Starch Physicochemical Properties of Normal Maize under Different Fertilization Modes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Starch Isolation
2.3. Starch Granule Size Distribution
2.4. Amylopectin Chain Length Distribution
2.5. Molecular Weight Distribution
2.6. X-ray Diffraction Pattern
2.7. Pasting Properties
2.8. Thermal Properties
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
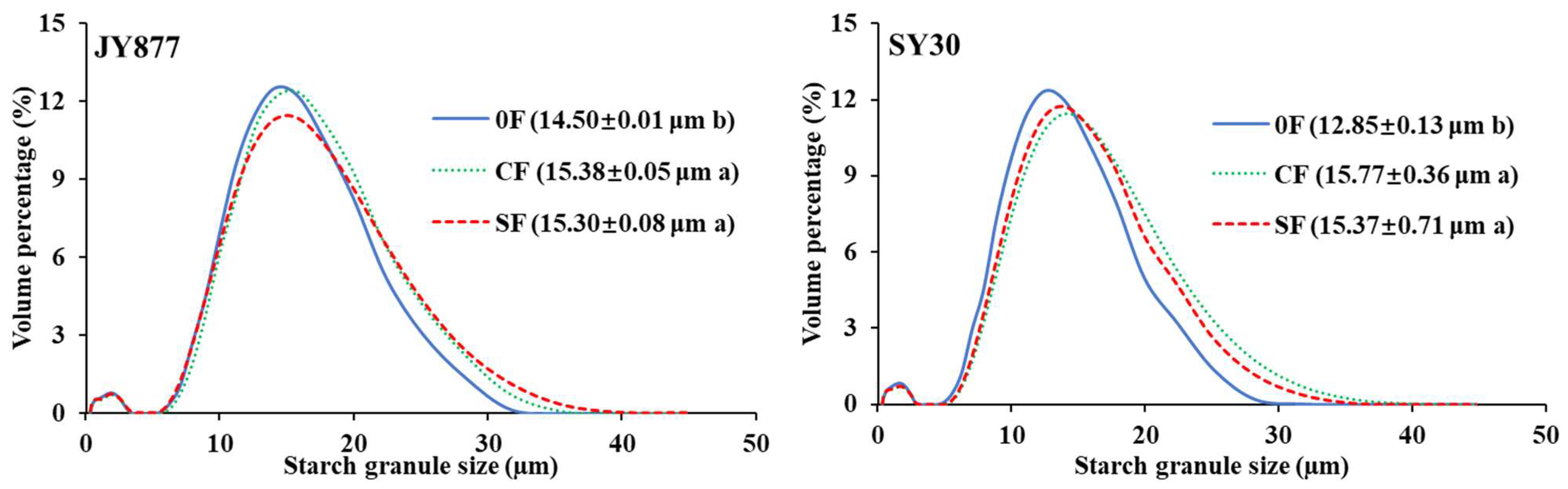
3.1. Starch Granule Size
3.2. Molecular Weight Distribution
3.3. Amylopectin Chain Length Distribution
3.4. XRD Pattern
3.5. Pasting Property
3.6. Thermal Property
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaplan, M.; Karaman, K.; Kardes, Y.M.; Kale, H. Phytic acid content and starch properties of maize (Zea mays L.): Effects of irrigation process and nitrogen fertilizer. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correndo, A.A.; Fernandez, J.A.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Ciampitti, I.A. Do Water and Nitrogen Management Practices Impact Grain Quality in Maize? Agronomy 2021, 11, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P. Timing and rate of nitrogen application influence grain quality and yield in maize planted at high and low densities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Jahangirlou, M.R.; Akbari, G.A.; Alahdadi, I.; Soufizadeh, S.; Parsons, D. Grain Quality of Maize Cultivars as a Function of Planting Dates, Irrigation and Nitrogen Stress: A Case Study from Semiarid Conditions of Iran. Agriculture 2021, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wen, Z.R.; Fu, P.X.; Lu, W.P.; Lu, D.L. Effects of Nitrogen Rates on the Physicochemical Properties of Waxy Maize Starch. Starch-Stärke 2019, 71, 1900146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Xu, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wu, Y.F.; Yu, X.R.; Chen, G.; Xiong, F. Agronomic Traits and Physicochemical Properties of Starch of Different Grain Positions in Wheat Spike Under Nitrogen Treatment. Starch-Stärke 2022, 74, 2100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.P.; Yu, X.R.; Li, Y.Q.; Zou, J.C.; Deng, J.W.; Pan, J.Y.; Xiong, F. Analysis of development, accumulation and structural characteristics of starch granule in wheat grain under nitrogen application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3739–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.C.; Bai, W.M.; Xia, M.J.; Wan, C.X.; Wang, M.; Wang, P.K.; Gao, X.L.; Gao, J.F. Diverse effects of nitrogen fertilizer on the structural, pasting, and thermal properties of common buckwheat starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 179, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.C.; Wan, C.X.; Wang, J.L.; Wang, P.K.; Gao, X.L.; Eeckhout, M.; Gao, J.F. Relationship between nitrogen fertilizer and structural, pasting and rheological properties on common buckwheat starch. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 132664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, Q.; Xia, M.; Bai, W.; Wang, P.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Feng, B.; Gao, J. Effects of nitrogen level on the physicochemical properties of Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaertn.) starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xia, M.; Wan, C.; Jia, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, P.; Yang, Q.; Yang, P.; Gao, X.; et al. Analysis of synthesis, accumulation and physicochemical properties of Tartary buckwheat starches affected by nitrogen fertilizer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.J.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, L.H.E.; Zheng, Q.H.; Wang, C.L. Characterization of eating quality and starch properties of two Wx alleles japonica rice cultivars under different nitrogen treatments. J. Integr. Agr. 2020, 19, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.J.; Cong, S.M.; Zhang, H.C. Comparison of the Grain Quality and Starch Physicochemical Properties between Japonica Rice Cultivars with Different Contents of Amylose, as Affected by Nitrogen Fertilization. Agriculture 2021, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, W.; Qiu, S.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; Xing, Z.; Hu, Y.; Guo, B.; et al. Effects of mid-stage nitrogen application timing on the morphological structure and physicochemical properties of japonica rice starch. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, E.; Yuan, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Gu, J. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on structure and physicochemical properties of ‘super’ rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.Y.; Li, Z.K.; Li, E.P.; Wang, W.L.; Yuan, L.M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Gu, J.F.; Yang, J.C. Optimization of nitrogen fertilization improves rice quality by affecting the structure and physicochemical properties of starch at high yield levels. J. Integr. Agr. 2022, 21, 1576–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.M.; Sun, H.Y.; Wang, C.G.; Ren, X.J.; Liu, H.F.; Zhang, Z.J. Effects of late-stage nitrogen fertilizer application on the starch structure and cooking quality of rice. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2018, 98, 2332–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.W.; Zhang, H.C.; Guo, B.W.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.G.; Wei, C.X.; Wei, H.Y.; Gao, H.; Hu, Y.J.; Cui, P.Y.; et al. Effect of Nitrogen Management on the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Rice Starch. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8019–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.J.; Fan, J.L.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Zhang, F.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yan, S.C.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, J.M.; Zheng, J.; Yan, F.L. Synchronizing nitrogen supply and uptake by rainfed maize using mixed urea and slow-release nitrogen fertilizer. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2022, 122, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.Y.; Chen, Z.F.; Xing, Z.P.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Y.J.; Zhu, J.Y.; Cui, P.Y.; et al. Effects of slow or controlled release fertilizer types and fertilization modes on yield and quality of rice. J. Integr. Agr. 2018, 17, 2222–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, M.A.; Irshad, M.; Irshad, S.; Khan, S.; Hasnain, Z.; Ibrar, D.; Khan, A.R.; Saleem, M.F.; Bashir, S.; Alotaibi, S.S.; et al. Nitrogenous Fertilizer Coated With Zinc Improves the Productivity and Grain Quality of Rice Grown Under Anaerobic Conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 914653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chen, T.T.; Zheng, J.L.; Sun, Y.D.; Chi, D.C. Soil nitrogen regulation using clinoptilolite for grain filling and grain quality improvements in rice. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Ying, Z.; Zhu, H.B.; Qun, H.; Liu, G.D.; Wei, H.Y.; Zhang, H.C. Effects of a one-time application of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on quality and yield of rice. Food Energy Secur. 2022, e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.J.; Anders, M.; McClung, A. Impact of production practices on physicochemical properties of rice grain quality. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2012, 92, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandino, M.; Marinaccio, F.; Vaccino, P.; Reyneri, A. Nitrogen Fertilization Strategies Suitable to Achieve the Quality Requirements of Wheat for Biscuit Production. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, M.A.; Giuliani, M.M.; Flagella, Z.; Reyneri, A.; Blandino, M. Impact of nitrogen fertilisation strategies on the protein content, gluten composition and rheological properties of wheat for biscuit production. Field Crops Res. 2020, 254, 107829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, D.D.; Liu, M.; Geng, Y.Q. Controlled Release Urea Improved Nitrogen Use Efficiency, Yield, and Quality of Wheat. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, A.; Peltonen-Sainio, P. Slow-release fertilizer to increase grain N content in spring wheat. Agr. Food Sci. 2013, 22, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, I.; Rahman, M.H.U.; Hasnain, M.U.; Ikram, R.M.; Khan, M.A.; Iqbal, R.; Hussain, M.I.; Sabagh, A.E. Effect of slow-release nitrogenous fertilizers on dry matter accumulation, grain nutritional quality, water productivity and wheat yield under an arid environment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, S.Y.; Lu, D.L. Fertilization time of slow-release fertilizer affects the physicochemical properties of starch from spring-sown waxy maize. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2022, 102, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.H.; Ruan, S.H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.R.; Li, S.S.; Wen, W.J.; Liu, H.B. Effects and potential of optimized fertilization practices for rice production in China. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Fu, P.X.; Cheng, G.G.; Lu, W.P.; Lu, D.L. Delaying application time of slow-release fertilizer increases soil rhizosphere nitrogen content, root activity, and grain yield of spring maize. Crop J. 2022, 10, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.L.; Lu, W.P. Effects of protein removal on the physicochemical properties of waxy maize flours. Starch-Stärke 2012, 64, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Gu, X.T.; Lu, W.P.; Lu, D.L. Effects of weak-light stress during grain filling on the physicochemical properties of normal maize starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gu, Z.; Donner, E.; Tetlow, I.; Emes, M. Investigation of digestibility in vitro and physicochemical properties of A- and B-type starch from soft and hard wheat flour. Cereal Chem. 2007, 84, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.S.; Guo, D.W.; Zhao, L.X.; Zhang, X.D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.M.; Wei, C.X. Comparative structure of starches from high-amylose maize inbred lines and their hybrids. Food Hydrocolloid 2016, 52, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.H.; Lin, L.S.; Man, J.M.; Zhao, L.X.; Wang, Z.F.; Wei, C.X. Different Structural Properties of High-Amylose Maize Starch Fractions Varying in Granule Size. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11711–11721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.W.; Zhang, H.C.; Guo, B.W.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.G.; Wei, C.X.; Zhou, G.S.; Huo, Z.Y. Effects of nitrogen level on structure and physicochemical properties of rice starch. Food Hydrocolloid 2017, 63, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeveld, S.M.; van Wijk, R.; Stuurman, N.; Kijne, J.W.; de Pater, S. B-type granule containing protrusions and interconnections between amyloplasts in developing wheat endosperm revealed by transmission electron microscopy and GFP expression. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Blanco, M.; Jane, J. Physicochemical properties of endosperm and pericarp starches during maize development. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.T.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lu, W.P.; Lu, D.L. Starch structural and functional properties of waxy maize under different temperature regimes at grain formation stage. Food Chem. X 2022, 16, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Y.; Bi, J.G.; Gilbert, R.G.; Li, G.H.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, S.H.; Ding, Y.F. Amylopectin chain length distribution in grains of japonica rice as affected by nitrogen fertilizer and genotype. J. Cereal. Sci. 2016, 71, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, H.X.; Liu, W.Z.; Dou, Z.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Chen, W.Z.; Wang, S.H.; Ding, Y.F. Nitrogen fertilizer at heading stage effectively compensates for the deterioration of rice quality by affecting the starch-related properties under elevated temperatures. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, G.M.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, L.T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.L.; Xu, K.; Li, G.H.; et al. The Starch Physicochemical Properties between Superior and Inferior Grains of Japonica Rice under Panicle Nitrogen Fertilizer Determine the Difference in Eating Quality. Foods 2022, 11, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotna, A.; Gambuś, H.; Kratsch, G.; Krawontka, J.; Gambuś, F.; Sabat, R.; Ziobro, R. ffect of Nitrogen Fertilization on the Physico-chemical Properties of Starch Isolated from German Triticale Varieties. Starch-Stärke 2007, 59, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
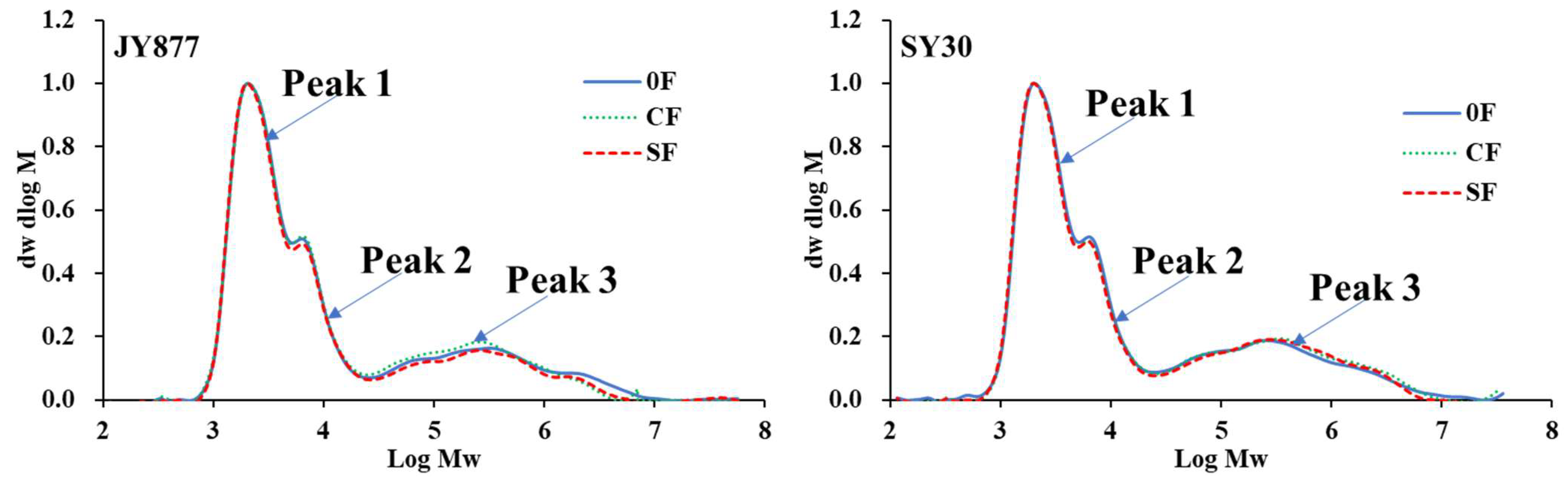
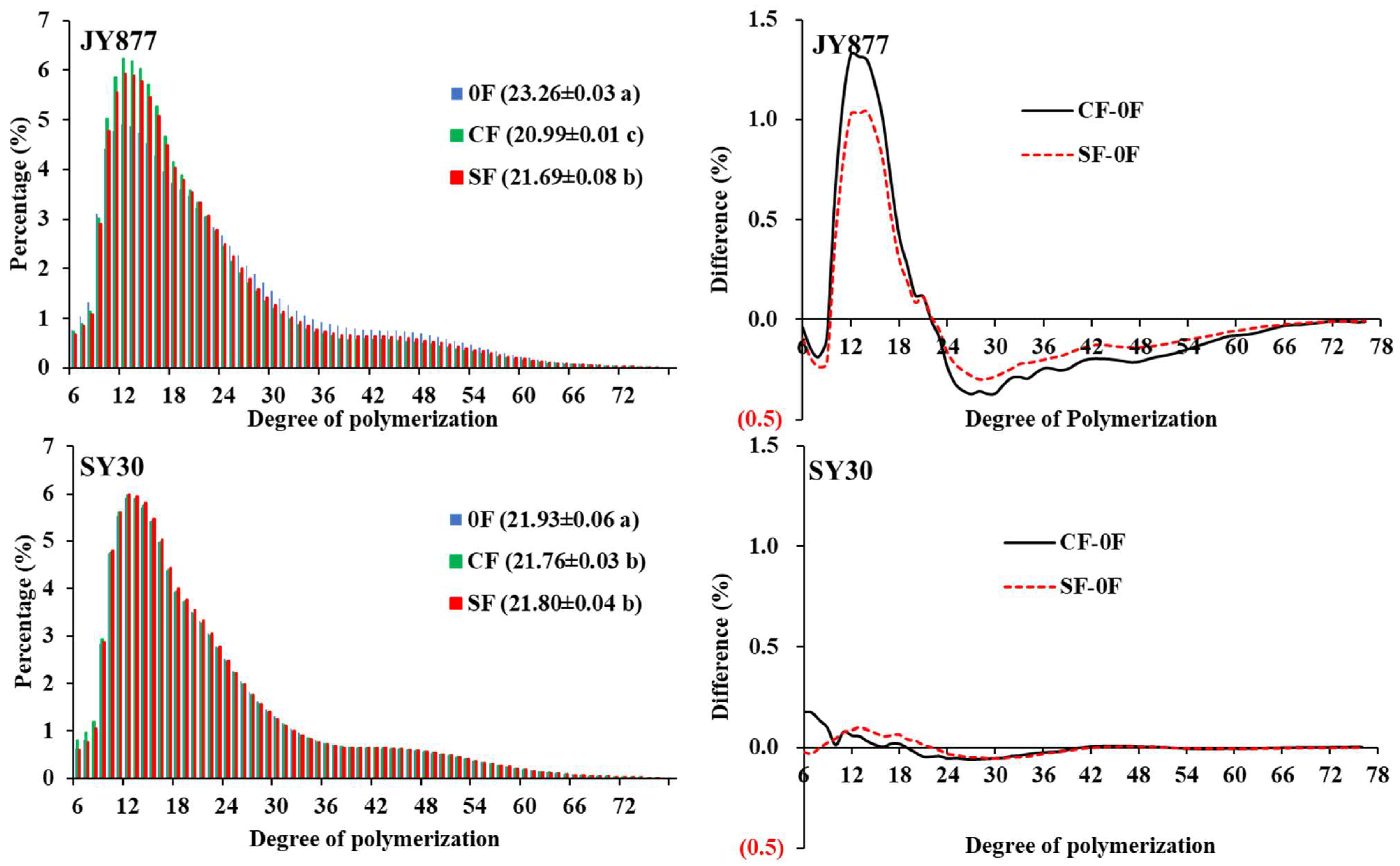

| Hybrid | Fertilization | Peak 1 (%) | Peak 2 (%) | Peak 3 (%) | Peak 1/Peak 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JY877 | 0F | 53.12 ± 0.22 b | 19.58 ± 0.43 b | 27.30 ± 0.21 c | 2.71 ± 0.07 b |
| CF | 52.91 ± 0.06 b | 20.22 ± 0.24 a | 26.87 ± 0.18 c | 2.62 ± 0.03 c | |
| SF | 54.48 ± 0.00 a | 20.13 ± 0.21 a | 25.39 ± 0.21 d | 2.71 ± 0.03 b | |
| SY30 | 0F | 50.48 ± 0.01 c | 18.26 ± 0.79 d | 31.25 ± 0.79 a | 2.77 ± 0.12 a |
| CF | 49.69 ± 0.10 d | 18.92 ± 0.09 c | 31.39 ± 0.19 a | 2.63 ± 0.01 c | |
| SF | 50.81 ± 0.21 c | 18.79 ± 0.07 c | 30.40 ± 0.14 b | 2.70 ± 0.02 b |
| Hybrid | Fertilization | PV (mPa.s) | TV (mPa.s) | BD (mPa.s) | FV (mPa.s) | SB (mPa.s) | Ptemp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JY877 | 0F | 672 ± 31 d | 622 ± 28 e | 50 ± 3 b | 668 ± 27 e | 46 ± 4 c | 86.5 ± 1.3 a |
| CF | 735 ± 12 c | 687 ± 11 c | 47 ± 0 b | 735 ± 13 d | 48 ± 1 c | 87.0 ± 0.4 a | |
| SF | 728 ± 14 c | 698 ± 16 c | 30 ± 2 c | 869 ± 17 a | 170 ± 11 a | 79.1 ± 0.4 b | |
| SY30 | 0F | 689 ± 14 d | 655 ± 11 d | 34 ± 3 c | 786 ± 10 c | 130 ± 5 b | 78.0 ± 0.0 b |
| CF | 864 ± 5 a | 792 ± 10 a | 72 ± 8 a | 910 ± 14 a | 117 ± 24 b | 79.3 ± 1.0 b | |
| SF | 769 ± 67 b | 716 ± 62 b | 54 ± 9 b | 818 ± 68 b | 103 ± 14 b | 79.1 ± 1.0 b |
| Hybrid | Fertilization | ΔHgel (J/g) | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔHret (J/g) | %R (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JY877 | 0F | 10.3 ± 0.3 b | 68.3 ± 0.2 c | 73.4 ± 0.1 b | 80.9 ± 0.2 a | 4.3 ± 0.2 b | 41.9 ± 1.3 c |
| CF | 10.3 ± 0.4 b | 69.4 ± 0.1 a | 74.0 ± 0.0 a | 79.0 ± 0.4 b | 5.4 ± 0.1 a | 52.4 ± 3.3 b | |
| SF | 9.6 ± 0.5 c | 69.6 ± 0.2 a | 74.4 ± 0.0 a | 80.2 ± 0.4 a | 3.2 ± 0.2 d | 32.8 ± 1.1 e | |
| SY30 | 0F | 11.4 ± 0.5 a | 69.1 ± 0.2 b | 73.9 ± 0.1 ab | 80.8 ± 0.5 a | 3.8 ± 0.2 c | 35.8 ± 0.3 d |
| CF | 8.7 ± 0.1 d | 69.5 ± 0.0 a | 74.2 ± 0.0 a | 78.8 ± 0.1 b | 5.4 ± 0.1 a | 61.2 ± 1.8 a | |
| SF | 8.8 ± 0.8 d | 68.5 ± 0.6 c | 73.6 ± 0.3 b | 78.7 ± 0.2 b | 5.2 ± 0.3 a | 59.4 ± 2.5 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Lu, D. Starch Physicochemical Properties of Normal Maize under Different Fertilization Modes. Polymers 2023, 15, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010083
Wang J, Lu D. Starch Physicochemical Properties of Normal Maize under Different Fertilization Modes. Polymers. 2023; 15(1):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010083
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jue, and Dalei Lu. 2023. "Starch Physicochemical Properties of Normal Maize under Different Fertilization Modes" Polymers 15, no. 1: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010083
APA StyleWang, J., & Lu, D. (2023). Starch Physicochemical Properties of Normal Maize under Different Fertilization Modes. Polymers, 15(1), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010083






