The 3D Printing of Novel Honeycomb–Hollow Pyramid Sandwich Structures for Microwave and Mechanical Energy Absorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
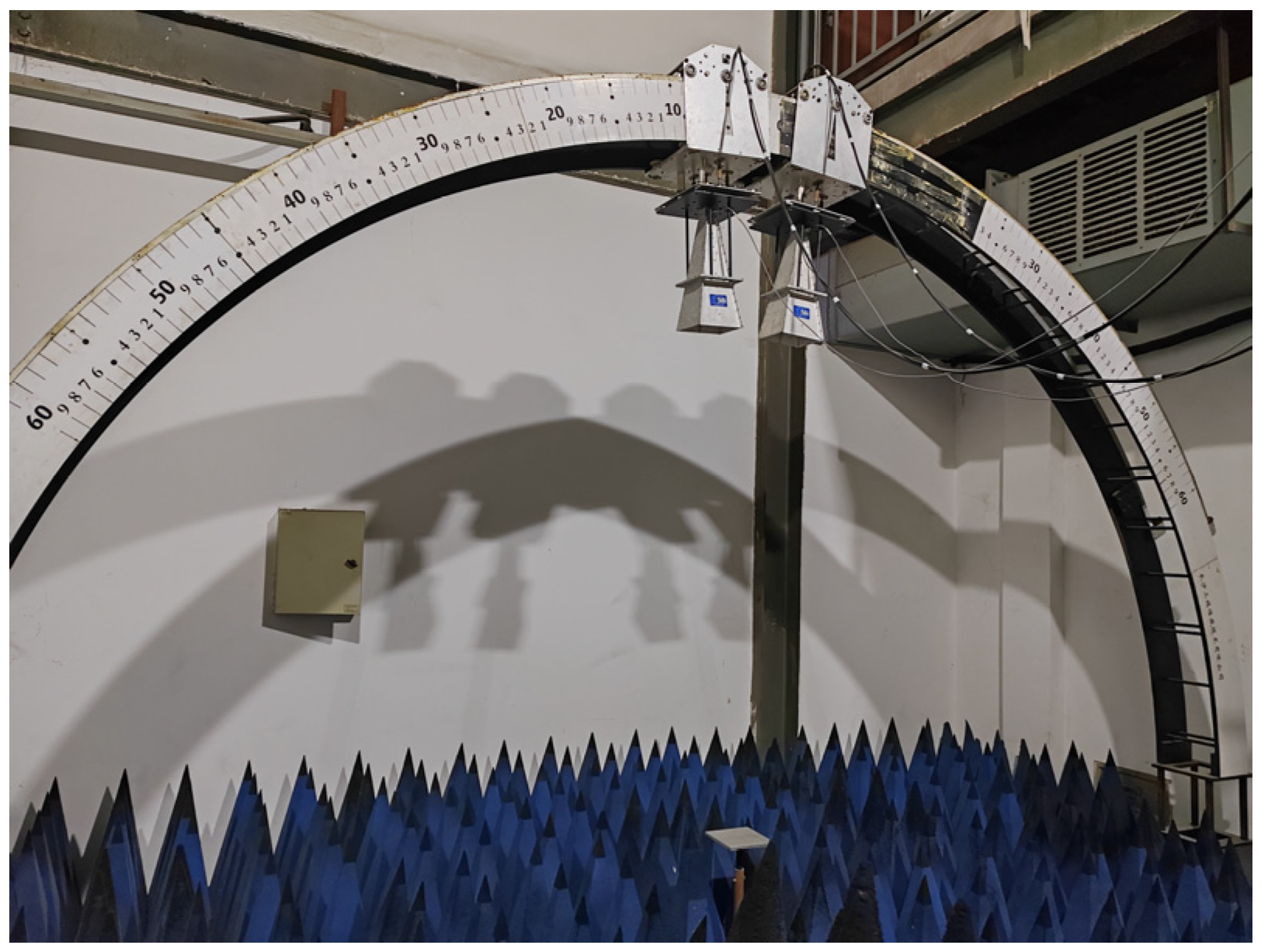
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
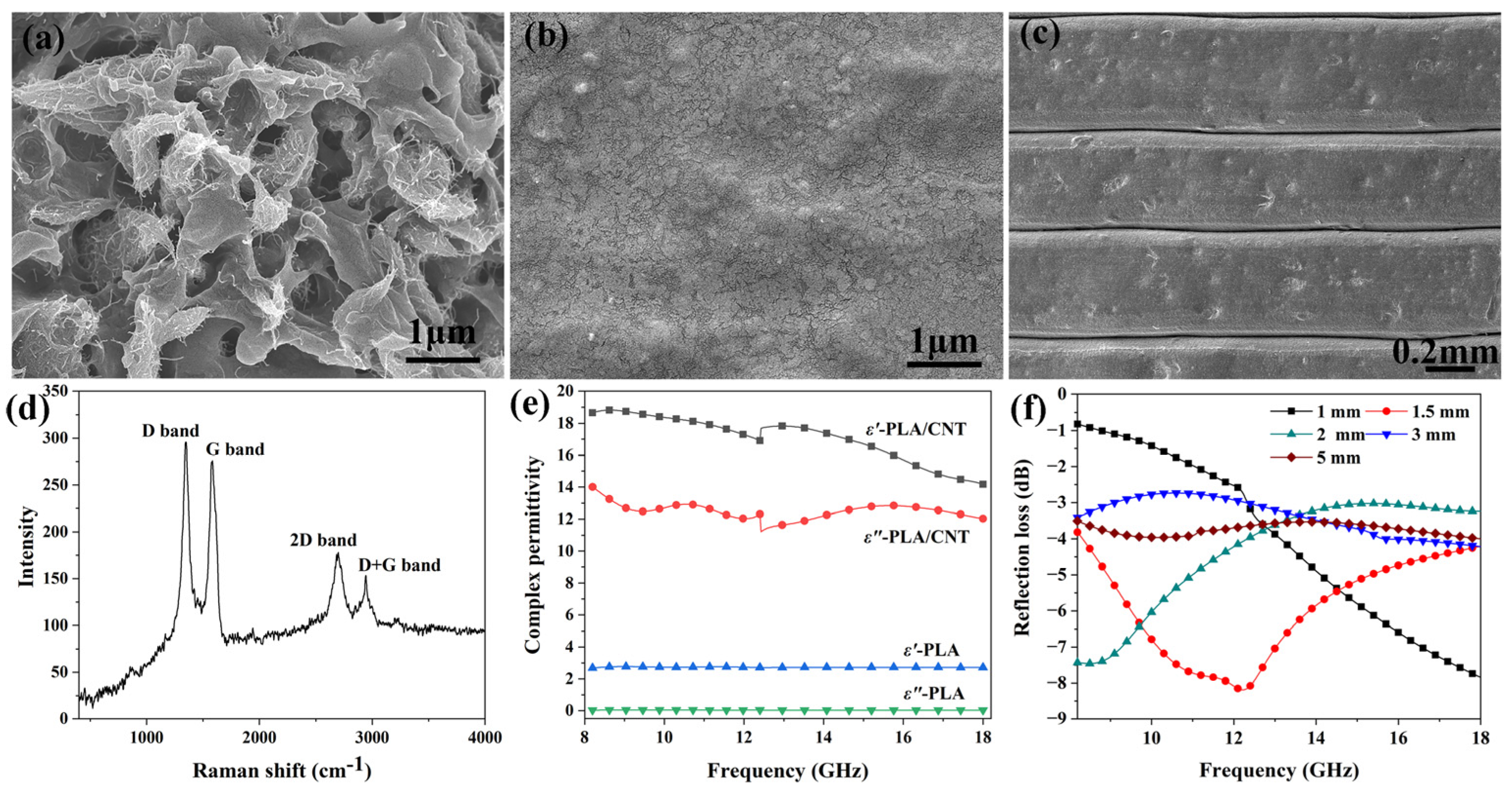
3.1. Microstructure and Electromagnetic Characterization of PLA/CNT Composites
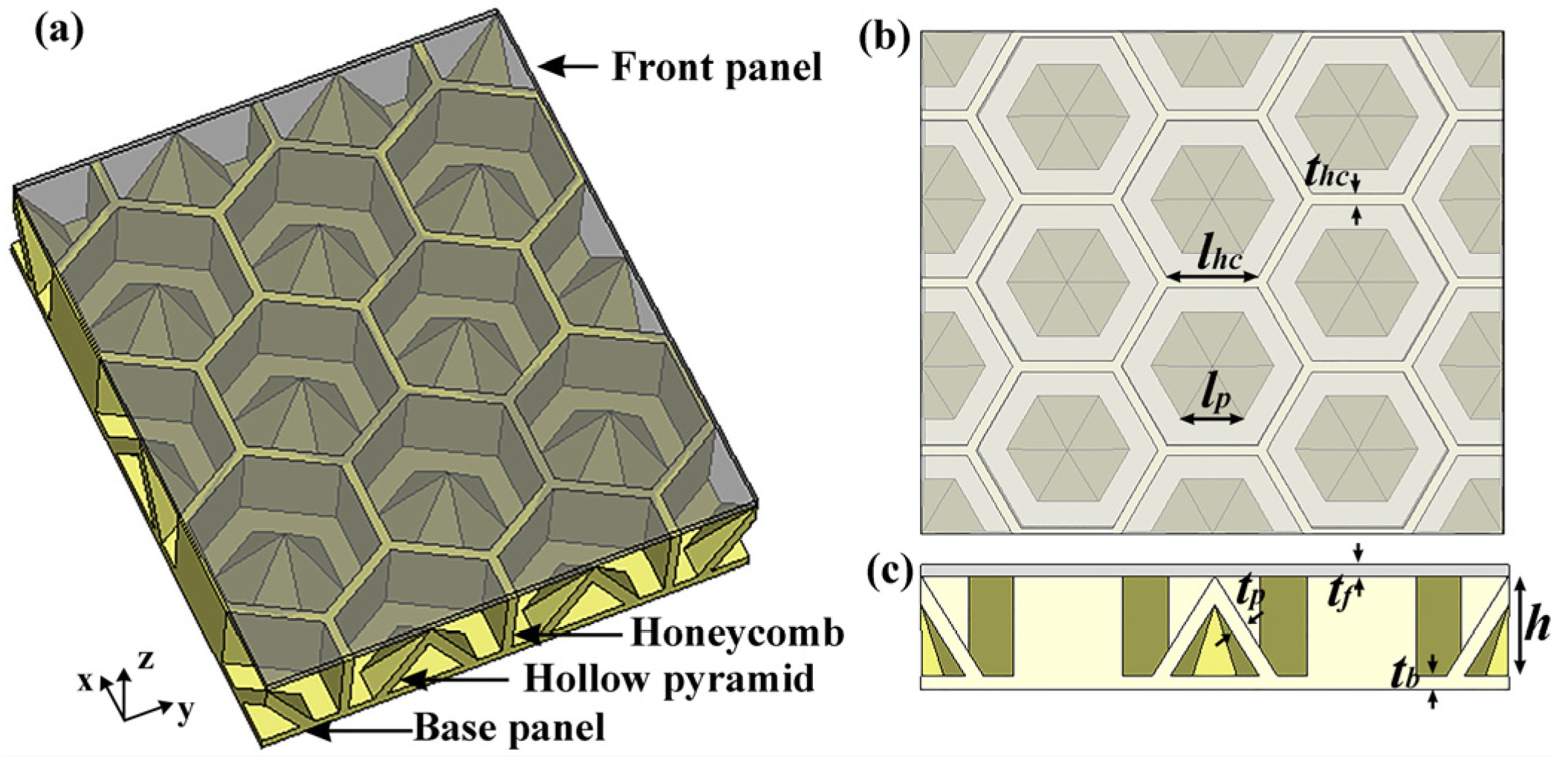
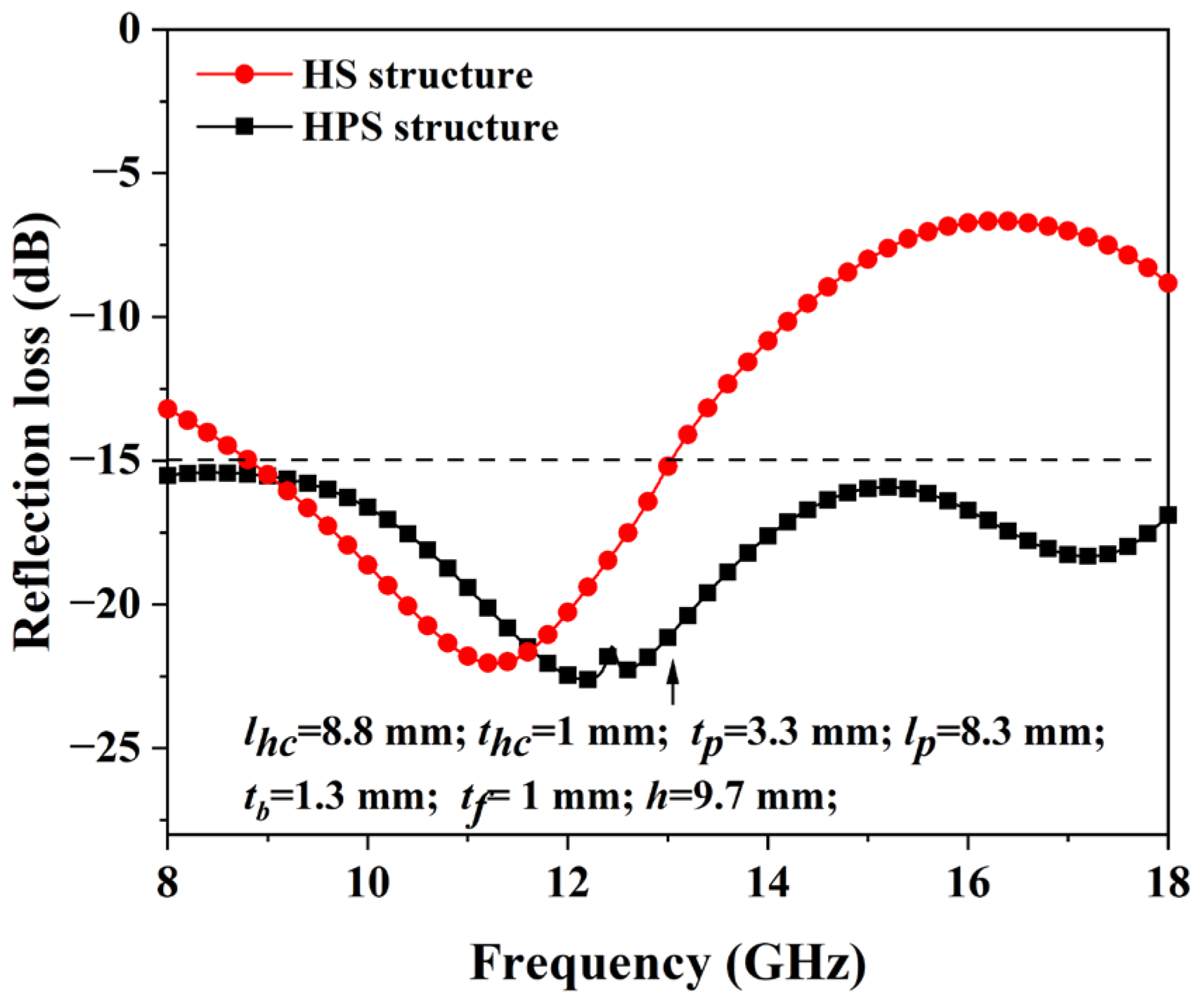
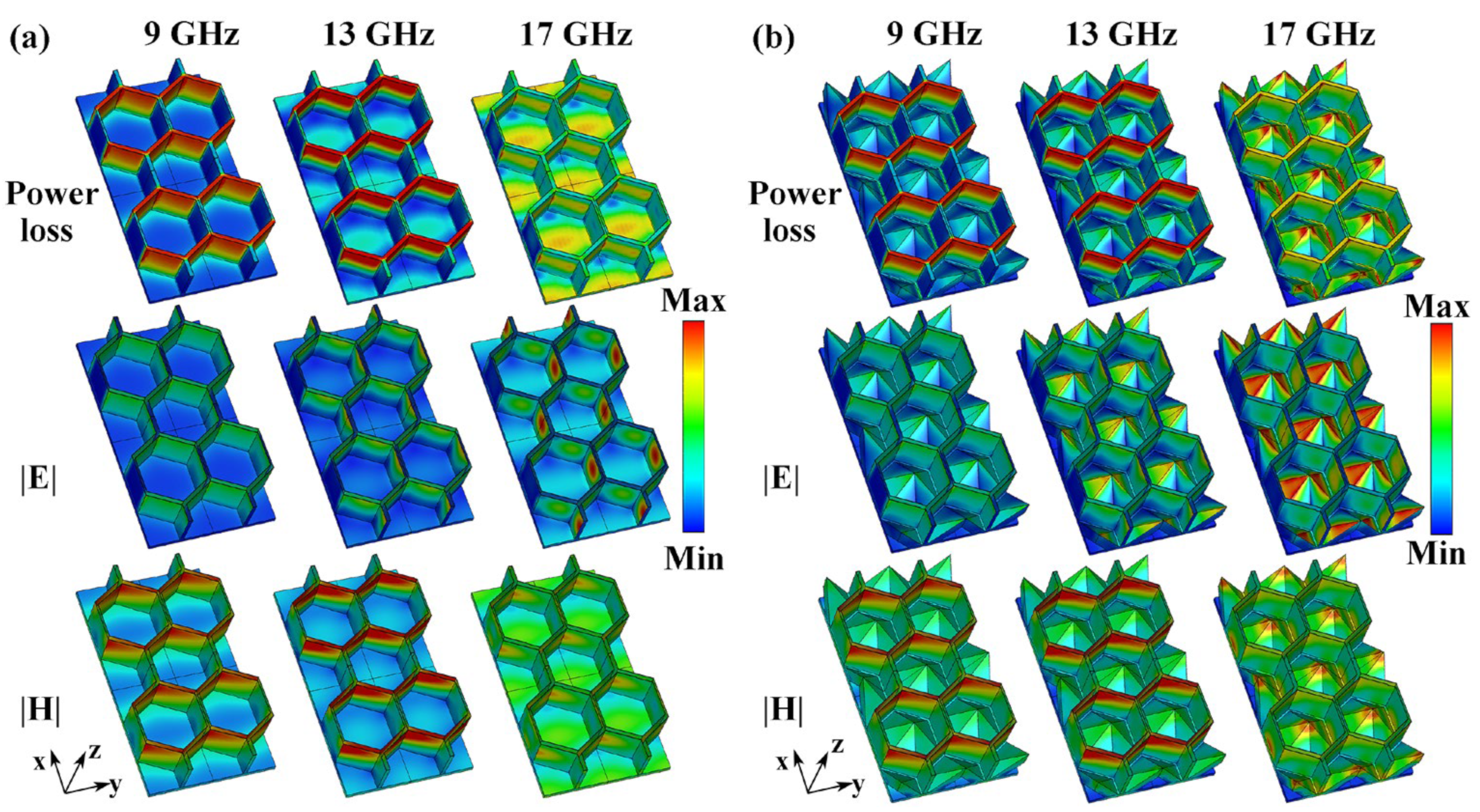
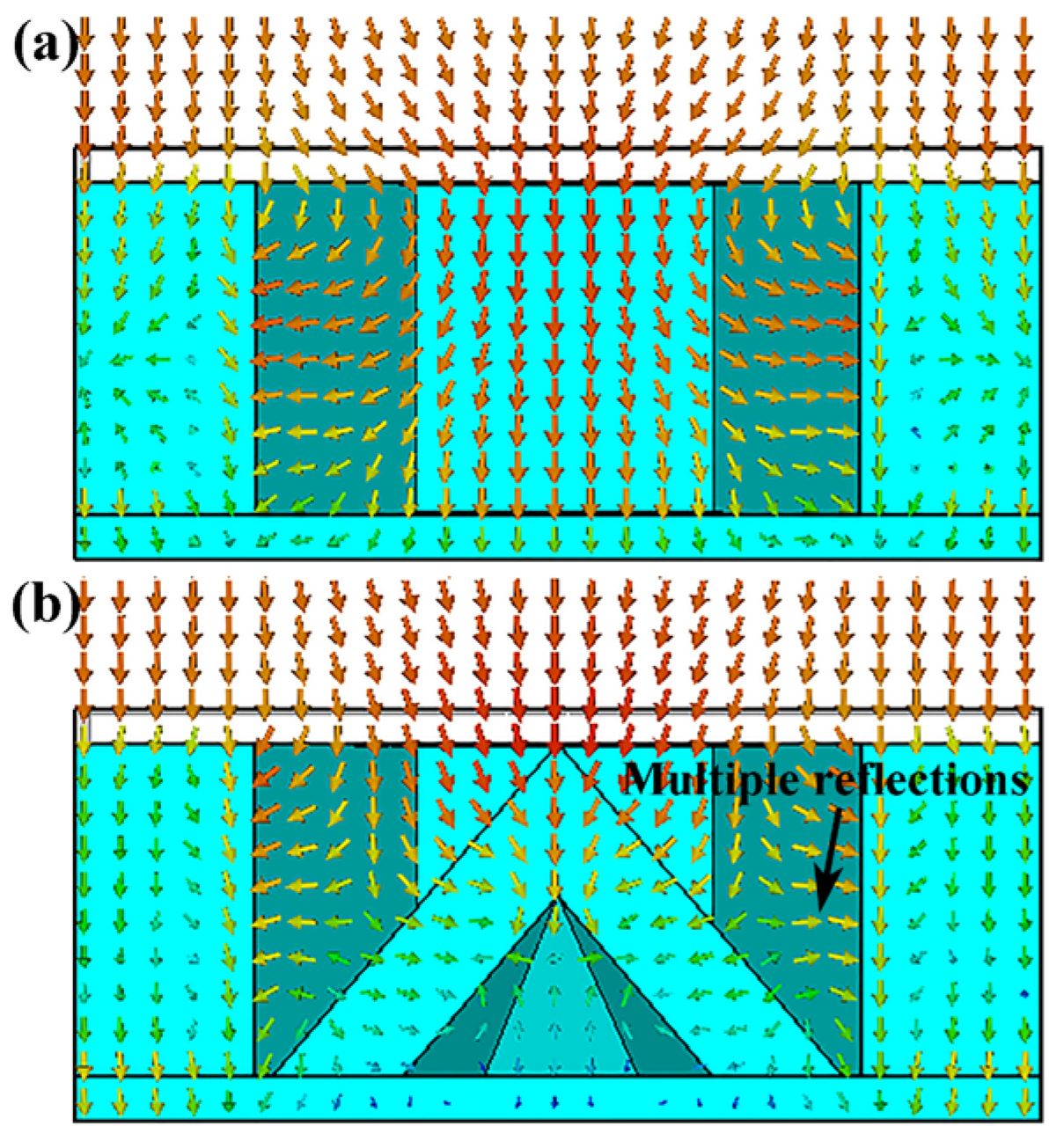
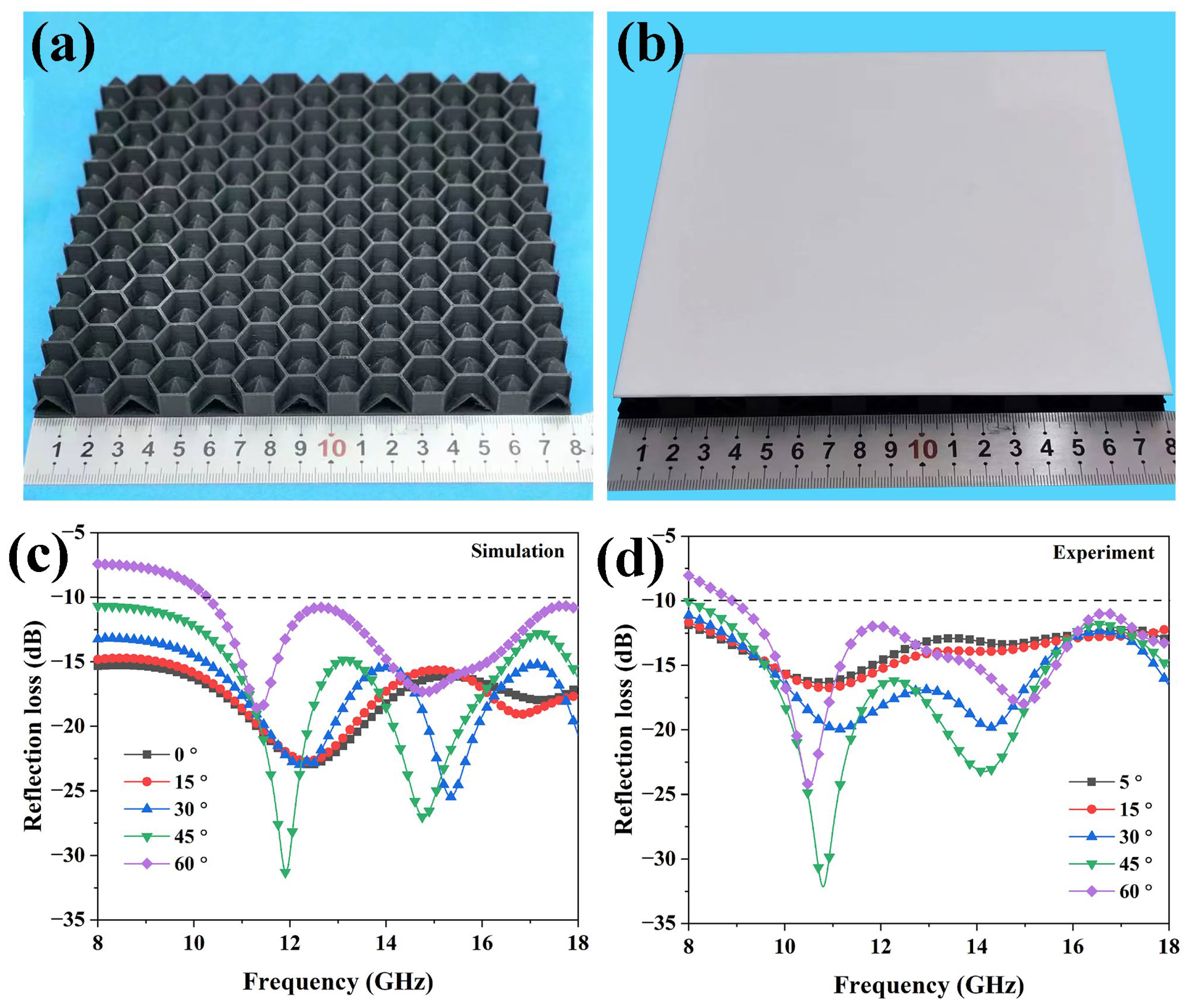
3.2. Microwave Absorption Performance of the HPS Structure
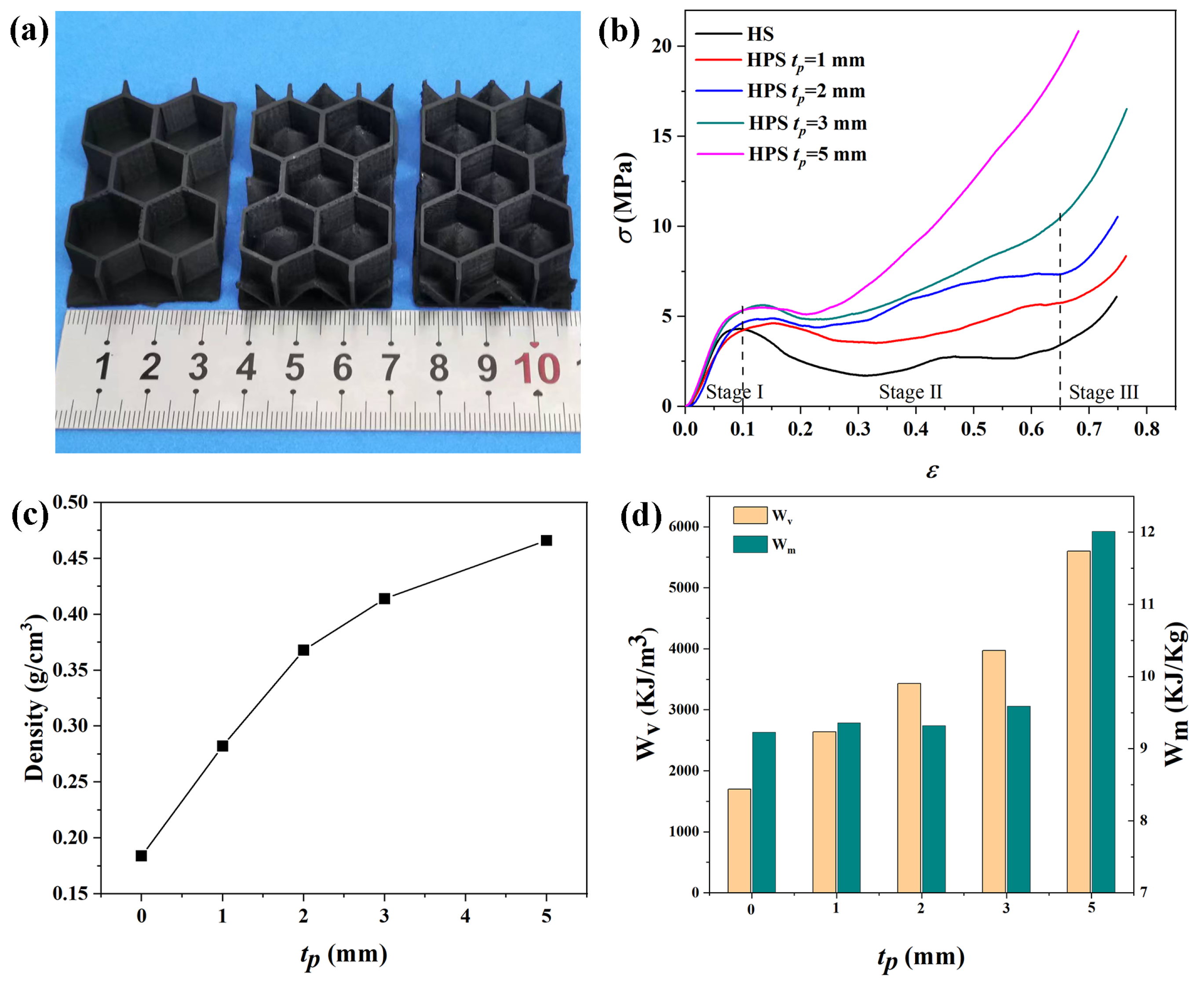
3.3. Mechanical Property of Honeycomb-Pyramid Structure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qi, C.; Jiang, F.; Yang, S. Advanced honeycomb designs for improving mechanical properties: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 227, 109393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, L.; Zhang, W.; Su, P.; Han, B.; Guo, S. Metallic tube-reinforced aluminum honeycombs: Compressive and bending performances. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 171, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanie, B.; Bouvet, C.; Ginot, M. Review of composite sandwich structure in aeronautic applications. Compos. C Open Access 2020, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Gong, Y.; Ying, Y.; Yu, J.; Zheng, J.; Qiao, L.; Che, S. Investigating the effect of honeycomb structure composite on microwave absorption properties. Compos. Commun. 2020, 19, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Jang, M.; Choi, J.; Jang, W.; Choi, W.; Kim, C. Multi-slab hybrid radar absorbing structure containing short carbon fiber layer with controllable permittivity. Compos. Struct. 2021, 273, 114279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Kim, C. Broadband microwave-absorbing honeycomb structure with novel design concept. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 83, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wen, K.; Su, X.; Liang, C.; Duan, H.; Zhao, G. Optimization design of a novel microwave absorbing honeycomb sandwich structure filled with magnetic shear-stiffening gel. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 232, 109883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollen, P.; Quiévy, N.; Huynen, I.; Bailly, C.; Detrembleur, C.; Thomassin, J.M.; Pardoen, T. Multifunctional architectured materials for electromagnetic absorption. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollen, P.; Quievy, N.; Detrembleur, C.; Thomassin, J.M.; Monnereau, L.; Bailly, C.; Huynen, I.; Pardoen, T. Processing of a new class of multifunctional hybrid for electromagnetic absorption based on a foam filled honeycomb. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanpour, J.; Beyraghi, S.; Oraizi, H. Reconfigurable honeycomb metamaterial absorber having incident angular stability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Duan, Y.; Dai, X.; Huang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X. The electromagnetic response of composition-regulated honeycomb structural materials used for broadband microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 88, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, N.I.; Sajuyigbe, S.; Mock, J.J.; Smith, D.R.; Padilla, W.J. Perfect Metamaterial Absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 207402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Pang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Pei, Z.; Qu, S. Origami-inspired metamaterial absorbers for improving the larger-incident angle absorption. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 445008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Chen, M.; Song, W.-L.; Chen, J.; Fan, Q.; Tang, L.; Fang, D. Ultrathin multifunctional carbon/glass fiber reinforced lossy lattice metastructure for integrated design of broadband microwave absorption and effective load bearing. Carbon 2019, 144, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Cui, Y.; Ge, X.; Jin, Y.; He, S. Ultra-broadband microwave metamaterial absorber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 103506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Song, W.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, M.; Tang, L.; Fang, D. Multi-scale design of electromagnetic composite metamaterials for broadband microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 162, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaaslan, M.; Bağmancı, M.; Ünal, E.; Akgol, O.; Sabah, C. Microwave energy harvesting based on metamaterial absorbers with multi-layered square split rings for wireless communications. Opt. Commun. 2017, 392, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Long, C.; Li, J.; Zhu, H.; Chen, L.; Guan, J.; Li, X. Ultra-wideband microwave absorber by connecting multiple absorption bands of two different-sized hyperbolic metamaterial waveguide arrays. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Kang, F.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, H.; Ding, H. An ‘H’-shape three-dimensional meta-material used in honeycomb structure absorbing material. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 118, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Lim, S. Perforated Lightweight Broadband Metamaterial Absorber Based on 3D Printed Honeycomb. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 2379–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Si, K.; Zha, D.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Miao, L.; Bie, S.; Jiang, J. Broadband Microwave Absorption Properties of a Frequency-Selective Surface Embedded in a Patterned Honeycomb Absorber. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2021, 63, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Gou, J.; Hui, D. 3D printing of polymer matrix composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 110, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laur, V.; Maalouf, A.; Chevalier, A.; Comblet, F. Three-Dimensional Printing of Honeycomb Microwave Absorbers: Feasibility and Innovative Multiscale Topologies. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2021, 63, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Suetake, K. Application of Ferrite to Electromagnetic Wave Absorber and its Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory. Tech. 1971, 19, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; You, W.; Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Che, R. 3D Seed-Germination-Like MXene with In Situ Growing CNTs/Ni Heterojunction for Enhanced Microwave Absorption via Polarization and Magnetization. Nanomicro. Lett. 2021, 13, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Duan, Y.; Liu, J.; Pang, H.; Huang, L.; Ma, X.; Shi, Y.; Ma, B. Polarization insensitive hierarchical metamaterial for broadband microwave absorption with multi-scale optimization and integrated design. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 228, 109643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidi, A.; Rajabalipanah, H.; Abdolali, A.; Cheldavi, A. A honeycomb-like three-dimensional metamaterial absorber via super-wideband and wide-angle performances at millimeter wave and low THz frequencies. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.; Leite, M.; Biswal, B.B.; Niu, X.; Garg, A. Experimental and numerical modelling of mechanical properties of 3D printed honeycomb structures. Measurement 2018, 116, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Cao, Y. Wide-angle microwave absorption properties of multilayer metamaterial fabricated by 3D printing. Mater. Lett. 2020, 281, 128571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, T.; Kanahashi, H.; Miyoshi, T.; Mabuchi, M.; Nieh, T.G.; Higashi, K. Experimental study of energy absorption in a close-celled aluminum foam under dynamic loading. Scr. Mater. 1999, 40, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, X.; Cai, P.; Liu, J.; Yao, H.; Zhang, L.; Duan, J. Mechanical metamaterials made of freestanding quasi-BCC nanolattices of gold and copper with ultra-high energy absorption capacity. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, X. Effect of Absorbent Foam Filling on Mechanical Behaviors of 3D-Printed Honeycombs. Polymers 2020, 12, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J. The 3D Printing of Novel Honeycomb–Hollow Pyramid Sandwich Structures for Microwave and Mechanical Energy Absorption. Polymers 2023, 15, 4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244719
Li Q, Wang Z, Wang X, Wang Y, Yang J. The 3D Printing of Novel Honeycomb–Hollow Pyramid Sandwich Structures for Microwave and Mechanical Energy Absorption. Polymers. 2023; 15(24):4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244719
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Quan, Zhicheng Wang, Xueyang Wang, Yang Wang, and Jian Yang. 2023. "The 3D Printing of Novel Honeycomb–Hollow Pyramid Sandwich Structures for Microwave and Mechanical Energy Absorption" Polymers 15, no. 24: 4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244719
APA StyleLi, Q., Wang, Z., Wang, X., Wang, Y., & Yang, J. (2023). The 3D Printing of Novel Honeycomb–Hollow Pyramid Sandwich Structures for Microwave and Mechanical Energy Absorption. Polymers, 15(24), 4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244719




