, V.; Nemet, A.; Stehlík, P. Waste-to-energy technologies: Impact on environment. Energy 2012, 44, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Samadder, S.R. A review on technological options of waste to energy for effective management of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Bui-Vinh, D.; Lee, S.-H.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, S.; Yun, J.; Baek, M.; Lee, H.-W.; Park, J.; Kim, M.; et al. Evaporation-Driven Energy Generation Using an Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Mat with Different Support Substrates. Polymers 2024, 16, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, S.; Yun, J.; Kim, E.; Jang, G.; Song, Y.; Kim, B.S.; Oh, C.-S.; Choa, Y.-H. A novel water electrolysis hydrogen production system powered by a renewable hydrovoltaic power generator. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizizadeh, T.; She, Z.; Stamplecoskie, K.; Liu, G. Empowerment of water-evaporation-induced electric generators via the use of metal electrodes. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 28275–28283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Jia, T.; Wang, Z.; Xu, T.; An, N.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, C. Boosting Water Evaporation by Construction of Photothermal Materials with a Biomimetic Black Soil Aggregate Structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 37609–37618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Feng, L.; Wen, X.; Wang, L.; Qin, X.; Yu, J. Ceramic nanofiber-based water-induced electric generator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 56226–56232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.J. Solar evaporation-based energy harvesting using a leaf-inspired energy-harvesting foam. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 5027–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Peng, M.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, L. Printed honeycomb-structured reduced graphene oxide film for efficient and continuous evaporation-driven electricity generation from salt solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 26989–26997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garemark, J.; Ram, F.; Liu, L.; Sapouna, I.; Ruiz, M.F.C.; Larsson, P.T.; Li, Y. Advancing hydrovoltaic energy harvesting from wood through cell wall nanoengineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2208933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Xue, G.; Chen, Q.; Huang, L.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J. All-printed porous carbon film for electricity generation from evaporation-driven water flow. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Akbar, A.; Mohamed, A.M.; Fathi, D.; Saeed, F. Saeed. Recycling of waste facial masks as a construction material, a step towards sustainability. Materials 2022, 15, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Lim, C. Effective recycling of disposable medical face masks for sustainable green concrete via a new fiber hybridization technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 344, 128245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, P.; Maity, S.; Singha, K.; Annu; Uzun, M.; Shekh, M.; Ahmed, S. Potential biodegradable face mask to counter environmental impact of COVID-19. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 4, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, E.-J.; Hsieh, Y.-Y.; Hsu, T.-W.; Huang, C.-S.; Lee, Y.-C.; Han, Y.-S.; Chu, H.-T. Using the concept of circular economy to reduce the environmental impact of COVID-19 face mask waste. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 33, e00475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Hassan, I.; Ibn-Mohammed, T.; Mostafa, H.; Reaney, I.M.; Koh, L.S.C.; Zu, J.; Wang, Z.L. Environmental life cycle assessment and techno-economic analysis of triboelectric nanogenerators. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zi, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, X. High-voltage applications of the triboelectric nanogenerator—Opportunities brought by the unique energy technology. MRS Energy Sustain. 2019, 6, E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najini, H.; Muthukumaraswamy, S.A. Piezoelectric energy generation from vehicle traffic with technoeconomic analysis. J. Renew. Energy 2017, 2017, 9643858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Goel, A.; Verma, A. A review on energy harvesting based piezoelectric system. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.B.; ur Rashid, T.; Awan, W.N.; ul Haq, F.; Khan, S.A. Energy Generation Potential through utilization of Piezoelectric materials in Smart Motorway System (SMS) of Pakistan. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering, Sciences and Technology (ICEEST), Karachi, Pakistan, 10–11 December 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Geffroy, C.; Lilley, D.; Parez, P.S.; Prasher, R. Techno-economic analysis of waste-heat conversion. Joule 2021, 5, 3080–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sharafi, A.; Sahin, A.Z.; Ayar, T.; Yilbas, B.S. Techno-economic analysis and optimization of solar and wind energy systems for power generation and hydrogen production in Saudi Arabia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, C.; Pratt, D.; Clarke, J.; Grant, A. A techno-economic analysis of tidal energy technology. Renew. Energy 2013, 49, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Abrha, H.; Wang, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, J.; Kang, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Emerging hydrovoltaic technology based on carbon black and porous carbon materials: A mini review. Carbon 2022, 193, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.G.; Bae, J.; Rothschild, A.; Kim, I.-D. Transpiration driven electrokinetic power generator. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 12703–12709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Gao, S.; Hao, M.; Yang, X.; Feng, S.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Xiong, Z.; Sun, F.; Li, Y.; et al. A novel, flexible dual-mode power generator adapted for wide dynamic range of the aqueous salinity. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 105970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Yun, T.G.; Suh, B.L.; Kim, J.; Kim, I.-D. Self-operating transpiration-driven electrokinetic power generator with an artificial hydrological cycle. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Chu, W.; Fang, S.; Tan, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, W. Materials for evaporation-driven hydrovoltaic technology. Interdiscip. Mater. 2022, 1, 449–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Liu, C.; Che, L.; Li, D.; Fan, K.; Li, Q.; Yang, W.; Dong, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Water-Evaporation-Induced Electricity Based on Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2201586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Gong, F.; Li, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Xiao, R. A flexible electrokinetic power generator derived from paper and ink for wearable electronics. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Types | Definitions | Sizes |
|---|---|---|
| MHPG-1 | Original mask form | 97 × 170 × 0.24 mm3 |
| MHPG-2 | Equally cut in 2 pieces and put together | 97 × 85 × 0.48 mm3 |
| MHPG-3 | Equally cut in 3 pieces and put together | 97 × 57 × 0.72 mm3 |
| MHPG-4 | Unfolded mask cut in half and rolled together | 75 mm × 1.47 mm2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, Y.; Bui-Vinh, D.; Lee, S.-H.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, H.-W.; Yun, J.; Cho, I.; Lee, J.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, H.; et al. A New Paradigm on Waste-to-Energy Applying Hydrovoltaic Energy Harvesting Technology to Face Masks. Polymers 2024, 16, 2515. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172515
Kwon Y, Bui-Vinh D, Lee S-H, Baek SH, Lee H-W, Yun J, Cho I, Lee J, Lee MH, Lee H, et al. A New Paradigm on Waste-to-Energy Applying Hydrovoltaic Energy Harvesting Technology to Face Masks. Polymers. 2024; 16(17):2515. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172515
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Yongbum, Dai Bui-Vinh, Seung-Hwan Lee, So Hyun Baek, Hyun-Woo Lee, Jeungjai Yun, Inhee Cho, Jeonghoon Lee, Mi Hye Lee, Handol Lee, and et al. 2024. "A New Paradigm on Waste-to-Energy Applying Hydrovoltaic Energy Harvesting Technology to Face Masks" Polymers 16, no. 17: 2515. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172515
APA StyleKwon, Y., Bui-Vinh, D., Lee, S.-H., Baek, S. H., Lee, H.-W., Yun, J., Cho, I., Lee, J., Lee, M. H., Lee, H., & Jeong, D.-W. (2024). A New Paradigm on Waste-to-Energy Applying Hydrovoltaic Energy Harvesting Technology to Face Masks. Polymers, 16(17), 2515. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172515








