Mechanical Properties of Protein-Based Food Packaging Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
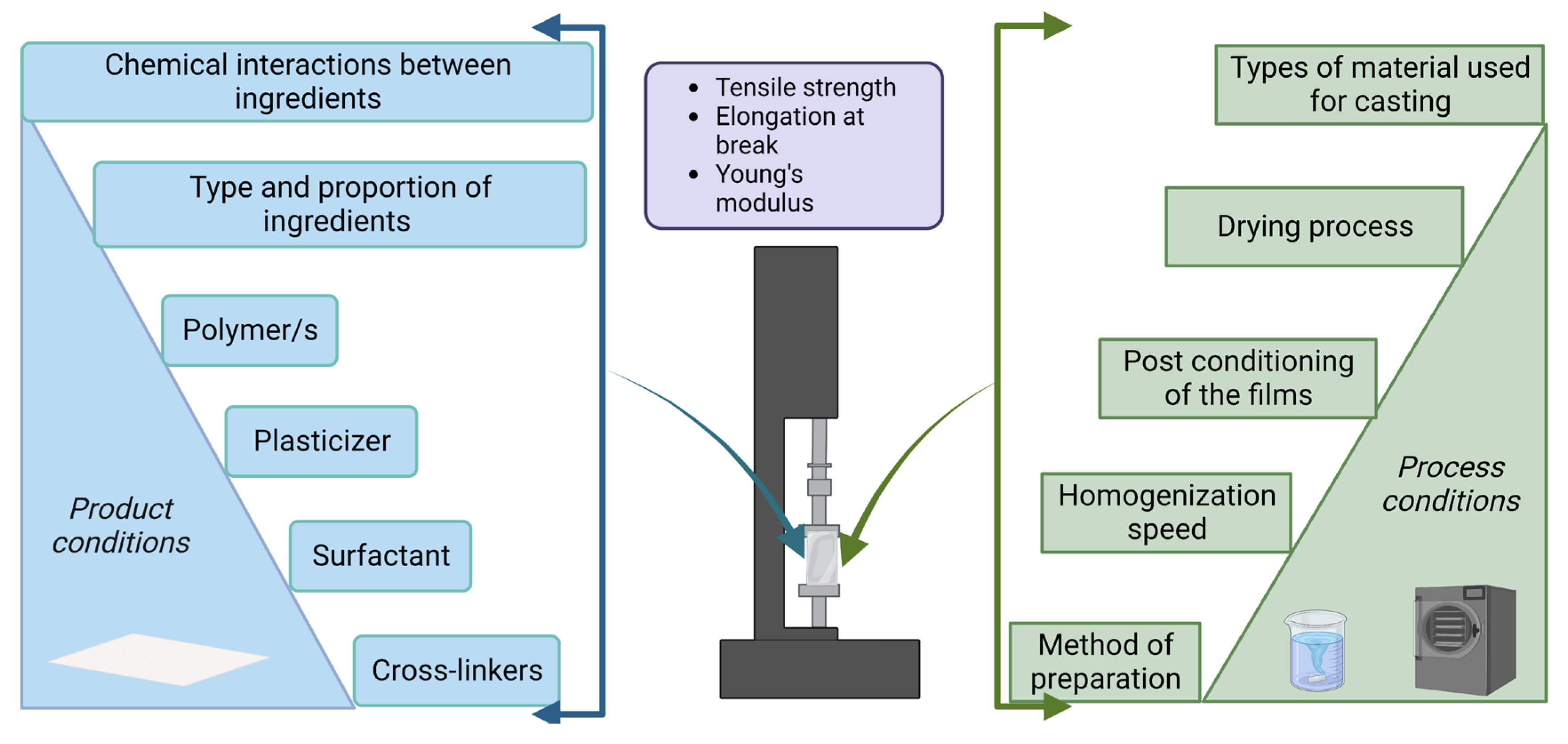
2. Mechanical Attributes of Edible Films
3. Assessment of the Mechanical Properties
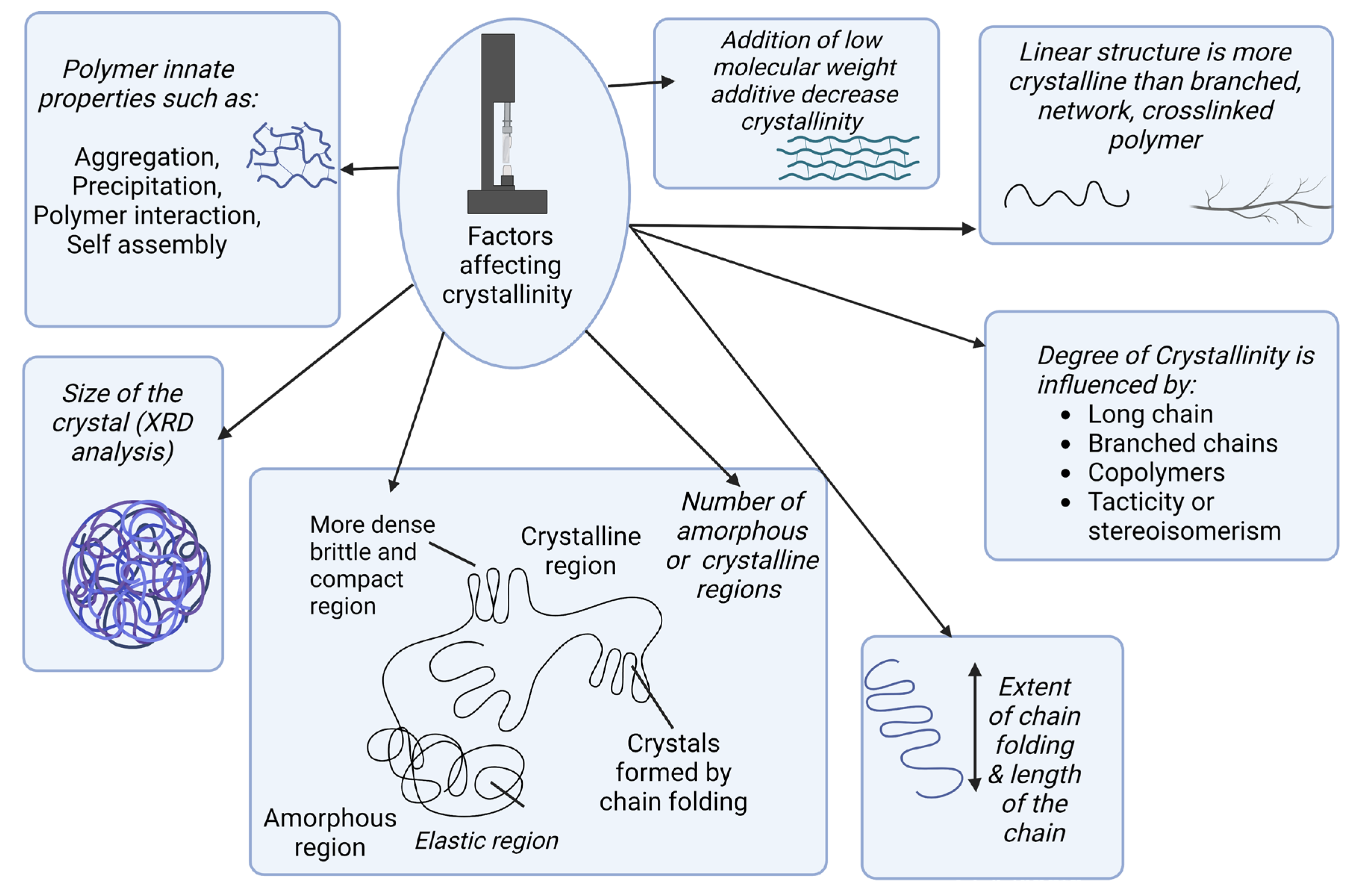
4. The Effect of Crystallinity on Mechanical Properties
5. Mechanical Properties of Plant-Based Protein
5.1. Soy Protein
5.2. Zein Corn
5.3. Wheat Gluten
| Plant-Based Protein | Composite Material (CM) | Plasticizer | Tensile Strength (TS) | Elongation at Break (EAB) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zein | Hydroxypropyl Starch (HPS) | Glycerol | TS significantly increased from 14.65 to 17.35 MPa | EAB decreased from 20.42 to 13.33% | [53] |
| Zein | Tapioca starch | Glycerol | Firmness at Break improved from 9.73 to 39.79 MPa | EAB reduced from 0.64 to 0.30% | [54] |
| Soy protein Isolate | Galactomannan (GM) | Glycerol | TS increased from 1.88 to 3.72 MPa | EAB decreased from 55.8 to 38.0% | [55] |
| Soy protein Isolate | Egg white composite (EW) + Cinnamaldehyde (CIN) | Glycerol | TS decreased from 8.05 to 7.23 MPa | EAB increased from 177.42 to 191.70% | [56] |
| Soy protein Isolate | Edible grasshopper protein + pullulan | Glycerol | TS improved from 3.4 to 7.0 MPa | No positive impact on EAB | [57] |
6. Mechanical Properties of Animal-Based Protein
6.1. Gelatin
6.2. Casein
6.3. Whey Protein
| Animal-Based Protein | Composite Material (CM) | Plasticizer | Tensile Strength (TS) | Elongation at Break (EAB) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelatin | Casein phosphopeptides (CPPs) | Glycerol | TS increased from 9.60 to 18.14 MPa | EAB increased from 23.4 to 84.1% | [73] |
| Gelatin | Blood Orange peel pectin (BOPP) | Glycerol | TS increased from 6.23 to 14.36 Mpa | EAB decreased from 10.97 to 4.36% | [74] |
| Gelatin | Pullulan dialdehyde (PDA) | Glycerol | TS increased from 5.8 to 15.4 MPa | EAB decreased from 471 to 421% | [75] |
| Whey protein isolate (WPI) | Furcellaran (FUR) + Pu-erh extract (PE) + Greentea extract (GT) | Glycerol | TS increased from 6.87 to 8.20 MPa | EAB decreased from 72.40 to 65.32% | [76] |
| Whey protein isolate (WPI) | γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) | Glycerol | TS decreased with the addition of GABA | EAB increased with the addition of GABA | [77] |
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeevahan, J.J.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Venkatesan, S.; Sriram, V.; Joseph, G.B.; Mageshwaran, G.; Durairaj, R. Scaling up difficulties and commercial aspects of edible films for food packaging: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harrasi, A.; Bhtaia, S.; Al-Azri, M.S.; Makeen, H.A.; Albratty, M.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Mohan, S.; Sharma, A.; Behl, T. Development and characterization of chitosan and porphyran based composite edible films containing ginger essential oil. Polymers 2022, 14, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.H. Edible films and coatings: A review. In Innovations in Food Packaging; Pepsico Inc.: Plano, TX, USA, 2014; pp. 213–255. [Google Scholar]
- Nandane, A.S.; Jain, R. Study of mechanical properties of soy protein based edible film as affected by its composition and process parameters by using RSM. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3645–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuq, B.; Aymard, C.; CUQ, J.L.; Guilbert, S. Edible packaging films based on fish myofibrillar proteins: Formulation and functional properties. J. Food Sci. 1995, 60, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Rezaei, M.; Zandi, M.; Ghavi, F.F. Preparation and functional properties of fish gelatin–chitosan blend edible films. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarés, L.; De Jesús, C.; Talens, P.; Chiralt, A. Characterization of SPI-based edible films incorporated with cinnamon or ginger essential oils. J. Food Eng. 2010, 99, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamari, M.A.; Amiri, S.; Rezazadeh-Bari, M.; Rezazad-Bari, L. Physical, mechanical, and antimicrobial properties of active edible film based on milk proteins incorporated with Nigella sativa essential oil. Polym. Bull. 2021, 79, 1097–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, E.; Juszczak, L.; Kucharek, M. Development of starch-furcellaran-gelatin films containing tea tree essential oil. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Shah, Y.A.; Jawad, M.; Al-Azri, M.S.; Ullah, S.; Anwer, M.K.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Koca, E.; Aydemir, L.Y. The Effect of Sage (Salvia sclarea) Essential Oil on the Physiochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Sodium Alginate and Casein-Based Composite Edible Films. Gels 2023, 9, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adilah, Z.M.; Jamilah, B.; Hanani, Z.N. Functional and antioxidant properties of protein-based films incorporated with mango kernel extract for active packaging. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiralt, A.; González-Martínez, C.; Vargas, M.; Atarés, L. Edible films and coatings from proteins. In Proteins in Food Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 477–500. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, V.G.; Romani, V.P.; Martins, P.C.; da Silva Filipini, G. Innovative packaging that saves food. In Saving Food; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 171–202. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, J.; Paula, C.D.d.; Souza, V.G.L.; Fernando, A.L.; Coelhoso, I. Understanding the barrier and mechanical behavior of different nanofillers in chitosan films for food packaging. Polymers 2021, 13, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, I.; Degraeve, P.; Pui, L.P. Polysaccharide-Based Edible Films Incorporated with Essential Oil Nanoemulsions: Physico-Chemical, Mechanical Properties and Its Application in Food Preservation—A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, N.; Bangar, S.P.; Petrů, M.; Ilyas, R.; Singh, A.; Kumar, P. Development and characterization of fenugreek protein-based edible film. Foods 2021, 10, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazón, P.; Vázquez, M. Mechanical and barrier properties of chitosan combined with other components as food packaging film. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Ramakanth, D.; Akhila, K.; Gaikwad, K.K. Edible films and coatings for food packaging applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 20, 875–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gu, Y.; Castellarin, S.D.; Kitts, D.D.; Pratap-Singh, A. Development and characterization of the edible packaging films incorporated with blueberry pomace. Foods 2020, 9, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, V.; Romani, S.; Gigli, M.; Mannozzi, C.; Cecchini, J.P.; Tylewicz, U.; Lotti, N. Characterization of active edible films based on citral essential oil, alginate and pectin. Materials 2018, 11, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socaciu, M.-I.; Fogarasi, M.; Semeniuc, C.A.; Socaci, S.A.; Rotar, M.A.; Mureşan, V.; Pop, O.L.; Vodnar, D.C. Formulation and characterization of antimicrobial edible films based on whey protein isolate and tarragon essential oil. Polymers 2020, 12, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawuyi, I.F.; Lee, W.Y. Development and Characterization of Biocomposite Films Based on Polysaccharides Derived from Okra Plant Waste for Food Packaging Application. Polymers 2022, 14, 4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-García, M.; Calderón-Domínguez, G.; Chanona-Pérez, J.J.; Mendoza-Madrigal, A.G.; Di Pierro, P.; García-Almendárez, B.E.; Amaro-Reyes, A.; Regalado-González, C. Physical, structural, barrier, and antifungal characterization of chitosan–zein edible films with added essential oils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafa, K.D.; Satheesh, N.; Abera, W. Mechanical properties of tef starch based edible films: Development and process optimization. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utama, G.L.; Dinika, I.; Nurmilah, S.; Masruchin, N.; Nurhadi, B.; Balia, R.L. Characterization of Antimicrobial Composite Edible Film Formulated from Fermented Cheese Whey and Cassava Peel Starch. Membranes 2022, 12, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aprilia, S.; Arahman, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Suhaimi, H.; Munawar, A.A.; Nasution, I.S. Bio-Nanocomposite Based on Edible Gelatin Film as Active Packaging from Clarias gariepinus Fish Skin with the Addition of Cellulose Nanocrystalline and Nanopropolis. Polymers 2022, 14, 3738. [Google Scholar]
- Gheribi, R.; Puchot, L.; Verge, P.; Jaoued-Grayaa, N.; Mezni, M.; Habibi, Y.; Khwaldia, K. Development of plasticized edible films from Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage: A comparative study of various polyol plasticizers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balani, K.; Verma, V.; Agarwal, A.; Narayan, R.B. Physical, Thermal, and Mechanical Properties of Polymers; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; p. 337. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, J. Packaging Materials: 9. Multilayer Packaging for Food and Beverages; ILSI Europe: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Van Belle, A.; Demets, R.; Mys, N.; Van Kets, K.; Dewulf, J.; Van Geem, K.; De Meester, S.; Ragaert, K. Microstructural contributions of different polyolefins to the deformation mechanisms of their binary blends. Polymers 2020, 12, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya-Escobar, N.; Ospina-Acero, D.; Velásquez-Cock, J.A.; Gómez-Hoyos, C.; Serpa Guerra, A.; Gañan Rojo, P.F.; Vélez Acosta, L.M.; Escobar, J.P.; Correa-Hincapié, N.; Triana-Chávez, O. Use of Fourier Series in X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) for Estimation of Crystallinity in Cellulose from Different Sources. Polymers 2022, 14, 5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kets, K.; Delva, L.; Ragaert, K. Onset critical strains as an effective parameter for compatibilizer efficiency in a polypropylene-poly (ethylene terephthalate) blend. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balani, K.; Verma, V.; Agarwal, A.; Narayan, R. Biosurfaces: A Materials Science and Engineering Perspective; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Fang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Kang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiang, M.; Li, L.; Sheng, X.; Hao, Z. Exploring the effects of stereo-defect distribution on nonisothermal crystallization and melting behavior of β-nucleated isotactic polypropylene/graphene oxide composites. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 3020–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Prakash, P.C.; Kadeppagari, R.-K. Zein-Based Nanoproducts in Nutrition and Food Sectors. In Handbook of Consumer Nanoproducts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 735–749. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Potkule, J.; Punia, S.; Dhakane-Lad, J.; Singh, S.; Dhumal, S.; Pradhan, P.C.; Bhushan, B.; Anitha, T. Functional characterization of plant-based protein to determine its quality for food applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 106986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsafi, S.R.; Karaca, A.C.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Askari, G.; Rostamabadi, H. Insights into whey protein-based carriers for targeted delivery and controlled release of bioactive components. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 108002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, S.; Hosseini, S.V.; Regenstein, J.M. Edible films and coatings in seafood preservation: A review. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez, M.T.; Bhathena, S.J. Role of dietary soy protein in obesity. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, N.; Fu, Y.; He, J. Preparation and physical properties of soy protein isolate and gelatin composite films. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, W.; Su, C.; Ge, X.; Shen, H.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Muratkhan, M. Insight into crosslinked chitosan/soy protein isolate/PVA plastics by revealing its structure, physicochemical properties, and biodegradability. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 187, 115548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabato, S.; Ouattara, B.; Yu, H.; D’aprano, G.; Le Tien, C.; Mateescu, M.; Lacroix, M. Mechanical and barrier properties of cross-linked soy and whey protein based films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Du, Y.; Zheng, H.; Fan, L. Preparation and characterization of soy protein isolate–carboxymethylated konjac glucomannan blend films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüello-García, E.; Solorza-Feria, J.; Rendón-Villalobos, J.R.; Rodríguez-González, F.; Jiménez-Pérez, A.; Flores-Huicochea, E. Properties of edible films based on oxidized starch and zein. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 2014, 292404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tihminlioglu, F.; Atik, İ.D.; Özen, B. Water vapor and oxygen-barrier performance of corn–zein coated polypropylene films. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, E.; Khalil, A.; Deraz, S.; El-Fawal, G.; Elrahman, S.A. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of biodegradable films prepared from Schiff bases of zein. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torun, M.; Ozdemir, F. Milk protein and zein coatings over peeled garlic cloves to extend their shelf life. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 291, 110571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-García, M.; Calderon-Dominguez, G.; Chanona-Perez, J.J.; Farrera-Rebollo, R.R.; Andraca-Adame, J.A.; Arzate-Vazquez, I.; Mendez-Mendez, J.V.; Moreno-Ruiz, L. Physical and structural characterisation of zein and chitosan edible films using nanotechnology tools. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 61, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Effect of α-tocopherol antioxidant on rheological and physicochemical properties of chitosan/zein edible films. LWT 2020, 118, 108799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca-Smith, J.R.; Marcuzzo, E.; Karbowiak, T.; Centa, J.; Giacometti, M.; Scapin, F.; Venir, E.; Sensidoni, A.; Debeaufort, F. Effect of lipid incorporation on functional properties of wheat gluten based edible films. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 69, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Khatkar, B.; Kaushik, R.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, R. Isolation and development of wheat based gluten edible film and its physicochemical properties. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Marcuzzo, E.; Peressini, D.; Debeaufort, F.; Sensidoni, A. Effect of ultrasound treatment on properties of gluten-based film. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, F.; Zi, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiao, J. Development and characterization of a hydroxypropyl starch/zein bilayer edible film. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, P.F.; Ollé Resa, C.P.; Gerschenson, L.N.; Jagus, R.J. Addition of zein for the improvement of physicochemical properties of antimicrobial tapioca starch edible film. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Barrera, G.N.; Galimberti, P.I.; Ribotta, P.D.; Igarzabal, C.I.A. Development of edible films prepared by soy protein and the galactomannan fraction extracted from Gleditsia triacanthos (Fabaceae) seed. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Mu, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Chi, Y.; Song, G.; Li, H.; Wang, L. Effect of cinnamaldehyde incorporation on the structural and physical properties, functional activity of soy protein isolate-egg white composite edible films. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Changqing, F.; Zhang, W.; Lei, W.; Wang, D.; Zhou, X. Novel grasshopper protein/soy protein isolate/pullulan ternary blend with hesperidin derivative for antimicrobial edible film. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calva-Estrada, S.J.; Jiménez-Fernández, M.; Lugo-Cervantes, E. Protein-based films: Advances in the development of biomaterials applicable to food packaging. Food Eng. Rev. 2019, 11, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamp, A.; Kaltschmitt, M.; Dethloff, J. Options to Improve the Mechanical Properties of Protein-Based Materials. Molecules 2022, 27, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanin, F.; Sobral, P.; Menegalli, F.; Carvalho, R.; Habitante, A. Effects of plasticizers and their concentrations on thermal and functional properties of gelatin-based films. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuaynukul, K.; Nagarajan, M.; Prodpran, T.; Benjakul, S.; Songtipya, P.; Songtipya, L. Comparative characterization of bovine and fish gelatin films fabricated by compression molding and solution casting methods. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopel, B.S.; Ribeiro, M.E.; Dettmer, A.; Baldasso, C. Cornstarch-gelatin films: Commercial gelatin versus chromed leather waste gelatin and evaluation of drying conditions. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1998–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergo, P.; Sobral, P. Effects of plasticizer on physical properties of pigskin gelatin films. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1285–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, E.; Assezat, G.; Prochazka, F.; Oulahal, N. Development and characterization of a novel edible extruded sheet based on different casein sources and influence of the glycerol concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-L.; Gowen, A.A. Investigation of plasticizer aggregation problem in casein based biopolymer using chemical imaging. Talanta 2019, 193, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, B.U.; Aytac, A. Poly (vinyl alcohol) and casein films: The effects of glycerol amount on the properties of films. Res. Eng. Struct. Mater. 2019, 5, 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Arnon-Rips, H.; Poverenov, E. Improving food products’ quality and storability by using Layer by Layer edible coatings. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczewska, J. Peptides and protein hydrolysates as food preservatives and bioactive components of edible films and coatings-A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fematt-Flores, G.E.; Aguiló-Aguayo, I.; Marcos, B.; Camargo-Olivas, B.A.; Sánchez-Vega, R.; Soto-Caballero, M.C.; Salas-Salazar, N.A.; Flores-Córdova, M.A.; Rodríguez-Roque, M.J. Milk protein-based edible films: Influence on mechanical, hydrodynamic, optical and antioxidant properties. Coatings 2022, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfi, M.; Khodaiyan, F.; Mousavi, M.; Hashemi, M. Development and characterization of the kefiran-whey protein isolate-TiO2 nanocomposite films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, S.; Yoo, J.; Yun, J.; Kang, H.-B.; Seol, K.-H.; Kim, H.-W.; Ham, J.-S. Application of whey protein-based edible films and coatings in food industries: An updated overview. Coatings 2021, 11, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.-j.; Zhang, T.; Song, Y.; Qian, F.; Tuo, Y.; Mu, G. Mechanical properties of whey protein concentrate based film improved by the coexistence of nanocrystalline cellulose and transglutaminase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedri, S.; Sadeghi, E.; Rouhi, M.; Delshadian, Z.; Mortazavian, A.M.; de Toledo Guimarães, J.; Mohammadi, R. Bioactive edible films: Development and characterization of gelatin edible films incorporated with casein phosphopeptides. LWT 2021, 138, 110649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jridi, M.; Abdelhedi, O.; Salem, A.; Kechaou, H.; Nasri, M.; Menchari, Y. Physicochemical, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of fish gelatin-based edible films enriched with orange peel pectin: Wrapping application. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Zheng, X.; Tang, K. Tuning structure and properties of gelatin edible films through pullulan dialdehyde crosslinking. LWT 2021, 138, 110607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta-Kubica, A.; Jamróz, E.; Juszczak, L.; Krzyściak, P.; Zimowska, M. Characterization of furcellaran-whey protein isolate films with green tea or pu-erh extracts and their application as packaging of an acid-curd cheese. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Ameliorating effect of γ-aminobutyric acid on the physical performance of whey protein films. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | Manufacturer | Sample Nature | Purpose | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attopuls Texture Analyser | Stable Micro Systems, UK | Starch-based (potato, corn, sweet potato, green bean and tapioca) edible packaging film incorporated with blueberry pomace powder | tensile grip (TA 96B) attachment, initial grip separation of 20 mm, and a pre-test and test speed of 1 mm/s. | To determine the tensile strength | [19] |
| Zwick Roell Texture machine mod. Z2.5 | ZwickRoell, Ulm, Germany | Edible Films based on Citral Essential Oil, Alginate and Pectin | 500 N load cell, pre-load of 1MPa with a pre-load speed of 5 mm/min, crosshead speed of 5 mm/min. | Elastic modulus, stress at yield and at break, and elongation at yield and at break | [20] |
| CT3, Brookfield Engineering Laboratories Inc. | Middleboro, MA, USA | Edible Films Based on Whey Protein Isolate and Tarragon Essential Oil | puncture head (a cylindrical rod of 2 mm in diameter-TA39), was set to a target distance of 5.0 mm with a speed of 0.5 mm/s. | puncture resistance and puncture deformation | [21] |
| QMESYS Universal Material Testing Machine, QM100s, 1.96 kN | Komachine, Gyeonggi-do, Korea | Mucilage polysaccharides (OLP) and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) extracted from okra leafstalk wastes | gauge distance and crosshead speed were set at 20 mm and 10 mm/s | tensile strength (TS) and elongation at break (EB) | [22] |
| Nanoindenter | CSM, Peseux, Switzerland | Chitosan–Zein Edible Films with Added Essential Oils | load of 2.5 mN at loading and unloading rates of 7.5 mN/min, and a pause of 35 s using a Berkovich tip | Elastic modulus | [23] |
| Auto tensile tester | XLW (EC) or XLW-PC, China | tef starch based edible films | tensile strength, elongation at break, elastic modulus, puncture force, and puncture deformation | [24] | |
| AG-IS 50kN-Universal texture Machine | Shimadzu AG-IS 50kN, Kyoto, Japan | Edible Film from Fermented Cheese Whey and Cassava Peel Starch | elongation at break and tensile strength | [25] | |
| Type HT-8503, Universal Testing Machine | Seremban, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia | Bio-nano composite gelatin-based edible film by combining nanogelatin, cellulose nanocrystal and nanopropolis fillers | tensile strength, elongation at break, and Young’s modulus | [26] | |
| INSTRON 3345 universal testing machine | High Wycombe, UK | Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage | a head speed of 100 mm/min using a double clamp with a separation of 50 mm | tensile strength, elastic modulus and elongation at break | [27] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shah, Y.A.; Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Anwer, M.K.; Khan, M.R.; Jawad, M.; Akram, N.; Faisal, Z. Mechanical Properties of Protein-Based Food Packaging Materials. Polymers 2023, 15, 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071724
Shah YA, Bhatia S, Al-Harrasi A, Afzaal M, Saeed F, Anwer MK, Khan MR, Jawad M, Akram N, Faisal Z. Mechanical Properties of Protein-Based Food Packaging Materials. Polymers. 2023; 15(7):1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071724
Chicago/Turabian StyleShah, Yasir Abbas, Saurabh Bhatia, Ahmed Al-Harrasi, Muhammad Afzaal, Farhan Saeed, Md Khalid Anwer, Mahbubur Rahman Khan, Muhammad Jawad, Noor Akram, and Zargham Faisal. 2023. "Mechanical Properties of Protein-Based Food Packaging Materials" Polymers 15, no. 7: 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071724
APA StyleShah, Y. A., Bhatia, S., Al-Harrasi, A., Afzaal, M., Saeed, F., Anwer, M. K., Khan, M. R., Jawad, M., Akram, N., & Faisal, Z. (2023). Mechanical Properties of Protein-Based Food Packaging Materials. Polymers, 15(7), 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071724









