Polyolefin Blends with Selectively Crosslinked Disperse Phase Based on Silane-Modified Polyethylene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
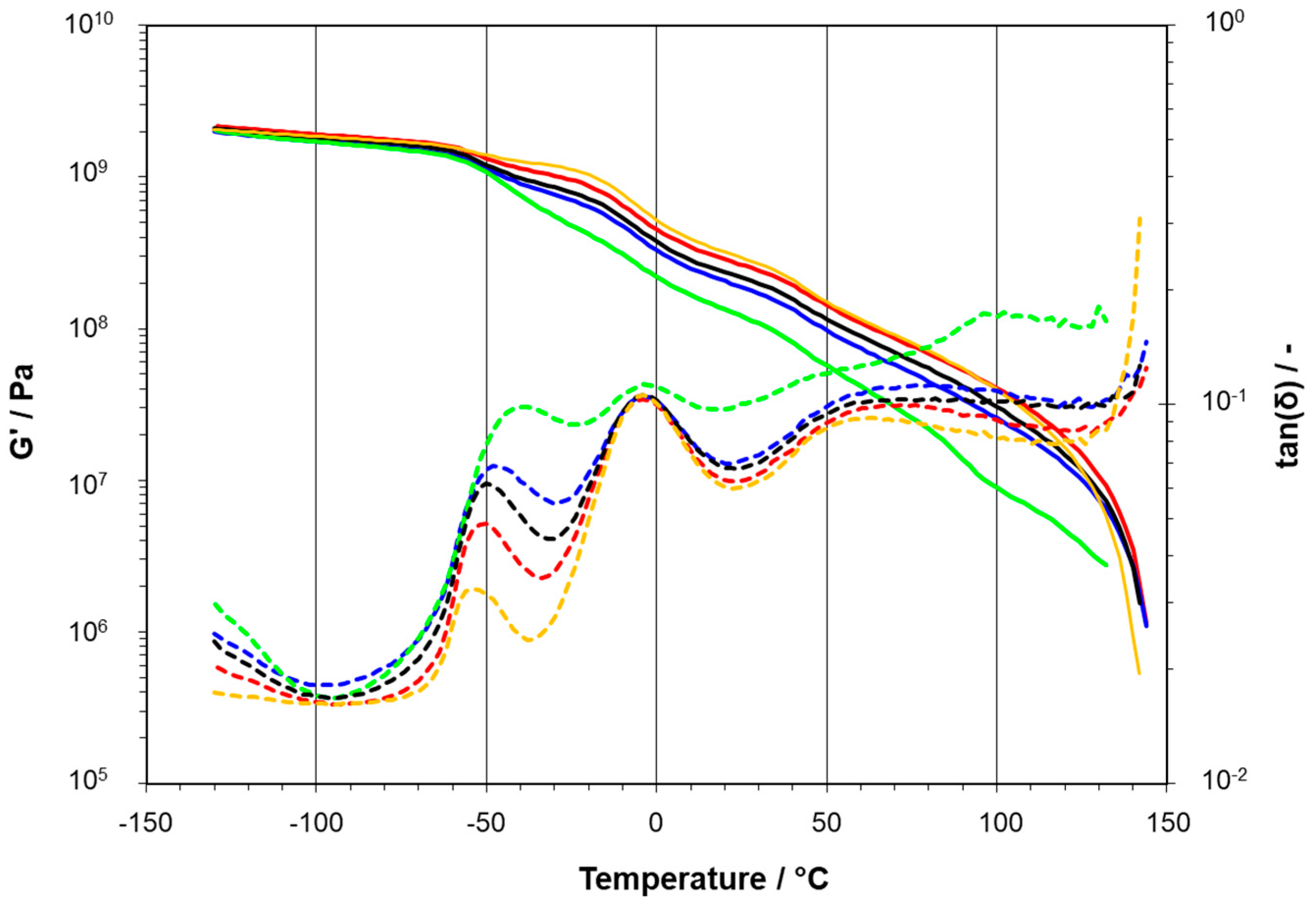
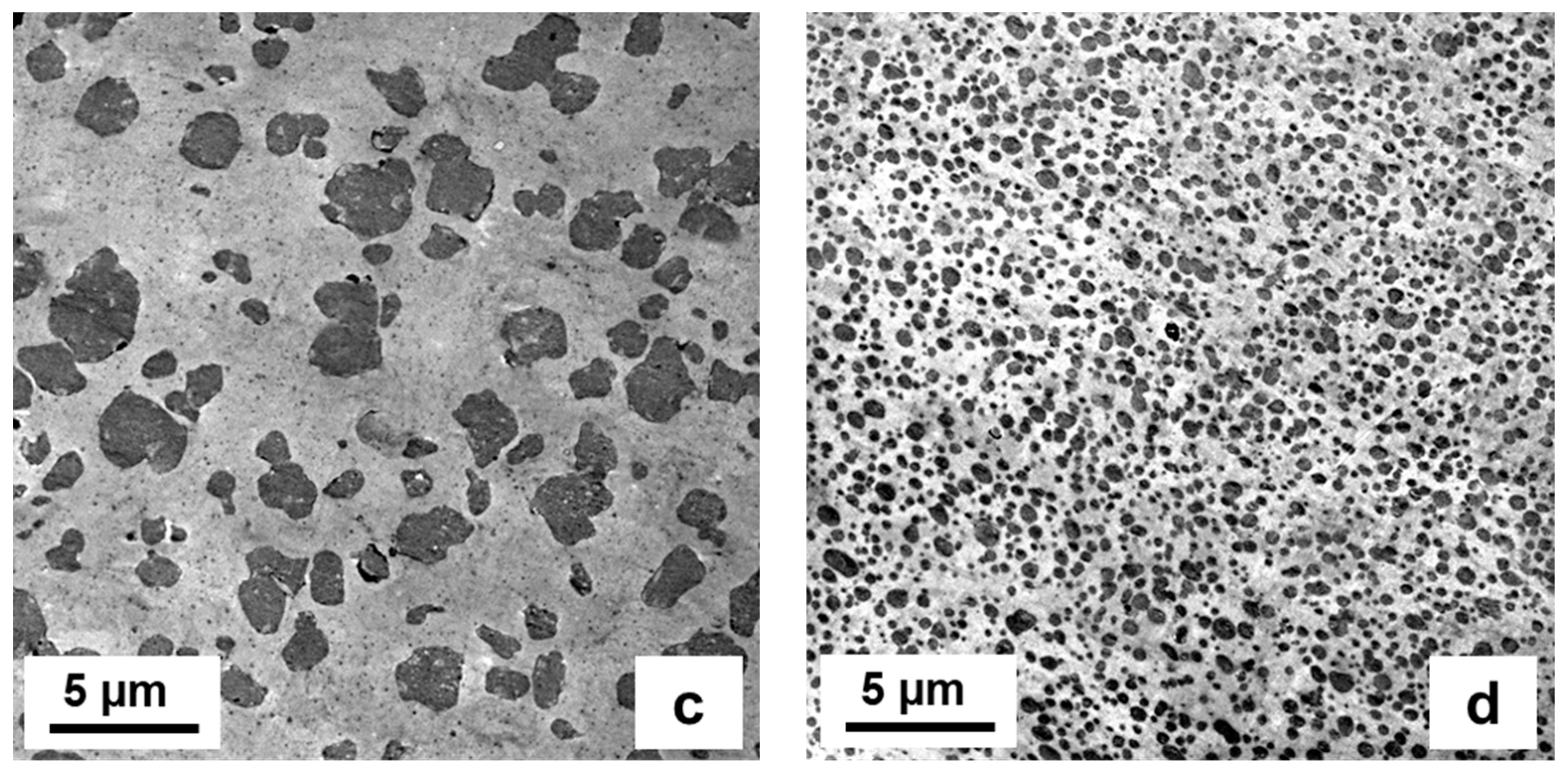
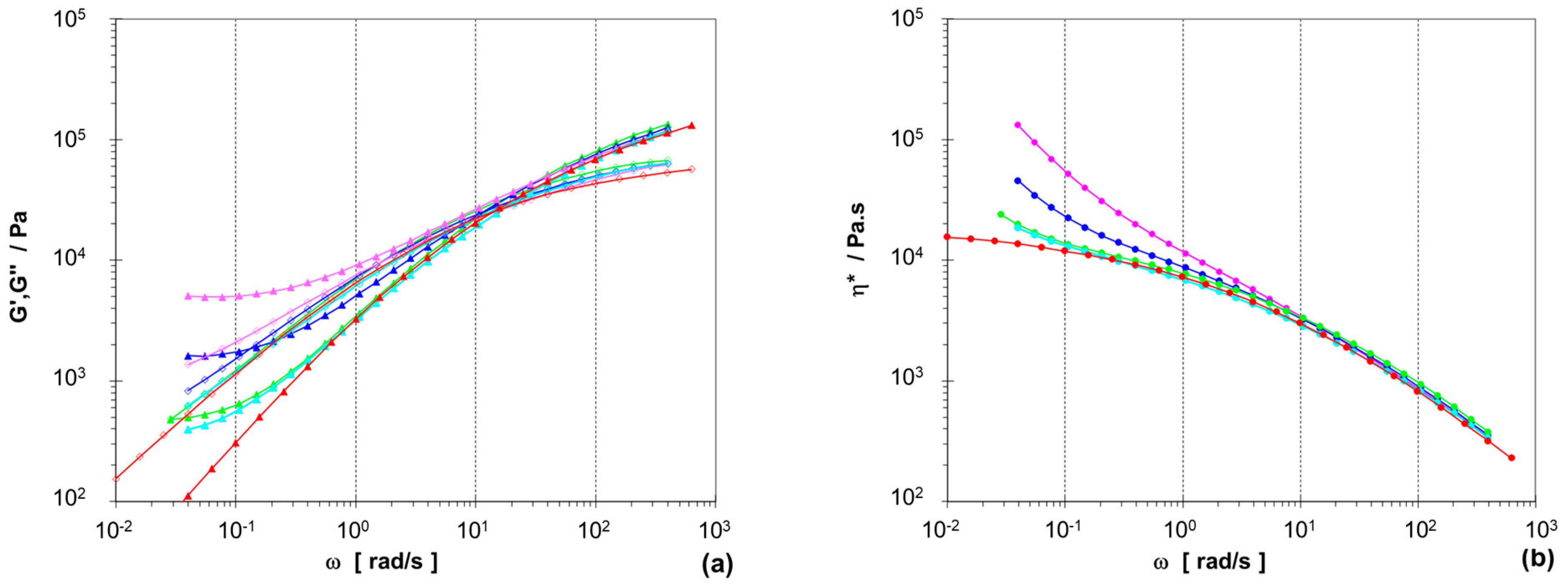
3.1. Two-Phase Compositions
3.2. Three-Phase Compositions
- ●
- ●
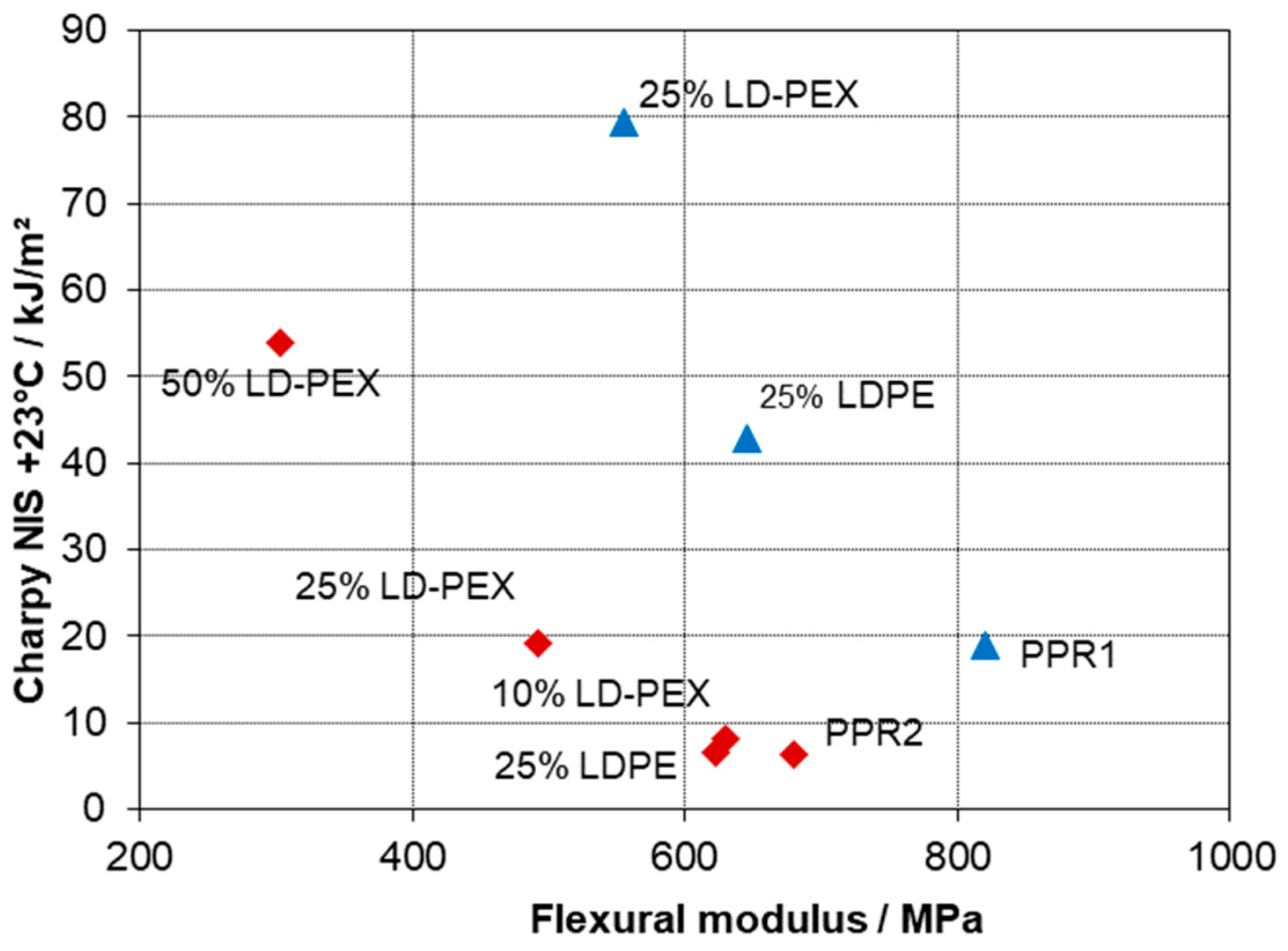
- Despite the higher absolute toughness levels reached for PPRI-based blends with LD-PEX, the relative improvement is higher for PPR-base.
4. Conclusions and Outlook
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doshev, P.; Lach, R.; Lohse, G.; Heuvelsland, A.; Grellmann, W.; Radusch, H.-J. Fracture characteristics and deformation behavior of heterophasic ethylene–propylene copolymers as a function of the dispersed phase composition. Polymer 2005, 46, 9411–9422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahleitner, M.; Doshev, P.; Tranninger, C. Heterophasic copolymers of polypropylene–Development, design principles and future challenges. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3028–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grellmann, W.; Langer, B. (Eds.) Deformation and Fracture Behaviour of Polymer Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabella, F.M. Phase separation and the Kinetics of Phase Coarsening in Commercial Impact Polypropylene Copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 1994, 32, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Mouzakis, D.E. Effects of Injection Molding-Induced Morphology on the Work of Fracture Parameters in Rubber-Toughened Polypropylenes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1999, 39, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, M.; Rharbi, Y.; Chen, W.; Tong, J.-D.; Winnik, M.A.; Thurman, D.W.; Oberhauser, J.P.; Kornfield, J.A.; Ryntz, R.A. Stratified morphology of a polypropylene/elastomer blend following channel flow. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2002, 40, 2842–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grestenberger, G.; Potter, G.D.; Grein, C. Polypropylene/ethylene-propylene rubber (PP/EPR) blends for the automotive industry: Basic correlations between EPR-design and shrinkage. Expr. Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.; Alex, R.; Kuriakose, B. Natural rubber–isotactic polypropylene thermoplastic blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 2063–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasador, F.R.; Rojas, G.J.A.; Pessan, L.A. Thermoplastic Elastomers Based on Natural Rubber/Polypropylene Blends: Effect of Blend Ratios and Dynamic Vulcanization on Rheological, Thermal, Mechanical, and Morphological Properties. J. Macromol. Sci. B 2012, 52, 1142–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Konar, B.B. Cure characteristics of ethylene propylene diene rubber-polypropylene blends. I. Calculation of state of cure in blends containing conventional sulfur curing system under variable time-temperature conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 66, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naskar, K. Thermoplastic Elastomers Based on PP/EPDM Blends by Dynamic Vulcanization. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2007, 80, 504–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T. Selective crosslinking in polymer blends. II. Its effect on impact strength and other mechanical properties of polypropylene/unsaturated elastomer blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 54, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Sugimoto, M.; Inoune, T. Mechanism of toughening for polypropylene blended with ethylene–propylene–diene rubber following selective crosslinking. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 62, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellul, M.D.; Tsou, A.H.; Hu, W. Crosslink densities and phase morphologies in thermoplastic vulcanizates. Polymer 2004, 45, 3351–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.A.L.; van Duin, M.; Spoelstra, A.B.; Goossens, J.G.P. The rubber particle size to control the properties-processing balance of thermoplastic/cross-linked elastomer blends. Soft Matter. 2010, 6, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharescu, T.; Setnescu, R.; Jipa, S.; Setnescu, T. Radiation processing of polyolefin blends. I. Crosslinking of EPDM–PP blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 77, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharescu, T.; Chipară, M.; Postolache, M. Radiation processing of polyolefin blends. II. Mechanical properties of EPDM-PP blends. Polym. Deg. Stab. 1999, 66, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Do, I.H. Effect of viscosity ratio, rubber composition, and peroxide/coagent treatment in PP/EPR blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 61, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, I.H.; Yoon, L.K.; Kim, B.K.; Jeong, H.M. Effect of viscosity ratio and peroxide/coagent treatment in PP/EPR/PE ternary blends. Eur. Polym. J. 1996, 32, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsig, E.; Fiedlerová, A.; Rychlá, L.; Lazár, M.; Rätzsch, M.; Haudel, G. Crosslinking of polypropylene–polyethylene blends by peroxide and the effect of pentaerythritol tetrallyl ether. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1989, 37, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettema, R.; Van Tol, J.; Janssen, L.P.B.M. In-situ reactive blending of polyethylene and polypropylene in co-rotating and counter-rotating extruders. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1999, 39, 1628–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.-M.; Chiu, F.-C.; Chiu, T.-Y. Fracture behaviors of PP/mPE thermoplastic vulcanizate via peroxide crosslinking. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 3031–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Chen, X.; He, B. Studies on rheology and morphology of POE/PP thermoplastic elastomer dynamically crosslinked by peroxide. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 14, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.; Chen, R.; Jin, L.; Zheng, Q. Study on degradation and crosslinking of impact polypropylene copolymer by dynamic rheological measurement. Polymer 2010, 51, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Gahleitner, M. Interfacial strengthening of high-impact polypropylene compounds by reactive modification. Compos. Interf. 2005, 12, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Dong, J.-Y. Simultaneous cross-linking as a way to control physical growth of random ethylene-propylene copolymer during formation of high-impact polypropylene. Polymer 2016, 85, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-J.; Wang, L.; Hong, L.-T.; Qin, Y.-W.; Dong, J.-Y. Particle Morphology Control of Polypropylene Heterophasic Copolymer at Increased EPR Content by Simultaneous Cross-linking. Acta Polym. Sin. 2020, 51, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grein, C.; Bernreitner, K.; Hauer, A.; Gahleitner, M.; Neißl, W. Impact modified isotatic polypropylene with controlled rubber intrinsic viscosities: Some new aspects about morphology and fracture. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grein, C.; Gahleitner, M.; Knogler, B.; Nestelberger, S. Melt viscosity effects in Ethylene-Propylene Copolymers. Rheol. Acta 2007, 46, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutomo, I.; Mitsugo, I.; Takeo, S.; Takayuki, I. Crosslinkable Polyethylene Resin Compositions. US Patent 4413066 A, 1 November 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Hjertberg, T.; Palmlöf, M.; Sultan, B.-Å. Chemical reactions in crosslinking of copolymers of ethylene and vinyltrimethoxy silane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 42, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.K.; Mukherjee, B.A.S.; De Bhattacharyya, P.P.; Bhowmick, A.K. Kinetics of Silane Grafting and Moisture Crosslinking of Polyethylene and Ethylene Propylene Rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1992, 44, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celina, M.; George, G.A. Characterisation and degradation studies of peroxide and silane crosslinked polyethylene. Polym. Deg. Stab. 1995, 48, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, H.G.; Bölz, U.; Cai, Q. Innovative TPV two-phase polymers: Formulation, morphology formation, property profiles and processing characteristics. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1999, 39, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J.A.; Royer, J.R.; Hwang, C.R.; Khan, S.A. Tailored Rheology of a Metallocene Polyolefin through Silane Grafting and Subsequent Silane Crosslinking. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2000, 38, 2468–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmlöf, M.; Ek, C.-G.; Röhne, G. Method for Cross-Linking a Polymer Article. European Patent EP 1256593 A1, 13 November 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gahleitner, M.; Hauer, A.; Bernreitner, K.; Ingolic, E. Polypropylene-based model compounds as tools for the development of high-impact ethylene-propylene copolymers. Int. Polym. Proc. 2002, 17, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulik, C.; Tranninger, C.; Wang, J.; Shutov, P.; Mileva, D.; Gahleitner, M. Catalyst type effects on structure/property relations of polypropylene random copolymers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2021, 222, 2100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimke, K.; Doshev, P.; Filipe, S.; Tran, A.T. Heterophasic Polypropylene Resin with Long Chain Branching. European Patent EP 2319885 A1, 11 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 16152:2022; Plastics—Determination of Xylene-Soluble Matter in Polypropylene. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- ISO 11357-3:2018; Plastics—Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), Part 3: Determination of Temperature and Enthalpy of Melting and Crystallization. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Palmlöf, M.; Hjertberg, T. Catalysis of the crosslinking reactions of ethylene vinyl silane copolymers using carboxylic acids and DBTDL. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 72, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshedian, J.; Hoseinpour, P.M. Polyethylene Cross-linking by Two-step Silane Method: A Review. Iran. Polym. J. 2009, 18, 103–128. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 6721-1:2019; Plastics—Determination of Dynamic Mechanical Properties, Part 1: General Principles. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- ISO 6721-10:2015; Plastics—Determination of Dynamic Mechanical Properties, Part 10: Complex Shear Viscosity Using a Parallel-Plate Oscillatory Rheometer. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- ISO 6721-7:2019; Plastics—Determination of Dynamic Mechanical Properties, Part 7: Torsional Vibration. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Lin, J.-C.; Huang, Y.; Harris, J.; Weinlander, B.; Jones, M.A. Three Dimensional Microstructure Characterization of Polypropylene Blends. Microsc. Microanal. 2017, 23, 1786–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 19069-2:2016; Plastics—Polypropylene (PP) Moulding and Extrusion Materials, Part 2: Preparation of Test Specimens and Determination of Properties. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- ISO 527-2:2012; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties, Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastics. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- ISO 178:2019; Plastics—Determination of Flexural Properties. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- ISO 179-1:2010. Plastics—Determination of Charpy Impact Properties, Part 1: Non-Instrumented Impact Test. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- ISO 75-1:2020; Plastics—Determination of Temperature of Deflection Under Load, Part 1: General Test Method. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Tai, C.M.; Li, R.K.Y.; Ng, C.N. Impact behaviour of polypropylene/polyethylene blends. Polym. Test. 2000, 19, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strapasson, R.; Amico, S.C.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Sydenstricker, T.H.D. Tensile and impact behavior of polypropylene/low density polyethylene blends. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofokeng, T.G.; Ojijo, V.; Ray, S.S. The Influence of Blend Ratio on the Morphology, Mechanical, Thermal, and Rheological Properties of PP/LDPE Blends. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.M.C.; Demarquette, N.R. Influence of coalescence and interfacial tension on the morphology of PP/HDPE compatibilized blends. Polymer 2002, 43, 3959–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Aprem, A.S.; Francis, B.; Chandy, M.C.; Werner, P.; Alstaedt, V.; Thomas, S. Phase morphology, crystallisation behaviour and mechanical properties of isotactic polypropylene/high density polyethylene blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 2105–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, C.; Gahleitner, M.; Schausberger, A.; Ingolic, E. Polypropylene/polyethylene blends as models for high-impact propylene-ethylene copolymers. 1: Interaction between rheology and morphology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 1484–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, C.; Aust, N.; Grein, C.; Gahleitner, M. Polypropylene/polyethylene blends as models for high-impact propylene-ethylene copolymers. 2: Relation between composition and mechanical performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, L.; Greco, R.; Mancarella, C.; Martuscelli, E.; Ragosta, G.; Silvestre, C. Effect of the addition of ethylene-propylene random copolymers on the properties of high-density polyethylene/isotactic polypropylene blends: Part 1–Morphology and impact behavior of molded samples. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1982, 22, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, L. Structure and properties of PP/POE/HDPE blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 121, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Kim, S.-D.; Choi, W.; Chun, Y.S. Morphology and Stress Whitening of Heterophasic Poly (propylene) Copolymer / High Density Polyethylene Blends. Macromol. Symp. 2012, 312, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Miao, X.; Guo, M.; Song, W.; Shao, J. Influence of the HDPE molecular weight and content on the morphology and properties of the impact polypropylene copolymer/HDPE blends. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 80297–80306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi-Mazidi, M.; Sharifi, H. Post-consumer recycled high density polyethylene/polypropylene blend with improved overall performance through modification by impact polypropylene copolymer: Morphology, properties and fracture resistance. Polym. Int. 2021, 70, 1701–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranz-Andrés, J.; Benavente, R.; Peña, B.; Pérez, E.; Cerrada, M.L. Toughening of a propylene-b-(ethylene-co-propylene) copolymer by a plastomer. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2002, 40, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levij, M.; Maurer, F.H.J. Morphology and rheological properties of polypropylene-linear low density polyethylene blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1988, 28, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghijsels, A.; Ente, J.J.S.M.; Raadsen, J. Melt Strength Behavior of Polyethylene Blends. Int. Polym. Proc. 1992, 7, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, L.; Mancarella, C.; Martuscelli, E.; Cecchin, G.; Corrieri, R. Isotactic polypropylene/ethylene-co-propylene blends: Effects of the copolymer microstructure and content on rheology, morphology and properties of injection moulded samples. Polymer 1999, 40, 2745–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, G.; Beccarini, E.; Caputo, T.; Fritze, C.; Massari, P.; Agnoletto, D.; Pitteri, S. Recent Technical Advances in Polypropylene. J. Plast. Film Sheet. 2009, 25, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvanimoghaddam, K.; Balaji, K.V.; Yadav, R.; Zabihi, O.; Ahmadi, M.; Adetunji, P.; Naebe, M. Balancing the toughness and strength in polypropylene composites. Compos. B Eng. 2021, 223, 109121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Gahleitner, M. Polypropylene Composition with Selective Cross-Linkable Dispersed Phase. European Patent EP 1834987 A1, 19 September 2007. [Google Scholar]





| Type | Density | MFR 1 | C2 Total | XCS | Tm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg/m3 | g/10 min | wt.-% | wt.-% | °C | |
| PPR1 | 905 | 0.25 | 3.9 | 7.0 | 143 |
| PPR2 | 905 | 8.0 | 4.8 | 6.8 | 139 |
| PPI | 900 | 1.10 | 7.5 | 16.5 | 165 |
| PPRI | 900 | 1.00 | 9.5 | 23.0 | 143 |
| Type | Density | MFR 1 | VTMS 2 | Acrylate | Tm |
| kg/m3 | g/10 min | wt.-% | wt.-% | °C | |
| LD-PEX | 927 | 5.0 | 1.75 | 18 | 93 |
| LDPE | 929 | 3.0 | 0.00 | 0 | 115 |
| HD-PEX | 942 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0 | 128 |
| HDPE | 954 | 4.0 | 0.00 | 0 | 132 |
| Compound | Base | Modifier | MFR 1 | XHU | X-Linked 2 | DSC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm,PE | Hm,PE | Tm,PP | Hm,PP | Tc,PP | |||||||
| Type | Type | wt.-% | g/10 min | wt.-% | % | °C | J/g | °C | J/g | °C | |
| PPR1 | PPR1 | - | 0 | 0.25 | 0.0 | 0 | - | - | 143 | 95.6 | 106 |
| PPR1/LD-PEX25 | PPR1 | LD-PEX | 25 | 0.15 | 14.5 | 58 | 91 | 7.1 | 142 | 66.7 | 104 |
| PPR1/LDPE25 | PPR1 | LDPE | 25 | 0.60 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 114 | 51.0 | 142 | 42.2 | 102 |
| PPR1/HD-PEX05 | PPR1 | HD-PEX | 5 | 0.20 | 2.5 | 51 | 127 | 4.9 | 143 | 67.2 | 110 |
| PPR1/HD-PEX25 | PPR1 | HD-PEX | 25 | 0.15 | 17.7 | 59 | 128 | 47.1 | 144 | 36.7 | 114 |
| PPR1/HDPE25 | PPR1 | HDPE | 25 | 0.80 | 0.1 | 0 | 131 | 64.8 | 144 | 44.3 | 115 |
| PPR2 | PPR2 | - | 0 | 8.0 | 0.0 | 0 | - | - | 139 | 86.0 | 99 |
| PPR2/LD-PEX10 | PPR2 | LD-PEX | 10 | 6.5 | 4.9 | 49 | 92 | 0.6 | 140 | 81.1 | 99 |
| PPR2/LD-PEX25 | PPR2 | LD-PEX | 25 | 1.2 | 10.8 | 43 | 93 | 5.2 | 139 | 69.1 | 99 |
| PPR2/LD-PEX50 | PPR2 | LD-PEX | 50 | 0.20 | 22.2 | 44 | 93 | 41.8 | 138 | 36.7 | 98 |
| PPR2/LDPE25 | PPR2 | LDPE | 25 | 8.5 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 114 | 41.1 | 139 | 63.6 | 100 |
| Compound | Base | Modifier | MFR 1 | XHU | X-Linked 2 | DSC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm,PE | Hm,PE | Tm,PP | Hm,PP | Tc,PP | |||||||
| Type | Type | wt.-% | g/10 min | wt.-% | % | °C | J/g | °C | J/g | °C | |
| PPI | PPI | - | 0 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0 | 123 | 0.8 | 166 | 89.6 | 118 |
| PPI/HD-PEX25 | PPI | HD-PEX | 25 | 0.80 | 15.7 | 63 | 125 | 38.4 | 166 | 60.9 | 119 |
| PPI/HDPE25 | PPI | HDPE | 25 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 128 | 31.6 | 166 | 72.1 | 117 |
| PPRI | PPRI | - | 0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 111 | 0.8 | 143 | 65.3 | 102 |
| PPRI/LD-PEX10 | PPRI | LD-PEX | 10 | 0.50 | 3.6 | 36 | 92 | 1.2 | 144 | 54.4. | 125 |
| PPRI/LD-PEX25 | PPRI | LD-PEX | 25 | 0.13 | 9.2 | 37 | 92 | 8.2 | 144 | 43.1 | 126 |
| PPRI/LD-PEX50 | PPRI | LD-PEX | 50 | 0.05 | 19.1 | 38 | 92 | 22.9 | 143 | 12.2 | 126 |
| PPRI/LDPE25 | PPRI | LDPE | 25 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 112 | 6.9 | 143 | 56.6 | 117 |
| Compound | Tensile Test | Flexural | Charpy NIS ISO 179 1eA | HDT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modulus | Yield Stress | Strain at Break | Modulus | +23 °C | −20 °C | ISO75B | |
| MPa | MPa | wt.-% | MPa | kJ/m2 | °C | °C | |
| PPR1 | 890 | 24.5 | 320 | 820 | 19.0 | 2.0 | 65 |
| PPR1/LD-PEX25 | 540 | 18.9 | 580 | 555 | 80 | 5.8 | 59 |
| PPR1/LDPE25 | 635 | 20.5 | 333 | 646 | 43 | 1.2 | 61 |
| PPR1/HD-PEX05 | 841 | 25.9 | 379 | 849 | 19.9 | 1.5 | 70 |
| PPR1/HD-PEX25 | 751 | 24.1 | 465 | 763 | 88 | 3.5 | 68 |
| PPR1/HDPE25 | 854 | 24.5 | 374 | 836 | 14.3 | 1.1 | 69 |
| PPR2 | 730 | 23.0 | 212 | 680 | 6.2 | 1.2 | 60 |
| PPR2/LD-PEX10 | 603 | 19.2 | 582 | 630 | 8.2 | 1.9 | 59 |
| PPR2/LD-PEX25 | 482 | 16.1 | 724 | 492 | 19.2 | 2.0 | 55 |
| PPR2/LD-PEX50 | 310 | 11.9 | 531 | 302 | 54 | 4.9 | 48 |
| PPR2/LDPE25 | 624 | 19.4 | 383 | 622 | 6.5 | 1.0 | 59 |
| Compound | Tensile Test | Flexural | Charpy NIS ISO 179 1eA | HDT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modulus | Yield Stress | Strain at Break | Modulus | +23 °C | −20 °C | ISO75B | |
| MPa | MPa | wt.-% | MPa | kJ/m2 | °C | °C | |
| PPI | 1190 | 22.1 | 105 | 1100 | 35 | 3.8 | 73 |
| PPI/HD-PEX25 | 1068 | 25.3 | 129 | 1057 | 75 | 5.0 | 74 |
| PPI/HDPE25 | 1164 | 25.9 | 370 | 1091 | 42 | 3.6 | 76 |
| PPRI | 508 | 16.6 | 484 | 476 | 92 | 8.4 | 53 |
| PPRI/LD-PEX10 | 460 | 14.4 | 689 | 412 | 94 | 9.2 | 51 |
| PPRI/LD-PEX25 | 374 | 12.5 | 734 | 335 | 95 | 15.1 | 49 |
| PPRI/LD-PEX50 | 222 | -1 | 507 | 208 | 118 | 76 | 45 |
| PPRI/LDPE25 | 355 | 12.4 | 724 | 315 | 93 | 41 | 48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gahleitner, M.; Pham, T.; Machl, D. Polyolefin Blends with Selectively Crosslinked Disperse Phase Based on Silane-Modified Polyethylene. Polymers 2023, 15, 4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244692
Gahleitner M, Pham T, Machl D. Polyolefin Blends with Selectively Crosslinked Disperse Phase Based on Silane-Modified Polyethylene. Polymers. 2023; 15(24):4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244692
Chicago/Turabian StyleGahleitner, Markus, Tung Pham, and Doris Machl. 2023. "Polyolefin Blends with Selectively Crosslinked Disperse Phase Based on Silane-Modified Polyethylene" Polymers 15, no. 24: 4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244692
APA StyleGahleitner, M., Pham, T., & Machl, D. (2023). Polyolefin Blends with Selectively Crosslinked Disperse Phase Based on Silane-Modified Polyethylene. Polymers, 15(24), 4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244692







