Rheological Properties and Kinetics of Gelation of Binary Polymers between Xanthan Gum and Locust Bean Gum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Rheological Characterizations
2.4. Determination of Structure Development Rate
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope Observation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
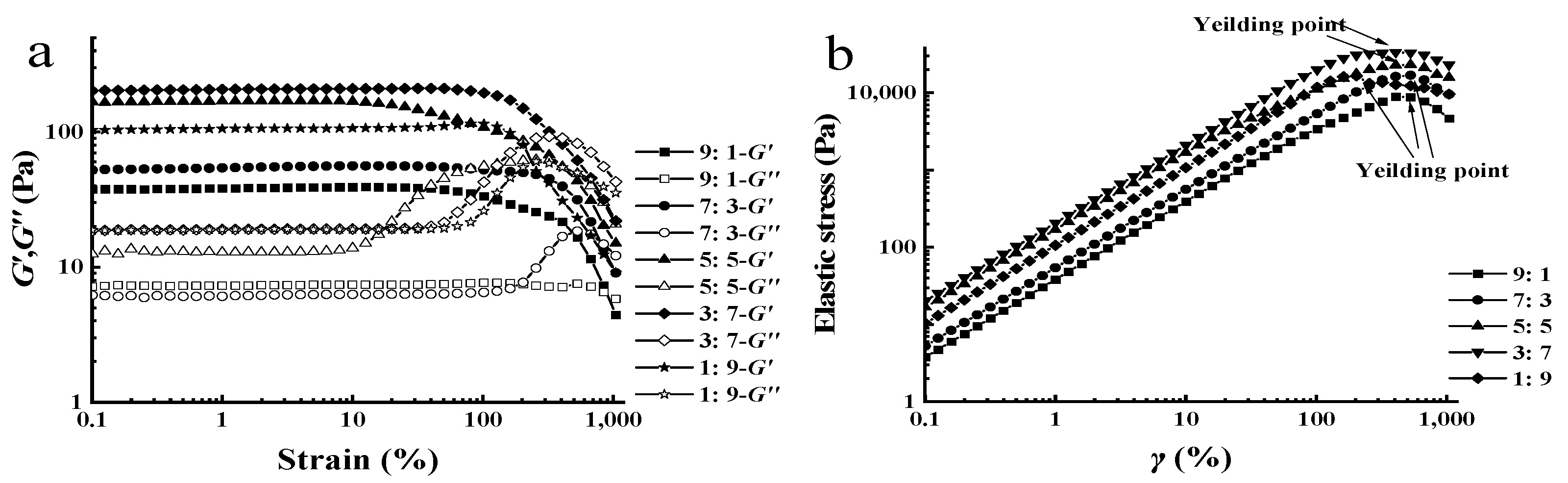
3.1. Oscillation Amplitude Tests
3.2. Oscillation Frequency Sweeps
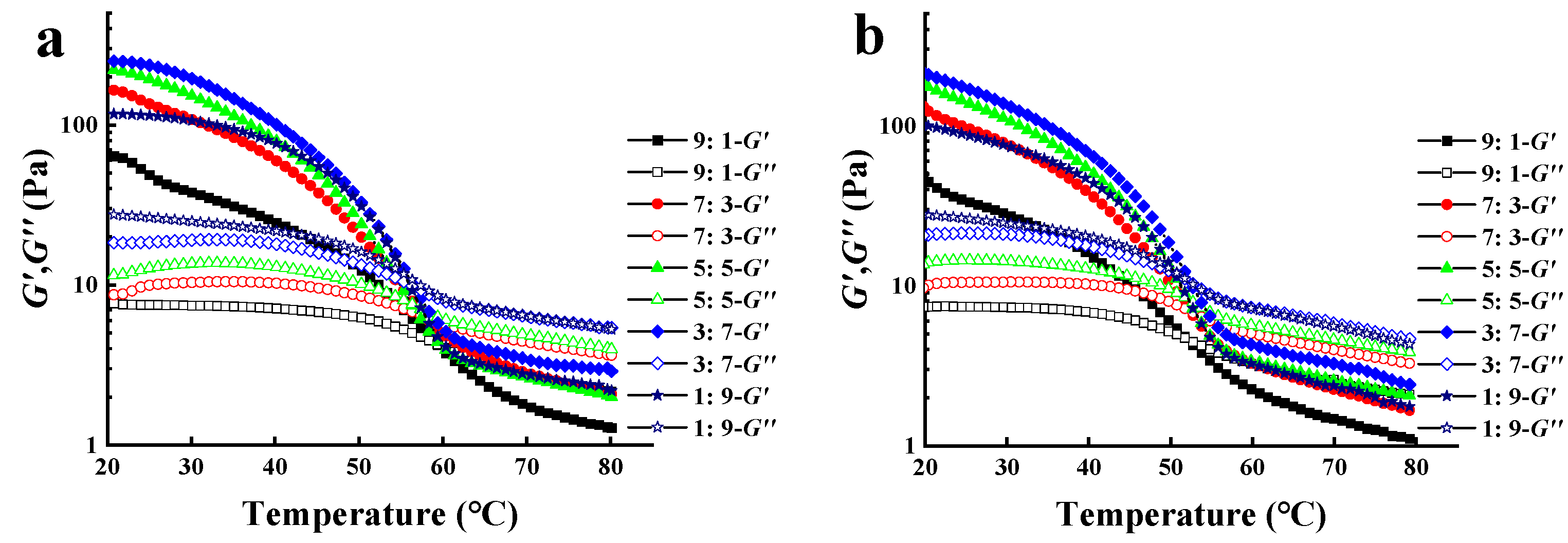
3.3. Temperature Ramp Tests
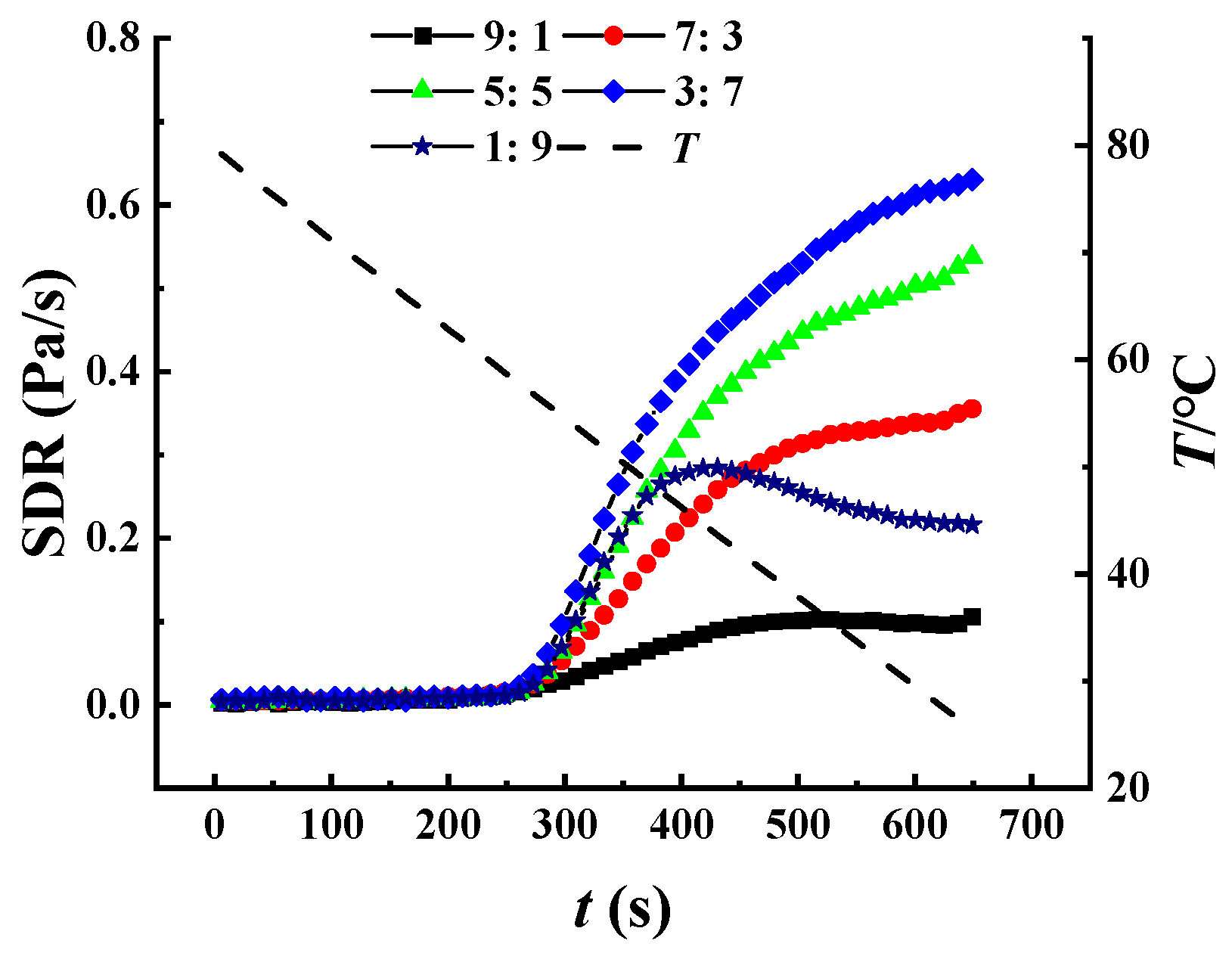
3.4. Structure Developing Rate (SDR) Analysis during Cooling
3.5. Non-Isothermal Kinetics Analysis for Gel Formation
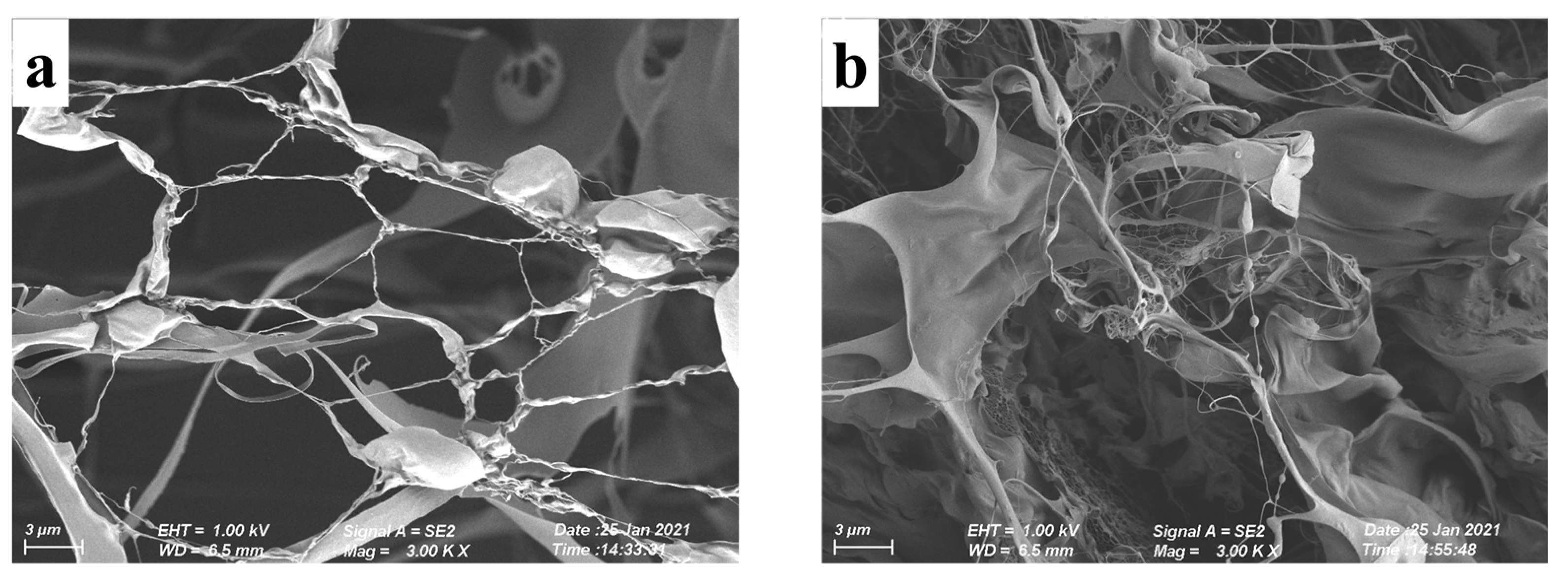
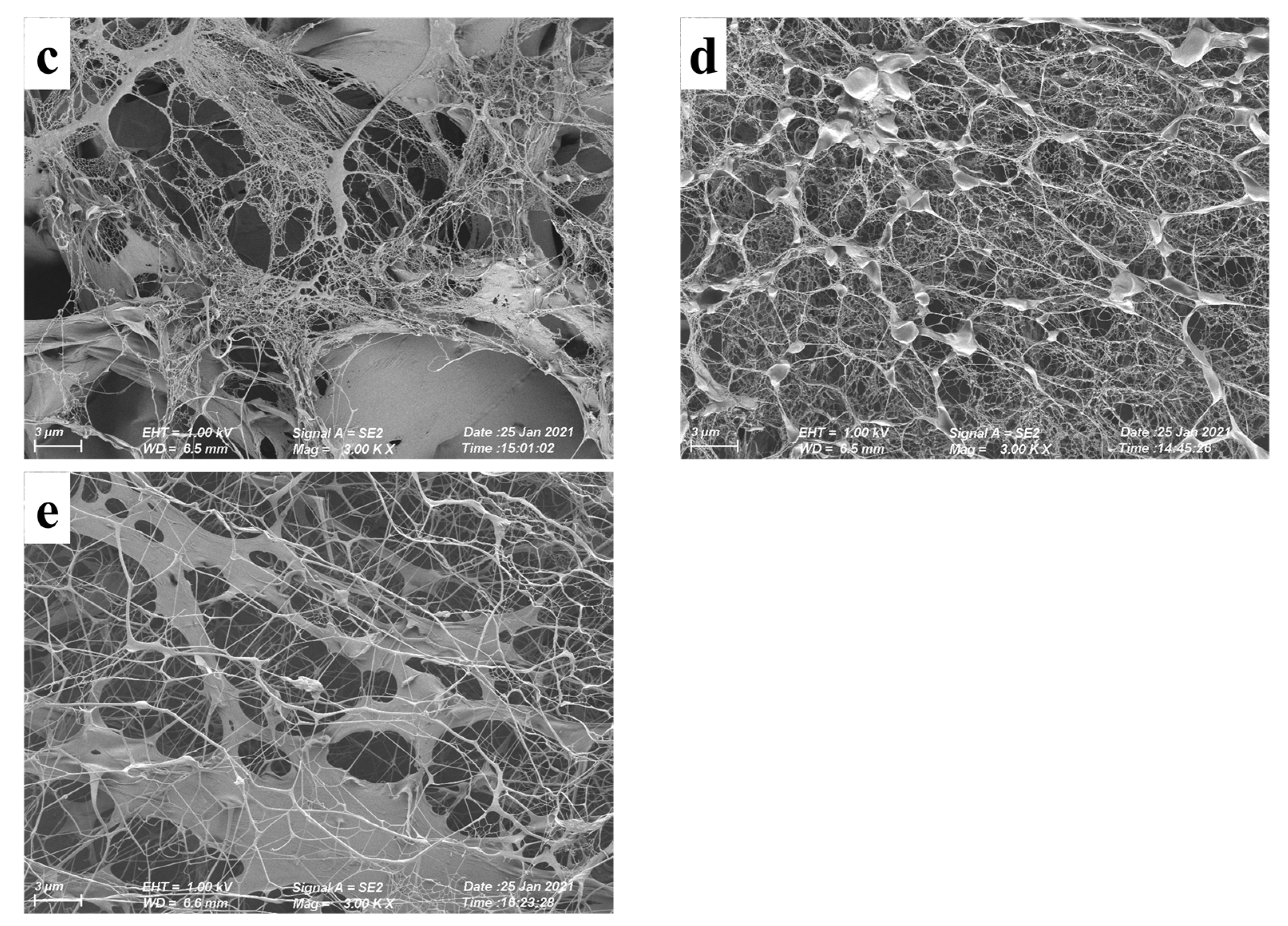
3.6. Microstructure of XG/LBG Gels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pirsa, S.; Hafezi, K. Hydrocolloids: Structure, preparation method, and application in food industry. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, G.O.; Williams, P.A. Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nazir, A.; Asghar, A.; Aslam Maan, A. Chapter 13—Food Gels: Gelling Process and New Applications. In Advances in Food Rheology and Its Applications; Ahmed, J., Ptaszek, P., Basu, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 335–353. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Goff, H.D.; Cui, S.W. Comparison of synergistic interactions of yellow mustard gum with locust bean gum or κ-carrageenan. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 132, 107804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rao, K.M.; Han, S.S. Application of xanthan gum as polysaccharide in tissue engineering: A review. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 180, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Ochoa, F.; Santos, V.E.; Casas, J.A.; Gómez, E. Xanthan gum: Production, recovery, and properties. Biotechnol. Adv. 2000, 18, 549–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peidayesh, H.; Heydari, A.; Mosnáčková, K.; Chodák, I. In situ dual crosslinking strategy to improve the physico-chemical properties of thermoplastic starch. Carbohyd. Polym. 2021, 269, 118250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Mu, R.; Pang, J.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, Y. A review on konjac glucomannan gels: Microstructure and application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, S.; Mudgil, D. Locust bean gum: Processing, properties and food applications—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 66, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, V.D.; Jani, G.K.; Moradiya, N.G.; Randeria, N.P.; Nagar, B.J. Locust bean gum: A versatile biopolymer. Carbohyd. Polym. 2013, 94, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copetti, G.; Grassi, M.; Lapasin, R.; Pricl, S. Synergistic gelation of xanthan gum with locust bean gum: A rheological investigation. Glycoconjugate J. 1997, 14, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dea, I.C.M.; Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Welsh, E.J.; Barnes, H.A.; Price, J. Associations of like and unlike polysaccharides: Mechanism and specificity in galactomannans, interacting bacterial polysaccharides, and related systems. Carbohyd. Res. 1977, 57, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tako, M.; Asato, A.; Nakamura, S. Rheological aspects of the intermolecular interaction between xanthan and locust bean gum in aqueous media. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1984, 48, 2995–3000. [Google Scholar]
- Higiro, J.; Herald, T.J.; Alavi, S. Rheological study of xanthan and locust bean gum interaction in dilute solution. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tako, M.; Teruya, T.; Tamaki, Y.; Ohkawa, K. Co-gelation mechanism of xanthan and galactomannan. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renou, F.; Petibon, O.; Malhiac, C.; Grisel, M. Effect of xanthan structure on its interaction with locust bean gum: Toward prediction of rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tian, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Xiang, D. Insights into interaction mechanism between xanthan gum and galactomannan based on density functional theory and rheological properties. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, R.; Ma, A.; Zhang, H. Rheological characterization of polysaccharide thickeners oriented for dysphagia management: Carboxymethylated curdlan, konjac glucomannan and their mixtures compared to xanthan gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, E.E.S.; O’Byrne, S.; Liow, J.L. Yield stress measurement of a thixotropic colloid. Rheol. Acta 2019, 58, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.; Kim, S.H.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, S.J. Large amplitude oscillatory shear as a way to classify the complex fluids. J. Non-Newt. Fluid Mech. 2002, 107, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, H.J.; Caines, S.B.; Sanchez, A.M.; Khan, S.A. Yield stress and wall slip phenomena in colloidal silica gels. J. Rheol. 2003, 47, 847–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, S.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Dogan, M.; Yetim, H.; Kayacier, A. Dynamic oscillatory shear properties of O/W model system meat emulsions: Linear viscoelastic analysis for effect of temperature and oil concentration on protein network formation. J. Food Eng. 2011, 107, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandolo, C.; Bulone, D.; Mangione, M.R.; Margheritelli, S.; Di Meo, C.; Alhaique, F.; Matricardi, P.; Coviello, T. Synergistic interaction of Locust Bean Gum and Xanthan investigated by rheology and light scattering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.H. Structural and Mechanical Properties of Biopolymer Gels. In Food Polymers, Gels and Colloids; Dickinson, E., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 1991; pp. 322–338. [Google Scholar]
- Hesarinejad, M.A.; Koocheki, A.; Razavi, S.M.A. Dynamic rheological properties of Lepidium perfoliatum seed gum: Effect of concentration, temperature and heating/cooling rate. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, H.; Khosravi-Darani, K. Effective variables on production and structure of xanthan gum and its food applications: A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djabourov, M.; Leblond, J.; Papon, P. Gelation of aqueous gelatin solutions. I. Structural investigation. J. Phys. France 1988, 49, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, A.; Bourbon, A.; Rocha, C.; Ribeiro, C.; Maia, J.; Gonçalves, M.; Teixeira, J.; Vicente, A. Rheological characterization of κ-carrageenan/galactomannan and xanthan/galactomannan gels: Comparison of galactomannans from non-traditional sources with conventional galactomannans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-C.; Brant, D.A. Rheology of Concentrated Isotropic and Anisotropic Xanthan Solutions: 3. Temperature Dependence. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsengiyumva, E.M.; Alexandridis, P. Xanthan gum in aqueous solutions: Fundamentals and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 583–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, H.; Einhorn-Stoll, U.; Senge, B. Structure formation in sugar containing pectin gels–Influence of Ca2+ on the gelation of low-methoxylated pectin at acidic pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.M.; Coimbra, M.A.; Lopes da Silva, J.A. Temperature dependence of the formation and melting of pectin–Ca2+ networks: A rheological study. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braudo, E.E.; Muratalieva, I.R.; Plashchina, I.G.; Tolstoguzov, V.B. Correlation between the temperatures of formation/breakdown of the gel network and conformational transitions of agarose macromolecules. Carbohydr. Polym. 1991, 15, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartzel, K. Non-Isothermal Kinetic Data Generation for Food Constituents, Food Properties and Computer-Aided Engineering of Food Processing Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Rhim, J.W.; Nunes, R.V.; Jones, V.A.; Swartzel, K.R. Determination of kinetic parameters using linearly increasing temperature. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Q.; Hamann, D.D.; Foegeding, E.A. Myosin gelation kinetic study based on rheological measurements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.L.; Gonçalves, M.; Rao, M. Kinetics and thermal behaviour of the structure formation process in HMP/sucrose gelation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1995, 17, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Rao, M. Rheology and structure development during gelation of low-methoxyl pectin gels: The effect of sucrose. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, J.E.; Ferry, J.D. Studies of the cross-linking process in gelatin gels. III. Dependence of melting point on concentration and molecular weight. J. Phys. Chem. 1954, 58, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.B.; Gunasekaran, S. Evaluation of structure development of xanthan and carob bean gum mixture using non-isothermal kinetic model. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2007, 16, 954–957. [Google Scholar]


| Mass Ratio of XG/LBG | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | R2 | |
| 9:1 | 1.59 ± 0.02 e | 0.13 ± 0.00 a | 0.995 |
| 7:3 | 1.79 ± 0.01 d | 0.09 ± 0.00 b | 0.998 |
| 5:5 | 2.15 ± 0.01 b | 0.06 ± 0.00 d | 0.999 |
| 3:7 | 2.29 ± 0.00 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 e | 0.999 |
| 1:9 | 1.99 ± 0.02 c | 0.07 ± 0.00 c | 0.999 |
| Mass Ratio of XG/LBG (w/w) | High-Temperature Region (55~39 °C) | Low-Temperature Region (39~20 °C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ea/(kJ/mol) | R2 | Ea/(kJ/mol) | R2 | |
| 9:1 | 111.97 | 0.994 | 76.93 | 0.981 |
| 7:3 | 150.67 | 0.993 | 85.31 | 0.987 |
| 5:5 | 189.56 | 0.991 | 81.98 | 0.994 |
| 3:7 | 199.20 | 0.991 | 74.33 | 0.981 |
| 1:9 | 184.07 | 0.992 | 84.55 | 0.988 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Yan, Z.; Xie, F.; Tian, Y.; Ai, L. Rheological Properties and Kinetics of Gelation of Binary Polymers between Xanthan Gum and Locust Bean Gum. Polymers 2023, 15, 4604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234604
Zhang H, Yan Z, Xie F, Tian Y, Ai L. Rheological Properties and Kinetics of Gelation of Binary Polymers between Xanthan Gum and Locust Bean Gum. Polymers. 2023; 15(23):4604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234604
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hui, Zhun Yan, Fan Xie, Yanjun Tian, and Lianzhong Ai. 2023. "Rheological Properties and Kinetics of Gelation of Binary Polymers between Xanthan Gum and Locust Bean Gum" Polymers 15, no. 23: 4604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234604
APA StyleZhang, H., Yan, Z., Xie, F., Tian, Y., & Ai, L. (2023). Rheological Properties and Kinetics of Gelation of Binary Polymers between Xanthan Gum and Locust Bean Gum. Polymers, 15(23), 4604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234604






