Sustainable Particleboards Based on Brewer’s Spent Grains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. BSG Conditioning and Characterization
2.3. Particleboard Preparation
2.3.1. Binderless Boards
2.3.2. PA Adhesive Boards (Control)
2.4. Particleboard Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
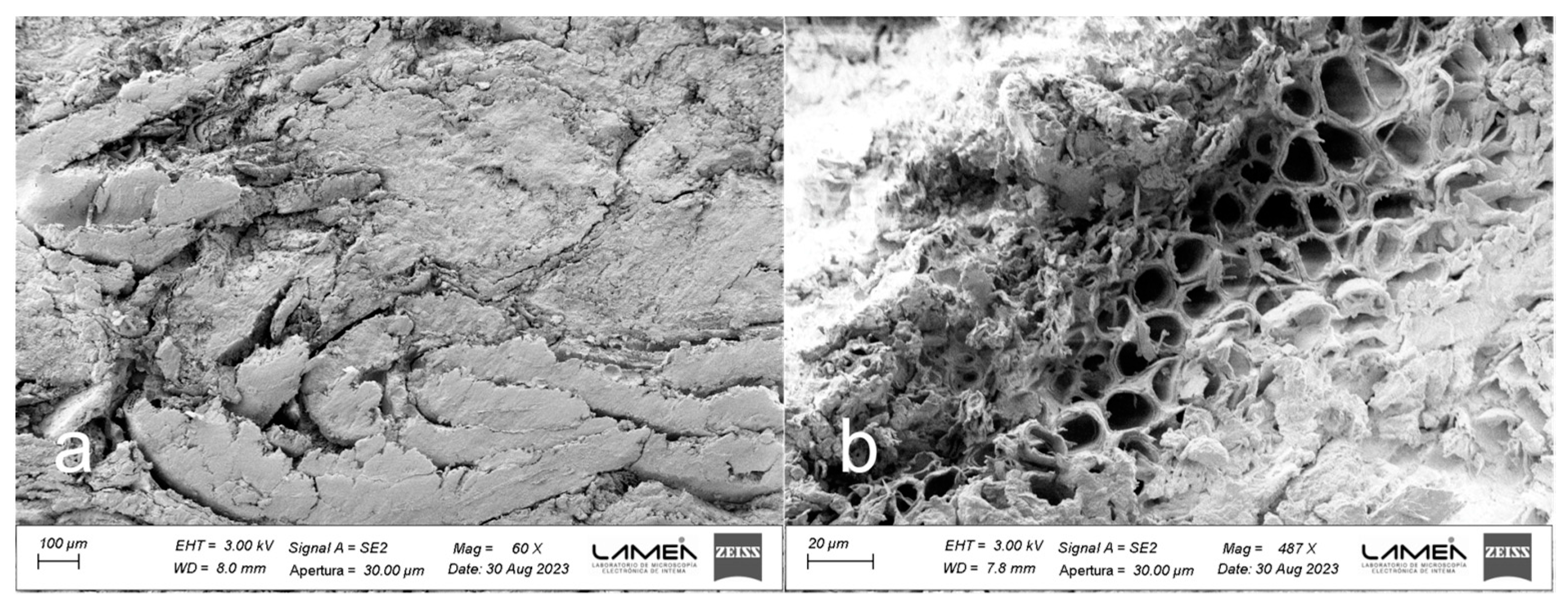
3.1. BSG Characterization
3.2. BSG-Based Particleboard
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT Forestry Production and Trade. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/FO (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Mehrzad, S.; Taban, E.; Soltani, P.; Samaei, S.E.; Khavanin, A. Sugarcane Bagasse Waste Fibers as Novel Thermal Insulation and Sound-Absorbing Materials for Application in Sustainable Buildings. Build. Environ. 2022, 211, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbe, M.A.; Pizzi, A.; Zhang, H.; Halis, R. Critical Links Governing Performance of Self-Binding and Natural Binders for Hot-Pressed Reconstituted Lignocellulosic Board without Added Formaldehyde: A Review. BioResources 2018, 13, 2049–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almusawi, A.; Lachat, R.; Atcholi, K.E.; Gomes, S. Proposal of Manufacturing and Characterization Test of Binderless Hemp Shive Composite. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 115, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Khali, D.P.; Jawaid, M.; Tahir, P.M.; Siakeng, R.; Asim, M.; Khan, T.A. Recent Development in Binderless Fiber-Board Fabrication from Agricultural Residues: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamani, F.A.; Ramatia, D.; Sudarmanto; Akbar, F.; Kusumah, S.S.; Hermawan, D. Combination of Citric Acid and Maltodextrin as Bonding Agent in Sorghum Bagasse Particleboard. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 935, 012058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Galih, N.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Kang, S. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Particleboard Mixed with Waste ACQ-Treated Wood. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitrone, F.; Ramos, D.; Ferrando, F.; Salvadó, J. Binderless Fiberboards for Sustainable Construction. Materials, Production Methods and Applications. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pędzik, M.; Janiszewska, D.; Rogoziński, T. Alternative Lignocellulosic Raw Materials in Particleboard Production: A Review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 174, 114162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doosthoseini, K.; Hosseinabadi, H.Z.; Moradpour, P. Oksidativna Aktivacija Površine Vlakanaca u Proizvodnji MDF Ploča. Drv. Ind. 2013, 64, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.C.; Hendrikse, S.I.S.; Sherrell, P.C.; Ellis, A.V. Grapevine Waste in Sustainable Hybrid Particleboard Production. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciannamea, E.M.; Marin, D.C.; Ruseckaite, R.A.; Stefani, P.M. Particleboard Based on Rice Husk: Effect of Binder Content and Processing Conditions. J. Renew. Mater. 2017, 5, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbu, M.C.; Montecuccoli, Z.; Förg, J.; Barbeck, U.; Klímek, P.; Petutschnigg, A.; Tudor, E.M. Potential of Brewer’s Spent Grain as a Potential Replacement of Wood in Pmdi, Uf or Muf Bonded Particleboard. Polymers 2021, 13, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klímek, P.; Wimmer, R.; Kumar Mishra, P.; Kúdela, J. Utilizing Brewer’s-Spent-Grain in Wood-Based Particleboard Manufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokochi, Y.; Saito, Y. Heat Treatment to Increase Self-Bonding Property of Binderless Boards Manufactured from Rice Straw. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1063, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, E.; Alshebani, M.; Elhrari, W.; Klash, A.; Shebani, A. Production of Particleboard Using Olive Stone Waste for Interior Design. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 29, 101119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaeian, A.; Ashori, A.; Dizaj, M.Y. Suitability of Sorghum Stalk Fibers for Production of Particleboard. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 120, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahieu, A.; Vivet, A.; Poilane, C.; Leblanc, N. Performance of Particleboards Based on Annual Plant Byproducts Bound with Bio-Adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2021, 107, 102847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahieu, A.; Alix, S.; Leblanc, N. Properties of Particleboards Made of Agricultural By-Products with a Classical Binder or Self-Bound. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 130, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, A.; Ashaari, Z.; Bawon, P.; Lee, S.H. Reducing Formaldehyde Emission of Urea Formaldehyde-Bonded Particleboard by Addition of Amines as Formaldehyde Scavenger. Build. Environ. 2018, 142, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Jahan, S.A.; Lee, J.T. Exposure to Formaldehyde and Its Potential Human Health Hazards. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2011, 29, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, S.; Kızılcan, N.; Bengu, B. Oxidized Cornstarch—Urea Wood Adhesive for Interior Particleboard Production. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2021, 110, 102947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frihart, C.R.; Birkeland, M.J.; Allen, A.J.; Wescott, J.M. Soy Adhesives That Can Form Durable Bonds for Plywood, Laminated Wood Flooring, and Particleboard. In Proceedings of the International Convention of Society of Wood Science and Technology and United Nations Economic Commission for Europe—Timber Committee, Geneva, Switzerland, 11–14 October 2010; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chalapud, M.C.; Ciannamea, E.M.; Martucci, J.F.; Ruseckaite, R.A.; Stefani, P.M. Biobased Particleboards from Rice Husk and Soy Protein Concentrate: Evaluation of Flexural Properties and Dimensional Stability under Indoor Environmental Conditions. DYNA 2023, 90, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunky, M. Wood Adhesives Based on Natural Resources: A Critical Review: Part II. Carbohydrate-Based Adhesives. Rev. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 8, 333–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordqvist, P.; Nordgren, N.; Khabbaz, F.; Malmström, E. Plant Proteins as Wood Adhesives: Bonding Performance at the Macro- and Nanoscale. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 44, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolao, E.S.; Leiva, P.; Chalapud, M.C.; Ruseckaite, R.A.; Ciannamea, E.M.; Stefani, P.M. Flexural and Tensile Properties of Biobased Rice Husk-Jute-Soybean Protein Particleboards. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larregle, A.; Chalapud, M.; Fangio, F.; Ciannamea, E.M.; Stefani, P.M.; Martucci, J.F.; Ruseckaite, R.A. Antifungal Soybean Protein Concentrate Adhesive as Binder of Rice Husk Particleboards. Polymers 2021, 13, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urstöger, J.; Kain, G.; Prändl, F.; Barbu, M.C.; Kristak, L. Physical-Mechanical Properties of Light Bark Boards Bound with Casein Adhesives. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillol, S. Cardanol: A Promising Building Block for Biobased Polymers and Additives. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 14, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.; González-García, S.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T. Tannin-Based Bio-Adhesives for the Wood Panel Industry as Sustainable Alternatives to Petrochemical Resins. J. Ind. Ecol. 2022, 26, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Shui, T.; Wang, H.; Ai, X.; Kuboki, T.; Xu, C.C. Properties of Phenolic Adhesives Formulated with Activated Organosolv Lignin Derived from Cornstalk. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 161, 113225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Pereira, J.; Almeida, M.; Ferra, J.; Paiva, N.; Martins, J.; Magalhães, F.D.; Carvalho, L.H. Low-Cost Natural Binder for Particleboards Production: Study of Manufacture Conditions and Stability. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 93, 102325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajuddin, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Ismail, H. A Review of Natural Fibers and Processing Operations for the Production of Binderless Boards. BioResources 2016, 11, 5600–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, A.; Xue, L. A Review of Preparation of Binderless Fiberboards and Its Self-Bonding Mechanism. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 661–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouajila, J.; Limare, A.; Joly, C.; Dole, P. Lignin Plasticization to Improve Binderless Fiberboard Mechanical Properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, N.; Hori, K.; Sato, M. Chemical Changes of Kenaf Core Binderless Boards during Hot Pressing (I): Influence of the Pressing Temperature Condition. J. Wood Sci. 2006, 52, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadhari, W.N.A.W.; Karim, N.A.; Boon, J.G.; Salleh, K.M.; Mustapha, A.; Hashim, R.; Sulaiman, O.; Azni, M.E. Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarium L.) Bagasse Binderless Particleboard: Effect of Hot Pressing Time Study. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, J.G.; Hashim, R.; Danish, M.; Nadhari, W.N.A.W. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Binderless Particleboard Made from Steam-Pretreated Oil Palm Trunk Particles. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, R.; Peijs, T. Binderless All-Cellulose Fibreboard from Microfibrillated Lignocellulosic Natural Fibres. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 83, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, G.; Velásquez, J.; Betancourt, S.; Gañán, P. Binderless Fiberboard from Steam Exploded Banana Bunch. Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 29, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokochi, Y.; Sato, M. Steam Treatment to Enhance Rice Straw Binderless Board Focusing Hemicellulose and Cellulose Decomposition Products. J. Wood Sci. 2020, 66, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Cordero, J.F.; García-Ortuño, T.; García-Navarro, J. Comparison of Binderless Boards Produced with Different Tissues of Totora (Schoenoplectus californicus (C.A. Mey) Soják) Stems. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 27, 100961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenormand, H.; Glé, P.; Leblanc, N. Investigation of the Acoustical and Thermal Properties of Sunflower Particleboards. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2017, 103, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zheng, S.; Wu, J.; Xu, J. Study on Preparation of High-Performance Binderless Board from Broussonetia Papyrifera. J. Wood Sci. 2023, 69, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, D.; Gopaliya, D.; Willoughby, N.; Khare, S.K.; Kumar, V. Recycling Potential of Brewer’s Spent Grains for Circular Biorefineries. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 40, 100748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetrariu, A.; Dabija, A. Brewer’s Spent Grains: Possibilities of Valorization, a Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejna, A. More than Just a Beer—The Potential Applications of by-Products from Beer Manufacturing in Polymer Technology. Emergent Mater. 2022, 5, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terefe, G. Preservation Techniques and Their Effect on Nutritional Values and Microbial Population of Brewer’s Spent Grain: A Review. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2022, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Johansen, A.Z.; Mussatto, S.I. Evaluation of Different Pretreatment Strategies for Protein Extraction from Brewer’s Spent Grains. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiago, R.d.S.M.; Pedro, P.M.d.M.; Eliana, F.C.S. Solid Wastes in Brewing Process: A Review. J. Brew. Distill. 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackowski, M.; Niedzwiecki, L.; Lech, M.; Wnukowski, M.; Arora, A.; Tkaczuk-Serafin, M.; Baranowski, M.; Krochmalny, K.; Veetil, V.K.; Seruga, P.; et al. HTC of Wet Residues of the Brewing Process: Comprehensive Characterization of Produced Beer, Spent Grain and Valorized Residues. Energies 2020, 13, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackowski, M.; Niedźwiecki, Ł.; Jagiełło, K.; Uchańska, O.; Trusek, A. Brewer’s Spent Grains—Valuable Beer Industry by-Product. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolwig, S.; Mark, M.S.; Happel, K.; Brekke, A. Beyond Animal Feed? The Valorisation of Brewers’ Spent Grain. In From Waste to Value; Klitkou, A., Fevolden, A.M., Capasso, M., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2019; p. 20. ISBN 9780429460289. [Google Scholar]
- Allegretti, C.; Bellinetto, E.; D’arrigo, P.; Griffini, G.; Marzorati, S.; Rossato, L.A.M.; Ruffini, E.; Schiavi, L.; Serra, S.; Strini, A.; et al. Towards a Complete Exploitation of Brewers’ Spent Grain from a Circular Economy Perspective. Fermentation 2022, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaristo, R.B.W.; Costa, A.A.; Nascimento, P.G.B.D.; Ghesti, G.F. Biorefinery Development Based on Brewers’ Spent Grain (BSG) Conversion: A Forecasting Technology Study in the Brazilian Scenario. Biomass 2023, 3, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Chamorro, J.A.; Cara, C.; Romero, I.; Ruiz, E.; Romero-García, J.M.; Mussatto, S.I.; Castro, E. Ethanol Production from Brewers’ Spent Grain Pretreated by Dilute Phosphoric Acid. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 5226–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavalopoulos, M.; Stoumpou, V.; Christofi, A.; Mai, S.; Barampouti, E.M.; Moustakas, K.; Malamis, D.; Loizidou, M. Sustainable Valorisation Pathways Mitigating Environmental Pollution from Brewers’ Spent Grains. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, P.L.; Santos, M.V.; Montanari, J.; Zaritzky, N. Nanoferulic: From a by-Product of the Beer Industry toward the Regeneration of the Skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 2958–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, S.; Bala, M. Brewer’s Spent Grain: A Review of Its Potentials and Applications. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 324–331. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, A.; Cermeño, M.; Alashi, A.M.; Aluko, R.E.; FitzGerald, R.J. Generation of Phenolic-Rich Extracts from Brewers’ Spent Grain and Characterisation of Their in Vitro and in Vivo Activities. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 68, 102617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Dragone, G.; Roberto, I.C. Brewers’ Spent Grain: Generation, Characteristics and Potential Applications. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T 222 Cm-21; Acid-Insoluble Lignin in Wood and Pulp. Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry TAPPI: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 2021.
- T 203 Cm-09; Alpha-, Beta- and Gamma-Cellulose in Pulp. Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry TAPPI: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 2022.
- T 204 Cm-17; Solvent Extractives of Wood and Pulp. Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry TAPPI: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 2017.
- IRAM 3143-2004; Papel, Cartón y Pastas Celulósicas. Determinación Del Residuo Por Calcinación (Ceniza). Instituto Argentino de Normalización y Certificación (IRAM): Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2004.
- Browning, B.L. Methods of Wood Chemistry; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Interscience Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1967; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Patrignani, M.; Conforti, P.A.; Lupano, C.E. Lipid Oxidation in Biscuits: Comparison of Different Lipid Extraction Methods. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2015, 9, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.A.; I’Anson, K.J.A.; Treimo, J.; Faulds, C.B.; Brocklehurst, T.F.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Waldron, K.W. Profiling Brewers’ Spent Grain for Composition and Microbial Ecology at the Site of Production. LWT 2010, 43, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 16634-1:2008; Food Products—Determination of the Total Nitrogen Content by Combustion According to the Dumas Principle and Calculation of the Crude Protein Content. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- ASTM D1037; Standard Test Method for Evaluating Properties of Wood-Base Fiber and Particle Panel Materials. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1993; Volume 30.
- Lynch, K.M.; Steffen, E.J.; Arendt, E.K. Brewers’ Spent Grain: A Review with an Emphasis on Food and Health. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, M.A.; Montero, G.; Montes, D.G.; Valdez-Salas, B.; Ayala, J.R.; García, C.; Carrillo, M.; León, J.A.; Moreno, A. Physicochemical Characterization and SEM-EDX Analysis of Brewer’s Spent Grain from the Craft Brewery Industry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyorini, R.; Xu, J.; Umemura, K.; Kawai, S. Manufacture and Properties of Binderless Particleboard from Bagasse I: Effects of Raw Material Type, Storage Methods, and Manufacturing Process. J. Wood Sci. 2005, 51, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milawarni; Nurlaili; Sariadi; Amra, S.; Yassir. Influence of Press Temperature on the Properties of Binderless Particleboard. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 536, 012066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintiaux, T.; Viet, D.; Vandenbossche, V.; Rigal, L.; Rouilly, A. Binderless Materials Obtained by Thermo-Compressive Processing of Lignocellulosic Fibers: A Comprehensive Review. BioResources 2015, 10, 1915–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandez-Garcia, A.; Ferrandez-Garcia, M.T.; Garcia-Ortuño, T.; Ferrandez-Villena, M. Influence of the Density in Binderless Particleboards Made from Sorghum. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, C.G.; Frihart, C.R.; Dunky, M.; Rohumaa, A. Understanding Wood Bonds-Going beyond What Meets the Eye: A Critical Review. Rev. Adhes. Adhes. 2018, 6, 369–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrilmis, N.; Kwon, J.H.; Han, T.H. Effect of Resin Type and Content on Properties of Composite Particleboard Made of a Mixture of Wood and Rice Husk. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2012, 38, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascault, J.-P.; Sautereau, H.; Verdu, J.; Williams, R.J.J. Thermosetting Polymers, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; ISBN 9780429208072. [Google Scholar]
- Baharuddin, M.N.M.; Zain, N.M.; Harun, W.S.W.; Roslin, E.N.; Ghazali, F.A.; Md Som, S.N. Development and Performance of Particleboard from Various Types of Organic Waste and Adhesives: A Review. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2023, 124, 103378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, R.; Said, N.; Lamaming, J.; Baskaran, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Sato, M.; Hiziroglu, S.; Sugimoto, T. Influence of Press Temperature on the Properties of Binderless Particleboard Made from Oil Palm Trunk. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2520–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, P.M.; Cyras, V.P.; Tejeira Barchi, A.; Vazquez, A. Mechanical Properties and Thermal Stability of Rice Husk Ash Filled Epoxy Foams. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 99, 2957–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Gregor, T.; Wimmer, R. Utilising Brewer’s Spent Grain as a Source of Cellulose Nanofibres Following Separation of Protein-Based Biomass. BioResources 2017, 12, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, L.D.M.S.; Lira, T.S.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Ataíde, C.H.; Barrozo, M.A.S. Pyrolysis of Brewer’s Spent Grain: Kinetic Study and Products Identification. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 121, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

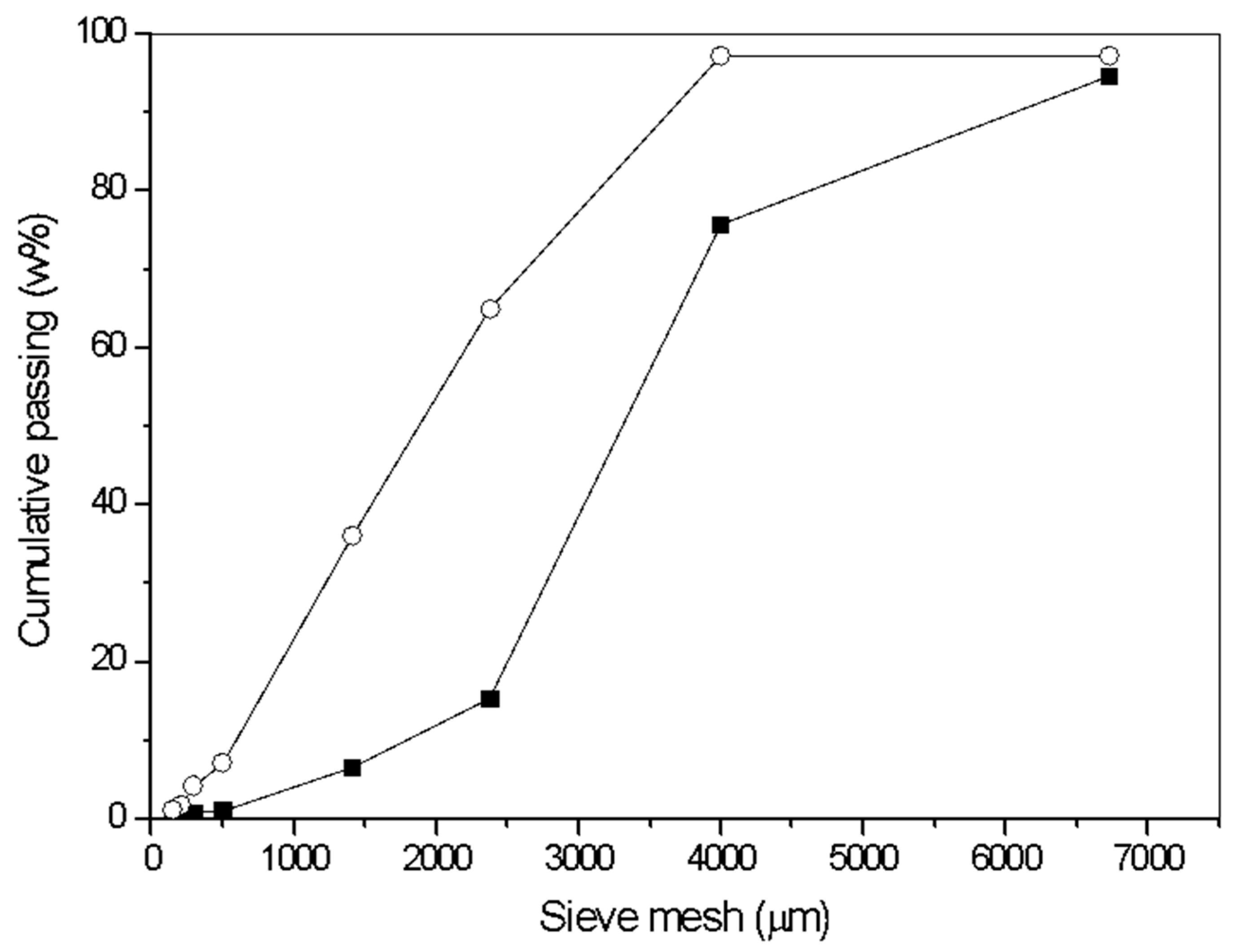
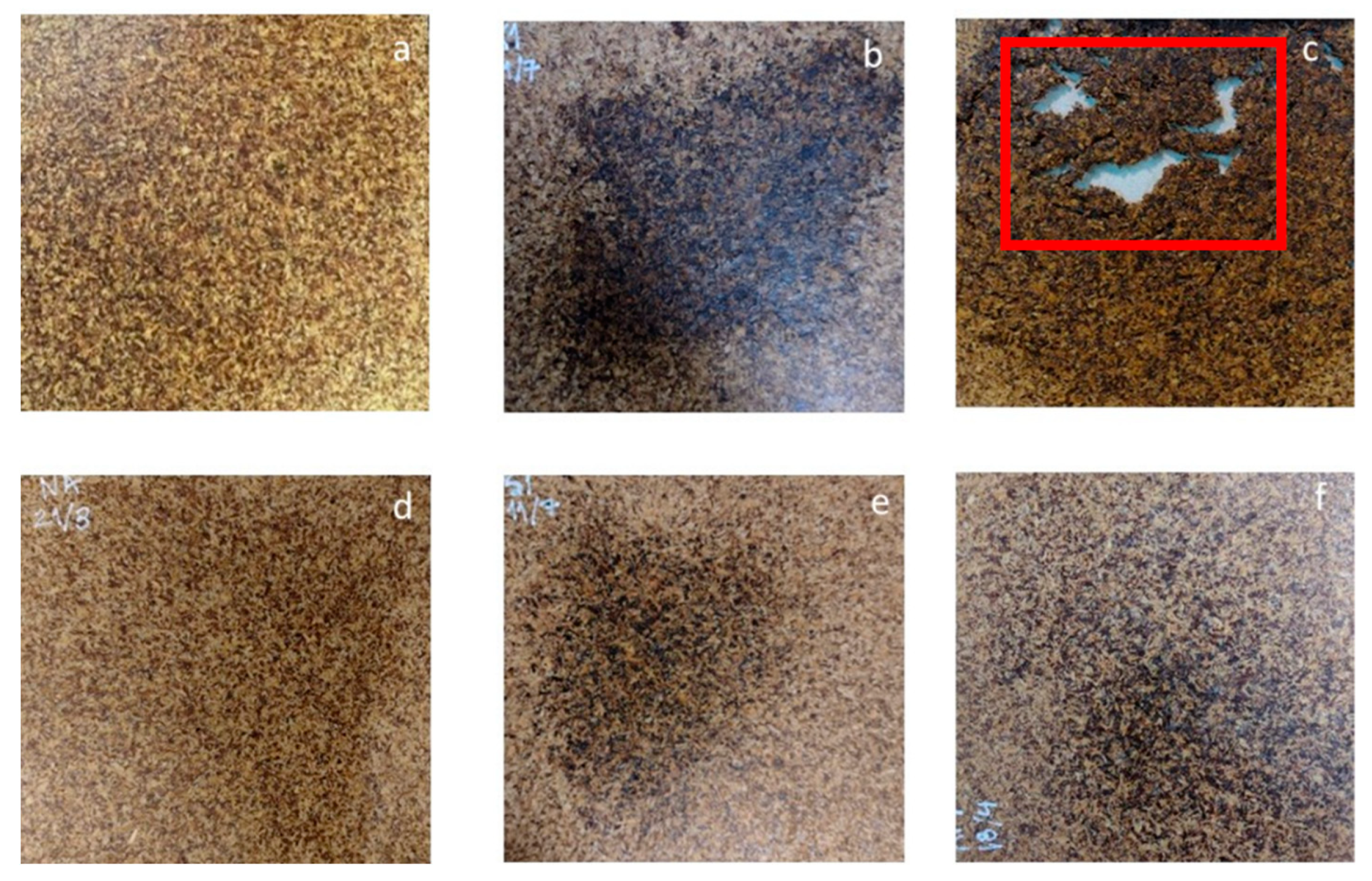
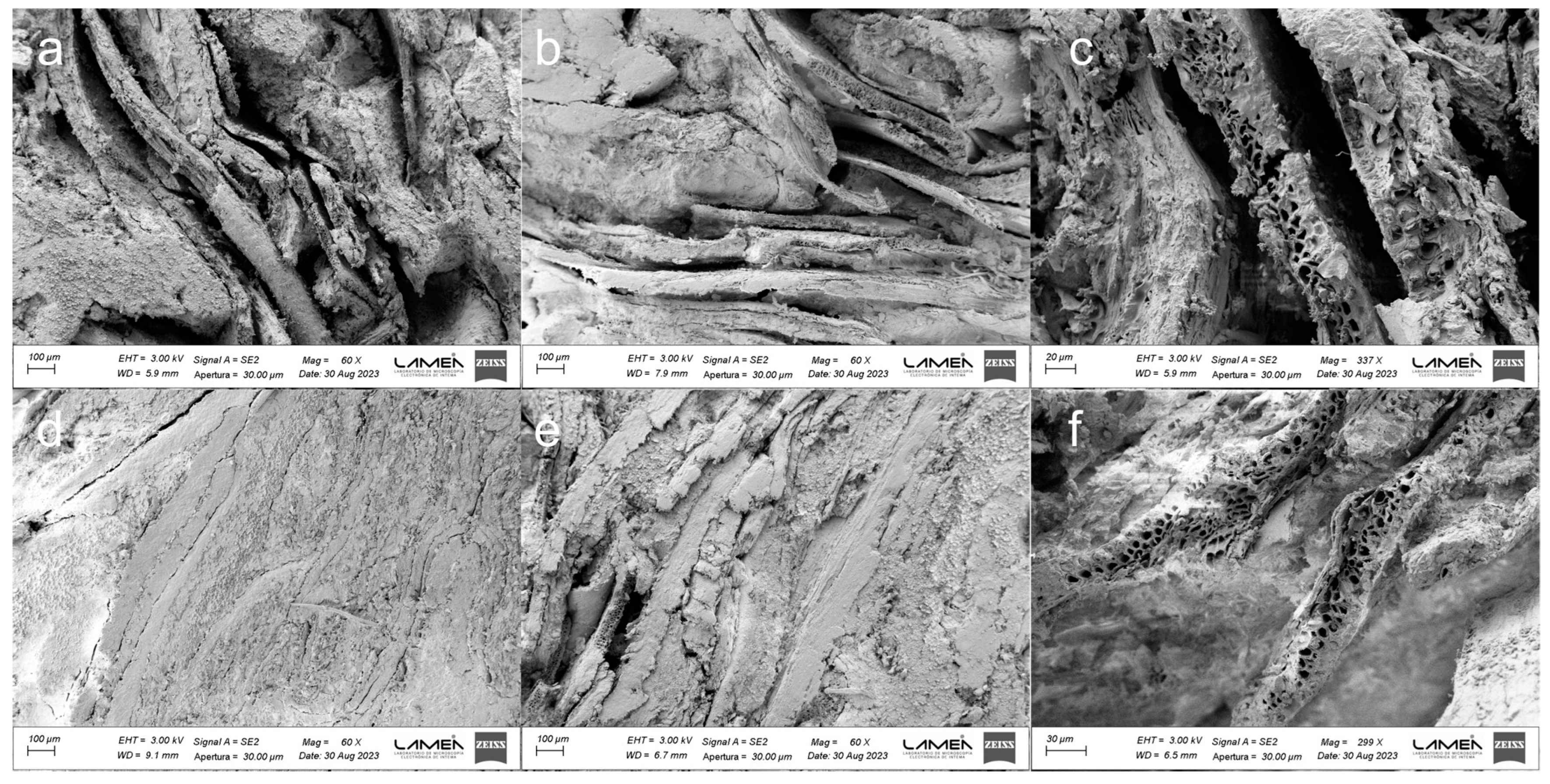

| Board | Pressing Temperature (°C) | Pressing Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| BB160 | 160 | 15 |
| BB170 | 170 | 15 |
| BB180 | 180 | 15 |
| BBG160 | 170 | 15 |
| BBG170 | 170 | 15 |
| PAB | 150 | 20 |
| Cellulose | Lignin | Hemicellulose | Protein | Ash | Fat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 9.5 | 11.2 | 28.7 | 17.3 | 3.3 | 7.5 |
| Board | Density (kg/m3) | Thickness (mm) | Moisture Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BB160 | 990 ± 50 a | 5.27 ± 0.11 a | 8.59 ± 0.26 a |
| BB170 | 1020 ± 41 a | 5.00 ± 0.14 b | 8.58 ± 0.38 a |
| BBG160 | 980 ± 60 a | 5.20 ± 0.13 a | 8.50 ± 0.45 a |
| BBG170 | 1040 ± 39 a | 4.99 ± 0.13 b | 8.52 ± 0.07 a |
| PAB | 1050 ± 51 a | 5.20 ± 0.10 a | 8.23 ± 0.18 a |
| Board | MOR (MPa) | MOE (GPa) | IB (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BB160 | 1.82 ± 0.25 a | 0.46 ± 0.06 a | 0.09 ± 0.03 a |
| BB170 | 2.43 ± 0.62 a | 0.54 ± 0.23 a | 0.15 ± 0.06 b |
| BBG160 | 2.06 ± 0.56 a | 0.61 ± 0.13 b | 0.09 ± 0.03 a |
| BBG170 | 4.14 ± 0.83 b | 0.77 ± 0.15 c | 0.23 ± 0.09 c |
| PAB | 8.96 ± 0.72 c | 1.09 ± 0.09 d | 0.68 ± 0.13 d |
| Board | WA 2 h (%) | WA 24 h (%) | TS 2 h (%) | TS 24 h (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BB160 | 153.2 ± 25.4 a | nd | 126.5 ± 10.5 a | nd |
| BB170 | 83.6 ± 28.6 b | 137.0 ± 4.2 a | 45.4 ± 32.4 b | 53.5 ± 13.4 a |
| BBG160 | 136.0 ± 25.0 a | 171.6 ±11.2 b | 80.2 ± 19.1 c | 100.3 ± 10.2 a |
| BBG170 | 35.8 ± 9.5 b | 79.8 ± 19.5 c | 29.1 ± 8.7 b | 52.3 ± 10.2 a |
| PAB | 16.7 ± 2.4 c | 35.4 ± 2.9 d | 12.3 ± 2.2 d | 34.5 ± 2.9 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rossi, L.; Wechsler, L.; Peltzer, M.A.; Ciannamea, E.M.; Ruseckaite, R.A.; Stefani, P.M. Sustainable Particleboards Based on Brewer’s Spent Grains. Polymers 2024, 16, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010059
Rossi L, Wechsler L, Peltzer MA, Ciannamea EM, Ruseckaite RA, Stefani PM. Sustainable Particleboards Based on Brewer’s Spent Grains. Polymers. 2024; 16(1):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010059
Chicago/Turabian StyleRossi, Lucia, Lucia Wechsler, Mercedes A. Peltzer, Emiliano M. Ciannamea, Roxana A. Ruseckaite, and Pablo M. Stefani. 2024. "Sustainable Particleboards Based on Brewer’s Spent Grains" Polymers 16, no. 1: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010059
APA StyleRossi, L., Wechsler, L., Peltzer, M. A., Ciannamea, E. M., Ruseckaite, R. A., & Stefani, P. M. (2024). Sustainable Particleboards Based on Brewer’s Spent Grains. Polymers, 16(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010059










