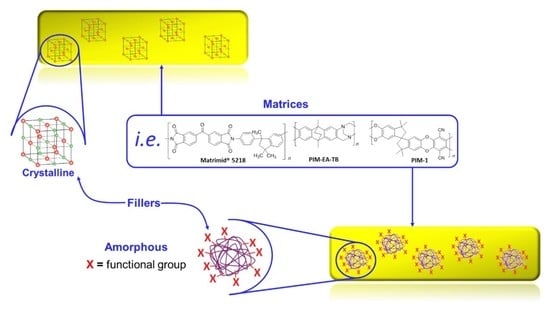
The Difference in Performance and Compatibility between Crystalline and Amorphous Fillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation (MMMs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mixed Matrix Membranes
2.1. Description of the Transport in MMMs
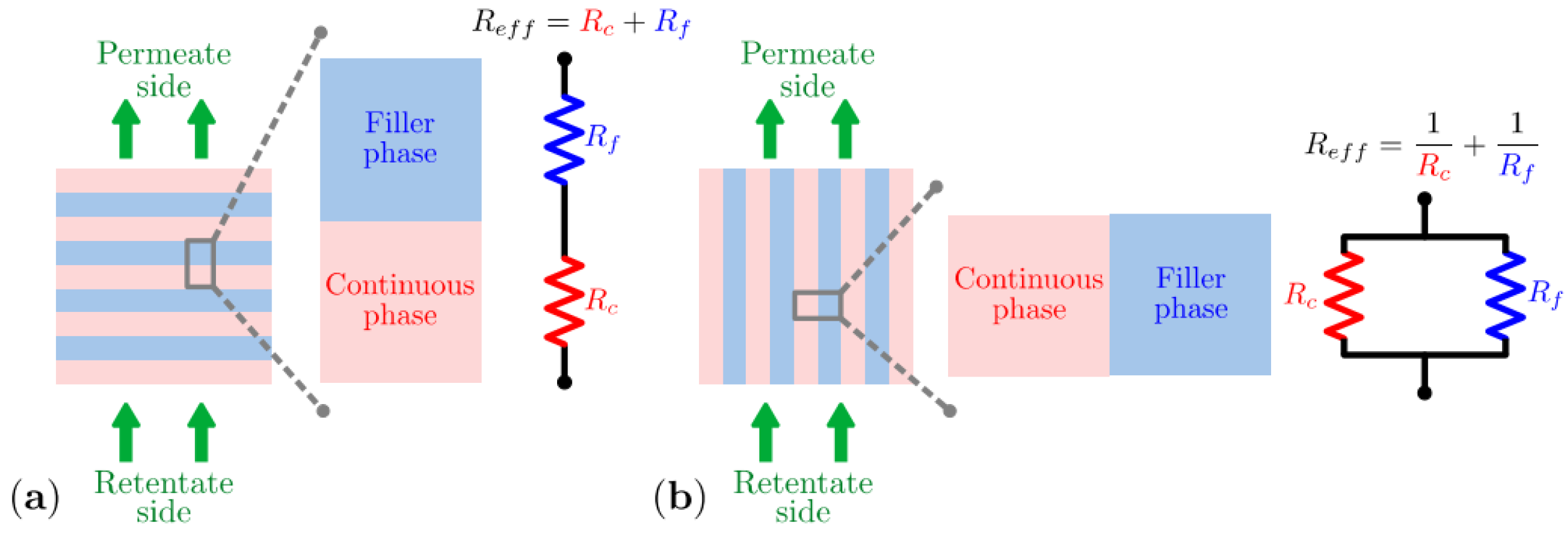
2.1.1. Computational Approaches
2.1.2. Permeation Models
2.1.3. Sorption Models
2.2. Advances in the Field of MMMs with Crystalline Fillers
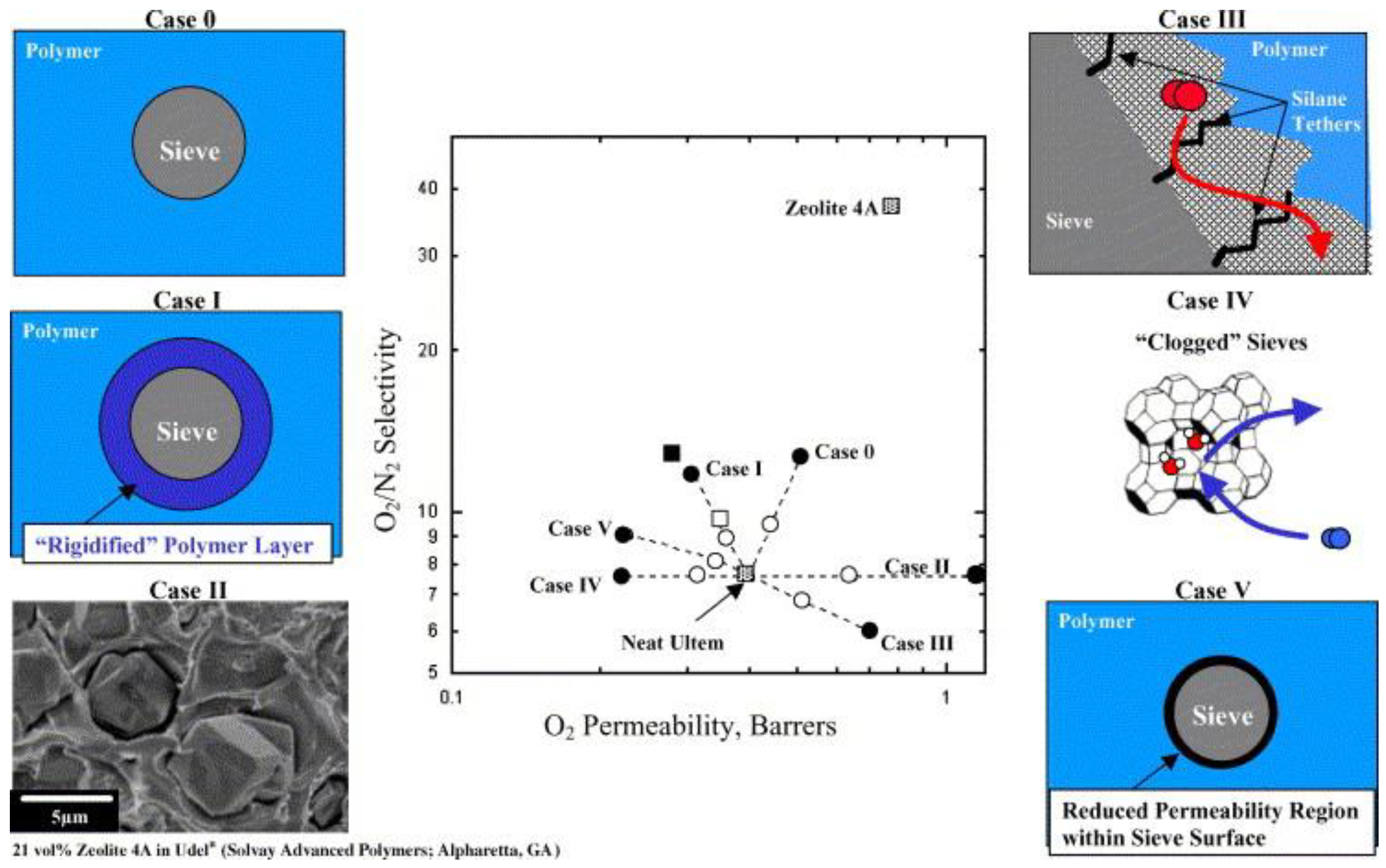
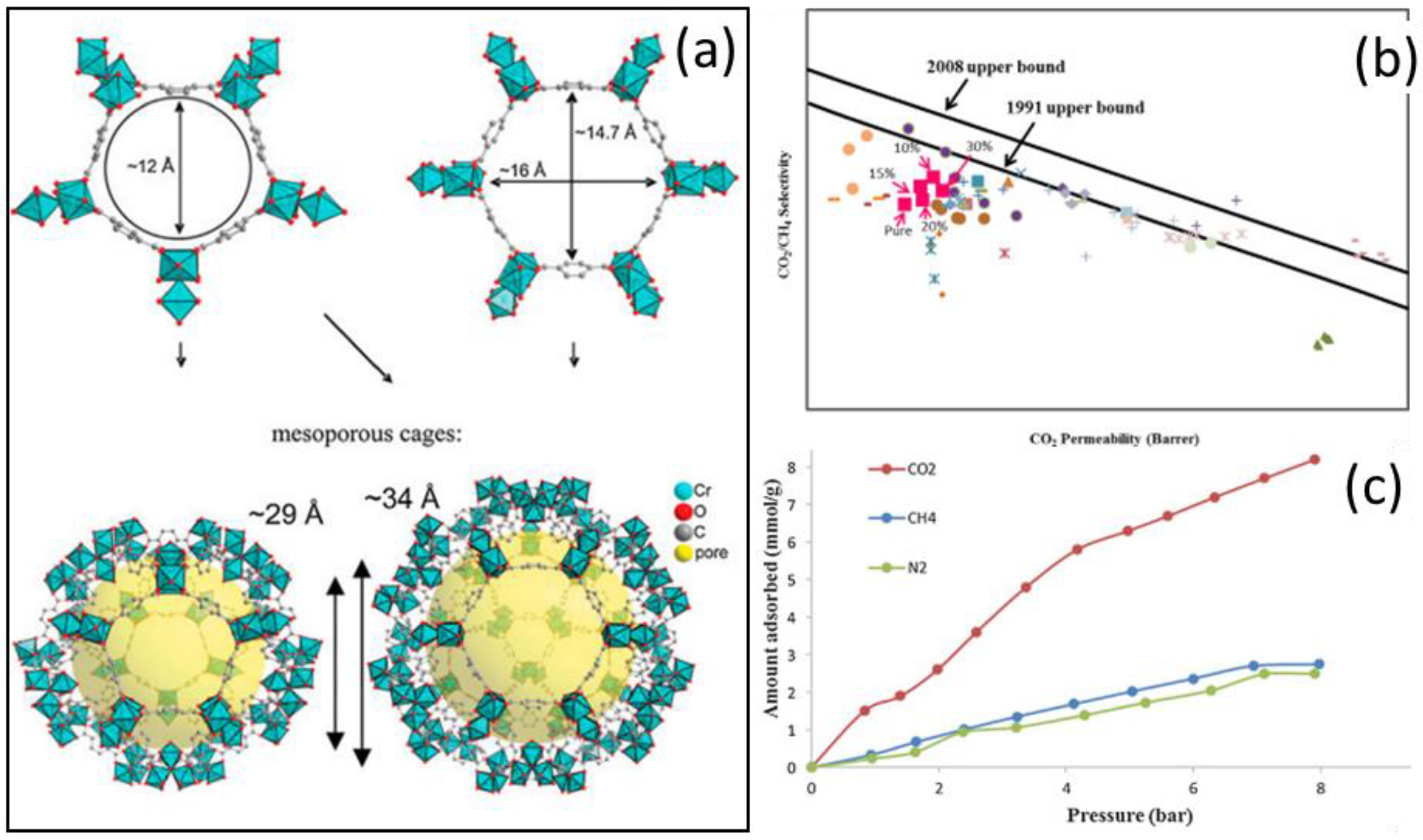
2.2.1. Improvement in Selectivity with Crystalline Fillers
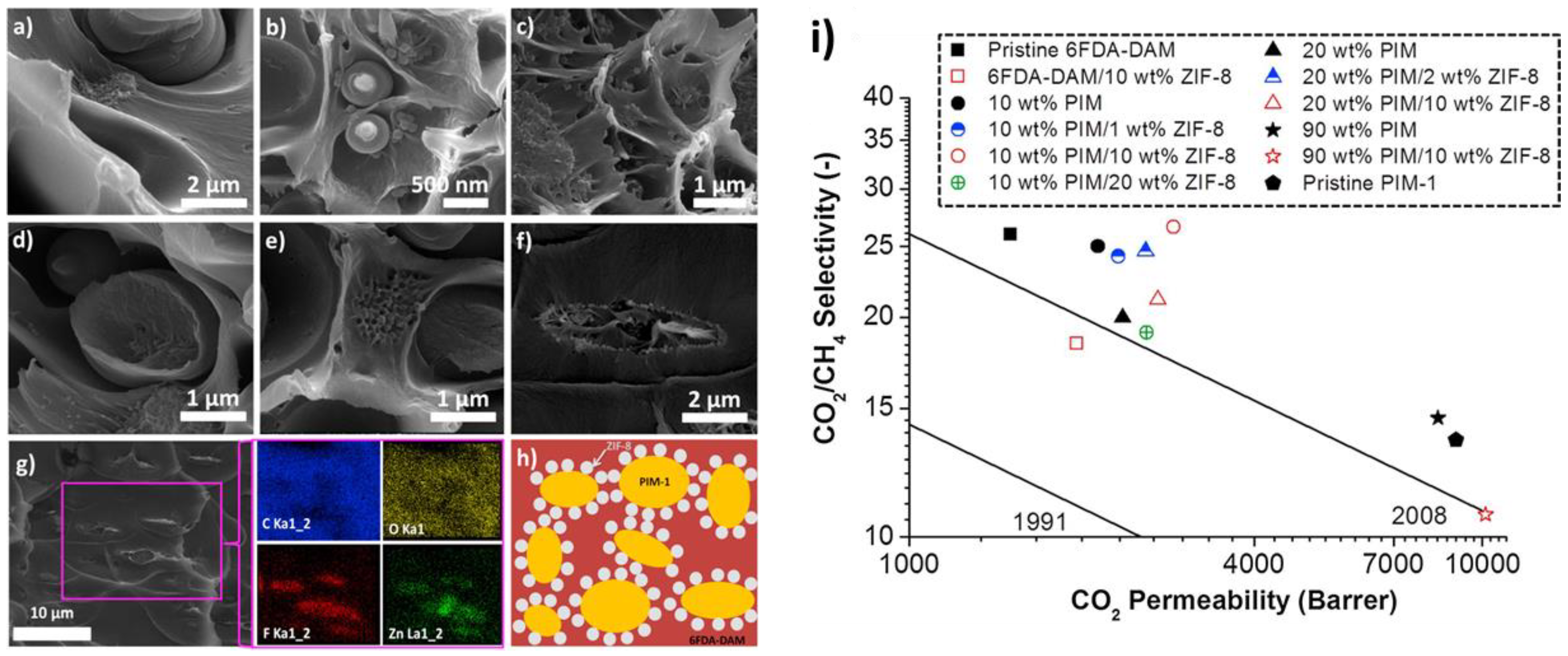
2.2.2. Improvement in Permeability with Crystalline Fillers
2.3. Advances in the Field of MMMs with Amorphous Fillers
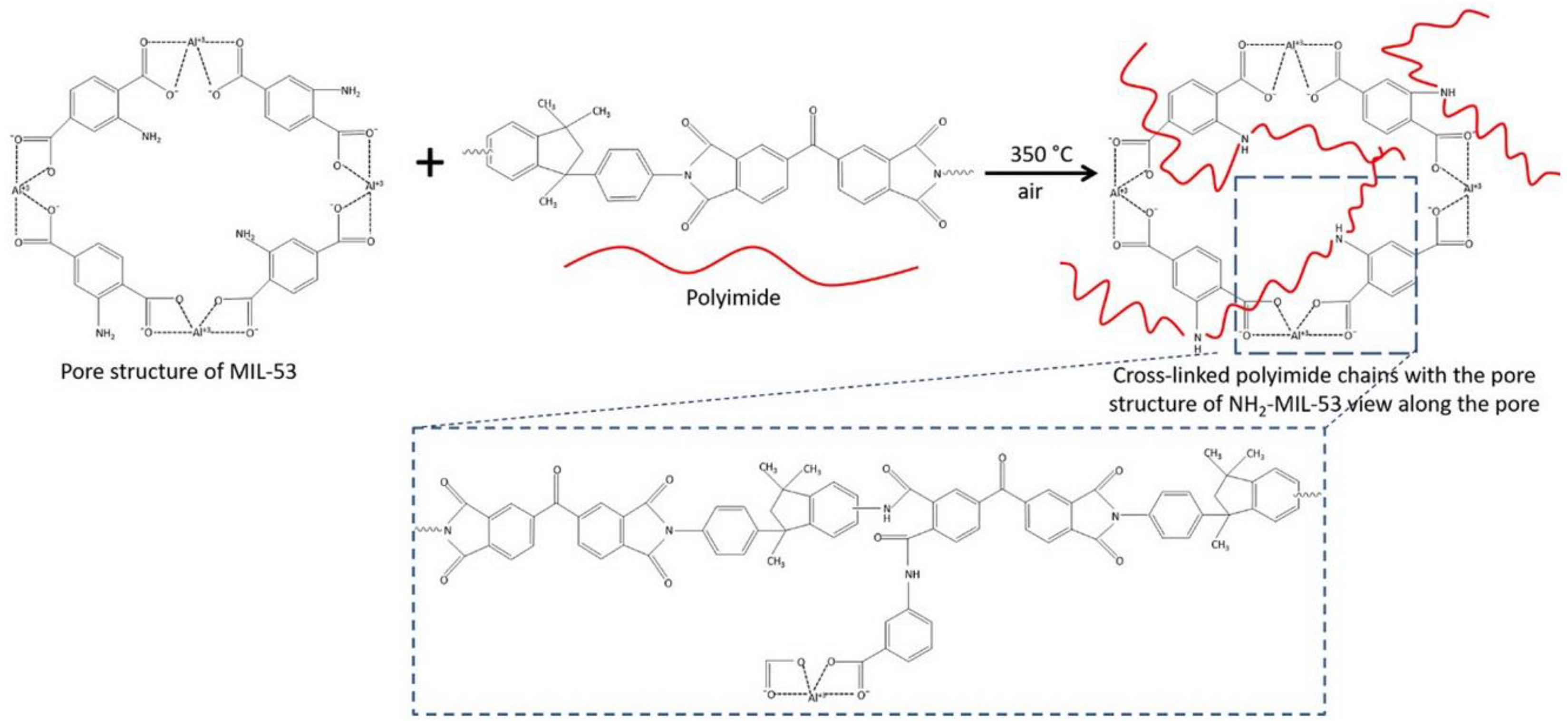
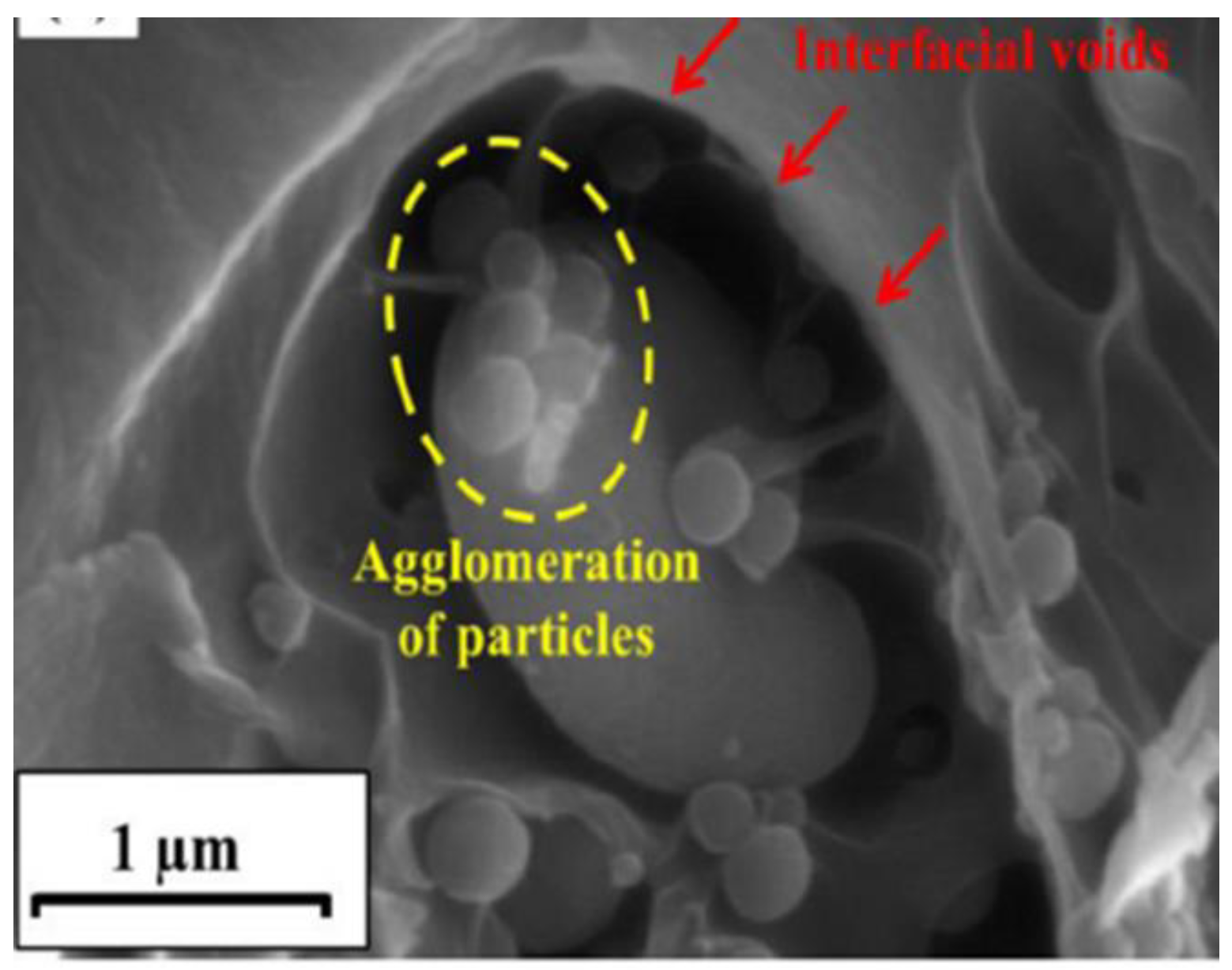
2.3.1. The Importance of Addressing the Potential Lack of Compatibility at the Interface between Filler and Matrix
2.3.2. Improvement in Selectivity with Amorphous Fillers
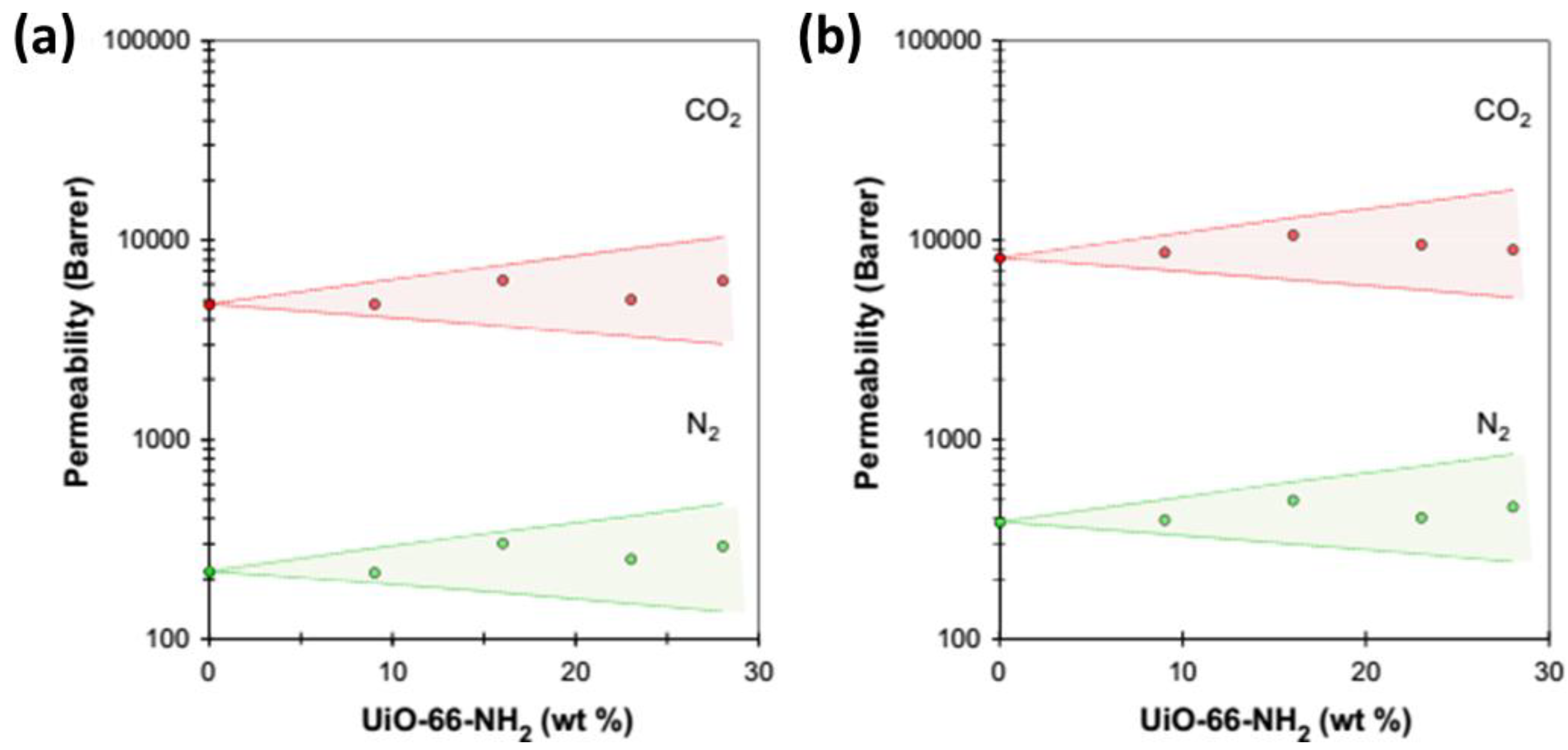
2.3.3. Improvement in Permeability with Amorphous Fillers
2.4. Practical Notes
3. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ackley, M.W.; Rege, S.U.; Saxena, H. Application of natural zeolites in the purification and separation of gases. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 61, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerry, F.G. Industrial Gas Handbook: Gas Separation and Purification; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; White, L.S.; Lokhandwala, K.; Baker, R.W. Natural gas purification. Encycl. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2013, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, M.J.C.; Balkus, K.J., Jr.; Ferraris, J.P.; Musselman, I.H. Molecular sieving realized with ZIF-8/Matrimid® mixed-matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 361, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yampolskii, Y. Polymeric gas separation membranes. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 3298–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.F.; Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T. Gas separation membranes. Switz. Springer 2015, 10, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Drioli, E.; Golemme, G. Membrane gas separation: A review/state of the art. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2009, 48, 4638–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W.; Low, B.T. Gas separation membrane materials: A perspective. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 6999–7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, D.F.; Smith, Z.P.; Guo, R.; Robeson, L.M.; McGrath, J.E.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Energy-efficient polymeric gas separation membranes for a sustainable future: A review. Polymer 2013, 54, 4729–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullumbi, P.; Brandani, F.; Brandani, S. Gas separation by adsorption: Technological drivers and opportunities for improvement. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2019, 24, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Li, J.-Y.; Tseng, H.-H.; Wey, M.-Y. Insights into the Role of Polymer Conformation on the Cutoff Size of Carbon Molecular Sieving Membranes for Hydrogen Separation and Its Novel Pore Size Detection Technology. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, C.A. Advances in pressure swing adsorption for gas separation. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2012, 2012, 982934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Jin, W. Natural Gas Purification by Asymmetric Membranes: An Overview. Green Energy Environ. 2021, 6, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. Correlation of separation factor versus permeability for polymeric membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 62, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. The upper bound revisited. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaidan, R.; Ghanem, B.; Pinnau, I. Fine-Tuned Intrinsically Ultramicroporous Polymers Redefine the Permeability/Selectivity Upper Bounds of Membrane-Based Air and Hydrogen Separations. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comesaña-Gándara, B.; Chen, J.; Bezzu, C.G.; Carta, M.; Rose, I.; Ferrari, M.-C.; Esposito, E.; Fuoco, A.; Jansen, J.C.; McKeown, N.B. Redefining the Robeson upper bounds for CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 separations using a series of ultrapermeable benzotriptycene-based polymers of intrinsic microporosity. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2733–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Rahim, R.; Rahman, W. Characterization of polyethersulfone/Matrimid® 5218 miscible blend mixed matrix membranes for O2/N2 gas separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wind, J.D.; Paul, D.R.; Koros, W.J. Natural gas permeation in polyimide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 228, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, R.S.; Rani, K.Y.; Sankarshana, T.; Ismail, A.; Sridhar, S. Separation of binary mixtures of propylene and propane by facilitated transport through silver incorporated poly (ether-block-amide) membranes. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. –Rev. D’ifp Energ. Nouv. 2015, 70, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomekian, A.; Behbahani, R.M.; Mohammadi, T.; Kargari, A. CO2/CH4 separation by high performance co-casted ZIF-8/Pebax 1657/PES mixed matrix membrane. J. Nat. Gas Eng. 2016, 31, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Paul, D.R. Physical aging of thin glassy polymer films monitored by gas permeability. Polymer 2004, 45, 8377–8393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, B.W.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R. Physical aging of ultrathin glassy polymer films tracked by gas permeability. Polymer 2009, 50, 5565–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.M.; Langhe, D.; Ponting, M.; Baer, E.; Freeman, B.; Paul, D. Physical aging of layered glassy polymer films via gas permeability tracking. Polymer 2011, 52, 6117–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechnik, J.; Gascon, J.; Doonan, C.J.; Janiak, C.; Sumby, C.J. Mixed-matrix membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9292–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadi Amooghin, A.; Mashhadikhan, S.; Sanaeepur, H.; Moghadassi, A.; Matsuura, T.; Ramakrishna, S. Substantial breakthroughs on function-led design of advanced materials used in mixed matrix membranes (MMMs): A new horizon for efficient CO2 separation. Prog. Mater Sci. 2019, 102, 222–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süer, M.G.; BaC, N.; Yilmaz, L. Gas permeation characteristics of polymer-zeolite mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 91, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroon, M.; Ismail, A.; Matsuura, T.; Montazer-Rahmati, M. Performance studies of mixed matrix membranes for gas separation: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.D. Perspectives on mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galizia, M.; Chi, W.S.; Smith, Z.P.; Merkel, T.C.; Baker, R.W.; Freeman, B.D. 50th Anniversary Perspective: Polymers and Mixed Matrix Membranes for Gas and Vapor Separation: A Review and Prospective Opportunities. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7809–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.; Lau, C.H.; Mardel, J.I.; Kitchin, M.; Konstas, K.; Ladewig, B.P.; Hill, M.R. Physical aging in glassy mixed matrix membranes; tuning particle interaction for mechanically robust nanocomposite films. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 10627–10634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Goh, K.; Weerachanchai, P.; Bae, T.-H. 3D covalent organic framework for morphologically induced high-performance membranes with strong resistance toward physical aging. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi Shamsabadi, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Seidi, F.; Riazi, H.; Aminabhavi, T.; Soroush, M. Next generation polymers of intrinsic microporosity with tunable moieties for ultrahigh permeation and precise molecular CO2 separation. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2021, 84, 100903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, E.; Sadeghi, M.; Zarei, N.; Pournaghshband, A. Enhancement of the gas separation properties of polyurethane membranes by alumina nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 479, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.T.; Koros, W.J. Gas sorption in polymers, molecular sieves, and mixed matrix membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 4053–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Kulprathipanja, S. Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) comprising organic polymers with dispersed inorganic fillers for gas separation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, B.; Seoane, B.; Zamaro, J.M.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Combination of MOFs and Zeolites for Mixed-Matrix Membranes. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 2781–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Jia, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, D. Ultrathin mixed matrix membranes containing two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanosheets for efficient CO2/CH4 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 539, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Chernikova, V.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Shekhah, O.; Zhang, C.; Yi, S.; Eddaoudi, M.; Koros, W.J. Publisher Correction: Mixed matrix formulations with MOF molecular sieving for key energy-intensive separations. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodenas, T.; van Dalen, M.; García-Pérez, E.; Serra-Crespo, P.; Zornoza, B.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. Visualizing MOF Mixed Matrix Membranes at the Nanoscale: Towards Structure-Performance Relationships in CO2/CH4 Separation Over NH2-MIL-53(Al)@PI. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechnik, J.; Sumby, C.J.; Janiak, C. Enhancing Mixed-Matrix Membrane Performance with Metal-Organic Framework Additives. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 4467–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Villacorta Hernandez, B.; Ge, L.; Zhu, Z. Metal organic framework based mixed matrix membranes: An overview on filler/polymer interfaces. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ying, Y.; Japip, S.; Jiang, S.-D.; Chung, T.-S.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, D. Advanced Porous Materials in Mixed Matrix Membranes. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaqui, M.; Semino, R.; Menguy, N.; Carn, F.; Kundu, T.; Guigner, J.-M.; McKeown, N.B.; Msayib, K.J.; Carta, M.; Malpass-Evans, R.; et al. Toward an Understanding of the Microstructure and Interfacial Properties of PIMs/ZIF-8 Mixed Matrix Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27311–27321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ciston, J.; Zheng, B.; Miao, X.; Czarnik, C.; Pan, Y.; Sougrat, R.; Lai, Z.; Hsiung, C.-E.; Yao, K.; et al. Unravelling surface and interfacial structures of a metal–organic framework by transmission electron microscopy. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Moreton, J.C.; Tavares, S.R.; Semino, R.; Maurin, G.; Cohen, S.M.; Schmidt-Rohr, K. Polymer Infiltration into Metal–Organic Frameworks in Mixed-Matrix Membranes Detected in Situ by NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7589–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.T.; Koros, W.J. Non-ideal effects in organic–inorganic materials for gas separation membranes. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 739, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.A.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, R.; Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. (Cross-Linked Poly(Ionic Liquid)–Ionic Liquid–Zeolite) Mixed-Matrix Membranes for CO2/CH4 Gas Separations Based on Curable Ionic Liquid Prepolymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 58, 4704–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. The solution-diffusion model: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, J. Metal–Organic Framework/Polymer Mixed-Matrix Membranes for H2/CO2 Separation: A Fully Atomistic Simulation Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 19268–19277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, A.; Satilmis, B.; Uyar, T.; Monteleone, M.; Esposito, E.; Muzzi, C.; Tocci, E.; Longo, M.; De Santo, M.P.; Lanč, M.; et al. Comparison of pure and mixed gas permeation of the highly fluorinated polymer of intrinsic microporosity PIM-2 under dry and humid conditions: Experiment and modelling. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 594, 117460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-Y.; Lee, J.S.; Lin, L.-C. X-ray Diffraction and Molecular Simulations in the Study of Metal–Organic Frameworks for Membrane Gas Separation. Langmuir 2022, 38, 9441–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.; Ozcan, A.; Ramsahye, N.A.; Zhao, D.; Maurin, G.; Semino, R. Is Porosity at the MOF/Polymer Interface Necessarily an Obstacle to Optimal Gas-Separation Performances in Mixed Matrix Membranes? ACS Mater. Lett. 2021, 3, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, J.C. A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1873; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, M.; Seoane, B.; Pustovarenko, A.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Yarulina, I.; Abou-Hamad, E.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. Benzimidazole linked polymers (BILPs) in mixed-matrix membranes: Influence of filler porosity on the CO2/N2 separation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 566, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khdhayyer, M.R.; Esposito, E.; Fuoco, A.; Monteleone, M.; Giorno, L.; Jansen, J.C.; Attfield, M.P.; Budd, P.M. Mixed matrix membranes based on UiO-66 MOFs in the polymer of intrinsic microporosity PIM-1. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 173, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Alkaş, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Telfer, S.G. Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) using an emerging metal-organic framework (MUF-15) for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 609, 118245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetghadam, A.; Seoane, B.; Keskin, D.; Duim, N.; Rodenas, T.; Shahid, S.; Sorribas, S.; Guillouzer, C.L.; Clet, G.; Tellez, C.; et al. Metal Organic Framework Crystals in Mixed-Matrix Membranes: Impact of the Filler Morphology on the Gas Separation Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3154–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsalve-Bravo, G.M.; Bhatia, S.K. Modeling Permeation through Mixed-Matrix Membranes: A Review. Processes 2018, 6, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, S.; Alsoy Altinkaya, S. A Review on Computational Modeling Tools for MOF-Based Mixed Matrix Membranes. Computation 2019, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chung, T.S.; Paul, D.R. Temperature dependence of gas sorption and permeation in PIM-1. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenheim, E. Chapter 11. Localized monolayer and multilayer adsorption of gases. In Applications of Statistical Mechanics; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1966; pp. 186–206. [Google Scholar]
- Lanč, M.; Pilnáček, K.; Mason, C.R.; Budd, P.M.; Rogan, Y.; Malpass-Evans, R.; Carta, M.; Gándara, B.C.; McKeown, N.B.; Jansen, J.C. Gas sorption in polymers of intrinsic microporosity: The difference between solubility coefficients determined via time-lag and direct sorption experiments. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570, 522–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ren, G.; Wei, K.; Liu, D.; Wu, T.; Jiang, J.; Qian, J.; Pan, Y. Improved dispersion performance and interfacial compatibility of covalent-grafted MOFs in mixed-matrix membranes for gas separation. Green Chem. 2021, 2, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushell, A.F.; Budd, P.M.; Attfield, M.P.; Jones, J.T.A.; Hasell, T.; Cooper, A.I.; Bernardo, P.; Bazzarelli, F.; Clarizia, G.; Jansen, J.C. Nanoporous Organic Polymer/Cage Composite Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, S.; Duan, J.; Jin, W. Mixed-matrix membranes with soluble porous organic molecular cage for highly efficient C3H6/C3H8 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, M.; Mobili, R.; Milanese, C.; Esposito, E.; Fuoco, A.; La Cognata, S.; Amendola, V.; Jansen, J.C. PEEK–WC-Based Mixed Matrix Membranes Containing Polyimine Cages for Gas Separation. Molecules 2021, 26, 5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cognata, S.; Mobili, R.; Milanese, C.; Boiocchi, M.; Gaboardi, M.; Armentano, D.; Jansen, J.C.; Monteleone, M.; Antonangelo, A.R.; Carta, M.; et al. CO2 Separation by Imide/Imine Organic Cages. Chem. Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202201631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, G.; Van Puyvelde, P.; Van der Bruggen, B. Covalent organic frameworks for membrane separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2665–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Qian, Y.; Yuan, D.; Addicoat, M.A.; Heine, T.; Hu, Z.; Tee, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, D. Mixed Matrix Membranes (MMMs) Comprising Exfoliated 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) for Efficient CO2 Separation. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, M.; Seoane, B.; Rozhko, E.; Dikhtiarenko, A.; Clet, G.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. Azine-Linked Covalent Organic Framework (COF)-Based Mixed-Matrix Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 14467–14470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) for Membrane Separation: A Mini Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 58, 15394–15406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; Kong, Y.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, H.; Ren, Y.; Pu, Y.; Liang, X.; et al. MOF–COF “Alloy” Membranes for Efficient Propylene/Propane Separation. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Jilani, A.; Khan, I.U.; Kamaludin, R.; Samuel, O. ZIF-filler incorporated mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) for efficient gas separation: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, M.; Mousavi, S.F.; Mohammadi, T.; Bakhtiari, O. Synthesis and gas transport performance of MIL-101/Matrimid mixed matrix membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férey, G.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Dutour, J.; Surblé, S.; Margiolaki, I. A Chromium Terephthalate-Based Solid with Unusually Large Pore Volumes and Surface Area. Science 2005, 309, 2040–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuhnen, A.; Dietrich, D.; Millan, S.; Janiak, C. Role of Filler Porosity and Filler/Polymer Interface Volume in Metal–Organic Framework/Polymer Mixed-Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33589–33600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. Facile synthesis of Al-fumarate metal–organic framework nano-flakes and their highly selective adsorption of volatile organic compounds. Mater. Lett. 2017, 197, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couck, S.; Denayer, J.F.; Baron, G.V.; Rémy, T.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. An amine-functionalized MIL-53 metal- organic framework with large separation power for CO2 and CH4. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6326–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertik, A.; Wee, L.H.; Sentosun, K.; Navarro, J.A.; Bals, S.; Martens, J.A.; Vankelecom, I.F. High-Performance CO2-Selective Hybrid Membranes by Exploiting MOF-Breathing Effects. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 12, 2952–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalei, B.; Sakurai, K.; Kinoshita, Y.; Wakimoto, K.; Isfahani, A.P.; Song, Q.; Doitomi, K.; Furukawa, S.; Hirao, H.; Kusuda, H.; et al. Enhanced selectivity in mixed matrix membranes for CO2 capture through efficient dispersion of amine-functionalized MOF nanoparticles. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chung, T.S.; Paul, D.R. Gas sorption and permeation in PIM-1. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 432, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, P.M.; McKeown, N.B.; Ghanem, B.S.; Msayib, K.J.; Fritsch, D.; Starannikova, L.; Belov, N.; Sanfirova, O.; Yampolskii, Y.; Shantarovich, V. Gas permeation parameters and other physicochemical properties of a polymer of intrinsic microporosity: Polybenzodioxane PIM-1. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandiah, M.; Nilsen, M.H.; Usseglio, S.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Tilset, M.; Larabi, C.; Quadrelli, E.A.; Bonino, F.; Lillerud, K.P. Synthesis and Stability of Tagged UiO-66 Zr-MOFs. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6632–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Fang, W.; Shrestha, B.B.; Huang, M.; Jin, J. Constructing Strong Interfacial Interactions under Mild Conditions in MOF-Incorporated Mixed Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 3166–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Laínez, J.; Pardillos-Ruiz, A.; Carta, M.; Malpass-Evans, R.; McKeown, N.B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Polymer engineering by blending PIM-1 and 6FDA-DAM for ZIF-8 containing mixed matrix membranes applied to CO2 separations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tan, X. High Performance of PIM-1/ZIF-8 Composite Membranes for O2/N2 Separation. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 16572–16577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahia, M.; Phan Le, Q.N.; Ismail, N.; Essalhi, M.; Sundman, O.; Rahimpour, A.; Dal-Cin, M.M.; Tavajohi, N. Effect of incorporating different ZIF-8 crystal sizes in the polymer of intrinsic microporosity, PIM-1, for CO2/CH4 separation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 312, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Wu, A.X.; Chi, W.S.; Asinger, P.A.; Lin, S.; Hypsher, A.; Smith, Z.P. Mixed-Matrix Membranes Formed from Imide-Functionalized UiO-66-NH2 for Improved Interfacial Compatibility. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 31257–31269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavka, J.H.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Guillou, N.; Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K.P. A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13850–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winarta, J.; Shan, B.; McIntyre, S.M.; Ye, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Mu, B. A Decade of UiO-66 Research: A Historic Review of Dynamic Structure, Synthesis Mechanisms, and Characterization Techniques of an Archetypal Metal–Organic Framework. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 1347–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessling, M.; Schoeman, S.; Van der Boomgaard, T.; Smolders, C. Plasticization of gas separation membranes. Gas Sep. Purif. 1991, 5, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, S.; Li, K.; Ma, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Chang, X.; Zhu, L.; Xue, Q. Enhanced gas separation performance of Pebax mixed matrix membranes by incorporating ZIF-8 in situ inserted by multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.O.; Balkus, K.J.; Ferraris, J.P.; Musselman, I.H. MIL-53 frameworks in mixed-matrix membranes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 196, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serre, C.; Bourrelly, S.; Vimont, A.; Ramsahye, N.A.; Maurin, G.; Llewellyn, P.L.; Daturi, M.; Filinchuk, Y.; Leynaud, O.; Barnes, P.; et al. An Explanation for the Very Large Breathing Effect of a Metal–Organic Framework during CO2 Adsorption. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2246–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, R.; Koros, W.J. Factors controlling successful formation of mixed-matrix gas separation materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 2692–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazvini, O.T.; Babarao, R.; Shi, Z.-L.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Telfer, S.G. A Robust Ethane-Trapping Metal–Organic Framework with a High Capacity for Ethylene Purification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5014–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dai, Z.; Deng, L. H2-selective Troger’s base polymer based mixed matrix membranes enhanced by 2D MOFs. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 610, 118262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, M.; Malpass-Evans, R.; Croad, M.; Rogan, Y.; Jansen, J.C.; Bernardo, P.; Bazzarelli, F.; McKeown, N.B. An efficient polymer molecular sieve for membrane gas separations. Science 2013, 339, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khdhayyer, M.; Bushell, A.F.; Budd, P.M.; Attfield, M.P.; Jiang, D.; Burrows, A.D.; Esposito, E.; Bernardo, P.; Monteleone, M.; Fuoco, A.; et al. Mixed matrix membranes based on MIL-101 metal–organic frameworks in polymer of intrinsic microporosity PIM-1. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shiotsuki, M.; Sanda, F.; Freeman, B.D.; Masuda, T. Synthesis and Properties of Indan-Based Polyacetylenes That Feature the Highest Gas Permeability among All the Existing Polymers. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 8525–8532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
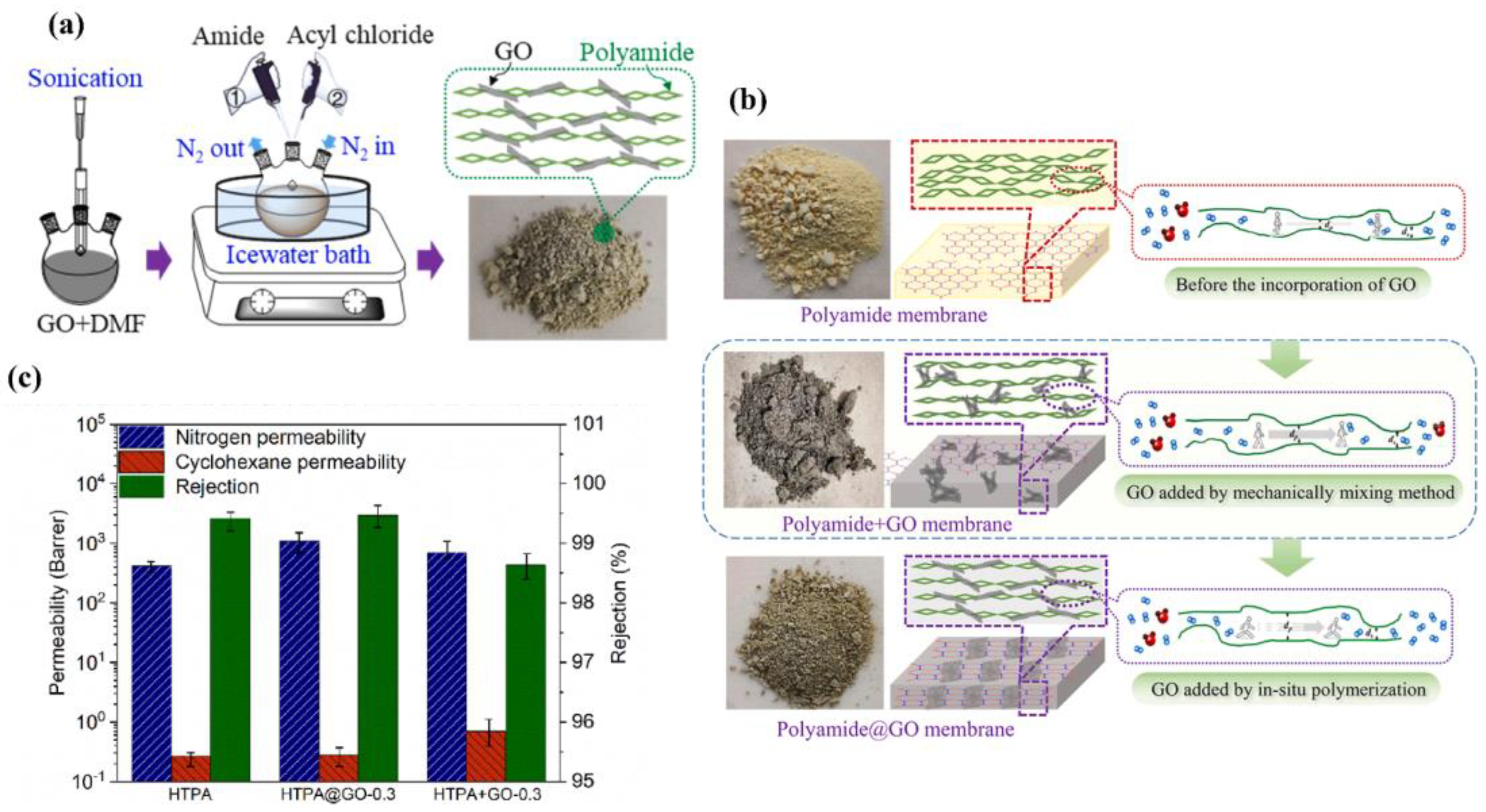
- Mao, G.; Liu, T.; Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; Qin, J.; Zhou, H.; Jin, W. Polyamide@GO microporous membrane with enhanced permeability for the molecular sieving of nitrogen over VOC. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 652, 120443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Chuah, C.Y.; Lee, J.; Bae, T.-H. Effective functionalization of porous polymer fillers to enhance CO2/N2 separation performance of mixed-matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 647, 120309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.H.; Konstas, K.; Doherty, C.M.; Kanehashi, S.; Ozcelik, B.; Kentish, S.E.; Hill, A.J.; Hill, M.R. Tailoring Physical Aging in Super Glassy Polymers with Functionalized Porous Aromatic Frameworks for CO2 Capture. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4756–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaddondar, M.; Foster, A.B.; Carta, M.; Gorgojo, P.; McKeown, N.B.; Budd, P.M. Mitigation of Physical Aging with Mixed Matrix Membranes Based on Cross-Linked PIM-1 Fillers and PIM-1. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 46756–46766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaddondar, M.; Foster, A.B.; Luque-Alled, J.M.; Msayib, K.J.; Carta, M.; Sorribas, S.; Gorgojo, P.; McKeown, N.B.; Budd, P.M. Intrinsically Microporous Polymer Nanosheets for High-Performance Gas Separation Membranes. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 1900572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semino, R.; Ramsahye, N.A.; Ghoufi, A.; Maurin, G. Microscopic Model of the Metal–Organic Framework/Polymer Interface: A First Step toward Understanding the Compatibility in Mixed Matrix Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafisi, V.; Hägg, M.-B. Development of dual layer of ZIF-8/PEBAX-2533 mixed matrix membrane for CO2 capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 459, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Ni, Z.; Côté, A.P.; Choi, J.Y.; Huang, R.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Chae, H.K.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10186–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushell, A.F.; Attfield, M.P.; Mason, C.R.; Budd, P.M.; Yampolskii, Y.; Starannikova, L.; Rebrov, A.; Bazzarelli, F.; Bernardo, P.; Carolus Jansen, J.; et al. Gas permeation parameters of mixed matrix membranes based on the polymer of intrinsic microporosity PIM-1 and the zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-8. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghaei, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Ghalei, B.; Shahrooz, M. The role of compatibility between polymeric matrix and silane coupling agents on the performance of mixed matrix membranes: Polyethersulfone/MCM-41. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 513, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barooah, M.; Mandal, B. Enhanced CO2 separation performance by PVA/PEG/silica mixed matrix membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, A.G.; Little, M.A.; Briggs, M.E.; Jelfs, K.E.; Cooper, A.I. A solution-processable dissymmetric porous organic cage. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2018, 3, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-Alled, J.M.; Ameen, A.W.; Alberto, M.; Tamaddondar, M.; Foster, A.B.; Budd, P.M.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; Gorgojo, P. Gas separation performance of MMMs containing (PIM-1)-functionalized GO derivatives. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 623, 118902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, T.; Ren, H.; Ma, S.; Cao, D.; Lan, J.; Jing, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Deng, F.; Simmons, J.M.; et al. Targeted Synthesis of a Porous Aromatic Framework with High Stability and Exceptionally High Surface Area. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9457–9460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.H.; Konstas, K.; Doherty, C.M.; Smith, S.J.D.; Hou, R.; Wang, H.; Carta, M.; Yoon, H.; Park, J.; Freeman, B.D.; et al. Tailoring molecular interactions between microporous polymers in high performance mixed matrix membranes for gas separations. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 17405–17410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpass-Evans, R.; Rose, I.; Fuoco, A.; Bernardo, P.; Clarizia, G.; McKeown, N.B.; Jansen, J.C.; Carta, M. Effect of Bridgehead Methyl Substituents on the Gas Permeability of Tröger’s-Base Derived Polymers of Intrinsic Microporosity. Membranes 2020, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Sculley, J.P.; Yuan, D.; Krishna, R.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, H.C. Polyamine-tethered porous polymer networks for carbon dioxide capture from flue gas. Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 7598–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Yuan, D.; Sculley, J.; Zhao, D.; Krishna, R.; Zhou, H.-C. Sulfonate-grafted porous polymer networks for preferential CO2 adsorption at low pressure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18126–18129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Ghanem, B.S.; Smith, S.J.D.; Doherty, C.M.; Setter, C.; Wang, H.; Pinnau, I.; Hill, M.R. Highly permeable and selective mixed-matrix membranes for hydrogen separation containing PAF-1. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 14713–14720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, B.S.; Swaidan, R.; Ma, X.; Litwiller, E.; Pinnau, I. Energy-Efficient Hydrogen Separation by AB-Type Ladder-Polymer Molecular Sieves. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6696–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
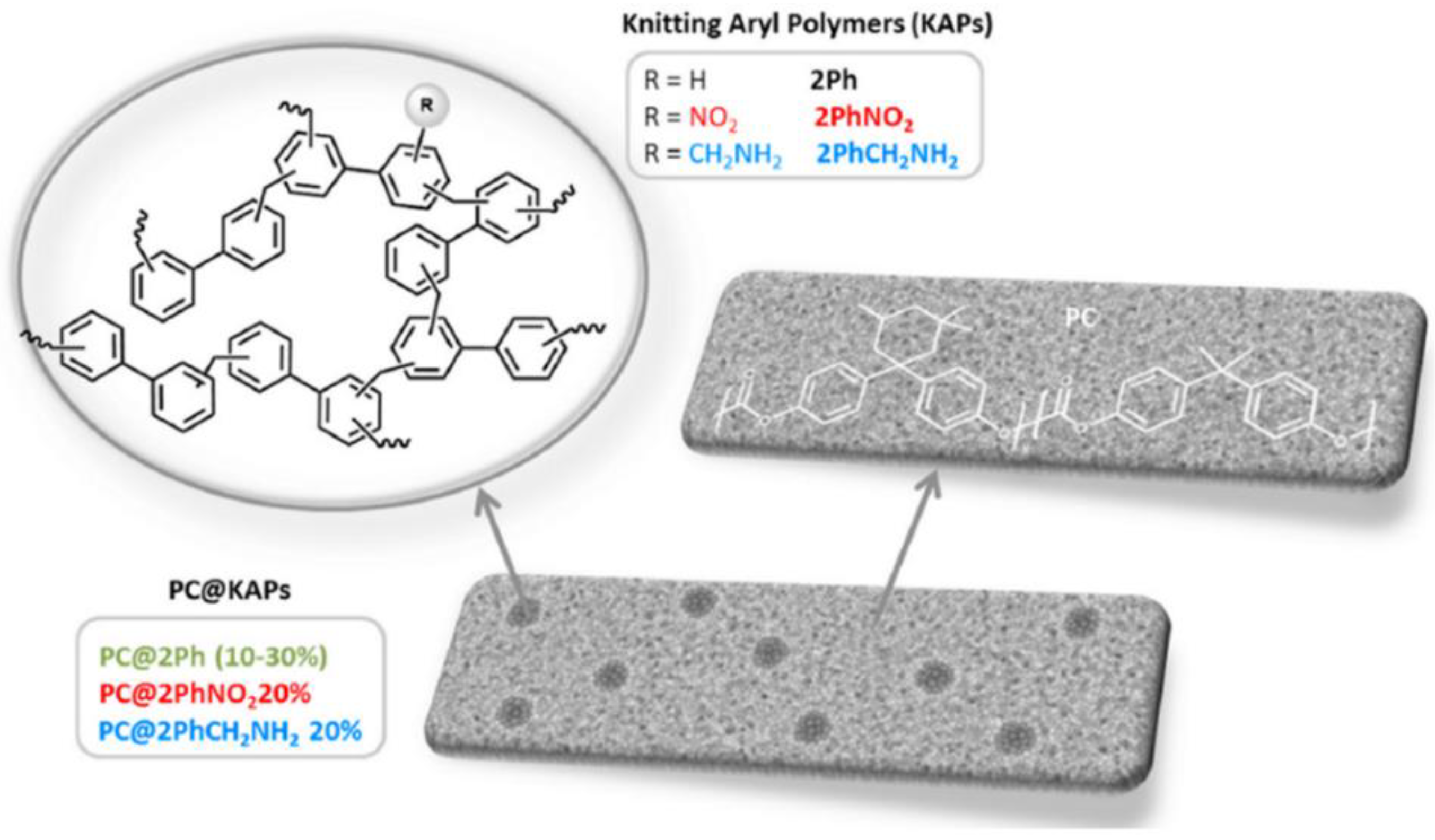
- Rodríguez-Jardón, L.; López-González, M.; Iglesias, M.; Maya, E.M. Effect of porous organic polymers in gas separation properties of polycarbonate based mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 619, 118795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.; Man, Z.; Maulud, A.S.; Mannan, H.A.; Shafie, A. Effect of silane coupling agents on properties and performance of polycarbonate/silica MMMs. Polym. Test. 2019, 73, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Aslam, M.; Khan, A.; Gilani, M.A.; Khan, A.L. Mixed matrix membranes incorporated with sonication-assisted ZIF-8 nanofillers for hazardous wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 35913–35923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ike, I.A.; Dumée, L.F.; Groth, A.; Orbell, J.D.; Duke, M. Effects of dope sonication and hydrophilic polymer addition on the properties of low pressure PVDF mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 540, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Lugo, C.; Suárez-García, F.; Hernández, A.; Miguel, J.A.; Lozano, Á.E.; de la Campa, J.G.; Álvarez, C. New Materials for Gas Separation Applications: Mixed Matrix Membranes Made from Linear Polyimides and Porous Polymer Networks Having Lactam Groups. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 58, 9585–9595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Feng, L.; Ding, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Y. The nitrogen-doped porous carbons/PIM mixed-matrix membranes for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, K.; Izák, P.; Kárászová, M.; Pasichnyk, M.; Lanč, M.; Nikolaeva, D.; Luis, P.; Jansen, J.C. A Review on Ionic Liquid Gas Separation Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabais, A.R.; Ahmed, S.; Younis, M.; Zhou, J.-X.; Pereira, J.R.; Freitas, F.; Mecerreyes, D.; Crespo, J.G.; Huang, M.-H.; Neves, L.A.; et al. Mixed matrix membranes based on ionic liquids and porous organic polymers for selective CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 660, 120841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bügel, S.; Spieß, A.; Janiak, C. Covalent triazine framework CTF-fluorene as porous filler material in mixed matrix membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 316, 110941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-C.; Cheng, P.-H.; Chou, S.-C.; Lai, C.-L.; Huang, S.-H.; Tsai, H.-A.; Hung, W.-S.; Lee, K.-R. Separation behavior of amorphous amino-modified silica nanoparticle/polyimide mixed matrix membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xin, Q.; Li, X.; Yun, M.; Xu, R.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Ding, X.; Ye, H.; et al. Mixed matrix membranes comprising aminosilane-functionalized graphene oxide for enhanced CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570–571, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tao, F.; Liu, Q.; Zong, C.; Yang, W.; Cao, X.; Jin, W.; Xu, N. Microporous Polyamide Membranes for Molecular Sieving of Nitrogen from Volatile Organic Compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5755–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mixed Matrix Membranes with Crystalline Fillers | |||||
| Matrix | Filler a | Type | Selectivity Improvement b | Main Gas Pairs c | Ref. |
| Matrimid® 5218 | MIL-101 (Cr) (10%) | MOF | +62% | CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 | [75] |
| Matrimid® 5218 | Al-fum (20%) | Mesoporous | +63% | CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 | [77] |
| Matrimid® 5218 | NH2-MIL-53(Al) (40%) | MOF | +100% | CO2/CH4 | [80] |
| PIM-1 | UiO-66-NH2 (10%) | MOF | +35% | CO2/N2 | [81] |
| Durene COOH-PI | UiO-66(Zr)-NH2 (10%) | MOF | +59% | CO2/CH4 | [85] |
| PIM-1 + 6FDA-DAM | ZIF-8 (10%) | MOF | +30% | CO2/CH4 | [86] |
| Matrix | Filler a | Type | Permeability Improvement b | Main Gases c | |
| 6FDA–Durene | UiO-66-NH2 (40%) | MOF | +60% | CO2, CH4 and N2 | [89] |
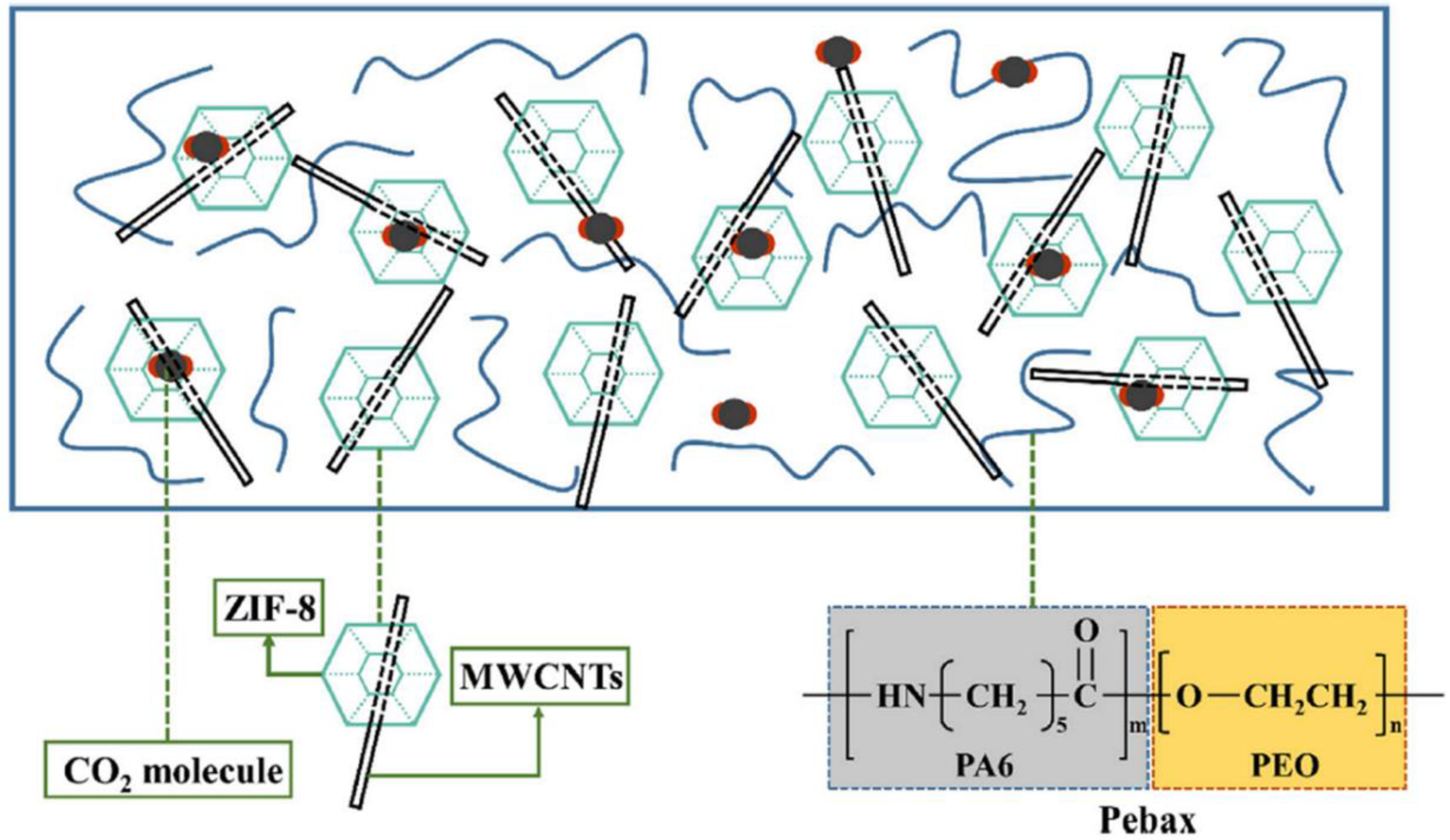
| Pebax®-MH-1657 | MWCNTs@ZIF-8 (12%) | Nanotubes | +30% | CO2, CH4 and N2 | [93] |
| Matrimid® 5218 | MIL-53 | MOF | +102% | CO2, CH4 and N2 | [94] |
| PIM-1 | MUF-15 (2–5%) | MOF | +36% | CO2 and N2 | [57] |
| TB-PIM | ZIF-L-Zn (20%) | MOF | +271% | CO2 and H2 | [98] |
| PIM-1 | MIL-101 (47%) | MOF | +178% | CO2, CH4 and N2 | [100] |
| Mixed Matrix Membranes with Amorphous fillers | |||||
| Matrix | Filler a | Type | Selectivity Improvement b | Main Gas Pairs c | Ref. |
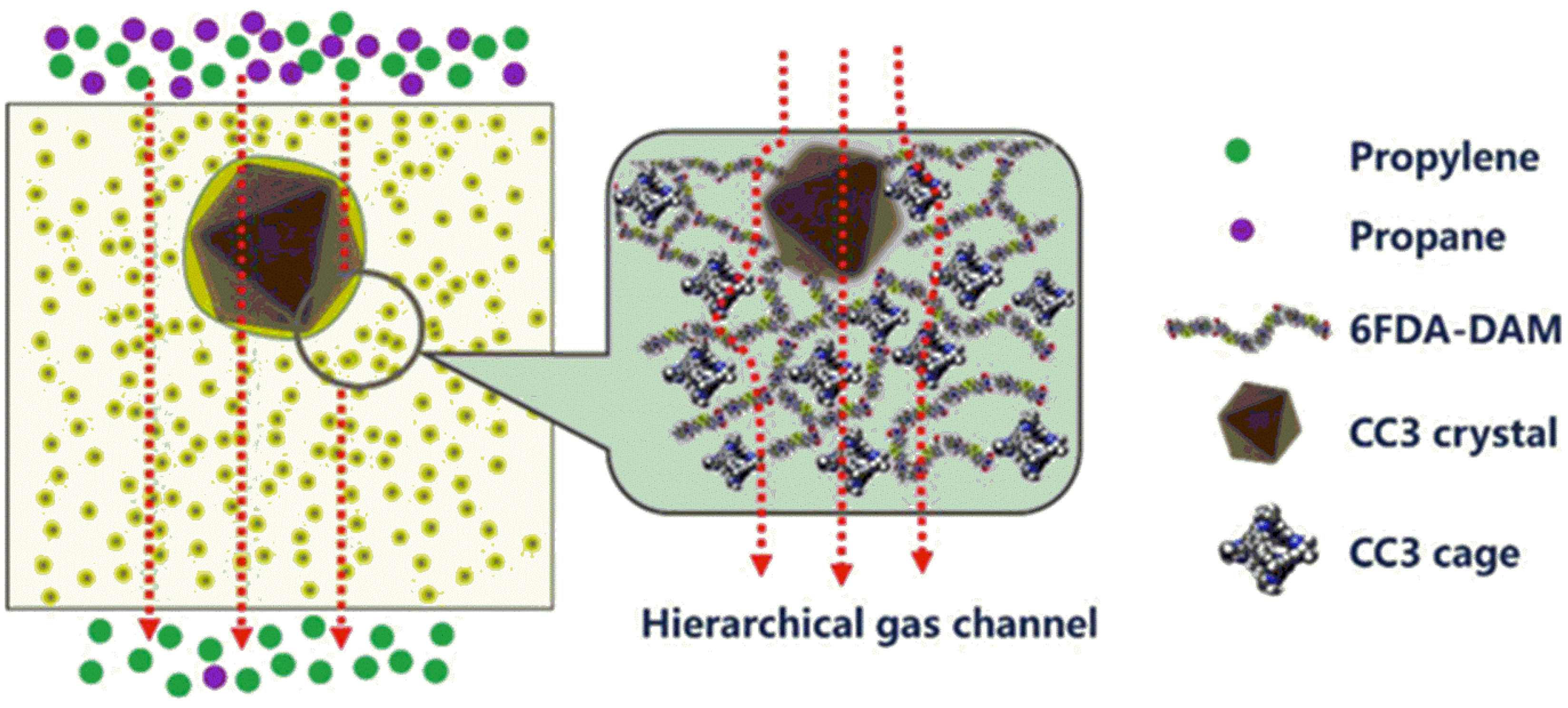
| 6FDA-DAM | CC3 (20%) | Organic cage | +140% | C3H6/C3H8 | [66] |
| PIM-1 | APTS-GO (10%) | Graphene oxide | +27% | CO2/CH4 | [114] |
| PIM-1 | Networked PIM-1 (0.5–10%) | Network polym. | +46% | CO2/CH4 | [106] |
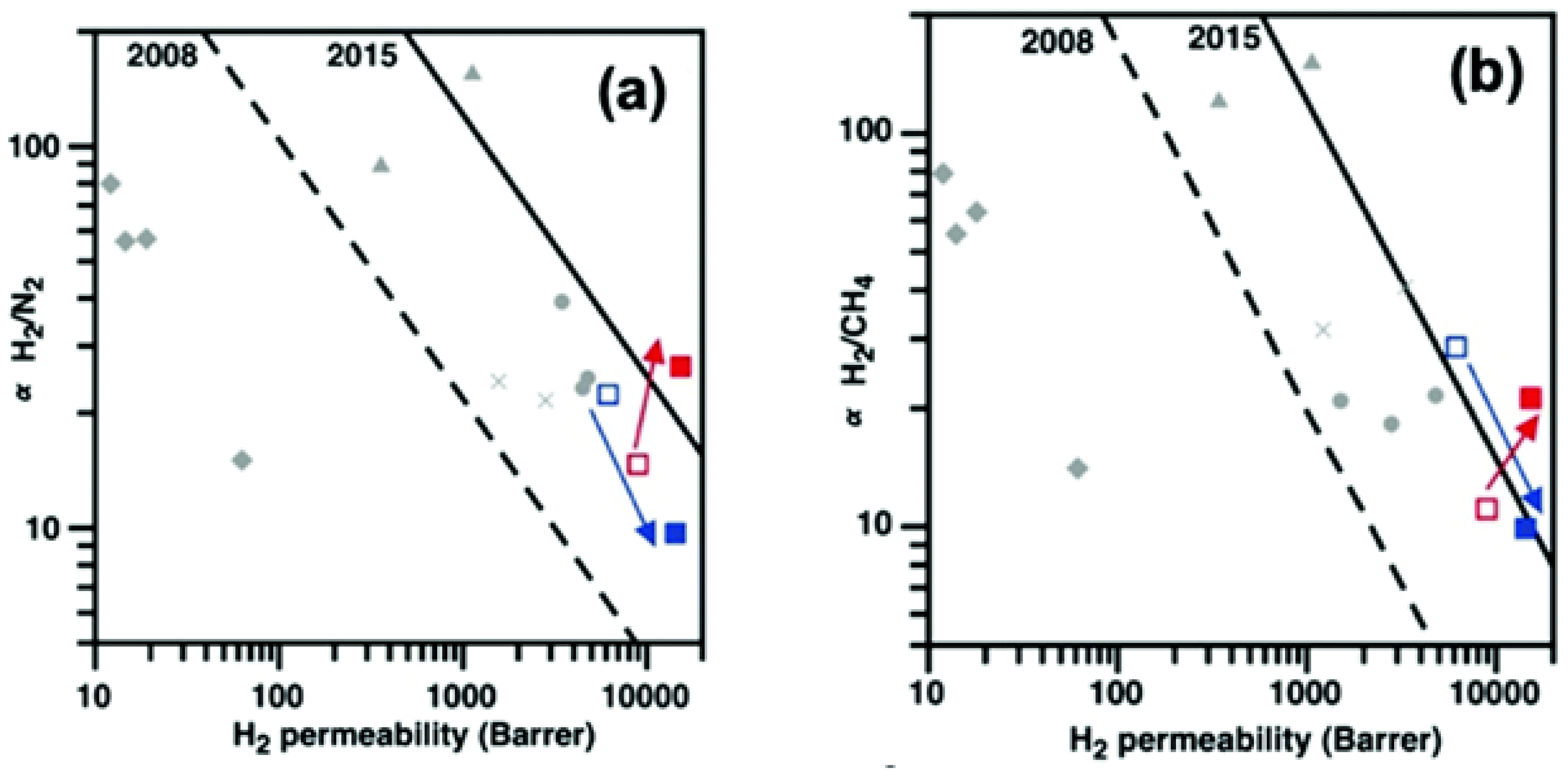
| PIM-EA-TB | PAF-1 (10%) | Porous framew. | +80% | H2/N2 and H2/CH4 | [116] |
| TPIM-2 | PAF-1 (5%) | Porous framew. | +42% | H2/N2 and H2/CH4 | [120] |
| PC | PhCH2NH2 (20%) | Porous framew. | +43% | H2/CH4 and CO2/CH4 | [122] |
| Matrix | Filler a | Type | Permeability Improvement b | Main Gases c | |
| 6FDA-6FpDA | Triptycene-isatin (30%) | Porous framew. | +170% | CO2 and N2 | [126] |
| Matrimid® 5218 | BILPs (24%) | Porous framew. | +181% | CO2 and N2 | [55] |
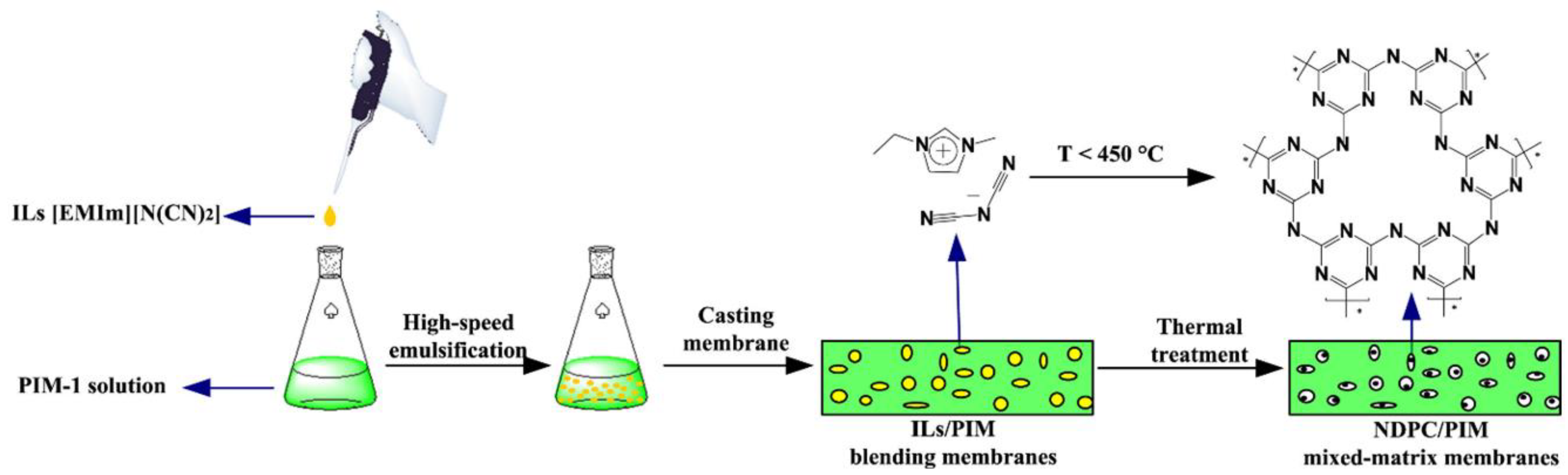
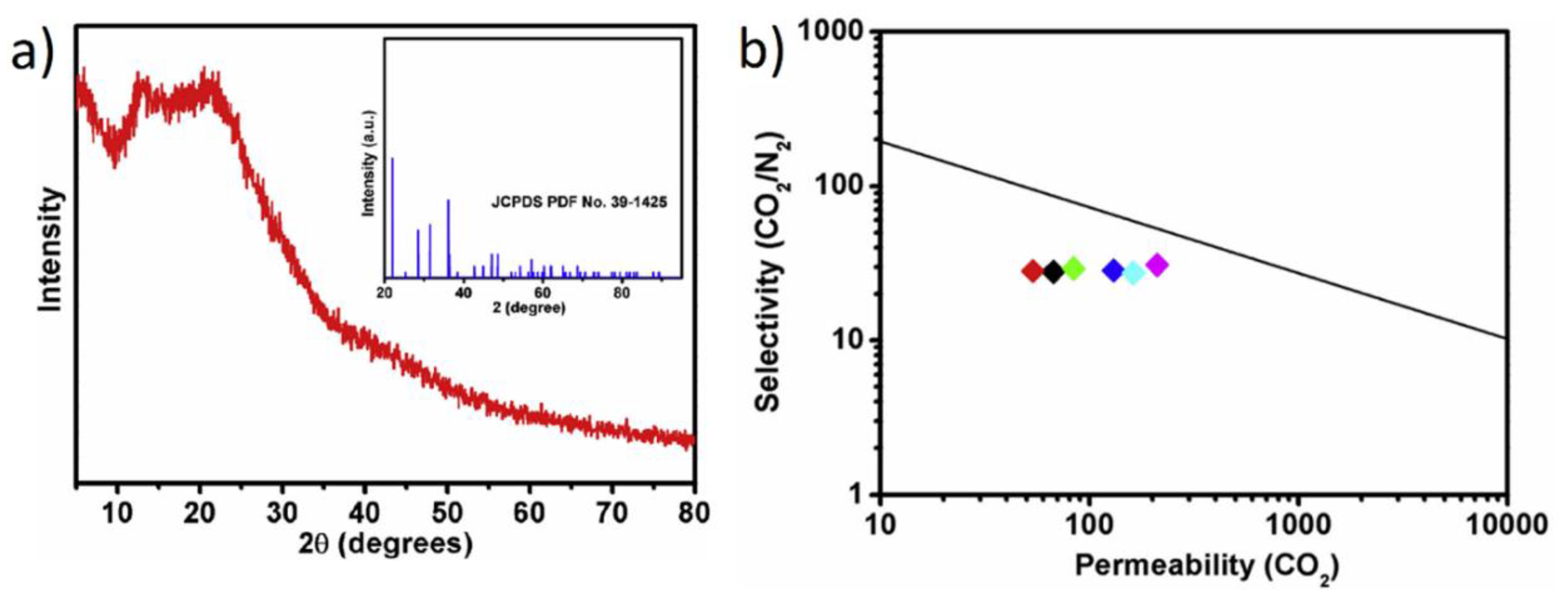
| PIM-1 | NDPC (5%) | Porous framew. | +650% | CO2 and N2 | [127] |
| PEGDA | POP (0.5%) | Network polym. | +47% | CO2, CH4 and N2 | [129] |
| Matrimid® | Triazine-fluorene (24%) | Porous framew. | +161% | CO2, CH4 and N2 | [130] |
| ODPA-TFMB | Silica nanoparticles (20%) | Mesoporous filler | +213% | CO2 and N2 | [131] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carta, M.; Antonangelo, A.R.; Jansen, J.C.; Longo, M. The Difference in Performance and Compatibility between Crystalline and Amorphous Fillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation (MMMs). Polymers 2023, 15, 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132951
Carta M, Antonangelo AR, Jansen JC, Longo M. The Difference in Performance and Compatibility between Crystalline and Amorphous Fillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation (MMMs). Polymers. 2023; 15(13):2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132951
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarta, Mariolino, Ariana R. Antonangelo, Johannes Carolus Jansen, and Mariagiulia Longo. 2023. "The Difference in Performance and Compatibility between Crystalline and Amorphous Fillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation (MMMs)" Polymers 15, no. 13: 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132951
APA StyleCarta, M., Antonangelo, A. R., Jansen, J. C., & Longo, M. (2023). The Difference in Performance and Compatibility between Crystalline and Amorphous Fillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation (MMMs). Polymers, 15(13), 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132951