A High-Linearity Glucose Sensor Based on Silver-Doped Con A Hydrogel and Laser Direct Writing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Fabrication of Graphene Electrode by Laser Direct Writing
2.3. Fabrication of Con-A-Based Silver Composites
2.4. Fabrication of the Silver-Doped Glucose Sensor
2.5. Characterization of the Con-A-Based Silver Composite
2.6. Performance of the Silver-Doped Glucose Sensor
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Principle of the Proposed Silver-Doped Hydrogel Sensor
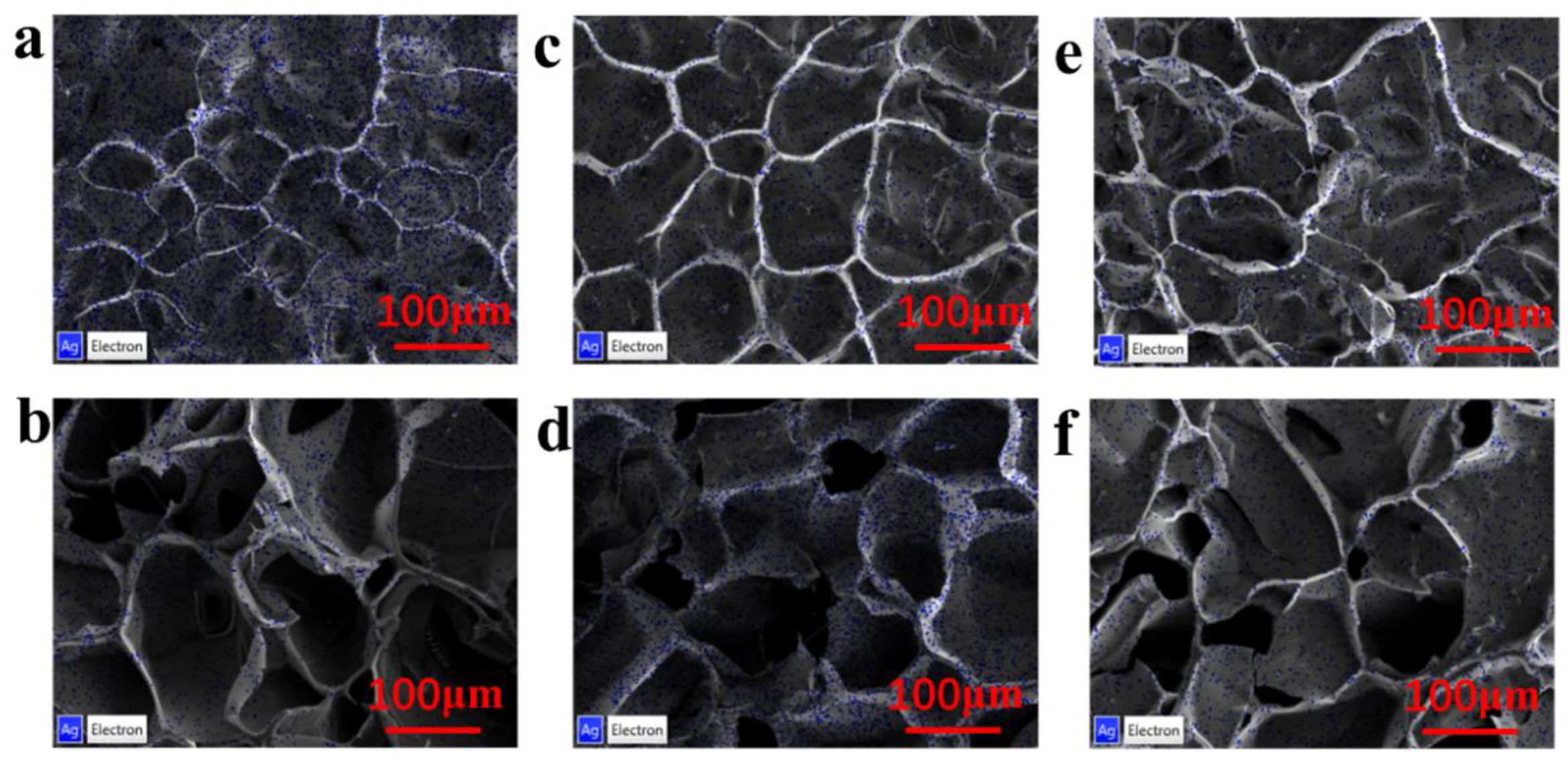
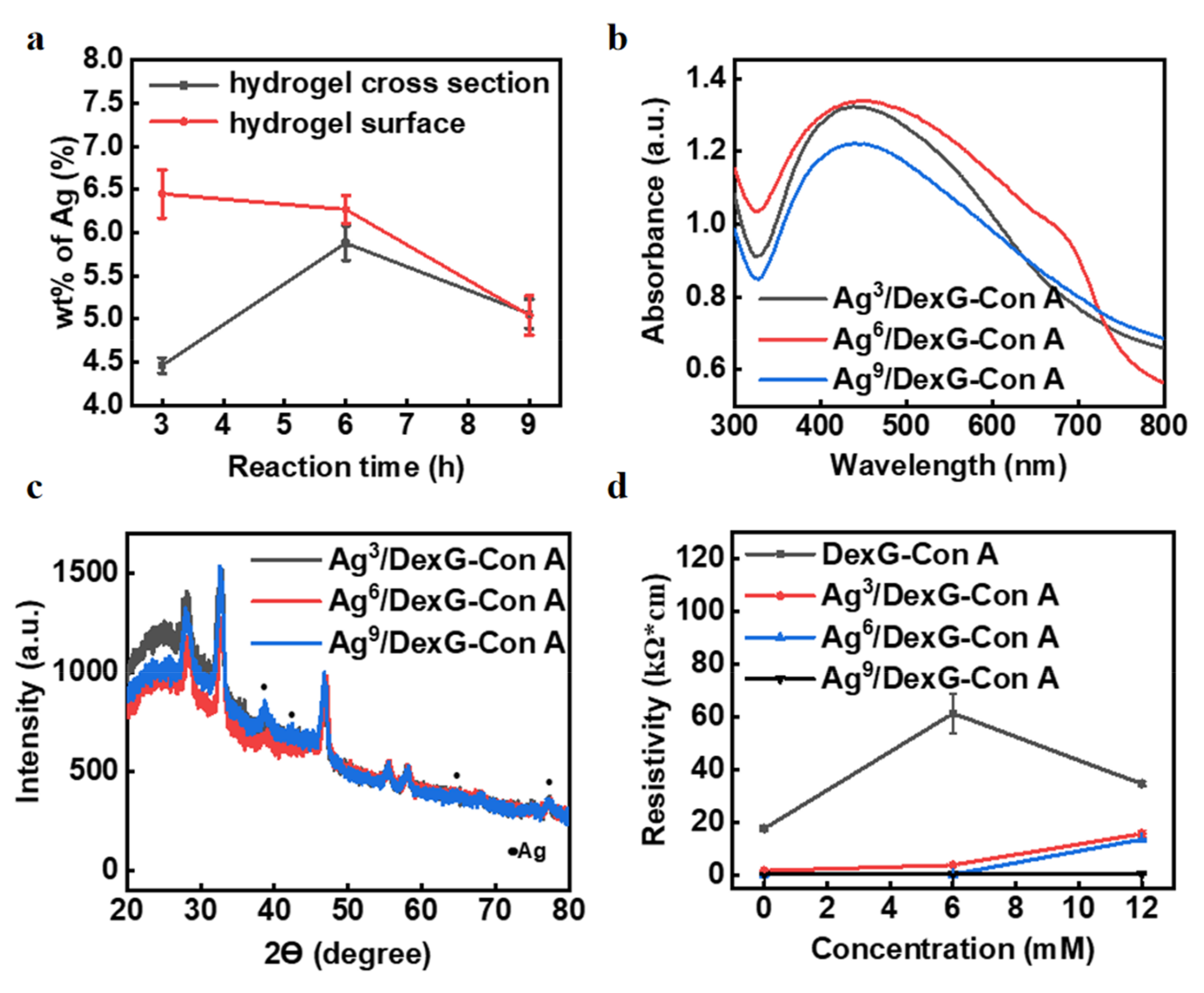
3.2. Characterization of the Con-A-Based Silver Composites
3.3. Performance of the Silver-Doped Hydrogel Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeedi, P.; Salpea, P.; Karuranga, S.; Petersohn, I.; Malanda, B.; Gregg, E.W.; Unwin, N.; Wild, S.H.; Williams, R. Mortality attributable to diabetes in 20–79 years old adults, 2019 estimates: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, J. Unraveling the causes of diabetes. Science 2002, 296, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gingras, V.; Taleb, N.; Roy-FlemSAing, A.; Legault, L.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R. The challenges of achieving postprandial glucose control using closed-loop systems in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.A.; Shin, J.H. Recent developments in nanostructure based electrochemical glucose sensors. Talanta 2016, 149, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, L.C., Jr.; Lyons, C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Updike, S.J.; Hicks, G.P. The enzyme electrode. Nature 1967, 214, 986–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajeu, K.Y.; Ymele, E.; Jiokeng, S.L.Z.; Tonle, I.K. Electrochemical Sensor for Caffeine Based on a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with an Attapulgite/Nafion Film. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrowski, T.; Schuhmann, W. Long-term implantable glucose biosensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 10, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, L.; Bellagamba, M.; Zhang, H.; Lei, Y. Electrospun Co3O4 nanofibers for sensitive and selective glucose detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.-W.; Lee, S.; Seo, M.; Chung, T.D. Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors-A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1033, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Yoon, H.S.; Xuan, X.; Park, J.Y.; Paik, S.-J.; Allen, M.G. A patch type non-enzymatic biosensor based on 3D SUS micro-needle electrode array for minimally invasive continuous glucose monitoring. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2016, 222, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, T.Y.; Niwa, O.; Tomita, M.; Ando, H.; Suzuki, M.; Hirono, S. Characterization and electrochemical properties of highly dispersed copper oxide/hydroxide nanoparticles in graphite-like carbon films prepared by RF sputtering method. Electrochem. Commun. 2002, 4, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooten, M.; Shim, J.H.; Gorski, W. Amperometric Determination of Glucose at Conventional vs. Nanostructured Gold Electrodes in Neutral Solutions. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodbard, D. Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Review of Successes, Challenges, and Opportunities. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2016, 18, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battelino, T.; Alexander, C.M.; Amiel, S.A.; Arreaza-Rubin, G.; Beck, R.W.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Buckingham, B.A.; Carroll, J.; Ceriello, A.; Chow, E.; et al. Continuous glucose monitoring and metrics for clinical trials: An international consensus statement. Lancet. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevich, E.; Fuji, K.T.; Larson, K.; Muniz, G. A Cross-Sectional Survey Study Examining the Provision of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Education in U.S. Doctor of Pharmacy Programs. Pharmacy 2022, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabit, H.; Hovorka, R. Coming of age: The artificial pancreas for type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Cui, Y. Transdermal amperometric biosensors for continuous glucose monitoring in diabetes. Talanta 2023, 253, 1–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-C.; Lee, A.-R. Recent developments in blood glucose sensors. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, S.; Schultz, J.S.; Wang, Q.; Lin, Q. A MEMS affinity glucose sensor using a biocompatible glucose-responsive polymer. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2009, 140, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Leduc, C.; Ravussin, Y.; Li, S.; Davis, E.; Song, B.; Li, D.; Xu, K.; Accili, D.; Wang, Q.; et al. A differential dielectric affinity glucose sensor. Lab A Chip 2014, 14, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsherif, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Yetisen, A.K.; Butt, H. Hydrogel optical fibers for continuous glucose monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 137, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yu, A.; Lai, G. Self-assembly of phenoxyl-dextran on electrochemically reduced graphene oxide for nonenzymatic biosensing of glucose. Carbon 2018, 127, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.B.; Stokke, B.T.; Hanke, U.; Johannessen, A.; Johannessen, E.A. The Characterisation and Quantification of Immobilised Concanavalin A on Quartz Surfaces Based on The Competitive Binding to Glucose and Fluorescent Labelled Dextran. Appl. Sci.-Basel 2019, 9, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, K.; Lakowicz, J.R.; Geddes, C.D. Tunable plasmonic glucose sensing based on the dissociation of Con A-aggregated dextran-coated gold colloids. Anal Chim Acta 2004, 517, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; You, H. Recent Applications of Point-of-Care Devices for Glucose Detection on the Basis of Stimuli-Responsive Volume Phase Transition of Hydrogel. Biochip J. 2021, 15, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Wang, K.; Du, S.; Chen, L.; Nie, J.; Zhang, W. Design of genipin-crosslinked microgels from concanavalin A and glucosyloxyethyl acrylated chitosan for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Bai, M.; He, J.; Nie, J.; Zhang, W. Concanavalin A-sugar affinity based system: Binding interactions, principle of glucose-responsiveness, and modulated insulin release for diabetes care. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballerstadt, R.; Schultz, J.S. A fluorescence affinity hollow fiber sensor for continuous transdermal glucose monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 4185–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, S.-H.; Cho, I.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Jeon, J.-W.; Lim, G.-S.; Paek, S.-H. Label-free, needle-type biosensor for continuous glucose monitoring based on competitive binding. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, D.; Yin, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. An enzyme-free capacitive glucose sensor based on dual-network glucose-responsive hydrogel and coplanar electrode. Analyst 2021, 146, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurskjold, B.W. Exact analysis of competition ligand binding by displacement isothermal titration calorimetry. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 277, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Nie, J. Glucose-responsive composite microparticles based on chitosan, concanavalin A and dextran for insulin delivery. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Yu, M. Preparation of Ag Nanoparticles Based on Photoirradiation Method with Plasmid Dna-Templated. Acta Metall. Sin. 2012, 48, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y. Simple, Low-Cost Fabrication of Highly Uniform and Reproducible SERS Substrates Composed of Ag-Pt Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xu, W.; Wang, L. Research on Optical Absorption Characteristics of Ag Nanoparticles. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2013, 27, 1350079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S.; Chakarvarti, S.K. Structural and electrical studies of template synthesized copper nanowires. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2014, 14, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; He, D.; You, B. Laser engraving and punching of graphene films as flexible all-solid-state planar micro-supercapacitor electrodes. Mater. Today Sustain. 2022, 17, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Thin hydrogel films based on lectin-saccharide biospecific interaction for label-free optical glucose sensing. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2018, 272, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Xin, J.; Yang, D.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, W. High-Linearity Hydrogel-Based Capacitive Sensor Based on Con A-Sugar Affinity and Low-Melting-Point Metal. Polymers 2022, 14, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Maturavongsadit, P.; Song, B.; Jia, Y.; Ma, T.; Li, D.; Xu, K.; et al. A hydrogel-based glucose affinity microsensor. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2016, 237, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daikuzono, C.M.; Delaney, C.; Tesfay, H.; Florea, L.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Morrin, A.; Diamond, D. Impedance spectroscopy for monosaccharides detection using responsive hydrogel modified paper-based electrodes. Analyst 2017, 142, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yin, R. A High-Linearity Glucose Sensor Based on Silver-Doped Con A Hydrogel and Laser Direct Writing. Polymers 2023, 15, 1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061423
Hu Y, Yang D, Zhang H, Gao Y, Zhang W, Yin R. A High-Linearity Glucose Sensor Based on Silver-Doped Con A Hydrogel and Laser Direct Writing. Polymers. 2023; 15(6):1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061423
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yulin, Dasheng Yang, Hongbo Zhang, Yang Gao, Wenjun Zhang, and Ruixue Yin. 2023. "A High-Linearity Glucose Sensor Based on Silver-Doped Con A Hydrogel and Laser Direct Writing" Polymers 15, no. 6: 1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061423
APA StyleHu, Y., Yang, D., Zhang, H., Gao, Y., Zhang, W., & Yin, R. (2023). A High-Linearity Glucose Sensor Based on Silver-Doped Con A Hydrogel and Laser Direct Writing. Polymers, 15(6), 1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061423







