Effect of Amino-Functionalized Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes on Structure-Property Relationships of Thermostable Hybrid Cyanate Ester Resin Based Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis Procedure
2.3. Characterization Techniques
| Name | Chemical Structure | Physical Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Dicyanate ester of bisphenol E, DCBE |  | M = 264 g·mol−1 Tm = 29 °C Tb > 240 °C = 1.18 g·cm−3 η = 75 mPa·s [2] |
| Aminopropylisobutyl POSS, APIB-POSS | 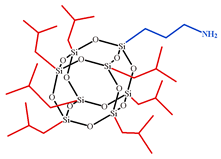 | M = 1.46 [78] |
| Aminoethyl aminopropylisobutyl POSS, AEAPIB-POSS | 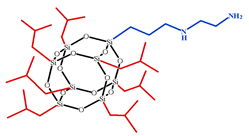 | M = 918 g·mol−1 = 1.50 [78] |
| N-Phenylaminopropyl POSS, NPAP-POSS | 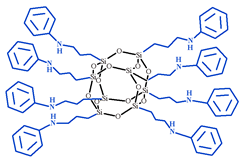 | M = 1490 g·mol−1 = 1.57 [78] |
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Investigation of Viscoelastic Properties by DMTA
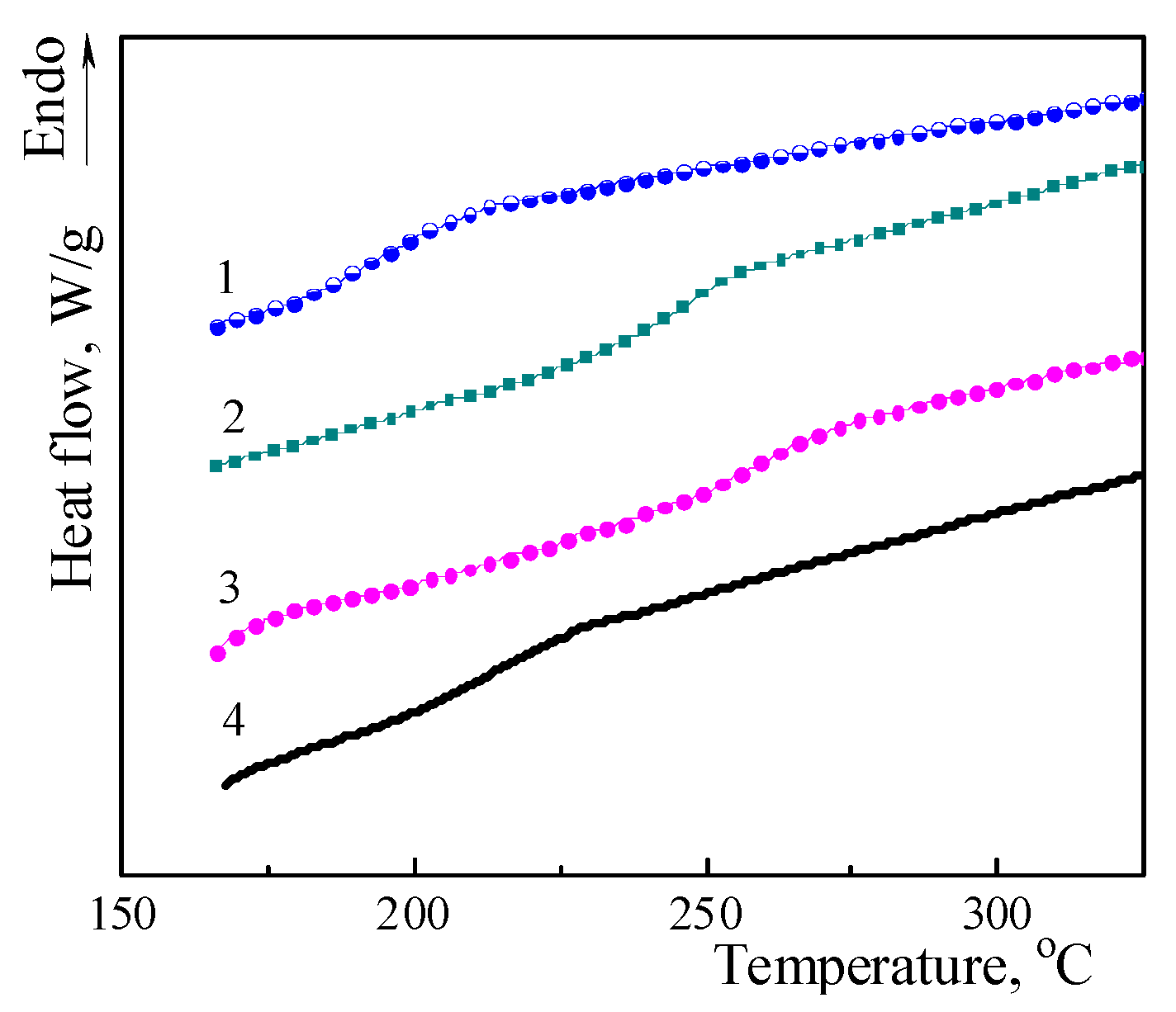
3.2. Investigation of Thermophysical Properties by DSC
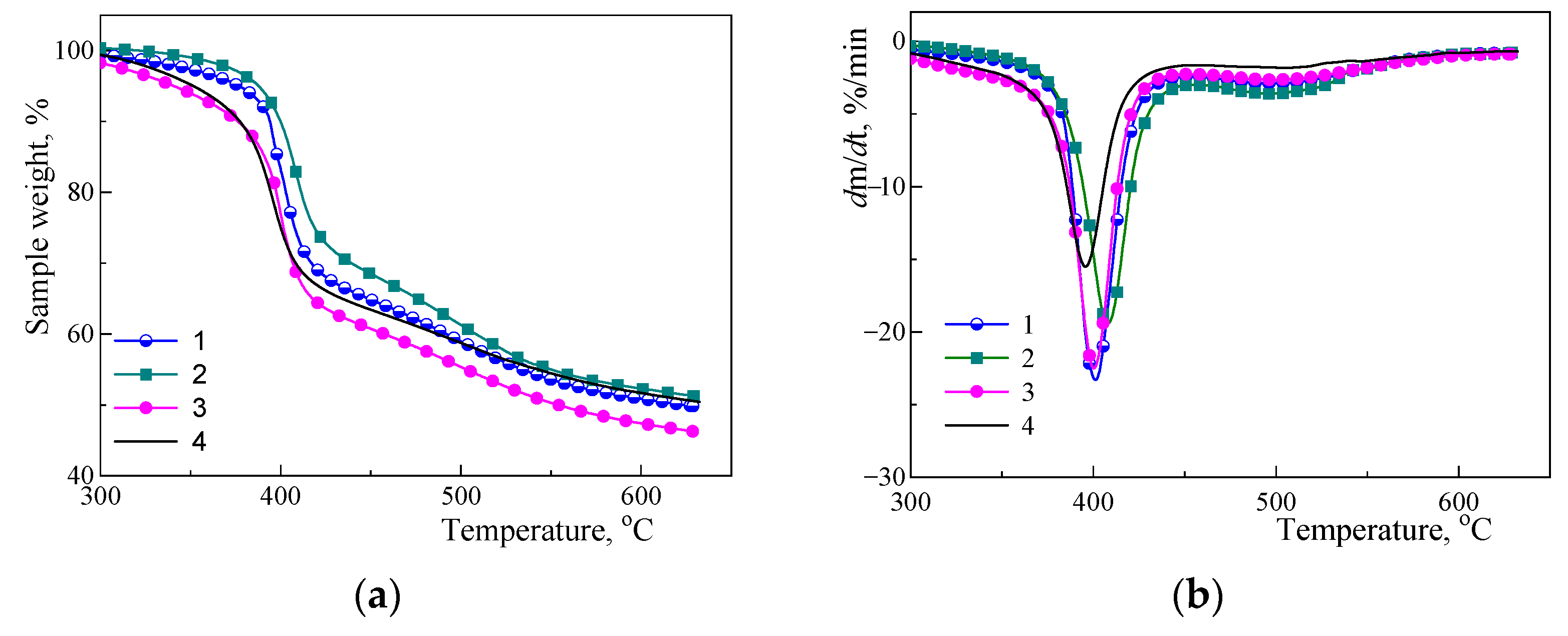
3.3. Investigation of Thermal Stability by TGA
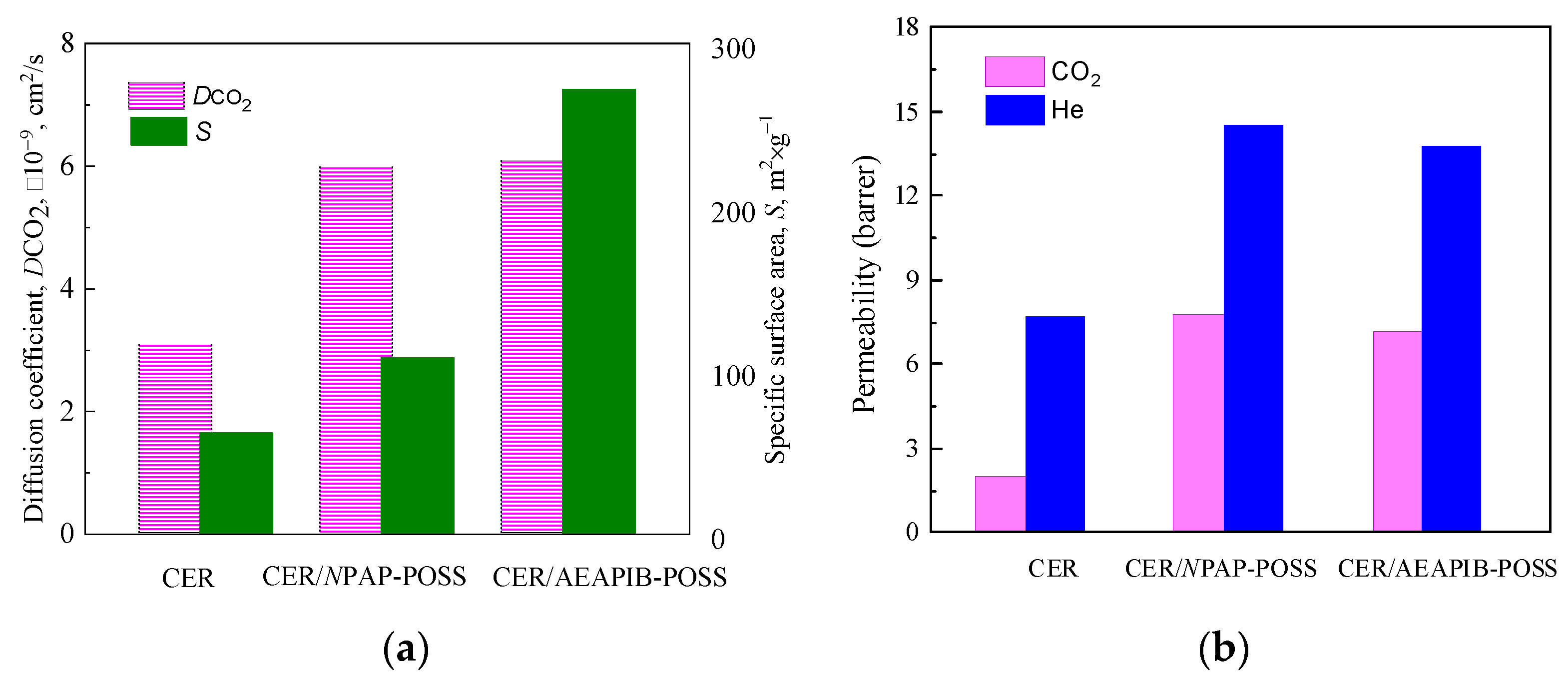
3.4. Investigation of Gas Transport Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Acs | adsorbate cross sectional area |
| aw | water activity |
| AEAPIB-POSS | aminoethyl aminopropylisobutyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane |
| amino-POSS | amino-functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane |
| APIB-POSS | aminopropylisobutyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| CER | Cyanate Ester Resin |
| CPPHCP-POSS | 3-cyanopropylheptacyclopentyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane |
| D | diffusion coefficient |
| DCBE | dicyanate ester of bisphenol E |
| DDAP-POSS | dodecaaminophenyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane |
| density at T = 20 °C | |
| DMTA | dynamic mechanical thermal analysis |
| DSC | differential scanning calorimetry |
| DTG | derivative thermogravimetric analysis |
| DVS | dynamic vapor sorption analyzer |
| ECH-POSS | epoxycyclohexyl-functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane |
| E′ | storage modulus |
| E″ | loss modulus |
| EDXS | energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry |
| f | network functionality |
| far-IR | far infrared spectroscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| G | water sorption |
| IPN | interpenetrating polymer network |
| L | film thickness |
| M | molar mass |
| mash | ash content at T = 630 °C |
| Mc | molar mass between crosslinks |
| meq | mass of the sample at equilibrium |
| mt | mass of the sample |
| m0 | equilibrated dry mass |
| MMT | montmorillonite |
| N | Avogadro’s number |
| NPAP-POSS | N-phenylaminopropyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane |
| OAP-POSS | octaaminophenyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane |
| OAPr-POSS | octaaminopropyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane |
| P | permeability coefficient |
| Pi | partial pressure of vapor |
| P1 | upstream pressure |
| P2 | downstream pressure |
| PCN | polycyanurate |
| POSS | polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane |
| PT-15 | Bisphenol-F Cyanate Ester Resin |
| PTFE-coated | polytetrafluoroethylene coated |
| R | ideal gas constant |
| S | specific surface area |
| St | total surface area |
| SAXS | small-angle X-ray scattering |
| Tb | boiling temperature |
| Td max | temperature value of maximal degradation rate |
| Td5% | temperature of 5% mass loss |
| Tg | glass transition temperature |
| Tg onset | glass transition onset temperature |
| Tg(end) | glass transition end temperature |
| Tm | melting temperature |
| Tα | temperature of α relaxation |
| Tβ | temperature of β relaxation |
| Tγ | temperature of γ relaxation |
| t1/2 | half sorption time |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| TGA | thermogravimetric analysis |
| w | sample mass |
| Wm | mass of adsorbate as monolayer, |
| ΔCp | heat capacity |
| Δm | mass loss at maximal degradation rate |
| ε | dielectric permittivity |
| η | dynamic viscosity |
| refractive index | |
| θ | time lag |
| ϕ | factor linked to the network model |
References
- Shimp, D.A.; Christenson, J.R.; Ising, S.J. Cyanate esters. An emerging family of versatile composite resins. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual International SAMPE Symposium, Reno, NV, USA, 8–11 May 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hamerton, I. (Ed.) Chemistry and Technology of Cyanate Ester Resins; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1994; 357p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamerton, I.; Hay, J.N. Recent technological developments in cyanate ester resins. High Perfom. Polym. 1998, 10, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, C.P.R.; Mathew, D.; Ninan, K.N. Cyanate Ester Resins, Recent Developments. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2000, 155, 1–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainleib, A. (Ed.) Thermostable Polycyanurates: Synthesis, Modification, Structure, and Properties; Nova Science Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 2010; 362p. [Google Scholar]
- McConnell, V.P. Resins for the Hot Zone, Part II: BMIs, CEs, benzoxazines and phthalonitriles. High Perform. Compos. 2009, 21, 49–54. Available online: https://www.compositesworld.com/articles/resins-for-the-hot-zone-part-ii-bmis-ces-benzoxazines-and-phthalonitriles (accessed on 18 August 2009).
- Bershtein, V.A.; Egorova, L.M.; Ryzhov, V.P.; Yakushev, P.N.; Fainleib, A.M.; Shantalii, T.A.; Pissis, P. Structure and segmental dynamics heterogeneity in hybrid polycyanurate-polyurethane networks. J. Macromol. Sci. Phys. B 2001, 40, 105–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainleib, A.; Grigoryeva, O.; Hourston, D. Synthesis of inhomogeneous modified polycyanurates by reactive blending of bisphenol A dicyanate ester and polyoxypropylene glycol. Macromol. Symp. 2001, 164, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainleib, A.M.; Grigoryeva, O.P.; Hourston, D.J. Structure-properties relationships for bisphenol A polycyanurate network modified with polyoxytetramethylene glycol. Int. J. Polym. Mat. 2002, 51, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, T.; Kunimi, T.; Oyama, T.; Tomoi, M. Modification of cyanate ester resin by soluble polyarylates. Polym. Int. 2003, 52, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.W.; Park, S.D.; Cho, K.; Kim, J.K.; Park, C.E. Toughening of cyanate ester resins with cyanated polysulfones. Polymer 1997, 38, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Min, H.S.; Choi, W.J.; Kim, S.C. Dynamic mechanical modeling of PEI/dicyanate semi-IPNs. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2000, 40, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harismendy, I.; Rio, M.D.; Marieta, C.; Gavalda, J.; Mondragon, I. Dicyanate ester-polyetherimide semi-interpenetrating polymer networks. II. Effects of morphology on the fracture toughness and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ding, N.; Xu, R.; He, Q.; Shen, J.; Hu, B. Cyanate ester resin modified by hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene: Morphology, thermal, and mechanical properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 1404–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainleib, A.; Kozak, N.; Grigoryeva, O.; Nizelskii, Y.; Gritsenko, V.; Pissis, P.; Boiteux, G. Structure-thermal property relationships for polycyanurate-polyurethane linked interpenetrating polymer networks. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 76, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.C. Properties of polyetherimide/dicyanate semi-interpenetrating polymer network having the morphology spectrum. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 2334–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolotta, A.; Di Marco, G.; Lanza, M.; Carini, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Tripodo, G.; Fainleib, A.; Danilenko, I.; Grytsenko, V.; Sergeeva, L. Thermal and mechanical properties of simultaneous and sequential full-interpenetrating polymer networks. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 370, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, T.; Katsurayama, S.; Fukuda, W.; Tomoi, M.J. Modification of cyanate ester resin by poly(ethylene phthalate) and related copolyesters. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 76, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Q.; Mechin, F.; Pascault, J.P. Influence of cure cycles on morphologies and properties of rubber- or thermoplastic-modified cyanate ester networks. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1995, 71, 752–753. [Google Scholar]
- Seminovych, G.M.; Fainleib, A.M.; Slinchenko, E.A.; Brovko, A.A.; Sergeeva, L.M.; Dubkova, V.I. Influence of carbon fibre on formation kinetics of cross-linked copolymer from bisphenol A dicyanate and epoxy olygomer. React. Funct. Polym. 1999, 40, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.W.; Cho, K.; Yoon, T.H.; Park, C.E. Effects of molecular weight of polysulfone on phase separation behavior for cyanate ester/polysulfone blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 77, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-Y.; Hong, J.-L. Morphology and fracture toughness of poly(ether sulfone)-blended polycyanurates. Polymer 2000, 41, 4513–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.W.; Cho, K.; Park, C.E.; Huh, W. Phase separation behavior of cyanate ester resin/polysulfone blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recalde, I.B.; Campos, A.; Mondragon, I.; Gomez, C.M. Miscibility and kinetic behaviour of cyanate resin/polysulfone blends. Macromol. Symp. 2001, 174, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.A.; Rau, A.V.; Loos, A.C.; McGrath, J.E. Toughened cyanate ester networks as matrix resin for carbon fiber composites. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1995, 71, 750–751. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, S.A.; McGrath, J.E. Amorphous phenolphthalein-based poly(arylene ether)- modified cyanate ester networks: Effect of thermal cure cycle on morphology and toughenability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 64, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, A.V.; Srinivasan, S.A.; McGrath, J.E.; Loos, A.C. Resin transfer molding (RTM) with toughened cyanate ester resin systems. Polym. Comp. 1998, 19, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marieta, C.; Rio, M.D.; Harismendy, I.; Mondragon, I. Effect of the cure temperature on the morphology of a cyanate ester resin modified with a thermoplastic: Characterization by atomic force microscopy. Eur. Polym. J. 2000, 36, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-Y.; Hong, J.-L. Polar interaction in a cyanated poly(ether sulfone)-modified polycyanurate. Polymer 1998, 39, 7119–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillermeier, R.W.; Seferis, J.C. Environmental effects on thermoplastic and elastomer toughened cyanate ester composite systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 77, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Srinivasan, S.A.; Rau, A.V.; Ward, T.C.; McGrath, J.E.; Loos, A.C.; Hood, D.; Kranbeuhl, D.E. Production of controlled networks and morphologies in toughened thermosetting resins using real-time, in situ cure monitoring. Polymer 1996, 37, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainleib, A.M.; Sergeeva, L.M.; Novikova, T.I.; Shantalii, T.A. Synthesis, structure and some properties of the polycyanurate-polyurethane semi-IPNs. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1992, 66, 131–132. [Google Scholar]
- Bartolotta, A.; Di Marco, G.; Lanza, M.; Carini, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Tripodo, G.; Fainleib, A.M.; Slinchenko, E.A.; Privalko, V.P. Molecular mobility in semi-IPNs of linear polyurethane and heterocyclic polymer networks. J. Adhes. 1997, 64, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta Calleja, F.J.; Privalko, E.G.; Sukhorukov, D.I.; Fainleib, A.M.; Sergeeva, L.M.; Shantalii, T.A.; Shtompel, V.I.; Monleon Pradas, M.; Gallego Ferrer, G.; Privalko, V.P. Structure-properties relationships for cyanurate-containing, full interpenetrating polymer networks. Polymer 2000, 41, 4699–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroulas, P.; Kripotou, S.; Pissis, P.; Fainleib, A.; Bei, I.; Bershtein, V.; Gomza, Y. Molecular mobility in polycyanurate/clay nanocomposites studied by dielectric techniques. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthoulis, G.I.; Kontou, E.; Fainleib, A.; Bei, I. Polytetramethylene glycol-modified polycyanurate matrices reinforced with nanoclays: Synthesis and thermomechanical performance. Mech. Comp. Mater. 2009, 45, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershtein, V.A.; Fainleib, A.M.; Pissis, P.; Bei, I.M.; Dalmas, F.; Egorova, L.M.; Gomza, Y.P.; Kripotou, S.; Maroulas, P.; Yakushev, P.N. Polycyanurate-organically modified montmorillonite nanocomposites: Structure-dynamics-properties relationships. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 47, 555–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthoulis, G.I.; Kontou, E.; Fainleib, A.; Bei, I.; Gomza, Y. Synthesis and characterization of polycyanurate/montmorillonite nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 1036–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, T.J.; Abrol, S.; MacFarlane, D.R. Rheological and mechanical properties of percolated cyanate ester nanocomposites. Polymer 2005, 46, 8011–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershtein, V.; Fainleib, A.; Egorova, L.; Gusakova, K.; Grigoryeva, O.; Kirilenko, D.; Konnikov, S.; Ryzhov, V.; Yakushev, P.; Lavrenyuk, N. The impact of ultra-low amounts of amino-modified MMT on dynamics and properties of densely cross-linked cyanate ester resins. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, D.D.; Laskoski, M.; Keller, T.M. Modification of oligomeric cyanate ester polymer properties with multi-walled carbon nanotube-containing particles. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2009, 210, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainleib, A.; Bardash, L.; Boiteux, G. Catalytic effect of carbon nanotubes on polymerization of cyanate ester resins. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2009, 3, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Han, J. Performance of aluminum borate whisker reinforced cyanate ester resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 4131–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, T. ZnO whisker reinforced M40/BADCy composite. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, P.; Rogalski, M.K.; Kessler, M.R. Carbon fiber-reinforced cyanate ester/nano-ZrW2O8 composites with tailored thermal expansion. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershtein, V.; Fainleib, A.; Kirilenko, D.; Yakushev, P.; Gusakova, K.; Lavrenyuk, N.; Ryzhov, V. Dynamics and properties of high performance amorphous polymer subnanocomposites with ultralow silica content and quasi-regular structure. Polymer 2016, 103, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershtein, V.; Fainleib, A.; Gusakova, K.; Kirilenko, D.; Yakushev, P.; Egorova, L.; Lavrenyuk, N.; Ryzhov, V. Silica subnanometer-sized nodes, nanoclusters and aggregates in cyanate ester resin-based networks: Structure and properties of hybrid subnano- and nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 85C, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershtein, V.; Fainleib, A.; Kirilenko, D.; Yakushev, P.; Gusakova, K.; Lavrenyuk, N.; Ryzhov, V. Incorporating silica into cyanate ester-based network by sol-gel method: Structure and properties of subnano- and nanocomposite. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Naples, Italy, 19–23 June 2016; Volume 1736, p. 020045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Li, G.; Toghiani, H.; Koo, J.H.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Cyanate ester/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) nanocomposites: Synthesis and characterization. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-S.; Liang, K.; Chatterjee, S.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Synthesis, morphology, and viscoelastic properties of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanocomposites with epoxy and cyanate ester matrices. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2005, 15, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Li, G.-Z.; Ni, H. Hybrid inorganic/organic crosslinked resins containing polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes. Macromol. Symp. 2003, 196, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Toghiani, H.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Synthesis, morphology and viscoelastic properties of epoxy/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) and epoxy/cyanate ester/POSS nanocomposites. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2011, 21, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Toghiani, H.; Li, G.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Synthesis, morphology, and viscoelastic properties of cyanate ester/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 3887–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.E.; Petteys, B.J.; Guenthner, A.J.; Yandek, G.R.; Baldwin, L.C.; Jones, C.; Roberts, M.J. Synthesis and chemistry of a monotethered-POSS bis(cyanate) ester: Thermal curing of micellar aggregates leads to discrete nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 3891–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jin, J.; Song, M.; Shaw, S.J.; Stone, C.A. Curing dynamics and network formation of cyanate ester resin/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanocomposites. Polymer 2011, 52, 1716–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, Q. Gelation behavior, morphology, thermal and viscoelastic properties of epoxy-cyanate ester/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2006, 11–12, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Liang, G.; Guo, Z. Preparation and characterization of organic–inorganic hybrid composites based on multiepoxy silsesquioxane and cyanate resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 3652–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershtein, V.; Fainleib, A.; Yakushev, P.; Egorova, L.; Grigoryeva, O.; Ryzhov, V.; Starostenko, O. Thermostable cyanate ester resins and POSS-containing nanocomposites: Influence of matrix chemical structure on their properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liang, G.; Wang, X. Epoxy-functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane/cyanate ester resin organic–inorganic hybrids with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties. Polym. Int. 2014, 63, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starostenko, O.; Bershtein, V.; Fainleib, A.; Egorova, L.; Grigoryeva, O.; Sinani, A.; Yakushev, P. Thermostable polycyanurate-polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane hybrid networks: Synthesis, dynamics and thermal behavior. Macromol. Symp. 2012, 316, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershtein, V.; Fainleib, A.; Egorova, L.; Grigoryeva, O.; Kirilenko, D.; Konnikov, S.; Ryzhov, V.; Starostenko, O.; Yakushev, P.; Yagovkina, M.; et al. The impact of ultra-low amounts of introduced reactive POSS nanoparticles on structure, dynamics and properties of densely cross-linked cyanate ester resins. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starostenko, O.; Grigoryeva, O.; Fainleib, A.; Saiter, J.M.; Youssef, B.; Grande, D. Effect of epoxy-functionalized POSS on thermal stability of nanocomposites based on crosslinked polycyanurates. Polim. Zhurnal 2014, 36, 233–244. Available online: http://polymerjournal.kiev.ua/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/3_233_244Starostenko.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2016).
- Grigoryeva, O.P.; Starostenko, O.N.; Gusakova, K.G.; Fainleib, A.M.; Saiter, J.M.; Youssef, B.; Grande, D. Effect of epoxyfunctionalized POSS on chemical structure and viscoelastic properties of polycyanurate based nanocomposites. Polim. Zhurnal 2014, 36, 341–351. Available online: http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/Polimer_2014_36_4_4 (accessed on 1 December 2014).
- Bershtein, V.; Fainleib, A.; Yakushev, P.; Kirilenko, D.; Egorova, L.; Grigoryeva, O.; Ryzhov, V.; Starostenko, O. High performance multifunctional cyanate ester oligomer-based network and epoxy-POSS containing nanocomposites: Structure, dynamics, and properties. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 1900–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Lv, P.; Cui, Y.; Wu, G. A novel hybrid functional nanoparticle and its effects on the dielectric, mechanical, and thermal properties of cyanate ester. Polym. Compos. 2015, 37, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piness, J.; Wiggins, J. Effects of POSS addition on bisphenol-E cyanate ester network. In Proceedings of the 57th AIAA/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–8 January 2016; p. 0934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariraman, M.; Sasikumar, R.; Alagar, M. Cyanate ester tethered POSS/BACY nanocomposites for low-k dielectrics. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhao, L.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L. Toughening of cyanate resin with low dielectric constant by glycidyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane. High Perform. Polym. 2016, 29, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Yan, H.; Li, S.; Bai, L.; Lv, Q. Effects of novel polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane containing hydroxyl group and epoxy group on the dicyclopentadiene bisphenol dicyanate ester composites. Polym. Test. 2017, 59, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Shao, Y.; Huang, F.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z. Toughening of POSS–MPS composites with low dielectric constant prepared with structure controllable micro/mesoporous nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 40836–40845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, H.; Ran, Q.; Fu, Q.; Gu, Y. A novel ultra low-k nanocomposites of benzoxazinyl modified polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane and cyanate ester. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 103, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Song, M. Effect of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanoparticles on thermal decomposition of cyanate ester resin. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 129, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, W.; Sui, Y.; Wang, G.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, D. Curing behaviors and thermomechanical properties of novolac cyanate–polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane copolymers. Compos. Commun. 2021, 28, 100932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigat, E.; Pütter, R. Umsetzung von cyansäureestern mit amino-bzw. Imino-gruppenhaltigen substanzen. Chem. Ber. 1964, 97, 3027–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Bauer, M. Curing of cyanates with primary amines. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2001, 202, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallary, J.-L.; Lauprêtre, F.; Monnerie, L. (Eds.) Polymer Materials, Macroscopic Properties and Molecular Interpetrations; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; 432p. [Google Scholar]
- Flory, P.J. (Ed.) Principles of Polymer Chemistry; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1953; 688p. [Google Scholar]
- DeArmitt, C. Polyherdral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Handbook. In Phantom Plastics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; p. 28. Available online: https://phantomplastics.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/POSS-Handbook.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2013).
- Gregg, S.J.; Sing, K.S.W. Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1982; 303р, ISBN 0123009561/9780123009562. [Google Scholar]
- Crank, J.; Park, G.S. Diffusion in Polymers; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1968; 452p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liang, G.; Wang, J.; Ren, P. Epoxy/POSS organic-inorganic hybrids: Viscoelastic, mechanical properties and micromorphologies. Polym. Compos. 2007, 28, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liang, G.; Wang, X.; Adhikari, S.; Pei, J. Curing behavior and dielectric properties of amino-functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane/cyanate ester resin hybrids. High Perform. Polym. 2013, 25, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashchuk, A.; Rios de Anda, A.; Starostenko, O.; Grigoryeva, O.; Sotta, P.; Rogalsky, S.; Smertenko, P.; Fainleib, A.; Grande, D. Structure-property relationships in nanocomposites based on cyanate ester resins and 1-heptyl pyridinium tetrafluoroborate ionic liquid. Polymer 2018, 148, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damian, C.; Escoubes, M.; Espuche, E. Gas and water transport properties of epoxy-amine networks: Influence of crosslink density. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damian, C.; Espuche, E.; Escoubes, M. Influence of three ageing types (thermal oxidation, radiochemical and hydrolytic ageing) on the structure and gas transport properties of epoxy-amine networks. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 72, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolmaire, N.; Méchin, F.; Espuche, E.; Pascault, J.P. Modification of a hydrophilic linear polyurethane by crosslinking with a polydimethylsiloxane: Influence of the crosslink density and of the hydrophobic/hydrophilic balance on the water transport properties. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

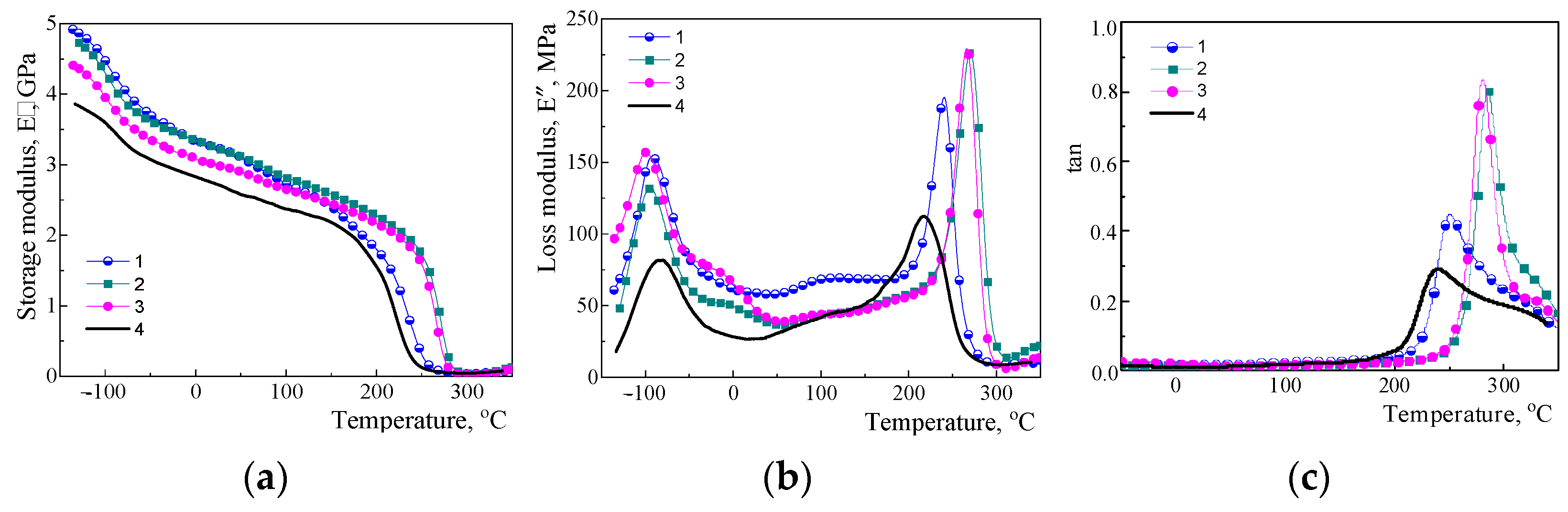

| Sample | Tγ, °C | Tβ, °C | Tα, °C | E′ at 25 °C, GPa | Mc, g/mol | Surface of E″ Peak at Tα, MPa/K | Height of tan δ (at Tα) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −92 | −43 | 241 | 3.24 | 49 | 13.61 | 0.45 |
| −95 | −11 | 270 | 3.23 | 83 | 9.83 | 0.81 |
| −99 | −28 | 266 | 2.99 | 48 | 12.92 | 0.84 |
| −85 | −37 | 218 | 2.72 | 31 | 13.83 | 0.29 |
| Sample | Tg onset, °C | Tg, °C | ΔCp, J·g−1·K−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 204 | 216 | 0.363 |
| 257 | 269 | 0.415 |
| 249 | 259 | 0.314 |
| 203 | 214 | 0.351 |
| Sample | Td5%(a), °C | Td max(b), °C | Δm (c), % | mash (d), % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 377 | 401 | 23 | 50 |
| 388 | 408 | 18 | 51 |
| 341 | 401 | 23 | 46 |
| 352 | 396 | 21 | 51 |
| CER Matrix | Amino-POSS | Curing Schedule | POSS Content, wt.% | Tg, °C | E′, GPa (at 40 °C) | Tg’s Method Condition | Td5%, °C, TGA, 20 °C/min | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bisphenol-F based CER (PT-15) | DDAP-POSS | 188 °C/120 min | 1 | ~225 | ~2.69 | DMTA, 10 Hz (tan δ data) | - | [50] |
| Bisphenol-F based CER (PT-15) | - | 188 °C/120 min + to 250 °C at 5 °C/min + 250 °C/180 min | 0 | 305 | 1.50 | DMTA, 1 Hz (tan δ data) | - | [53] |
| OAP-POSS | 1 | 336 | 1.61 | - | ||||
| OAP-POSS | 3 | 300 | 2.12 | - | ||||
| OAP-POSS | 5 | 258 | 1.41 | - | ||||
| Bisphenol-F based CER (PT-15) | CPPHCP-POSS | 188 °C/120 min + to 250 °C at 5 °C/min + 250 °C/180 min + 300 °C/30 min | 1 | 323 | 1.96 | DMTA, 1 Hz (tan δ data) | - | [53] |
| CPPHCP-POSS | 3 | 320 | 2.01 | - | ||||
| CPPHCP-POSS | 5 | 331 | 1.85 | - | ||||
| CPPHCP-POSS | 10 | 333 | 1.66 | - | ||||
| Bisphenol-A based CER (BADCy) | - | 120 °C/60 min + 150 °C/60 min + 180 °C/120 min + 200 °C/240 min | 0 | 268 | - | DSC, 10 °C/min (Tg(end)) | - | [82] |
| OAPr-POSS | 1 | 285 | - | - | ||||
| OAPr-POSS | 5 | 306 | - | - | ||||
| OAPr-POSS | 10 | 308 | - | - | ||||
| OAPr-POSS | 20 | 311 | - | - | ||||
| Bisphenol-E based CER (LECy) | - | 65 °C/120 min (1500 rpm) + 20 °C to 300 °C at 0.5 °C/min | 0 | 218 | 2.60 | DMTA, 1 Hz, 3 °C/min (tan δ data) | 352 | this manuscrip |
| APIB-POSS | 0.1 | 241 | 3.17 | 377 | ||||
| AEAPIB-POSS | 0.1 | 270 | 3.17 | 388 | ||||
| NPAP-POSS | 0.1 | 266 | 2.94 | 341 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigoryeva, O.; Fainleib, A.; Starostenko, O.; Shulzhenko, D.; Rios de Anda, A.; Gouanve, F.; Espuche, E.; Grande, D. Effect of Amino-Functionalized Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes on Structure-Property Relationships of Thermostable Hybrid Cyanate Ester Resin Based Nanocomposites. Polymers 2023, 15, 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244654
Grigoryeva O, Fainleib A, Starostenko O, Shulzhenko D, Rios de Anda A, Gouanve F, Espuche E, Grande D. Effect of Amino-Functionalized Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes on Structure-Property Relationships of Thermostable Hybrid Cyanate Ester Resin Based Nanocomposites. Polymers. 2023; 15(24):4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244654
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigoryeva, Olga, Alexander Fainleib, Olga Starostenko, Diana Shulzhenko, Agustin Rios de Anda, Fabrice Gouanve, Eliane Espuche, and Daniel Grande. 2023. "Effect of Amino-Functionalized Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes on Structure-Property Relationships of Thermostable Hybrid Cyanate Ester Resin Based Nanocomposites" Polymers 15, no. 24: 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244654
APA StyleGrigoryeva, O., Fainleib, A., Starostenko, O., Shulzhenko, D., Rios de Anda, A., Gouanve, F., Espuche, E., & Grande, D. (2023). Effect of Amino-Functionalized Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes on Structure-Property Relationships of Thermostable Hybrid Cyanate Ester Resin Based Nanocomposites. Polymers, 15(24), 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244654










