Antifungal Activity of Chitosan/Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Blend Electrospun Polymeric Fiber Mat Doped with Metallic Silver Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
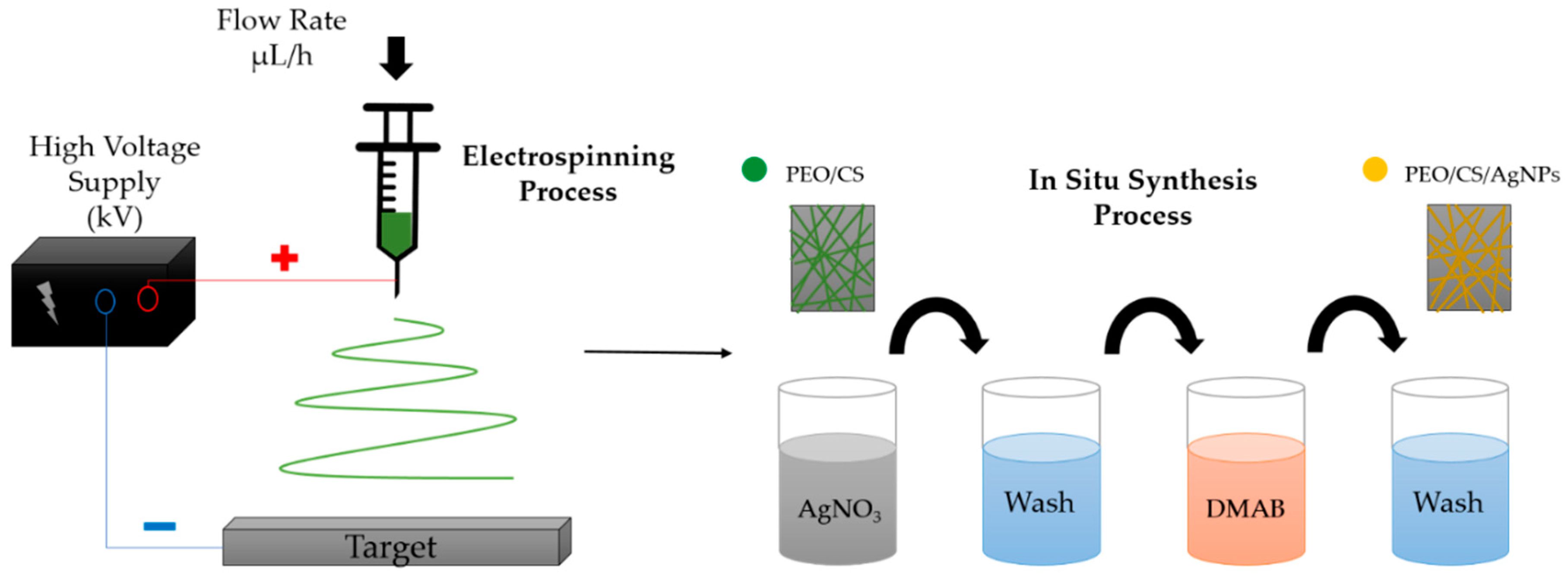
2.2. Thin-Film Fabrication Process
2.2.1. Preparation of PEO/CS Blend Structure
2.2.2. Electrospinning of PEO/CS Blend
2.2.3. In Situ Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
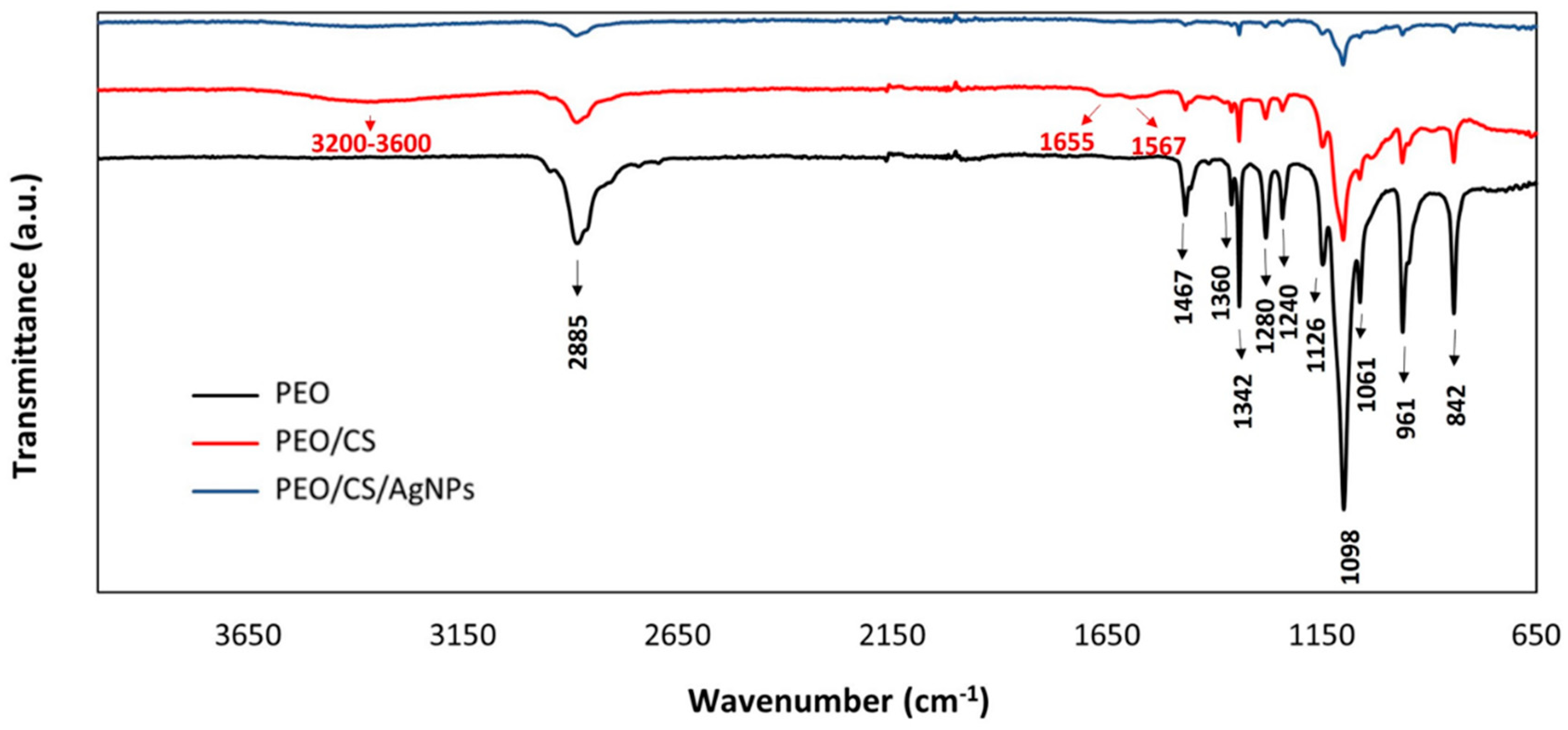
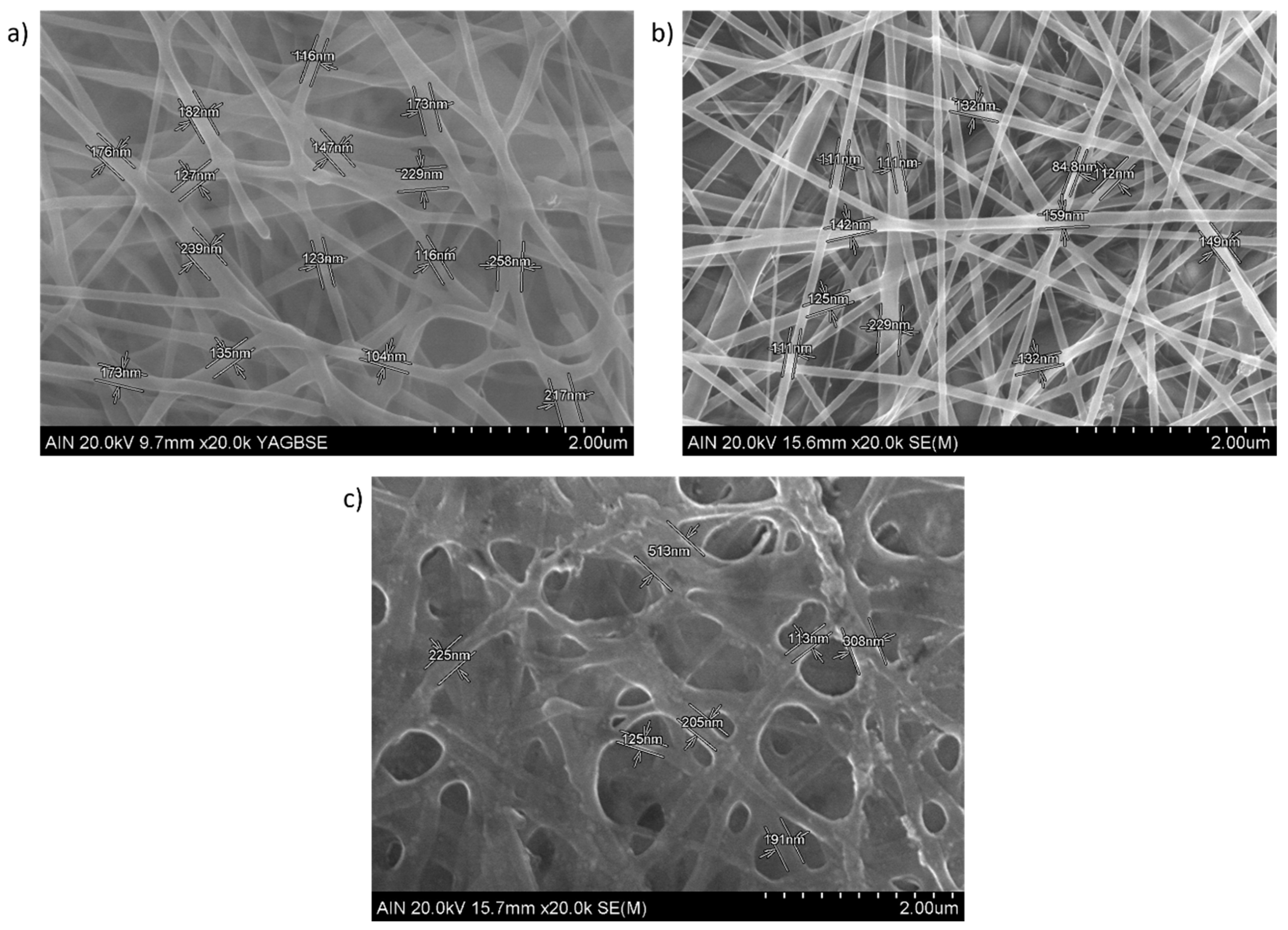
2.3. Characterization Techniques
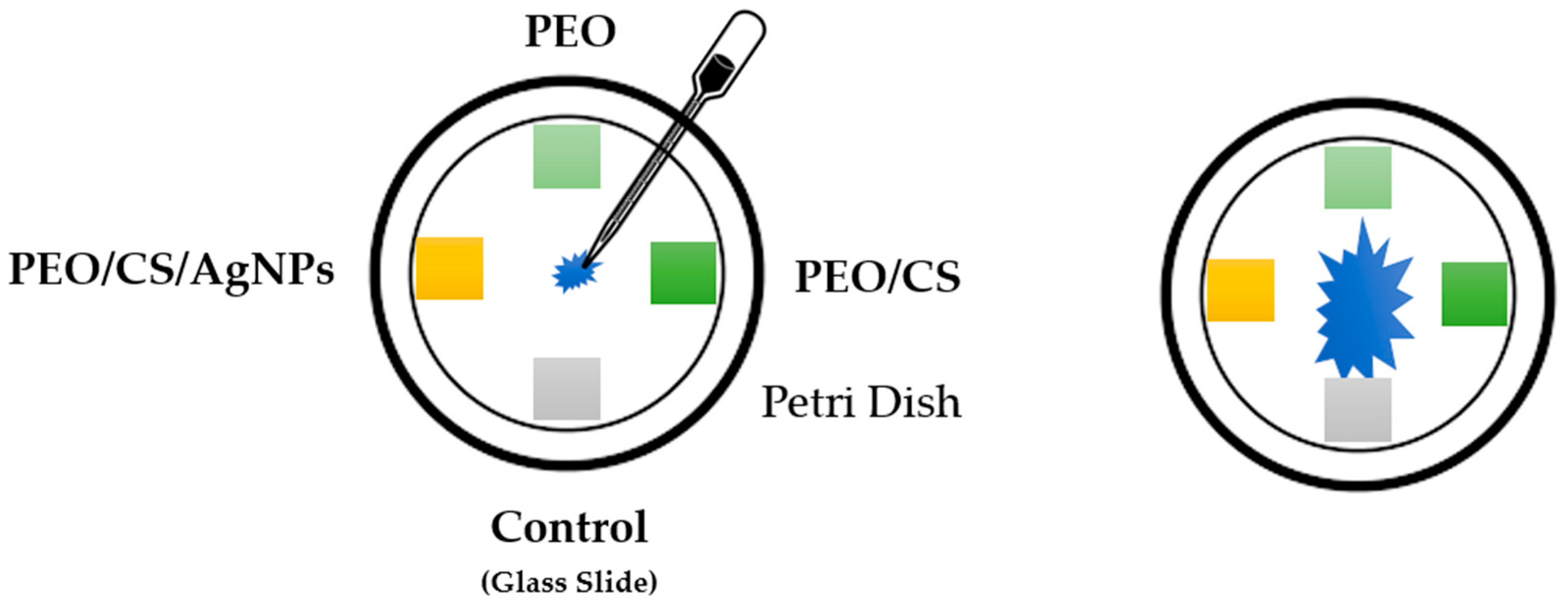
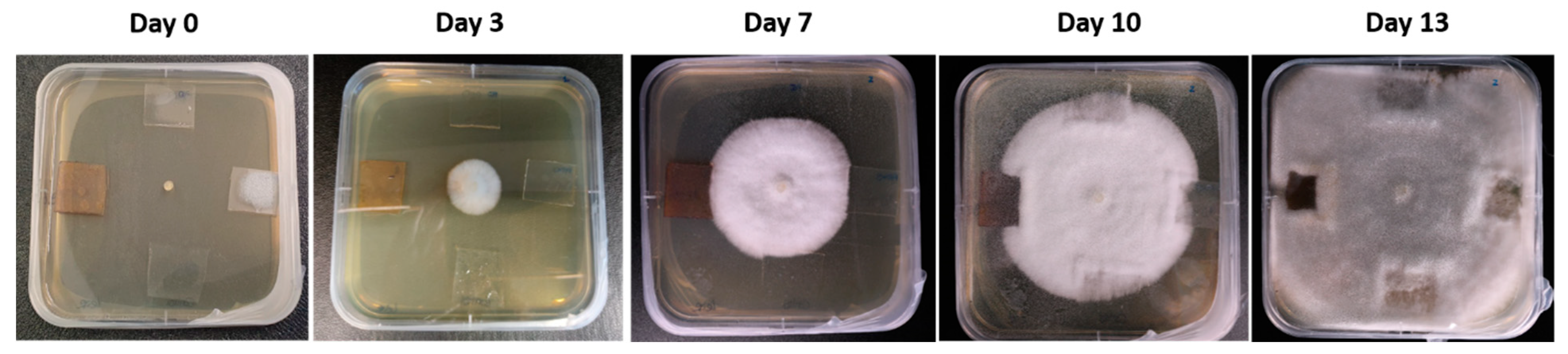
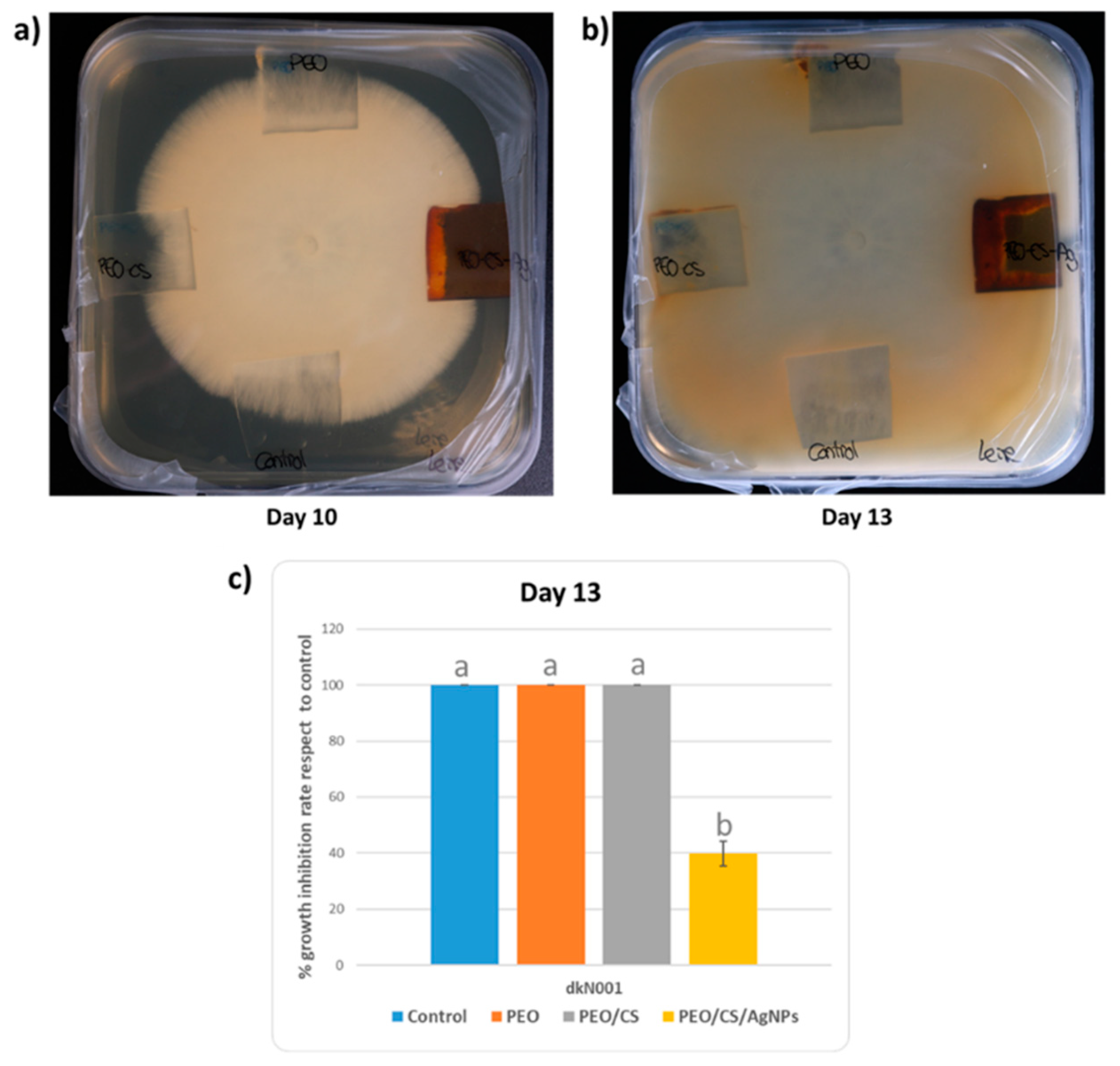
2.4. Antifungal Test against “Pleurotus Ostreatus”
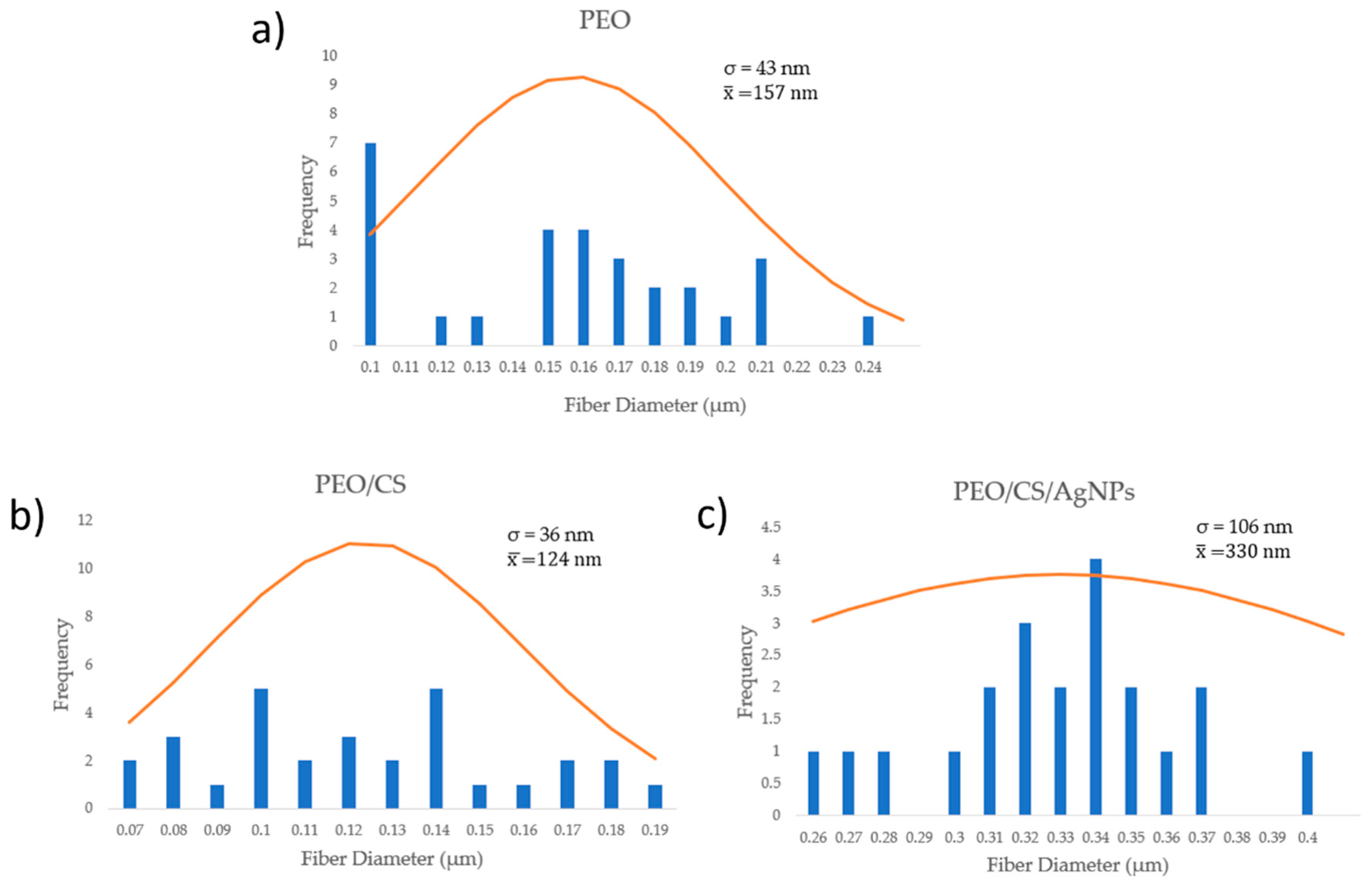
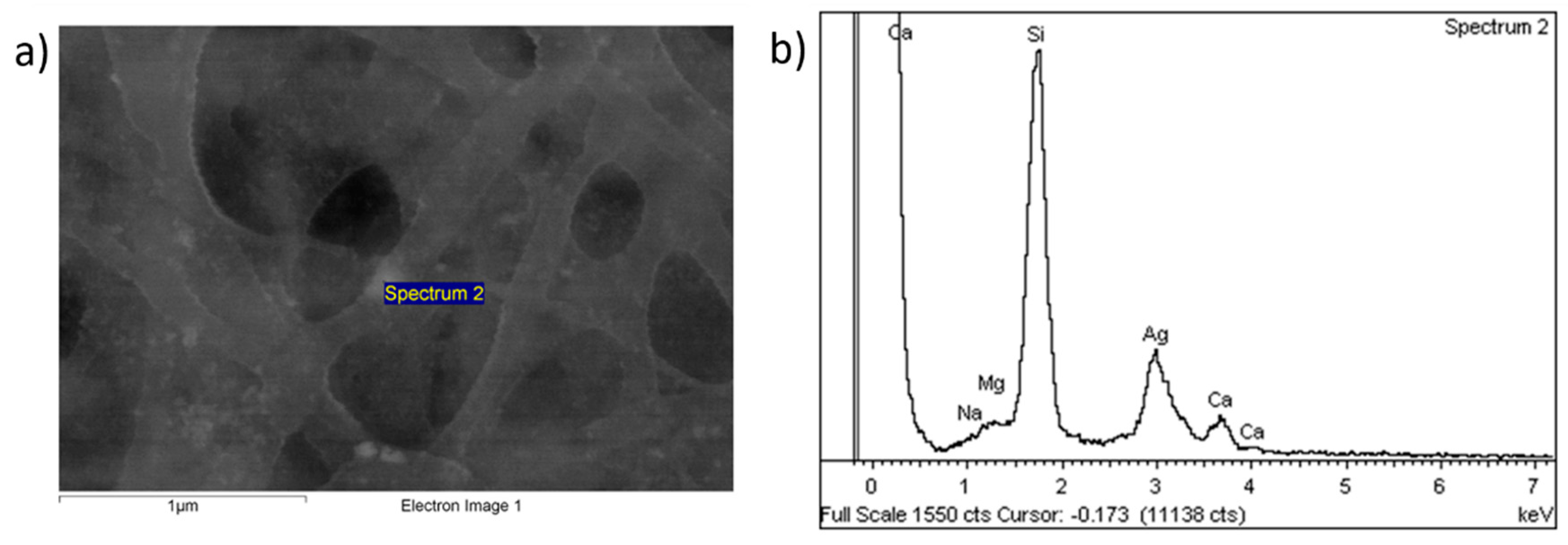
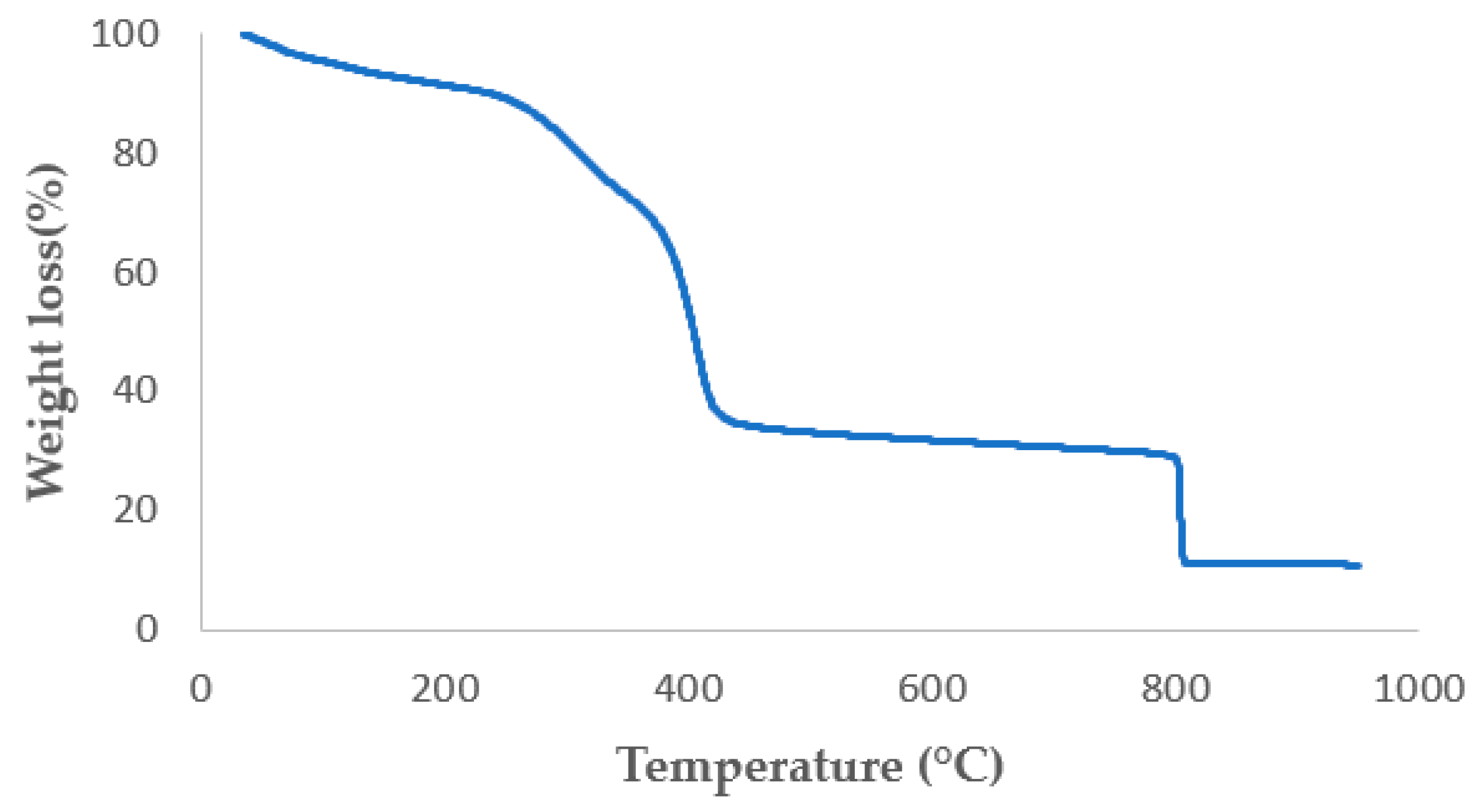
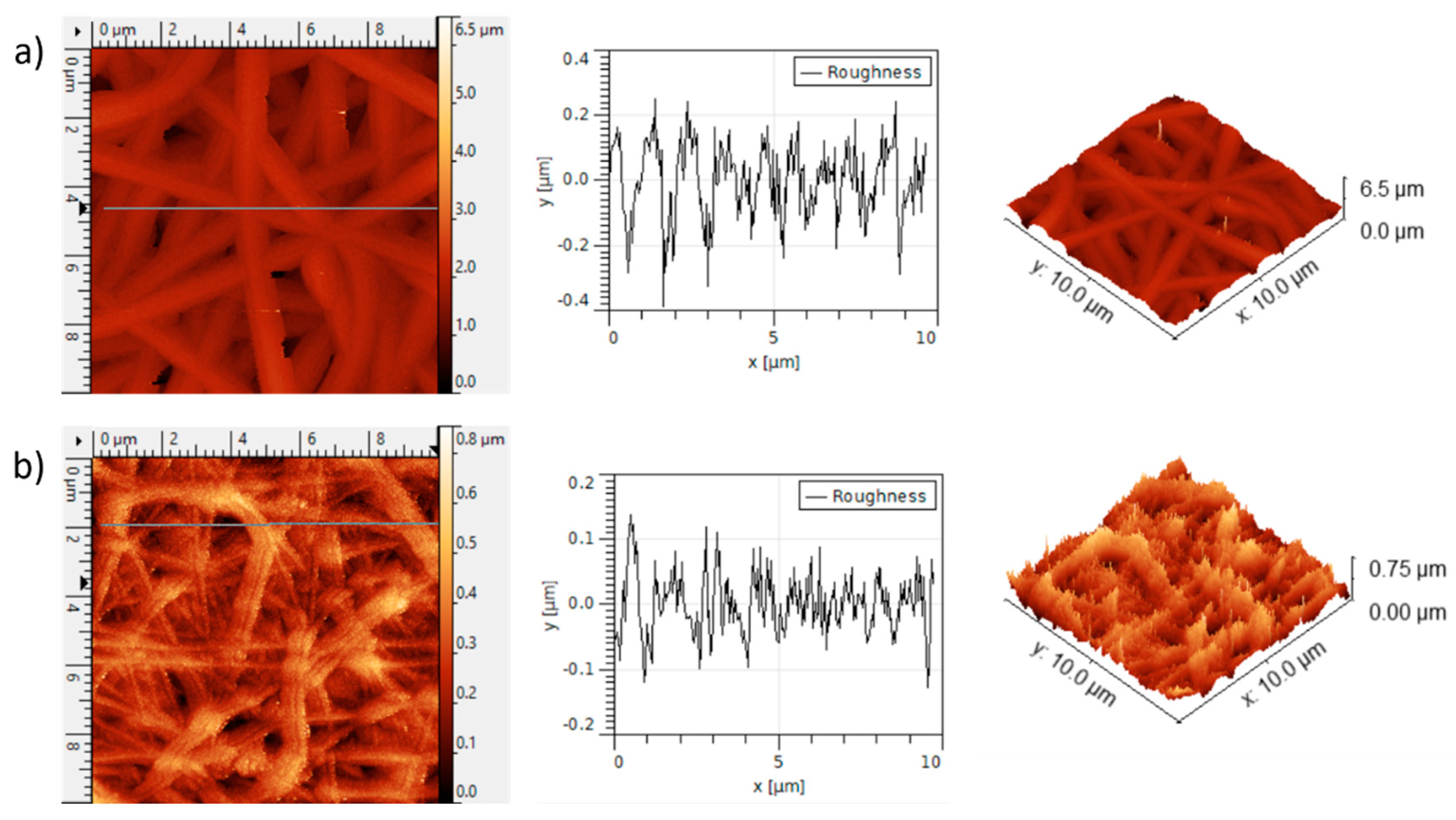
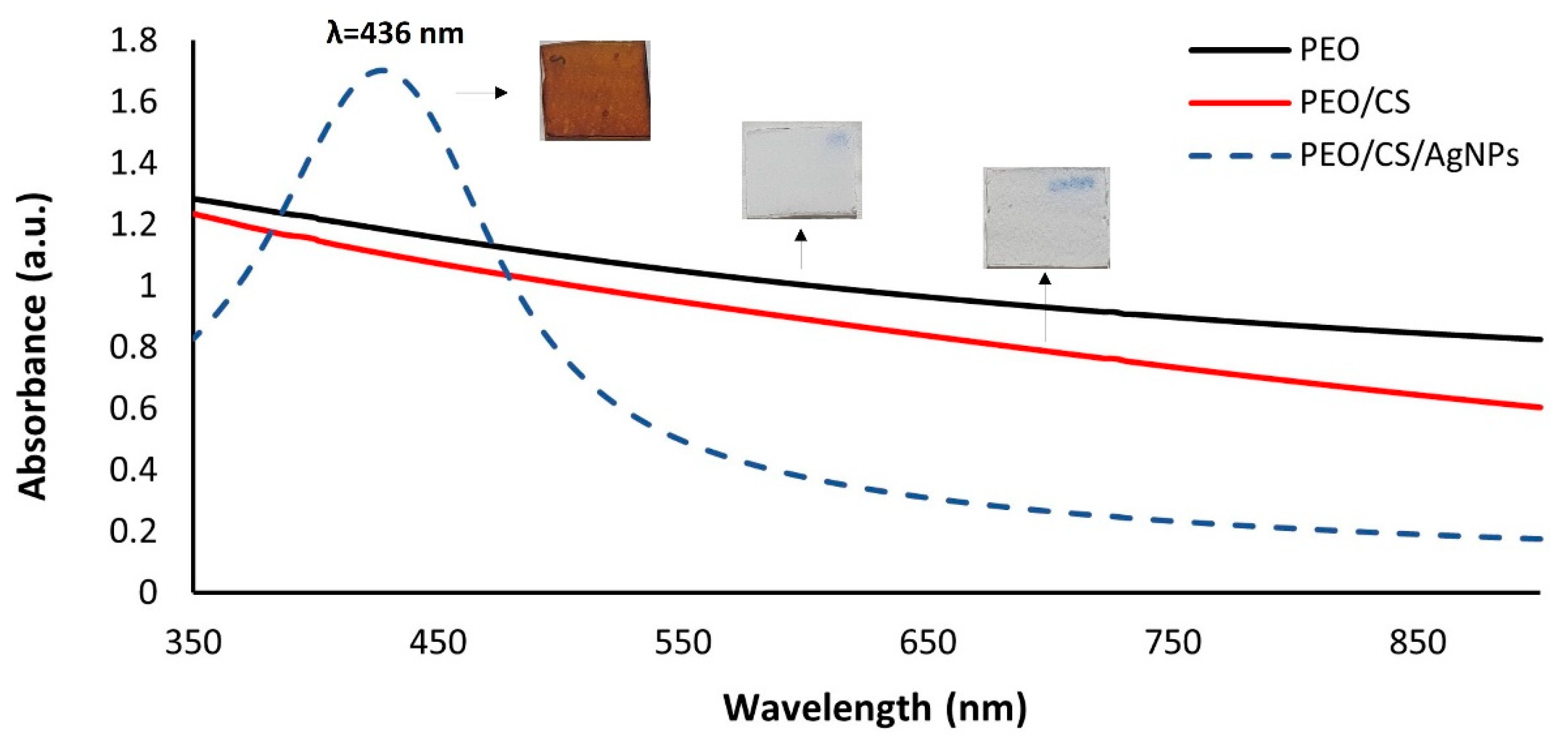
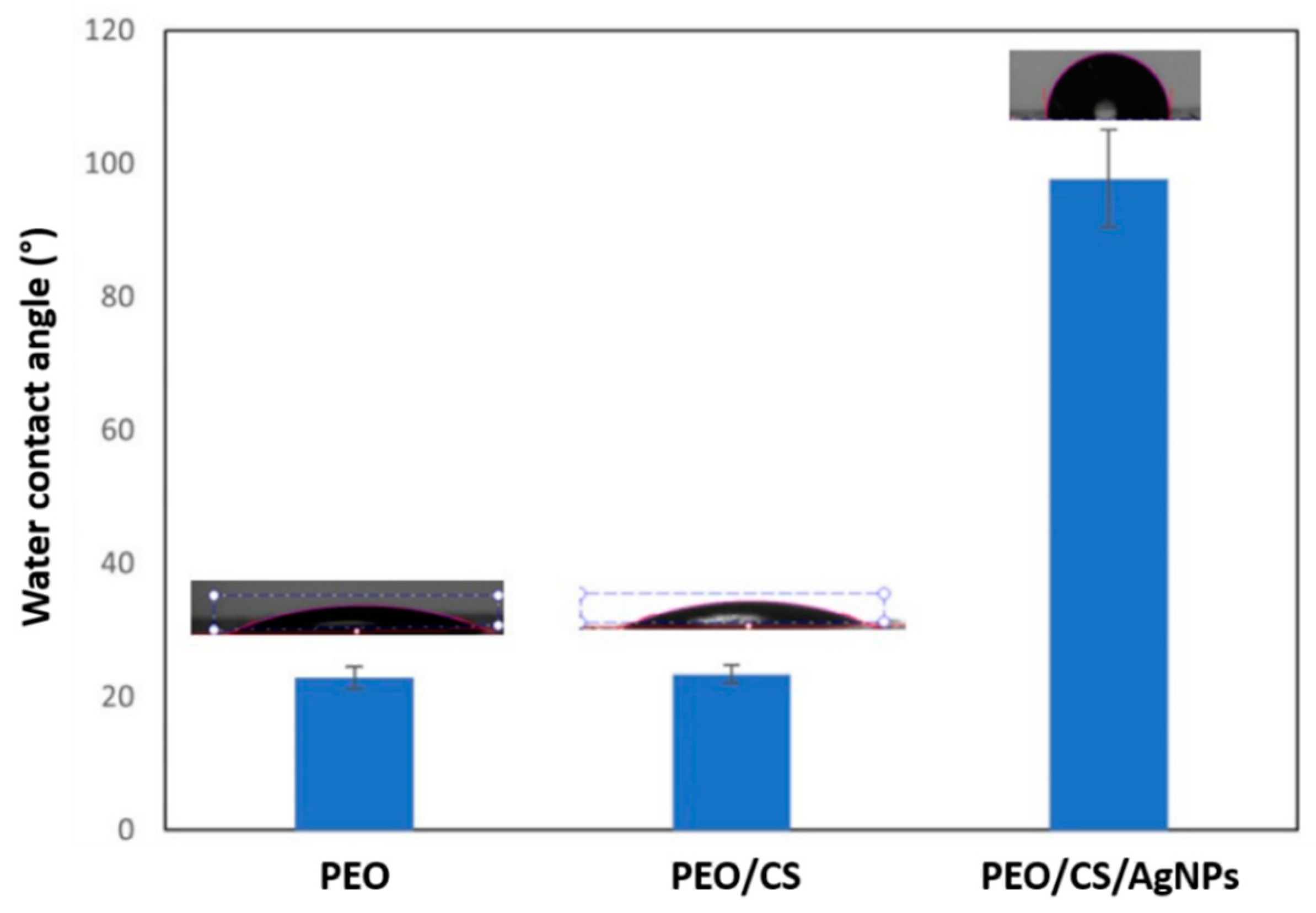
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Reinventing the Wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Electrospinning: A Fascinating Method for the Preparation of Ultrathin Fibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5670–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, P.J.; Rosagaray, I.; Fuertes, J.P.; Palacio, J.F.; Rodríguez, R.J. Designing Multifunctional Protective PVC Electrospun Fibers with Tunable Properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Yurrita, D.; Berlanga, C.; Palacio, J.F.; Rodríguez, R. Functionalized Electrospun Fibers for the Design of Novel Hydrophobic and Anticorrosive Surfaces. Coatings 2018, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.; Harris, D.; Tan, N.C.B. The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer 2001, 42, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.J.; Stoyanov, S.D.; Stride, E.; Pelan, E.; Edirisinghe, M. Electrospinning versus fibre production methods: From specifics to technological convergence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4708–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.-K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, A.; Rivero, P.J.; Berlanga, C.; Larumbe, S.; Miguel, A.; Palacio, J.F.; Rodriguez, R. Multifunctional protective PVC-ZnO nanocomposite coatings deposited on aluminum alloys by electrospinning. Coatings 2019, 9, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A.; Rivero, P.J.; García, P.; Mora, J.; Carreño, F.; Palacio, J.F.; Rodríguez, R. Icephobic and Anticorrosion Coatings Deposited by Electrospinning on Aluminum Alloys for Aerospace Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albistur, A.; Rivero, P.J.; Esparza, J.; Rodríguez, R. Evaluation of the Photocatalytic Activity and Anticorrosion Performance of Electrospun Fibers Doped with Metallic Oxides. Polymers 2021, 13, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandua, X.; Rivero, P.J.; Esparza, J.; Fernández-Palacio, J.; Conde, A.; Rodríguez, R.J. Design of Photocatalytic Functional Coatings Based on the Immobilization of Metal Oxide Particles by the Combination of Electrospinning and Layer-by-Layer Deposition Techniques. Coatings 2022, 12, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Kim, K.; Fang, D.; Ran, S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer 2002, 43, 4403–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.-F.; Shakir, I.; Hussain, R. Electrospun fibers for tissue engineering, drug delivery, and wound dressing. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 3027–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Duan, X.P.; Li, Y.M.; Yang, D.P.; Long, Y.Z. Electrospun nanofibers for wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Deng, H.; Du, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q. Emerging chitin and chitosan nanofibrous materials for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9477–9493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.B.; Zafar, M.S.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Shah, A.H.; Husain, S.; Rehman, I.U. Electrospinning of Chitosan-Based Solutions for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, K.; Afifi, A.M.; Jahangirian, H.; Webster, T.J. Biomedical applications of chitosan electrospun nanofibers as a green polymer—Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, A.A.; James, R.; Shelke, N.B.; Harmon, M.D.; Awad, H.M.; Nagarale, R.K.; Kumbar, S.G. A smart methodology to fabricate electrospun chitosan nanofiber matrices for regenerative engineering applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2014, 25, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Liu, Y.; Fang, D.; Chen, J.; Peng, C.; Fei, X.; Nie, J. Hyaluronic acid/chitosan polyelectrolyte complexes nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2012, 74, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; Costa, S.M.; Ferreira, D.P.; Abidi, H.; Fangueiro, R. Development of Chitosan-Gelatin Nanofibers with Cellulose Nanocrystals for Skin Protection Applications. Key Eng. Mater. 2021, 893, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsasulak, S.; Puttipaiboon, N.; Yoovidhya, T. Fabrication, Gastromucoadhesivity, Swelling, and Degradation of Zein-Chitosan Composite Ultrafine Fibers. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, N926–N935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cui, S. Preparation and characterization of biomimetic tussah silk fibroin/chitosan composite nanofibers. Iran. Polym. J. 2013, 22, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Duan, B.; Wu, L.; Li, S.; Yuan, X. Preparation of electrospun chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2007, 285, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, M.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Ajji, A. A fundamental study of chitosan/PEO electrospinning. Polymer 2011, 52, 4813–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K.; Park, K.; Seo, J. Development of poly (vinyl alcohol)/regenerated chitosan blend film with superior barrier, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 183, 107749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, K.; Kit, K. Effect of spinning temperature and blend ratios on electrospun chitosan/poly(acrylamide) blends fibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 4046–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassiba, A.J.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Webster, T.J.; Abdullah, A.M.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Khalil, K.A.; Luyt, A.S.; Elzatahry, A.A. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial properties of novel double layer nanocomposite electrospun fibers for wound dressing applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X. Preparation and antibacterial activity of electrospun chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) membranes containing silver nanoparticles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Edmondson, D.; Veiseh, O.; Matsen, F.A.; Zhang, M. Electrospun chitosan-based nanofibers and their cellular compatibility. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6176–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegel, C.; Kit, K.M.; McClements, D.J.; Weiss, J. Electrospinning of chitosan–poly(ethylene oxide) blend nanofibers in the presence of micellar surfactant solutions. Polymer 2008, 50, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Dong, C.; Yuan, X.; Yao, K. Electrospinning of chitosan solutions in acetic acid with poly(ethylene oxide). J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2004, 15, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penchev, H.; Paneva, D.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Electrospun Hybrid Nanofibers Based on Chitosan or N -Carboxyethylchitosan and Silver Nanoparticles. Macromol. Biosci. 2009, 9, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penchev, H.; Paneva, D.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Hybrid nanofibrous yarns based on N-carboxyethylchitosan and silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity prepared by self-bundling electrospinning. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 2374–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korniienko, V.; Husak, Y.; Yanovska, A.; Banasiuk, R.; Yusupova, A.; Savchenko, A.; Holubnycha, V.; Pogorielov, M. Functional and biological characterization of chitosan electrospun nanofibrous membrane nucleated with silver nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 12, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champer, J.; Patel, J.; Fernando, N.; Salehi, E.; Wong, V.; Kim, J. Chitosan against cutaneous pathogens. AMB Express 2013, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matica, M.A.; Aachmann, F.L.; Tøndervik, A.; Sletta, H.; Ostafe, V. Chitosan as a Wound Dressing Starting Material: Antimicrobial Properties and Mode of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, D.; von Bargen, K.; Haas, A.; Sahl, H.-G. Insights into the Mode of Action of Chitosan as an Antibacterial Compound. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3764–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabea, E.I.; Badawy, M.E.-T.; Stevens, C.V.; Smagghe, G.; Steurbaut, W. Chitosan as Antimicrobial Agent: Applications and Mode of Action. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segala, K.; Nista, S.V.G.; Cordi, L.; Bizarria, M.T.M.; de Ávila, J.; Kleinubing, S.A.; Cruz, D.C.; Brocchi, M.; Lona, L.M.F.; Caballero, N.E.D.; et al. Silver nanoparticles incorporated into nanostructured biopolymer membranes produced by electrospinning: A study of antimicrobial activity. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 51, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Mun, G.L.K.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Human Cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia, A.; Rivero, P.J.; Ruete, L.; Goicoechea, J.; Matías, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Single-stage in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles in antibacterial self-assembled overlays. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Urrutia, A.; Goicoechea, J.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Arregui, F.J.; Matías, I.R. An antibacterial coating based on a polymer/sol-gel hybrid matrix loaded with silver nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz-Marzán, L.M. Nanometals: Formation and color. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz-Marzán, L.M. Tailoring Surface Plasmons through the Morphology and Assembly of Metal Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2005, 22, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Liu, Z.-G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.-Y.; et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Boil. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101, Erratum in Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, e1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernousova, S.; Epple, M. Silver as Antibacterial Agent: Ion, Nanoparticle, and Metal. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1636–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benn, T.; Cavanagh, B.; Hristovski, K.; Posner, J.D.; Westerhoff, P. The Release of Nanosilver from Consumer Products Used in the Home. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgawad, A.M.; Hudson, S.M.; Rojas, O.J. Antimicrobial wound dressing nanofiber mats from multicomponent (chitosan/silver-NPs/polyvinyl alcohol) systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 100, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Gomes, D.; Esteruelas, G.; Bonilla, L.; Lopez-Machado, A.L.; Galindo, R.; Cano, A.; Espina, M.; Ettcheto, M.; Camins, A.; et al. Metal-Based Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agents: An Overview. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambhy, V.; MacBride, M.M.; Peterson, B.R.; Sen, A. Silver Bromide Nanoparticle/Polymer Composites: Dual Action Tunable Antimicrobial Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9798–9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, M.; Validi, M.; Gholipour, A.; Makvandi, P.; Sharifi, E. Chitosan nanofiber biocomposites for potential wound healing applications: Antioxidant activity with synergic antibacterial effect. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2021, 7, e10254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohsari, I.; Shariatinia, Z.; Pourmortazavi, S.M. Antibacterial electrospun chitosan–polyethylene oxide nanocomposite mats containing bioactive silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, M.M.; Abu-Rayyan, A.; Elsayed, N.H.; Alatawi, F.A.; Al-Anazi, M.; Mustafa, S.K.; Albalawi, R.K.; Abdelmonem, R. One-pot microwave synthesis of chitosan-stabilized silver nanoparticles entrapped polyethylene oxide nanofibers, with their intrinsic antibacterial and antioxidant potency for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Remmers, S.J.; Shao, J.; Kolwijck, E.; Walboomers, X.F.; Jansen, J.A.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.; Yang, F. Antibacterial effects of electrospun chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibrous membranes loaded with chlorhexidine and silver. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereydouni, N.; Zangouei, M.; Darroudi, M.; Hosseinpour, M.; Gholoobi, A. Antibacterial activity of chitosan-polyethylene oxide nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1274, 134304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, T.; Chatterjee, B.K.; Majumdar, D.; Chakrabarti, P. Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles and the modeling of bacterial growth kinetics using a modified Gompertz model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2015, 1850, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, M.M.G.; El-Aassar, M.R.; Al-Deyab, S.S. Antimicrobial activity of carboxymethyl chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers embedded silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, M.; Ghanim, M.; Nageh, H.; Hassanin, A.H.; Abdel-Moneim, A. Antimicrobial Activity of O-Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanofibers Containing Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Green Method. J. Nano Res. 2016, 40, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgognone, A.; Castanera, R.; Muguerza, E.; Pisabarro, A.G.; Ramírez, L. Somatic transposition and meiotically driven elimination of an active helitron family in Pleurotus ostreatus. DNA Res. 2017, 24, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larray, L.M.; Pérez, G.; Peñas, M.M.; Baars, J.J.P.; Mikosch, T.S.P.; Pisabarro, A.G.; Ramírez, L. Molecular Karyotype of the White Rot Fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3413–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ing, L.Y.; Zin, N.M.; Sarwar, A.; Katas, H. Antifungal Activity of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Correlation with Their Physical Properties. Int. J. Biomater. 2012, 2012, 632698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, L.G.; Specht, C.A.; Donlin, M.J.; Lodge, J.K. Chitosan, the Deacetylated Form of Chitin, Is Necessary for Cell Wall Integrity in Cryptococcus neoformans. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, G.; Lopez-Moya, F.; Chuina, E.; Ibañez-Vea, M.; Garde, E.; López-Llorca, L.V.; Pisabarro, A.G.; Ramírez, L. Strain Degeneration in Pleurotus ostreatus: A Genotype Dependent Oxidative Stress Process Which Triggers Oxidative Stress, Cellular Detoxifying and Cell Wall Reshaping Genes. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Urrutia, A.; Goicoechea, J.; Rodríguez, Y.; Corres, J.M.; Arregui, F.J.; Matías, I.R. An antibacterial submicron fiber mat with in situ synthesized silver nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Goicoechea, J.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. A comparative study of two different approaches for the incorporation of silver nanoparticles into layer-by-layer films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinali, T.; Alemzadeh, E.; Zarban, A.; Khorashadizadeh, M.; Ansarifar, E. Fabrication and characterization of jujube extract-loaded electrospun polyvinyl alcohol nanofiber for strawberry preservation. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6353–6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, E.P.D.; Pires, J.B.; Santos, F.N.D.; Fonseca, L.M.; Radünz, M.; Dal Magro, J.; Gandra, E.A.; Zavareze, E.D.R.; Dias, A.R.G. Encapsulation of lemongrass essential oil into cassava starch fibers for application as antifungal agents in bread. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Chen, P.; Guo, J.; Yu, H.; Zhong, S.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, B. A Novel Intelligent Indicator Film: Preparation, Characterization, and Application. Molecules 2023, 28, 3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardhani, R.A.K.; Asri, L.; Nasir, M.; Purwasasmita, B.S. Preparation of Chitosan-Polyethylene Oxide-Colocasia esculenta Flour Nanofibers using Electrospinning Method. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2019, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nate, Z.; Moloto, M.J.; Mubiayi, P.K.; Sibiya, P.N. Green synthesis of chitosan capped silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activity. MRS Adv. 2018, 3, 2505–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Guo, G.; Zhao, L.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y. Antifungal pentachloronitrobenzene/hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complex nanofibers by electrospun with no polymer: Fabrication and characterization. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 413, 137499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Ding, B.; Sone, Y.; Shiratori, S. Super-hydrophobic surfaces of layer-by-layer structured film-coated electrospun nanofibrous membranes. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 165607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfi, D.M.; Lemes, A.P.; De Oliveira, S.; Justo, G.Z.; Palladino, M.V.; Durán, N. Electrospun poly(ethylene oxide)/chitosan nanofibers with cellulose nanocrystals as support for cell culture of 3T3 fibroblasts. Cellulose 2017, 24, 3353–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, M.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Ajji, A. Core–Shell Structured PEO-Chitosan Nanofibers by Coaxial Electrospinning. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, P.J.; Urrutia, A.; Goicoechea, J.; Matias, I.; Arregui, F. A Lossy Mode Resonance optical sensor using silver nanoparticles-loaded films for monitoring human breathing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 187, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalde-Cela, S.; Ho, S.; Rodríguez-González, B.; Correa-Duarte, M.A.; Álvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Kotov, N.A. Loading of Exponentially Grown LBL Films with Silver Nanoparticles and Their Application to Generalized SERS Detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5326–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malikova, N.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Schierhorn, M.; Kotov, N.A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Layer-by-Layer Assembled Mixed Spherical and Planar Gold Nanoparticles: Control of Interparticle Interactions. Langmuir 2002, 18, 3694–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Goicoechea, J.; Urrutia, A.; Arregui, F.J. Effect of both protective and reducing agents in the synthesis of multicolor silver nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neukäufer, J.S.; Seyfang, B.; Gruetzner, T. Investigation of Contact Angles and Surface Morphology of 3D-Printed Materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 6761–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, A.; Choi, W.; Ma, M.; Mabry, J.M.; Mazzella, S.A.; Rutledge, G.C.; McKinley, G.H.; Cohen, R.E. Designing Superoleophobic Surfaces. Science 2007, 318, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharat, Z.; Goushki, M.A.; Sarvian, N.; Asad, S.; Dehghan, M.M.; Kabiri, M. Chitosan/PEO nanofibers containing Calendula officinalis extract: Preparation, characterization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation for wound healing applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 609, 121132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinca, R.B.; Westin, C.B.; da Silva, J.A.F.; Moraes, M. Electrospun multilayer chitosan scaffolds as potential wound dressings for skin lesions. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratoddi, I. Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Au and Ag Nanoparticles. Breakthroughs and Perspectives. Nanomaterials 2017, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandua, X.; Rivero, P.J.; Palacio, J.F.; Esparza, J.; Rodríguez, R. An Alternative Methodology for the Evaluation of Photocatalytic Activity of Polymeric Coatings by Monitoring Dye Degradation. Coatings 2022, 12, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgers, R.; Eidt, A.; Frankenberger, R.; Rosentritt, M.; Schweikl, H.; Handel, G.; Hahnel, S. The anti-adherence activity and bactericidal effect of microparticulate silver additives in composite resin materials. Arch. Oral Biol. 2009, 54, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, D.; Cheeseman, S.; Wang, Y.; Funnell, B.; Leung, S.; Tricoli, A.; Nisbet, D. Superhydrophobic Surfaces to Combat Bacterial Surface Colonization. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2300324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.; Zahoor, I.; Baba, T.R.; Padder, S.A.; Bhat, Z.A.; Koul, A.M.; Jiang, L. Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles Against Fungal Pathogens. Front. Nanotechnol. 2021, 3, 679358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Samad, L.M.; Hassan, M.A.; Bakr, N.R.; El-Ashram, S.; Radwan, E.H.; Aziz, K.K.A.; Hussein, H.K.; El Wakil, A. Insights into Ag-NPs-mediated pathophysiology and ultrastructural aberrations in ovarian tissues of darkling beetles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matras, E.; Gorczyca, A.; Przemieniecki, S.W.; Oćwieja, M. Surface properties-dependent antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murillo, L.; Rivero, P.J.; Sandúa, X.; Pérez, G.; Palacio, J.F.; Rodríguez, R.J. Antifungal Activity of Chitosan/Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Blend Electrospun Polymeric Fiber Mat Doped with Metallic Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers 2023, 15, 3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183700
Murillo L, Rivero PJ, Sandúa X, Pérez G, Palacio JF, Rodríguez RJ. Antifungal Activity of Chitosan/Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Blend Electrospun Polymeric Fiber Mat Doped with Metallic Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2023; 15(18):3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183700
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurillo, Leire, Pedro J. Rivero, Xabier Sandúa, Gumer Pérez, José F. Palacio, and Rafael J. Rodríguez. 2023. "Antifungal Activity of Chitosan/Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Blend Electrospun Polymeric Fiber Mat Doped with Metallic Silver Nanoparticles" Polymers 15, no. 18: 3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183700
APA StyleMurillo, L., Rivero, P. J., Sandúa, X., Pérez, G., Palacio, J. F., & Rodríguez, R. J. (2023). Antifungal Activity of Chitosan/Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Blend Electrospun Polymeric Fiber Mat Doped with Metallic Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers, 15(18), 3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183700







