Current Concerns about Microplastics and Nanoplastics: A Brief Overview
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification
3. Sources and Concerns
3.1. Overview
3.2. Paints
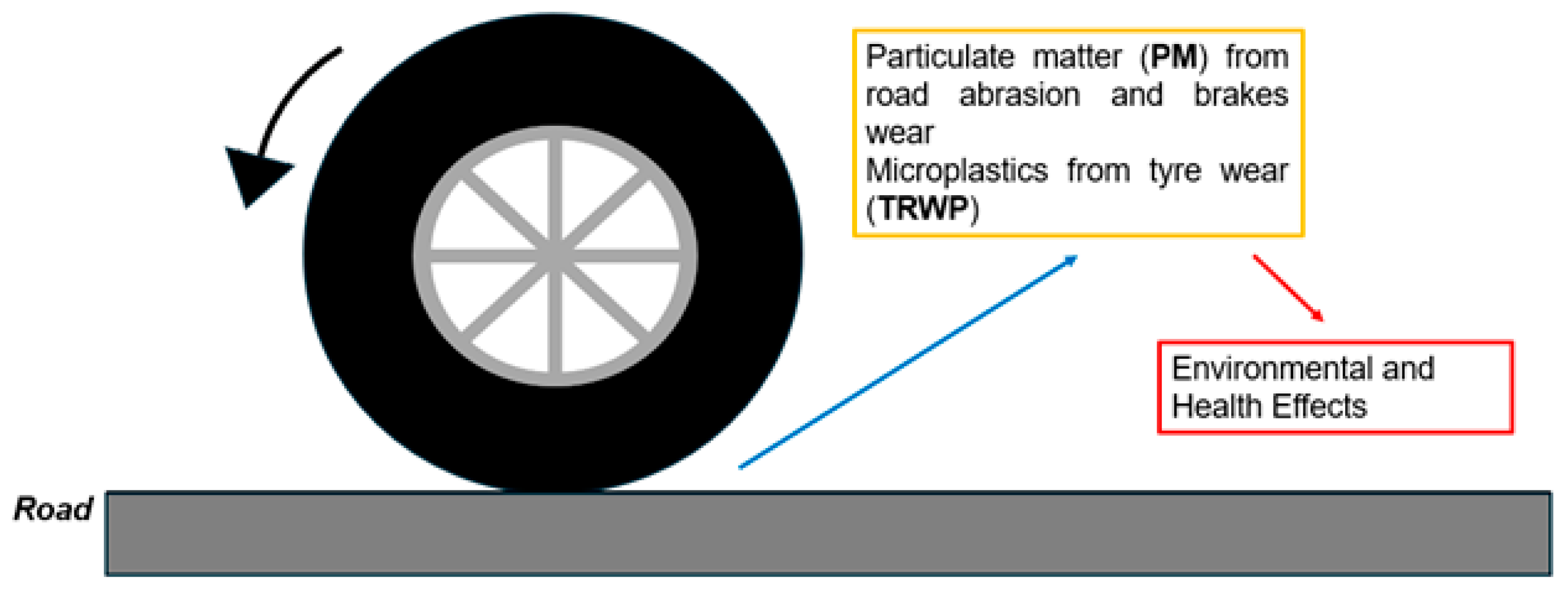
3.3. Tires
3.4. Textiles
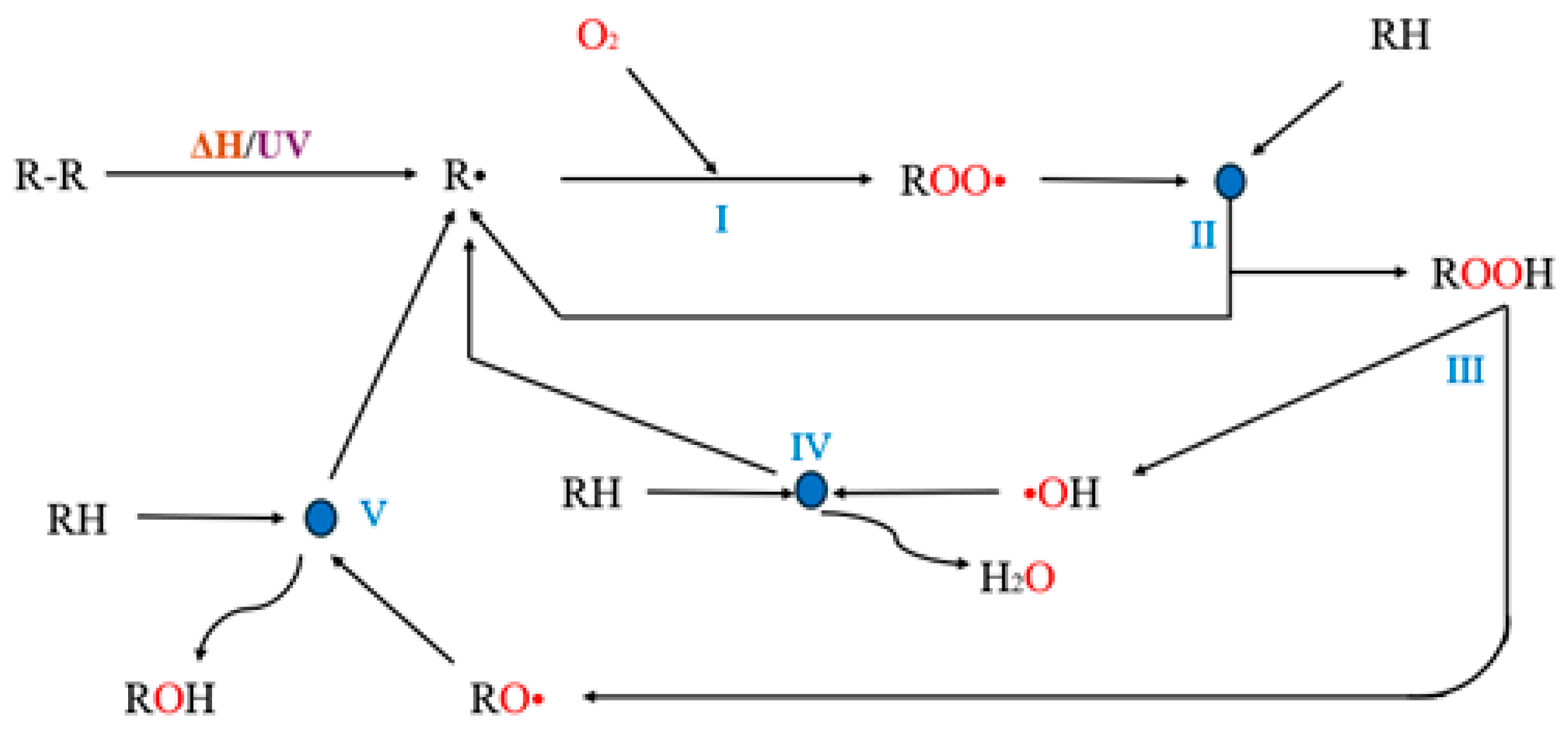
3.5. Degradation and Fragmentation
3.6. What about Biodegradable Polymers?
3.7. Additional Concerns and Possible Workarounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weber, C.J.; Hahn, J.; Opp, C. Spatial connections between microplastics and heavy metal pollution within floodplain soils. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, R. Phytoremediation and nanoremediation. In New Frontiers of Nanomaterials in Environmental Science; Kumar, R., Kaur, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021; pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Nguyen, B.S.; Le, D.T.; Alomar, T.S.; AlMasoud, N.; Ghotekar, S.; Oza, R.; Raizada, P.; Singh, P.; Nguyen, V.H. A concept for Biotechnological minimizing of emerging plastic, micro and nano-plastics pollutants from the environment: A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Kapoor, D.; Bhardwaj, S.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Pawar, A.; Ramamurthy, P.; Singh, J. Fate and occurrence of micro and nano-plastic pollution in industrial wastewater. In Biodegradation and Detoxification of Micropollutants in Industrial Wastewater; Haq, I., Kalamdhad, A.S., Shah, M.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, P.A. Review on the impacts of microplastic beads used in cosmetics. Acta Biomed. Sci. 2016, 3, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Monkul, M.M.; Özhan, H.O. Microplastic contamination in soils: A review from geotechnical engineering view. Polymers 2021, 13, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelleman, C.; Henriksen, R.; Kreilhuber, A.; Stewart, D.; Kotsovou, M.; Raxter, P.; Mrema, E.; Barrat, S. The Raise of Environmental Crime: A Growing Threat to Natural Resources, Peace, Development, and Security; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelkader, N.; Ismail, S.B.; Zakhama-Sraieb, R. Macro-, meso-and microplastic debris in three sandy beaches of north-eastern Tunisian coasts. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 67, 103229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, S.; Park, J.; Din, M.F.M.; Taib, S.M.; Talaiekhozani, A.; Yadav, K.K.; Kamyab, H. Microplastics pollution in different aquatic environments and biota: A review of recent studies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, H.K.; Arnott, J.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Plastic degradation and its environmental implications with special reference to poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polymers 2013, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, I.O.; Auta, H.S.; Ilyasu, U.S.; Aransiola, S.A.; Makun, H.A.; Adabara, N.U.; Abioye, O.P.; Aziz, A.; Jayanthi, B.; Maddela, N.R.; et al. Micro-and Nanoplastics in Environment: Degradation, Detection, and Ecological Impact. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2024, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, B.; Azimi, P.; El Orch, Z.; Ramos, T. Ultrafine particle emissions from desktop 3D printers. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Mohamed Nor, N.H.; Hermsen, E. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Wagner, M. Characterisation of nanoplastics during the degradation of polystyrene. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chatterjee, S. Microplastic pollution, a threat to marine ecosystem and human health: A short review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21530–21547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, M.N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Effect of microplastics in water and aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19544–19562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vighi, M.; Bayo, J.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Gago, J.; Gómez, M.; Hernández-Borges, J.; Rosal, R. Micro and nano-plastics in the environment: Research priorities for the near future. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 257, 163–218. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, B.R.; Kopperi, H.; Venkata Mohan, S. Micro/nano-plastics occurrence, identification, risk analysis and mitigation: Challenges and perspectives. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotech. 2022, 21, 169–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignattelli, S.; Broccoli, A.; Piccardo, M.; Terlizzi, A.; Renzi, M. Effects of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) microplastics and acid rain on physiology and growth of Lepidium sativum. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 282, 116997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, S.H.; Abioye, O.P.; Aransiola, S.A.; Bala, J.D.; Chukwuemeka, V.I.; Hassan, A.; Aziz, A.; Fauziah, S.H. Enhanced microbial degradation of PET and PS microplastics under natural conditions in mangrove environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, M.; Khadir, A.; Muthu, S.S. (Eds.) Microplastics Pollution in Aquatic Media; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nikiema, J.; Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Asiedu, Z.; Saad, D.; Lamizana, B. Water Pollution by Plastics and Microplastics: A Review of Technical Solutions from Source to Sea; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bank, M.S. (Ed.) Microplastic in the Environment: Pattern and Process; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development Global Plastic Waste Set to Almost Triple by 2060 Says OECD, Paris, France. 2023. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/newsroom/global-plastic-waste-set-to-almost-triple-by-2060.htm (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Yee, M.S.L.; Hii, L.W.; Looi, C.K.; Lim, W.M.; Wong, S.F.; Kok, Y.Y.; Tan, B.K.; Wong, C.Y.; Leong, C.O. Impact of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Human Health. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Katsouli, J.; Marczylo, E.L.; Gant, T.W.; Wright, S.; de la Serna, J.B. The potential impacts of micro-and-nano plastics on various organ systems in humans. EBioMedicine 2024, 99, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopatz, V.; Wen, K.; Kovács, T.; Keimowitz, A.S.; Pichler, V.; Widder, J.; Vethaak, A.D.; Hollóczki, O.; Kenner, L. Micro- and Nanoplastics Breach the Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB): Biomolecular Corona’s Role Revealed. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forest, V.; Pourchez, J. Can the impact of micro-and nanoplastics on human health really be assessed using in vitro models? A review of methodological issues. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashaei, R.; Dzingelevičienė, R.; Abbasi, S.; Szultka-Młyńska, M.; Buszewski, B. Determination of the pharmaceuticals–nano/microplastics in aquatic systems by analytical and instrumental methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafeev, K.V.; Apicella, A.; Incarnato, L.; Scarfato, P. Understanding the Impact of Biodegradable Microplastics on Living Organisms Entering the Food Chain: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouin, T.; Cunliffe, D.; De France, J.; Fawell, J.; Jarvis, P.; Koelmans, A.A.; Marsden, P.; Testai, E.E.; Asami, M.; Bevan, R.; et al. Clarifying the absence of evidence regarding human health risks to microplastic particles in drinking-water: High quality robust data wanted. Environ. Int. 2021, 150, 106141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Xu, G.; Du, F.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Shi, H. Analysis of environmental nanoplastics: Progress and challenges. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, N.; Gao, X.; Lang, X.; Deng, H.; Bratu, T.M.; Chen, Q.; Min, W. Rapid single-particle chemical imaging of nanoplastics by SRS microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2300582121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufnagl, B.; Stibi, M.; Martirosyan, H.; Wilczek, U.; Möller, J.N.; Löder, M.G.; Lohninger, H. Computer-assisted analysis of microplastics in environmental samples based on μFTIR imaging in combination with machine learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, M.; Ussia, M.; Novotný, F.; Pumera, M. Trapping and detecting nano-plastics by MXene-derived oxide microrobots. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directorate-General for Environment. EU Action Against Microplastics, Publications Office of the European Union. 2023. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2779/917472 (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Kibria, G.; Nugegoda, D.; Yousuf Haroon, A.K. Microplastic (MP) Pollution in the Context of Occurrence, Distribution, Composition and Concentration in Surface Waters and Sediments: A Global Overview. In Microplastic Pollution: Environmental Occurrence and Treatment Technologies; Hashmi, M.Z., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Alimi, O.; Farner, J.; Hernandez, L.; Tufenkji, N. Microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments: Aggregation, deposition, and enhanced contaminant transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWF (World Wildlife Fund) Italia. Fiumi, la Minaccia Arriva da Insetticidi e Plastica. Available online: https://www.wwf.it/cosa-facciamo/pubblicazioni/fiumi-la-minaccia-arriva-da-insetticidi-e-plastica/ (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Devriese, L.; Galgani, F.; Robbens, J.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in sediments: A review of techniques, occurrence and effects. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauert, C.; Rødland, E.S.; Okoffo, E.D.; Reid, M.J.; Meland, S.; Thomas, K.V. Challenges with quantifying tire road wear particles: Recognizing the need for further refinement of the ISO technical specification. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Grigoratos, T.; Mathissen, M.; Quik, J.; Tromp, P.; Gustafsson, M.; Franco, V.; Dilara, P. Contribution of Road Vehicle Tyre Wear to Microplastics and Ambient Air Pollution. Sustainability 2024, 16, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, K.; Hansson, L.A.; Cedervall, T. Nano-plastics in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Imp. 2015, 17, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Council of the Paint, Printing Ink, and Artist’s Colours Industry. 2023. Available online: https://www.cepe.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/09.3_Annex-3_Is-there-plastic-in-paint-FINAL-1.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2024).
- Unice, K.M.; Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M. Use of a Deuterated Internal Standard with Pyrolysis-GC/MS Dimeric Marker Analysis to Quantify Tire Tread Particles in the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 4033–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüffer, T.; Wagner, S.; Reemtsma, T.; Hofmann, T. Sorption of organic substances to tire wear materials: Similarities and differences with other types of microplastic. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Hüffer, T.; Klöckner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire wear particles in the aquatic environment—A review on generation, analysis, occurrence, fate and effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Lambert, S. Freshwater Microplastics: Emerging Environmental Contaminants? Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kole, P.J.; Löhr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.; Ragas, A.M. Wear and tear of tyres: A stealthy source of microplastics in the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, L.J.; Parker-Jurd, F.N.; Al-Sid-Cheikh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Tyre wear particles: An abundant yet widely unreported microplastic? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18345–18354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP)—A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, Q.T.; Potter, P.M.; Pinto, P.X.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Al-Abed, S.R. Sources, transport, measurement and impact of nano and microplastics in urban watersheds. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotech. 2020, 19, 275–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, L.; Masseroni, A.; Rizzi, C.; Villa, S. Silent Contamination: The State of the Art, Knowledge Gaps, and a Preliminary Risk Assessment of Tire Particles in Urban Parks. Toxics 2023, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreider, M.L.; Unice, K.M.; Panko, J.M. Human Health Risk Assessment of Tire and Road Wear Particles (TRWP) in Air. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 2567–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabani, N.V.S.; Gruzieva, O.; Elihn, K.; Juárez-Facio, A.T.; Steimer, S.S.; Kuhn, J.; Silvergren, S.; Portugal, J.; Piña, B.; Olofsson, U. Toxicity and Health Effects of Ultrafine Particles: Towards an Understanding of the Relative Impacts of Different Transport Modes. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschoor, A.; De Poorter, L.; Dröge, R.; Kuenen, J.; De Valk, E. Emission of Microplastics and Potential Mitigation Measures. Abrasive Cleaning Agents, Paints and Tyre Wear; National Institute for Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mennekes, D.; Nowack, B. Tire Wear Particle Emissions: Measurement Data Where Are You? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yin, H.; Tan, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Hao, L.; Du, T.; Niu, Z.; Ge, Y. A Comprehensive Review of Tyre Wear Particles: Formation, Measurements, Properties, and Influencing Factors. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 297, 119597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieré, R.; Dietze, V. Tire-Abrasion Particles in the Environment. In Degradation of Elastomers in Practice, Experiments and Modeling; Heinrich, G., Kipscholl, R., Stŏcek, R., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 289, pp. 71–101. [Google Scholar]
- Grigoratos, T.; Martini, G. Non-Exhaust Traffic Related Emissions. Brake and Tyre Wear PM; European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute of Energy and Transport: Ispra, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hesse, D.; Feißel, T.; Kunze, M.; Bachmann, E.; Bachmann, T.; Gramstat, S. Comparison of Methods for Sampling Particulate Emissions from Tires under Different Test Environments. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Maitre, O.; Süssner, M.; Zarak, C. Evaluation of Tire Wear Performance (No. 980256); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- European TRWP Platform. Way Forward Report, Brussels, Belgium. 2019. Available online: https://www.etrma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/20200330-FINAL-Way-Forward-Report.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Sjödin, Å.; Ferm, M.; Björk, A.; Rahmberg, M.; Gudmundsson, I.A.; Swietlicki, E. Wear Particles from Road Traffic; IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M.; McAtee, B.L.; Sweet, L.I.; Finley, B.L. Physical and Chemical Characterization of Tire-Related Particles: Comparison of Particles Generated Using Different Methodologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNECE Task Force on Studded Tyres (TF ST). Available online: https://wiki.unece.org/download/attachments/166724916/TA-02-02%20Study_ADAC_tyre_abrasion_110522_en-GB.pdf?api=v2 (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Marchioni, M.; Fedele, R.; Raimondi, A.; Sansalone, J.; Becciu, G. Permeable Asphalt Hydraulic Conductivity and Particulate Matter Separation With XRT. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 1879–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, I.; Schläfle, S.; Bertling, R.; Öz, M.; Gregory, K. Mitigation Measures to Reduce Tire and Road Wear Particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Fang, T.; Men, Z.; Wei, N.; Peng, J.; Du, T.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wu, L.; Mao, H. Direct Measurement of Brake and TireWear Particles Based on Real-World Driving Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, F.; Alastuey, A.; de la Rosa, J.; Gonzalez Castanedo, Y.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Pandolfi, M.; Lozano, A.; Contreras González, J.; Querol, X. Trends of road dust emissions contributions on ambient air particulate levels at rural, urban and industrial sites in southern Spain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3533–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Kim, H.; Lee, S. Characteristics of tire wear particles generated in a laboratory simulation of tire/road contact conditions. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2018, 124, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Jones, A.M.; Gietl, J.; Yin, J.; Green, D.C. Estimation of the contributions of brake dust, tire wear, and resuspension to nonexhaust traffic particles derived from atmospheric measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6523–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panko, J.M.; Hitchcock, K.M.; Fuller, G.W.; Green, D. Evaluation of Tire Wear Contribution to PM2.5 in Urban Environments. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEP). Marine Plastic Debris & Microplastics—Global Lessons and Research to Inspire Action and Guide Policy Change; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tadiello, L.; D’Arienzo, M.; Di Credico, B.; Hanel, T.; Matejka, L.; Mauri, M.; Scotti, R. The filler–rubber interface in styrene butadiene nanocomposites with anisotropic silica particles: Morphology and dynamic properties. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 4022–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environmental Agency. Microplastics from Textiles: Towards a Circular Economy for Textiles in Europe. 2023. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/microplastics-from-textiles-towards-a/microplastics-from-textiles-towards-a (accessed on 24 January 2024).
- Hale, R.C.; Seeley, M.E.; La Guardia, M.J.; Mai, L.; Zeng, E.Y. A Global Perspective on Microplastics. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2024, 125, e2018JC014719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: A Global Evaluation of Sources; International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN): Gland, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of microplastics on shorelines worldwide: Sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, M.C.; Pawlak, J.J.; Daystar, J.; Ankeny, M.; Cheng, J.J.; Venditti, R.A. Microfibers generated from the laundering of cotton, rayon and polyester based fabrics and their aquatic biodegradation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abigail, P.W.; Barrows, K.S.; Christiansen, E.T.; Bode, T.J.; Hoellein, A. Watershed-scale, citizen science approach to quantifying microplastic concentration in a mixed land-use river. Water Res. 2018, 147, 382–392. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrullah, A.; Basharat, H.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Ashfaq, M. Chemical Technologies to Degrade Microplastic Pollution. In Microplastic Pollution: Environmental Occurrence and Treatment Technologies; Hashmi, M.Z., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dimassi, S.N.; Hahladakis, J.N.; Yahia, M.N.D.; Ahmad, M.I.; Sayadi, S.; Al-Ghouti, M. Degradation-fragmentation of marine plastic waste and their environmental implications: A critical review. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Yu, H.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. A review on the occurrence and influence of biodegradable microplastics in soil ecosystems: Are biodegradable plastics substitute or threat? Environ. Int. 2023, 163, 107244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Q. A review of the occurrence and degradation of biodegradable microplastics in soil environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Chen, Q. Biodegradable plastics in the air and soil environment: Low degradation rate and high microplastics formation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Qi, Z.; Guy, C.; An, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q. Insights into the abiotic fragmentation of biodegradable mulches under accelerated weathering conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.; Li, T.; Li, M.; Yang, S.; Shen, M.; Liu, H. Research advances on the toxicity of biodegradable plastics derived micro/nanoplastics in the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojt, J.; David, J.; Přikryl, R.; Řezáčová, V.; Kučerík, J. A critical review of the overlooked challenge of determining micro-bioplastics in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degli-Innocenti, F.; Barbale, M.; Chinaglia, S.; Esposito, E.; Pecchiari, M.; Razza, F.; Tosin, M. Analysis of the microplastic emission potential of a starch-based biodegradable plastic material. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 199, 109934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degli-Innocenti, F. The pathology of hype, hyperbole and publication bias is creating an unwarranted concern towards biodegradable mulch films. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 463, 132923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, F.P.; Baiamonte, M.; Santangelo, S.; Scaffaro, R.; Mistretta, M.C. Influence of Different Environments and Temperatures on the Photo-Oxidation Behaviour of the Polypropylene. Polymers 2023, 15, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavia, F.C.; Brucato, V.; Mistretta, M.C.; Botta, L.; La Mantia, F.P. A Biodegradable, Bio-Based Polymer for the Production of Tools for Aquaculture: Processing, Properties and Biodegradation in Sea Water. Polymers 2023, 15, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Kind | Size Range | Source |
|---|---|---|
| MACROPLASTICS | ≥2.5 cm [7,8,9] | “Whole” objects or fragments of packaging and various objects in polymeric material, mainly due to braking processes or direct, intentional release |
| MESOPLASTICS | 5 mm–2.5 cm [7,8,9] | As above |
| PRIMARY MICROPLASTICS | ≤5 mm [8,9], 1–5 mm [7,10] | Scrubbers in cosmetics, liquid soaps, paints, abrasive products; pharmaceuticals; pellets; textile fibers; release of particles and fibers from production and maintenance operations of objects made of polymeric material |
| SECONDARY MICROPLASTICS | ≤5 mm [8,9], 1–5 mm [7,10] | Coming from macroplastics and mesoplastics (but also from primary microplastics) essentially through environmental degradation processes: thermal, thermo-oxidative, photo-oxidative, biological; above all, from UV radiation; also mechanical, like washing and drying of fabrics, or tire abrasion |
| MINIMICROPLASTICS | 1 µm–1 mm [11] | As for microplastics in general (and secondary plastics in particular) |
| NANOPLASTICS | 1 nm–100 nm [7,10,12], <1 µm [11] | According to some: the same of microplastics in general and primary plastics in particular, so much that “paints, adhesives, drugs, electronics, and new 3D printing technologies” are cited [13,14]; according to others: mainly like secondary microplastics, especially washing and drying of fabrics, deterioration of tires and other products such as polystyrene [15,16] or even almost exclusively fabrics and tires [12,17] |
| Main Sources of UMR to the EU Environment | Lower Estimates (2019—Tonnes/Year) | Higher Estimates (2019—Tonnes/Year) |
|---|---|---|
| Paints | 231,000 | 863,000 |
| Tires | 360,000 | 540,000 |
| Pellets | 52,140 | 184,290 |
| Textiles | 1649 | 61,078 |
| Geotextiles | 6000 | 19,750 |
| Detergent capsules | 4140 | 5980 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morreale, M.; La Mantia, F.P. Current Concerns about Microplastics and Nanoplastics: A Brief Overview. Polymers 2024, 16, 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111525
Morreale M, La Mantia FP. Current Concerns about Microplastics and Nanoplastics: A Brief Overview. Polymers. 2024; 16(11):1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111525
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorreale, Marco, and Francesco Paolo La Mantia. 2024. "Current Concerns about Microplastics and Nanoplastics: A Brief Overview" Polymers 16, no. 11: 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111525
APA StyleMorreale, M., & La Mantia, F. P. (2024). Current Concerns about Microplastics and Nanoplastics: A Brief Overview. Polymers, 16(11), 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111525







