β-Tricalcium Phosphate-Loaded Chitosan-Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Periodontal Regeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
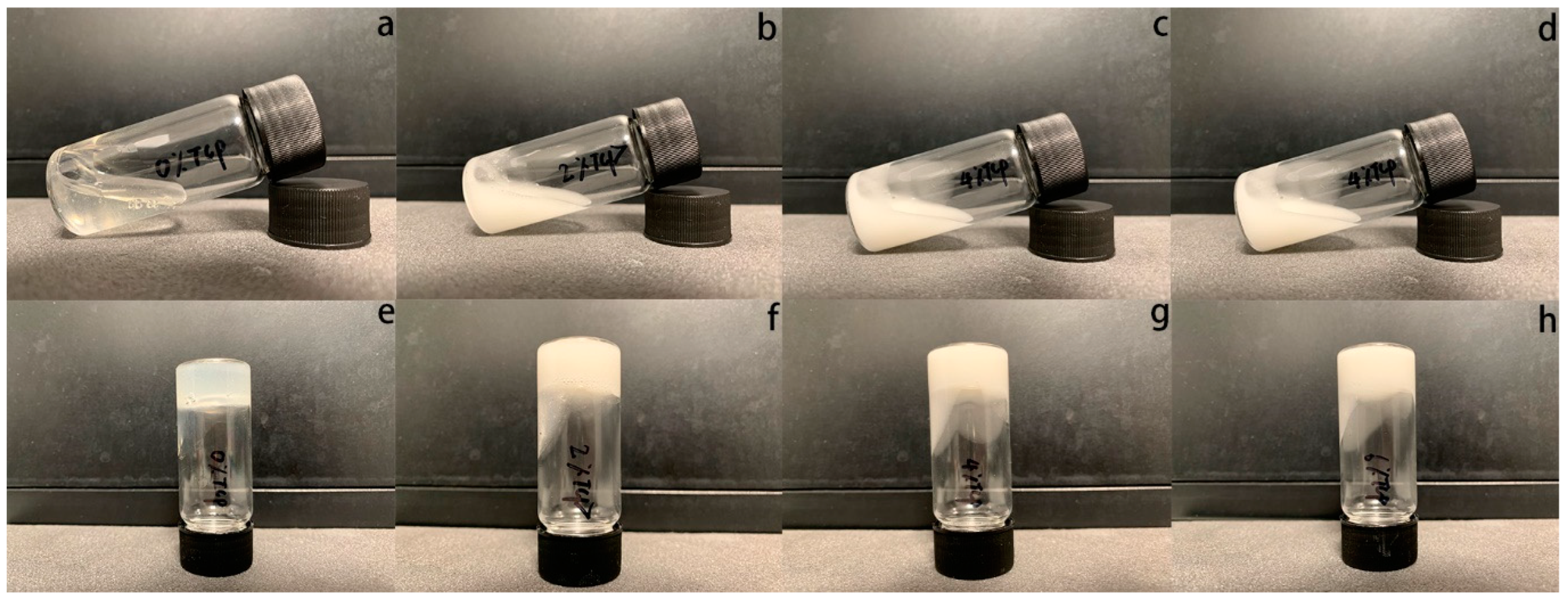
2.1. Hydrogel Preparation
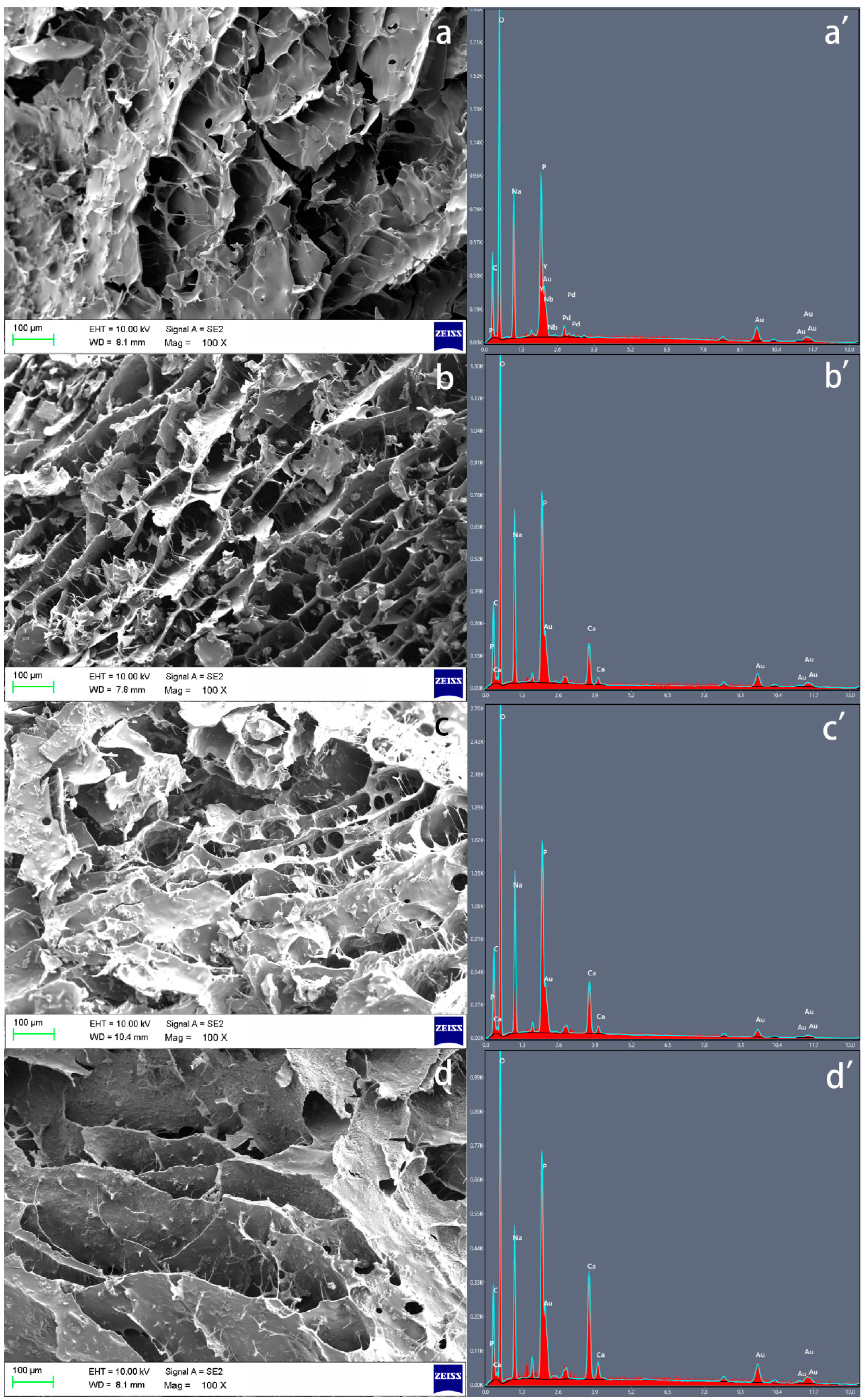
2.2. Morphology of the Samples Observed through Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) Analysis
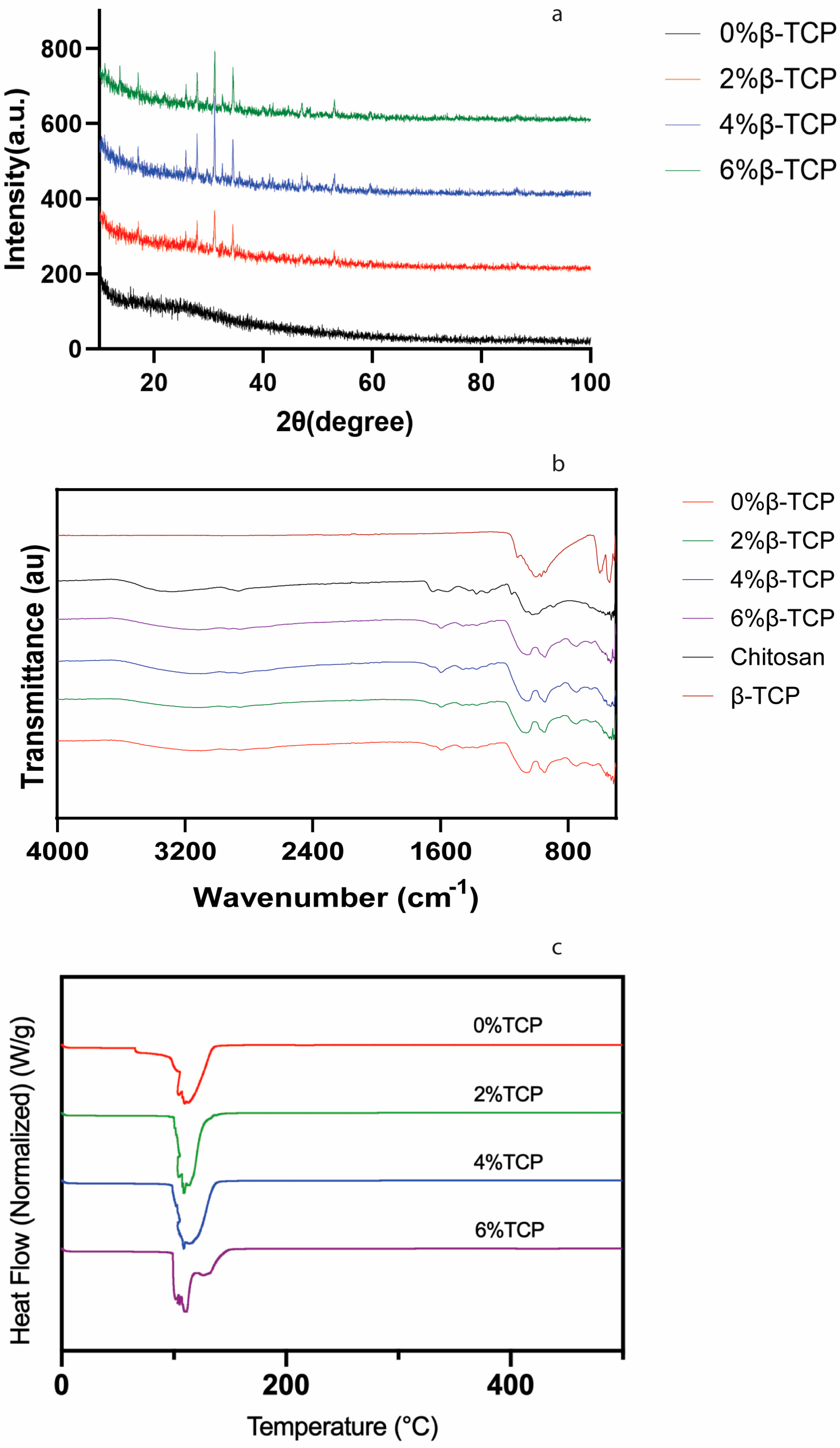
2.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.4. Spectroscopic Analysis
2.5. Thermal Analysis
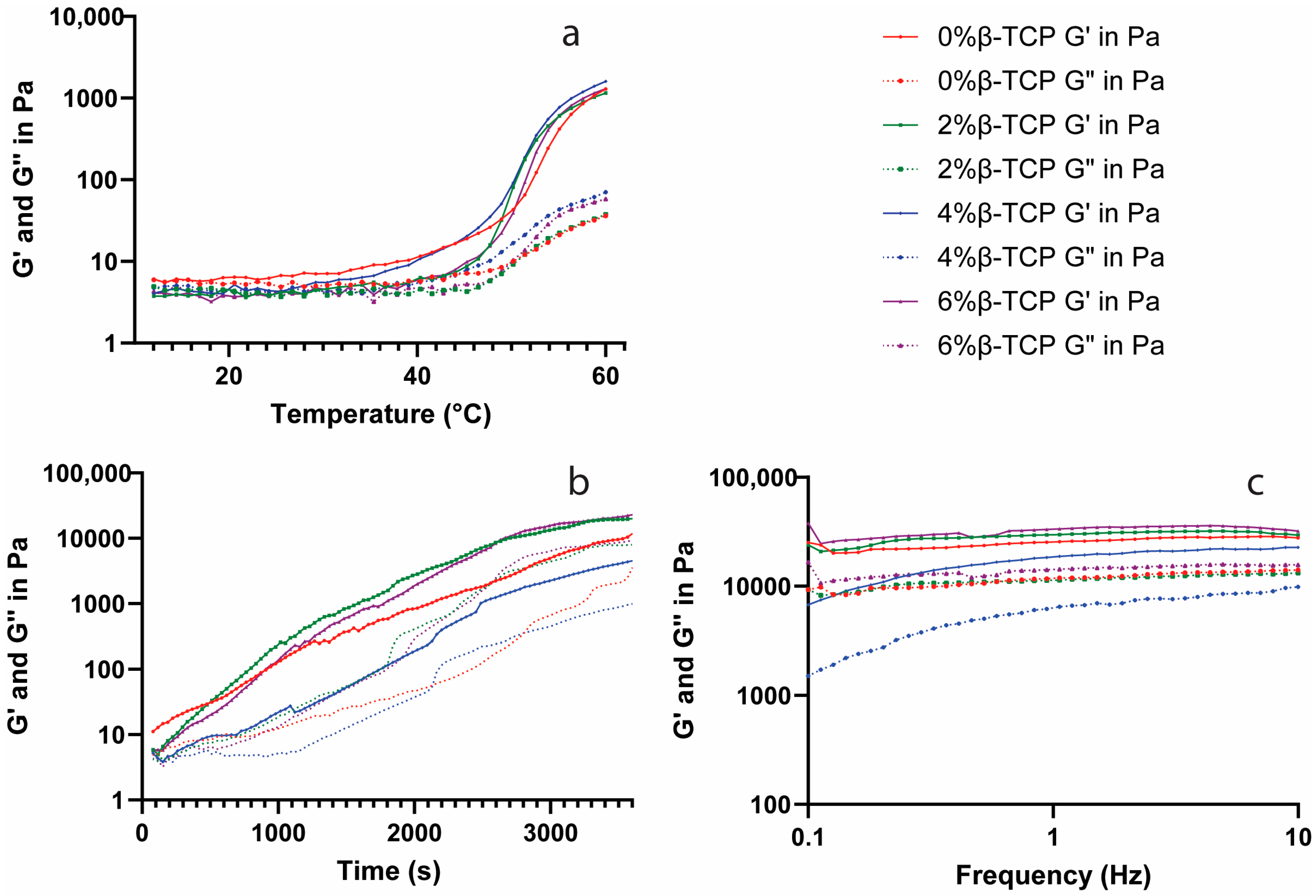
2.6. Rheological Analysis
2.7. Degradation Analysis
2.8. Biological Analyses
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) Analysis
3.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
3.3. Spectroscopic Analysis
3.4. Thermal Analysis
3.5. Rheological Analysis
3.6. Degradation Test
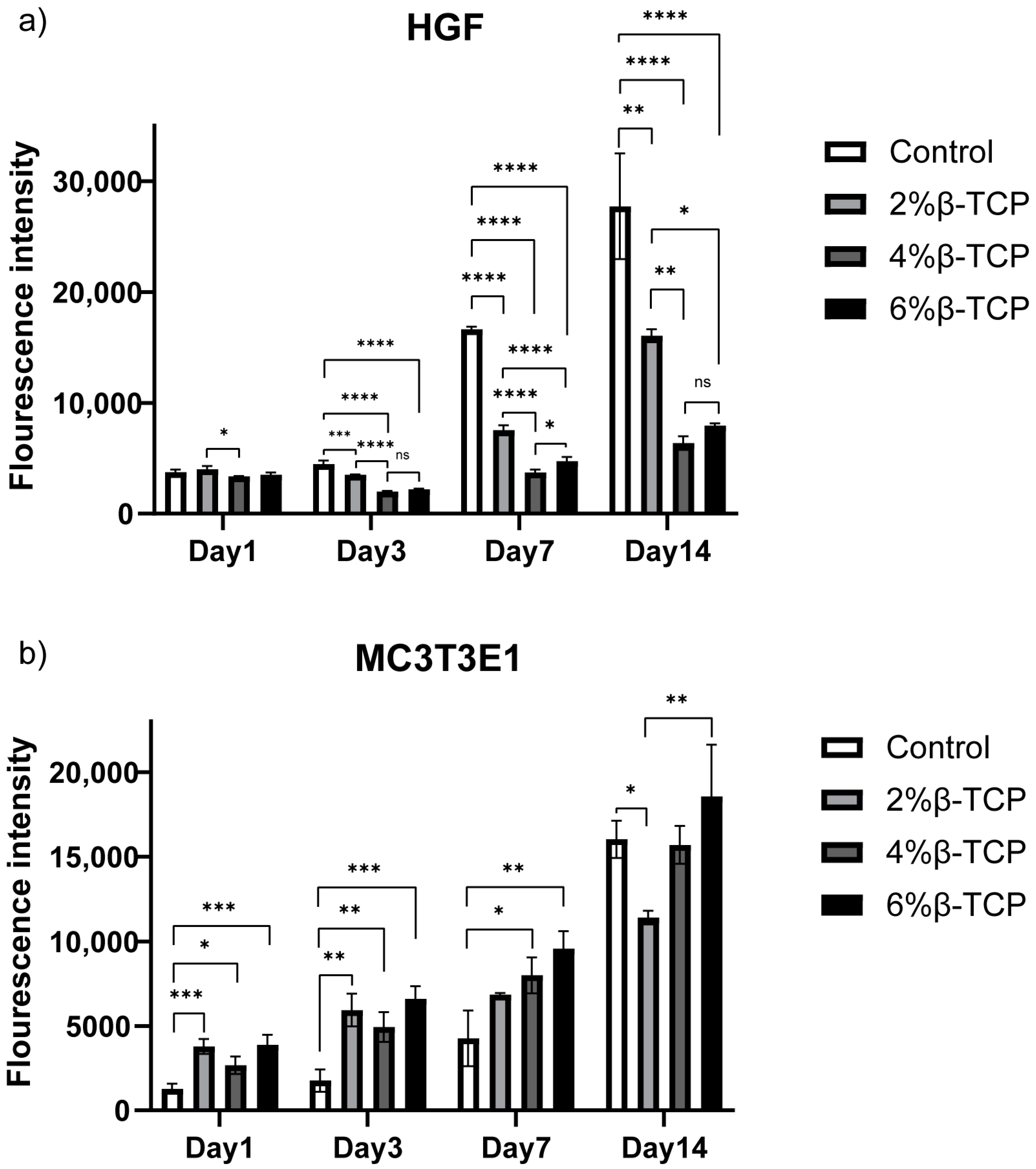
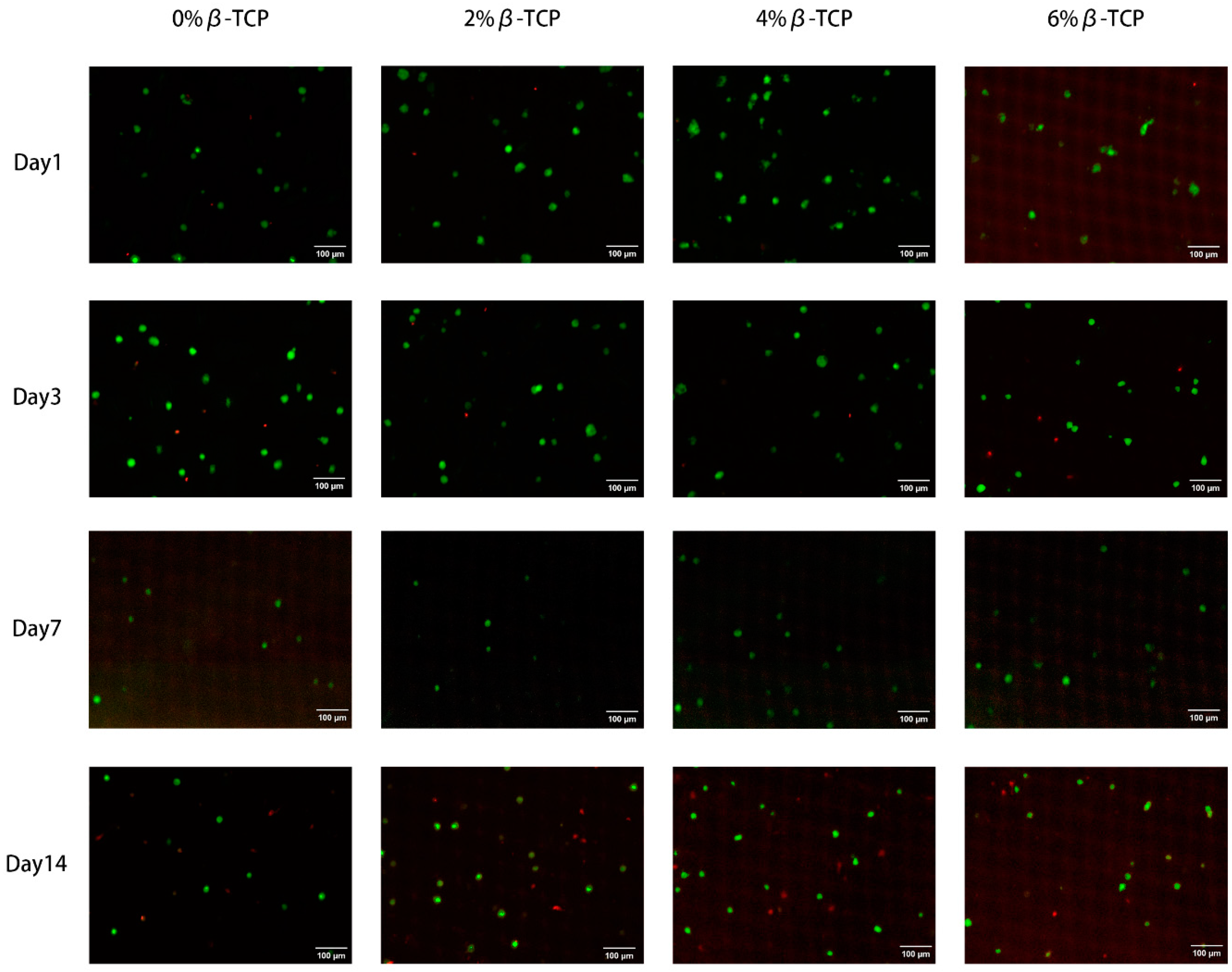
3.7. In Vitro Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Periodontology: A.A.o. Periodontitis: Chronic Periodontitis. Available online: https://members.perio.org/libraries/glossary/entry?GlossaryKey=961be2e7-2a1a-4e8a-96ff-b6d611cc2dd4&tab=groupdetails (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Armitage, G.C. Development of a Classification System for Periodontal Diseases and Conditions. Ann. Periodontol. 1999, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Buduneli, N.; Dietrich, T.; Feres, M.; Fine, D.H.; Flemmig, T.F.; Garcia, R.; Giannobile, W.V.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S173–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.; Herrera, D.; Kebschull, M.; Chapple, I.; Jepsen, S.; Berglundh, T.; Sculean, A.; Tonetti, M.S.; Consultants, E.W.P.A.M.; Consultants, T.E.W.P.A.M.; et al. Treatment of stage I–III periodontitis—The EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47 (Suppl. 22), 4–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D.; Sanz, M.; Kebschull, M.; Jepsen, S.; Sculean, A.; Berglundh, T.; Papapanou, P.N.; Chapple, I.; Tonetti, M.S.; Consultant, E.W.P.A.M. Treatment of stage IV periodontitis: The EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2022, 49 (Suppl. 24), 4–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartold, P.M.; Xiao, Y.; Lyngstaadas, S.P.; Paine, M.L.; Snead, M.L. Principles and applications of cell delivery systems for periodontal regeneration. Periodontology 2000 2006, 41, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacanti, C.A.; Vacanti, J.P. Engineering Cartilage and Other Structural Tissues: Principles of Bone and Cartilage Reconstruction. In Principles of Tissue Engineering; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 1267–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Galli, M.; Yao, Y.; Giannobile, W.V.; Wang, H.-L. Current and future trends in periodontal tissue engineering and bone regeneration. Plast. Aesthetic Res. 2021, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Zhou, J. Recent Advances on Synthetic and Polysaccharide Adhesives for Biological Hemostatic Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, Y.M.; Vimala, K.; Thomas, V.; Varaprasad, K.; Sreedhar, B.; Bajpai, S.; Raju, K.M. Controlling of silver nanoparticles structure by hydrogel networks. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gu, Z.; Chen, X.; Shi, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Sun, M.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Q.; et al. An injectable and thermosensitive hydrogel: Promoting periodontal regeneration by controlled-release of aspirin and erythropoietin. Acta Biomater. 2019, 86, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Lan, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, B.; Xue, W.; Guo, R. Enhanced cutaneous wound healing by functional injectable thermo-sensitive chitosan-based hydrogel encapsulated human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, A.; Pascadopoli, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Gallo, S.; Zampetti, P.; Cuggia, G.; Scribante, A. Domiciliary Use of Chlorhexidine vs. Postbiotic Gels in Patients with Peri-Implant Mucositis: A Split-Mouth Randomized Clinical Trial. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Gallo, S.; Garofoli, A.; Poggio, C.; Arciola, C.R.; Scribante, A. Ozone Gel in Chronic Periodontal Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial on the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ozone Application. Biology 2021, 10, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavya, K.; Jayakumar, R.; Nair, S.; Chennazhi, K.P. Fabrication and characterization of chitosan/gelatin/nSiO2 composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, J.; Hu, J.; Sun, G.; Chen, S.; Jiang, P.; Shen, X.; Tong, H. A novel chitosan- tussah silk fibroin/nano-hydroxyapatite composite bone scaffold platform with tunable mechanical strength in a wide range. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93 Pt A, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H. Injectable hydrogels delivering therapeutic agents for disease treatment and tissue engineering. Biomater. Res. 2018, 22, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, S.; Vimalraj, S.; Thanikaivelan, P.; Banudevi, S.; Manivasagam, G. A review on injectable chitosan/beta glycerophosphate hydrogels for bone tissue regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 121, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denry, I.; Kuhn, L.T. Design and characterization of calcium phosphate ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuba, S.; Okada, M.; Nohara, K.; Iwata, T. Alloplastic Bone Substitutes for Periodontal and Bone Regeneration in Dentistry: Current Status and Prospects. Materials 2021, 14, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempe, S.; Metz, H.; Bastrop, M.; Hvilsom, A.; Contri, R.V.; Mäder, K. Characterization of thermosensitive chitosan-based hydrogels by rheology and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoemann, C.; Chenite, A.; Sun, J.; Hurtig, M.; Serreqi, A.; Lu, Z.; Rossomacha, E. Buschmann Cytocompatible gel formation of chitosan-glycerol phosphate solutions supplemented with hydroxyl ethyl cellulose is due to the presence of glyoxal. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 83A, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Kalappura, U.G.; Laheurte, J.-M.; Mathew, K.T. Biocompatibility study of beta tricalcium phosphate bioceramics and chitosan biopolymer and their use as phantoms for medical imaging applications. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2009, 51, 2923–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessì, M.; Borzacchiello, A.; Mohamed, T.H.; Abdel-Fattah, W.I.; Ambrosio, L. Novel biomimetic thermosensitive beta-tricalcium phosphate/chitosan-based hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 2984–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanyacharoen, T.; Chuysinuan, P.; Techasakul, S.; Nooeaid, P.; Ummartyotin, S. Development of a gallic acid-loaded chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel composite: Release characteristics and antioxidant activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Jiang, L.J.; Cao, P.P.; Li, J.B.; Chen, X.G. Glycerophosphate-based chitosan thermosensitive hydrogels and their biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atak, B.H.; Buyuk, B.; Huysal, M.; Isik, S.; Senel, M.; Metzger, W.; Cetin, G. Preparation and characterization of amine functional nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan bionanocomposite for bone tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Bégin, A.; Carreau, P.J. Physical Gelation of Chitosan in the Presence of β-Glycerophosphate: The Effect of Temperature. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3267–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenbach, F.; Handschel, J. Effects of dexamethasone, ascorbic acid and beta-glycerophosphate on the osteogenic differentiation of stem cells in vitro. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.F.; Yan, J.Q.; Li, J.J.; Cheng, X.J.; Liu, C.S.; Chen, X.G. Controlled gelation temperature, pore diameter and degradation of a highly porous chitosan-based hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Gao, X.; Wan, Q.; Pei, X. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan/beta-Glycerophosphate Thermal-Sensitive Hydrogel Reinforced by Graphene Oxide. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, A.; Güldal, N.S.; Boccaccini, A.R. A review of the biological response to ionic dissolution products from bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2757–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-H.; Jun, Y.-K.; Hong, S.-H.; Kim, H.-E. Synthesis and dissolution behavior of β-TCP and HA/β-TCP composite powders. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 23, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Hass, M.; Wu, W.; Gulde, S.; Nancollas, G.H. Constant composition dissolution of mixed phases: II. Selective dissolution of calcium phosphates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 260, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogose, A.; Hotta, T.; Kawashima, H.; Kondo, N.; Gu, W.; Kamura, T.; Endo, N. Comparison of hydroxyapatite and beta tricalcium phosphate as bone substitutes after excision of bone tumors. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2005, 72, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finisie, M.R.; Josué, A.; Fávere, V.T.; Laranjeira, M.C.M. Synthesis of calcium-phosphate and chitosan bioceramics for bone regeneration. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2001, 73, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kean, T.; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yomota, C.; Komuro, T.; Kimura, T. Studies on the Degradation of Chitosan Films by Lysozyme and Release of Loaded Chemicals. Yakugaku Zasshi 1990, 110, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-W.; Liu, X.; Miller, A.L.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Yeh, M.-L.; Lu, L. Strengthening injectable thermo-sensitive NIPAAm-g-chitosan hydrogels using chemical cross-linking of disulfide bonds as scaffolds for tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, S.; Mu, R.; Chen, F.; Wei, X.; Zhu, L.; Han, B.; Yu, H.; Bi, B.; Chen, B.; Wang, Q.; et al. Injectable chitosan/beta-glycerophosphate hydrogels with sustained release of BMP-7 and ornidazole in periodontal wound healing of class III furcation defects. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 99, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Niu, L.; Liang, H.; Tan, H.; Liu, C.; Zhu, F. pH and Glucose Dual-Responsive Injectable Hydrogels with Insulin and Fibroblasts as Bioactive Dressings for Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 37563–37574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, H.; Heo, Y.J.; Okitsu, T.; Matsunaga, Y.; Kawanishi, T.; Takeuchi, S. Injectable hydrogel microbeads for fluorescence-based in vivo continuous glucose monitoring. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17894–17898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Tian, M.; Feng, R.; Dang, Y.; Zhang, M. Novel Self-Healing Hydrogel with Injectable, pH-Responsive, Strain-Sensitive, Promoting Wound-Healing, and Hemostatic Properties Based on Collagen and Chitosan. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3855–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogina, A.; Ressler, A.; Matić, I.; Ferrer, G.G.; Marijanović, I.; Ivanković, M.; Ivanković, H. Cellular hydrogels based on pH-responsive chitosan-hydroxyapatite system. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 166, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, J.W.S.; Waldman, S.D.; Amsden, B.G. A Photocurable Hydrogel/Elastomer Composite Scaffold with Bi-Continuous Morphology for Cell Encapsulation. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 1672–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, N.; Sabalic-Schoener, M.; Nguyen, L.; D’Aiuto, F. β-Tricalcium Phosphate-Loaded Chitosan-Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Periodontal Regeneration. Polymers 2023, 15, 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204146
Tan N, Sabalic-Schoener M, Nguyen L, D’Aiuto F. β-Tricalcium Phosphate-Loaded Chitosan-Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Periodontal Regeneration. Polymers. 2023; 15(20):4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204146
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Naiwen, Maja Sabalic-Schoener, Linh Nguyen, and Francesco D’Aiuto. 2023. "β-Tricalcium Phosphate-Loaded Chitosan-Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Periodontal Regeneration" Polymers 15, no. 20: 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204146
APA StyleTan, N., Sabalic-Schoener, M., Nguyen, L., & D’Aiuto, F. (2023). β-Tricalcium Phosphate-Loaded Chitosan-Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Periodontal Regeneration. Polymers, 15(20), 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204146






