Enhancing Textile Water Repellency with Octadecyltrichlorosilane (OTS) and Hollow Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
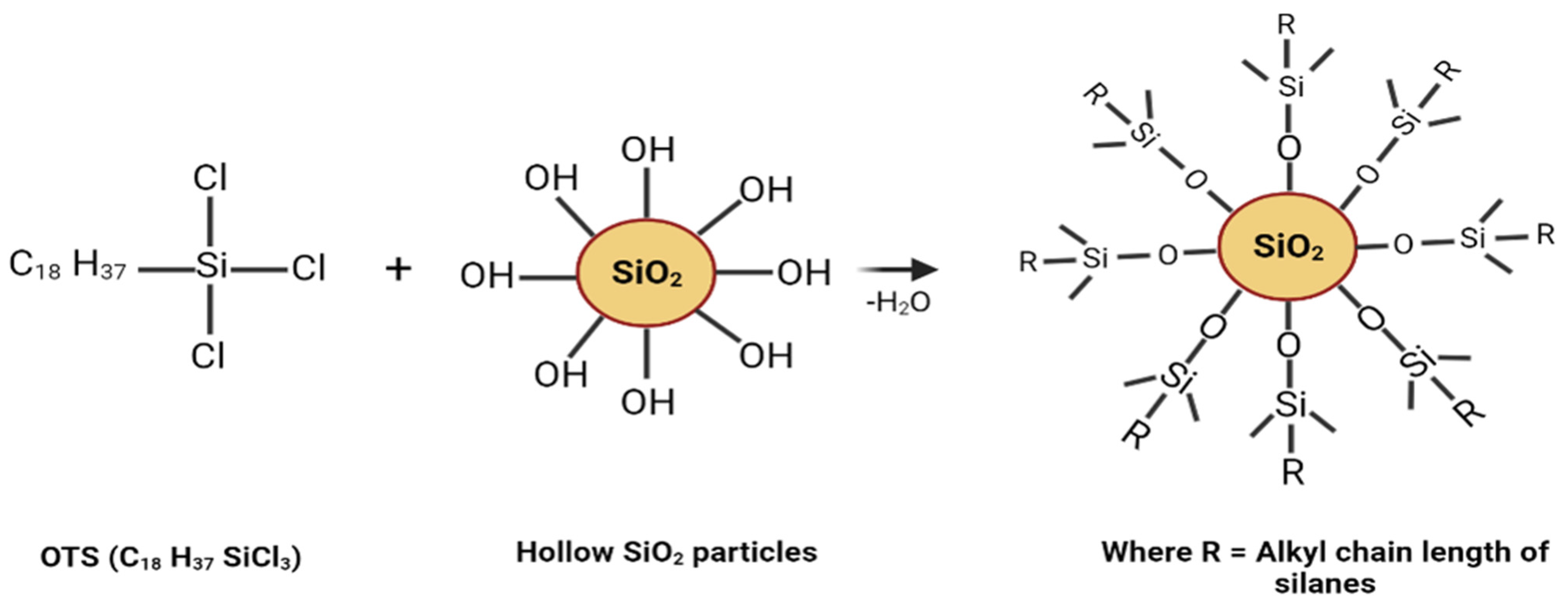
2.2. Preparation of Hollow Hydrophobic SiO2 Nanoparticles
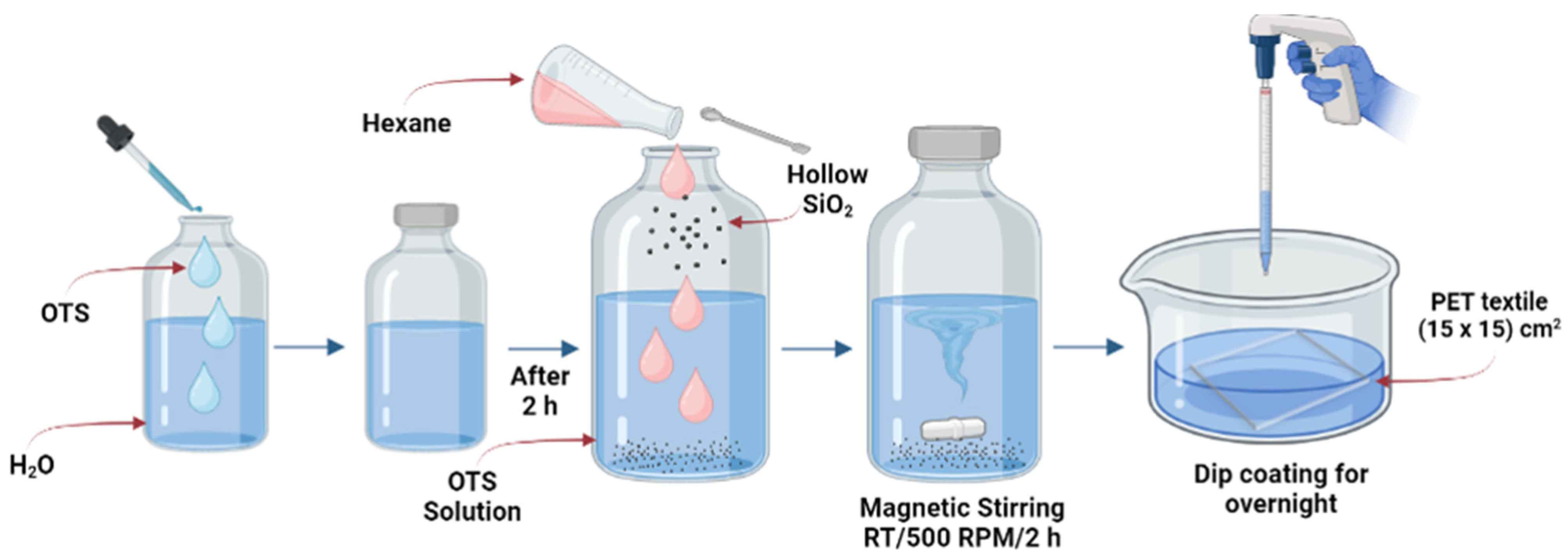
2.3. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Solution for Textile Coating
2.4. Characterization and Instrumentation
2.5. Water Contact Angle (WCA) and Washing Resistance (WR) Assays
3. Results and Discussion
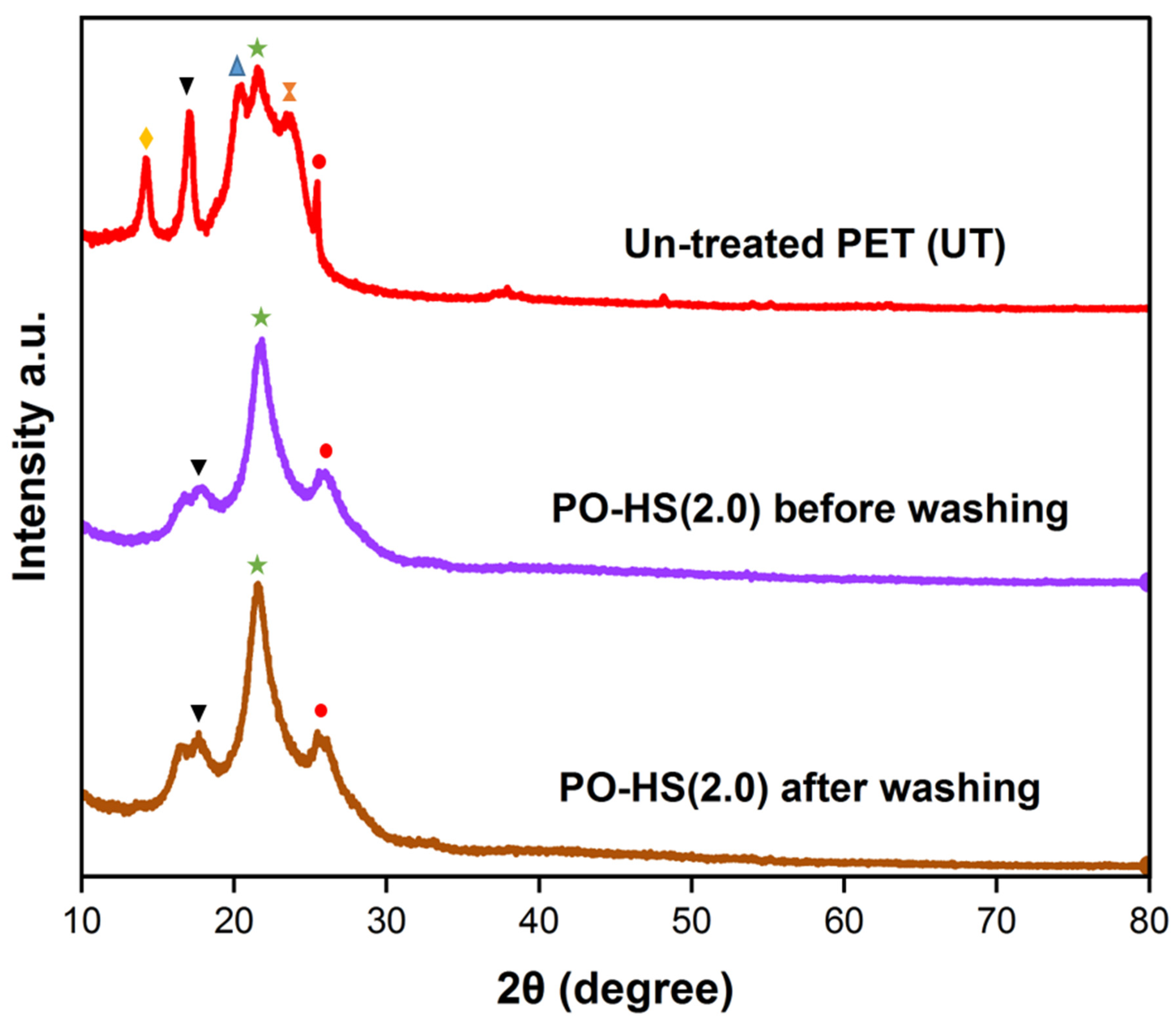
3.1. Superhydrophobic Surface: Reaction Mechanism and Surface Morphology
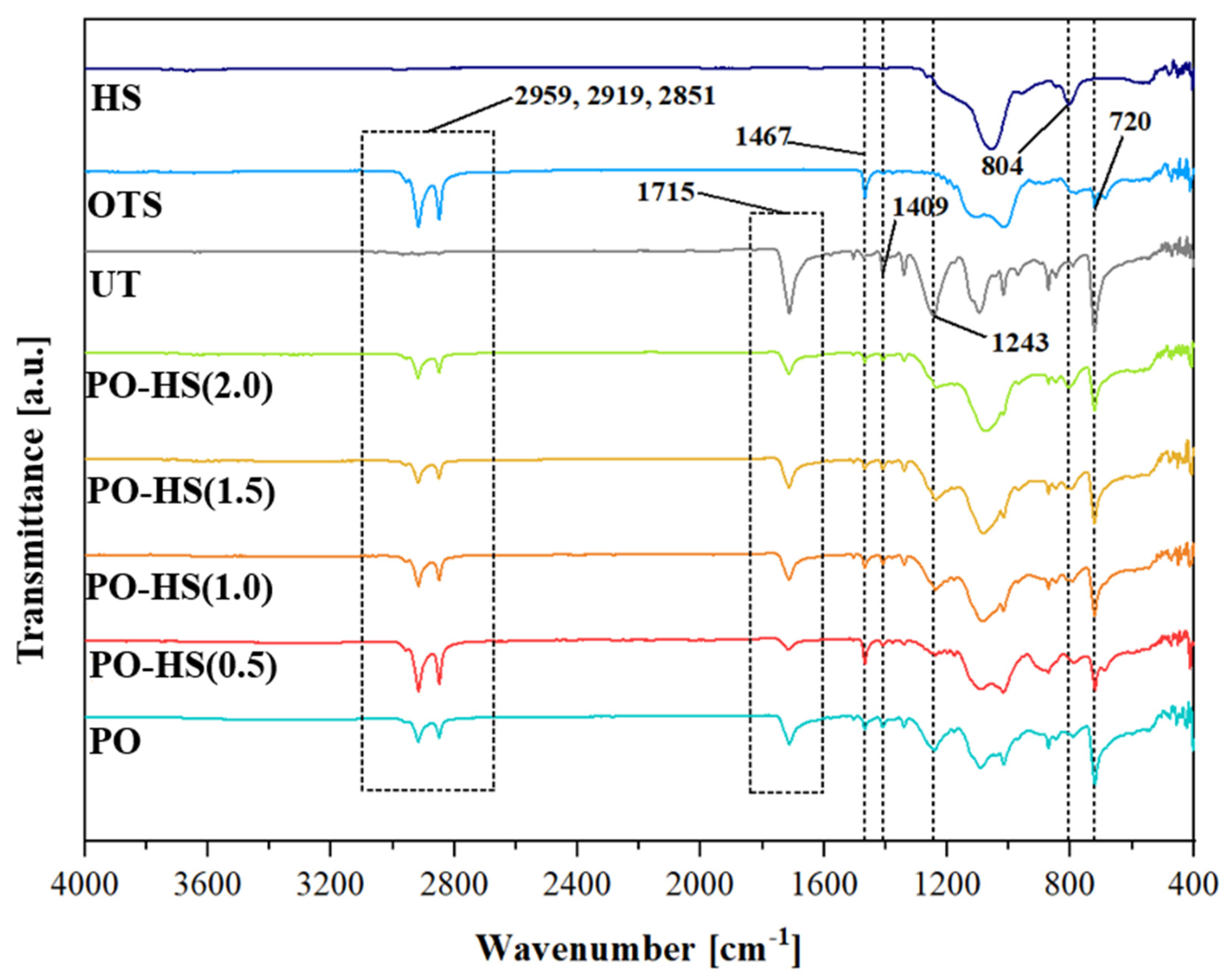
3.2. Chemical Properties
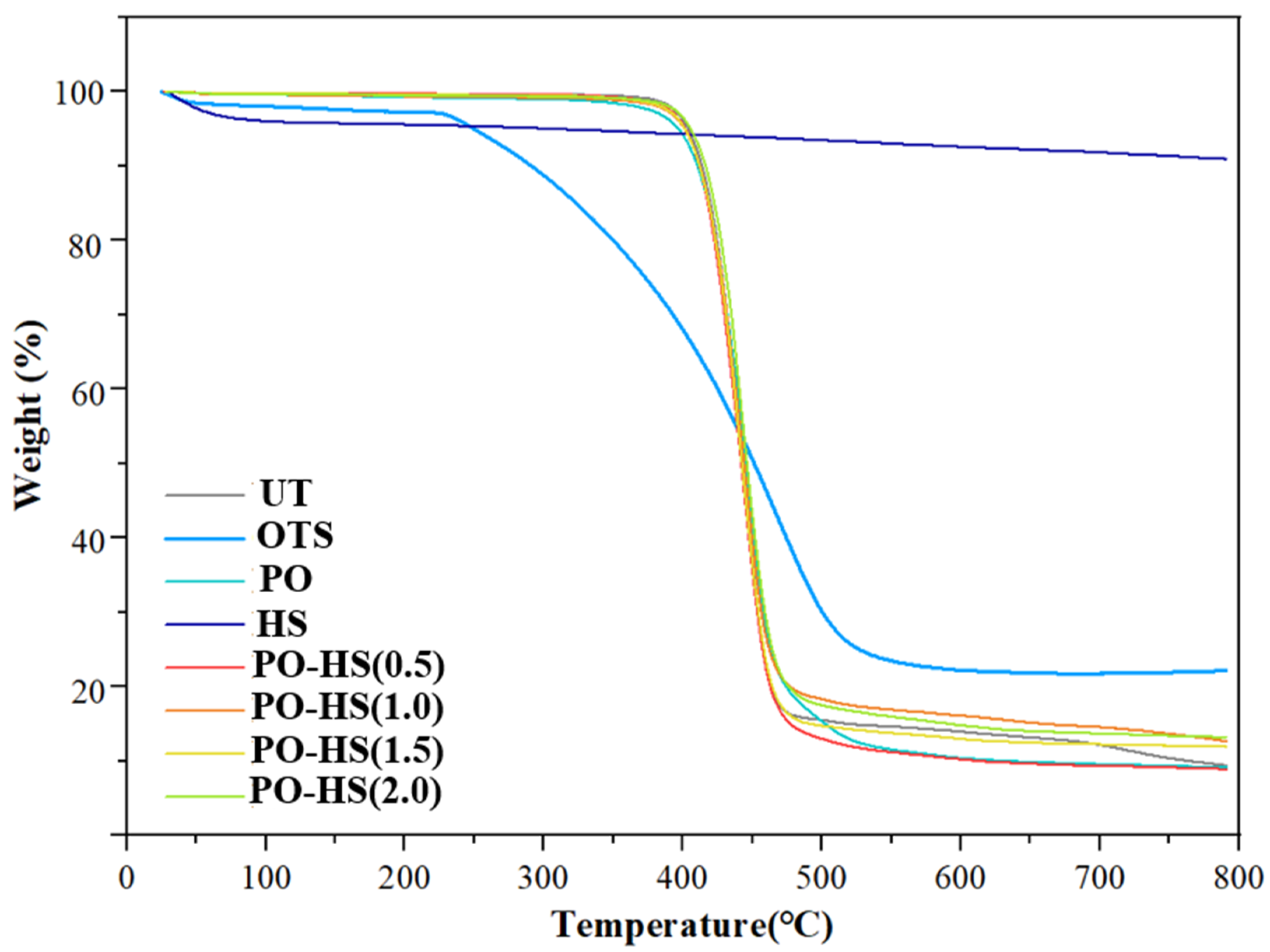
3.3. Thermal Properties
3.4. Wettability and Durability Test
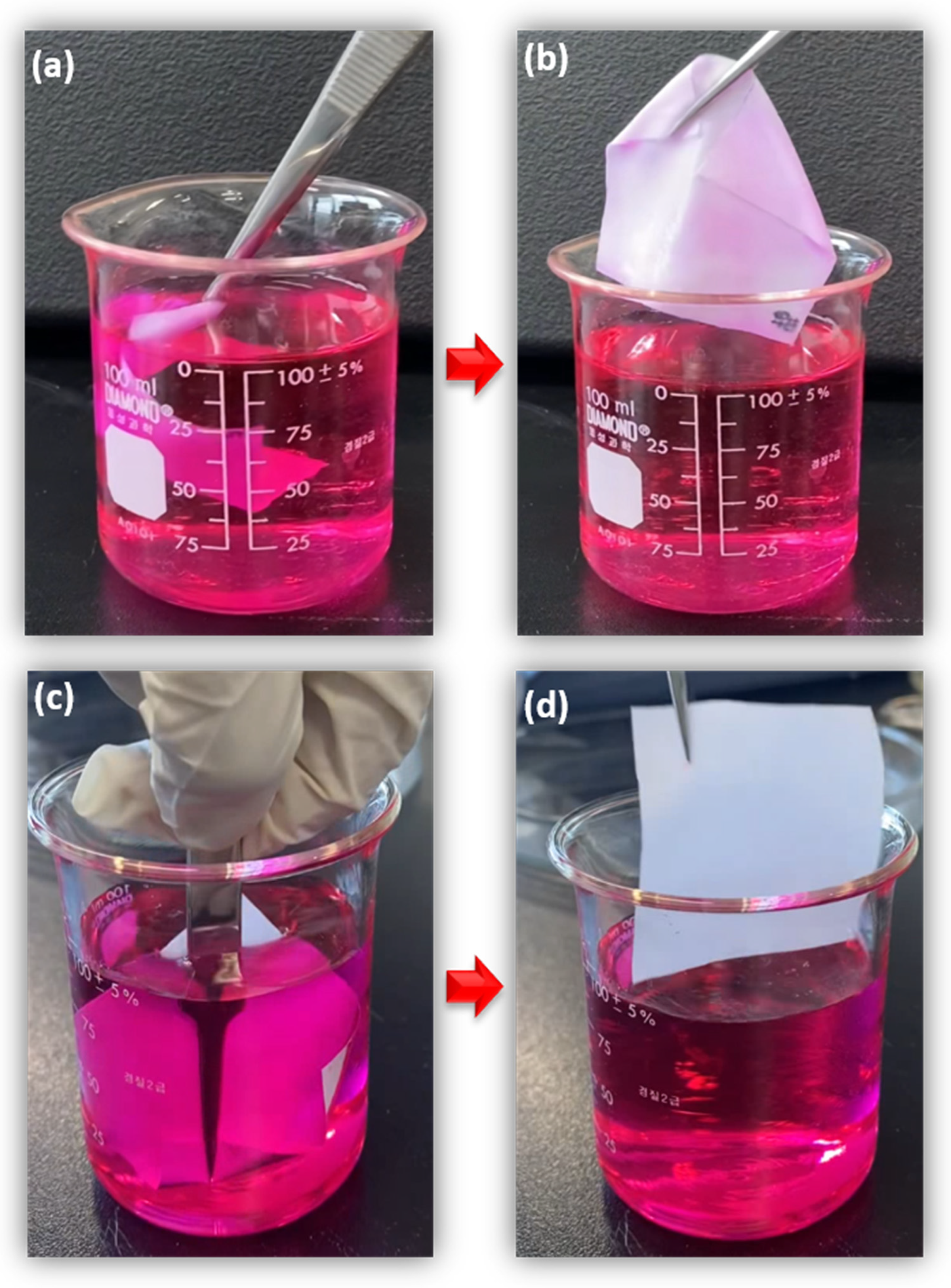
3.4.1. Wettability and Water Contact Angle (WCA)
3.4.2. Laundering Durability of the Treated Fabric
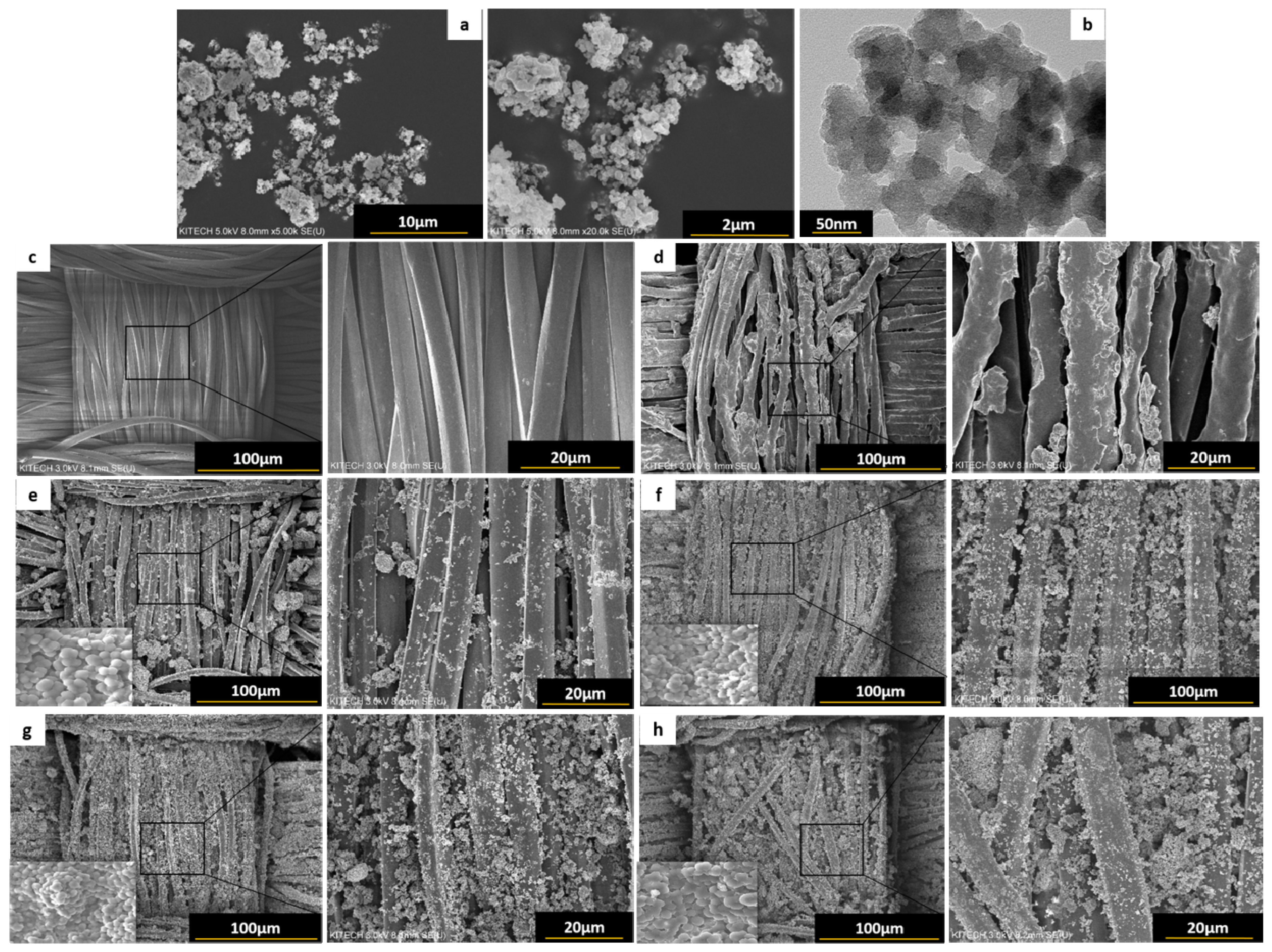
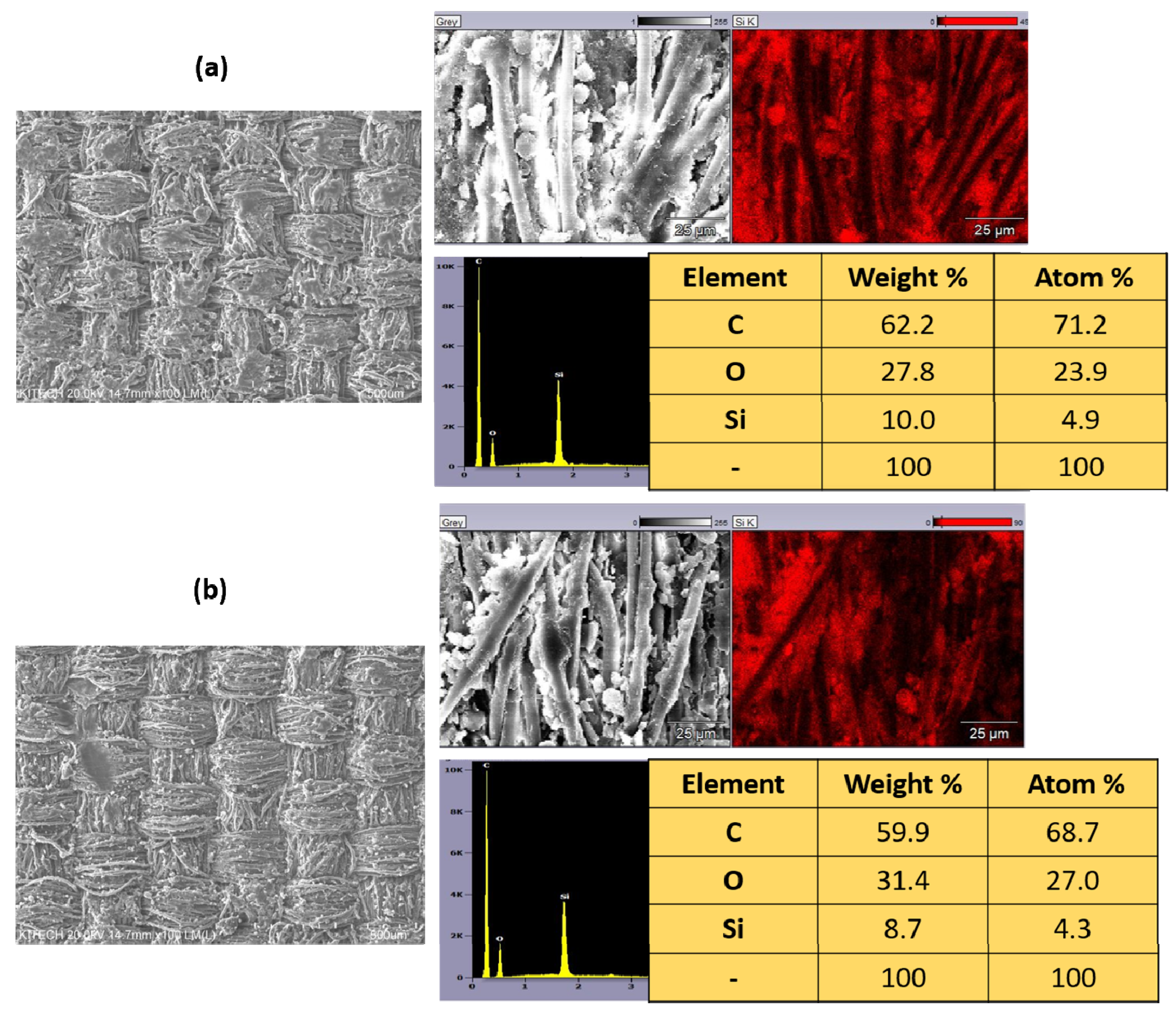
3.4.3. Morphological Transformation before and after Laundering of PO-HS(2.0) Fiber
4. Conclusions and Future Direction
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Sabin, S.; Xiao, T.; Jiang, L.; Chen, X. Facile Fabrication of a Mechanical, Chemical, Thermal, and Long-Term Outdoor Durable Fluorine-Free Superhydrophobic Coating. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2002209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, K.; Carmalt, C.J.; Parkin, I.P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X. Durable Fire Retardant, Superhydrophobic, Abrasive Resistant and Air/UV Stable Coatings. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Yang, C.Q. Formation of Highly Hydrophobic Surfaces on Cotton and Polyester Fabrics Using Silica Sol Nanoparticles and Nonfluorinated Alkylsilane. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 9797–9803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Feng, L.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Surfaces with Special Wettability. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürstner, R.; Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C.; Walzel, P. Wetting and Self-Cleaning Properties of Artificial Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Langmuir 2005, 21, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Fang, J.; Cheng, T.; Ding, J.; Qu, L.; Dai, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. One-Step Coating of Fluoro-Containing Silicananoparticles for Universal Generation of Surface Superhydrophobicity. Chem. Commun. 2008, 7, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Gu, G.; Meng, W.-D.; Qing, F.-L. Superhydrophobic Cotton Fabric Coating Based on a Complex Layer of Silica Nanoparticles and Perfluorooctylated Quaternary Ammonium Silane Coupling Agent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 3669–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A. The Lotus Effect: Superhydrophobicity and Metastability. Langmuir 2004, 20, 3517–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Gao, Q.; Guo, Y.; Yang, C.Q.; Shen, L. Modified Silica Sol Coatings for Highly Hydrophobic Cotton and Polyester Fabrics Using a One-Step Procedure. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 5881–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holme, I. Innovative Technologies for High Performance Textiles. Color. Technol. 2007, 123, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaper, H.; Velders, G.J.; Matthijsen, J. Ozone Depletion and Skin Cancer Incidence: A Source Risk Approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 1998, 61, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.M.; Barofsky, D.F.; Field, J.A. Fluorinated Alkyl Surfactants. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2003, 20, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi, V.H.; Rossky, P.J. Molecular Origins of Fluorocarbon Hydrophobicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13603–13607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, J.; Pei, R.; Ye, S.; Luo, Y. Ordered Water Layer on the Macroscopically Hydrophobic Fluorinated Polymer Surface and Its Ultrafast Vibrational Dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 13074–13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmawan, Y.; Xu, L.; Yang, S. Self-Assembly of Nanostructures towards Transparent, Superhydrophobic Surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 2955–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guo, Z. A Highly Fluorinated SiO2 Particle Assembled, Durable Superhydrophobic and Superoleophobic Coating for Both Hard and Soft Materials. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 18338–18346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; He, L.; Pan, A.; Zhao, Y. Hydrophobic and Durable Adhesive Coatings Fabricated from Fluorinated Glycidyl Copolymers Grafted on SiO2 Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, G.; Tong, Q.; Yang, W.; Hao, W. Fluorine-Free Superhydrophobic Coatings from Polydimethylsiloxane for Sustainable Chemical Engineering: Preparation Methods and Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, A.G.; Sun, B.R.; Chen, K.S.; Yu, H.-Z. Functional and Versatile Superhydrophobic Coatings via Stoichiometric Silanization. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintzer, K.; Schwertfeger, W. Fluoropolymers-Environmental Aspects. In Handbook of Fluoropolymer Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 495–520. [Google Scholar]
- Hays, H.L.; Spiller, H. Fluoropolymer-Associated Illness. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Rogers, J.M. The Developmental Toxicity of Perfluoroalkyl Acids and Their Derivatives. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 198, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurino, R.; Fabbri, E.; Messori, M.; Pilati, F.; Pospiech, D.; Synytska, A. Facile Preparation of Superhydrophobic Coatings by Sol–Gel Processes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 325, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, G.; Marques, P.A.A.P.; Trindade, T.; Neto, C.P.; Gandini, A. Superhydrophobic Cellulose Nanocomposites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 324, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Cai, Z. Fabrication of a Superhydrophobic ZnO Nanorod Array Film on Cotton Fabrics via a Wet Chemical Route and Hydrophobic Modification. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 5899–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, G.Y.; Min, B.G.; Jeong, Y.G.; Lee, S.C.; Jang, J.H.; Koo, G.H. Superhydrophobicity of Cotton Fabrics Treated with Silica Nanoparticles and Water-Repellent Agent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 337, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, G.Y.; Jang, J.; Jeong, Y.G.; Lyoo, W.S.; Min, B.G. Superhydrophobic PLA Fabrics Prepared by UV Photo-Grafting of Hydrophobic Silica Particles Possessing Vinyl Groups. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 344, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, T.; Meguro, M.; Nakamae, K.; Matsushita, M.; Ueda, Y. The Lowest Surface Free Energy Based on −CF 3 Alignment. Langmuir 1999, 15, 4321–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefnagels, H.F.; Wu, D.; de With, G.; Ming, W. Biomimetic Superhydrophobic and Highly Oleophobic Cotton Textiles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 13158–13163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arukalam, I.O.; Oguzie, E.E.; Li, Y. Fabrication of FDTS-Modified PDMS-ZnO Nanocomposite Hydrophobic Coating with Anti-Fouling Capability for Corrosion Protection of Q235 Steel. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 484, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.P.; Jena, B.K.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Besra, L. Development of Oxidation and Corrosion Resistance Hydrophobic Graphene Oxide-Polymer Composite Coating on Copper. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 232, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zou, X.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Y. Novel Waterborne Polyurethanes Containing Long-Chain Alkanes: Their Synthesis and Application to Water Repellency. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 31357–31369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D.; Bhushan, B. Transparent, Superhydrophobic, and Wear-Resistant Coatings on Glass and Polymer Substrates Using SiO2, ZnO, and ITO Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 11391–11399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhu, C.; Lv, J.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J. Robust Fluorine-Free Superhydrophobic Coating on Polyester Fabrics by Spraying Commercial Adhesive and Hydrophobic Fumed SiO2 Nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 138, 105342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodrati, M.; Mousavi-Kamazani, M.; Bahrami, Z. Synthesis of Superhydrophobic Coatings Based on Silica Nanostructure Modified with Organosilane Compounds by Sol–Gel Method for Glass Surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; He, S. Highly Durable Superhydrophobic Polydimethylsiloxane/Silica Nanocomposite Surfaces with Good Self-Cleaning Ability. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 4100–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Luo, W.; Sun, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X. Superhydrophobic Coatings Fabricated by Paraffin Wax and Silica Nanoparticles with Enhanced Adhesion Stability. Mater. Lett. 2022, 309, 131316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuji, M.; Takai, C.; Tarutani, Y.; Takei, T.; Takahashi, M. Surface Properties of Nanosize Hollow Silica Particles on the Molecular Level. Adv. Powder Technol. 2007, 18, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, M.T.; Noronha, V.T.; Oliveira, N.C.; Alves, A.C.; Faria, A.F.; Martinez, D.T.S.; Ferreira, O.P.; Paula, A.J. Silica Nanoparticles and Surface Silanization for the Fabrication of Water-Repellent Cotton Fibers. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 4634–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Richter, J.; Tywoniak, J.; Hajek, P.; Adamopoulos, S.; Šegedin, U.; Petrič, M. Surface Modification of Norway Spruce Wood by Octadecyltrichlorosilane (OTS) Nanosol by Dipping and Water Vapour Diffusion Properties of the OTS-Modified Wood. Holzforschung 2017, 72, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, R.; Takahashi, K.; Liu, L.; Li, R.; Liu, P.; Wang, J. Hierarchical Flower like Double-Layer Superhydrophobic Films Fabricated on AZ31 for Corrosion Protection and Self-Cleaning. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 12767–12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.S.; Chaudhari, S.B. Study on Structural, Mechanical and Functional Properties of Polyester Silica Nanocomposite Fabric. Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol. 2014, 21, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Ha, S.-W.; Kwon, D.; Lee, J.-K. Polyimide Nanocomposites with Functionalized SiO2 Nanoparticles: Enhanced Processability, Thermal and Mechanical Properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 43371–43377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Xu, Q. High-Temperature Mechanical Behaviors of SiO2-Based Ceramic Core for Directional Solidification of Turbine Blades. Materials 2020, 13, 4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Ren, S.; Yang, S. Mechanical Properties and Thermal Stability of Porous Polyimide/Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Composite Films Prepared by Using Polystyrene Microspheres as the Pore-forming Template. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai-Yamashita, C.; Fuji, M. Hollow Silica Nanoparticles: A Tiny Pore with Big Dreams. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 804–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gandarillas, L.; Aragón, D.; Manteca, C.; Gonzalez-Barriuso, M.; Soriano, L.; Casas, A.; Yedra, A. Highly Hydrophobic Organic Coatings Based on Organopolysilazanes and Silica Nanoparticles: Evaluation of Environmental Degradation. Coatings 2023, 13, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Wang, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xing, T.; Chen, G. Facile Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Polyester Fabric Based on Rapid Oxidation Polymerization of Dopamine for Oil–Water Separation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 26992–27002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G. Aminolysis of Polyethylene Terephthalate Fabric by a Method Involving the Gradual Concentration of Dilute Ethylenediamine. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 513, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhong, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G. Anti-Ultraviolet and Anti-Static Modification of Polyethylene Terephthalate Fabrics with Graphene Nanoplatelets by a High-Temperature and High-Pressure Inlaying Method. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 1488–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, B.; Behera, R.C.; Patel, T. Analysis of Microstress in Neutron Irradiated Polyester Fibre by X-ray Diffraction Technique. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2005, 28, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, B. Analysis of Strain-Induced Crystallinity in Neutron-Irradiated Amorphous PET Fiber. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 119, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashairya, L.; Barik, D.D.; Saha, P. Methyltrichlorosilane Functionalized Silica Nanoparticles-Treated Superhydrophobic Cotton for Oil–Water Separation. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2019, 16, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, T.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Bazarganipour, M.; Noori, E. Synthesis and Characterization of Spherical Silica Nanoparticles by Modified Stöber Process Assisted by Organic Ligand. Superlattices Microstruct. 2013, 61, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musić, S.; Filipović-Vinceković, N.; Sekovanić, L. Precipitation of Amorphous SiO2 Particles and Their Properties. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yang, G.; Huang, D.; Cao, W.; Ge, L.; Li, L. Synthesis and Characterization of Spherical Silica Nanoparticles by Modified Stöber Process Assisted by Slow-Hydrolysis Catalyst. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Name | Weight Ratio of Hollow SiO2 to OTS (wt.%) | |
|---|---|---|
| OTS | HS | |
| UT | - | - |
| PO | 100 | - |
| GO | 100 | - |
| PO-HS(0.5) | 100 | 0.5 |
| PO-HS(1.0) | 100 | 1.0 |
| PO-HS(1.5) | 100 | 1.5 |
| PO-HS(2.0) | 100 | 2.0 |
| Specimens | Water Contact Angle (°) | Residue at 790 °C (%) |
|---|---|---|
| UT | - | 9.4 |
| GO | 118.0 ± 3.8 | - |
| PO | 143.0 ± 8.2 | 9.2 |
| HS | - | 90.9 |
| PO-HS(0.5) | 149.5 ± 6.8 | 8.9 |
| PO-HS(1.0) | 153.0 ± 2.0 | 12.7 |
| PO-HS(1.5) | 156.5 ± 3.0 | 12.0 |
| PO-HS(2.0) | 158.5 ± 3.7 | 13.3 |
| PO-HS (2.0) | Water Contact Angle (°) | Rate of Durability (° per Cycle) |
|---|---|---|
| 1st cycle | 158.3 ± 0.2 | N/A |
| 5th cycle | 157.2 ± 0.6 | 0.275 |
| 8th cycle | 156.5 ± 0.5 | 0.257 |
| 12th cycle | 155.8 ± 0.3 | 0.227 |
| 16th cycle | 153.9 ± 0.4 | 0.293 |
| 20th cycle | 152.4 ± 0.8 | 0.312 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheraz, M.; Choi, B.; Kim, J. Enhancing Textile Water Repellency with Octadecyltrichlorosilane (OTS) and Hollow Silica Nanoparticles. Polymers 2023, 15, 4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204065
Sheraz M, Choi B, Kim J. Enhancing Textile Water Repellency with Octadecyltrichlorosilane (OTS) and Hollow Silica Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2023; 15(20):4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204065
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheraz, Mahshab, Byul Choi, and Juran Kim. 2023. "Enhancing Textile Water Repellency with Octadecyltrichlorosilane (OTS) and Hollow Silica Nanoparticles" Polymers 15, no. 20: 4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204065
APA StyleSheraz, M., Choi, B., & Kim, J. (2023). Enhancing Textile Water Repellency with Octadecyltrichlorosilane (OTS) and Hollow Silica Nanoparticles. Polymers, 15(20), 4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204065







