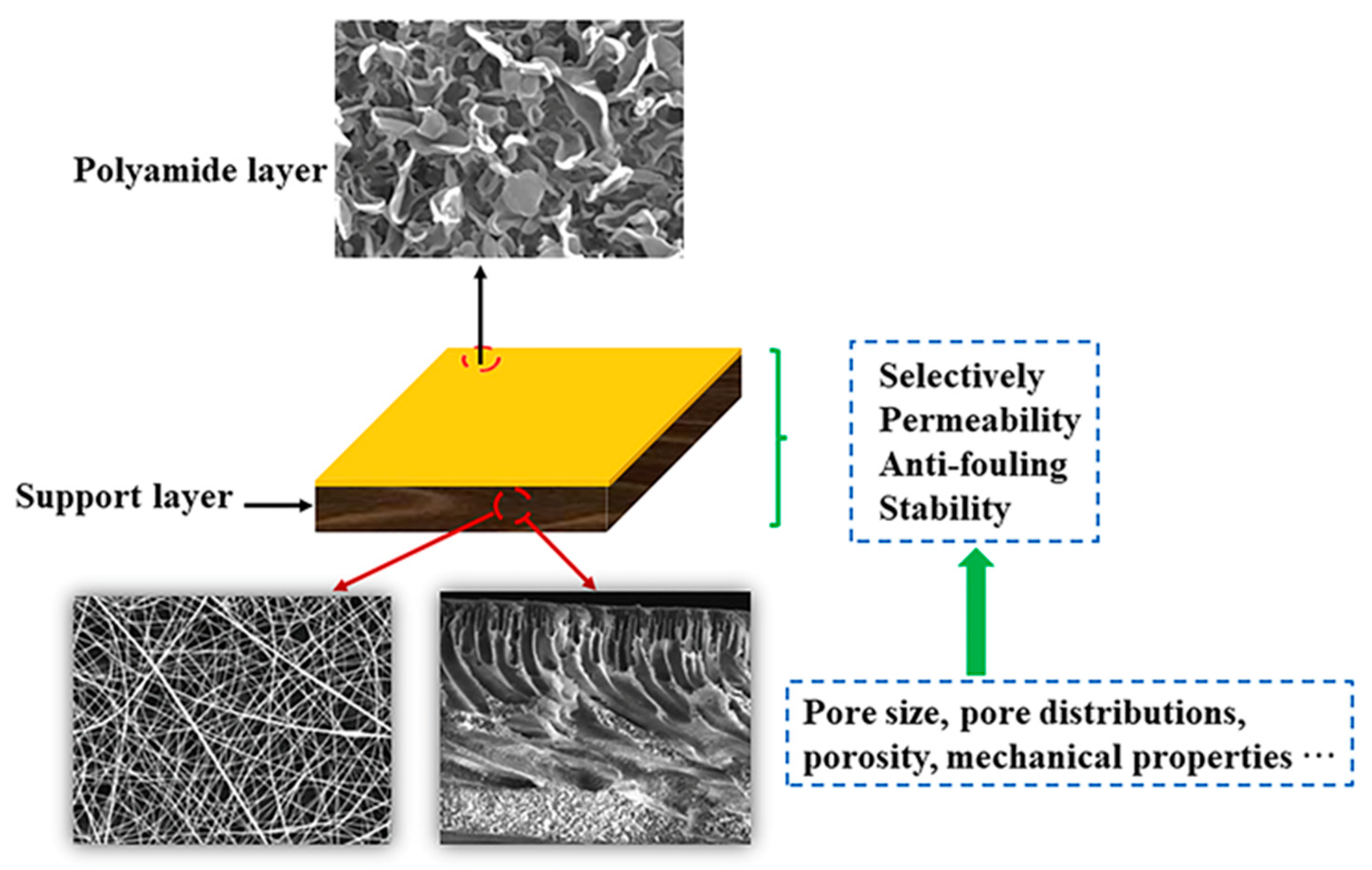
Development of Support Layers and Their Impact on the Performance of Thin Film Composite Membranes (TFC) for Water Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
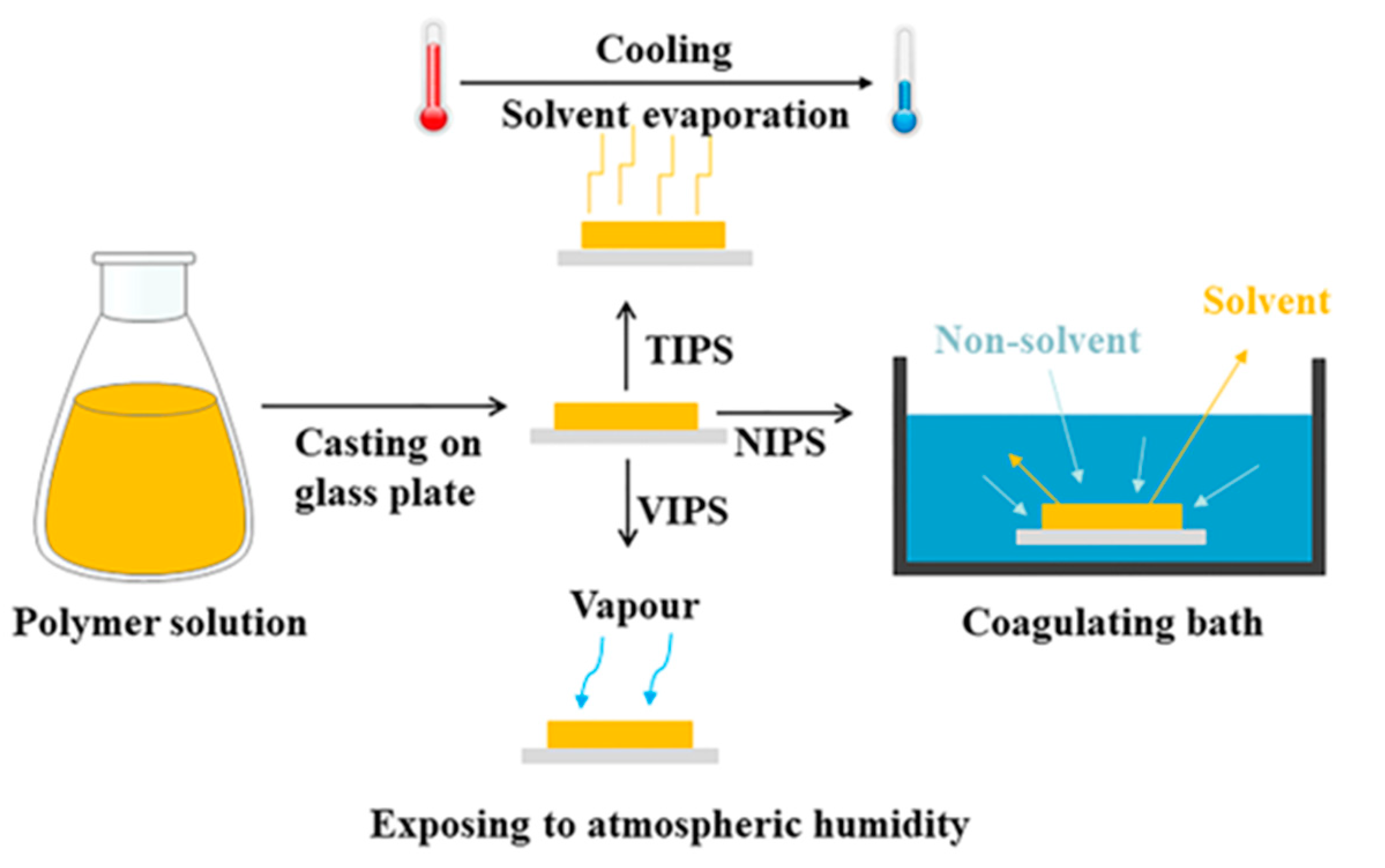
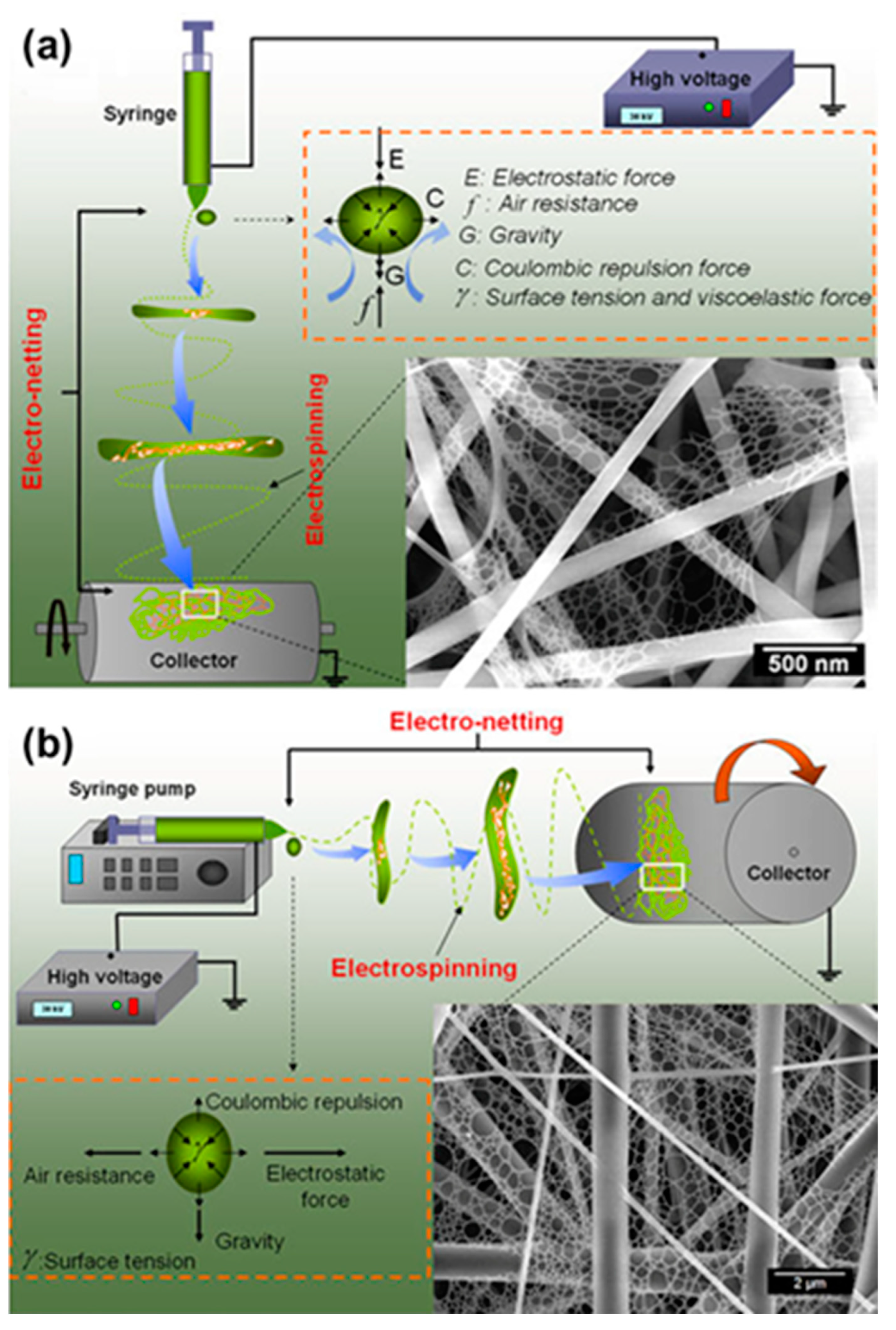
2. Fabrication of Supports
2.1. Fabrication of Phase Inversion Flat Sheet Supports
2.2. Fabrication of Patterned Electrospun Fiber Supports
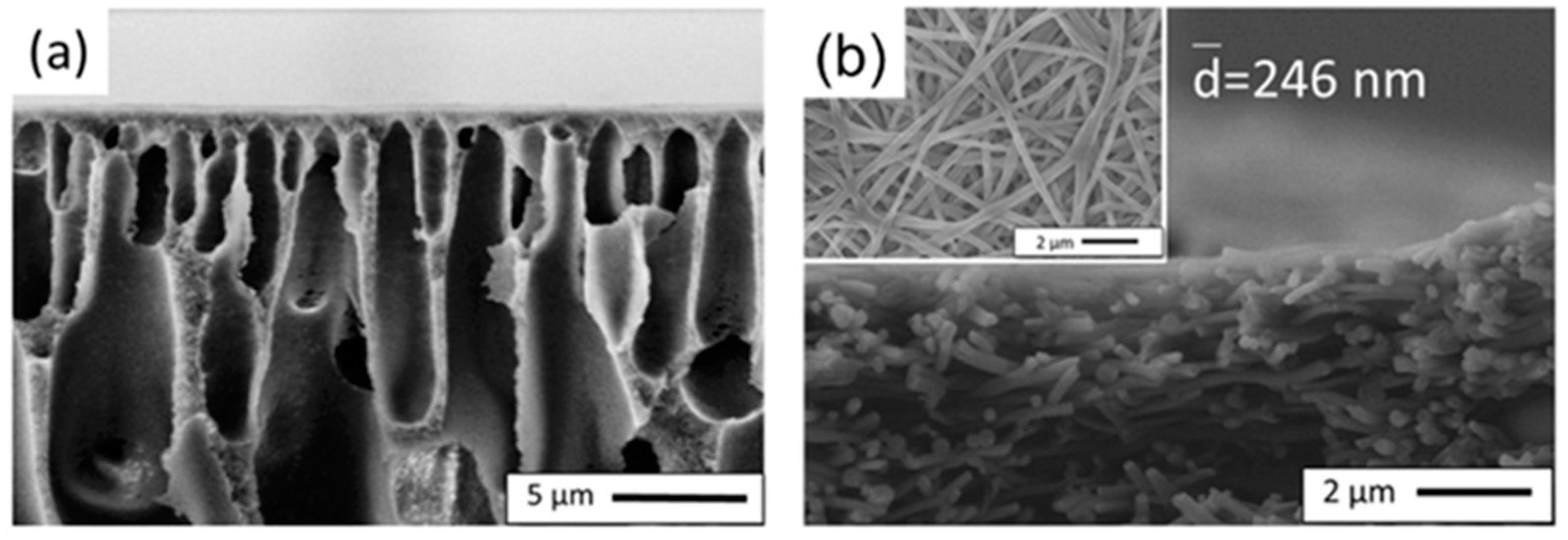
3. Effect of Fabrication Methods on the Structural Properties of Supports
4. Effect of Structural Properties and Patterns in Supports on the Performance of TFC Membrane
4.1. Mechanical Stability
4.2. Polymerization, Deposition, and Adhesion of the Selective (Active) Layer
4.3. Structural and Functional Properties of the Active Layer
4.4. Mitigating Fouling
5. Conclusions and Future Prospective
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Arjan, W.S. Self-Assembled Nanofibrous Membranes by Electrospinning as Efficient Dye Photocatalysts for Wastewater Treatment. Polymers 2023, 15, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fida, M.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Alam, S.M.K.; Nsabimana, A. Water Contamination and Human Health Risks in Pakistan: A Review. Expo. Health 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanbali, G.; Jodeh, S.; Hamed, O.; Bol, R.; Khalaf, B.; Qdemat, A.; Samhan, S.; Dagdag, O. Magnetic Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Decorated with Novel Functionalities: Synthesis and Application as Adsorbents for Lead Removal from Aqueous Medium. Processes 2020, 8, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zioui, D.; Martins, P.M.; Aoudjit, L.; Salazar, H.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Wastewater Treatment of Real Effluents by Microfiltration Using Poly (vinylidene fluoride–hexafluoropropylene) Membranes. Polymers 2023, 15, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotobuki, M.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Ceramic-polymer composite membranes for water and wastewater treatment: Bridging the big gap between ceramics and polymers. Molecules 2021, 26, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; An, Z.; Mi, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. Thin-film composite nanofiltration membranes with poly (amidoxime) as organic interlayer for effective desalination. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.R.; Huang, L.; McCutcheon, J.R. Thin film composite membranes for forward osmosis supported by commercial nanofiber nonwovens. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.Y.; Wang, R. From micro to nano: Polyamide thin film on microfiltration ceramic tubular membranes for nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 587, 117161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Han, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, B.; Xing, J. A Facile Strategy toward the Preparation of a High-Performance Polyamide TFC Membrane with a CA/PVDF Support Layer. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Solomon, M.F.; Gorgojo, P.; Munoz-Ibanez, M.; Livingston, A.G. Beneath the surface: Influence of supports on thin film composite membranes by interfacial polymerization for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 448, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazia, S.; Sekhar, S.C.; Jegatheesan, V.; Bhargava, S.K.; Sridhar, S. Performance of chemically resistant polyurea reverse osmosis membrane in the treatment of highly alkaline industrial wastewater containing sodium aluminate. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 2259–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.Y. The upper bound of thin-film composite (TFC) polyamide membranes for desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 590, 117297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, W.L.; Huang, Z.H.; Xu, Z.L. Polyamide reverse osmosis membranes containing 1D nanochannels for enhanced water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 618, 118681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harisha, R.S.; Hosamani, K.M.; Keri, R.S.; Nataraj, S.K.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Arsenic removal from drinking water using thin film composite nanofiltration membrane. Desalination 2010, 252, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-R.; Xu, J.-M.; Feng, H.-J.; Zhao, H.-L.; Wu, S.-B. Tailoring structures and performance of polyamide thin film composite (PA-TFC) desalination membranes via sublayers adjustment—A review. Desalination 2017, 417, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, B.; Elimelech, M. Organic fouling of forward osmosis membranes: Fouling reversibility and cleaning without chemical reagents. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 348, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, S.; Sourirajan, S. Sea Water Demineralization by Means of an Osmotic Membrane; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1963; Volume 38, pp. 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhom, M. A review on the polyamide thin film composite (TFC) membrane used for desalination: Improvement methods, current alternatives, and challenges. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 191, 472–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F. Chemically functionalized polyamide thin film composite membranes: The art of chemistry. Desalination 2020, 495, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F.; Misdan, N.; Kassim, M.A. A recent progress in thin film composite membrane: A review. Desalination 2012, 287, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, A.; Aktij, S.A.; Karami, P.; Sameoto, D.; Sadrzadeh, M. Micropatterned Thin-Film Composite Poly(piperazine-amide) Nanofiltration Membranes for Wastewater Treatment. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 6653–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourpanah, Y. MXenes and other 2D nanosheets for modification of polyamide thin film nanocomposite membranes for desalination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 289, 120777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liang, H.; Tang, X.; Bai, L.; Zhang, X.; Gan, Z.; Cheng, X.; Luo, X.; Xu, D.; Li, G. Supramolecular-Based Regenerable Coating Layer of a Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane for Simultaneously Enhanced Desalination and Antifouling Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 21137–21149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shan, C.; Xu, L.; Yu, L.; Gao, H. Enhancing the permeance and antifouling properties of thin-film composite nanofiltration membranes modified with hydrophilic capsaicin-mimic moieties. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 610, 118233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Low, Z.-X.; Hegab, H.M.; Xie, Z.; Ou, R.; Yang, G.; Simon, G.P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Enhancement of desalination performance of thin-film nanocomposite membrane by cellulose nanofibers. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 592, 117363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Preparation and characterization of anti-fouling β-cyclodextrin/polyester thin film nanofiltration composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, K.J.; Lin, N.H.; Cohen, Y. Biofouling and cleaning effectiveness of surface nanostructured reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Baek, Y.; Choi, K.; Kim, D.G.; Kang, H.; Choi, Y.S.; Yoon, J.; Lee, J.C. The improvement of antibiofouling properties of a reverse osmosis membrane by oxidized CNTs. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 32802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gol, R.M.; Jewrajka, S.K. Facile in situ PEGylation of polyamide thin film composite membranes for improving fouling resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, F.; Jia, J.; Lei, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, C. Investigation of forward osmosis performance and anti-fouling properties of the novel hydrophilic polymer brush-grafted TFC-type FO membranes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 2198–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Kim, S.S. Plasma treatment of polypropylene and polysulfone supports for thin film composite reverse osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 286, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, R.; Yang, F.; Kang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiang, M. Probing influences of support layer on the morphology of polyamide selective layer of thin film composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 556, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Guo, H.; Yang, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhu, B.; Dong, Y.; Tang, C.Y. Reactable substrate participating interfacial polymerization for thin film composite membranes with enhanced salt rejection performance. Desalination 2018, 436, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Chen, D.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Kang, J.; Xu, R.; Cao, Y.; Xiang, M. Influence of support layer pore size on interfacial polymerization and polyamide selective layer characterization. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.S.; Joshi, S.V.; Trivedi, J.J.; Devmurari, C.V.; Rao, A.P.; Ghosh, P.K. Probing the structural variations of thin film composite RO membranes obtained by coating polyamide over polysulfone membranes of different pore dimensions. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharabati, J.-A.-D.; Guclu, S.; Erkoc-Ilter, S.; Koseoglu-Imer, D.Y.; Unal, S.; Menceloglu, Y.Z.; Ozturk, I.; Koyuncu, I. Interfacially polymerized thin-film composite membranes: Impact of support layer pore size on active layer polymerization and seawater desalination performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsand-Ghayeni, M.; Barzin, J.; Zandi, M.; Kowsari, M. Fabrication of asymmetric and symmetric membranes based on PES/PEG/DMAc. Polym. Bull. 2016, 74, 2081–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, M.; Kang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yoon, M.-H.; Kim, C.-M.; Song, J.-h.; Kim, I.S. Fabrication of highly permeable thin-film nanocomposite forward osmosis membranes via the design of novel freestanding robust nanofiber substrates. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 11700–11713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van-Pham, D.T.; Quyen, T.T.B.; Toan, P.V.; Nguyen, C.N.; Ho, M.H.; Thien, D.V.H. Temperature effects on electrospun chitosan nanofibers. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidney, L.; Srinivasa, S. High Flow Porous Membranes for Separating Water from Saline Solutions; U.S. Patent and Trademark Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.S.; Zhou, X.J.; Sun, Y.Z.; Bai, R.B. Anticorrosion Performance of PVDF Membranes Modified by Blending PTFE Nanoemulsion and Prepared through Usual Non-Solvent-Induced Phase Inversion Method. Membranes 2021, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, X.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.D.; Kong, X.; Wu, C.R. Study of the dual role mechanism of water-soluble additive in low temperature thermally-induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 543, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrs, C.; Schwellenbach, J. Membrane formation via non-solvent induced phase separation using sustainable solvents: A comparative study. Polymer 2020, 186, 122071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.H. Effect of PEG additive on membrane formation by phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 138, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.U.; Iwama, T.; Chan, E.Y.; Tree, D.R.; Delaney, K.T.; Fredrickson, G.H. Mechanisms of Asymmetric Membrane Formation in Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, D.R.; Kinzer, K.E.; Tseng, H.S. Microporous membrane formation via thermally-induced phase separation. II. Liquid—Liquid phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 52, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, P.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Gonzales, R.R.; Li, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, S.; Hu, M.; Guan, K.; Matsuyama, H. Development of porous polyketone membrane via liquid–liquid thermally induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 677, 121639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsigmondy, R.; Bachmann, W. Ueber neue filter. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem 1918, 103, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alihemati, Z.; Hashemifard, S.A.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F. Feasibility of using polycarbonate as a substrate of thin film composite membrane in forward osmosis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Z.; Han, C.C. Role of wettability in interfacial polymerization based on PVDF electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 442, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, L.; Lang, W.Z.; Wang, Y. Improved performance of thin-film composite membrane with PVDF/PFSA substrate for forward osmosis process. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 535, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Thümmler, K.; Volkert, B.; Hettrich, K.; Schmidt, I.; Fischer, K. Properties and Applications of Cellulose Acetate. Macromol. Symp. 2008, 262, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.P.; Kallem, P.; Rasheed, P.A.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Banat, F.; Lau, W.J.; Hasan, S.W. Enhanced water flux and bacterial resistance in cellulose acetate membranes with quaternary ammoniumpropylated polysilsesquioxane. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H.; Takida, Y.; Maki, T.; Teramoto, M. Preparation of porous membrane by combined use of thermally induced phase separation and immersion precipitation. Polymer 2002, 43, 5243–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Xiao, T.; Cai, X.; Ding, L.; Fu, Y.; Yang, X. Preparation and Characterization of Hydrophilically Modified PVDF Membranes by a Novel Nonsolvent Thermally Induced Phase Separation Method. Membranes 2016, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basko, A.V.; Pochivalov, K.V.; Yurov, M.Y.; Lebedeva, T.N.; Yushkin, A.A.; Volkov, A.V. Preparation of thermostable polypropylene membranes with a controlled structure by nonsolvent thermally induced phase separation. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2022, 62, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-P.; Lang, W.-Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.-J. Preparation and characterizations of charged PVDF membranes via composite thermally induced phase separation (C-TIPS) method. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, X.; Qiu, C.; Wang, R.; Tang, C.Y. Influence of monomer concentrations on the performance of polyamide-based thin film composite forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 381, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Qiu, C.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Synthesis and characterization of flat-sheet thin film composite forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 372, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Widjojo, N.; Chung, T.-S. Thin film composite forward osmosis membranes based on polydopamine modified polysulfone substrates with enhancements in both water flux and salt rejection. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 80, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Goh, K.; Lai, G.S.; Zhao, Y.; Torres, J.; Wang, R. Unraveling the role of support membrane chemistry and pore properties on the formation of thin-film composite polyamide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgojo, P.; Jimenez-Solomon, M.F.; Livingston, A.G. Polyamide thin film composite membranes on cross-linked polyimide supports: Improvement of RO performance via activating solvent. Desalination 2014, 344, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Lau, C.H.; Xiong, S.; Wei, W.; Liao, R.; Shen, L.; Lu, A.; Wang, Y. Zwitterion-Ag Complexes That Simultaneously Enhance Biofouling Resistance and Silver Binding Capability of Thin Film Composite Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15698–15708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadzadeh, D.; Lau, W.J.; Matsuura, T.; Rahbari-Sisakht, M.; Ismail, A.F. A novel thin film composite forward osmosis membrane prepared from PSf–TiO2 nanocomposite substrate for water desalination. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, S.; Rezvani, A.; Vatanpour, V.; Cortina, J.L. Improving the chlorine resistance property of polyamide TFC RO membrane by polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) coating. Desalination 2018, 443, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, H.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X.; Yao, H.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Fabrication of polysulfone membrane with sponge-like structure by using different non-woven fabrics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, Y.; Pei, D. Mesh-embedded polysulfone/sulfonated polysulfone supported thin film composite membranes for forward osmosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2918–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Alberto, M.; Gorgojo, P.; Szekely, G.; Budd, P.M. High-flux PIM-1/PVDF thin film composite membranes for 1-butanol/water pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, B.; Yao, J. Hydrophobic SiO2 nanoparticle-induced polyvinylidene fluoride crystal phase inversion to enhance permeability of thin film composite membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-L.; Wang, D.-M.; Deratani, A.; Quémener, D.; Bouyer, D.; Lai, J.-Y. Insight into the preparation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes by vapor-induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 361, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, N.I.M.; Sait, N.R.; Bilad, M.R.; Shamsuddin, N.; Jaafar, J.; Nordin, N.A.H.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K.; Mohshim, D.F. Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane Via Vapour Induced Phase Separation for Oil/Water Emulsion Filtration. Polymers 2021, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Manríquez, L.; Aburabi’e, J.; Neelakanda, P.; Peinemann, K.-V. Cross-linked PAN-based thin-film composite membranes for non-aqueous nanofiltration. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 86, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaysom, C.; Hermans, S.; Gahlaut, A.; Van Craenenbroeck, S.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Polyamide/Polyacrylonitrile (PA/PAN) thin film composite osmosis membranes: Film optimization, characterization and performance evaluation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 445, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajighahremanzadeh, P.; Abbaszadeh, M.; Mousavi, S.A.; Soltanieh, M.; Bakhshi, H. Polyamide/polyacrylonitrile thin film composites as forward osmosis membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 44130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.-E.; Kwon, S.J.; Park, S.-J.; Shin, M.G.; Park, S.-H.; Park, M.S.; Park, H.; Lee, J.-H. High performance polyacrylonitrile-supported forward osmosis membranes prepared via aromatic solvent-based interfacial polymerization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.C.; Xing, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.Y. Preparation and Properties of Thin-Film Composite Forward Osmosis Membranes Supported by Cellulose Triacetate Porous Substrate via a Nonsolvent-Thermally Induced Phase Separation Process. Membranes 2022, 12, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahebi, S.; Phuntsho, S.; Woo, Y.C.; Park, M.J.; Tijing, L.D.; Hong, S.; Shon, H.K. Effect of sulphonated polyethersulfone substrate for thin film composite forward osmosis membrane. Desalination 2016, 389, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behdarvand, F.; Valamohammadi, E.; Tofighy, M.A.; Mohammadi, T. Polyvinyl alcohol/polyethersulfone thin-film nanocomposite membranes with carbon nanomaterials incorporated in substrate for water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Huang, G.-W.; Chu, M.-Y.; Millare, J.C.; Huang, S.-H.; Lee, K.-R. Use of aqueous polyol monomer for superior dye separation performance and high chlorine resistance of thin-film composite polyester nanofiltration membranes. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 48, 102843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Song, P.; Liu, L. TIPS-co-NIPS method to prepare PES substrate with enhanced permeability for TFC-FO membrane. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 80, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebru, K.A.; Das, C. Effects of solubility parameter differences among PEG, PVP and CA on the preparation of ultrafiltration membranes: Impacts of solvents and additives on morphology, permeability and fouling performances. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzi Dizajikan, B.; Asadollahi, M.; Musavi, S.A.; Bastani, D. Preparation of poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) ultrafiltration membranes from PVC/additive/solvent and application of UF membranes as substrate for fabrication of reverse osmosis membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, K.C.; Sasaki, Y.; Jia, Y.D.; Gonzales, R.R.; Zhang, P.F.; Lin, Y.Q.; Li, Z.; Matsuyama, H. Interfacial polymerization of thin film selective membrane layers: Effect of polyketone substrates. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gonzales, R.R.; Istirokhatun, T.; Lin, Y.; Segawa, J.; Shon, H.K.; Matsuyama, H. In situ engineering of an ultrathin polyamphoteric layer on polyketone-based thin film composite forward osmosis membrane for comprehensive anti-fouling performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 272, 118922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez Solomon, M.F.; Bhole, Y.; Livingston, A.G. High flux membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN)—Interfacial polymerization with solvent activation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, S.; Xiong, S.; Yi, M.; Wang, Y. Coordination-crosslinked polyimide supported membrane for ultrafast molecular separation in multi-solvent systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvilain, M.; Klaysom, C.; Szymczyk, A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Formation mechanism of sPEEK hydrophilized PES supports for forward osmosis. Desalination 2017, 419, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam-Cervantes, M.; León-Campos, I.; Sánchez, J.; Santiago-García, J.L.; Estrella-Gómez, N.E.; Aguilar-Vega, M. Poly(hydroxyamide) as support for thin-film composite membranes for water treatment. Polym. Bull. 2018, 76, 4613–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formhals, A. Process and Apparatus for Preparing Artificial Threads. U.S. Patent 1,975,504, 2 October 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. Electrically driven jets. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1969, 313, 453–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Sun, G.; Wang, M.; Yu, J. Electro-spinning/netting: A strategy for the fabrication of three-dimensional polymer nano-fiber/nets. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 1173–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodoplu, D.; Mutlu, M. Effects of Electrospinning Setup and Process Parameters on Nanofiber Morphology Intended for the Modification of Quartz Crystal Microbalance Surfaces. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, M.; Zohoori, S. Review for application of electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers technology in textile industry. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2016, 6, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Lee, J.S. Electrospinning-based carbon nanofibers for energy and sensor applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Lu, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Y. Application of electrospinning in antibacterial field. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, R.; Sofi, H.S.; Malik, A.; Beigh, M.A.; Hamid, R.; Sheikh, F.A. Recent Trends in the Fabrication of Starch Nanofibers: Electrospinning and Non-electrospinning Routes and Their Applications in Biotechnology. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 187, 47–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, S.; Johnson, B.; Smith, A.L. Optimizing electrospinning parameters for piezoelectric PVDF nanofiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, M.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Kook, S.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, I.S. Breakthroughs in the fabrication of electrospun-nanofiber-supported thin film composite/nanocomposite membranes for the forward osmosis process: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 50, 1727–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Yang, J. Large-scale fabrication of two-dimensional spider-web-like gelatin nano-nets via electro-netting. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 86, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Qian, J.; Sun, G. Controllable fabrication of soap-bubble-like structured polyacrylic acid nano-nets via electro-netting. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, W.; Huang, C. Electrospun nanofiber membranes for wastewater treatment applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, D.D. Nano Gives the Answer: Breaking the Bottleneck of Internal Concentration Polarization with a Nanofiber Composite Forward Osmosis Membrane for a High Water Production Rate. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3256–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhang, X.; Ding, C.; Xiong, S.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y. Improved performance of thin-film composite membrane supported by aligned nanofibers substrate with slit-shape pores for forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.-N.; McCutcheon, J.R. Hydrophilic nanofibers as new supports for thin film composite membranes for engineered osmosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, N.-N.; Lind, M.L.; Hoek, E.M.; McCutcheon, J.R. Electrospun nanofiber supported thin film composite membranes for engineered osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 385, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Niu, F.; Deng, P.; Li, N.; Lv, Y.; Huang, M. Electrospun nanofiber supports with bio-inspired modification enabled high-performance forward osmosis composite membranes. Compos. Commun. 2020, 22, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, I.; Chaoui, I.; Eddouibi, J.; Vaudreuil, S.; Bounahmidi, T. Synthesis of poly (vinylidene fluoride)/polyacrylonitrile electrospun substrate-based thin-film composite membranes for desalination by forward osmosis process. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2022, 181, 109132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Chong, J.Y.; Goh, K.S.; Tian, M.; Chew, J.W.; Wang, R. Electrospun polyimide-based thin-film composite membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Qiu, C.; Liao, Y.; Chou, S.; Wang, R. Preparation of polyamide thin film composite forward osmosis membranes using electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofibers as substrates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-R.; Zhao, H.-L.; Wu, S.-B. Polyamide nanofilm composite membranes (NCMs) supported by chitosan-coated polyvinyldenefluoride (PVDF) nanofibrous mats and their separation properties. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 23522–23535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, M.; Park, M.J.; Lim, S.; Phuntsho, S.; Matsuyama, H.; Shon, H.K. Novel CA/PVDF nanofiber supports strategically designed via coaxial electrospinning for high performance thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes for desalination. Desalination 2018, 445, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, H.; Moslehi, M. A new thin film composite nanofiltration membrane based on PET nanofiber support and polyamide top layer: Preparation and characterization. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.-D.; Chen, B.-Z.; Wang, J.; Jia, T.-Z.; Cao, X.-L. Electrospun nanofiber substrates that enhance polar solvent separation from organic compounds in thin-film composites. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. Energy Sustain. 2018, 6, 15047–15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Bakhtiari, O. Effective treatment of dye wastewater via positively charged TETA-MWCNT/PES hybrid nanofiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, Y.; Liu, M.; Song, X.; Duan, J. Porous nano-hydroxyapatites doped into substrate for thin film composite forward osmosis membrane to show high performance. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennessey, S.F.; Farris, R.J. Fabrication of aligned and molecularly oriented electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers and the mechanical behavior of their twisted yarns. Polymer 2004, 45, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, C.S.; Kim, J.W.; Hyun, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Hattori, M.; Rah, D.K.; Park, Y.H. Electrospun three-dimensional silk fibroin nanofibrous scaffold. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 3922–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Jung, Y.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, D.R.; Dharmaraj, N.; Choi, K.E. Effect of collector temperature on the porous structure of electrospun fibers. Macromol. Res. 2006, 14, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Jankovi, B.; Baumgartner, S.A.; Kocbek, P. The impact of relative humidity during electrospinning on the morphology and mechanical properties of nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casper, C.L.; Stephens, J.S.; Tassi, N.G.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Controlling Surface Morphology of Electrospun Polystyrene Fibers:Effect of Humidity and Molecular Weight in the Electrospinning Process. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Bui, N.-N.; Manickam, S.S.; McCutcheon, J.R. Controlling electrospun nanofiber morphology and mechanical properties using humidity. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, I.; Chaoui, I.; Vaudreuil, S.; Bounahmidi, T. Selection of substrate manufacturing techniques of polyamine-based thin-film composite membranes for forward osmosis process. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 1912–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-Y.; Xing, X.-Y.; Yu, Y.; Gu, L.; Xu, Z.-K. Novel thin film composite membranes supported by cellulose triacetate porous substrates for high-performance forward osmosis. Polymer 2018, 153, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhom, M.; Albayati, N.; Salih, S.; Al-Furaiji, M.; Bayati, M.; Deng, B. Role of Cellulose Micro and Nano Crystals in Thin Film and Support Layer of Nanocomposite Membranes for Brackish Water Desalination. Membranes 2019, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadhom, M.; Deng, B. Synthesis of high-performance thin film composite (TFC) membranes by controlling the preparation conditions: Technical notes. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 30, 100542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kahrizi, M.; Lu, P.; Wei, Y.Y.; Yang, H.; Yu, Y.F.; Wang, L.H.; Li, Y.S.; Zhao, S.F. Enhancing water permeability and antifouling performance of thin–film composite membrane by tailoring the support layer. Desalination 2021, 516, 115193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.F.; Yang, T.; Gai, W.; Lee, Y.D.; Chung, T.-S. Thin-film composite hollow fiber membrane with inorganic salt additives for high mechanical strength and high power density for pressure-retarded osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jang, J.H.; Chae, H.-R.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, C.-H.; Park, P.-K.; Won, Y.-J.; Kim, I.-C. A facile route to enhance the water flux of a thin-film composite reverse osmosis membrane: Incorporating thickness-controlled graphene oxide into a highly porous support layer. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 22053–22060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Huang, P.; Zhao, F.; Dong, H.; Niu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J. Enhancing the long-term separation stability of TFC membrane by the covalent bond between synthetic amino-substituted polyethersulfone substrate and polyamide layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 637, 119637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar Heidari, A.; Mahdavi, H.; Khodaei Kahriz, P. TFC solvent-resistant nanofiltration membrane prepared via a gyroid-like PE support coated with polydopamine/Tannic acid-Fe(III). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 106, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, M.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, M.; Niu, Q.J. Precise assembly of a zeolite imidazolate framework on polypropylene support for the fabrication of thin film nanocomposite reverse osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Khan, A.A. Synthesis and characterization of proton conducting polymer membranes for fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 225, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.; Zou, H.; Lu, D.; Gong, C.; Liu, Y. Polyethersulfone sulfonated by chlorosulfonic acid and its membrane characteristics. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadzadeh, D.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F. Synthesis of thin film nanocomposite forward osmosis membrane with enhancement in water flux without sacrificing salt rejection. Desalination 2013, 330, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Liang, S.; Zhou, T.; Mei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Umar, A.; Wang, Q. Layered double hydroxide/graphene oxide hybrid incorporated polysulfone substrate for thin-film nanocomposite forward osmosis membranes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56599–56609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-F.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Zhong, L.-B.; Yuan, Z.-H. Self-sustained hydrophilic nanofiber thin film composite forward osmosis membranes: Preparation, characterization and application for simulated antibiotic wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, R.; Kaur, S.; Ma, Z.; Chan, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Matsuura, T. Electrospun nanofibrous filtration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, C.; Yuan, X. Effect of hot-press on electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 48, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Górecki, R.P.; Stamate, E.; Norrman, K.; Aili, D.; Zuo, M.; Guo, W.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Zhang, W. Preparation of super-hydrophilic polyphenylsulfone nanofiber membranes for water treatment. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallem, P.; Gaur, R.; Pandey, R.P.; Hasan, S.W.; Choi, H.; Banat, F. Thin film composite forward osmosis membranes based on thermally treated PAN hydrophilized PVDF electrospun nanofiber substrates for improved performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Gonzales, R.R.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K. Hydrophilic polyvinyl alcohol coating on hydrophobic electrospun nanofiber membrane for high performance thin film composite forward osmosis membrane. Desalination 2018, 426, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Wang, J.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Polydopamine nanoparticles modified nanofiber supported thin film composite membrane with enhanced adhesion strength for forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Sun, P.; Henry, L.; Sun, B. Mechanisms of structure and performance controlled thin film composite membrane formation via interfacial polymerization process. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 251, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, B.; Thundat, T.; Fleck, B.A.; Sadrzadeh, M. A Novel Approach Toward Fabrication of High Performance Thin Film Composite Polyamide Membranes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhat Bojnourd, F.; Pakizeh, M. The effect of preparation parameters on performance of polyvinyl alcohol thin-film composite membrane: Experimental study, modeling, and optimization. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Deng, B. A review: The effect of the microporous support during interfacial polymerization on the morphology and performances of a thin film composite membrane for liquid purification. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 35417–35428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Ren, L.-F.; Ying, D.; Jia, J.; Shao, J. Electrospray interface-less polymerization to fabricate high-performance thin film composite polyamide membranes with controllable skin layer growth. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 632, 119369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viatcheslav, F. Kinetics of Film Formation by Interfacial Polycondensation. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misdan, N.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T.; Rana, D. Study on the thin film composite poly(piperazine-amide) nanofiltration membrane: Impacts of physicochemical properties of substrate on interfacial polymerization formation. Desalination 2014, 344, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Meng, L.; Li, B.; Niu, F.; Lv, Y.; Deng, Q.; Li, J. Fabrication of innovative forward osmosis membranes via multilayered interfacial polymerization on electrospun nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 136, 47247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, A.; Jahanshahi, M.; Mortazavian, N.; Madaeni, S.S.; Mansourpanah, Y. Preparation and characterization of asymmetric polyethersulfone and thin-film composite polyamide nanofiltration membranes for water softening. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, P.; Ding, S.; Wang, X. High permeability composite nanofiltration membrane assisted by introducing TpPa covalent organic frameworks interlayer with nanorods for desalination and NaCl/dye separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 270, 118802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, V.; Remigy, J.-C.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. UV-cured polysulfone-based membranes: Effect of co-solvent addition and evaporation process on membrane morphology and SRNF performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiver, M.D.; Robertson, G.P.; Foley, S. Chemical Modification of Polysulfones II: An Efficient Method for Introducing Primary Amine Groups onto the Aromatic Chain. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 7612–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Gao, S.; Tian, J.; Sun, Y.; Cui, F.; Tang, C.Y. Calcium-Carboxyl Intrabridging during Interfacial Polymerization: A Novel Strategy to Improve Antifouling Performance of Thin Film Composite Membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4371–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Fabrication of high-performance reverse osmosis membranes via dual-layer slot coating with tailoring interfacial adhesion. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Ge, H.; Wang, Y.; Bian, S.; Tong, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhu, G. Novel thin-film composite membrane with polydopamine-modified polyethylene support and tannic acid-Fe3+ interlayer for forward osmosis applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 642, 119976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.M.; Yoon, J.; Kelly, J.Y.; Howarter, J.A.; Stafford, C.M. Molecular layer-by-layer deposition of highly crosslinked polyamide films. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2012, 50, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizak, D.; Abbaszadeh, M.; Kundu, S. Desalination membranes by deposition of polyamide on polyvinylidene fluoride supports using the automated layer-by-layer technique. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 57, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.E.; Lee, S.; Stafford, C.M.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, W.; Kim, B.Y.; Baek, K.Y.; Chan, E.P.; Chung, J.Y.; Bang, J. Molecular layer-by-layer assembled thin-film composite membranes for water desalination. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4778–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Gu, J.-E.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, S.; Bang, J.; Baek, K.-Y.; Park, B.; Lee, J.S.; Chan, E.P.; Lee, J.-H. Tailor-made polyamide membranes for water desalination. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freger, V. Nanoscale Heterogeneity of Polyamide Membranes Formed by Interfacial Polymerization. Langmuir 2003, 19, 4791–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Huang, Y.; Yu, S.; Lawless, D.; Feng, X. Thin film composite nanofiltration membranes assembled layer-by-layer via interfacial polymerization from polyethylenimine and trimesoyl chloride. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 472, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ren, L.-F.; Ying, D.; Jia, J.; Shao, J. Sustainable electrospray polymerization fabrication of thin-film composite polyamide nanofiltration membranes for heavy metal removal. Desalination 2022, 539, 115952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-H.; Xie, F.; Ding, H.-Z.; Mo, J.-W.; Jin, X.-G.; Ma, X.-H.; Xu, Z.-L. Evading the permeance-selectivity trade-off dilemma in electrospray-assisted interfacial polymerization polyamide thin-film composite membrane through electrospinning nanofibers interlayer. Desalination 2023, 558, 116625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.-w.; Guo, H.; Yao, Z.; Ma, X.-h.; Song, X.; Feng, S.-P.; Tang, C.Y. Tannic acid/Fe3+ nanoscaffold for interfacial polymerization: Toward enhanced nanofiltration performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9341–9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.R.; Steffes, J.; Huey, B.D.; Mccutcheon, J.R. 3D printed polyamide membranes for desalination. Science 2018, 361, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seah, M.Q.; Khoo, Y.S.; Lau, W.J.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F. New Concept of Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane Fabrication Using a Mist-Based Interfacial Polymerization Technique. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 9167–9178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Chu, B.; Hsiao, B.S. Thin-film nanofibrous composite reverse osmosis membranes for desalination. Desalination 2017, 420, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mayyahi, A. Important approaches to enhance reverse osmosis (RO) thin film composite (TFC) membranes performance. Membranes 2018, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Lai, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Liang, H. Toward enhancing desalination and heavy metal removal of TFC nanofiltration membranes: A cost-effective interface temperature-regulated interfacial polymerization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 57998–58010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.S.; Lau, W.J.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Yusof, N.; Tan, Y.H. Graphene oxide incorporated thin film nanocomposite nanofiltration membrane for enhanced salt removal performance. Desalination 2016, 387, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.G.; Seo, J.Y.; Park, H.; Park, Y.I.; Lee, J.H. Overcoming the permeability-selectivity trade-off of desalination membranes via controlled solvent activation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 620, 118870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werber, J.R.; Deshmukh, A.; Elimelech, M. The critical need for increased selectivity, not increased water permeability, for desalination membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Abed, M.M.; Li, K. Progress in the production and modification of PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Park, M.J.; Phuntsho, S.; Tijing, L.D.; Nisola, G.M.; Shim, W.-G.; Chung, W.-J.; Shon, H.K. Dual-layered nanocomposite substrate membrane based on polysulfone/graphene oxide for mitigating internal concentration polarization in forward osmosis. Polymer 2017, 110, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadpour, S.; Tavakol, I.; Shabani, Z.; Mohammadi, T.; Tofighy, M.A.; Sahebi, S. Synthesis and characterization of novel thin film composite forward osmosis membrane using charcoal-based carbon nanomaterials for desalination application. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendoy, A.P.; Zeweldi, H.G.; Park, M.J.; Shon, H.K.; Kim, H.; Chung, W.-J.; Nisola, G.M. Silicene nanosheets as support fillers for thin film composite forward osmosis membranes. Desalination 2022, 536, 115817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Wei, J.; Qi, S.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Tang, C.Y. Nanocomposite substrates for controlling internal concentration polarization in forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 441, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergast, M.T.M.; Nygaard, J.M.; Ghosh, A.K.; Hoek, E.M. Using nanocomposite materials technology to understand and control reverse osmosis membrane compaction. Desalination 2010, 261, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Liu, C. Improving the separation performance of the forward osmosis membrane based on the etched microstructure of the supporting layer. Desalination 2017, 408, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Choi, H.-g.; Liu, L.; Celik, E.; Park, H.; Choi, H. Efficacy of carbon nanotube positioning in the polyethersulfone support layer on the performance of thin-film composite membrane for desalination. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Guo, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, Y.; Long, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Enhanced water permeance of a polyamide thin-film composite nanofiltration membrane with a metal-organic framework interlayer. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 625, 119154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Yuan, J.; Wu, H.; Su, Y.; Yang, H.; You, X.; Zhang, R.; He, X.; Khan, N.A.; Kasher, R. Ultrathin nanofiltration membrane with polydopamine-covalent organic framework interlayer for enhanced permeability and structural stability. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 576, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, N.; Dong, W.; Lan, H.; Wang, M.; Niu, Q.J. Fabrication of advanced nanofiltration membranes with nanostrand-hybrid morphology mediated by ultrafast Noria-polyethyleneimine co-deposition. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 21207–21215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Tian, L.; Zhai, Z.; Shen, Y.; Niu, Q.J. Thin-film composite membranes with aqueous template-induced surface nanostructures for enhanced nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 589, 117244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.; Chen, Y.; Niu, Q.J. Fabrication of thin-film composite polyamide nanofiltration membrane based on polyphenol intermediate layer with enhanced desalination performance. Desalination 2020, 488, 114525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Tang, C.Y. Immobilization of sulfonated polysulfone via 2D LDH nanosheets during phase-inversion: A novel strategy towards greener membrane synthesis and enhanced desalination performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ding, M.; Xu, H.; Yang, W.; Zhang, K.; Tian, H.; Wang, H.; Xie, Z. Scalable Ti3C2Tx MXene interlayered forward osmosis membranes for enhanced water purification and organic solvent recovery. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9125–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Furaiji, M.; Kadhom, M.; Kalash, K.; Waisi, B.; Albayati, N. Preparation of thin-film composite membranes supported with electrospun nanofibers for desalination by forward osmosis. Drink. Water Eng. Sci. 2020, 13, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Hoek, E.M.V. Impacts of support membrane structure and chemistry on polyamide–polysulfone interfacial composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 336, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, P.F.; Li, X.; Gan, B.; Wang, L.; Song, X.; Park, H.D.; Tang, C.Y. A Critical Review on Thin-Film Nanocomposite Membranes with Interlayered Structure: Mechanisms, Recent Developments, and Environmental Applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15563–15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ke, X.-X.; Zhong, L.-B.; Wu, R.-X.; Yuan, Z.-H.; Fan, J.-J.; Zheng, Y.-M. Super-hydrophilic nanofiber substrate supported forward osmosis membrane with less polyamide layer defects by polydopamine-graphene oxide modification for high salinity desulfurization wastewater desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 659, 120767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Mei, X.; Han, J.; Yao, L.; Chen, S.; You, X.; Liao, Y. Impacts of hydrophobic, hydrophilic, superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic nanofibrous substrates on the thin film composite forward osmosis membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsinger, D.M.; Swaminathan, J.; Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Arafat, H.A.; Lienhard, V.; John, H. Scaling and fouling in membrane distillation for desalination applications: A review. Desalination 2015, 356, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agenson, K.O.; Urase, T. Change in membrane performance due to organic fouling in nanofiltration (NF)/reverse osmosis (RO) applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 55, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-R.; Wang, J.-N.; Li, C.-J. Strategies for improving the performance of the polyamide thin film composite (PA-TFC) reverse osmosis (RO) membranes: Surface modifications and nanoparticles incorporations. Desalination 2013, 328, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Cao, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L. Dependable Performance of Thin Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane Tailored by Capsaicin-Derived Self-Polymer. Polymers 2022, 14, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Arena, J.T.; Mccutcheon, J.R. Surface modified PVDF nanofiber supported thin film composite membranes for forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, Y. Efficient surface modification of thin-film composite membranes with self-catalyzed tris(2-aminoethyl)amine for forward osmosis separation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 178, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akther, N.; Ali, S.M.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H. Surface modification of thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes with polyvinyl alcohol–graphene oxide composite hydrogels for antifouling properties. Desalination 2020, 491, 114591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Yang, J.; Ma, G.; Wu, G.; Zong, X.; Lei, Z.; Shi, J.; Li, C. Visible-light-driven hydrogen production with extremely high quantum efficiency on Pt–PdS/CdS photocatalyst. J. Catal. 2009, 266, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiong, S.; Liu, C.-X.; Shen, L.; Ding, C.; Guan, C.-Y.; Wang, Y. Confining migration of amine monomer during interfacial polymerization for constructing thin-film composite forward osmosis membrane with low fouling propensity. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 207, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.-Y.; Zhang, P.; Gong, J.-L.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G.-M.; Song, B.; Cao, W.-C.; Li, J.; Ye, J. Construction of highly water-stable metal-organic framework UiO-66 thin-film composite membrane for dyes and antibiotics separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Hui, H.; You, X.; Pei, Z.; Tian, M.; Wu, B. Design of nanofibre interlayer supported forward osmosis composite membranes and its evaluation in fouling study with cleaning. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

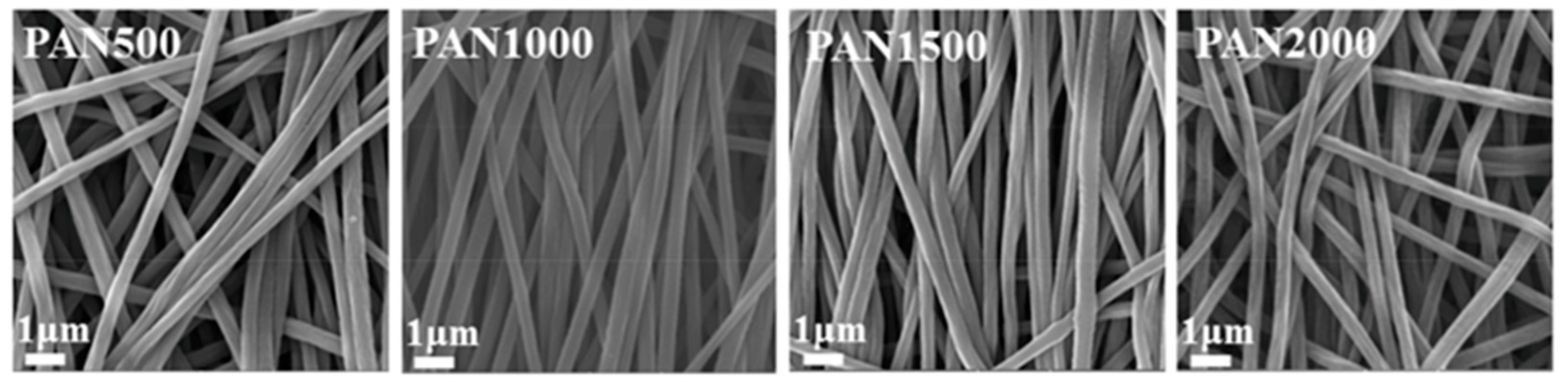
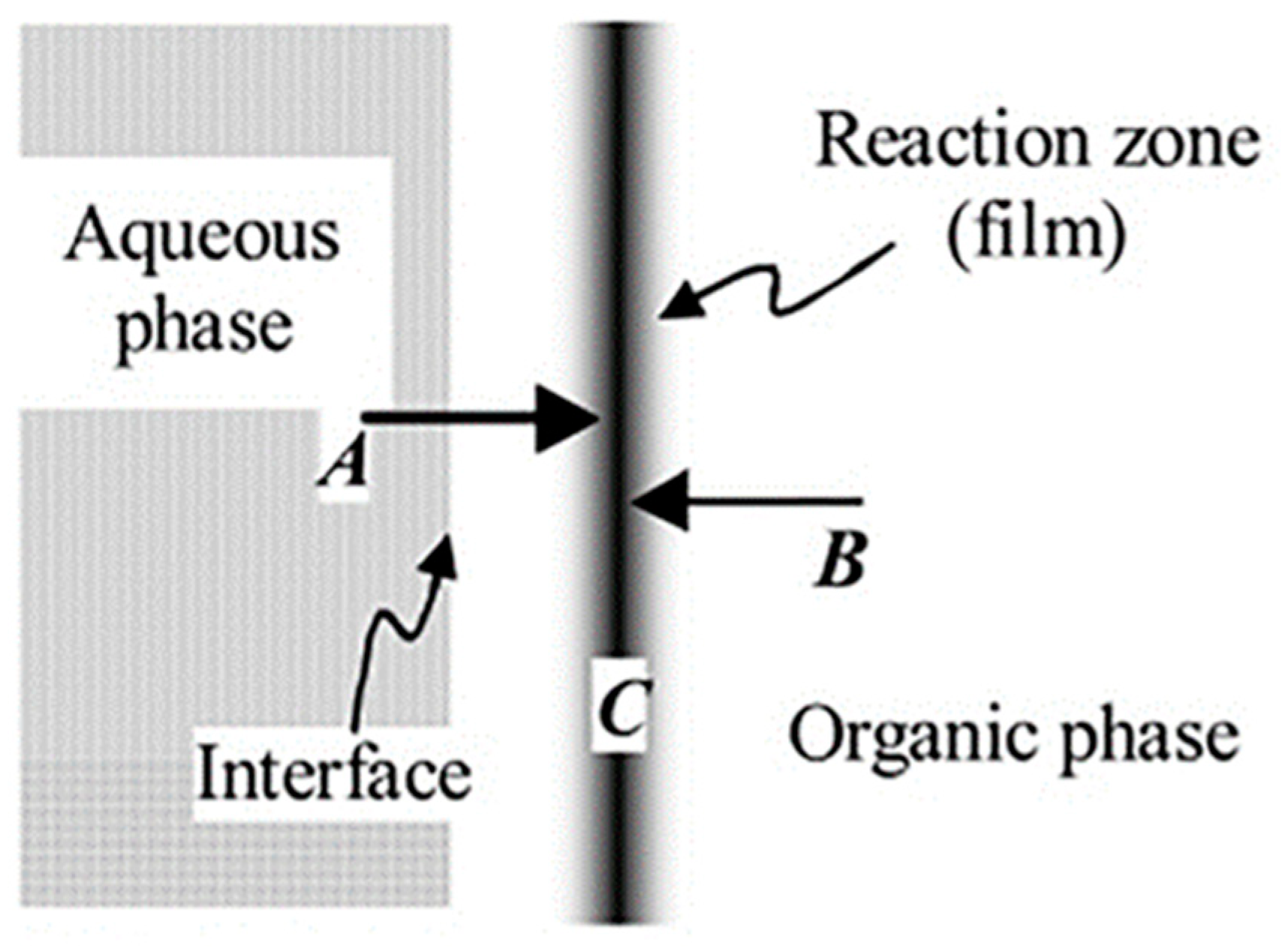
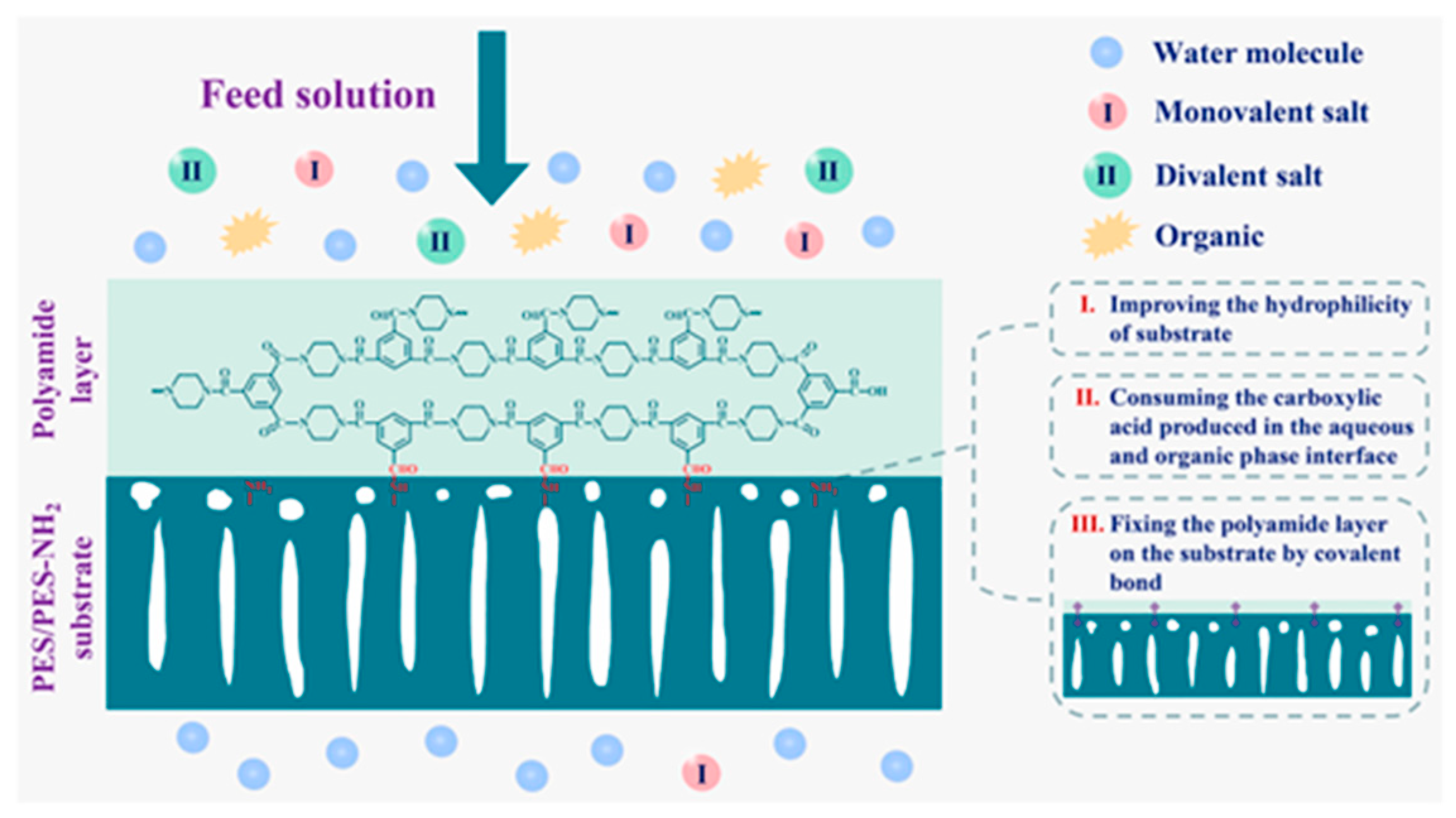
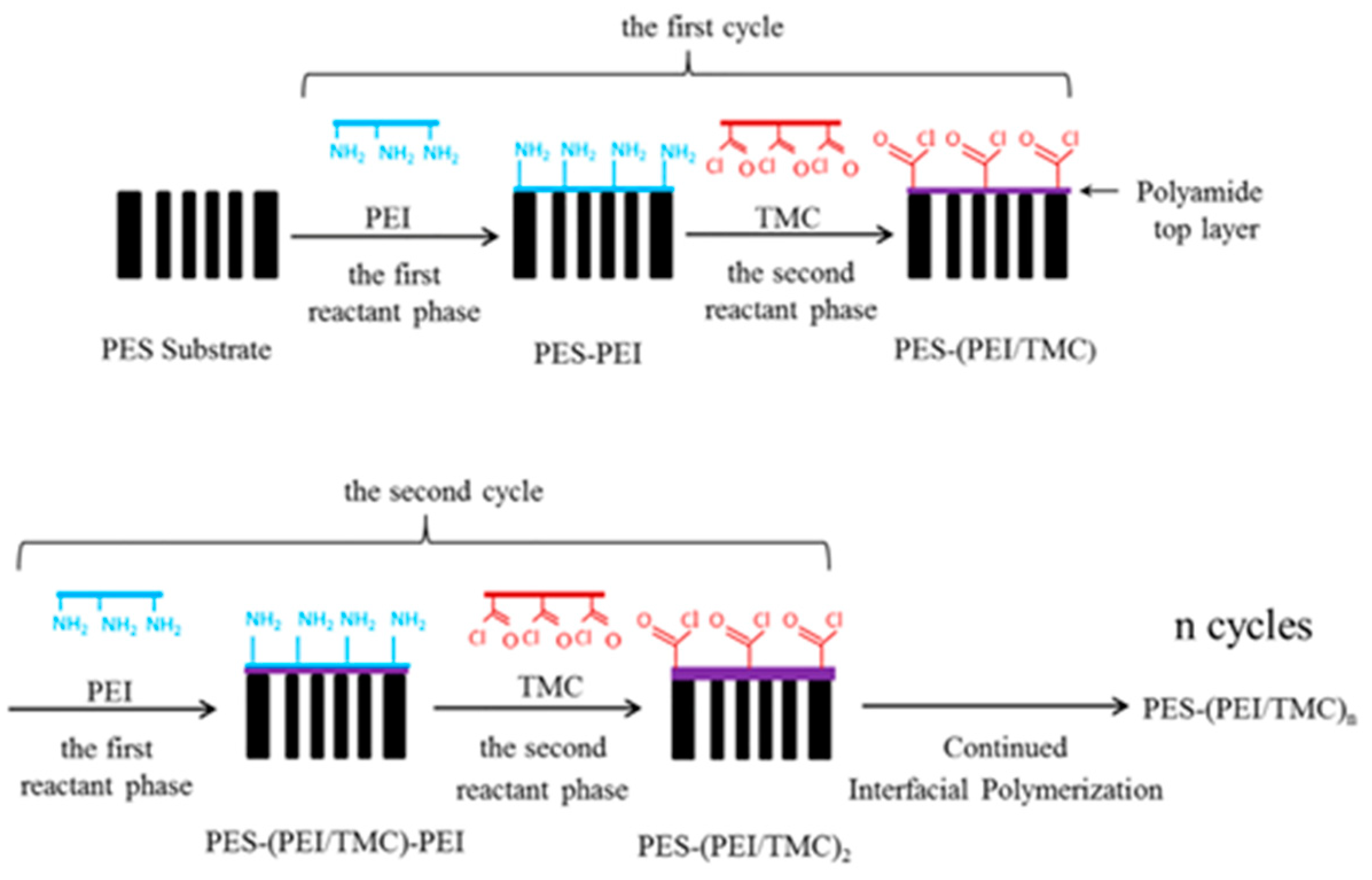

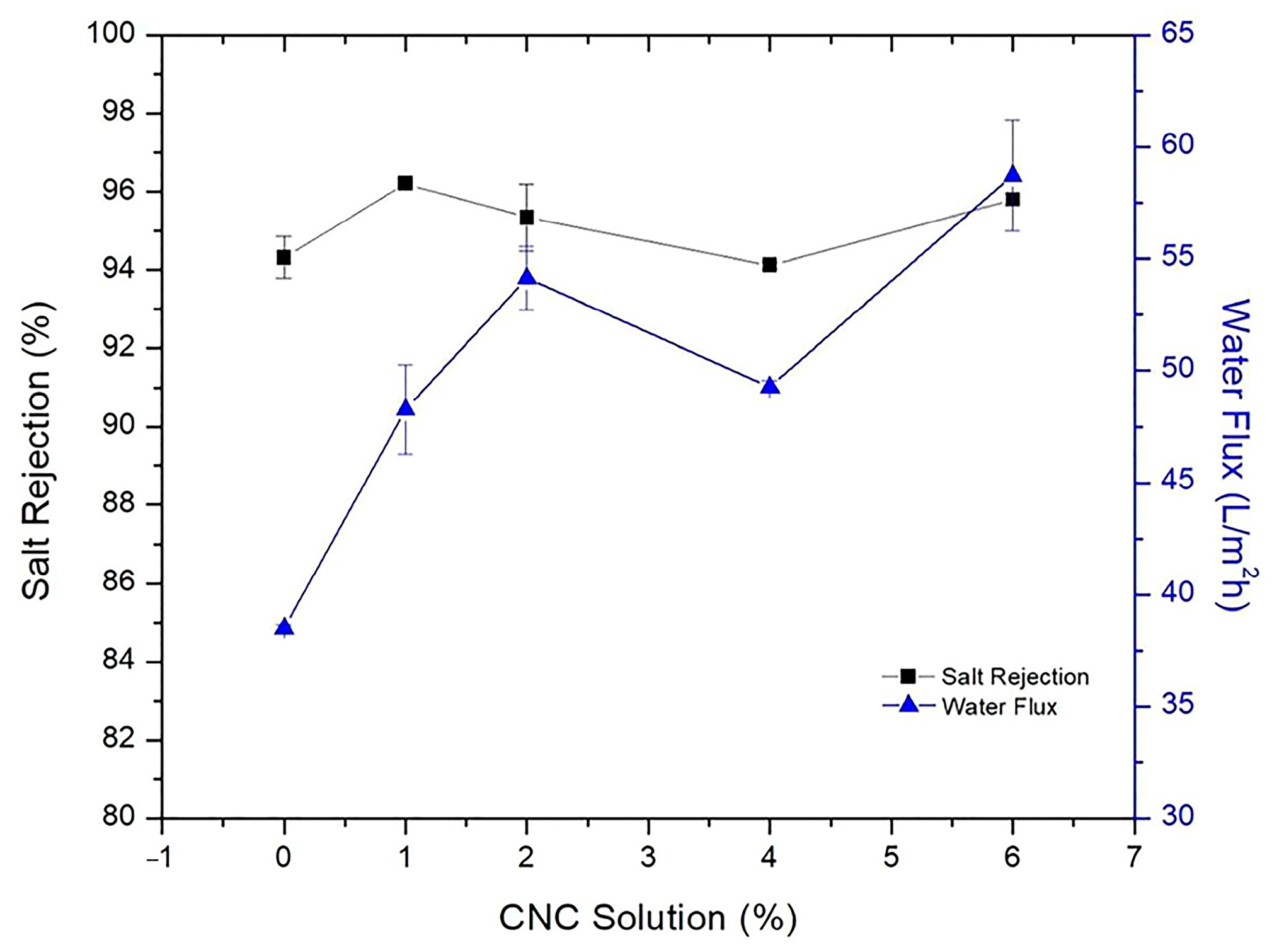


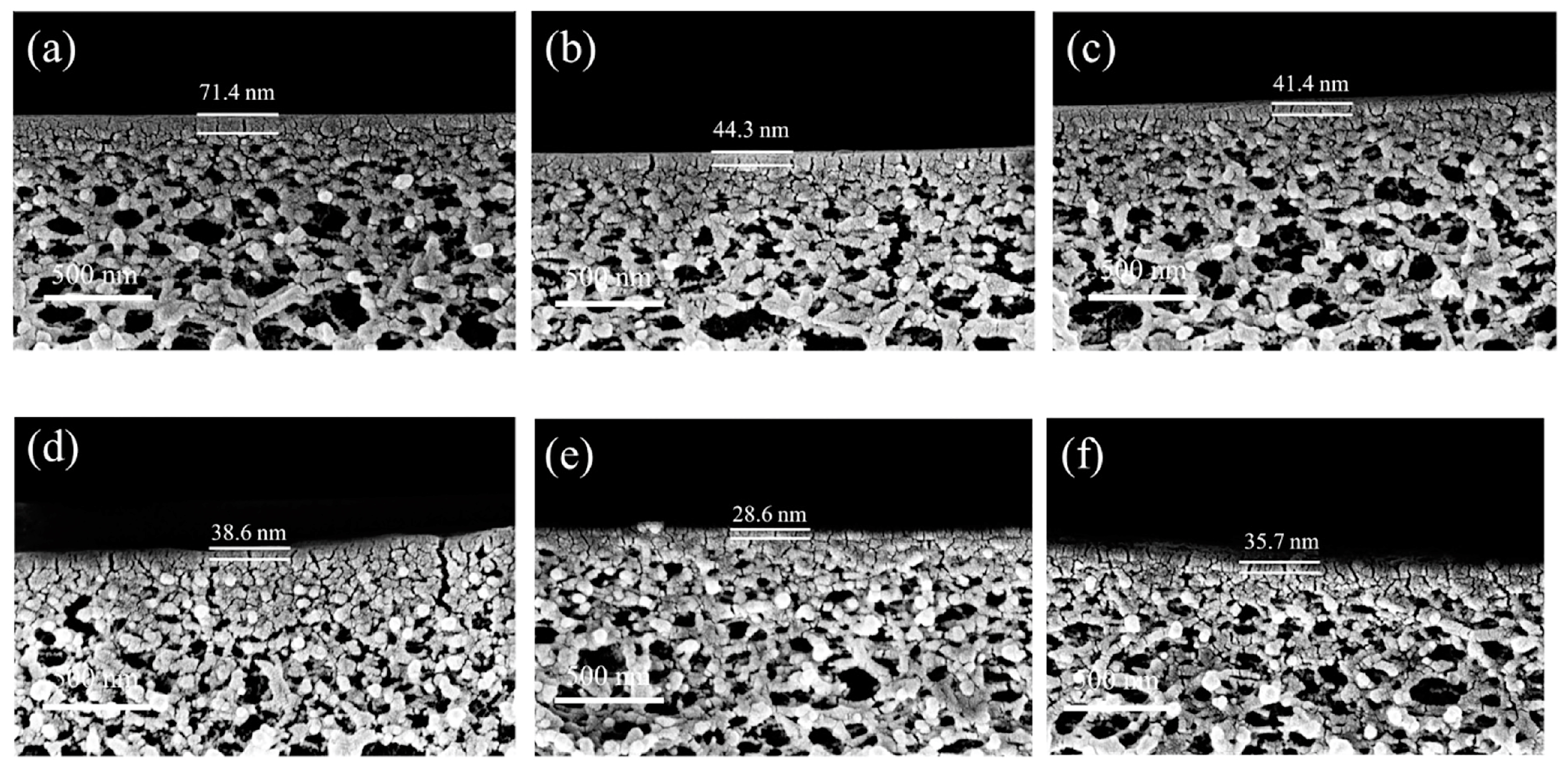

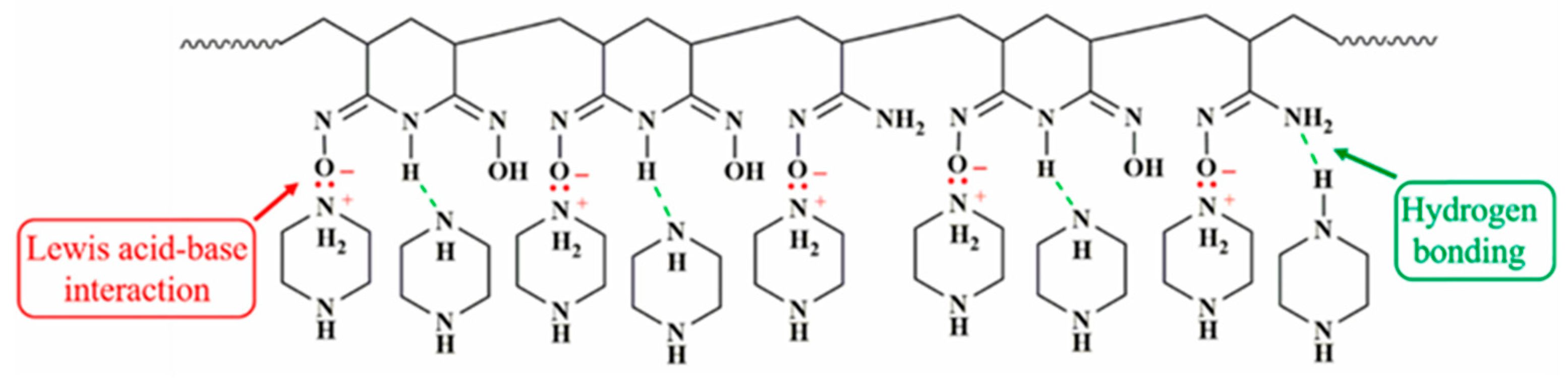
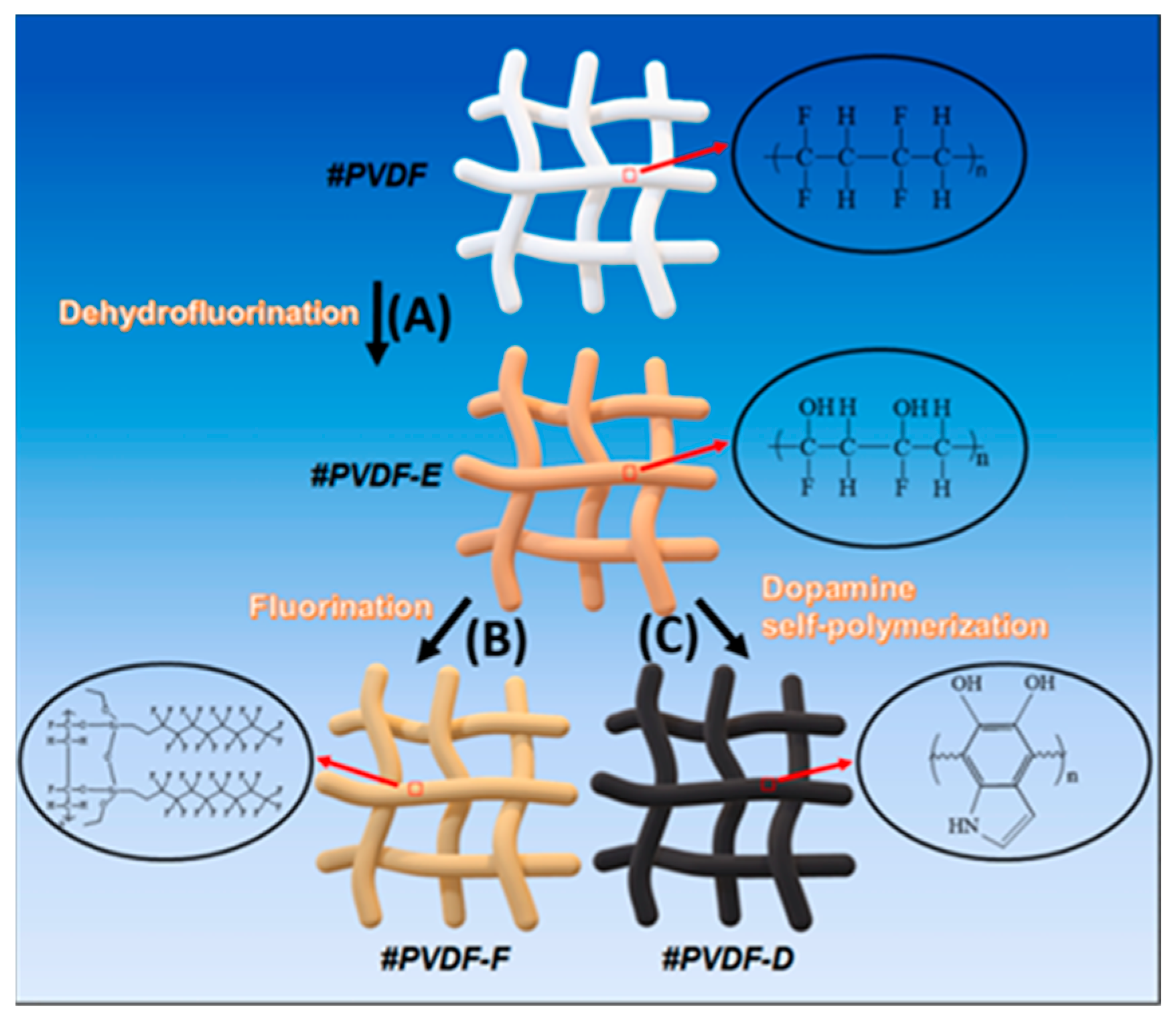
| Substrate | Method | Solvent | Polymer Additives | Coagulation Bath | Coagulation Temperature (°C) | Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSf | NIPS | N-methyl-2-pyrroli-done (NMP) | polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) | water | 23 | 2011 | [58] |
| PSf | NIPS | NMP | PVP/lithium chloride (LiCl) | water | 23 | 2011 | [59] |
| PSf | NIPS | NMP | diethylene glycol (DEG) | water | 25 | 2012 | [60] |
| PSf | NIPS | NMP/dimethylfor-mamide (DMF) | - | water | 24.5 | 2021 | [61] |
| PSf | NIPS | NMP | - | water | 22 | 2014 | [62] |
| PSf | NIPS | NMP | polyethylene glycol (PEG)-400 | water | 25 | 2019 | [63] |
| PSf | NIPS | NMP | PVP/titanium dioxide (TiO2) | water | 25 | 2014 | [64] |
| PSf | NIPS | DMF | - | water | 25 | 2018 | [65] |
| PSf | NIPS | DMF | PVP | water | 15, 20, 25, 30 | 2019 | [36] |
| PSf | NIPS | DMF | - | 0.1% (w/v) sodium lauryl sulfate in H2O/DMF (H2O:DMF = 96:4 v/v) | 24–25 | 2014 | [29] |
| PSf | NIPS | N,N-dimethylaceta-mide (DMAc) | PEG/PVP | water | 60 | 2022 | [66] |
| PSf/sPSf | NIPS | NMP | - | water | 25 | 2018 | [67] |
| PVDF | NIPS | NMP | perfluorosulfonic acid | water | 25 | 2017 | [51] |
| PVDF | NIPS | DMAc | - | water | 25 | 2017, 2016 | [68] |
| PVDF | NIPS | DMAc | silicon dioxide (SiO2)/PVP | water | 25 | 2019 | [69] |
| PVDF | VIPS | NMP/DMAc/DMF | - | water | 25 | 2010 | [70] |
| PVDF | VIPS | DMAc | PVP/LiCl | water | 25 | 2021 | [71] |
| PVDF | TIPS | Triethyl phosphate (TEP) | PEG-400 | water | 10 | 2017 | [42] |
| PAN | NIPS | DMF | - | water | 25 | 2015 | [72] |
| PAN | NIPS | NMP | - | water | 20 | 2013 | [73] |
| PAN | NIPS | NMP/DMF | - | water | 25 | 2016 | [74] |
| PAN | NIPS | NMP | - | water | 25 | 2019 | [75] |
| cellulose triacetate (CTA) | NIPS | dimethylsulfone (DMSO2) | PEG-400 | water | 95 | 2022 | [76] |
| CTA | TIPS | DMSO2 | PEG-400 | glycerin | 50 | 2022 | [76] |
| CTA | NTIPS | DMSO2 | PEG-400 | water | 50 | 2022 | [76] |
| PES/Sulphonatedpolyethersulfone(SPES) | NIPS | NMP | - | water | 25 | 2016 | [77] |
| PES | NIPS | DMAc | - | water | 25 | 2021 | [78] |
| PES | NIPS | NMP | PEG-2000 | water | 25 | 2022 | [79] |
| PES | NIPS | NMP | PVP | water | 25 | 2021 | [49] |
| PES | NIPS | NMP/DMF | - | water | 24.5 | 2021 | [61] |
| PES | NTPS | DMAc | DEG/PEG | water | 25 | 2017 | [80] |
| CA | NIPS | acetone (Ac)/DMAc | PVP/PEG | water | 25 | 2017 | [81] |
| polyvinyl- chloride (PVC) | NIPS | DMAc | PEG-400/LiCl | water | 25 | 2018 | [33] |
| PVC | NIPS | NMP | PVP | water | 25 | 2018 | [82] |
| polyketone (PK) | NIPS | resorcinol/water | - | methanol/water | 25 | 2021, 2021 | [83,84] |
| polyetherimide (PEI) | NIPS | NMP/DMF | - | water | 24.5 | 2021 | [61] |
| PI | NIPS | dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) | - | water | 21 | 2013,2012 | [10,85] |
| PI | NIPS | DMF | - | water | 21 | 2013 | [10] |
| PI | NIPS | NMP | - | water or 0.1 M NaOH solution | 25 | 2022 | [86] |
| PI | NIPS | DMSO/DMF | - | water | 22 | 2014 | [62] |
| PEEK | NIPS | methane sulfonic acid (MSA) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) | - | water | 21 | 2013 | [10] |
| PES/sulfonated polyetheretherketone (sPEEK) | NIPS | NMP | - | water | 25 | 2017 | [87] |
| PC | NIPS | NMP | PVP | water | 25 | 2021 | [49] |
| poly(hydroxyamide) (PHA) | NIPS | NMP | - | water | 30 | 2018 | [88] |
| Substrate | Solvent | Voltage (kV) | Distance (cm) | Flow Rate (mL/h) | Temperature (°C) | Humidity (%) | Fiber Diameter (nm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES | NMP/DMF | 25 | 15 | 0.6 | – | – | – | [102] |
| PAN | DMF | 20 | 15 | 0.8 | – | – | 475 ± 92 | [103] |
| PAN/CA | DMF | 28.5 | 16 | 1.0 | 25 | 50 | – | [104] |
| PSf | DMF/NMP | 27.5 | 16 | 1.2, 0.9, 0.6 | 25 | 10 | 250 | [105] |
| PSf | DMF/NMP | 25 | 12 | 1.0 | 25 | 25–30 | – | [106] |
| PVDF/PAN | DMAc | 18–21 | 16 | 0.8–1.0 | 25 | – | 745 ± 281 | [107] |
| polyimide (PI) | DMF/NMP | 60 | 18 | – | 21–23 | 30 ± 2 | – | [108] |
| PVDF | DMF | 27 | 12 | 0.18 | 25 | 70 | 280 ± 80 | [109] |
| PVDF | DMF | 18 | 25 | 1.5 | 25 | – | 302 | [110] |
| PVDF | DMAc/acetone | 21–24 | 18 | 2.0 | 22–25 | 40–60 | 1260.6 ± 308.9 | [111] |
| CA | DMAc/acetone | 21–24 | 18 | 2.0 | 22–25 | 40–60 | 259.2 ± 114.6 | [111] |
| CA/PVDF | DMAc/acetone | 21–24 | 18 | 2.0 | 22–25 | 40–60 | 788.6 ± 326.3 | [111] |
| polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | trifluoroacetic acid (TFA)/dichloromethane (DCM) | 25 | 12 | 1.2 | 25 | – | 105 ± 10 | [112] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Zhou, R.; Peng, X.; Li, N.; Dai, Z. Development of Support Layers and Their Impact on the Performance of Thin Film Composite Membranes (TFC) for Water Treatment. Polymers 2023, 15, 3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153290
Zhang Q, Zhou R, Peng X, Li N, Dai Z. Development of Support Layers and Their Impact on the Performance of Thin Film Composite Membranes (TFC) for Water Treatment. Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153290
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qing, Rui Zhou, Xue Peng, Nan Li, and Zhao Dai. 2023. "Development of Support Layers and Their Impact on the Performance of Thin Film Composite Membranes (TFC) for Water Treatment" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153290
APA StyleZhang, Q., Zhou, R., Peng, X., Li, N., & Dai, Z. (2023). Development of Support Layers and Their Impact on the Performance of Thin Film Composite Membranes (TFC) for Water Treatment. Polymers, 15(15), 3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153290








