Biodegradation of Polyurethane by Fungi Isolated from Industrial Wastewater—A Sustainable Approach to Plastic Waste Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
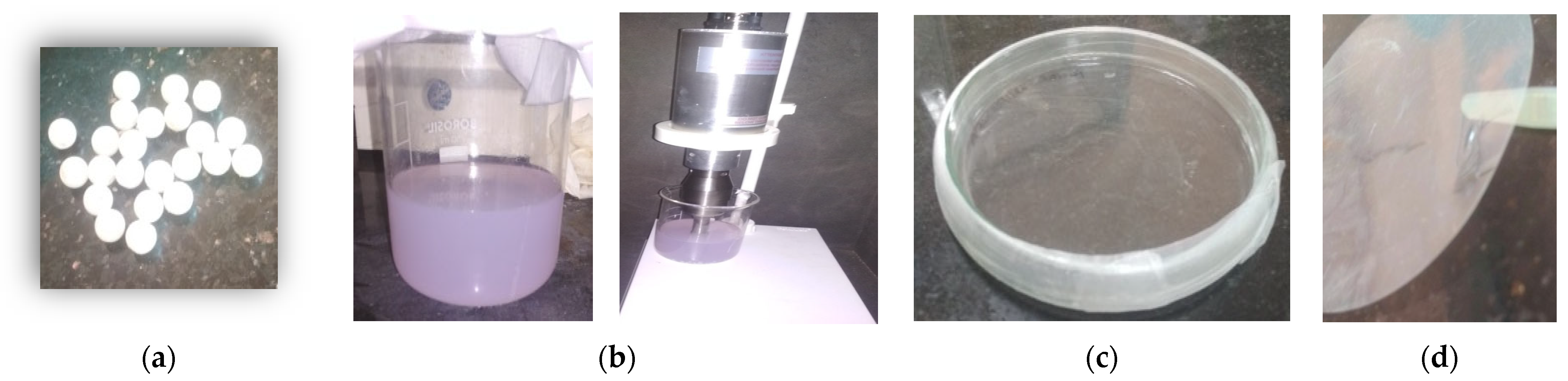
2.2. Preparation of Thin Polyurethane Films
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Soil Burial Test
2.5. Isolation of Selected Micro-Organism
2.6. Screening and Identification of Selected Colonies
2.7. Determination of Growth and PU Degradation
2.8. Degradation Analysis
2.8.1. Screening of Polyurethane Degrading Micro-Organisms Using the Clear Zone Method
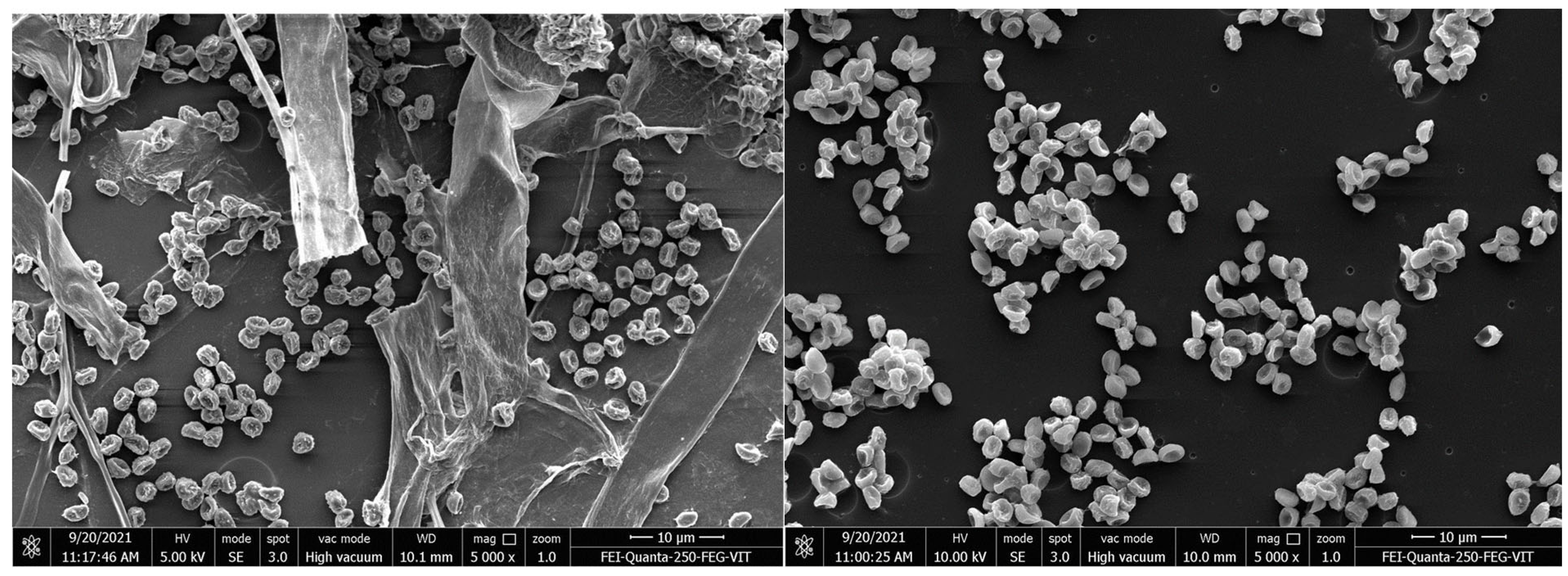
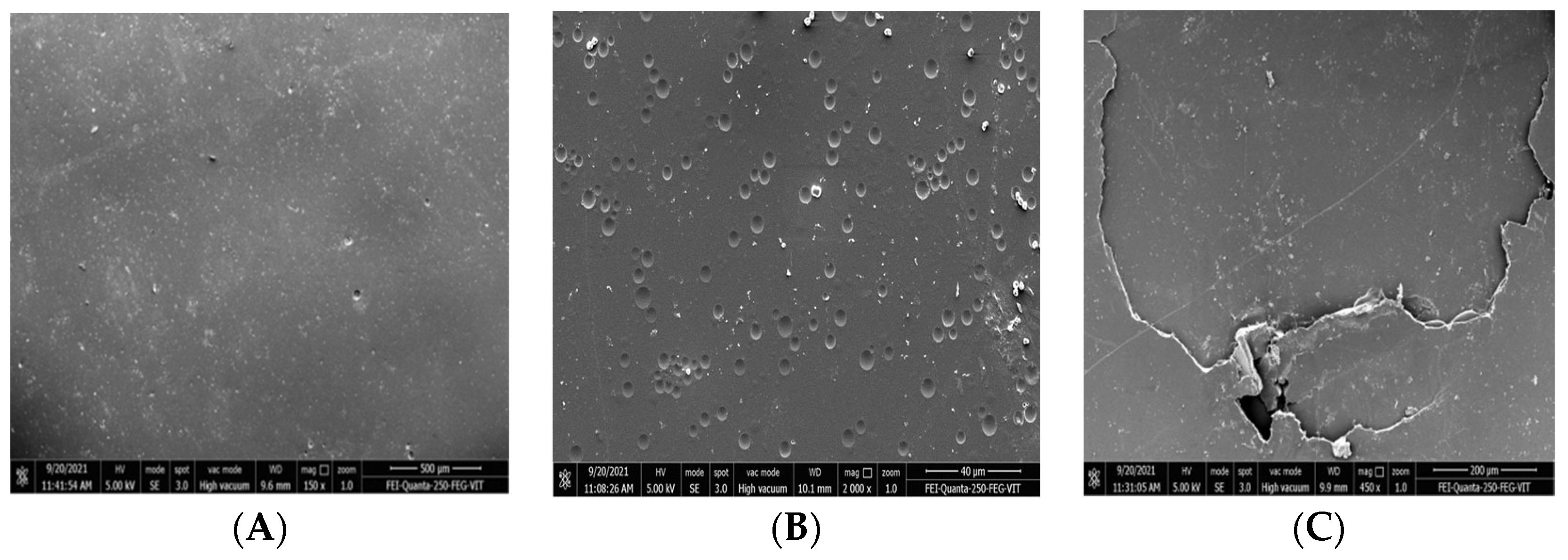
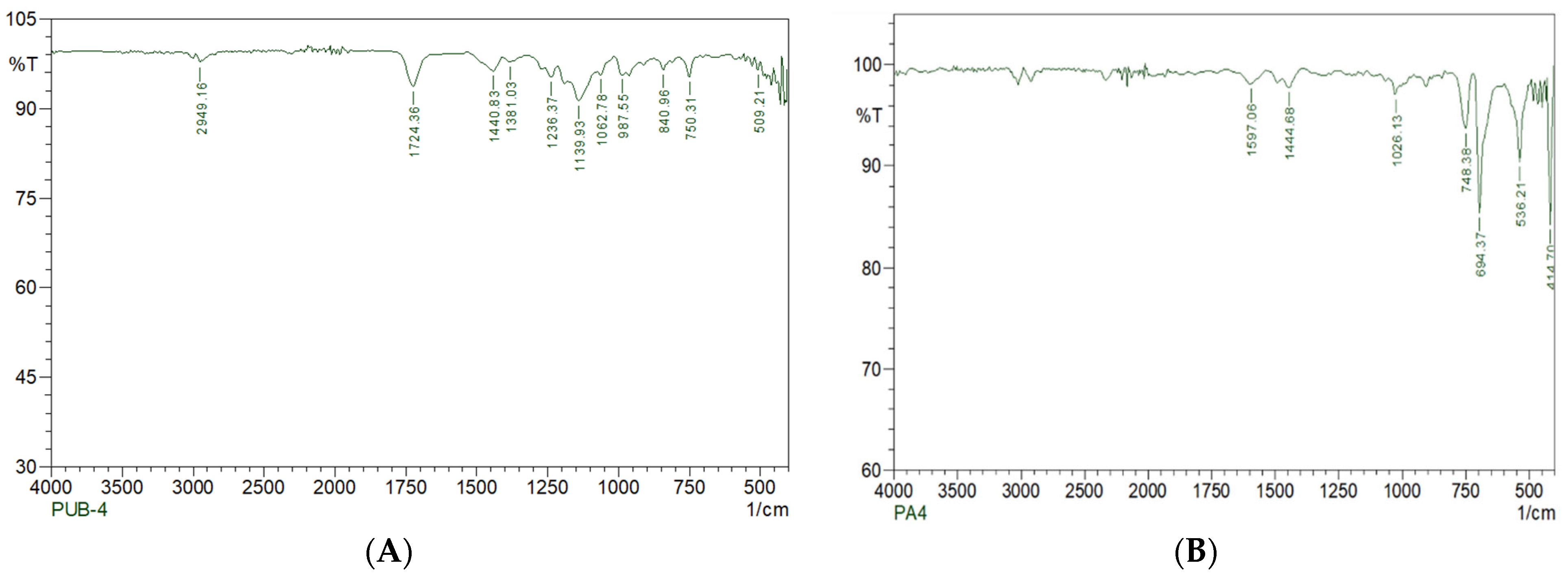
2.8.2. SEM and FTIR Analyses
2.8.3. Sturm Test
2.9. Optimization of Media for Maximum PU Degradation
2.9.1. Effect of Physical Parameters on PU Degradation
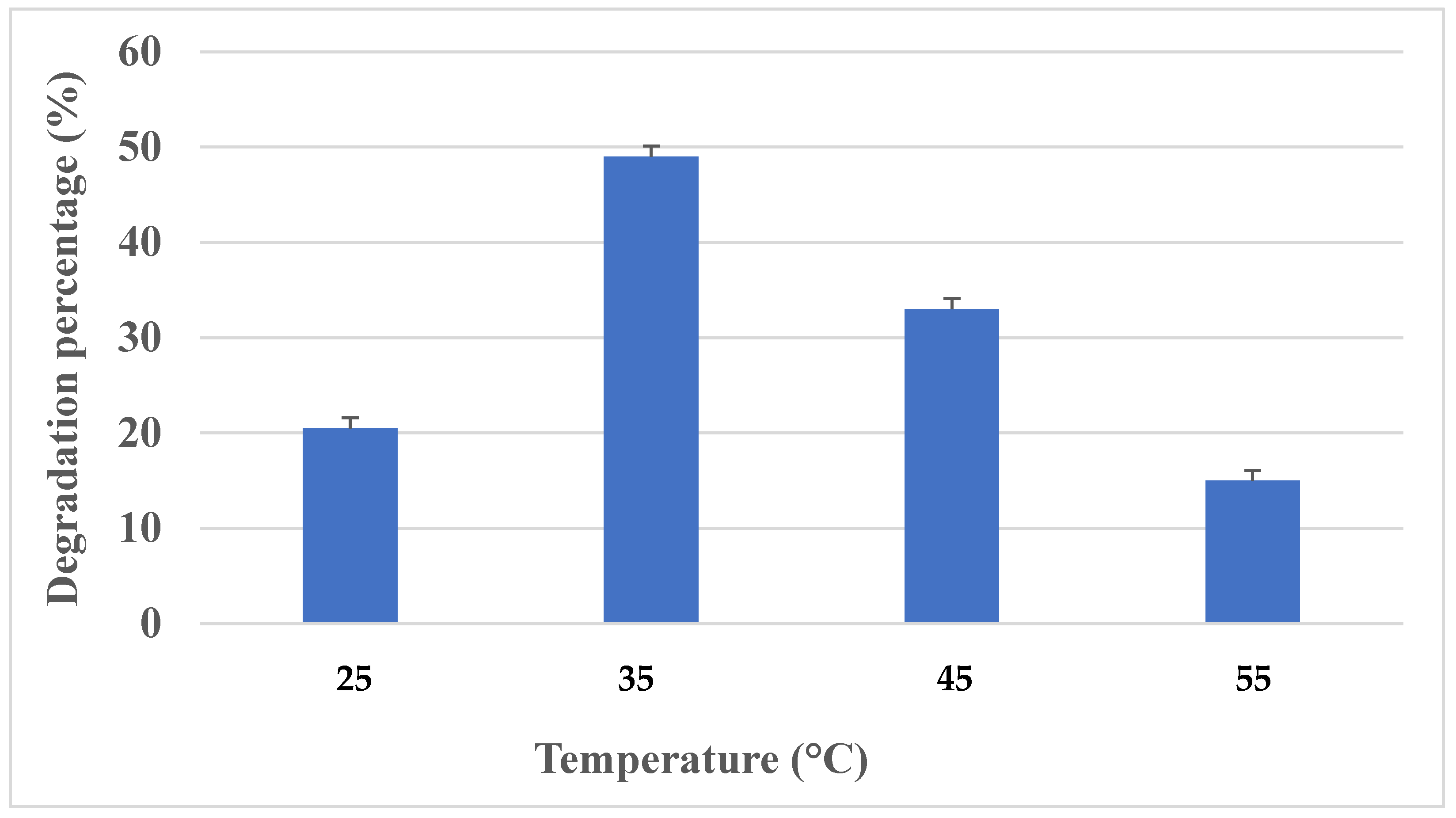
Effect of Temperature
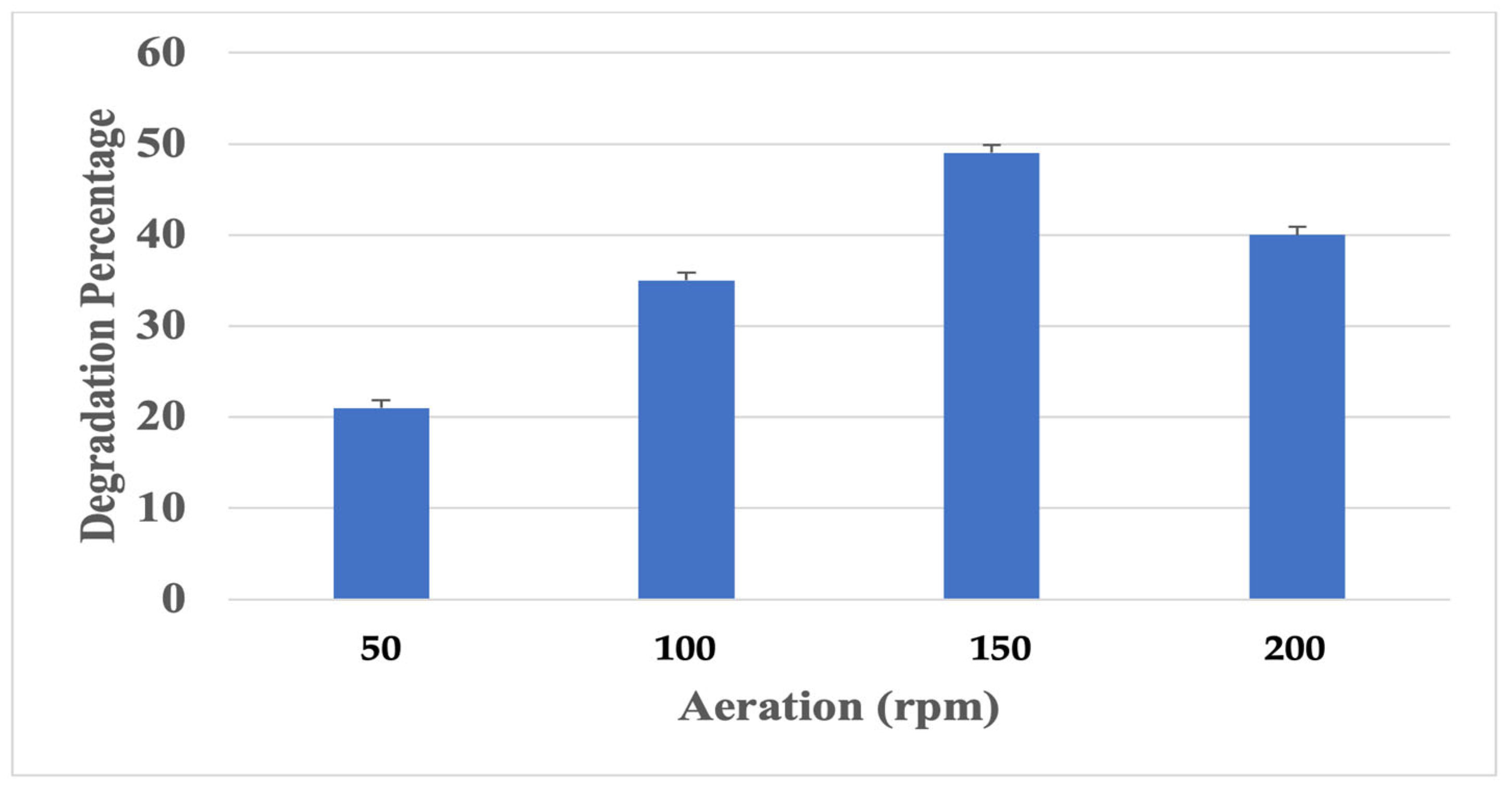
Effect of Aeration
Effect of pH
2.9.2. Effect of Nutrients on PU Degradation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation of PU Degrading Strains
3.2. Screening of Micro-Organisms
3.3. Optimization Parameters for Polyurethane Degradation
3.3.1. Effect of Temperature
3.3.2. Effect of Aeration on Polyurethane Degradation
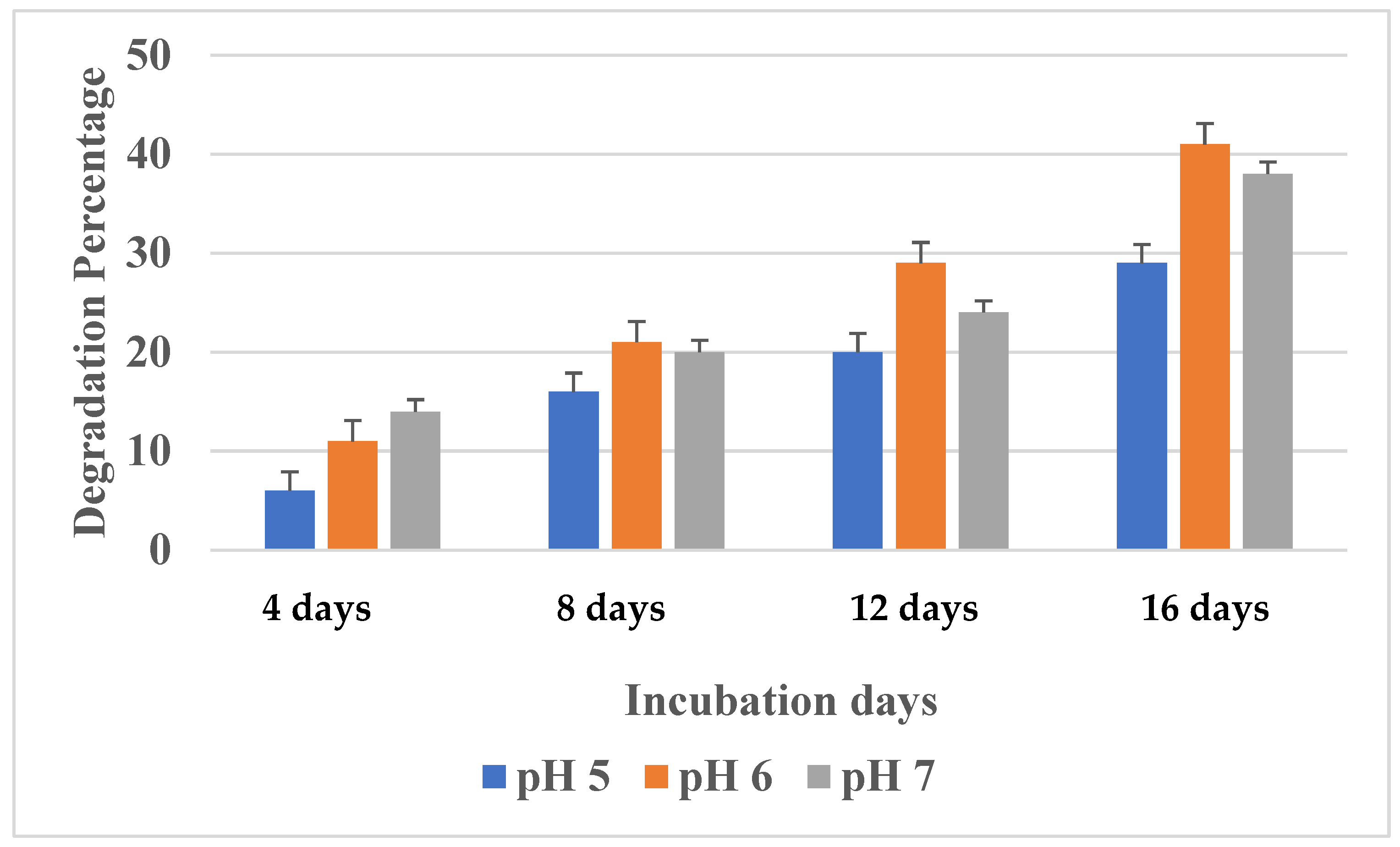
3.3.3. Effect of pH
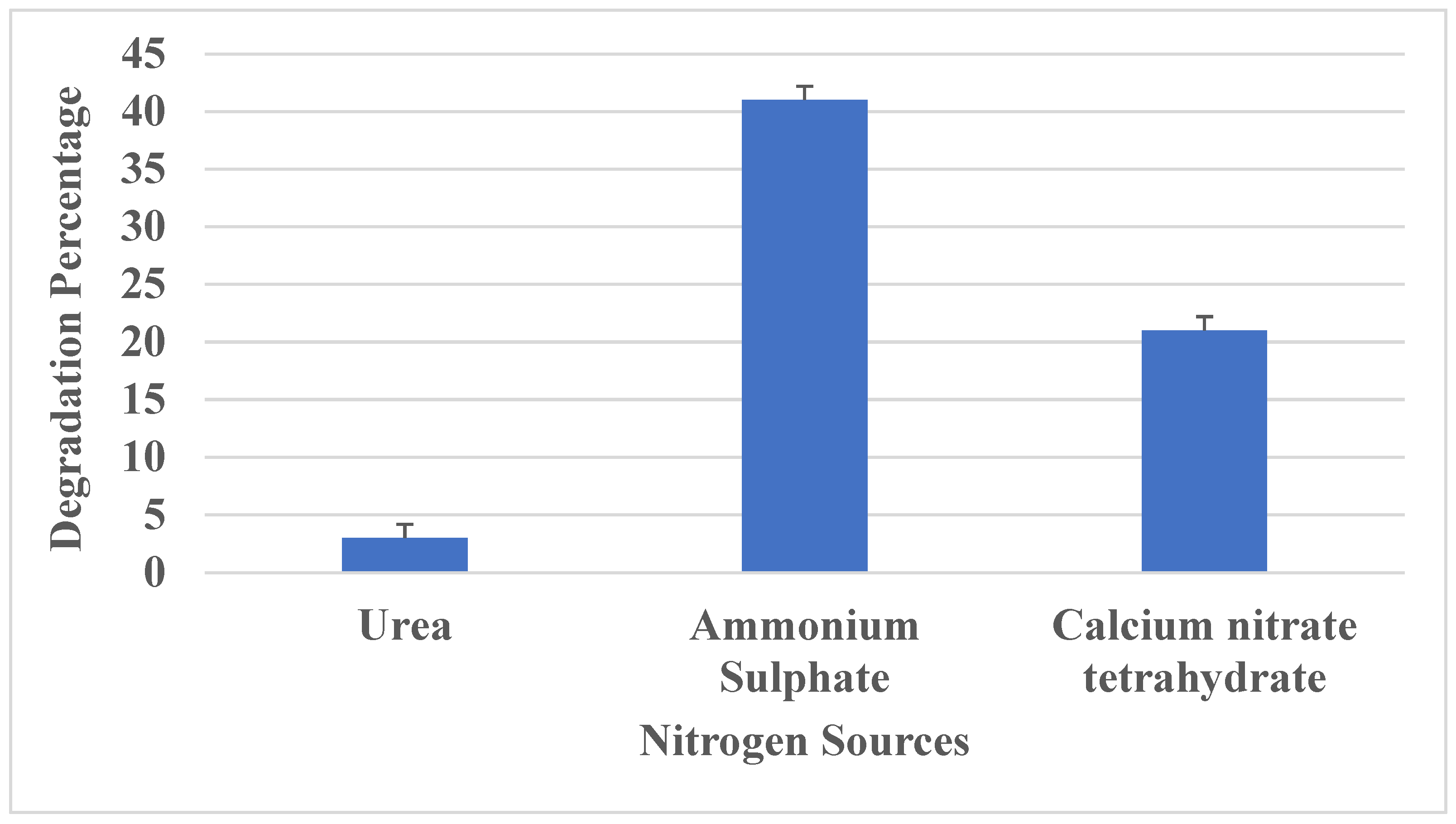
3.3.4. Effect of Nitrogen Sources
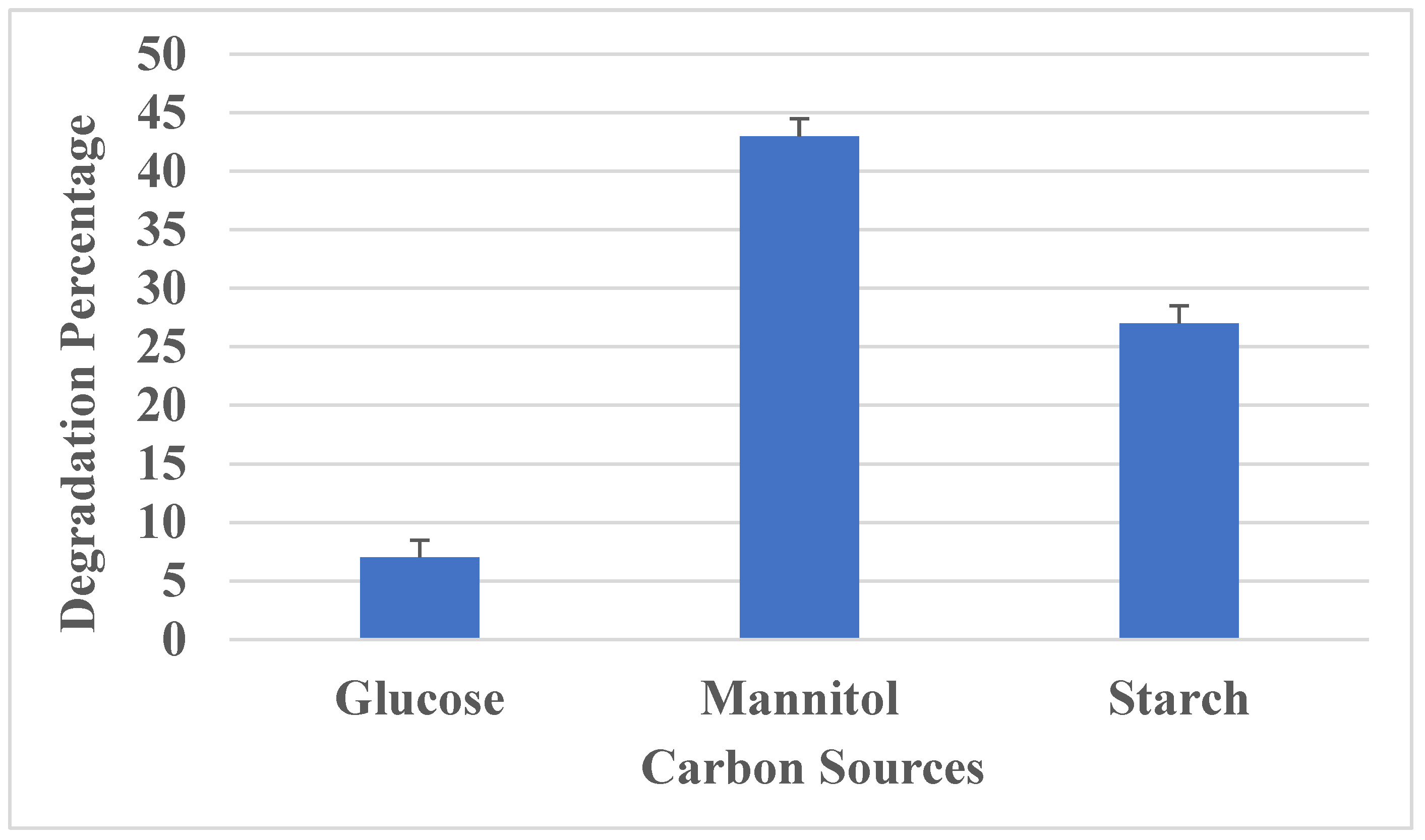
3.3.5. Effect of Carbon Source
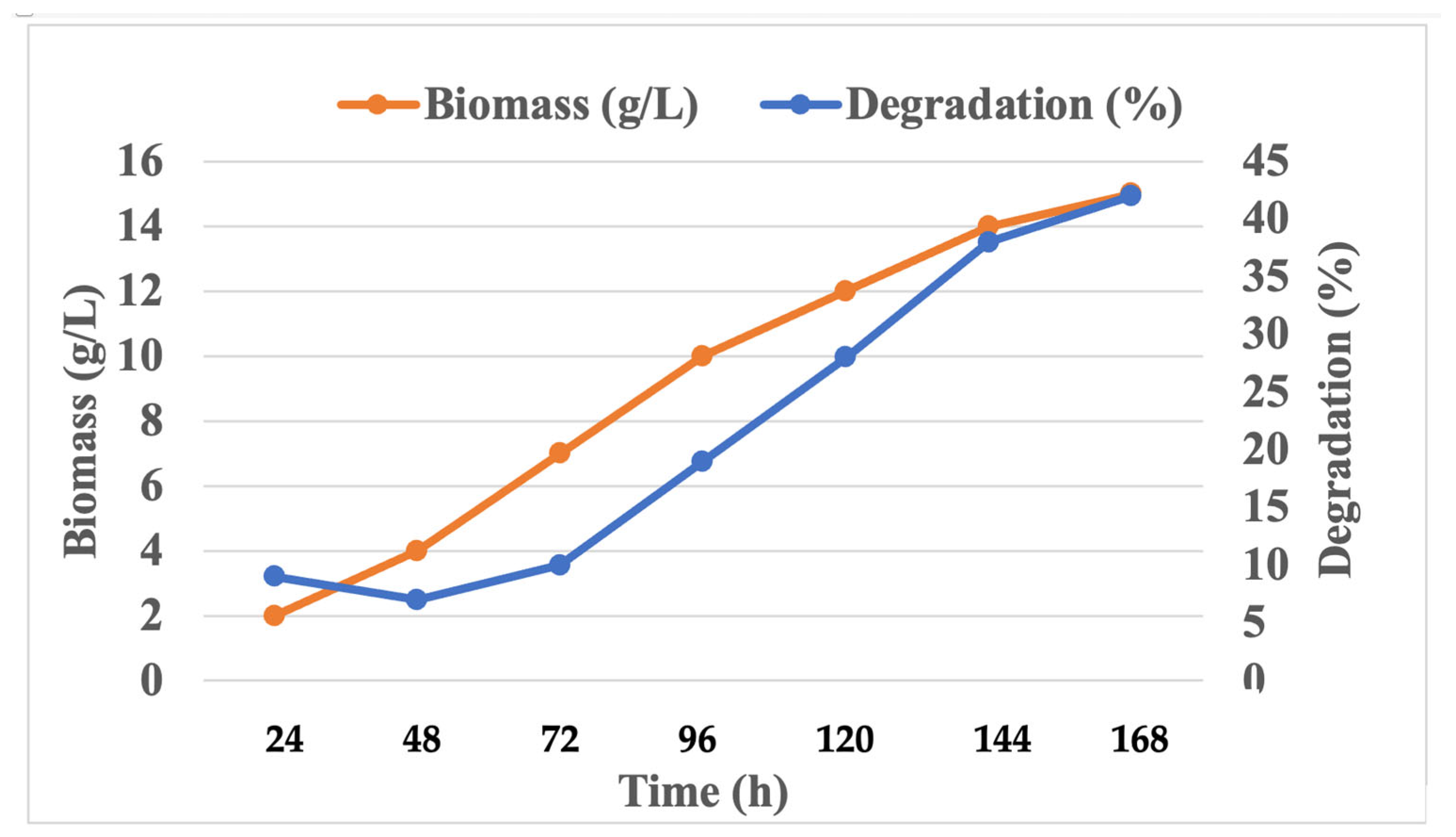
3.4. Determination of Growth and PU Degradation
3.5. Degradation Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Kumar, M.; Sarsaiya, S.; Sirohi, R.; Awasthi, S.K.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A.; Bolan, N.S.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Challenges and opportunities in bioremediation of micro-nano plastics: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 802, 149823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miloloža, M.; Cvetnić, M.; Grgić, D.K.; Bulatović, V.O.; Ukić, Š.; Rogošić, M.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Kušić, H.; Bolanča, T. Biotreatment strategies for the removal of microplastics from freshwater systems. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1377–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, S.T.; Hull, T.R. The fire toxicity of polyurethane foams. Fire Sci. Rev. 2016, 5, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaytán, I.; Sánchez-Reyes, A.; Burelo, M.; Vargas-Suárez, M.; Liachko, I.; Press, M.; Sullivan, S.; Cruz-Gómez, M.J.; Loza-Tavera, H. Degradation of recalcitrant polyurethane and xenobiotic additives by a selected landfill microbial community and its biodegradative potential revealed by proximity ligation-based metagenomic analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oprea, S.; Oprea, V. Mechanical behavior during different weathering tests of the polyurethane elastomers films. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Nadir, S.; Shah, Z.U.; Shah, A.A.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Xu, J.; Khan, A.; Munir, S.; Hasan, F. Biodegradation of Polyester Polyurethane by Aspergillus tubingensis. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cregut, M.; Bedas, M.; Durand, M.-J.; Thouand, G. New insights into polyurethane biodegradation and realistic prospects for the development of a sustainable waste recycling process. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1634–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, A.B.; Hilliard, N.P.; Howard, G.T. Purification and characterization of a solublepolyurethane degrading enzyme from Comamonasacidovorans. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1999, 43, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusta, J.; Widdecke, H.; Müller, R.-J. A rapid evaluation plate-test for the biodegradability of plastics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1993, 39, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akutsu, Y.; Nakajima-Kambe, T.; Nomura, N.; Nakahara, T. Purification and properties of a polyester polyurethane-degrading enzyme from Comamonas acidovorans TB-35. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo-Flórez, J.M.; Bassi, A.; Thompson, M.R. Microbial degradation and 470 deterioration of polyethylene–A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 88, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, Z. Decomposition of polyurethane in a garbage landfill leakage water and by soil microorganisms. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1978, 5, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, G.J.L. Synthetic polymers and the living environment. Pure Appl. Chem. 1980, 52, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, E.J. Bioremediation of organic contaminants in the subsurface. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 20, 517–523. [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove, L.; McGeechan, P.L.; Robson, G.D.; Handley, P.S. Fungal communities associated with degradation of polyester polyurethane in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5817–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabbe, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; Thompson, L.; Walz, S.L.; Schultz, W.W. Biodegradation of a colloidal ester-based polyurethane by soil fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1994, 33, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puszka, A. Thermal and Mechanical Behavior of New Transparent Thermoplastic Polyurethane Elastomers Derived from Cycloaliphatic Diisocyanate. Polymers 2018, 10, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggert, T.; Pencreac′h, G.; Douchet, I.; Verger, R.; Jaeger, K.E. A novel extracellular esterase from Bacillus subtilis and its conversion to a monoacylglycerol hydrolase. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 6459–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentham, R.; Morton, L.; Allen, N. Rapid assessment of the microbial deterioration of Polyurethanes. Int. Biodeterior. 1987, 23, 377–386. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, M.; Morton, L.; Prince, E. Bacterial degradation of polyester polyurethane. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1991, 27, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, M.J.; McCabe, R.W.; Morton, L.H.G. Chemical and physical changes occurring in polyester polyurethane during biodegradation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1993, 31, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.J.; Augusta, J.; Pantke, M. An interlaboratory investigation into biodegradation of plastics. Part 1: A modified Sturm-test. Mat. Organ. 1992, 27, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, G.T.; Hilliard, N.P. Use of Coomassie blue-polyurethane interaction inscreening of polyurethanase proteins andpolyurethanolytic bacteria. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1999, 43, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, R.E.; Main, T.; Howard, G.T. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of apolyurethane-degrading enzyme from Pseudomonasfluorescens. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1999, 43, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, G.T.; Ruiz, C.; Hilliard, N.P. Growth of Pseudomonas chlororaphis on apolyester–polyurethane and the purification andcharacterization of a polyurethanase–esterase enzyme. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1999, 43, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima-Kambe, T.; Shigeno-Akutsu, Y.; Nomura, N.; Onuma, F.; Nakahara, T. Microbial degradation of polyurethane, polyester polyurethanes and polyether polyurethanes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 51, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-N.; Lee, B.-Y.; Lee, I.-M.; Lee, H.-S.; Yoon, J.-S. Toxicity and biodegradation of products from polyester hydrolysis. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard Subst. Environ. Eng. 2001, 36, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Akhter, J.I.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Degradation of polyurethane by novel bacterial consortium isolated from soil. Ann. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, R.N. Biodegradability of nonionic surfactants: Screening test for predicting rate and ultimate biodegradation. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1973, 50, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, R.; Bassi, A.S.; Yanful, E.K. Candida rugosa lipase-catalyzed polyurethane degradation in aqueous medium. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, L.; Surman, S. Biofilms in biodeterioration—A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1994, 32, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, E. The Science of Composting; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima-Kambe, T.; Onuma, F.; Kimpara, N.; Nakahara, T. Isolation and characterization of a bacterium which utilizes poly-ester polyurethane as a sole carbon and nitrogen source. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 129, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima-Kambe, T.; Onuma, F.; Akutsu, Y.; Nakahara, T. Determination of the polyester polyurethane breakdown products and distribution of the polyurethane degrading enzyme of Comamonas acidovorans strain TB-35. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1997, 83, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, Y.; Hrenovic, J.; Buyukgungor, H. Biodegradation of plastic compost bags under controlled soil conditions. Acta Chim. Slov. 2004, 51, 579–588. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, U.; Houlden, A.; Robson, G.D. Fungal Communities Associated with the Biodegradation of Polyester Polyurethane Buried under Compost at Different Temperatures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7313–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Nadir, S.; Dong, Y.; Schaefer, D.A.; Mortimer, P.E.; Gui, H.; Khan, A.; Yu, M.; Iqbal, S.; Sheng, J.; et al. Biodegradation of polyester polyurethane by 2 Aspergillus flavus G10. bioRxiv 2020, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuter, G.A.; Hoitink, H.A.J.; Rossman, L.A. Effects of aeration and temperature on composting of municipal sludge in a full-scale vessel system. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1985, 57, 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jailawi, M.H.; Ameen, R.; Al-Saraf, A.A. Polyethylene degradation by Pseudomonas putida S3A. Int J Adv Res Biol Sci 2015, 2, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Islami, A.N.; Tazkiaturrizki, T.; Rinanti, A. The effect of pH-temperature on plastic allowance for LowDensity Polyethylene (LDPE) by Thiobacillus sp. and Clostridium sp. J. Phy Conf. Series. 2019, 1402, 033003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oceguera-Cervantes, A.; Carrillo-García, A.; López, N.; Bolanos-Nunez, S.; Cruz-Gómez, M.J.; Wacher, C.; Loza-Tavera, H. Characterization of the polyurethanolytic activity of two Alicycliphilus sp. strains able to degrade polyurethane and N-methylpyrrolidone. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 6214–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, S.; Dong, J.-Y. In Situ Promotion of Long-Chain Branching in Polyethylene from Ziegler–Natta Catalysts. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 6455–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Z.; Hasan, F.; Krumholz, L.; Aktas, D.F.; Shah, A.A. Degradation of polyester polyurethane by newly isolated Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain MZA-85 and analysis of degradation products by GC–MS. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 77, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Barragán, J.; Domínguez-Malfavón, L.; Vargas-Suárez, M.; González-Hernández, R.; Aguilar-Osorio, G.; Loza-Tavera, H. Biodegradative activities of selected environmental fungi on a polyester polyurethane varnish and polyether polyurethane foams. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5225–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oprea, S.; Doroftei, F. Biodegradation of polyurethane acrylate with acrylated epoxidized soybean oil blend elastomers by Chaetomium globosum. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, N.R.; Tessman, M.; Zhen, D.; Johnson, L.; Evans, P.; Clements, S.M.; Pomeroy, R.S.; Burkart, M.D.; Simkovsky, R.; Mayfield, S.P. Biodegradation of renewable polyurethane foams in marine environments occurs through depolymerization by marine microorganisms. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 850, 158761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
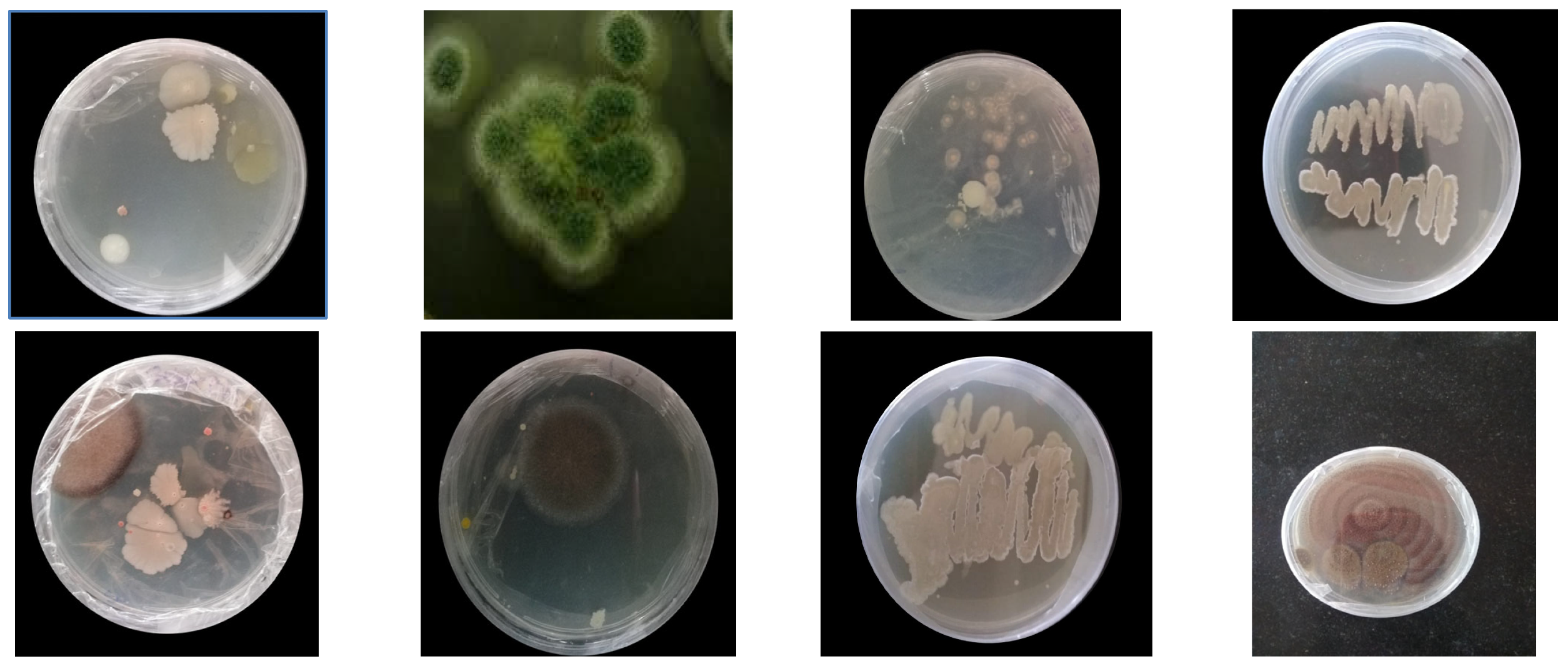

| S. No | Isolated Micro-Organism | Type of Organism | Colony Color | Genus Name as per Morphology | Degradation Percentage (Ao − At/Ao) × 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ARF1 | Fungi | Dark green | Aspergillus sp. | 40% |
| 2 | ARF2 | Fungi | Orange | Penicillium sp. | 16% |
| 3 | ARF3 | Fungi | Gray | Botrytis sp. | 55% |
| 4 | ARF4 | Fungi | White | Candida sp. | 17% |
| 5 | ARF5 | Fungi | Green | A. versicolor | 58% |
| 6 | ARF6 | Fungi | Black | A. niger | 19% |
| 7 | ARB2 | Bacteria | Pink | Serratia sp. | 3% |
| 8 | ARB3 | Bacteria | Red | Serratia sp. | 28% |
| 9 | ARB4 | Bacteria | White | Bacillus sp. | 12% |
| 10 | ARB5 | Bacteria | Pale yellow | Staphylococcus sp. | 24% |
| 11 | ARB6 | Bacteria | Orange | Rhodotorula sp. | 17% |
| 12 | ARB7 | Bacteria | Green | Pseudomonas sp. | 19% |
| Characteristics | Aspergillus versicolor ARF5 |
|---|---|
| Shape | Spherical |
| Stipes colour | Yellow |
| Surface | cheese surfaces |
| Conidia surface | Slightly rough |
| Metula covering | 1/3 to entire vesicle |
| Vesicle serration | Biseriate |
| Case Study | Before the Experiment (CFU/mL) | After the Experiment (CFU/mL) | CO2 Emitted per Liter (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test | 4.6 × 109 | 9.8 × 109 | 4.48 |
| Control | 4.6 × 109 | 2.3 × 109 | 2.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajan, A.; Ameen, F.; Jambulingam, R.; Shankar, V. Biodegradation of Polyurethane by Fungi Isolated from Industrial Wastewater—A Sustainable Approach to Plastic Waste Management. Polymers 2024, 16, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101411
Rajan A, Ameen F, Jambulingam R, Shankar V. Biodegradation of Polyurethane by Fungi Isolated from Industrial Wastewater—A Sustainable Approach to Plastic Waste Management. Polymers. 2024; 16(10):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101411
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajan, Aiswarya, Fuad Ameen, Ranjitha Jambulingam, and Vijayalakshmi Shankar. 2024. "Biodegradation of Polyurethane by Fungi Isolated from Industrial Wastewater—A Sustainable Approach to Plastic Waste Management" Polymers 16, no. 10: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101411
APA StyleRajan, A., Ameen, F., Jambulingam, R., & Shankar, V. (2024). Biodegradation of Polyurethane by Fungi Isolated from Industrial Wastewater—A Sustainable Approach to Plastic Waste Management. Polymers, 16(10), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101411





