Influence of Chitosan 0.2% in Various Final Cleaning Methods on the Bond Strength of Fiberglass Post to Intrarradicular Dentin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Endodontic Instrumentation and Obturation
2.2. Post-Space Preparation
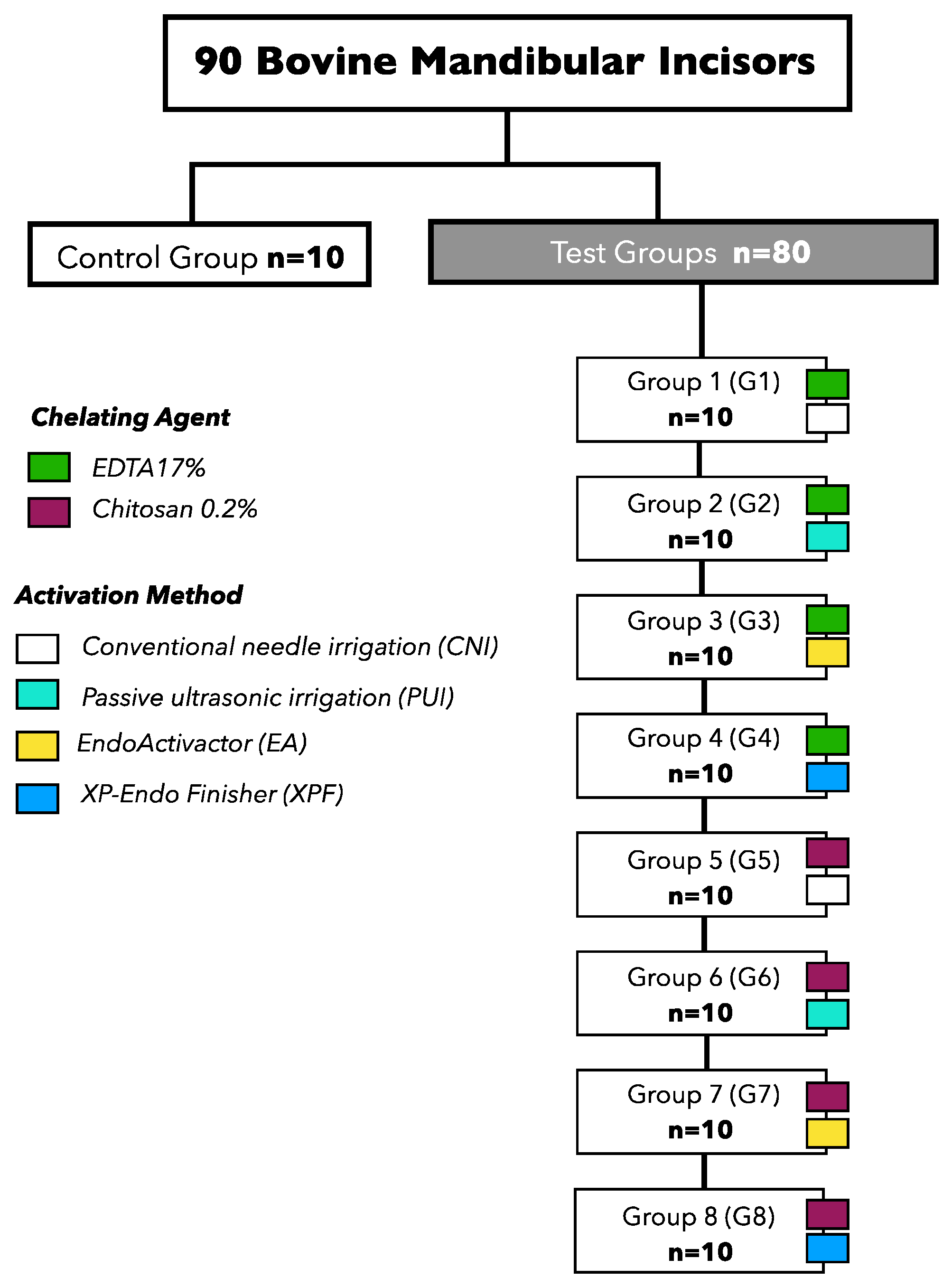
2.3. Experimental Groups
2.4. Formulation of Chelating Solutions
- CNI
- PUI
- EA
- XPF
2.5. Fiber Post Cementation
2.6. Root Sectioning Procedure
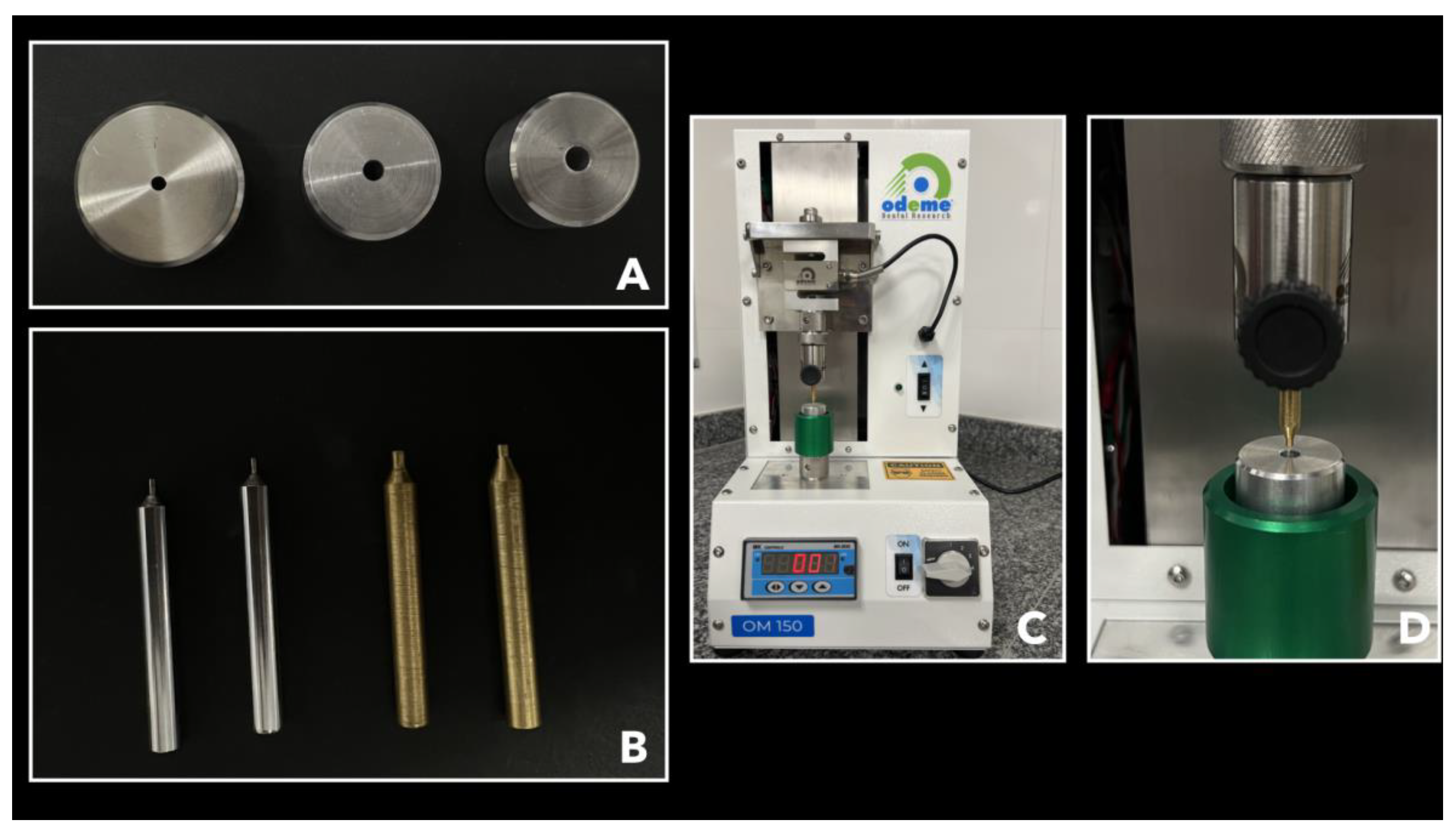
2.7. Micro Push-Out Mechanical Test (MPMT)
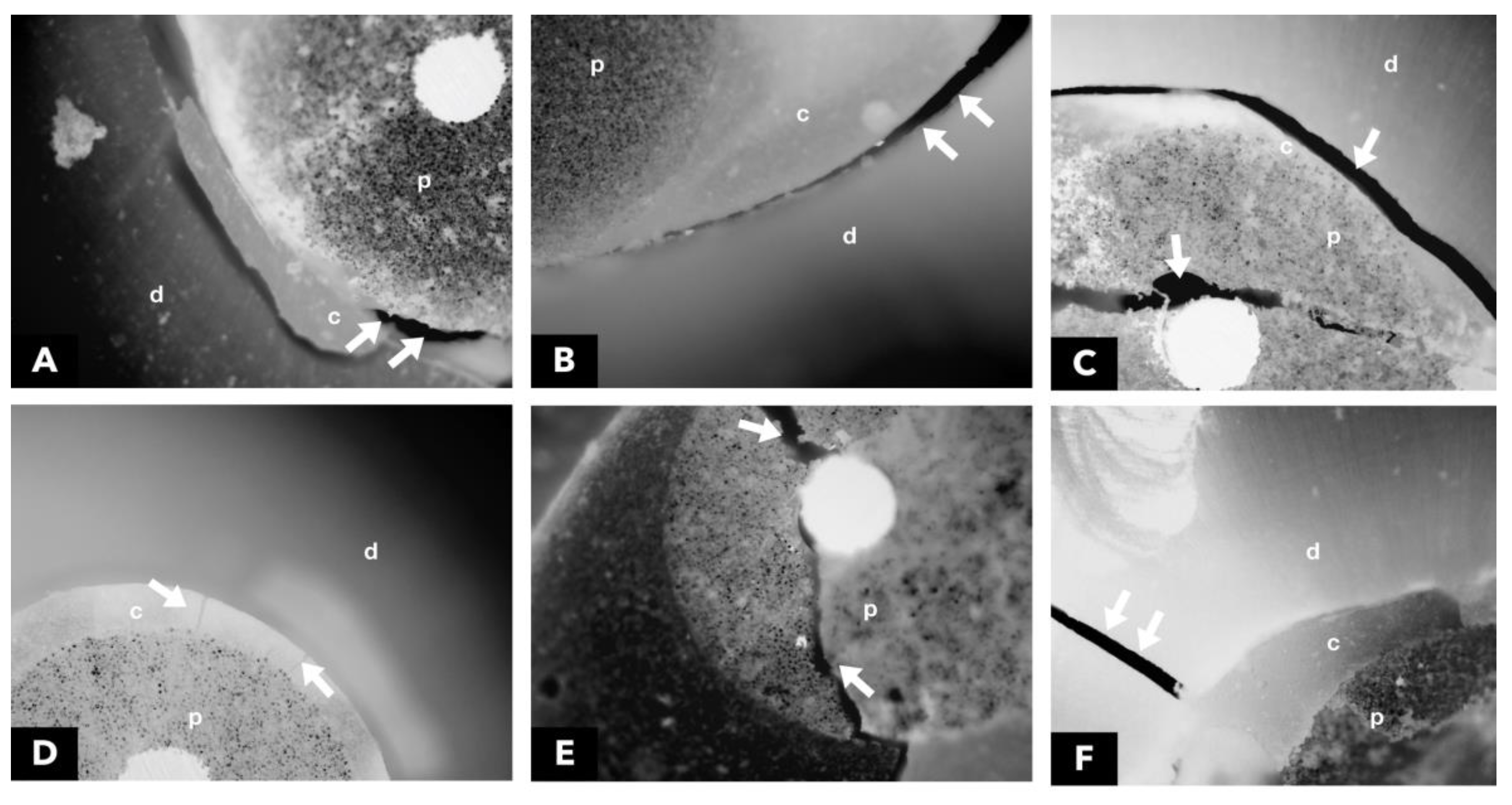
2.8. Analysis of the Failure Mode by Optical Microscopy
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- 1.
- the use of 0.2% chitosan + XPF as a final cleaning method positively influenced the bond strength between FP and intrarradicular dentin, with higher bond strength values in the cervical third.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menezes, M.S.; Queiroz, E.C.; Campos, R.E.; Martins, L.R.; Soares, C.J. Influence of endodontic sealer cement on fibreglass post bond strength to root dentine. Int. Endod. J. 2008, 41, 476–484. [Google Scholar]
- Baena, E.; Flores, A.; Ceballos, L. Influence of root dentin treatment on the push-out bond strength of fiber posts. Odontology 2017, 105, 170–177. [Google Scholar]
- Akman, M.; Eldeniz, A.U.; Ince, S.; Guneser, M.B. Push-out bond strength of a new post system after various post space treatments. Dent. Mater. J. 2016, 35, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.V.; Maia, T.S.; Zancopé, K.; Menezes, M.S.; Soares, C.J.; Moura, C.C.G. Can intra-radicular cleaning protocols increase the retention of fiberglass posts? A systematic review. Braz. Oral. Res. 2018, 32, e16. [Google Scholar]
- Haapasalo, M.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y. Irrigation in endodontics. Br. Dent. J. 2014, 216, 299–303. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L.S.; Kim, J.R.; Ling, J.; Choi, K.K.; Pashley, D.H.; Tay, F.R. Review of contemporary irrigant agitation techniques and devices. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 791–804. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, P.V.; Guedes, D.F.; Pécora, J.D.; da Cruz-Filho, A.M. Time-dependent effects of chitosan on dentin structures. Braz. Dent. J. 2012, 23, 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Barreto, M.S.; Rosa, R.A.; Seballos, V.G.; Machado, E.; Valandro, L.F.; Kaizer, O.B.; Só, M.V.R.; Bier, C.A.S. Effect of Intracanal Irrigants on Bond Strength of Fiber Posts Cemented with a Self-adhesive Resin Cement. Oper. Dent. 2016, 41, e159–e167. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, M.; Cerroni, L.; Iorio, L.; Dall’Asta, L.; Cianconi, L. FESEM evaluation of smear layer removal using different irrigant activation methods (EndoActivator, EndoVac, PUI and LAI). An in vitro study. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2018, 22, 993–999. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, B.H.; Ertürk, O.; Pişkin, B. The effect of different concentrations of EDTA on instrumented root canal walls. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 2009, 108, 622–627. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, P.V.; Guedes, D.F.; Nakadi, F.V.; Pécora, J.D.; Cruz-Filho, A.M. Chitosan: A new solution for removal of smear layer after root canal instrumentation. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akncbay, H.; Senel, S.; Ay, Z.Y. Application of chitosan gel in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 80, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bounegru, A.V.; Bounegru, I. Chitosan-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Pharmaceuticals and Clinical Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, N.; Rana, D.; Salave, S.; Gupta, R.; Patel, P.; Karunakaran, B.; Sharma, A.; Giri, J.; Benival, D.; Kommineni, N. Chitosan: A Potential Biopolymer in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herdiana, Y. Chitosan Nanoparticles for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment. Polymers 2023, 15, 3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K. Chemistry and application of chitin and chitosan. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1998, 59, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cruz-Filho, A.M.; Bordin, A.R.V.; Souza-Flamini, L.E.; Guedes, D.; Saquy, P.C.; Silva, R.G.; Pécora, J. Analysis of the shelf life of chitosan stored in different types of packaging, using colorimetry and dentin microhardness. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2017, 42, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K. Chitin and chitosan: Functional biopolymers from marine crustaceans. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanó, J.C.; Silva, R.G.; Guedes, D.F.; Sousa-Neto, M.D.; Estrela, C.; Pécora, J.D. Atomic absorption spectrometry and scanning electron microscopy evaluation of concentration of calcium ions and smear layer removal with root canal chelators. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaghy, A.M. Effect of QMix irrigant on bond strength of glass fibre posts to root dentine. Int. Endod. J. 2014, 47, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renovato, S.R.; Santana, F.R.; Ferreira, J.M.; Souza, J.B.; Soares, C.J.; Estrela, C. Effect of calcium hydroxide and endodontic irrigants on fibre post bond strength to root canal dentine. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, O.A.; Chaves, G.S.; Alencar, A.H.; Borges, A.H.; Estrela, C.R.; Soares, C.J.; Estrela, C. Effect of gutta-percha solvents on fiberglass post bond strength to root canal dentin. J. Oral. Sci. 2014, 56, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Santana, F.R.; Soares, C.J.; Silva, J.A.; Alencar, A.H.; Renovato, S.R.; Lopes, L.G.; Gonzaga, L.; Carlos, E. Effect of Instrumentation Techniques, Irrigant Solutions and Artificial accelerated Aging on Fiberglass Post Bond Strength to Intraradicular Dentin. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2015, 16, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boggian, L.C.; Silva, A.V.; Santos, G.R.; Oliveira, G.F.; Silva, W.L.; Nery Neto, I.; Guedes, O.A.; Estrela, C. Effect of intra-radicular cleaning protocols after post-space preparation on marginal adaptation of a luting agent to root dentin. J. Oral. Sci. 2023, 65, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorileo, M.C.G.O.; Guiraldo, R.D.; Lopes, M.B.; de Almeida Decurcio, D.; Guedes, O.A.; Aranha, A.M.F.; Gonini, Á.H.B.A., Jr. Effect of 0.2% Chitosan Associated with Different Final Irrigant Protocols on the Fiber Post Bond Strength to Root Canal Dentin of Bovine Teeth: An Study. Open Dent. J. 2022, 16, e2205310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.J.; Pereira, J.C.; Valdivia, A.D.; Novais, V.R.; Meneses, M.S. Influence of resin cement and post configuration on bond strength to root dentine. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 45, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.J.; Santana, F.R.; Castro, C.G.; Santos-Filho, P.C.; Soares, P.V.; Qian, F.; Armstrong, S.R. Finite element analysis and bond strength of a glass post to intraradicular dentin: Comparison between microtensile and push-out tests. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goracci, C.; Tavares, A.U.; Fabianelli, A.; Monticelli, F.; Raffaelli, O.; Cardoso, P.C.; Tay, F.; Ferrari, M. The adhesion between fiber posts and root canal walls: Comparison between microtensile and push-out bond strength measurements. Eur. J. Oral. Sci. 2004, 112, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, O.A.O.H.; Santana, G.; Raineri Capeletti, L.; De Araújo, E.C.R.; De Almeida, E.C.; Decurcio, D. Effect of Endodontic Retreatment Protocols on Bond Strength of Fiberglass Post to Root Canal Dentine: An In-vitro Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2021, 15, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.C.; McComb, D.; Anderson, J.D.; Tam, L.E. Effect of mode of polymerization of bonding agent on shear bond strength of autocured resin composite luting cements. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2003, 69, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamichi, I.; Iwaku, M.; Fusayama, T. Bovine teeth as possible substitutes in the adhesion test. J. Dent. Res. 1983, 62, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascon, F.M.; Kantovitz, K.R.; Sacramento, P.A.; Nobre-dos-Santos, M.; Puppin-Rontani, R.M. Effect of sodium hypochlorite on dentine mechanical properties. A review. J. Dent. 2009, 37, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartari, T.; Bachmann, L.; Zancan, R.F.; Vivan, R.R.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Bramante, C.M. Analysis of the effects of several decalcifying agents alone and in combination with sodium hypochlorite on the chemical composition of dentine. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, e42–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doğan, H.; Qalt, S. Effects of chelating agents and sodium hypochlorite on mineral content of root dentin. J. Endod. 2001, 27, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerth, H.U.; Dammaschke, T.; Züchner, H.; Schäfer, E. Chemical analysis and bonding reaction of RelyX Unicem and Bifix composites—A comparative study. Dent. Mater. 2006, 22, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Deus, G.; Paciornik, S.; Mauricio, M.H. Evaluation of the effect of EDTA, EDTAC and citric acid on the microhardness of root dentine. Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K.; Shimada, K.; Nishiyama, Y.; Shimojoh, M.; Nishimura, S.I. Nonnatural Branched Polysaccharides: Synthesis and Properties of Chitin and Chitosan Having alpha-Mannoside Branches. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 4764–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitter, K.; Paris, S.; Pfuertner, C.; Neumann, K.; Kielbassa, A.M. Morphological and bond strength evaluation of different resin cements to root dentin. Eur. J. Oral. Sci. 2009, 117, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Experimental Groups | Cervical Third | Middle Third | Apical Third | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | IQR (25–75%) | Median | IQR (25–75%) | Median | IQR (25–75%) | p-Value | |
| Control Group | 2.48 A,a | 1.87–3.81 | 2.00 A | 1.58–3.05 | 2.72 A | 1.39–3.79 | 0.387 |
| G1. EDTA 17% | 2.54 A,a | 1.79–3.74 | 3.42 A,a | 2.89–4.06 | 3.88 A,a | 1.98–5.00 | 0.116 |
| G2. EDTA 17% + PUI | 3.79 A,a,b | 2.93–5.13 | 3.76 A,a | 1.98–5.39 | 3.43 A,a | 1.21–4.78 | 0.387 |
| G3. EDTA 17% + EA | 2.71 A,a,b | 1.80–3.50 | 2.74 A,a | 1.63–4.61 | 2.27 A,a | 0.94–4.76 | 1.000 |
| G4. EDTA 17% + XPF | 3.16 A,a | 2.65–3.64 | 2.46 A,a | 1.72–3.76 | 3.09 A,a | 1.88–3.62 | 0.796 |
| G5. Chitosan 0.2% | 2.90 A,a,b | 2.33–4.33 | 2.83 A,a | 1.91–4.13 | 2.81 A,a | 1.54–3.70 | 0.705 |
| G6. Chitosan 0.2% + PUI | 2.45 A,a | 1.19–3.49 | 2.79 A,a | 1.89–3.29 | 2.52 A,a | 1.66–3.53 | 0.212 |
| G7. Chitosan 0.2%+ EA | 3.91 A,a,b | 2.34.5.46 | 2.59 A,a | 1.22–3.45 | 3.01 A,a | 1.26–3.91 | 0.200 |
| G8. Chitosan 0.2% + XPF | 5.35 A,b | 3.13–6.14 | 4.01 A,a | 2.64–5.26 | 4.11 A,a | 2.79–4.90 | 0.350 |
| p-Value | <0.01 | 0.017 | 0.159 | ||||
| Experimental Groups | Failures Modes N (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | TOTAL | |
| Control Group | 0 (0%) | 41 (68.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 19 (31.7%) | 60 (100%) |
| G1. EDTA 17% | 1 (1.7%) | 31 (51.71%) | 4 (6.71%) | 1 (1.7%) | 0 (0%) | 23 (38.3%) | 60 (100%) |
| G2. EDTA 17% + PUI | 1 (1.7%) | 41 (68.3%) | 3 (5%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 15 (25%) | 60 (100%) |
| G3. EDTA 17% + EA | 0 (0%) | 40 (66.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 20 (33.3%) | 60 (100%) |
| G4. EDTA 17% + XPF | 0 (0%) | 41 (68.3%) | 1 (1.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 18 (30%) | 60 (100%) |
| G5. Chitosan 0.2% | 0 (0%) | 35 (58.3% | 4 (6.7% | 1 (1.7%) | 0 (0%) | 20 (33.3%) | 60 (100%) |
| G6. Chitosan 0.2% + PUI | 0 (0%) | 50 (83.3% | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (16.7%) | 60 (100%) |
| G7. Chitosan 0.2% + EA | 0 (0%) | 40 (66.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 20 (33.3%) | 60 (100%) |
| G8. Chitosan 0.2% + XPF | 0 (0%) | 50 (83.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (16.7%) | 60 (100%) |
| TOTAL | 2 (0.4%) | 369 (68.3%) | 12 (2.2%) | 2 (0.4%) | 0 (0%) | 155 (28.7%) | 540 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camilo, N.G.; Gonçalves, A.d.R.; Flauzino, L.P.; Bernardes, C.M.R.; Aranha, A.M.F.; Lazari-Carvalho, P.C.; Carvalho, M.A.d.; Oliveira, H.F.d. Influence of Chitosan 0.2% in Various Final Cleaning Methods on the Bond Strength of Fiberglass Post to Intrarradicular Dentin. Polymers 2023, 15, 4409. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224409
Camilo NG, Gonçalves AdR, Flauzino LP, Bernardes CMR, Aranha AMF, Lazari-Carvalho PC, Carvalho MAd, Oliveira HFd. Influence of Chitosan 0.2% in Various Final Cleaning Methods on the Bond Strength of Fiberglass Post to Intrarradicular Dentin. Polymers. 2023; 15(22):4409. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224409
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamilo, Naira Geovana, Alex da Rocha Gonçalves, Larissa Pinzan Flauzino, Cristiane Martins Rodrigues Bernardes, Andreza Maria Fábio Aranha, Priscilla Cardoso Lazari-Carvalho, Marco Aurélio de Carvalho, and Helder Fernandes de Oliveira. 2023. "Influence of Chitosan 0.2% in Various Final Cleaning Methods on the Bond Strength of Fiberglass Post to Intrarradicular Dentin" Polymers 15, no. 22: 4409. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224409
APA StyleCamilo, N. G., Gonçalves, A. d. R., Flauzino, L. P., Bernardes, C. M. R., Aranha, A. M. F., Lazari-Carvalho, P. C., Carvalho, M. A. d., & Oliveira, H. F. d. (2023). Influence of Chitosan 0.2% in Various Final Cleaning Methods on the Bond Strength of Fiberglass Post to Intrarradicular Dentin. Polymers, 15(22), 4409. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224409