Enhancing Char Formation and Flame Retardancy of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer (EVA)/Aluminum Hydroxide (ATH) Composites by Grafting Ladder Phenyl/Vinyl Polysilsesquioxane (PhVPOSS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the EVA/ATH/PhVPOSS Composites
2.3. Characterization and Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
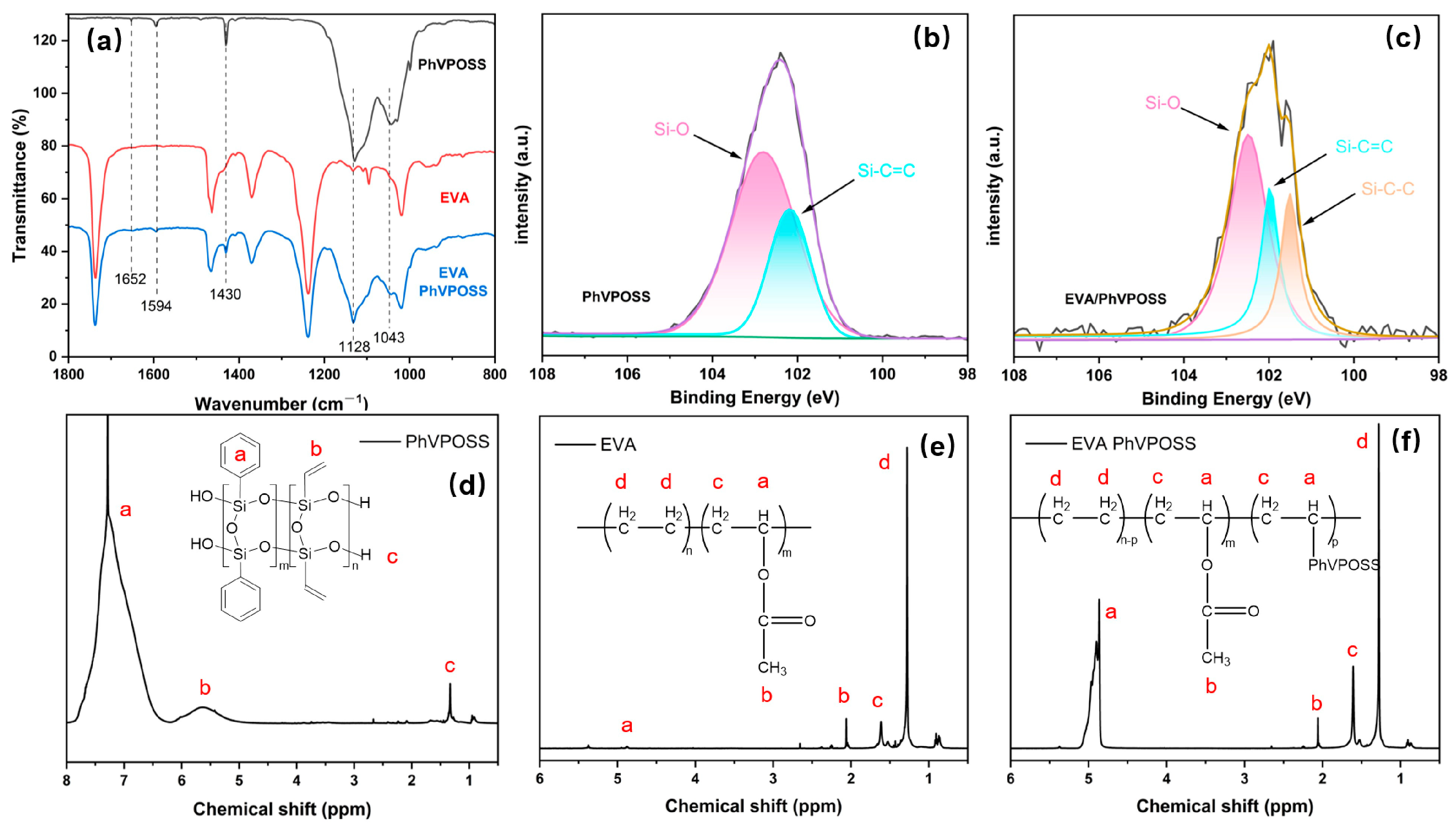
3.1. Grafting Reaction of PhVPOSS and EVA
3.2. Thermal Behavior of EVA/ATH/PhVPOSS
3.3. Fire Behaviors of EVA/ATH/PhVPOSS Composites
3.4. Flame-Retardant Mechanism
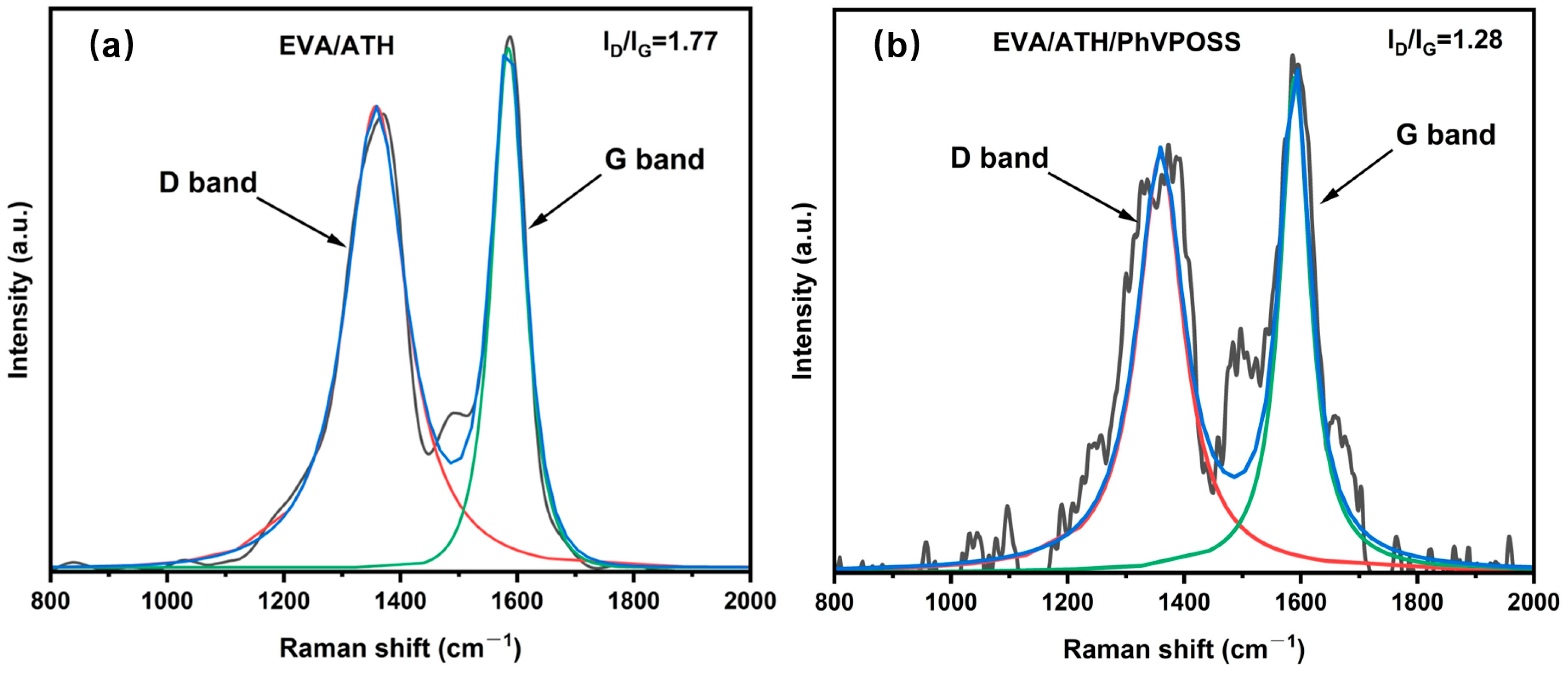
3.4.1. Char Residue Analysis
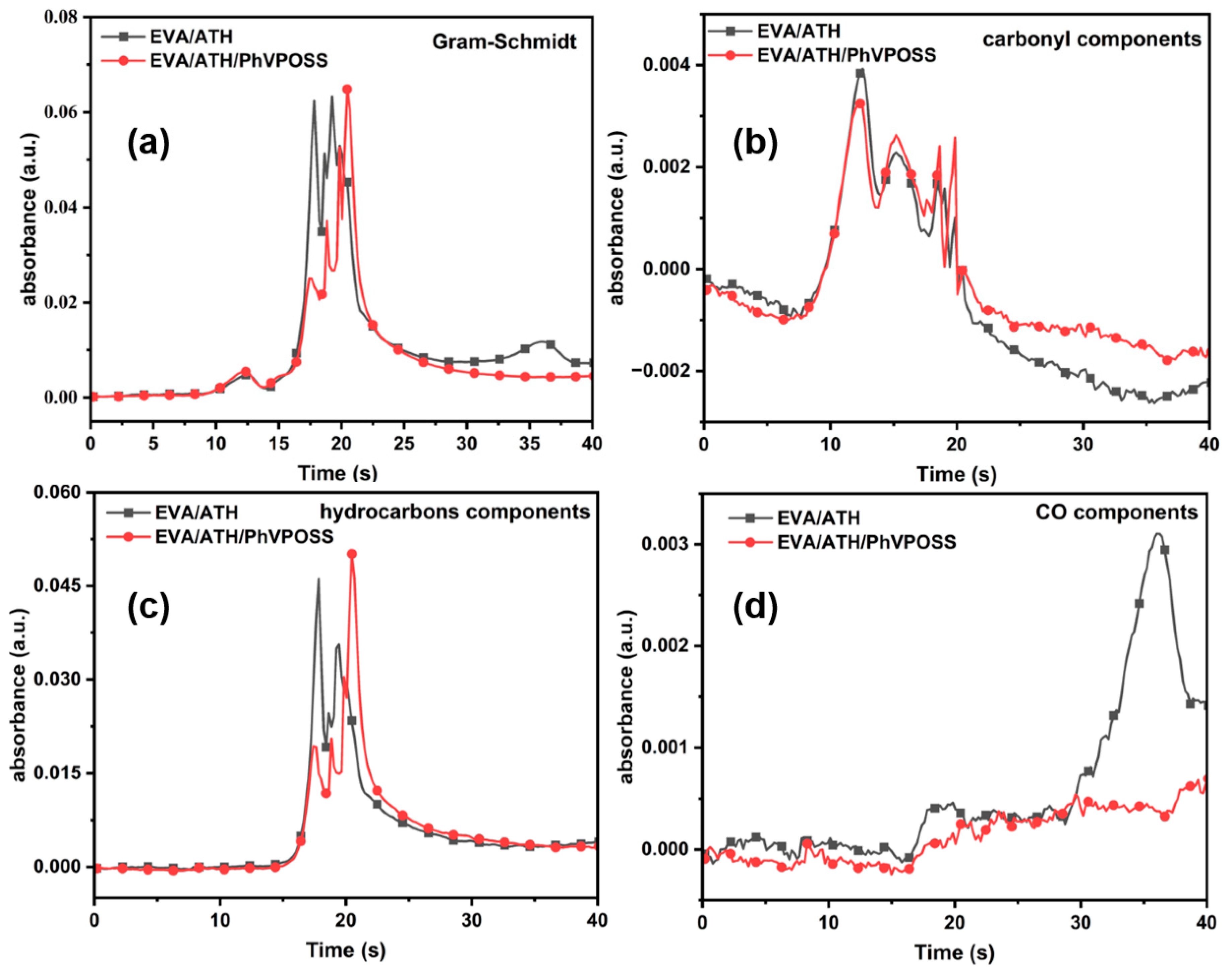
3.4.2. TG-IR Analysis
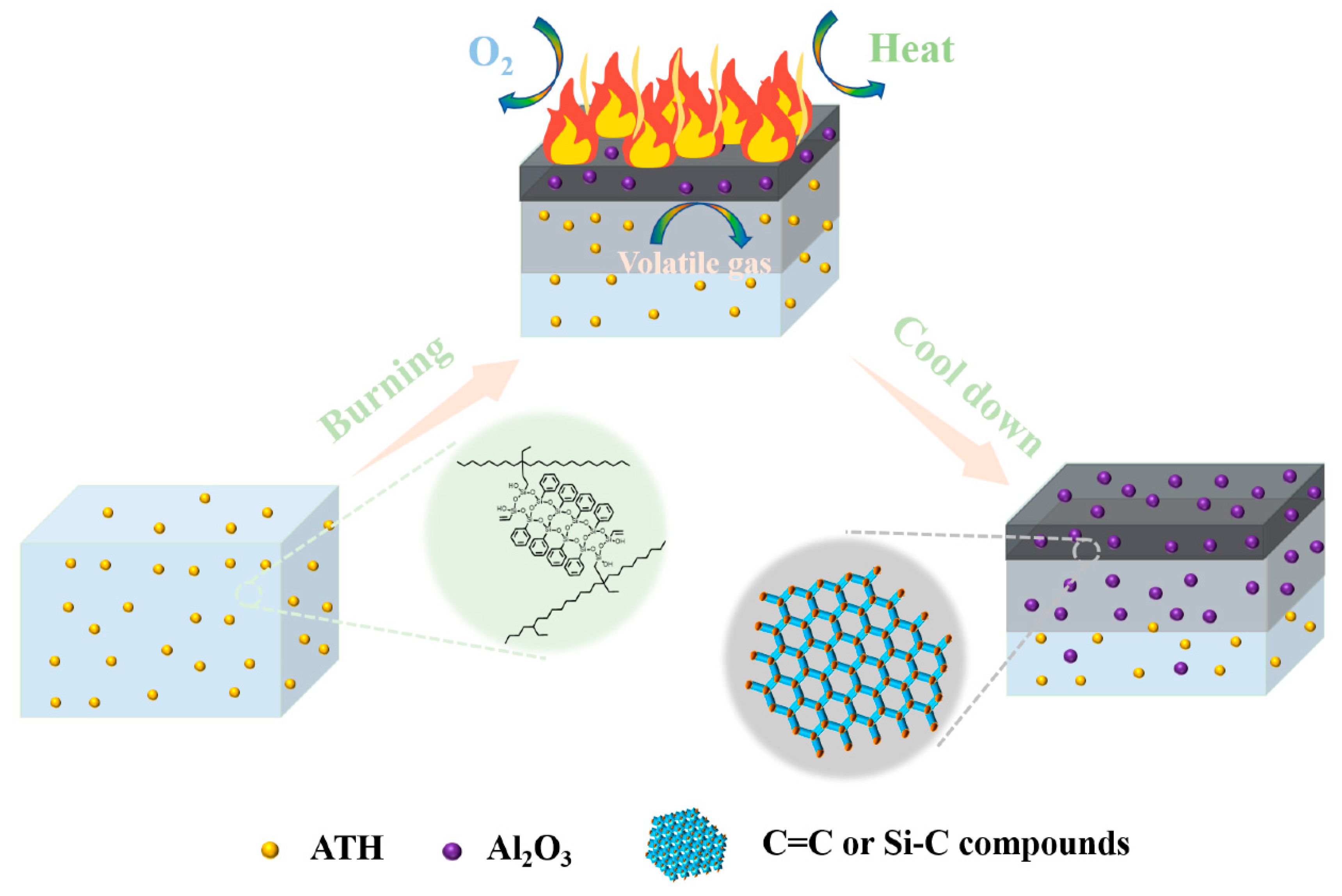
3.4.3. In-Depth Flame-Retardant Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holmes, M. Wire and cable: Some new developments. Plast. Addit. Compd. 2004, 6, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie, C.; Morgan, A. Fire Retardancy of Polymeric Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bourbigot, S.; Le Bras, M.; Flamebard, X.; Rochery, M.; Devaux, E.; Lichtenhan, J.D. Fire Retardancy of Polymers: New Applications of Mineral Fillers; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.W.; Zhao, H.B.; Wang, Y.Z. Advanced Flame-Retardant Methods for Polymeric Materials. Adv. Mater. 2021, 34, 2107905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, J.L.; Dong, J.; Jiao, C.M.; Chen, X.L. Synergistic effects between red phosphorus and alumina trihydrate in flame retardant silicone rubber composites. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2013, 42, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.D.; Liang, B.; Yang, D.X. Flame Retarded PE with MH/ATH/Microencapsulated Red Phosphorous and its Toughening by Polymeric Compatibilizers. Int. Polym. Process. 2014, 29, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, P.; Tshai, K.Y.; Hui, D.; Kong, I. Synergistic of ammonium polyphosphate and alumina trihydrate as fire retardants for natural fiber reinforced epoxy composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 114, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquesne, S.; Fontaine, G.; Cérin-Delaval, O.; Gardelle, B.; Tricot, G.; Bourbigot, S. Study of the thermal degradation of an aluminium phosphinate–aluminium trihydrate combination. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 551, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Han, L.; Guo, Z.; Fang, Z. Improving the flame-retardant efficiency of aluminum hydroxide with fullerene for high-density polyethylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Dong, Q.; Shu, Z.; Wang, W.-J.; He, K. Flame Retardant Properties of Polyurethane/Expandable Praphite Composites. Procedia Eng. 2014, 71, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ran, S.; Hu, H.; Fang, Z. Improving flame-retardant efficiency by incorporation of fullerene in styrene–butadiene–styrene block copolymer/aluminum hydroxide composites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 125, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Bras, M.L.; Leeuwendal, R.; Shen, K.K.; Schubert, D. Recent advances in the use of zinc borates in flame retardancy of EVA. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1999, 64, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnier, R.; Viretto, A.; Dumazert, L.; Longerey, M.; Buonomo, S.; Gallard, B.; Longuet, C.; Cavodeau, F.; Lamy, R.; Freitag, A. Fire retardant benefits of combining aluminum hydroxide and silica in ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 128, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Chen, X. Influence of fumed silica on the flame-retardant properties of ethylene vinyl acetate/aluminum hydroxide composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 1285–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, G.N. Flame retardant properties of EVA-nanocomposites and improvements by combination of nanofillers with aluminium trihydrate. Fire Mater. 2001, 25, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Tang, G.; Hu, W.; Wang, B.-B.; Pan, Y.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Aluminum hypophosphite microencapsulated to improve its safety and application to flame retardant polyamide 6. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 294, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C.; Chen, W.C.; Mohamed, M.G.; Huang, Y.C.; Kuo, S.W. Organic-Inorganic Phenolic/POSS Hybrids Provide Highly Ordered Mesoporous Structures Templated by High Thermal Stability of PS-b-P4VP Diblock Copolymer. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202300538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.G.; Kuo, S. Progress in the self-assembly of organic/inorganic polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) hybrids. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 5535–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Feng, S. New Functionalized Ionic Liquids Based on POSS for the Detection of Fe3+ Ion. Polymers 2021, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, X.; Yang, R. High-efficiency flame retardency of epoxy resin composites with perfect T8 caged phosphorus containing polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (P-POSSs). Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 127, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qin, Z.; Lan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Pan, Y.; Yang, R. Flame retardant composites of ladder phenyl/vinyl polysilsesquioxane-reinforced vinyl ester. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 56, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, W.; Guo, X.; Pan, Y.T.; Yang, R. Halogen-free and phosphorus-free flame-retarded polycarbonate using cyclic polyphenylsilsesquioxanes. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 10953–10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Geng, J.; Zhang, W.; Qian, L.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, W. Improved mechanical and flame resistance properties of vinyl ester resin composites by lithium containing polyhedral oligomeric phenyl silsesquioxane. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 5424–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R. Enhanced mechanical and flame retardancy properties of vinyl ester resin systems with the synthesis of two flame retardants with vinyl group. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Qiao, L.; Yang, R. Mechanical and flame-retardant properties and thermal decomposition of vinyl ester resin modified by different phenyl silsesquioxanes. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, G.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R. Flame retardant and mechanism of vinyl ester resin modified by octaphenyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 3061–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Li, D.; Cheng, B.; Song, T.; Yang, R. A cross-linked charring strategy for mitigating the hazards of smoke and heat of aluminum diethylphosphonate/polyamide 6 by caged octaphenyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R. Synthesis of incompletely caged silsesquioxane (T7-POSS) compounds via a versatile three-step approach. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4277–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didane, N.; Giraud, S.; Devaux, E.; Lemort, G. Development of fire resistant PET fibrous structures based on phosphinate-POSS blends. Polymer Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fina, A.; Tabuani, D.; Camino, G. Polypropylene–polysilsesquioxane blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, R. Investigations of epoxy resins flame-retarded by phenyl silsesquioxanes of cage and ladder structures. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Z.L.; Yang, H.; Zheng, Q. Crosslinking of low density polyethylene with octavinyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane as the crosslinker. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 44030–44038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, R.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, W. Study on the thermal behaviors of polyhedral oligomeric octaphenylsilsesquioxane (OPS). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.S.; Edge, M.; Rodriguez, M.; Liauw, C.M.; Fontan, E. Aspects of the thermal oxidation of ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 68, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, M.; Camino, G.; Thomann, R.; Mülhaupt, R. Synthesis and thermal behaviour of layered silicate-EVA nanocomposites. Polymer 2001, 42, 4501–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, A.; Zanetti, M.; Braglia, M.; Camino, G.; Falqui, L. Thermal degradation and rheological behaviour of EVA/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 77, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Preparation and flame retardancy of a novel flame-retardant poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate)/aluminum hydroxide composites containing phosphorus. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Zhang, W.; Lu, H.; Song, K.; Geng, Z.; Ye, X.; Pan, Y.-T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R. Multielement Flame-Retardant System Constructed with Metal POSS–Organic Frameworks for Epoxy Resin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 49326–49337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yuan, B.; Shang, S.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y.; Yu, B.; Qi, C.; Dong, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, X. Surface modification of ammonium polyphosphate by supramolecular assembly for enhancing fire safety properties of polypropylene. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 181, 107588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Song, K.; Ur Rehman, Z.; Song, T.; Lin, T.; Zhang, W.; Pan, Y.-T.; Yang, R. Precise Control of a Yolk-Double Shell Metal–Organic Framework-Based Nanostructure Provides Enhanced Fire Safety for Epoxy Nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 14805–14816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Hou, B.; Ur Rehman, Z.; Pan, Y.-T.; He, J.; Wang, D.-Y.; Yang, R. “Sloughing” of metal-organic framework retaining nanodots via step-by-step carving and its flame-retardant effect in epoxy resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 448, 137666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Composition (wt%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| EVA | ATH | PhVPOSS | |
| EVA | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| EVA/PhVPOSS | 95 | 0 | 5 |
| EVA/ATH | 40 | 60 | 0 |
| EVA/ATH/PhVPOSS | 40 | 55 | 5 |
| Sample | T5% (°C) | Rmax1 (wt%/min)/Tmax1 (°C) | Rmax2 (wt%/min)/Tmax2 (°C) | Residues at 800 °C (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVA | 344.7 | 0.30/359.91 | 2.50/466.59 | 0.40 |
| EVA/PhVPOSS | 346.2 | 0.28/360.01 | 2.52/468.10 | 2.56 |
| EVA/ATH | 289.3 | 0.36/316.17 | 1.02/469.50 | 38.15 |
| EVA/ATH/PhVPOSS | 297.8 | 0.30/325.22 | 1.06/470.81 | 40.69 |
| Samples | LOI (%) | UL-94 (3.2 mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rating | t1 (s) | t2 (s) | Dripping | ||
| EVA | 19.2 | NR | >60 | - | Yes |
| EVA/PhVPOSS | 20.4 | NR | >60 | - | Yes |
| EVA/ATH | 34.3 | NR | 2 | >60 | No |
| EVA/ATH/PhVPOSS | 34.4 | V-1 | 1 | 16 | No |
| Sample | TTI (s) | p-HRR (kW/m2) | THR (MJ/m2) | p-SPR (m2/s) | TSR (m2/m2) | p-COP (g/s) | p-CO2P (g/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVA | 65 | 1000.56 | 117.31 | 0.1124 | 1538.82 | 0.0069 | 0.49 |
| EVA/PhVPOSS | 67 | 766.32 | 118.95 | 0.1228 | 1698.73 | 0.0053 | 0.39 |
| EVA/ATH | 90 | 180.60 | 76.70 | 0.0298 | 838.26 | 0.0022 | 0.09 |
| EVA/ATH/PhVPOSS | 84 | 166.35 | 71.97 | 0.0127 | 495.22 | 0.0002 | 0.09 |
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 3735 and 3558 | -OH stretching vibration or water |
| 3087 | =C-H stretching vibration |
| 2933 and 2860 | R-CH3 stretching vibration of acetic acid |
| 1754 | -C=O stretching vibration |
| 1639 | C=C stretching vibration |
| 1583 | Aromatic rings vibration |
| 1213 | C-O/C-O-C stretching vibration |
| 912 | =C-H deformation vibration |
| 669 | CAr-H deformation vibration |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, F.; Cheng, B.; Cong, K.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Qin, Z.; Yang, R. Enhancing Char Formation and Flame Retardancy of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer (EVA)/Aluminum Hydroxide (ATH) Composites by Grafting Ladder Phenyl/Vinyl Polysilsesquioxane (PhVPOSS). Polymers 2023, 15, 3312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153312
Hu F, Cheng B, Cong K, Li D, Zhang W, Qin Z, Yang R. Enhancing Char Formation and Flame Retardancy of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer (EVA)/Aluminum Hydroxide (ATH) Composites by Grafting Ladder Phenyl/Vinyl Polysilsesquioxane (PhVPOSS). Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153312
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Fa, Bo Cheng, Kun Cong, Dinghua Li, Wenchao Zhang, Zhaolu Qin, and Rongjie Yang. 2023. "Enhancing Char Formation and Flame Retardancy of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer (EVA)/Aluminum Hydroxide (ATH) Composites by Grafting Ladder Phenyl/Vinyl Polysilsesquioxane (PhVPOSS)" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153312
APA StyleHu, F., Cheng, B., Cong, K., Li, D., Zhang, W., Qin, Z., & Yang, R. (2023). Enhancing Char Formation and Flame Retardancy of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer (EVA)/Aluminum Hydroxide (ATH) Composites by Grafting Ladder Phenyl/Vinyl Polysilsesquioxane (PhVPOSS). Polymers, 15(15), 3312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153312






