3D-Printed Filters for Efficient Heavy Metal Removal from Water Using PLA@CS/HAP Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Three-Dimensional PLA Scaffold and Column
2.3. Preparation of the CS/HAP Composites & PLA@CS/HAP Filter
2.4. Static Adsorption Experiments
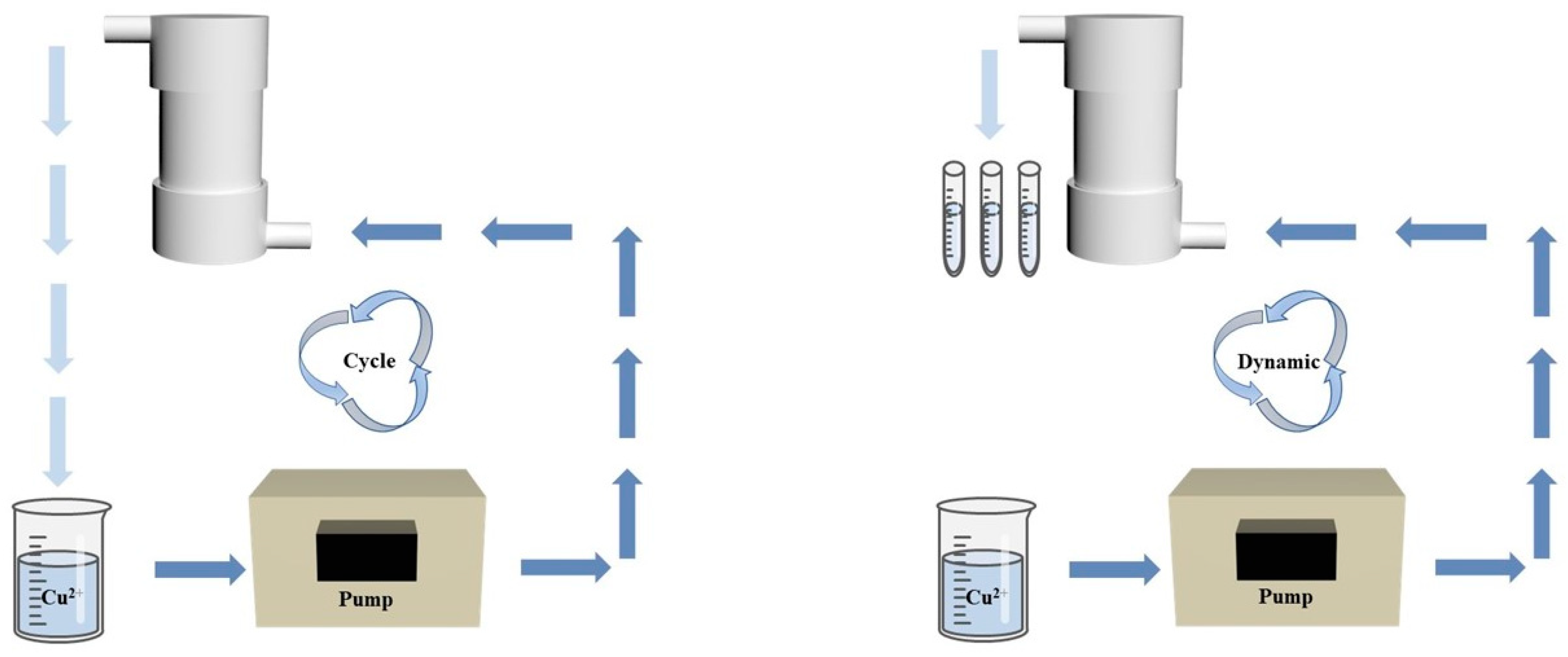
2.5. Cyclic & Dynamic Removal Experiments
2.6. Structural and Morphological Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
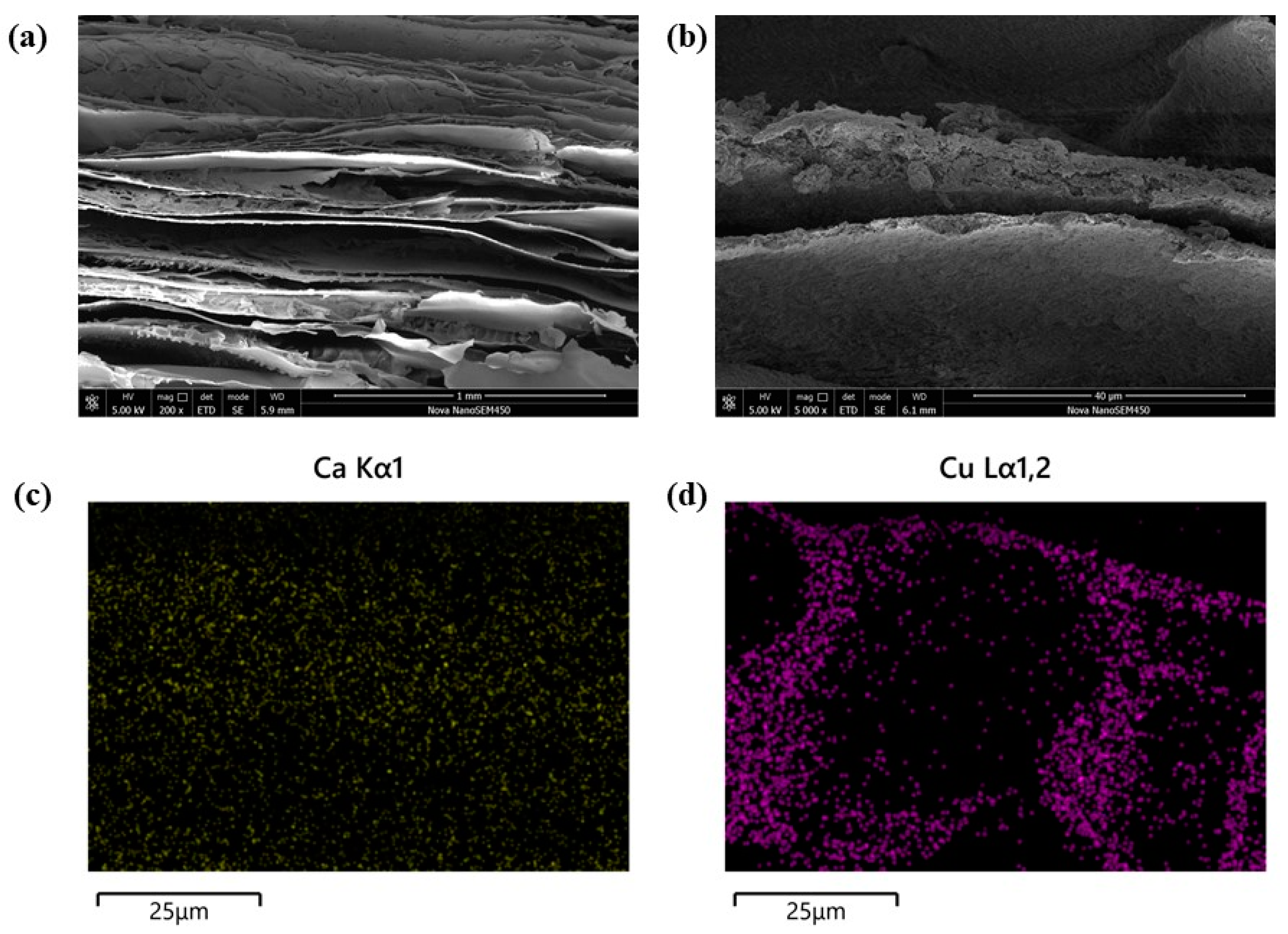
3.1. Characterization of CS/HAP Composites
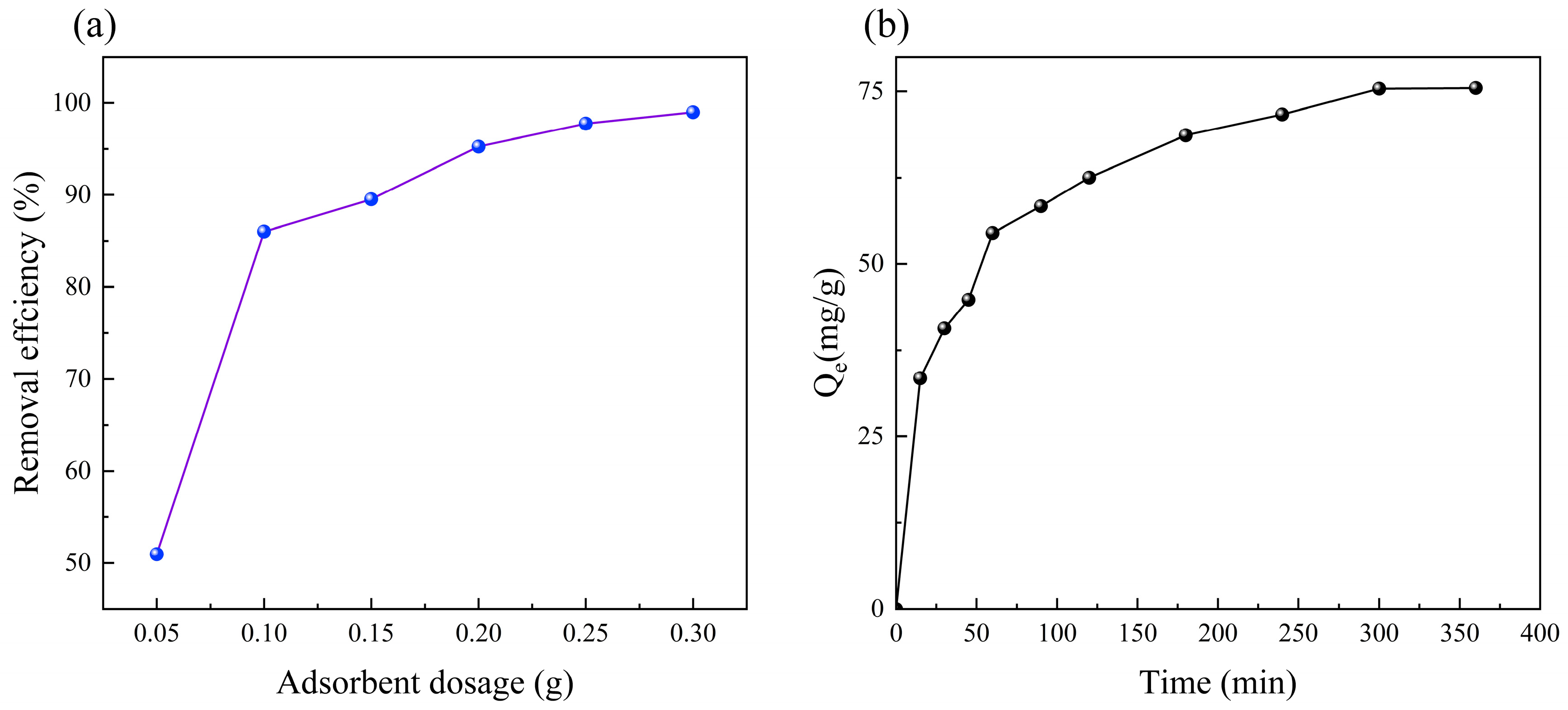
3.2. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
3.3. Effect of Adsorption Time
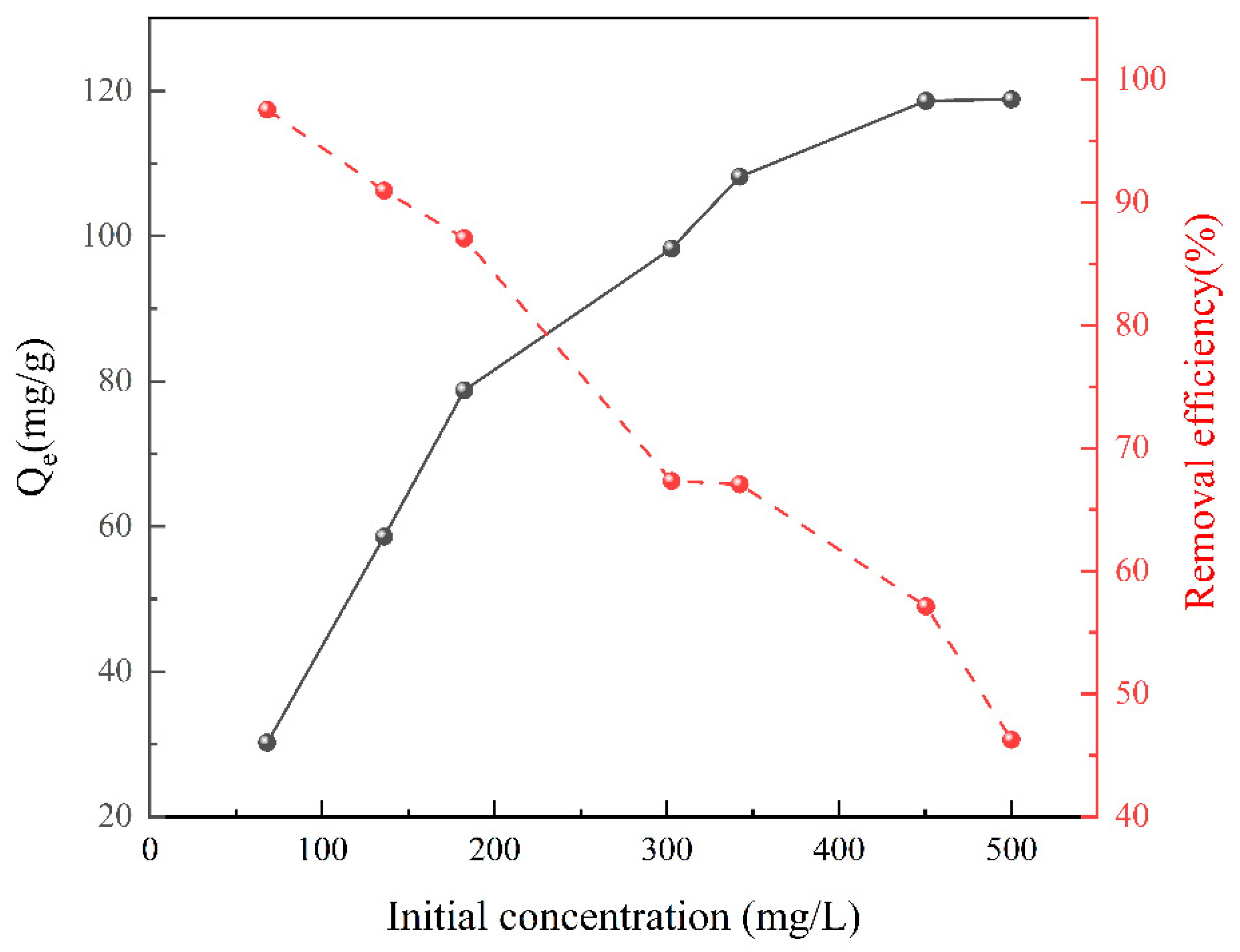
3.4. Effect of the Initial Cu2+ Concentration
3.5. Adsorption Isotherm
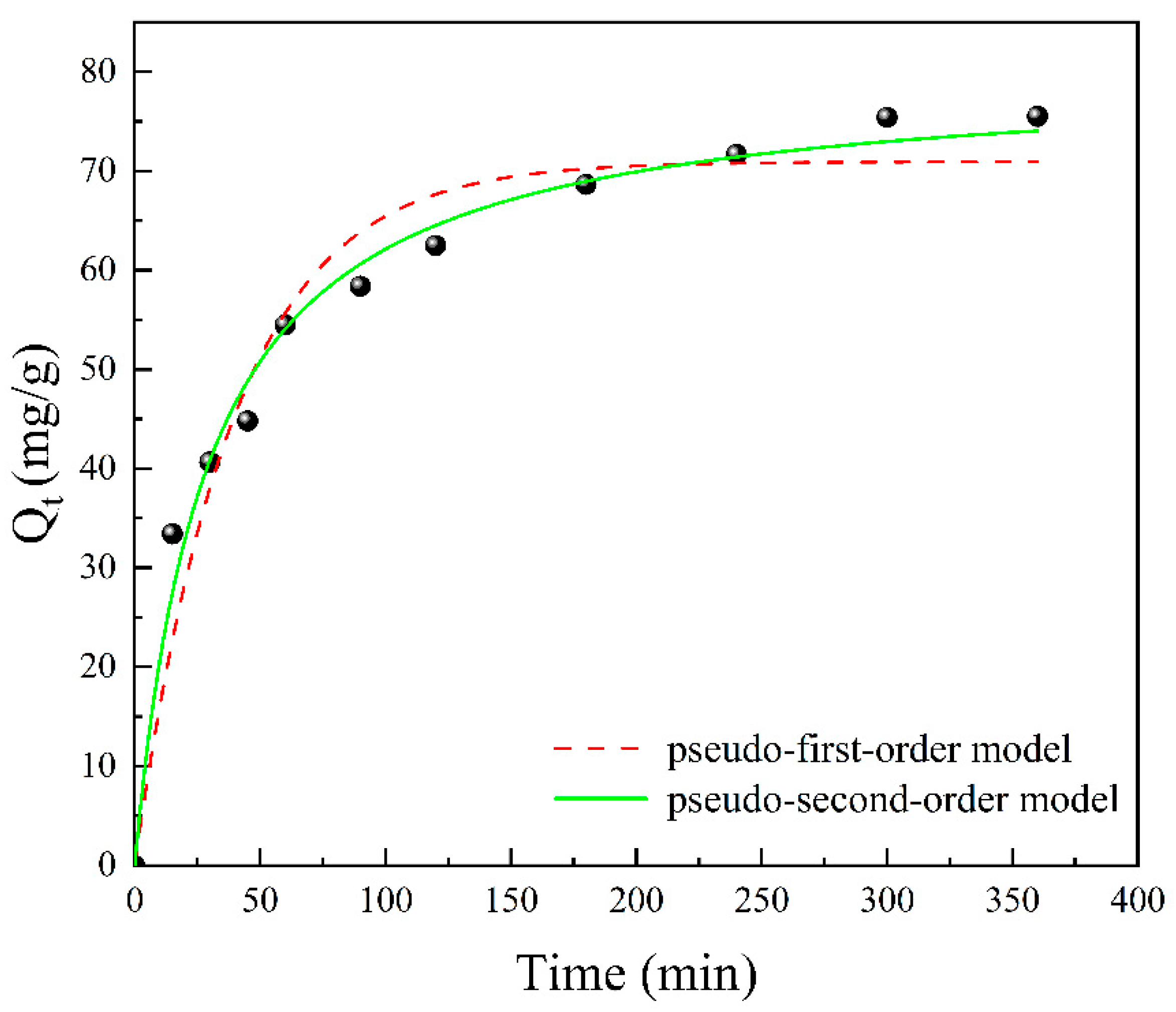
3.6. Adsorption Kinetics
3.7. Adsorption Thermodynamics
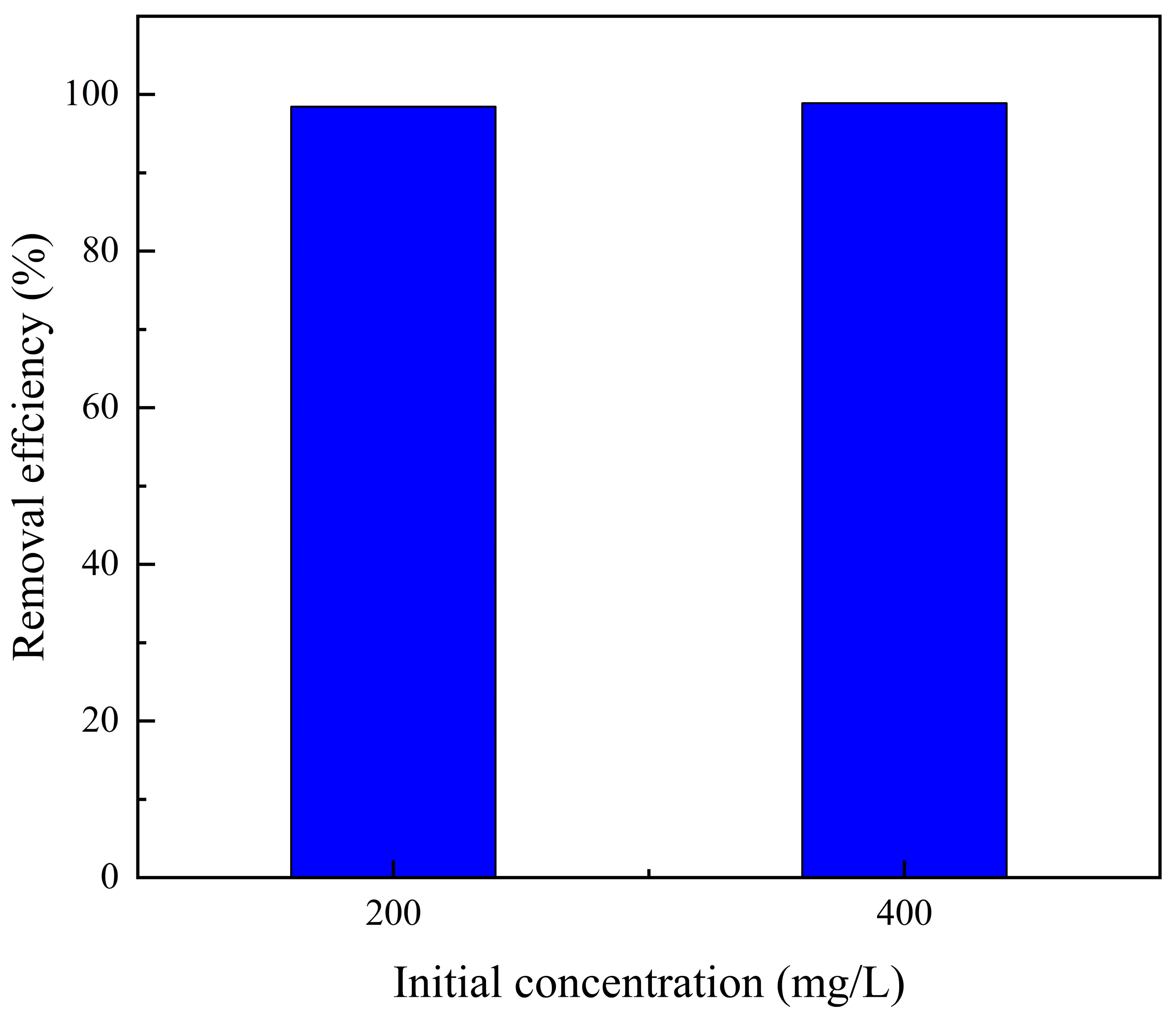
3.8. Properties of PLA@CS/HAP Filter
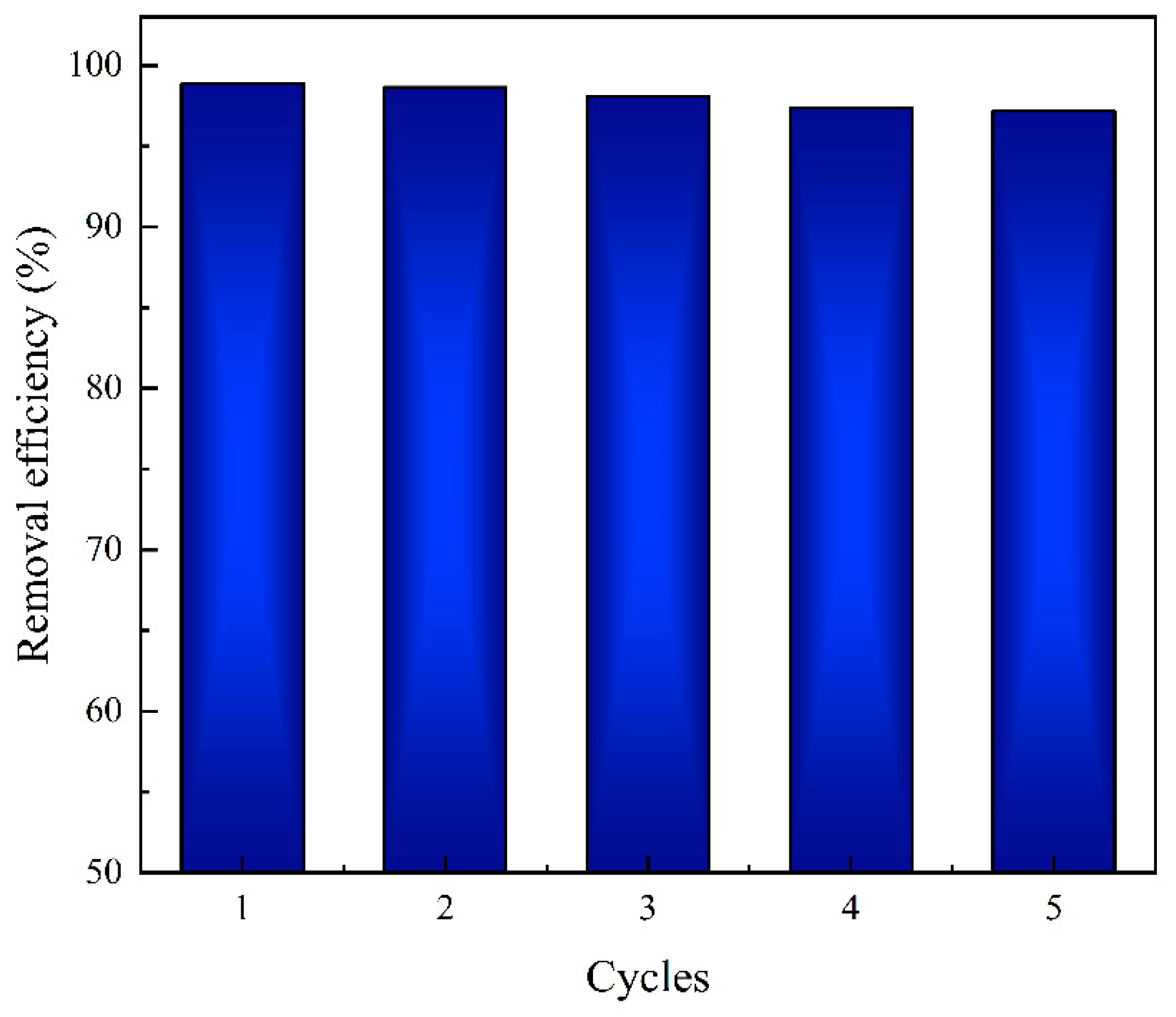
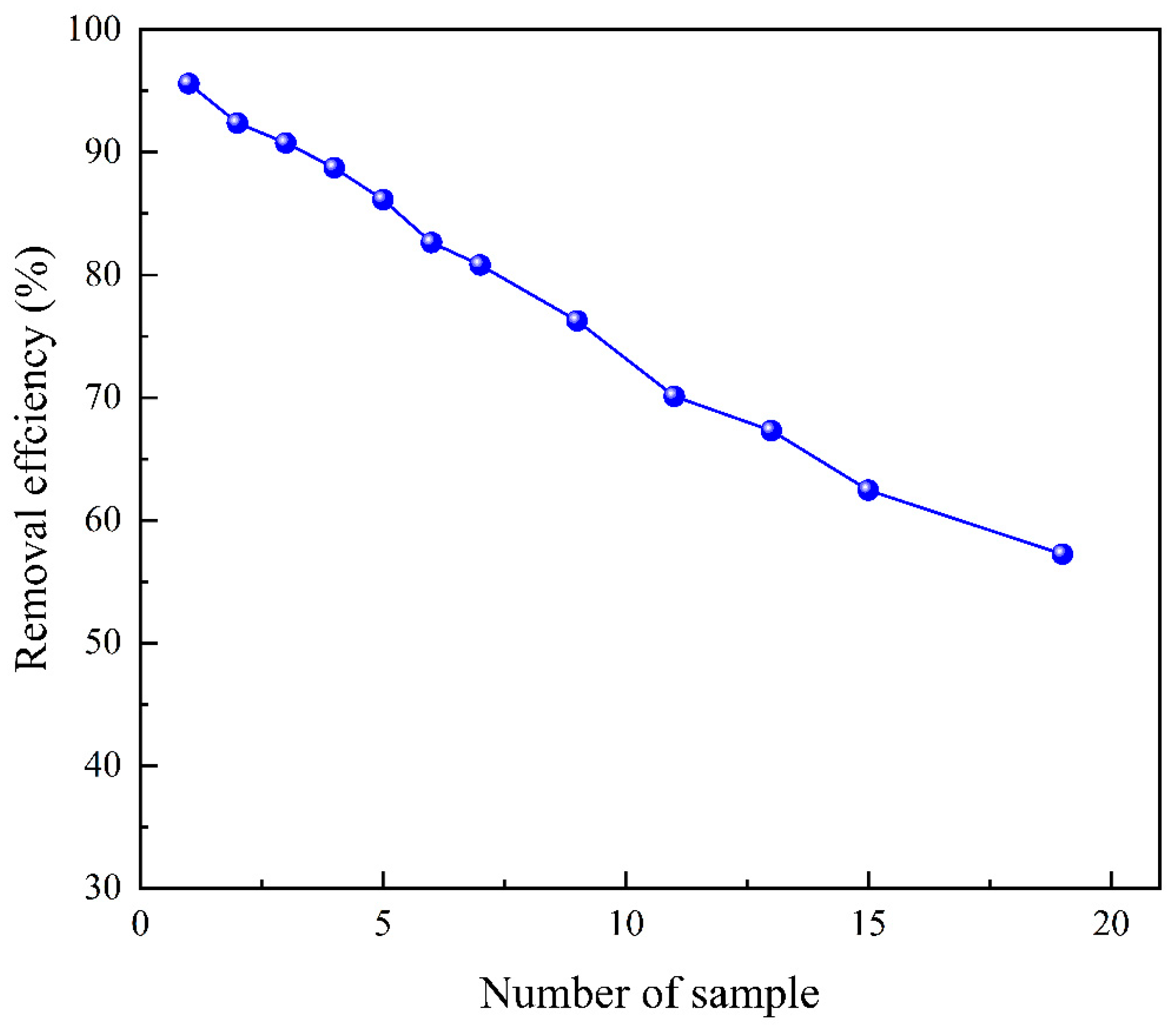
3.9. Reusability
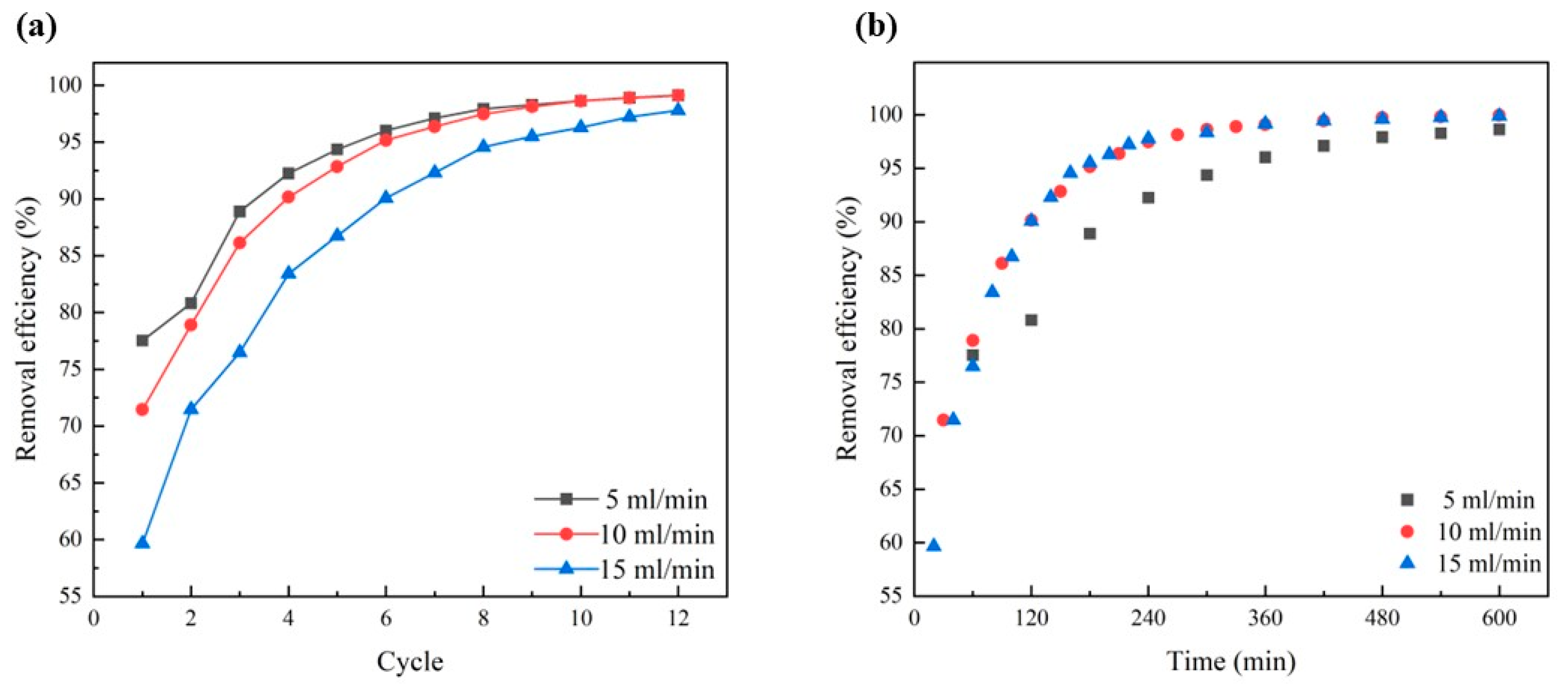
3.10. Cyclic & Dynamic Removal Experiment
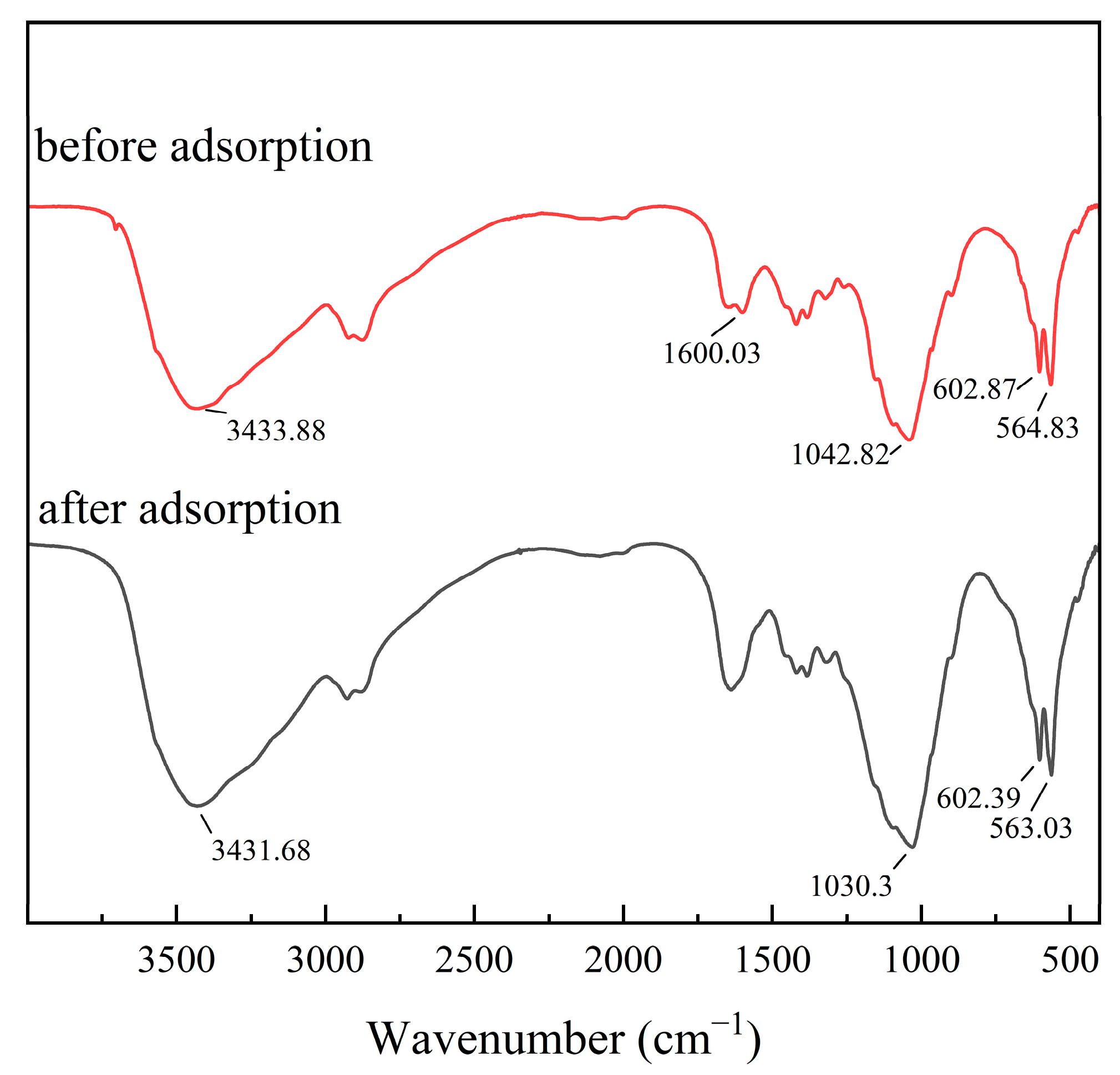
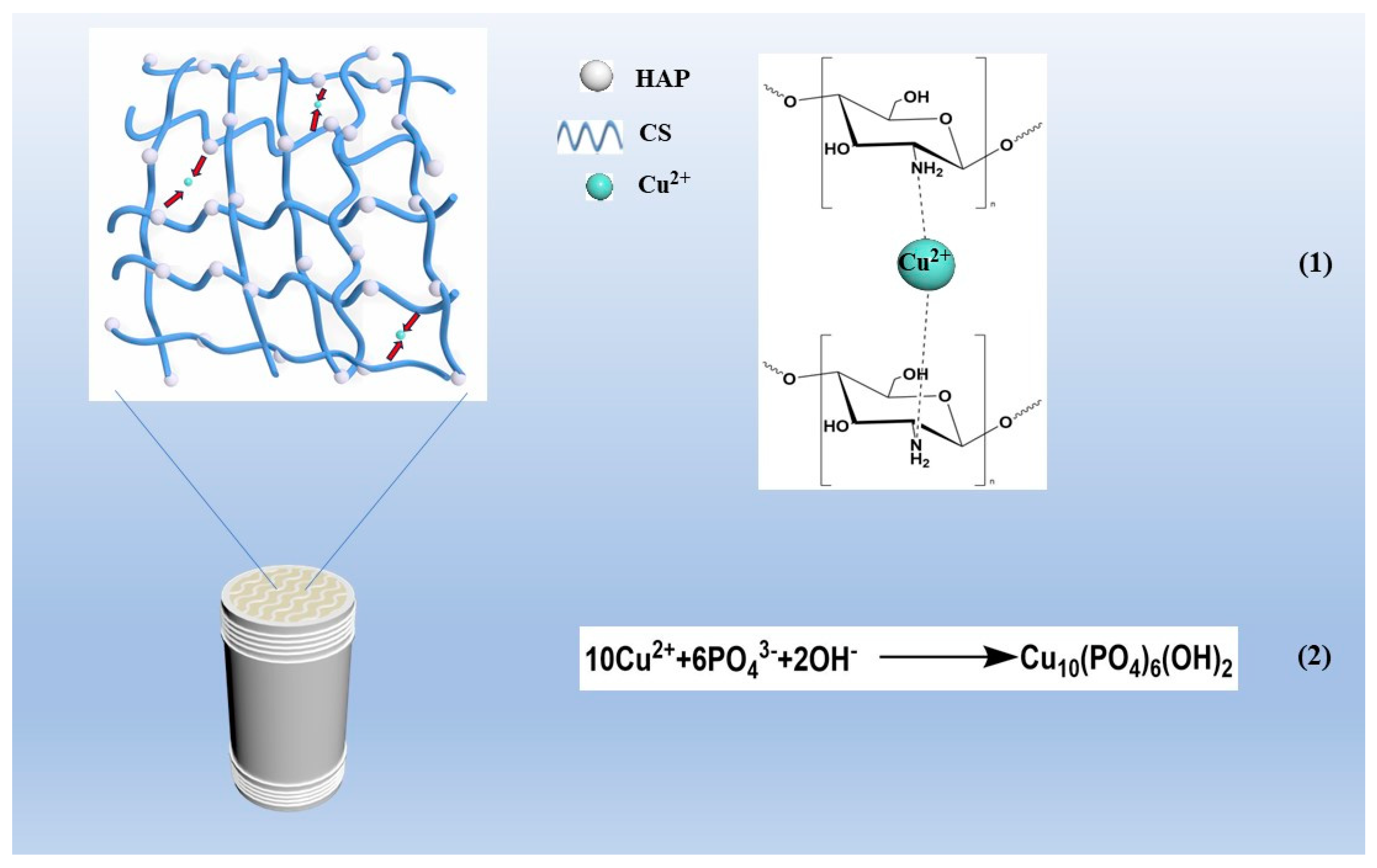
3.11. Removal Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajiv Gandhi, M.; Kousalya, G.N.; Meenakshi, S. Removal of copper(II) using chitin/chitosan nano-hydroxyapatite composite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoa, N.V.; Minh, N.C.; Cuong, H.N.; Dat, P.A.; Nam, P.V.; Viet, P.H.T.; Phuong, P.T.D.; Trung, T.S. Highly Porous Hydroxyapatite/Graphene Oxide/Chitosan Beads as an Efficient Adsorbent for Dyes and Heavy Metal Ions Removal. Molecules 2021, 26, 6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MT, A.L.; Sanchez, J. Adsorption of Copper and Arsenic from Water Using a Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network Based on Alginate and Chitosan. Polymers 2023, 15, 2192. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, H.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z. Application of Ionic Liquid Crosslinked Hydrogel for Removing Heavy Metal Ions from Water: Different Concentration Ranges with Different Adsorption Mechanisms. Polymers 2023, 15, 2784. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Hu, T.; Du, C.; Liao, Z.; Cheng, W.; Wang, F.; Hu, X.; Song, K. Fe-N-Doped Conjugated Organic Polymer Efficiently Enhanced the Removal Rate of Cr(VI) from Water. Polymers 2023, 15, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, N. A new approach to copper ion removal from water by polymeric nanocomposite membrane embedded with γ-alumina nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, A.; Mohebbi, A.; Amiri, M.; Izadi, N. Removal of iron ions from industrial copper raffinate and electrowinning electrolyte solutions by chemical precipitation and ion exchange. Miner. Eng. 2017, 113, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Revathi, M.; Ahmed Basha, C.; Velan, M. Removal of copper(II) ions from synthetic electroplating rinse water using polyethyleneimine modified ion-exchange resin. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 20350–20367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalim, Y.; Benayada, A.; El Ahmadi, Z. Cadmium Removal from Cadmium-Containing Apatites by Ion-Exchange Reactions. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202201862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambaeero, A.; Bazargan-Lari, R. Simultaneous removal of copper and zinc ions by low cost natural snail shell/hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 33, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, H. Nano-hydroxyapatite incorporated gelatin/zein nanofibrous membranes: Fabrication, characterization and copper adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1478–1489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hokkanen, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Srivastava, V.; Suorsa, V.; Sillanpaa, M. Removal of Cd(2+), Ni(2+) and PO(4)(3-) from aqueous solution by hydroxyapatite-bentonite clay-nanocellulose composite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118 Pt A, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucan-Altuntas, K.; Uzun, H.I.; Ustundag, C.B.; Debik, E. Adsorption of copper ion from aqueous solutions by well-crystalized nanosized hydroxyapatite. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 6, 125545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Ma, Y.; He, J.; Ren, Z. Highly Stable, Mechanically Enhanced, and Easy-to-Collect Sodium Alginate/NZVI-rGO Gel Beads for Efficient Removal of Cr(VI). Polymers 2023, 15, 3764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Villa-Reyna, A.-L.; Aguilar-Martínez, M.; Ochoa-Terán, A.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Leyva-Peralta, M.-A.; Vargas-Durazo, J.-T.; Salazar-Gastelum, M.I.; García-Elías, J.; Gálvez-Ruiz, J.-C. Efficient and Sustainable Bidentate Amines-Functionalized Resins for Removing Ag+, Cu2+, Pb2+, and Fe3+ from Water. Polymers 2023, 15, 2778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azzam, E.M.S.; Elsofany, W.I.; Abdulaziz, F.; AlGhamdi, H.A.; Al Alhareth, A.Y. Ecofriendly Elimination of Ni (II) Using Fabricated Nanocomposite Based on Chitosan/Silver Nanoparticles/Carbon Nanotubes. Polymers 2023, 15, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Garduno, O.; Martinez, M.E.; Gimeno, M.; Tecante, A.; Beristain-Cardoso, R.; Shirai, K. Copper removal from wastewater by a chitosan-based biodegradable composite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 28527–28535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Zhou, R.; Wu, P.; Wu, L. Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution with hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 336–342. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Guan, J.-J.; Chen, W.; Ke, Q.-F.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Guo, Y.-P. Fabrication of hydroxyapatite/chitosan porous materials for Pb(ii) removal from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 25462–25470. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Lv, C.; Wu, L.; Hou, X. Porous chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite membrane for dyes static and dynamic removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, D.N.; Novák, P.; Vejpravova, J.; Vu, H.N.; Lederer, J.; Munshi, T. Removal of copper and nickel from water using nanocomposite of magnetic hydroxyapatite nanorods. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 456, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Chen, W.; Lu, B.; Ke, Q.-F.; Guo, Y.-P. Bioinspired fabrication and lead adsorption property of nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan porous materials. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 98783–98795. [Google Scholar]
- Liakos, I.L.; Mondini, A.; Dottore, E.D.; Filippeschi, C.; Pignatelli, F.; Mazzolai, B. 3D printed composites from heat extruded polycaprolactone/sodium alginate filaments and their heavy metal adsorption properties. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 2472–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijol, N.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Pillai, B.; Hall, S.A.; Thomas, N.; Mathew, A.P. 3D-printed monolithic biofilters based on a polylactic acid (PLA)—Hydroxyapatite (HAp) composite for heavy metal removal from an aqueous medium. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 32408–32418. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Xiao, J.; Guo, Q.; Yang, J. 3D-printed highly porous and reusable chitosan monoliths for Cu(II) removal. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 6728–6741. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Ratri, M.C.; Choe, G.; Nam, M.; Cho, D.; Shin, K. Three-dimensional, printed water-filtration system for economical, on-site arsenic removal. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231475. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, K.P.; Liu, H.W.; Wang, L.; Xiao, X.F.; Dou, D.D.; Fan, Y.B. Three-dimensional polylactic acid@graphene oxide/chitosan sponge bionic filter: Highly efficient adsorption of crystal violet dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 792–803. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Zeng, J.; Tang, S.; Bai, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Preparation of reusable cross-linked amidoxime polyacrylonitrile microspheres and their efficient adsorption of Cu (II) and Pb (II). Polym. Bull. 2022, 80, 9811–9831. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Yan, M.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Facile preparation of core-shell structure β-cyclodextrin/diatomite as an efficient adsorbent for methylene blue. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 136, 109925. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhang, G.; Yan, T.; Yan, L.; Wei, Q.; Du, B. Removal of Pb(II) and methylene blue from aqueous solution by magnetic hydroxyapatite-immobilized oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 494, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condurache, B.C.; Cojocaru, C.; Samoila, P.; Cosmulescu, S.F.; Predeanu, G.; Enache, A.C.; Harabagiu, V. Oxidized Biomass and Its Usage as Adsorbent for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Molecules 2022, 27, 6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enache, A.-C.; Samoila, P.; Cojocaru, C.; Apolzan, R.; Predeanu, G.; Harabagiu, V. An Eco-Friendly Modification of a Walnut Shell Biosorbent for Increased Efficiency in Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2704. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, E.C.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; Anastopoulos, I. A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the Van’t Hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 425–434. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Dai, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L. Selective removal mechanism of the novel Zr-based metal organic framework adsorbents for gold ions from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123343. [Google Scholar]





| T (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (mg/g) | KL (mg/L) | R2 | RL | KF (mg/g) | n−1 | R2 | |
| 298 | 119.498 | 0.0881 | 0.945 | 0.0314 | 33.529 | 0.2365 | 0.968 |
| 318 | 117.121 | 0.3954 | 0.985 | 0.0058 | 59.784 | 0.1313 | 0.828 |
| T (K) | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe (mg/g) | k1 | R2 | Qe (mg/g) | k2 | R2 | |
| 298 | 70.93 | 0.02561 | 0.953 | 79.95 | 0.000436 | 0.986 |
| Temperature (K) | Kd | ΔG (kJ mol−1) | ΔH (kJ mol−1) | ΔS (J mol−1 K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 6.739∙103 | −21.84 | 59.16 | 271.8 |
| 318 | 3.025∙104 | −27.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, S.; Ma, H. 3D-Printed Filters for Efficient Heavy Metal Removal from Water Using PLA@CS/HAP Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204144
Wang Y, Wang Y, Qiu S, Wang C, Zhang H, Guo J, Wang S, Ma H. 3D-Printed Filters for Efficient Heavy Metal Removal from Water Using PLA@CS/HAP Composites. Polymers. 2023; 15(20):4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204144
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yisu, Yan Wang, Shuai Qiu, Chongyang Wang, Hong Zhang, Jing Guo, Shengfa Wang, and Huixia Ma. 2023. "3D-Printed Filters for Efficient Heavy Metal Removal from Water Using PLA@CS/HAP Composites" Polymers 15, no. 20: 4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204144
APA StyleWang, Y., Wang, Y., Qiu, S., Wang, C., Zhang, H., Guo, J., Wang, S., & Ma, H. (2023). 3D-Printed Filters for Efficient Heavy Metal Removal from Water Using PLA@CS/HAP Composites. Polymers, 15(20), 4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204144






