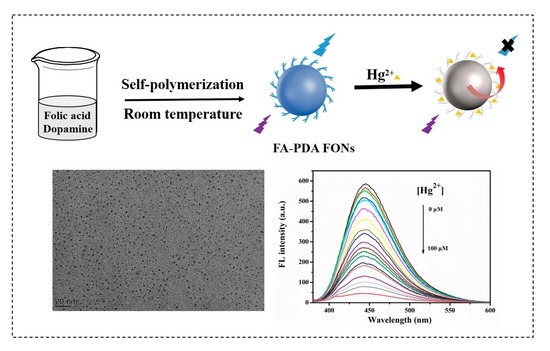
Folic Acid Adjustive Polydopamine Organic Nanoparticles Based Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Mercury Ions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instruments
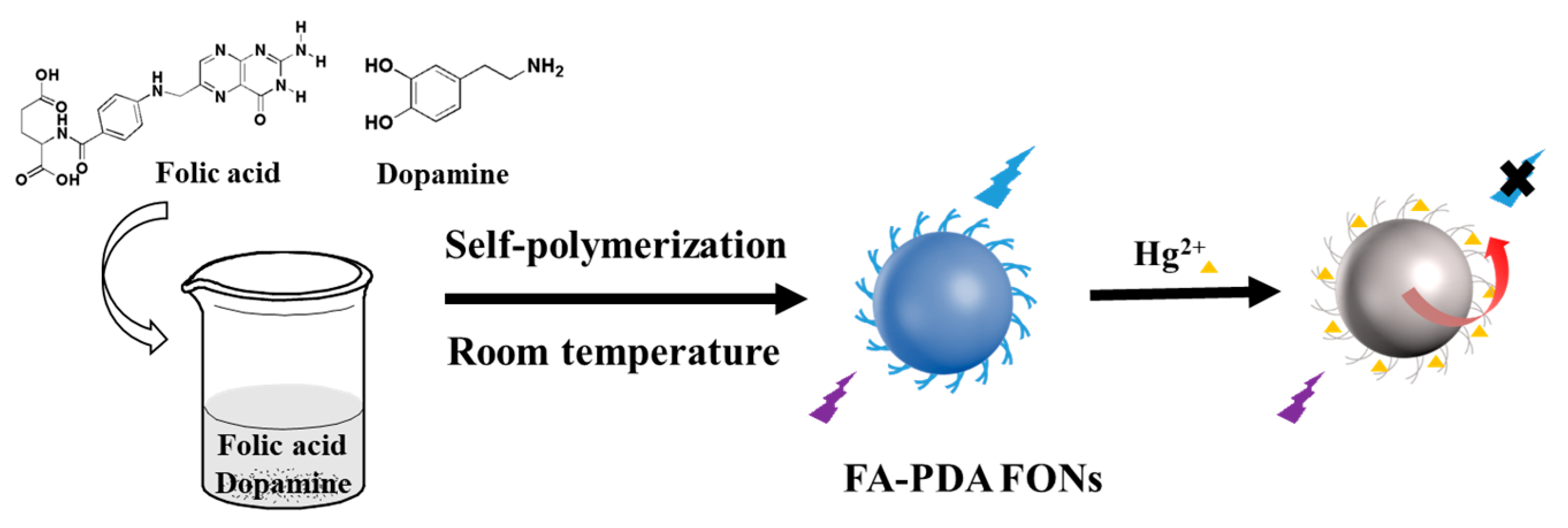
2.3. Synthesis of FA-PDA FONs
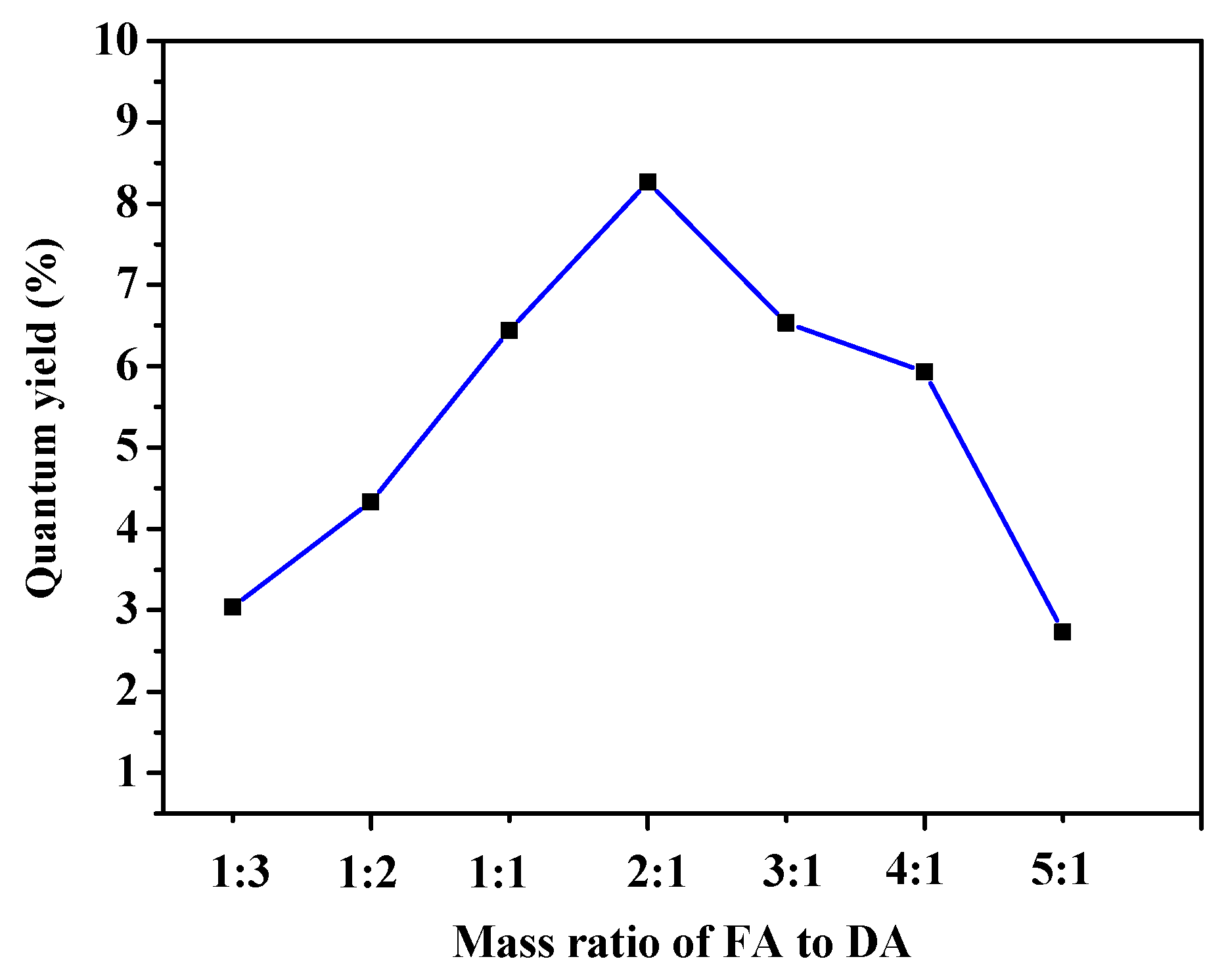
2.4. Quantum Yield
2.5. Fluorescence Selectivity of FA-PDA FONs for Detection of Hg2+
2.6. Fluorescence Sensitivity of FA-PDA FONs toward Hg2+
3. Results and Discussion
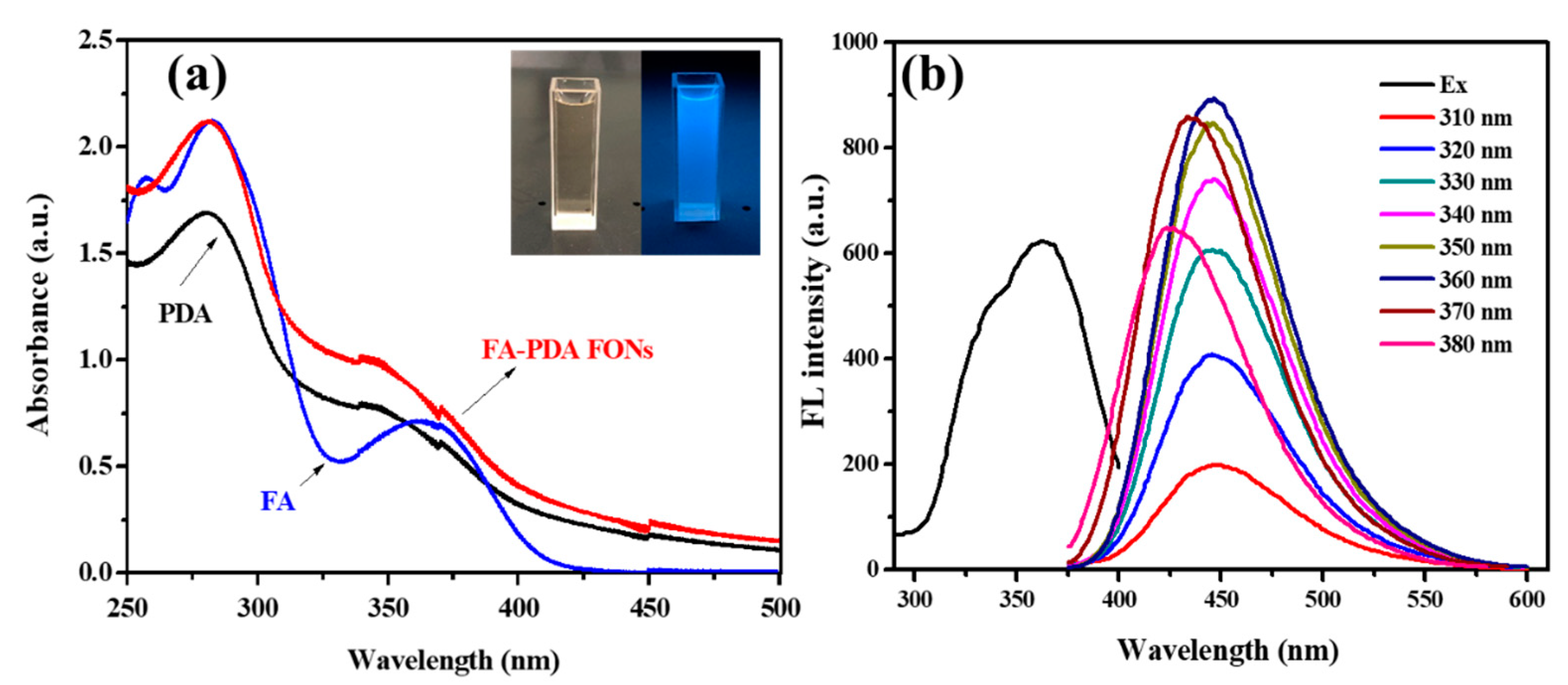
3.1. Synthesis of FA-PDA FONs
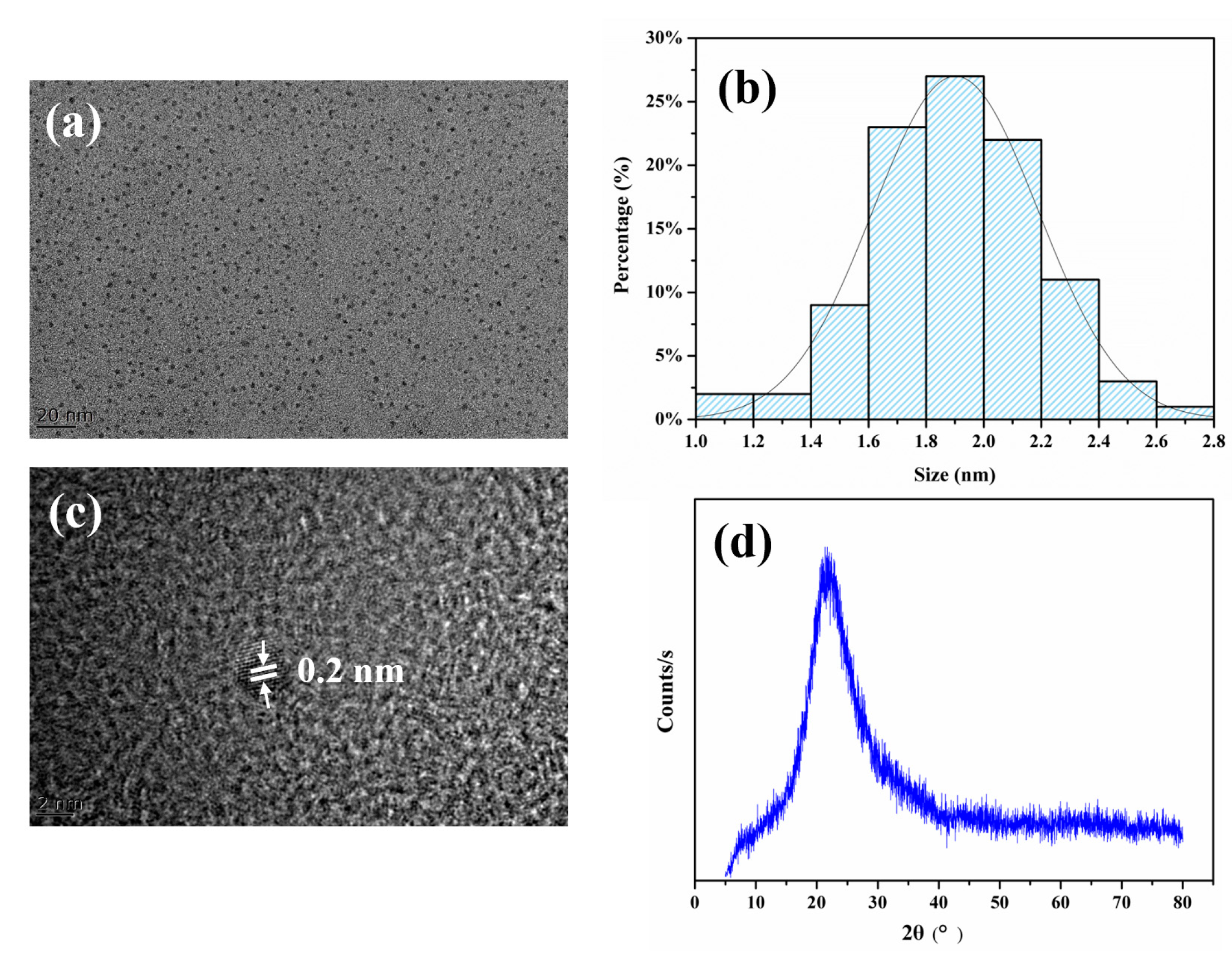
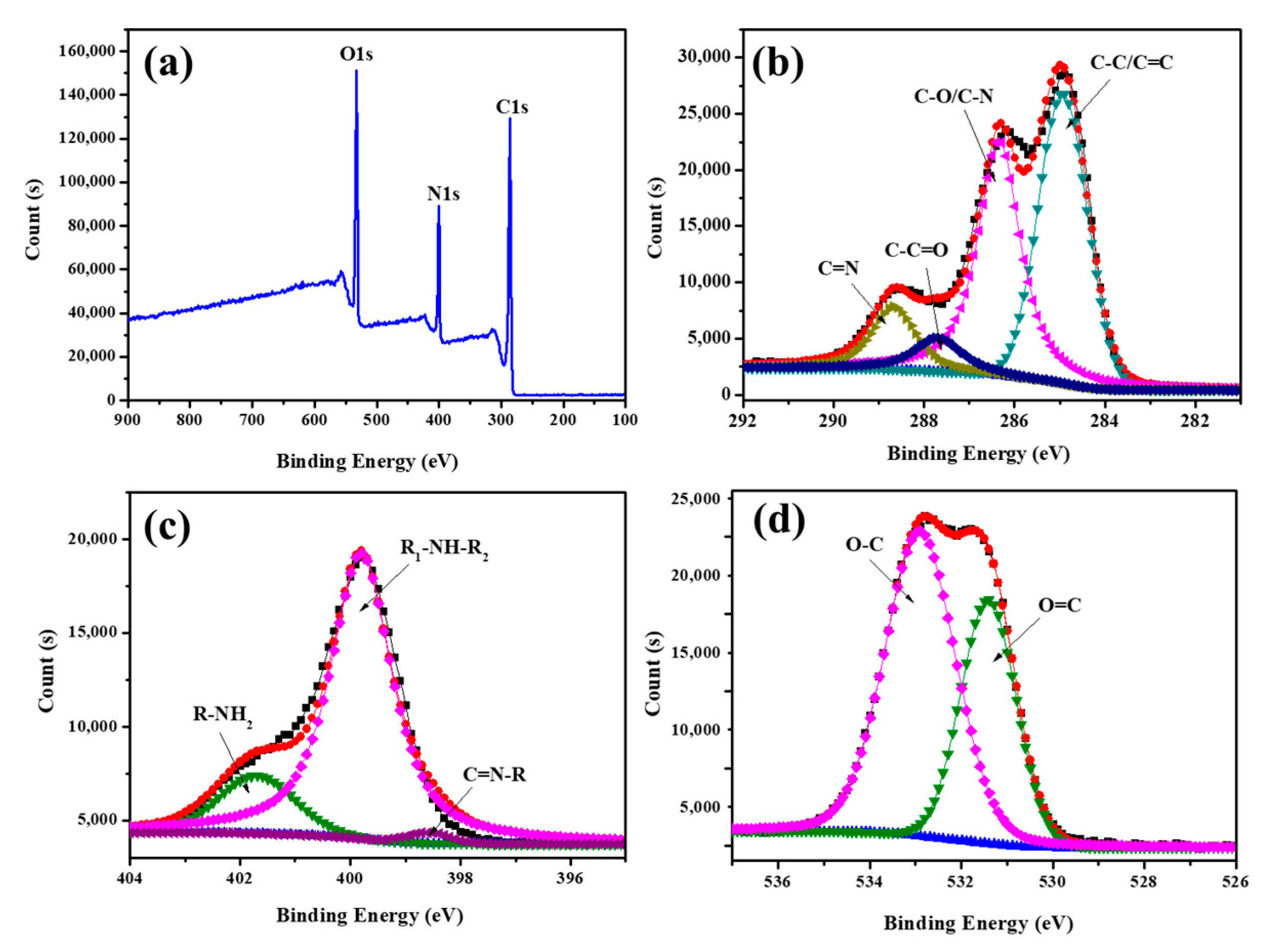
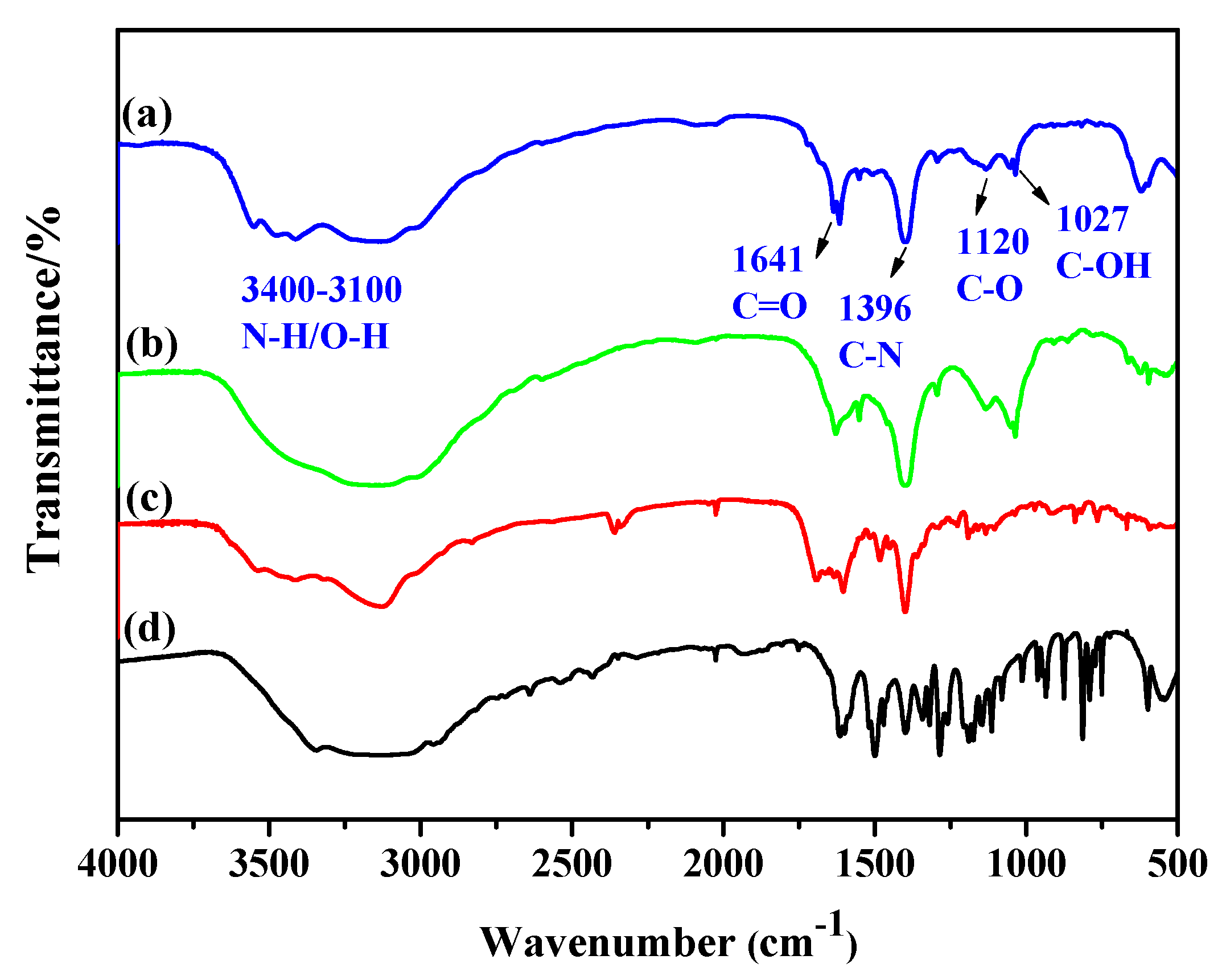
3.2. Characterization of FA-PDA FONs
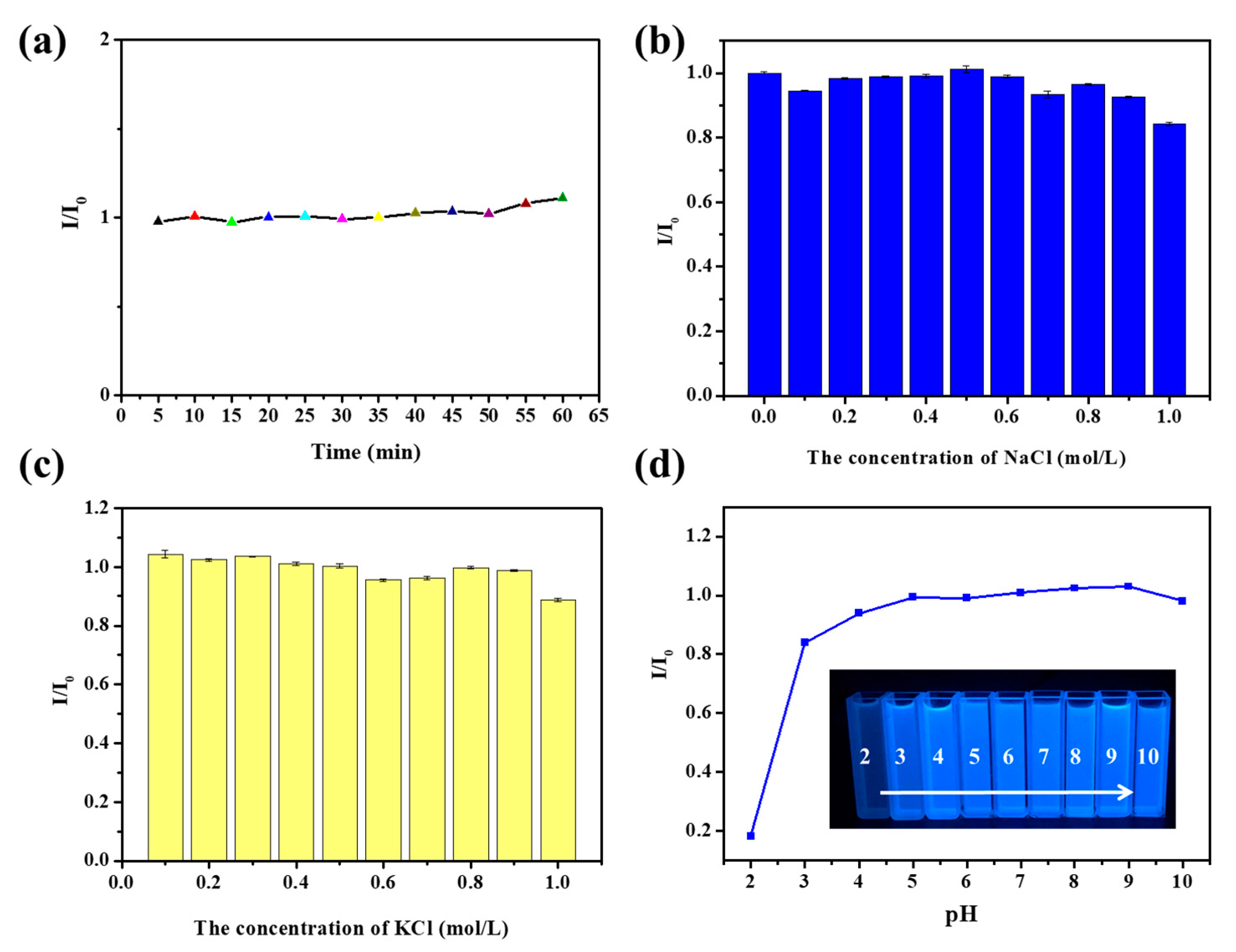
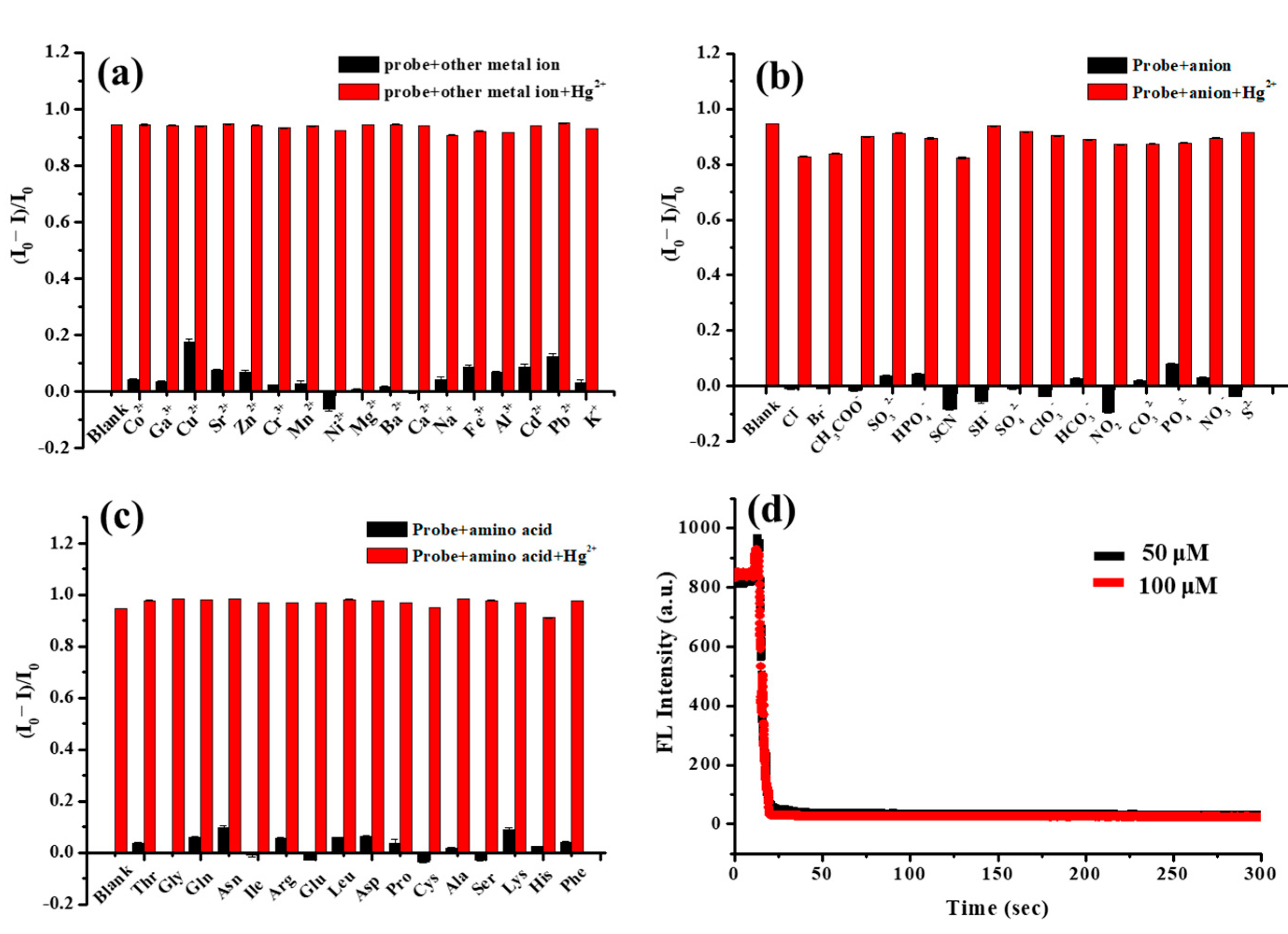
3.3. Fluorescence Selectivity of FA-PDA FONs for Detection of Hg2+
3.4. Fluorescence Sensitivity of FA-PDA FONs toward Hg2+
3.5. Recovery Tests in Real Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, D.; Cao, Z.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G. Polymer dots of DASA-functionalized polyethyleneimine: Synthesis, visible light/pH responsiveness, and their applications as chemosensors. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 254, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Gao, H.; Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Ju, H. Ratiometric fluorescent detection of miRNA-21 via pH-regulated adsorption of DNA on polymer dots and exonuclease III-assisted amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1232, 340450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Li, C.; Dong, B. Recent Progress in Fluorescent Probes for Metal Ion Detection. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 875256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Tao, L.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y. Polymeric AIE-based nanoprobes for biomedical applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11486–11508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zu, X.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. N, S-Doped Carbon Dots Prepared by Peanut Protein Isolates and Cysteamine as Highly Sensitive Fluorescent Sensors for Fe2+, Fe3+ and Lactoferrin. Polymers 2023, 15, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, P.; Shi, S.; Duan, G.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Size Regulation of Polydopamine Nanoparticles by Boronic Acid and Lewis Base. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2023, 44, 2100916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Recent developments in polydopamine fluorescent nanomaterials. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 746–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, A.; Panneerselvam, P. Polydopamine nanotube mediated fluorescent biosensor for Hg (ii) determination through exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Analyst 2018, 143, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, F.; Shi, B.; Lü, C. Mussel-inspired polydopamine-encapsulated carbon dots with dual emission for detection of 4-nitrophenol and Fe3+. Luminescence 2021, 36, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; Zhou, K.; Zeng, J.; Gao, D.; Xia, Z.; Fu, Q. Redox modulation of polydopamine surface chemistry: A facile strategy to enhance the intrinsic fluorescence of polydopamine nanoparticles for sensitive and selective detection of Fe3+. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 18064–18073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-Inspired Surface Chemistry for Multifunctional Coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangmeister, R.A.; Morris, T.A.; Tarlov, M.J. Characterization of Polydopamine Thin Films Deposited at Short Times by Autoxidation of Dopamine. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8619–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Na, Y.S.; Choi, S.; Song, I.T.; Kim, W.Y.; Lee, H. Non-Covalent Self-Assembly and Covalent Polymerization Co-Contribute to Polydopamine Formation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4711–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5361–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Singh, N.J.; Lim, J.; Pan, J.; Kim, H.N.; Park, S.; Kim, K.S.; Yoon, J. Unique Sandwich Stacking of Pyrene-Adenine-Pyrene for Selective and Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensing of ATP at Physiological pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15528–15533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-H.; Yu, C.-J.; Yang, Y.-C.; Tseng, W.-L. Formation of fluorescent polydopamine dots from hydroxyl radical-induced degradation of polydopamine nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 15124–15130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Chen, Y.; Shu, Y.; Shen, B.; Chan, H.N.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wu, H. Highly emissive and biocompatible dopamine-derived oligomers as fluorescent probes for chemical detection and targeted bioimaging. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13578–13580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Feng, L.; Ji, Y.; Tao, L.; Li, S.; Wei, Y. Biocompatible polydopamine fluorescent organic nanoparticles: Facile preparation and cell imaging. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5581–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Cao, X.; Zhang, C.; Xian, Y. Polydopamine nanodots are viable probes for fluorometric determination of the activity of alkaline phosphatase via the in situ regulation of a redox reaction triggered by the enzyme. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.-J.; Wu, S.; Chen, T.-T.; Yu, R.-Q.; Chu, X. MnO2-induced synthesis of fluorescent polydopamine nanoparticles for reduced glutathione sensing in human whole blood. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15604–15610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Y.; Li, L.; Yu, R.-Q.; Chen, T.-T.; Chu, X. CoOOH-induced synthesis of fluorescent polydopamine nanoparticles for the detection of ascorbic acid. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 5518–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Song, X.; Bu, X.; Zhu, C.; Wang, G.; Liao, F.; Yang, S.; Wang, M. Polydopamine dots as an ultrasensitive fluorescent probe switch for Cr(VI) in vitro. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ji, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Deng, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y. Self-polymerization of dopamine and polyethyleneimine: Novel fluorescent organic nanoprobes for biological imaging applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 3476–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zuo, F.; Liao, Z.; Qin, Z.; Du, S.; Zhao, Z. Mussel-Inspired One-Pot Synthesis of a Fluorescent and Water-Soluble Polydopamine-Polyethyleneimine Copolymer. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Jia, L. Room temperature preparation of water-soluble polydopamine-polyethyleneimine copolymer dots for selective detection of copper ions. Talanta 2019, 197, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wen, Q.; Gu, F.; Gao, J.; Zhang, C.C.; Wang, Q. Mussel chemistry assembly of a novel biosensing nanoplatform based on polydopamine fluorescent dot and its photophysical features. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atluri, R.; Hedin, N.; Garcia-Bennett, A.E. Nonsurfactant Supramolecular Synthesis of Ordered Mesoporous Silica. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3189–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanie, K.; Nishii, M.; Yasuda, T.; Taki, T.; Ujiie, S.; Kato, T. Self-assembly of thermotropic liquid-crystalline folic acid derivatives: Hydrogen-bonded complexes forming layers and columns. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 2875–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuchi, F.; Di Nicola, G.; Franz, H.; Gottarelli, G.; Mariani, P.; Ponzi Bossi, M.G.; Spada, G.P. Self-Recognition and Self-Assembly of Folic Acid Salts: Columnar Liquid Crystalline Polymorphism and the Column Growth Process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 7064–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Li, C.; Shi, G. Optically Active Supramolecular Complexes of Water-Soluble Achiral Polythiophenes and Folic Acid: Spectroscopic Studies and Sensing Applications. Langmuir 2008, 24, 12829–12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Bolisetty, S.; Handschin, S.; Mezzenga, R. Self-assembly and fibrillization of a Fmoc-functionalized polyphenolic amino acid. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 10239–10242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Fan, H.; Wang, L.; Jin, Z. Formation of Polydopamine Nanofibers with the Aid of Folic Acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12600–12604. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, F.; Pei, H.; Kong, R.; Zhu, S.; Xia, L. Novel turn-on fluorescent detection of alkaline phosphatase based on green synthesized carbon dots and MnO2 nanosheets. Talanta 2017, 165, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Kaneko, S.; Takehira, K.; Yoshihara, T.; Ishida, H.; Shiina, Y.; Oishi, S.; Tobita, S. Reevaluation of absolute luminescence quantum yields of standard solutions using a spectrometer with an integrating sphere and a back-thinned CCD detector. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 9850–9860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tan, H.; Zhang, T.; Duan, W.; Zhu, Y. Hydrothermal synthesis of N-doped carbon dots from an ethanolamine-ionic liquid gel to construct label-free multifunctional fluorescent probes for Hg2+, Cu2+ and S2O32−. Analyst 2019, 144, 3013–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, J.S.; Macairan, J.-R.; Macina, A.; Poulhazan, A.; Quattrocchi, V.; Marcotte, I.; Naccache, R. Effects of polydopamine-passivation on the optical properties of carbon dots and its potential use in vivo. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 16595–16605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Vecchia, N.F.; Avolio, R.; Alfè, M.; Errico, M.E.; Napolitano, A.; d'Ischia, M. Building-Block Diversity in Polydopamine Underpins a Multifunctional Eumelanin-Type Platform Tunable Through a Quinone Control Point. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Meng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. A New Cellulose-Based Fluorescent Probe for Specific and Sensitive Detection of Cu2+ and Its Applications in the Analysis of Environmental Water. Polymers 2022, 14, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhou, X.; Long, Y.; Li, W. Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on amino-functionalized carbon dots for the sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, J.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y. Natural polyphenol fluorescent polymer dots. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 1834–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Kong, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y. A composite consisting of bromine-doped carbon dots and ferric ions as a fluorescent probe for determination and intracellular imaging of phosphate. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zou, M.; Chen, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, S. Unique Approach to Develop Carbon Dot-Based Nanohybrid Near-Infrared Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensor for the Detection of Mercury Ions. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8044–8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Hao, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Tang, J. Protein as the source for synthesizing fluorescent carbon dots by a one-pot hydrothermal route. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 8599–8601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zou, S.; Huo, D.; Hou, C.; Yang, M.; Li, J.; Bian, M. Simple and sensitive fluorescence sensor for methotrexate detection based on the inner filter effect of N, S co-doped carbon quantum dots. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1047, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, B.; Ye, W.; Zhou, F. Highly Selective Uptake and Release of Charged Molecules by pH-Responsive Polydopamine Microcapsules. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, V. Impedance spectroscopy and zeta potential titration of dopa-melanin films produced by oxidation of dopamine. Colloids Surf. A 2010, 363, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Ding, S. The pH-controlled nanoparticles size of polydopamine for anti-cancer drug delivery. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Yu, X.-Q. Small molecular fluorescent probes for the detection of lead, cadmium and mercury ions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 429, 213691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Xie, H.; Wei, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Lan, W.; Zhou, C.; She, Y.; Fu, H. A novel thioctic acid-carbon dots fluorescence sensor for the detection of Hg2+ and thiophanate methyl via S-Hg affinity. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Iqbal, S.; Zhao, L.; Xiong, H. “ON-OFF-ON” fluorescence switches based on N,S-doped carbon dots: Facile hydrothermal growth, selective detection of Hg2+, and as a reversive probe for guanine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1183, 338977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, W. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots: Facile synthesis and application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe for detection of Hg2+ ions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, B.; You, T. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots for highly selective and sensitive detection of Hg (Ⅱ) ions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, S.; Feng, L. Highly luminescent N, S- Co-doped carbon dots and their direct use as mercury(II) sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 890, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, H.; Zou, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Lei, B. Carbon dots-based fluorescent probe for “off-on” sensing of Hg(II) and I−. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, T.; Liu, M.; Huang, N.; Li, Y.; Ding, L.; et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of carbon dots for “turn-on” fluorometric determination of Hg(II) via aggregation-induced emission. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Precursor | Synthetic Method | Linear Range (μM) | LOD (μM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Folic acid-ethylene glycol | Hydrothermal | 0–25 | 0.23 | [51] |
| Citric acid-urea-cysteine | Microwave | 0–40 | 2.0 | [52] |
| Citric acid-rubeane | Microwave | 0–20 | 0.18 | [53] |
| Citric acid-diethylenetriamine | Reflex | 0–80 | 0.2 | [54] |
| Cysteine | Microwave | 1–75 | 0.5 | [55] |
| Folic acid-dopamine | Self-polymerization | 0–18 | 0.18 | This work |
| Added (μM) | Mineral Water | Tap Water | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Found (μM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Found (μM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | |
| 5 | 4.75 ± 0.11 | 92.50–96.65 | 2.15 | 4.39 ± 0.15 | 84.47–90.17 | 3.00 |
| 10 | 8.75 ± 0.12 | 86.10–88.33 | 1.23 | 8.46 ± 0.07 | 84.03–85.37 | 0.72 |
| 15 | 14.29 ± 0.31 | 93.02–97.01 | 2.04 | 13.21 ± 0.17 | 86.92–89.18 | 1.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Chen, C.; Yan, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, C. Folic Acid Adjustive Polydopamine Organic Nanoparticles Based Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Mercury Ions. Polymers 2023, 15, 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081892
Chen L, Chen C, Yan Y, Yang L, Liu R, Zhang J, Zhang X, Xie C. Folic Acid Adjustive Polydopamine Organic Nanoparticles Based Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Mercury Ions. Polymers. 2023; 15(8):1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081892
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lijuan, Changchang Chen, Yehan Yan, Linlin Yang, Renyong Liu, Jiajia Zhang, Xin Zhang, and Chenggen Xie. 2023. "Folic Acid Adjustive Polydopamine Organic Nanoparticles Based Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Mercury Ions" Polymers 15, no. 8: 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081892
APA StyleChen, L., Chen, C., Yan, Y., Yang, L., Liu, R., Zhang, J., Zhang, X., & Xie, C. (2023). Folic Acid Adjustive Polydopamine Organic Nanoparticles Based Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Mercury Ions. Polymers, 15(8), 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081892