The Light-Fueled Self-Rotation of a Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fiber-Propelled Slider on a Circular Track
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model and Formulation
2.1. Dynamics of Self-Rotating System
2.2. Dynamic Model of LCE
2.3. Nondimensionalization
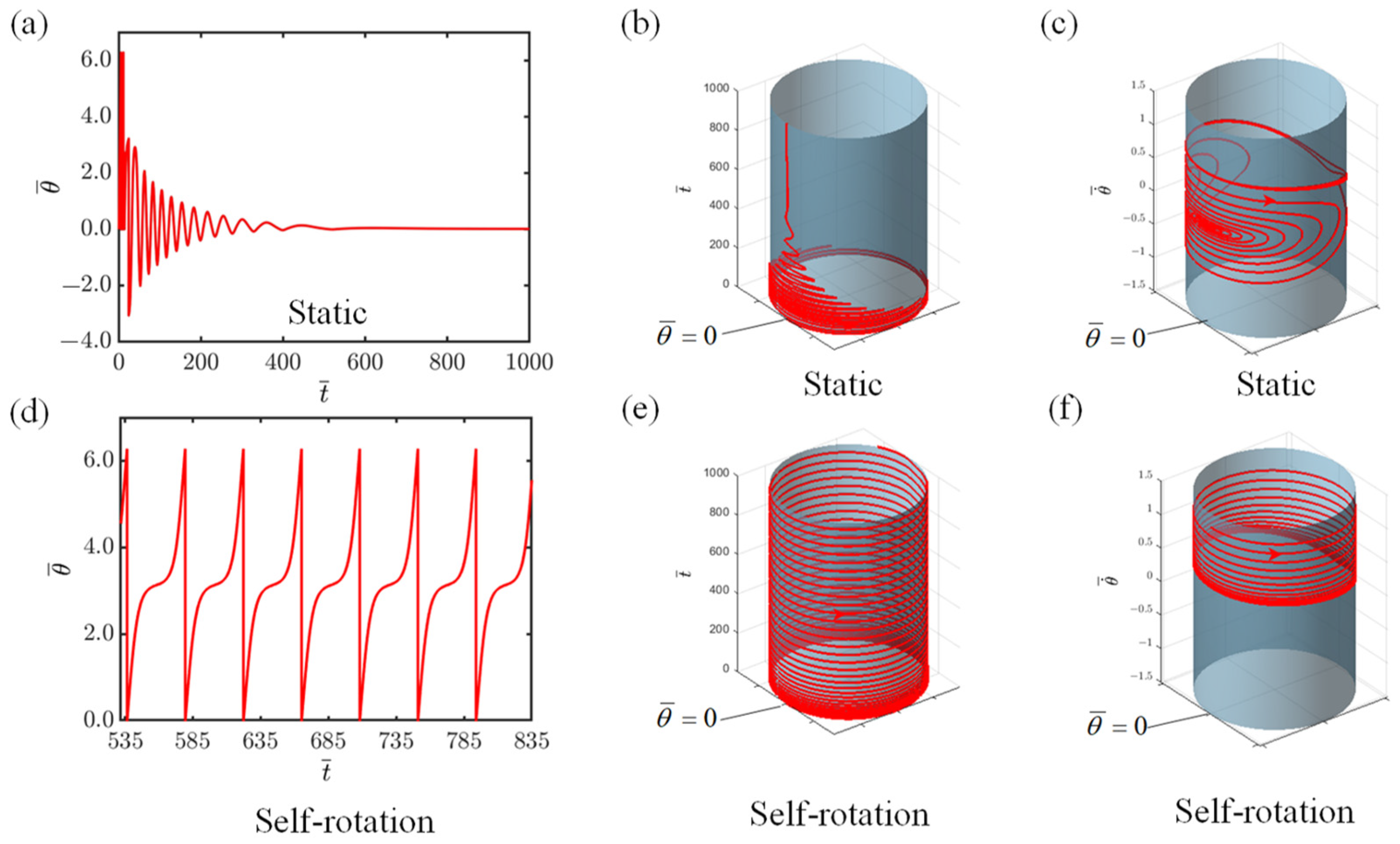
3. Two Dynamic States and Mechanism of Self-Rotation
3.1. Two Dynamic States
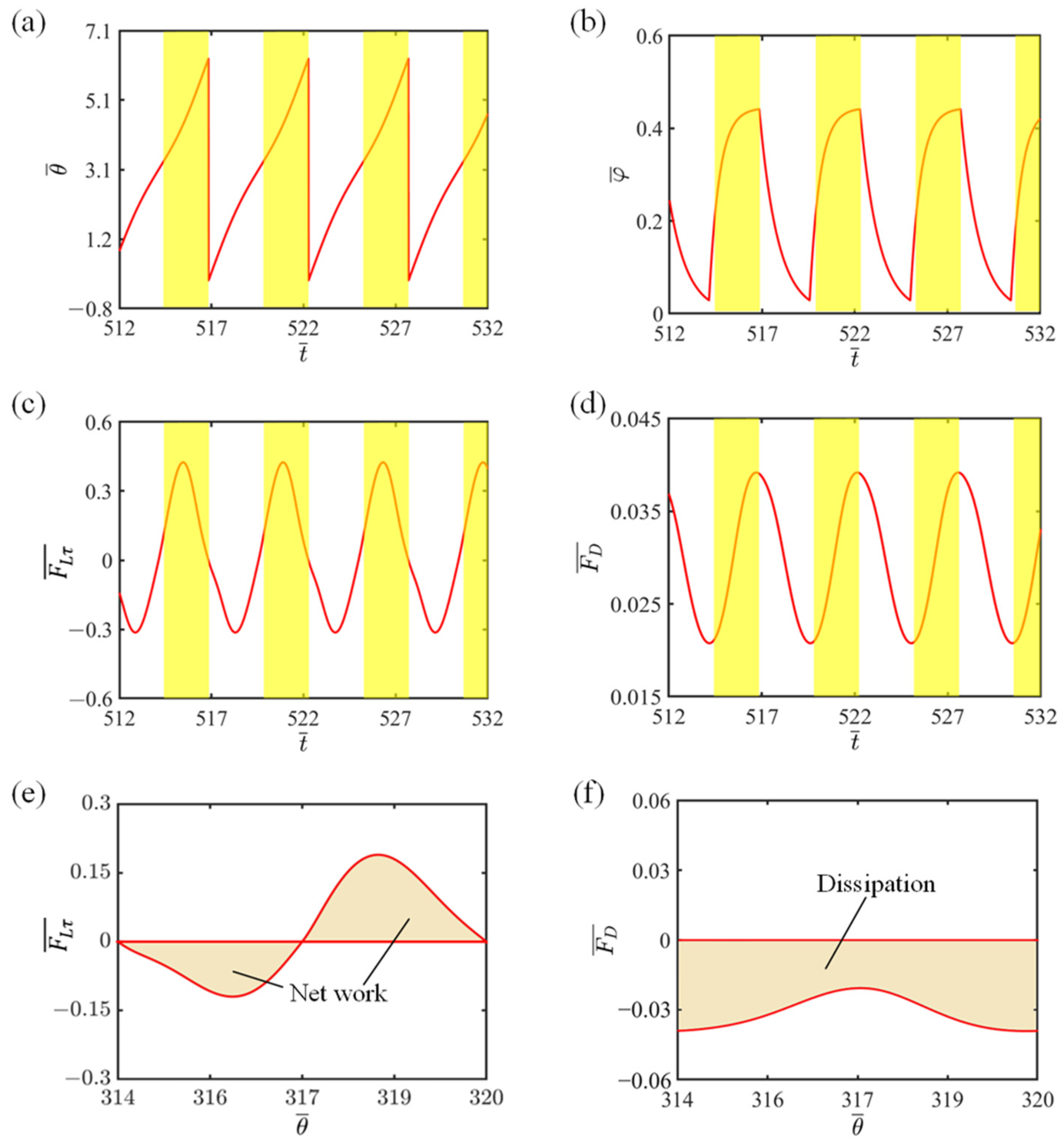
3.2. Mechanism of Self-Rotation
4. Parameter Study
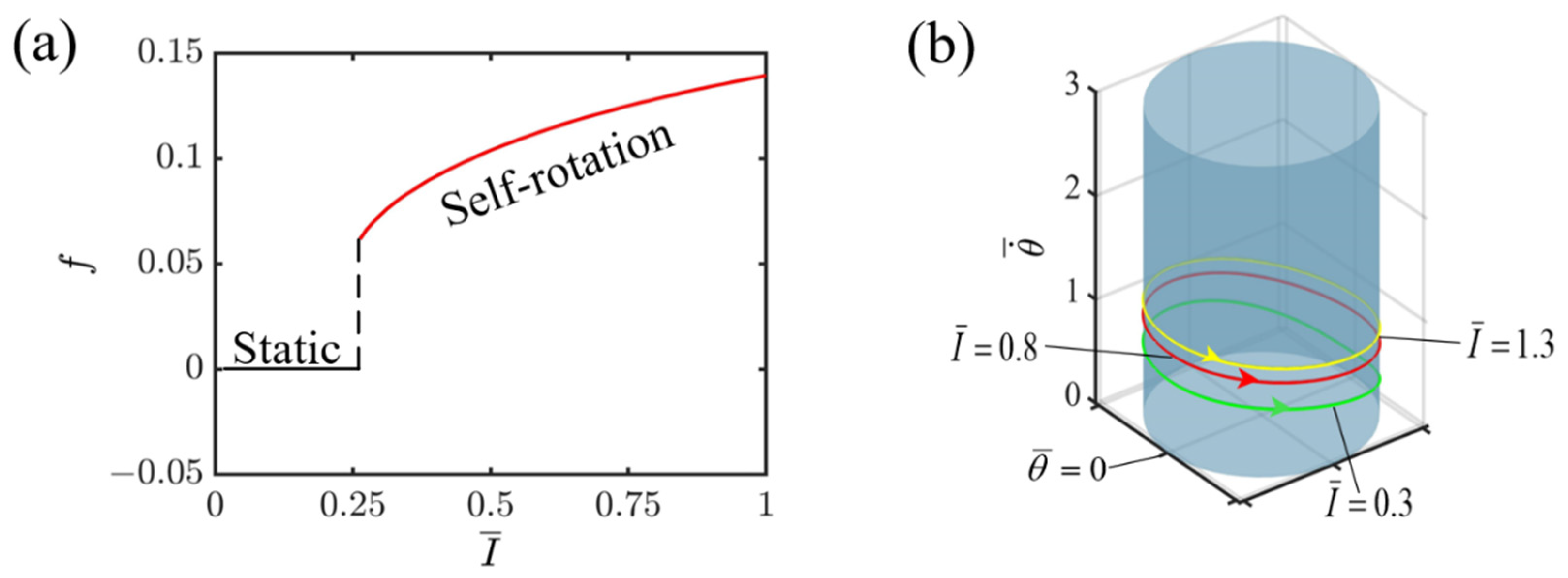
4.1. Effect of Light Intensity
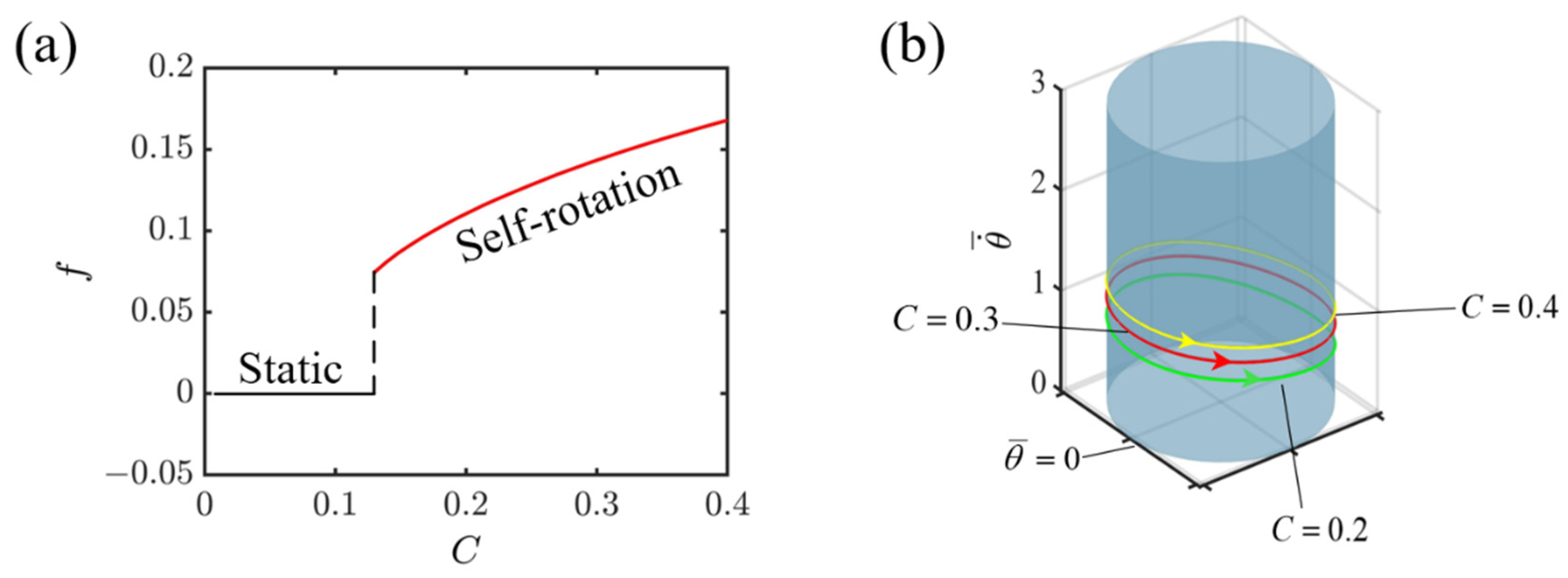
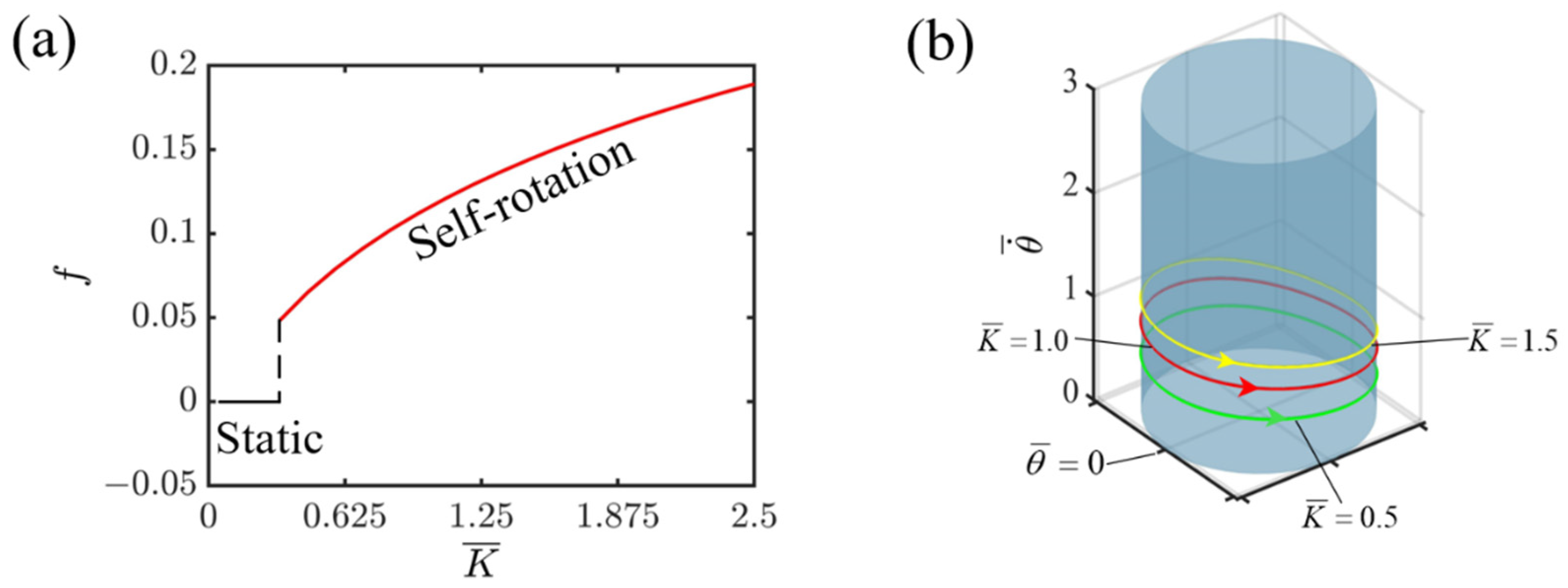
4.2. Effect of Contraction Coefficient of LCE
4.3. Effect of Elastic Coefficient of LCE
4.4. Effect of Initial Tangential Velocity
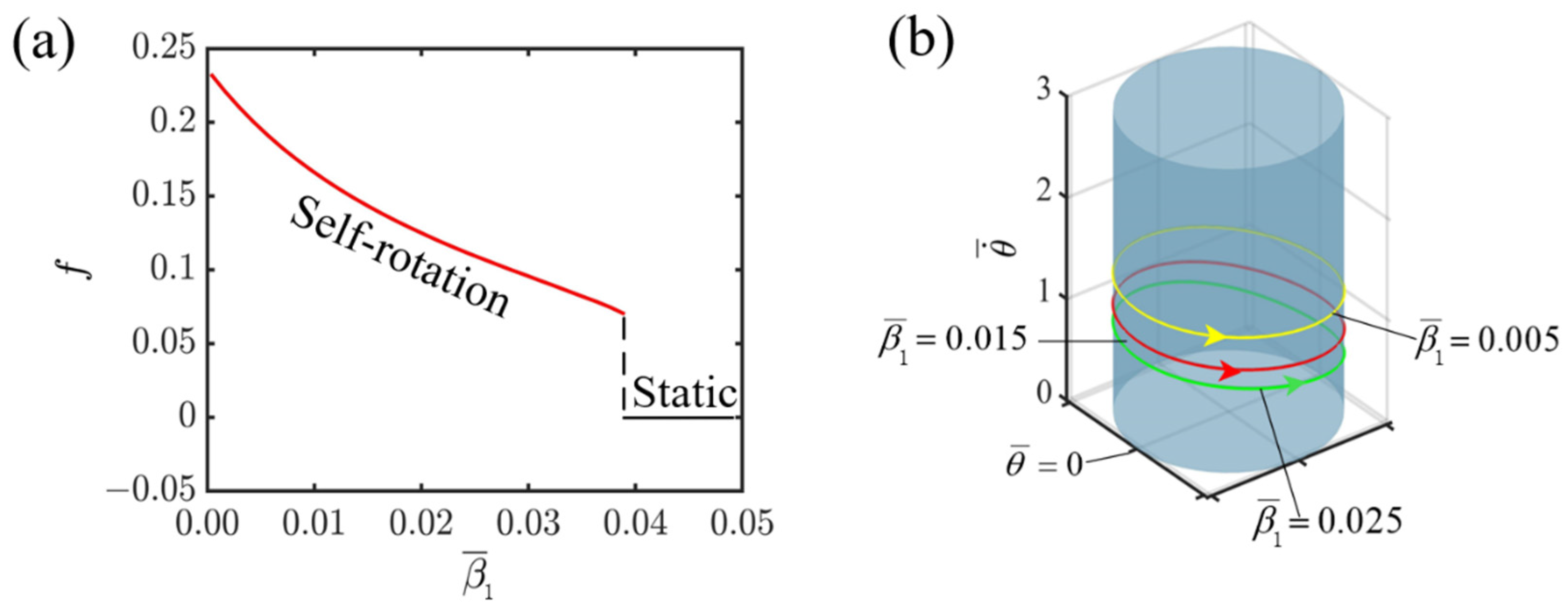
4.5. Effect of the First Damping Coefficient
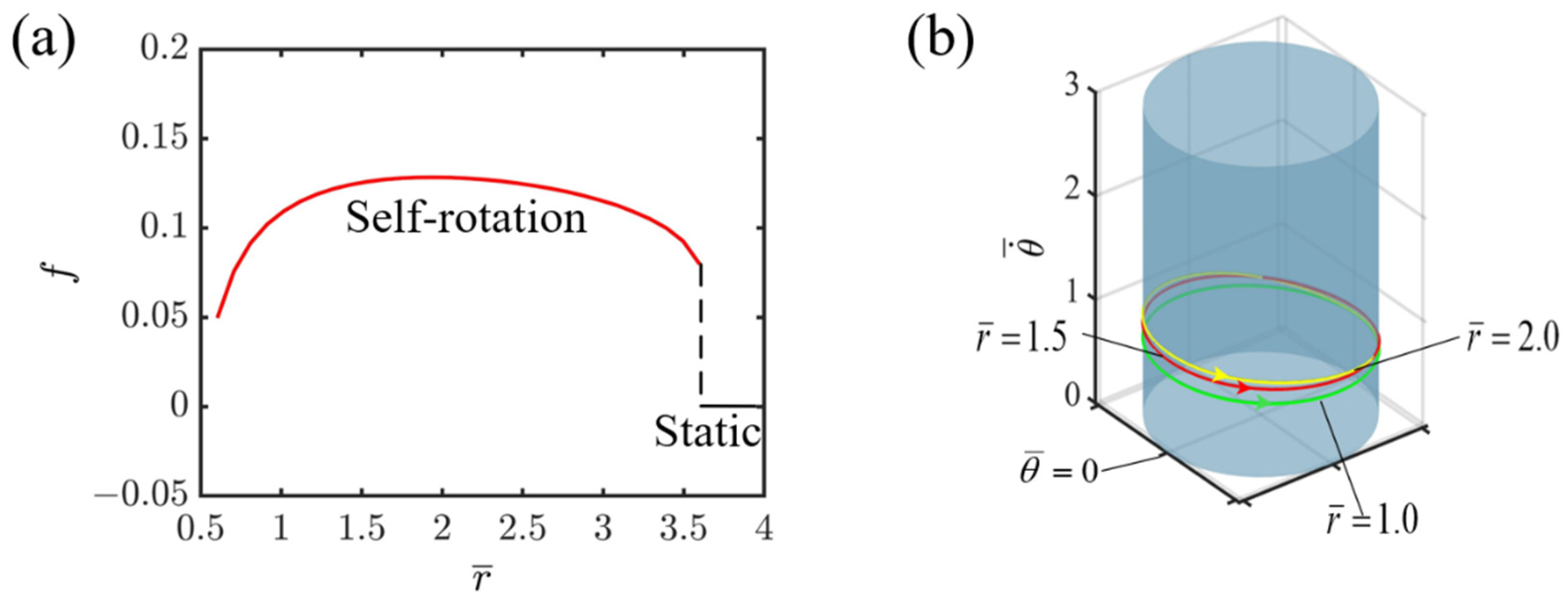
4.6. Effect of Radius of Circular Track
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, W. Self-Excited Vibration; Tsing-Hua University Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, W. Theory of Vibration with Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, A. Self-oscillation. Phys. Rep. 2013, 525, 167–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Duan, N.; Lin, C.; Hua, H. Coupled dynamic analysis of a heavily-loaded propulsion shafting system with continuous bearing-shaft friction. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 172, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, Y.; Jahan, R.A. Influence of initial substrate concentration of the Belouzov-Zhabotinsky reaction on transmittance self-oscillation for a nonthermoresponsive polymer chain. Polymers 2011, 3, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, H.; Fei, G.; Yu, B.; Tong, X.; Xia, H.; Zhao, Y. Liquid-crystalline dynamic networks doped with gold nanorods showing enhanced photocontrol of actuation. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrany, A.M. Nonlinear light-induced vibration behavior of liquid crystal elastomer beam. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 136, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Keller, P.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Brunet, M. Light-driven side-on nematic elastomer actuators. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Du, C.; Zhu, F.; Dai, Y.; Ge, D.; Li, K. Self-galloping of a liquid crystal elastomer catenary cable under a steady temperature field. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 202, 112071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, H.; Li, K. Optically-responsive liquid crystal elastomer thin film motors in linear/nonlinear optical fields. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 202, 112082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothemund, P.; Ainla, A.; Belding, L.; Preston, D.J.; Kurihara, S.; Suo, Z.; Whitesides, G.M. A soft, bistable valve for autonomous control of soft actuators. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaar7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Yu, M.; Wang, W.; Yu, H. Photothermal pneumatic wheel with high loadbearing capacity. Compos. Commun. 2021, 24, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendlein, A.; Jiang, H.; Jünger, O.; Langer, R. Light-induced shape-memory polymers. Nature 2005, 434, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubnov, A.; Domenici, V.; Hamplová, V.; Kašpar, M.; Zalar, B. First liquid single crystal elastomer containing lactic acid derivative as chiral co-monomer: Synthesis and properties. Polymer 2011, 52, 4490–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Huang, H.; Cao, D.; Qin, W.; Zhu, P.; Du, W. Harvest more bridge vibration energy by nonlinear multi-stable piezomagnetoelastic harvester. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2024, 57, 135501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.W.; Sundaram, S.; Hayward, R.C. Photothermocapillary oscillators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 158001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Sundaram, S.; Kang, J.-H.; Tanjeem, N.; Emrick, T.; Hayward, R.C. Coupled oscillation and spinning of photothermal particles in Marangoni optical traps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024581118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S. Self-excited oscillation under nonlinear feedback with time-delay. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 1860–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, L.; Petersen, K.; Lum, G.Z.; Sitti, M. Soft actuators for small-scale robotics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangwan, V.; Taneja, A.; Mukherjee, S. Design of a robust self-excited biped walking mechanism. Mech. Mach. Theory 2004, 39, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Li, K. Self-rotation-eversion of an anisotropic-friction-surface torus. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 281, 109584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Lum, G.Z.; Mastrangeli, M.; Sitti, M. Small-scale soft-bodied robot with multimodal locomotion. Nature 2018, 554, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ge, D.; Chen, J.; Xu, P.; Li, K. A light-fueled self-rolling unicycle with a liquid crystal elastomer rod engine. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 186, 115327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, Y.; Ikegami, T.; Satonaga, S.; Obara, K.; Sato, H.; Takeda, S. Light-Driven Flipping of Azobenzene Assemblies—Sparse Crystal Structures and Responsive Behaviour to Polarised Light. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 10759–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.; Pang, C.; Cho, S.B. A micropillar-assisted versatile strategy for highly sensitive and efficient triboelectric energy generation under in-plane stimuli. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Liu, Z.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Yu, L.; Yu, H. Optical pendulum generator based on photomechanical liquid-crystalline actuators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8393–8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serak, S.; Tabiryan, N.; Vergara, R.; White, T.J.; Vaia, R.A.; Bunning, T.J. Liquid crystalline polymer cantilever oscillators fueled by light. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Lahikainen, M.; Liu, L.; Ahmed, Z.; Wani, O.M.; Wang, M.; Yang, H.; Priimagi, A. Light-fuelled freestyle self-oscillators. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Tabiryan, N.V.; Serak, S.V.; Hrozhyk, U.A.; Tondiglia, V.P.; Koerner, H.; Vaia, R.A.; Bunning, T.J. A high frequency photodriven polymer oscillator. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 1796–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, F.; Rivkin, B.; Aziz, A.; Becker, C.; Karnaushenko, D.D.; Medina-Sánchez, M.; Karnaushenko, D.; Schmidt, O.G. Self-sufficient self-oscillating microsystem driven by low power at low Reynolds numbers. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabj0767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Miao, J.; Li, G.; Ren, H.; Zhang, T.; Guo, D.; Tang, Y.; Shang, W.; Shen, Y. Soft tunable gelatin robot with insect-like claw for grasping, transportation, and delivery. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 5431–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yao, S.; Zhang, H.; Man, W.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Fang, D.; Zhang, Y. Liquid crystal elastomer metamaterials with giant biaxial thermal shrinkage for enhancing skin regeneration. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissonade, J.; De Kepper, P. Multiple types of spatio-temporal oscillations induced by differential diffusion in the Landolt reaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4132–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicconofri, G.; Damioli, V.; Noselli, G. Nonreciprocal oscillations of polyelectrolyte gel filaments subject to a steady and uniform electric field. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2023, 173, 105225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; van den Berg, J.; Crosby, A.J. Autonomous snapping and jumping polymer gels. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rešetič, A.; Milavec, J.; Domenici, V.; Zupančič, B.; Bubnov, A.; Zalar, B. Deuteron NMR investigation on orientational order parameter in polymer dispersed liquid crystal elastomers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 23064–23072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charroyer, L.; Chiello, O.; Sinou, J.-J. Self-excited vibrations of a non-smooth contact dynamical system with planar friction based on the shooting method. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 144, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, M.; Terentjev, E.M. Liquid Crystal Elastomers; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007; Volume 120. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Dang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, R.; Gao, Y.; Feng, L.; Yang, S. Repeatable and reprogrammable shape morphing from photoresponsive gold nanorod/liquid crystal elastomers. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, B.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, R. Bioinspired design of stimuli-responsive artificial muscles with multiple actuation modes. Smart Mater. Struct. 2023, 32, 085023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Bhattacharya, K. Photomechanical coupling in photoactive nematic elastomers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2020, 144, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chang, L.; Hu, Y.; Huang, M.; Ji, Q.; Lu, P.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y. An autonomous soft actuator with light-driven self-sustained wavelike oscillation for phototactic self-locomotion and power generation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1908842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Hu, W.; Soon, R.H.; Davidson, Z.S.; Sitti, M. Liquid crystal elastomer-based magnetic composite films for reconfigurable shape-morphing soft miniature machines. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espíndola-Pérez, E.R.; Campo, J.; Sánchez-Somolinos, C. Multimodal and Multistimuli 4D-Printed Magnetic Composite Liquid Crystal Elastomer Actuators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 16, 2704–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, R.; Jin, L.; Liu, M.; Gao, Y.; Raney, J.; Yang, S. 3D-Printed Photoresponsive Liquid Crystal Elastomer Composites for Free-Form Actuation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2210614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrantini, C.; Pioner, J.M.; Martella, D.; Coppini, R.; Piroddi, N.; Paoli, P.; Calamai, M.; Pavone, F.S.; Wiersma, D.S.; Tesi, C. Development of light-responsive liquid crystalline elastomers to assist cardiac contraction. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, e44–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, R. Modeling the thermo-responsive behaviors of polydomain and monodomain nematic liquid crystal elastomers. Mech. Mater. 2024, 188, 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Shen, W.; Yao, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, H. Bioinspired humidity-responsive liquid crystalline materials: From adaptive soft actuators to visualized sensors and detectors. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 2824–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Chen, H.; Kim, H.; Zhu, B.; Adetiba, O.; Miranda, A.; Cristian Chipara, A.; Ajayan, P.M.; Jacot, J.G.; Verduzco, R. Electromechanically responsive liquid crystal elastomer nanocomposites for active cell culture. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 1386–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liang, H.; Xu, H.; Wei, Y.; Ji, Y. Rewritable Electrically Controllable Liquid Crystal Actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2302110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Liao, W.; Yang, Z. Ultrafast, high-contractile electrothermal-driven liquid crystal elastomer fibers towards artificial muscles. Small 2021, 17, 2103700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Yang, Z. The integration of sensing and actuating based on a simple design fiber actuator towards intelligent soft robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, S. Multi-functional liquid crystal elastomer composites. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022, 9, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Pei, D.; Yu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yi, M.; Li, C. Design of MXene composites with biomimetic rapid and self-oscillating actuation under ambient circumstances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 31978–31985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, R.K.; Shklyaev, O.E.; Balazs, A.C. Chemical pumps and flexible sheets spontaneously form self-regulating oscillators in solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2021, 118, e2022987118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazir, A.; Baumann, A.; Ziebert, F.; Kulić, I.M. Dynamics of fiberboids. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 5210–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vantomme, G.; Elands, L.C.; Gelebart, A.H.; Meijer, E.; Pogromsky, A.Y.; Nijmeijer, H.; Broer, D.J. Coupled liquid crystalline oscillators in Huygens’ synchrony. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelebart, A.H.; Jan Mulder, D.; Varga, M.; Konya, A.; Vantomme, G.; Meijer, E.; Selinger, R.L.; Broer, D.J. Making waves in a photoactive polymer film. Nature 2017, 546, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Trabia, S.; Stalbaum, T.; Palmre, V.; Kim, K.; Oh, I.-K. A multiple-shape memory polymer-metal composite actuator capable of programmable control, creating complex 3D motion of bending, twisting, and oscillation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Annapooranan, R.; Zeng, J.; Chen, R.; Cai, S. Electrospun liquid crystal elastomer microfiber actuator. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabi9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Light-powered self-sustained chaotic motion of a liquid crystal elastomer-based pendulum. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 184, 115027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Dai, Y.; Li, K.; Xu, P. Theoretical study of chaotic jumping of liquid crystal elastomer ball under periodic illumination. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 7799–7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, A.; Sánchez-Ferrer, A.; Jacomine, L.; Martinoty, P.; Le Houerou, V.; Ziebert, F.; Kulić, I.M. Motorizing fibres with geometric zero-energy modes. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dai, C.; Dai, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, K. Self-oscillation of cantilevered silicone oil paper sheet system driven by steam. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 203, 112270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, E.; Han, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y.-X.; Lu, C. Light-driven core-shell fiber actuator based on carbon nanotubes/liquid crystal elastomer for artificial muscle and phototropic locomotion. Carbon 2022, 187, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, N.W.; Tolley, M.T.; Overvelde, J.T.; Weaver, J.C.; Mosadegh, B.; Bertoldi, K.; Whitesides, G.M.; Wood, R.J. A 3D-printed, functionally graded soft robot powered by combustion. Science 2015, 349, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, M.; Truby, R.L.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Mosadegh, B.; Whitesides, G.M.; Lewis, J.A.; Wood, R.J. An integrated design and fabrication strategy for entirely soft, autonomous robots. Nature 2016, 536, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Mao, J.; Chirarattananon, P.; Helbling, E.F.; Hyun, N.-s.P.; Clarke, D.R.; Wood, R.J. Controlled flight of a microrobot powered by soft artificial muscles. Nature 2019, 575, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantomme, G.; Gelebart, A.; Broer, D.; Meijer, E. A four-blade light-driven plastic mill based on hydrazone liquid-crystal networks. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 4963–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelmann, H.; Nishikawa, E.; Pereira, G.; Warner, M. A new opto-mechanical effect in solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 015501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hu, H.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Modeling the light-powered self-rotation of a liquid crystal elastomer fiber-based engine. Phys. Rev. E 2024, 109, 034701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shi, F.; Song, W.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Modeling of self-oscillating flexible circuits based on liquid crystal elastomers. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 270, 109099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qian, G.; Dai, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Song, W.; Li, K. Nonlinear dynamics modeling of a light-powered liquid crystal elastomer-based perpetual motion machine. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 184, 114957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, C.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Modeling of a light-fueled self-paddling boat with a liquid crystal elastomer-based motor. Phys. Rev. E 2024, 109, 044705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Yin, R.; Hua, Y.; Jiao, W.; Mo, C.; Shu, H.; Raney, J.R. A modular strategy for distributed, embodied control of electronics-free soft robots. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade9247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Chen, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, K. Mathematical Modeling of the Displacement of a Light-Fuel Self-Moving Automobile with an On-Board Liquid Crystal Elastomer Propulsion Device. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Transverse vibration of nematic elastomer Timoshenko beams. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 012703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, Y. Effects of director rotation relaxation on viscoelastic wave dispersion in nematic elastomer beams. Math. Mech. Solids 2019, 24, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Lin, Y.; Huo, Y. A large deflection light-induced bending model for liquid crystal elastomers under uniform or non-uniform illumination. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2011, 48, 3232–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, Y. Photomechanical vibration energy harvesting based on liquid crystal elastomer cantilever. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 075017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Li, K. Theoretical Analysis of Light-Actuated Self-Sliding Mass on a Circular Track Facilitated by a Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fiber. Polymers 2024, 16, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartoff, R.P.; Menczel, J.D.; Dillman, S.H. Dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA). In Thermal Analysis of Polymers: Fundamentals Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 387–495. [Google Scholar]
- Menard, K.P.; Menard, N. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lüdde, S.C.; Dreizler, M.R. Theoretical Mechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Truesdell, C. Essays in the History of Mechanics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dugas, R. A History of Mechanics; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Nakano, M.; Ikeda, T. Directed bending of a polymer film by light. Nature 2003, 425, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, K.M.; Fowler, H.E.; McCracken, J.M.; Schlafmann, K.R.; Koch, J.A.; White, T.J. Synthesis and alignment of liquid crystalline elastomers. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nägele, T.; Hoche, R.; Zinth, W.; Wachtveitl, J. Femtosecond photoisomerization of cis-azobenzene. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1997, 272, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torras, N.; Zinoviev, K.; Marshall, J.; Terentjev, E.; Esteve, J. Bending kinetics of a photo-actuating nematic elastomer cantilever. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 254102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Lv, J.-A. Light-modulated liquid crystal elastomer actuator with multimodal shape morphing and multifunction. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 3796–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Definition | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| light intensity | 0–80 | kW/m2 | |
| contraction coefficient of LCE fiber | 0–0.4 | / | |
| elastic coefficient of LCE fiber | 20–40 | N/m | |
| Cis to trans thermal relaxation time | 0.02–0.45 | s | |
| light absorption constant | 0.002 | m2/(s·W) | |
| mass of the slider | 0–0.02 | kg | |
| the first damping coefficient | 0–0.3 | kg/s | |
| the second damping coefficient | 0–0.15 | kg/m | |
| initial tangential velocity | 0–5 | m/s | |
| range of illuminated zone | 0–2π | rad | |
| radius of circular track | 0.01–5 | m | |
| horizontal projection distance of LCE string | 0.01–2.5 | m | |
| original length of LCE fiber | 0.1–5 | m |
| Parameter | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 0–1 | 0–0.4 | 0–10 | 0–3 | π–2π | 0–0.2 | 0–0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, L.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Hu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Li, K. The Light-Fueled Self-Rotation of a Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fiber-Propelled Slider on a Circular Track. Polymers 2024, 16, 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162263
Wei L, Chen Y, Hu J, Hu X, Qiu Y, Li K. The Light-Fueled Self-Rotation of a Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fiber-Propelled Slider on a Circular Track. Polymers. 2024; 16(16):2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162263
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Lu, Yanan Chen, Junjie Hu, Xueao Hu, Yunlong Qiu, and Kai Li. 2024. "The Light-Fueled Self-Rotation of a Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fiber-Propelled Slider on a Circular Track" Polymers 16, no. 16: 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162263
APA StyleWei, L., Chen, Y., Hu, J., Hu, X., Qiu, Y., & Li, K. (2024). The Light-Fueled Self-Rotation of a Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fiber-Propelled Slider on a Circular Track. Polymers, 16(16), 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162263









