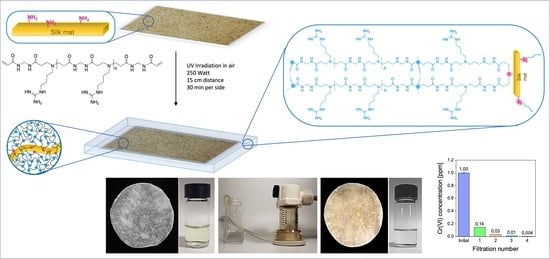
Silk/Polyamidoamine Membranes for Removing Chromium VI from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
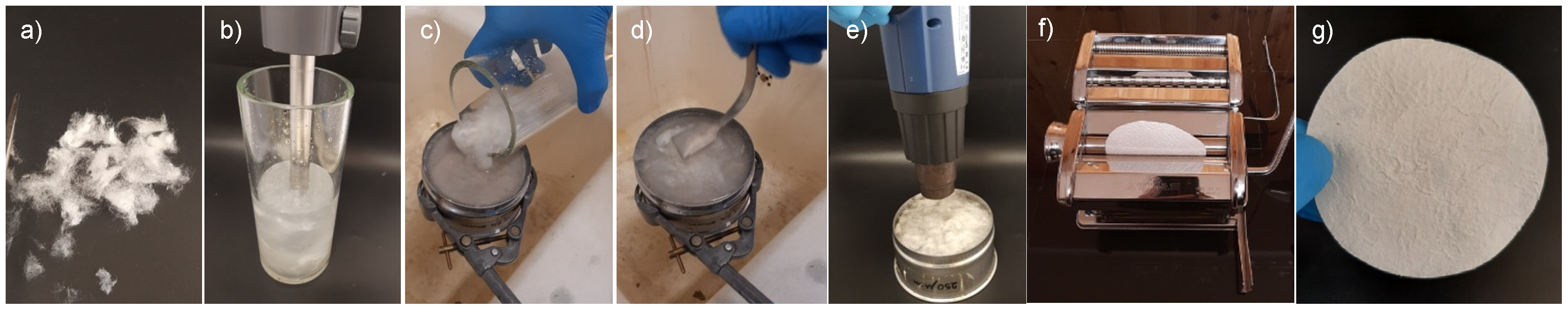
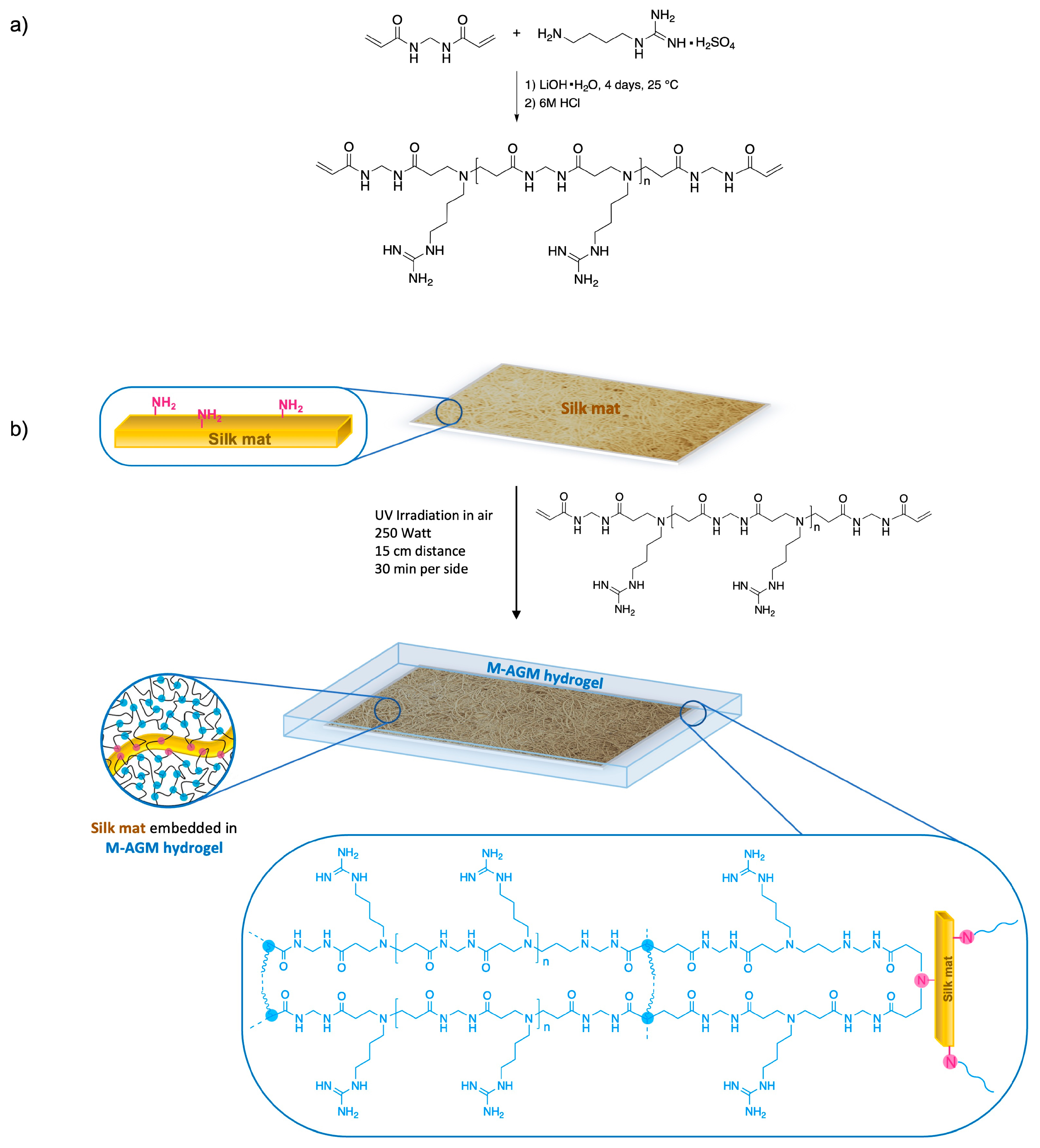
2.3. Silk Mat Preparation
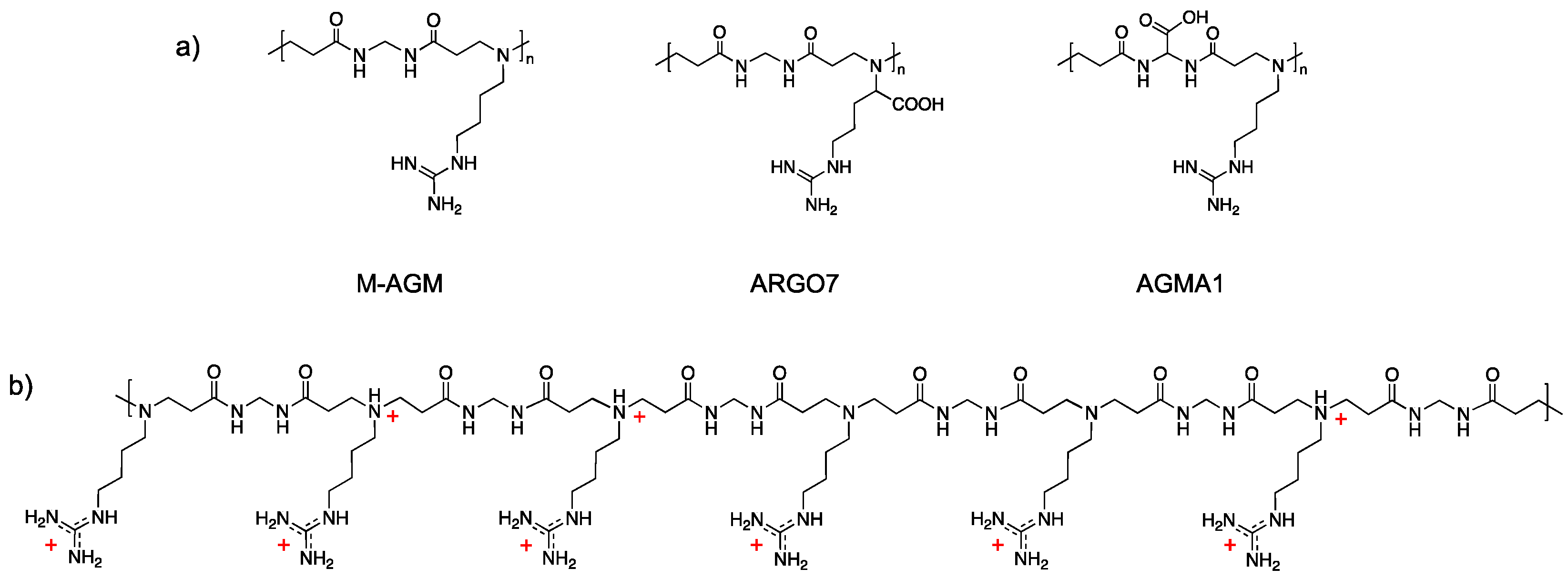
2.4. Synthesis of the α,ω-Bisacrylamide-Terminated M-AGM Oligomer
2.5. Synthesis of the Silk/M-AGM Membranes
2.6. Water Uptake Tests
2.7. Determination of Cr(VI) Concentrations
- (valid in the 0.05–0.25 ppm range)
- (valid in the 0.25–1.0 ppm range)
- where A is the absorbance of the calibrant solution and C is the Cr(VI) concentration of the calibrant solution expressed in ppm. The values of the proportionality constant of Equations (3) and (4), determined as the slopes of the straight line passing through the origin of the Cartesian axes and obtained by plotting the set of experimental data A vs. C, corresponded to linear regression coefficients (R2) of 0.9998 and 0.9954, respectively.
2.8. Cr(VI) Sorption Tests
2.8.1. Cr(VI) Sorption in Static Conditions
2.8.2. Cr(VI) Sorption under Flow Conditions
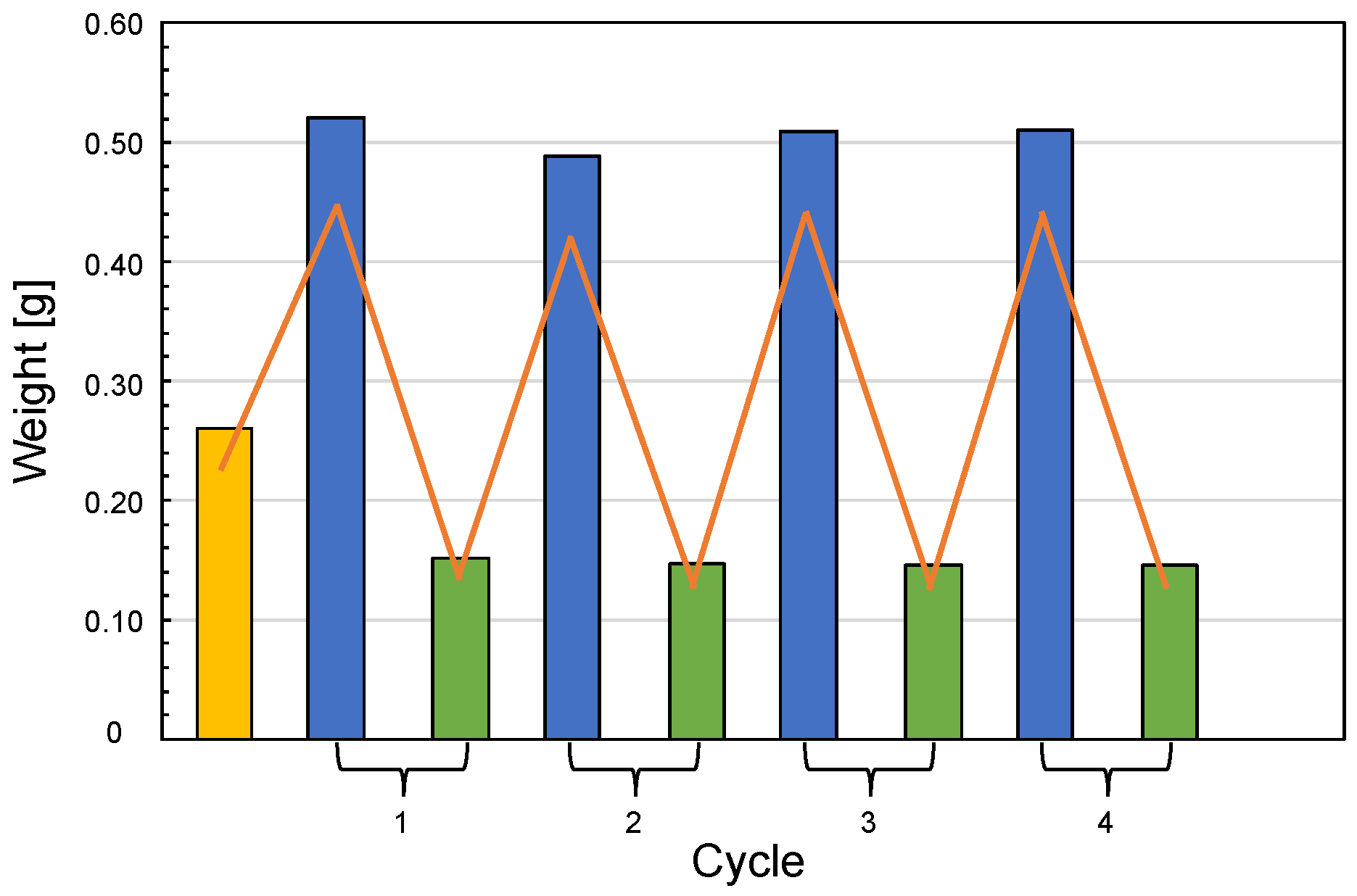
2.9. Regeneration Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rationale
3.2. Silk Mat Preparation
3.3. Synthesis of Silk/M-AGM Membranes
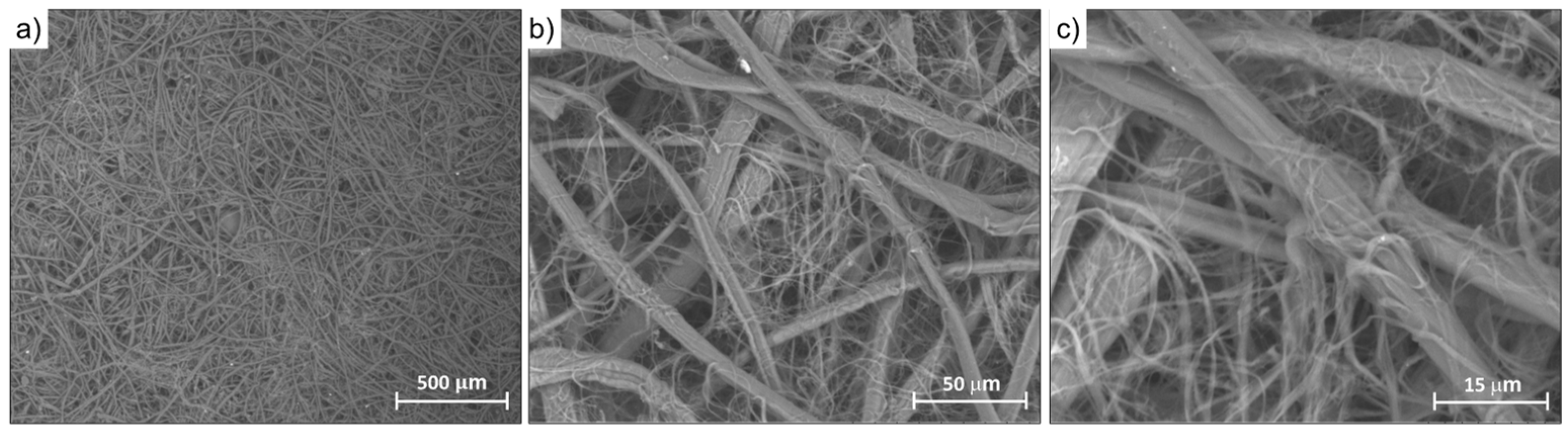
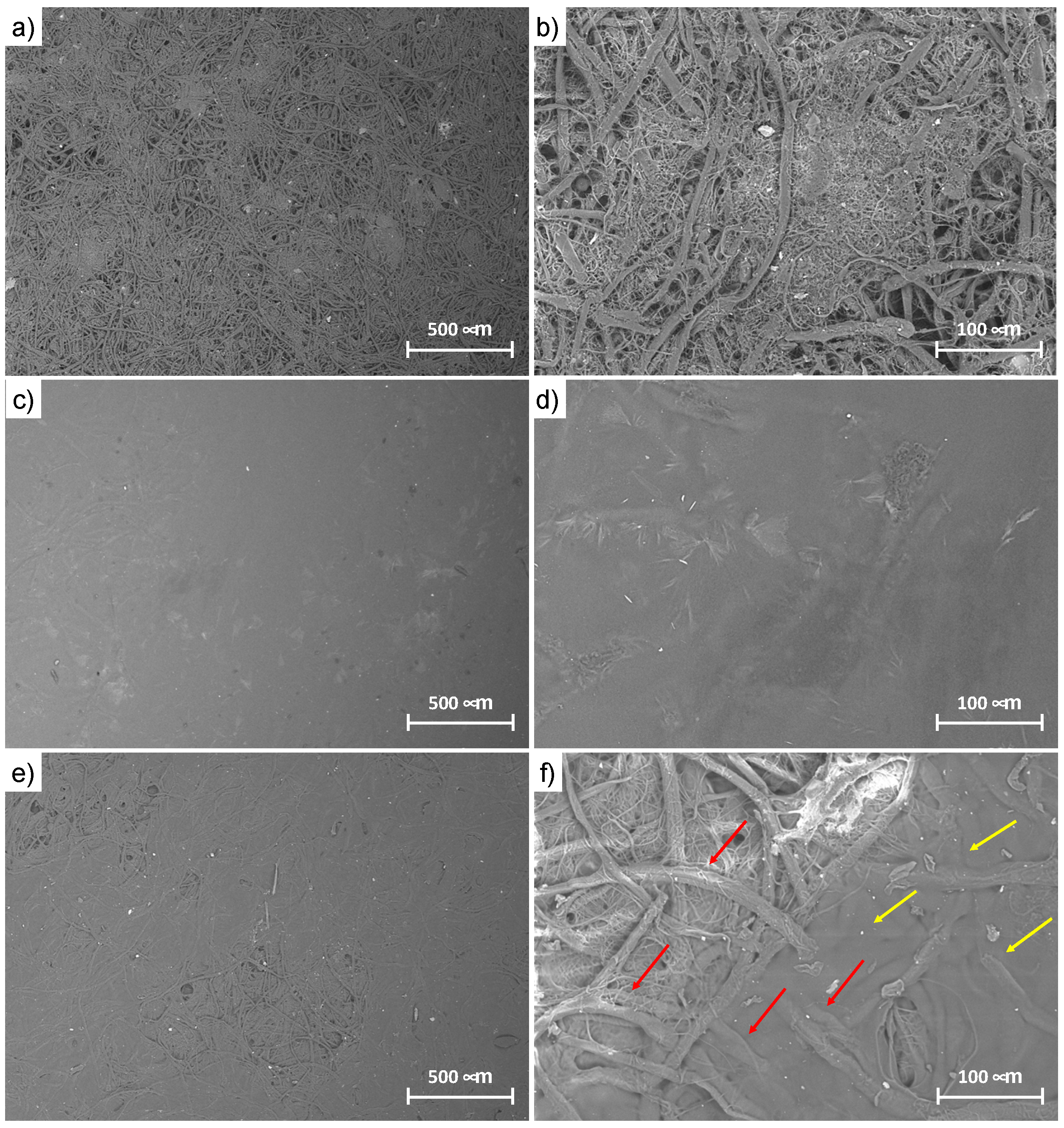
3.4. Morphological Characterization of Silk/M-AGM Membranes
3.5. Water Uptake of Silk/M-AGM Membranes
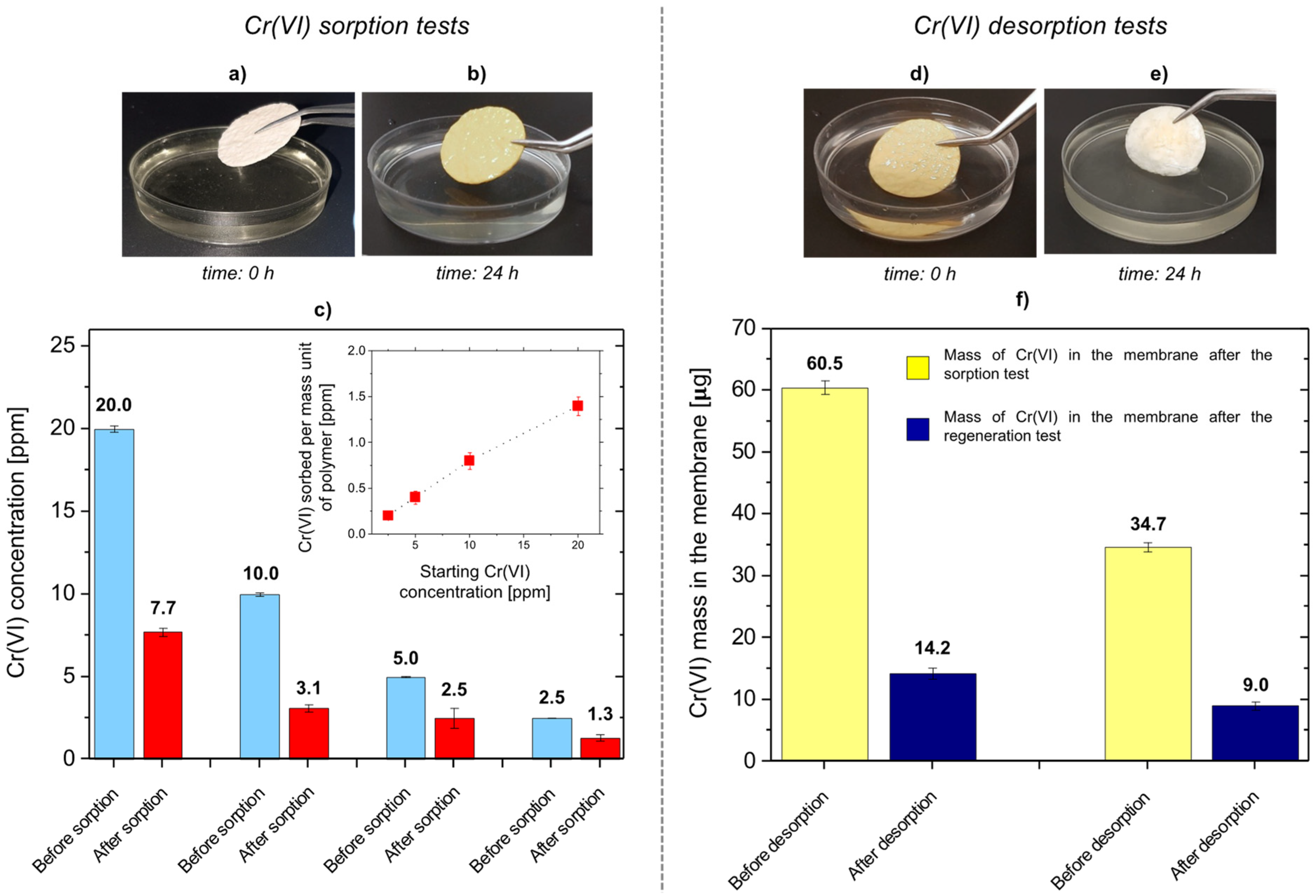
3.6. Cr(VI) Sorption Tests in Static Conditions
3.7. Cr(VI) Sorption Tests under Flow Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balan, C.; Volf, I.; Bilba, D. Chromium (VI) removal from aqueous solutions by Purolite base anion-exchange resins with gel structure. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2013, 19, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, S.M.; Jacobs, J.A. Overview of chromium (VI) in the environment. In Chromium (VI) Handbook; Guertin, J., Jacobs, J.A., Avakian, C.P., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oze, C.; Fendorf, S.; Bird, D.K.; Coleman, R.G. Chromium Geochemistry of Serpentine Soils. Int. Geol. Rev. 2004, 46, 97–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maret, W. Chromium Supplementation in Human Health, Metabolic Syndrome, and Diabetes. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2019, 19, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2016-09/documents/chromium-compounds.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2000).
- Vaiopoulou, E.; Gikas, P. Regulations for chromium emissions to the aquatic environment in Europe and elsewhere. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2017/01/16/17A00347/sg (accessed on 14 November 2016).
- Selvi, K.; Pattabhi, S.; Kadirvelu, K. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto activated carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 80, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.K.; Ali, I.; Saleh, T.A.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Agarwal, S. Chromium removal from water by activated carbon developed from waste rubber tires. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 20, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Hu, Q.; Tao, L.; Sun, D.; Shao, Q.; Qiu, B.; Guo, Z. Ultrasonic pretreated sludge derived stable magnetic active carbon for Cr(VI) removal from wastewater. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7283–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Pi, Y. Enhanced remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated groundwater by coupling electrokinetics with ZVI/Fe3O4/AC-based permeable reactive barrier. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 112, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, B.; Castañeda, D.; Ortiz, I. Removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from polluted ground waters: A comparative study of ion-exchange technologies. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4317–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rena, Y.; Hana, Y.; Lei, X.; Lu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q. A magnetic ion exchange resin with high efficiency of removing Cr (VI). Colloids Surfaces A 2020, 604, 125279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Lin, J.; Liang, J.; Li, M.; Fu, Y.; Wang, H.; Tu, S.; Li, J. Hypercrosslinked mesoporous poly(ionic liquid)s with high density of ion pairs: Efficient adsorbents for Cr(VI) removal via ion-exchange. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terangpi, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Ray, M. Improved removal of hexavalent chromium from 10 mg/L solution by new micron sized polymer clusters of aniline formaldehyde condensate. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, S.; Gorman, C.; Henrie, T.; Shimabuku, K.; Thompson, R.; Seidel, C. Optimization of strong-base anion exchange O & M costs for hexavalent chromium treatment. Water Res. 2018, 139, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, B.; Sundquist, J.; Schmitz, R.J. Removal of Cr(VI) from Cr-contaminated groundwater through electrochemical addition of Fe(II). J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 82, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigidi, I.; Anqi, A.E.; Elkhaleefa, A.; Mohamed, A.; Ali, I.H.; Brima, E.I. Temperature Impact on Reverse Osmosis Permeate Flux in the Remediation of Hexavalent Chromium. Water 2022, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorin, A.V.; Shorokhov, M.; Ozheredova, M.; Bliznjuk, O.; Ryshchenko, I.; Masalitina, N. Purification of Cr(VI)-containing wastewater by chemical precipitation: Test results of an experimental-industrial installation. Vopr. Khimii Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii 2021, 3, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; McGuire, M.; Blute, N.K.; Fong, L. Hexavalent Chromium Removal by Reduction with Ferrous Sulfate, Coagulation, and Filtration: A Pilot-Scale Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6321–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Luo, L.; Zhong, Z.; Xie, X. Advances in Sorptive Removal of Hexavalent Chromium (Cr(VI)) in Aqueous Solutions Using Polymeric Materials Polymers. Polymers 2023, 15, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Qian, L.; Song, W.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Miao, Z. Preparation of an ionic liquid-based hydrogel with hyperbranched topology for efficient removal of Cr(VI). J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 14821–14833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y. Magnetic chitosan-iron (III) hydrogel as a fast and reusable adsorbent for chromium (VI) removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 11956–11966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkanen, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Repo, E.; Lou, L.; Sillanpää, M. Calcium hydroxyapatite microfibrillated cellulose composite as a potential adsorbent for the removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, H.; Irani, M.; Hosseini, L.; Rahimi, A.; Aliabadi, M. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using chitosan/MWCNT/Fe3O4 composite nanofibers-batch and column studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, M.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.; Maity, A. Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using polypyrrole wrapped oxidized MWCNTs nanocomposites adsorbent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 470, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Cai, L.; Liang, J.; Guo, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Z. Green synthesis of expanded graphite/ layered double hydroxides nanocomposites and their application in adsorption removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Hua, Y.; Su, X.; Komarneni, S.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y. Cr(VI) adsorption by montmorillonite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 124–125, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miretzky, P.; Cirelli, A. Cr(VI) and Cr(III) removal from aqueous solution by raw and modified lignocellulosic materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Song, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhou, L. Facile functionalization of natural peach gum polysaccharide with multiple amine groups for highly efficient removal of toxic hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) ions from water. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 17309–17318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Qiao, Y.; An, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, H. High-capacity adsorption of Cr(VI) by lignin-based composite: Characterization, performance and mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; He, H. PEI-grafted magnetic cellulose for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4757–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Komarneni, S.; Yang, C. Polyethylenimine functionalized halloysite nanotubes for efficient removal and fixation of Cr(VI). Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2015, 207, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ming, Z.; Yang, S.; Arkin, A.; Fang, P. Functionalized agricultural biomass as a low-cost adsorbent: Utilization of rice straw incorporated with amine groups for the adsorption of Cr(VI) and Ni(II) from single and binary systems. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 105, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, M. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by polyamidoamine dendrimer polycondensate. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2022, 48, 3937–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Duan, Y.; Xu, X. Facile preparation of amine-rich polyamidoamine (PAMAM) gel for highly efficient removal of Cr(VI) ions. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 579, 123685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. A super biosorbent from dendrimer poly(amidoamine)-grafted cellulose nanofibril aerogels for effective removal of Cr(VI). J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14703–14711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, F.; Peng, Z. Adsorption mechanism of Cr(VI) onto GO/PAMAMs composites. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, B.; Maleki, A.; Najafi, F.; Gharibi, F.; McKay, G.; Gupta, V.K.; Puttaiah, S.H.; Marzban, N. Heavy metal adsorption using PAMAM/CNT nanocomposite from aqueous solution in batch and continuous fixed bed systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, B.; Arami, M.; Maleki, A.; Pajootan, E. Application of dendrimer/titania nanohybrid for the removal of phenol from contaminated wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 6809–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, M.; Steup, J.; Ohto, K.; Weigand, J.J. Recent Advances in Guanidinium Salt Based Receptors and Functionalized Materials for the Recognition of Anions. Chem. Lett. 2022, 51, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, A.S.; Ferré, S. Amazing Stability of the Arginine–Phosphate Electrostatic Interaction. J. Proteome Res. 2005, 4, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau, P.; Segura, M.; Pérez-Fernández, R.; de Mendoza, J. Molecular Recognition of Oxoanions Based on Guanidinium Receptors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custelcean, R.; Williams, N.J.; Seipp, C.A.; Ivanov, A.S.; Bryantsev, V.S. Aqueous Sulfate Separation by Sequestration of [(SO4)2(H2O)4]4- Clusters within Highly Insoluble Imine-Linked Bis-Guanidinium Crystals. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 1997–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haj-Zaroubi, M.; Schmidtchen, F.P. Probing Binding-Mode Diversity in Guanidinium-Oxoanion Host-Guest Systems. ChemPhysChem 2005, 6, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidtchen, F.P.; Berger, M. Artificial Organic Host Molecules for Anions. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1609–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seipp, C.A.; Williams, N.J.; Bryantsev, V.S.; Moyer, B.A. Simple guanidinium motif for the selective binding and extraction of sulfate. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, I.; Kruger, P.E. Theoretical Study of the Interaction between the Guanidinium Cation and Chloride and Sulfate Anions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2005, 1, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einkauf, J.D.; Williams, N.J.; Seipp, C.A.; Custelcean, R. Near Quantitative Removal of Selenate and Sulfate Anions from Wastewaters by Cocrystallization with Chelating Hydrogen-Bonding Guanidinium Ligands. JACS Au 2023, 3, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaelides, P.; Zamboulis, D.; Sarridis, P.; Warchoł, J.; Godelitsas, A. Chromium(VI) uptake by polyhexamethylene-guanidine-modified natural zeolitic materials. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2008, 108, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansone-Popova, S.; Moinel, A.; Schott, J.A.; Mahurin, S.M.; Popovs, I.; Veith, G.M.; Moyer, B.A. Guanidinium-Based Ionic Covalent Organic Framework for Rapid and Selective Removal of Toxic Cr(VI) Oxoanions from Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Damron, J.T.; Bryantsev, V.S.; Johnson, K.R.; Stamberga, D.; Mahurin, S.M.; Popovs, I.; Jansone-Popova, S. Guanidinium-Based Ionic Covalent-Organic Nanosheets for Sequestration of Cr(VI) and As(V) Oxoanions in Water. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 13319–13328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruti, P. Polyamidoamines: Past, Present and Perspectives. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 2319–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranucci, E.; Manfredi, A. Polyamidoamines: Versatile bioactive polymers with potential for biotechnological applications. Chem. Afr. 2019, 2, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranucci, E.; Bignotti, F.; Paderno, P.L.; Ferruti, P. Modification of albumins by grafting poly(amidoamine) chains. Polymer 1995, 36, 2989–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, A.; Carosio, F.; Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E.; Alongi, J. Linear polyamidoamines as novel biocompatible phosphorus-free surface confined intumescent flame retardants for cotton fabrics. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 151, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, J.; Ranucci, E.; Ferruti, P.; Rossi, M.; Cavalli, R. Synthesis, Physicochemical Properties, and Preliminary Biological Characterizations of a Novel Amphoteric Agmatine-Based Poly(amidoamine) with RGD-Like Repeating Units. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E.; Manfredi, A.; Mauro, N.; Ferrari, E.; Bruni, R.; Colombo, F.; Mussini, P.; Rossi, M. L-lysine and EDTA polymer mimics as resins for the quantitative and reversible removal of heavy metal ion water pollutants. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 5000–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruti, P.; Bertoglio Riolo, C.; Soldi, T.; Pesavento, M. Applied macroinorganics. II. Protonation and heavy metal ions complex-formation behavior of three crosslinked resins of poly(amido-amine) structure. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1982, 27, 2239–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E.; Bianchi, S.; Falciola, L.; Mussini, P.R.; Rossi, M. Novel polyamidoamine-based hydrogel with an innovative molecular architecture as a Co2+-, Ni2+-, and Cu2+-sorbing material: Cyclovoltammetry and extended X-ray absorption fine structure studies. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 2316–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagac, M.; Hajnys, J.; Ma, Q.P.; Jancar, L.; Jansa, J.; Stefek, P.; Mesicek, J. Review of Vat Photopolymerization Technology: Materials, Applications, Challenges, and Future Trends of 3D Printing. Polymers 2021, 13, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, F.; Manfredi, A.; Carosio, F.; Maddalena, L.; Alongi, J.; Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E. Toughening Polyamidoamine Hydrogels through Covalent Grafting of Short Silk Fibers. Molecules 2022, 78, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Hachair, A.; Hofmann, A. Hexavalent chromium quantification in solution: Comparing direct UV–visible spectrometry with 1,5-diphenylcarbazide colorimetry. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2018, 21, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajouyed, O.; Hurela, C.; Ammari, M.; Ben Allal, L.; Marmier, N. Sorption of Cr(VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 174, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

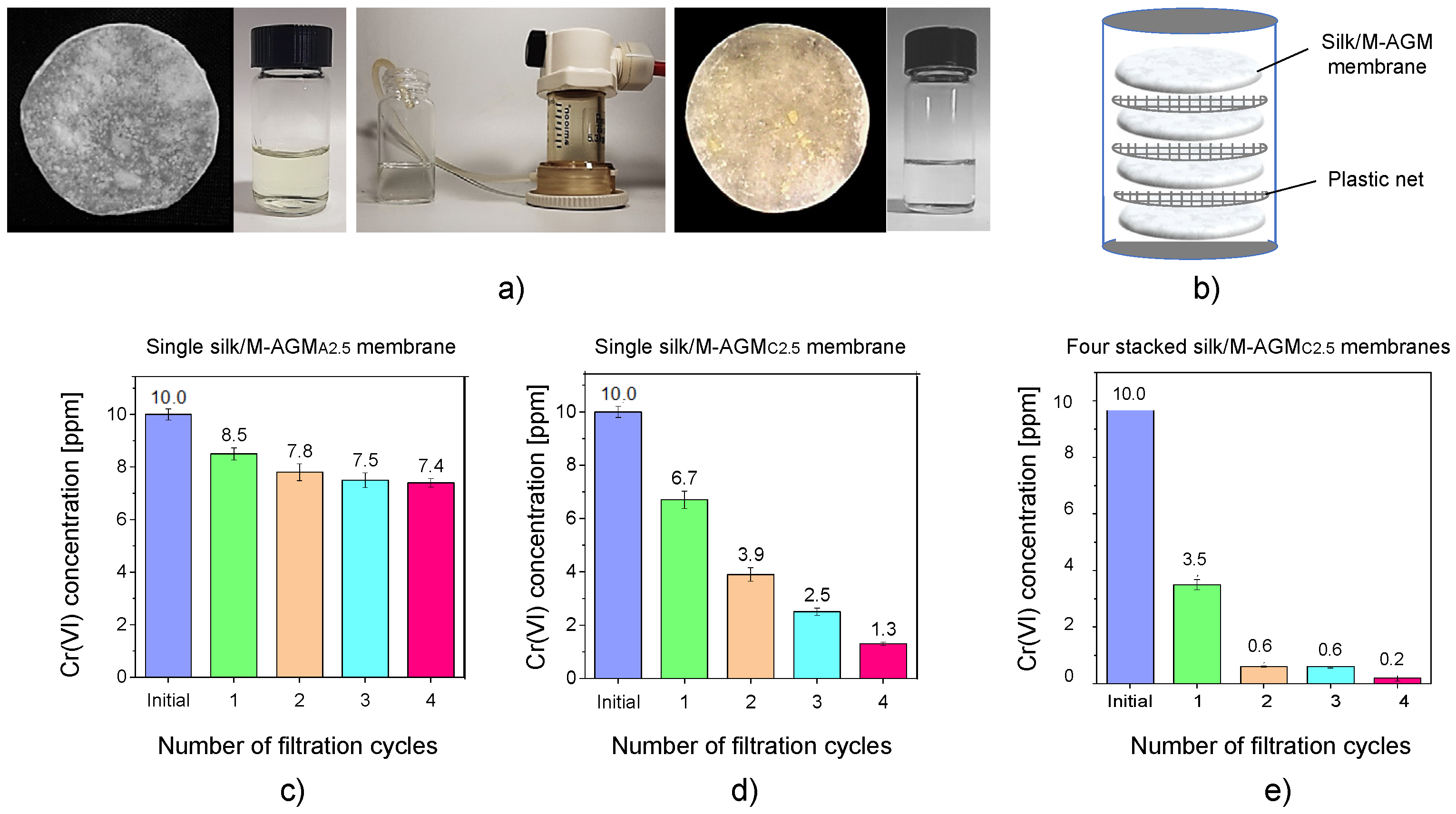
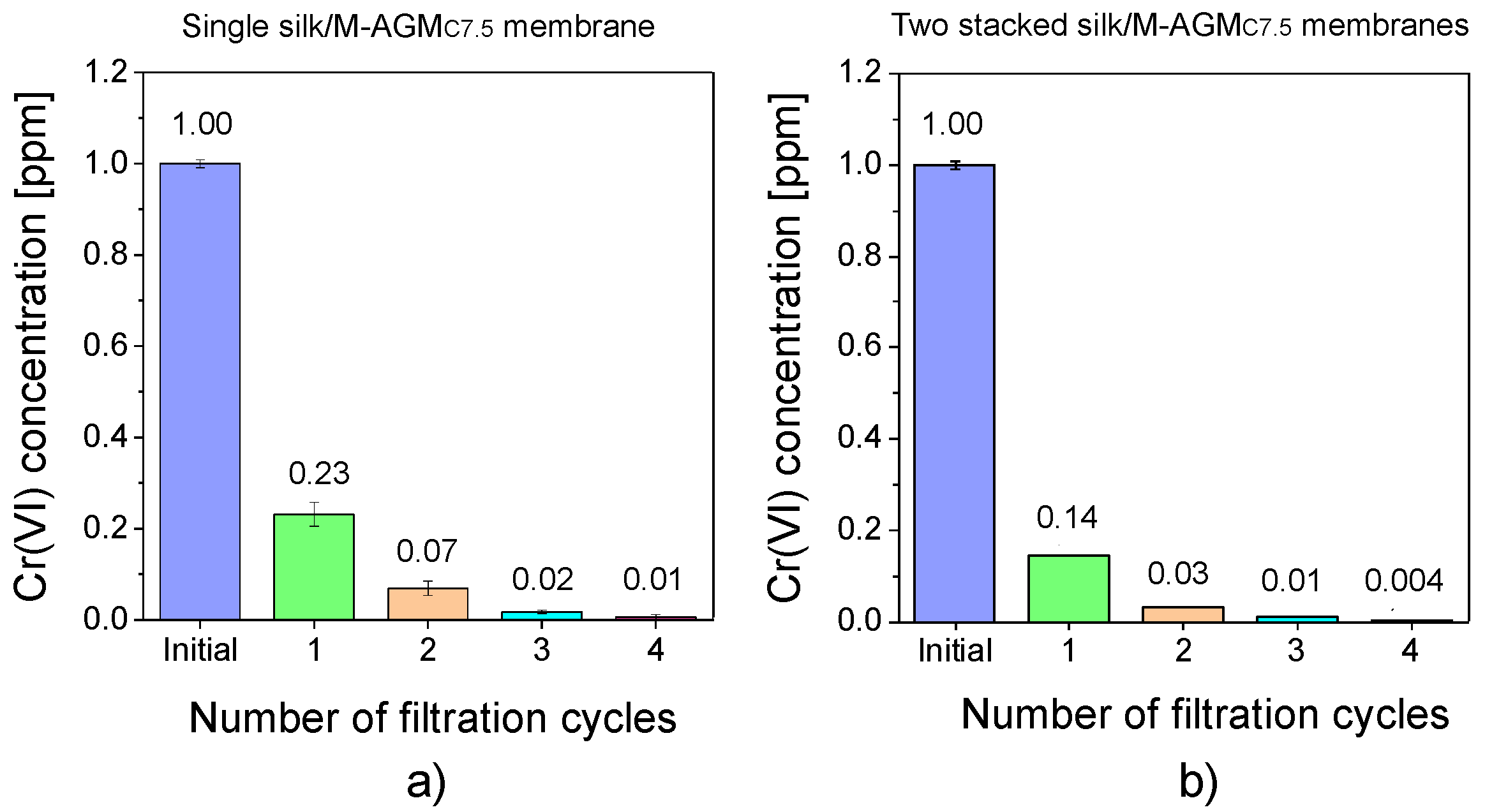
| Sample (a) | Silk Mat Weight (mg) | Silk/M-AGM Membrane Weight (mg) | Weight Percentage of M-AGM in the Membrane (%) | Silk/M-AGM Membrane Thickness (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| silk/M-AGMA2.5 (b) | 45.8 ± 3.6 | 86.9 ± 6.3 | 47 ± 4 | 127 ± 12 |
| silk/M-AGMB2.5 (c) | 33.1 ± 6.9 | 86.7 ± 12.3 | 61 ± 5 | 125 ± 9 |
| silk/M-AGMB7.5 (c) | 367.2 ± 32.3 | 1086.5 ± 83.8 | 66 ± 4 | 143 ± 24 |
| silk/M-AGMC2.5 (c) | 33.1 ± 6.9 | 56.4 ± 6.7 | 48 ± 6 | 125 ± 9 |
| silk/M-AGMC7.5 (c) | 367.2 ± 32.3 | 737.3 ± 58.8 | 46 ± 5 | 143 ± 24 |
| Cr(VI) Concentration before Sorption Test (ppm) | Cr(VI) Weight in the Starting Solution (mg) | Cr(VI) Concentration after Sorption Test (ppm) | Cr(VI) Weight in the Final Solution (mg) | Cr(VI) Removal (%) | Mass of Cr(VI) Sorbed for Mass Unit of Dry Weight of the M-AGM Matrix (mgmg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 100 | 7.7 ± 0.2 | 38.5 ± 1.2 | 62 | 1.4 ± 0.10 |
| 10 | 50 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 15.3 ± 0.8 | 69 | 0.8 ± 0.09 |
| 5 | 25 | 2.5 ± 0.6 | 12.7 ± 3.0 | 50 | 0.4 ± 0.07 |
| 2.5 | 12.5 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 6.7 ± 1.1 | 48 | 0.2 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferruti, P.; Alongi, J.; Barabani, E.; Manfredi, A.; Ranucci, E. Silk/Polyamidoamine Membranes for Removing Chromium VI from Water. Polymers 2023, 15, 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081871
Ferruti P, Alongi J, Barabani E, Manfredi A, Ranucci E. Silk/Polyamidoamine Membranes for Removing Chromium VI from Water. Polymers. 2023; 15(8):1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081871
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerruti, Paolo, Jenny Alongi, Emanuele Barabani, Amedea Manfredi, and Elisabetta Ranucci. 2023. "Silk/Polyamidoamine Membranes for Removing Chromium VI from Water" Polymers 15, no. 8: 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081871
APA StyleFerruti, P., Alongi, J., Barabani, E., Manfredi, A., & Ranucci, E. (2023). Silk/Polyamidoamine Membranes for Removing Chromium VI from Water. Polymers, 15(8), 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081871