Analysis of Correlation between Structure and Properties of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Film Loaded with Eu3+ and Tb3+ Fluorescence by Rheology at Different Drying Stages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of CET Composite
2.2.2. Preparation of Blend Films
2.2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dynamic Rheological Properties of Film Forming Solutions
3.1.1. Drying Kinetics Curves of Film-Forming Solutions
3.1.2. Dynamic Modulus Characterization of the Film-Forming Solutions during the Drying Processes
3.1.3. Han plots of the Film-Forming Solutions during the Drying Processes
3.1.4. Complex Viscosity of the Film-Forming Solutions during the Drying Processes
3.1.5. Study on Relaxation Spectra of the Film-Forming Solutions during the Drying Processes
3.2. Relationship between the Structure and Properties of Blend Films and the Rheology of Film-Forming Solution
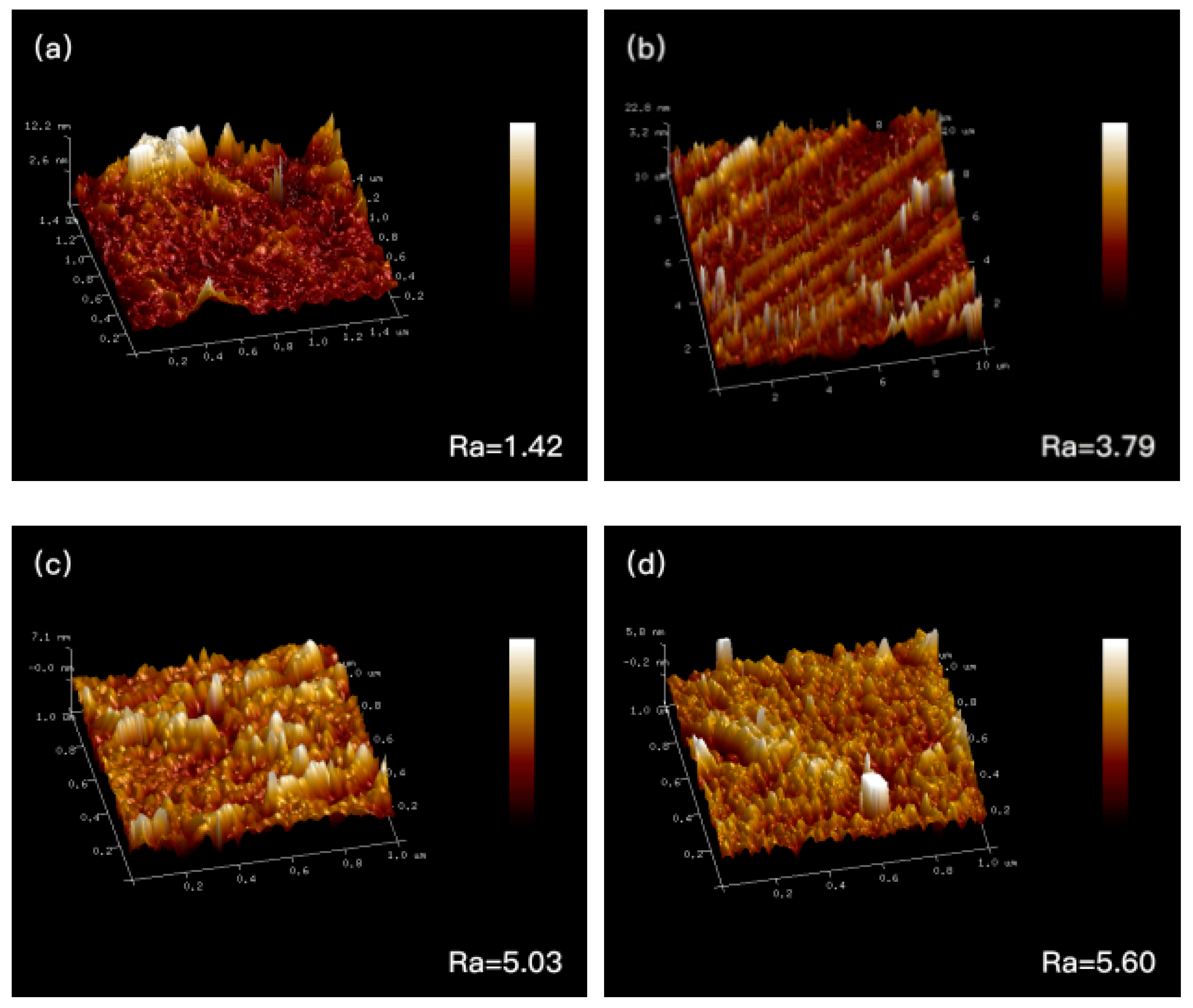
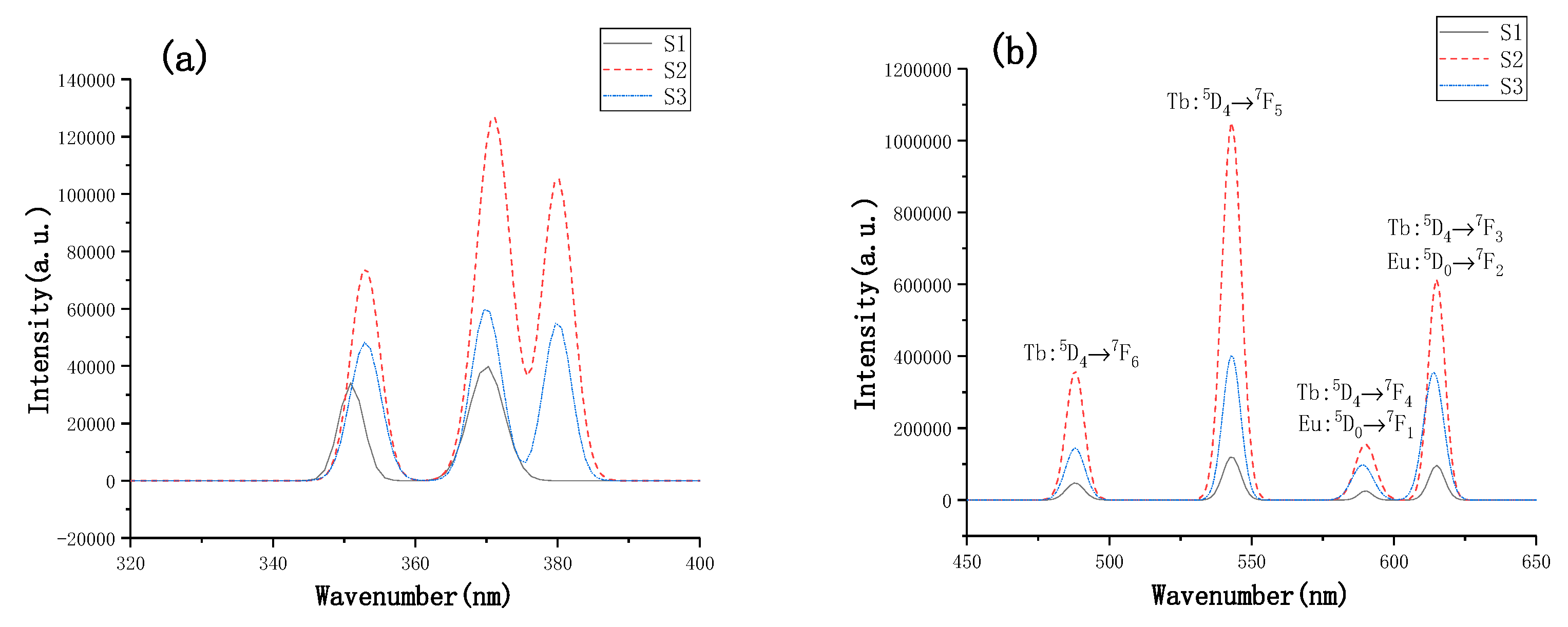
3.2.1. The Relationship between the Morphological Structure of Blend Films and the Rheology of the Film-Forming Solution
3.2.2. The Relationship between the Morphological Structure of Blend Films and the Rheology of Film-Forming Solution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noshirvani, N.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Mokarram, R.R.; Hashemi, M. Novel active packaging based on carboxymethyl cellulose-chitosan-ZnO NPs nanocomposite for increasing the shelf life of bread. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2017, 11, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadiah, M.A.; Zhang, D.; Nagao, Y.; Muzakir, S.K.; Samsudin, A.S. Reducing crystallinity on thin film based CMC/PVA hybrid polymer for application as a host in polymer electrolytes. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 511, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Liu, H.M.; Xiong, J. Preparation and Properties of Fluorescent Cellulosic Paper via Surface Coating of Anionic Cellulose Ethers/Rare Earth Metal Ions Composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 2370–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, D.; Raybon, R.B.; Wheeless, C.R. Hyaluronic acid–carboxymethylcellulose film and perianastomotic adhesions in previously irradiated rats. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 181, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alcantara, C.R.; Rumsey, T.R.; Krochta, A.M. Drying rate effect on the properties of whey protein films. J. Food Process Eng. 1998, 21, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, I.; Schabel, W.; Ferlin, P.; Castaing, J.C.; Kind, M. Drying, film formation and open time of aqueous polymer dispersions. Eur. Phys. J.-Spec. Top. 2009, 166, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayachiew, P.; Devahastin, S. Comparative evaluation of physical properties of edible chitosan films prepared by different drying methods. Dry. Technol. 2008, 26, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersson, M.; Stading, M. Water vapour permeability and mechanical properties of mixed starch-monoglyceride films and effect of film forming conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 19, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasa, P.C.; Ramesh, M.N.; Kumar, K.R.; Tharanathan, R.N. Properties of chitosan films prepared under different drying conditions. J. Food Eng. 2004, 63, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, T.; Hebraud, P.; Lequeux, F. Effects of the rate of evaporation and film thickness on nonuniform drying of film-forming concentrated colloidal suspensions. Eur. Phys. J. E 2005, 17, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Theeranun, J.; Kanitha, T.; Manusawee, L.; Thunyaluck, P.; Chaleeda, B. Effects of Hasten Drying and Storage Conditions on Properties and Microstructure of Konjac Glucomannan-Whey Protein Isolate Blend Films. Food Biophys. 2018, 13, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Gregorova, A.; Saha, N.; Kitano, T.; Saha, P. Hydrothermal effect and mechanical stress properties of carboxymethylcellulose based hydrogel food packaging. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 117, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushanta, G.; Carlos, M.; Paul, D.; Siegfried, S. Heterogeneities in gelatin film formation using single-sided NMR. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 16356–16363. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoshal, S. Study of Polymer Film Formation and Their Characterization Using NMR, XRD and DSC. Ph.D. Thesis, Shaker, Technische Univ. Ilmenau, Aachen, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Gago, M.B.; Krochta, J.M. Drying temperature effect on water vapor permeability and mechanical properties of whey protein-lipid emulsion films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2687–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denavi, G.; Tapia-Blácido, D.R.; Añón, M.C.; Sobral, P.J.A.; Mauri, A.N.; Menegalli, F.C. Effects of drying conditions on some physical properties of soy protein films. J. Food Eng. 2008, 90, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, M.S.; Ko, M.J. Rheological correlations of relaxation time for finite concentrated semiflexible polyelectrolytes in solvents. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2012, 61, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantia, F.P.L.; Ceraulo, M.; Mistretta, M.C.; Morreale, M. Rheological Behaviour, Mechanical Properties and Processability of Biodegradable Polymer Systems for Film Blowing. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munstedt, H.; Steffl, T.; Malmberg, A. Correlation between rheological behaviour in uniaxial elongation and film blowing properties of various polyethylenes. Rheol. Acta 2005, 45, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusova, A.A.; Lipatova, I.M. Rheological and Film-Forming Properties of Mixed Sodium Alginate and Hyaluronate Solutions. Fibre Chem. 2014, 46, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Miri, N.; Abdelouahdi, K.; Barakat, A.; Zahouily, M.; Fihri, A.; Solhy, A.; El Achaby, M. Bio-nanocomposite films reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals: Rheology of film-forming solutions, transparency, water vapor barrier and tensile properties of films. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 129, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Weiss, A.; Bifani, V.; Ihl, M.; Sobral, P.J.A.; Gomez-Guillen, M.C. Structural properties of films and rheology of film-forming solutions based on chitosan and chitosan-starch blend enriched with murta leaf extract. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lofflath, F.; Gebhard, M. Rheological changes during the drying of a waterborne latex coating. J. Coat. Technol. 1997, 69, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Ye, J.; Xiong, J. Energy transfer processes and structure of carboxymethyl cellulose-Tb/Eu nanocomplexes with color-tunable photoluminescence. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Chen, S.; Etzler, F. Rheological characterization of hydroxypropylcellulose gels. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1999, 25, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, S.K.; Seok, K.Y.; Shik, C.G. Rheology of concentrated xanthan gum solutions: Steady shear flow behavior. Fibers Polym. 2006, 7, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Giulia, B.; Marco, C.; Monica, M.-F.; Palmieri, G.F. Rheological evaluation of silicon/carbopol hydrophilic gel systems as a vehicle for delivery of water insoluble drugs. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, H.K.; Han, C.D. Rheological behavior of polymer blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1984, 29, 2205–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.Q.; Kaschta, J.; Pan, Y.M.; Liu, X.H.; Schubert, D.W. Intermolecular cooperativity and entanglement network in a miscible PLA/PMMA blend in the presence of nanosilica. Polymer 2016, 82, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Zuo, M.; Song, Y.H.; Yan, X.P.; Zheng, Q. Dynamic rheology and dielectric relaxation of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/poly(methyl methacrylate) blends. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 106, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L. An Empirical Method for Estimating the Degree of Crystallinity of Native Cellulose Using the X-Ray Diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, M.M. Analysis of flow data on molten polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 1966, 2, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souheng, W. Chain entanglement and melt viscosity of compatible polymer blends: Poly(methyl methacrylate) and poly(styrene-acrylonitrile). Polymer 1987, 28, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Behzadfar, E.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Viscoelastic properties and constitutive modelling of bitumen. Fuel 2013, 108, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnikov, I.E.; Tolstikova, D.V.; Kurochkin, A.V.; Manshina, A.A.; Mikhailov, M.D. Eu3+ concentration effect on luminescence properties of YAG: Eu3+ nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 2014, 37, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wang, B.; Xiong, J.; Sun, R. Enhanced fluorescence and structural characteristics of carboxymethyl cellulose/Eu(III) nano-complex: Influence of reaction time. Carbohyd. Polym. 2016, 135, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-F.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Li, M. Structure and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose/soy protein isolate blend edible films crosslinked by Maillard reactions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 79, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, N.; Saha, N.; Kitano, T.; Saha, P. Biodegradation of PVP–CMC hydrogel film: A useful food packaging material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Almasi, H.; Entezami, A.A. Physical properties of edible modified starch/carboxymethyl cellulose films. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Ye, J.; Xiong, J.; Abidi, N. Structures and High Fluorescence of Novel Nanocomposites of Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Tb(III) Prepared at Different pHs. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, E498–E507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Muhamad, I.I. Physical and Chemical Characterisation of Acrylamide-Based Hydrogels, Aam, Aam/NaCMC and Aam/NaCMC/MgO. J. Inorg. Organomet. P 2017, 27, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Muhamad, I.I.; PaLe, N.; Hashim, Z. Strategies in Improving Properties of Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Smart Applications. In Cellulose-Based Superabsorbent Hydrogels; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 887–908. [Google Scholar]
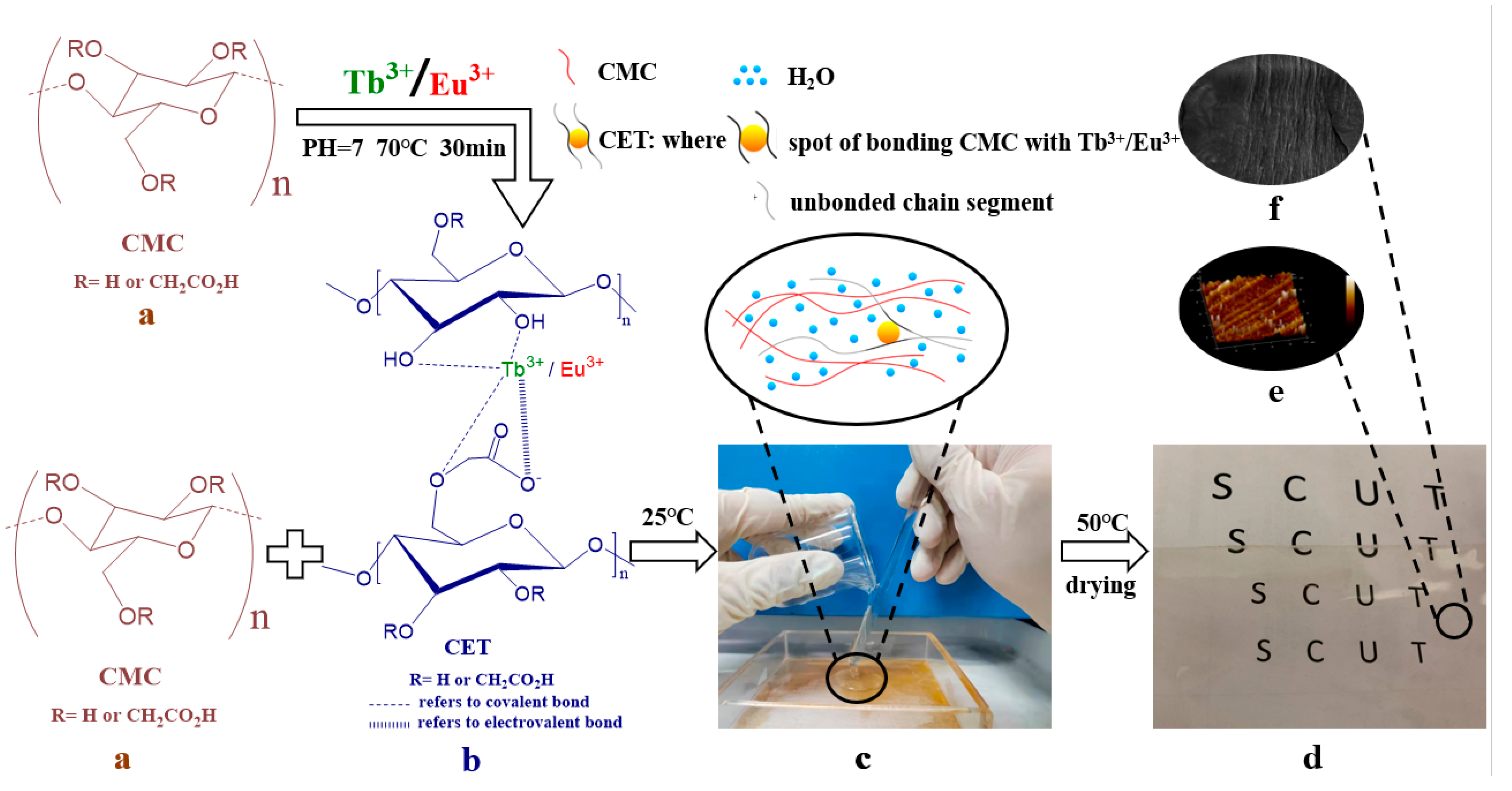
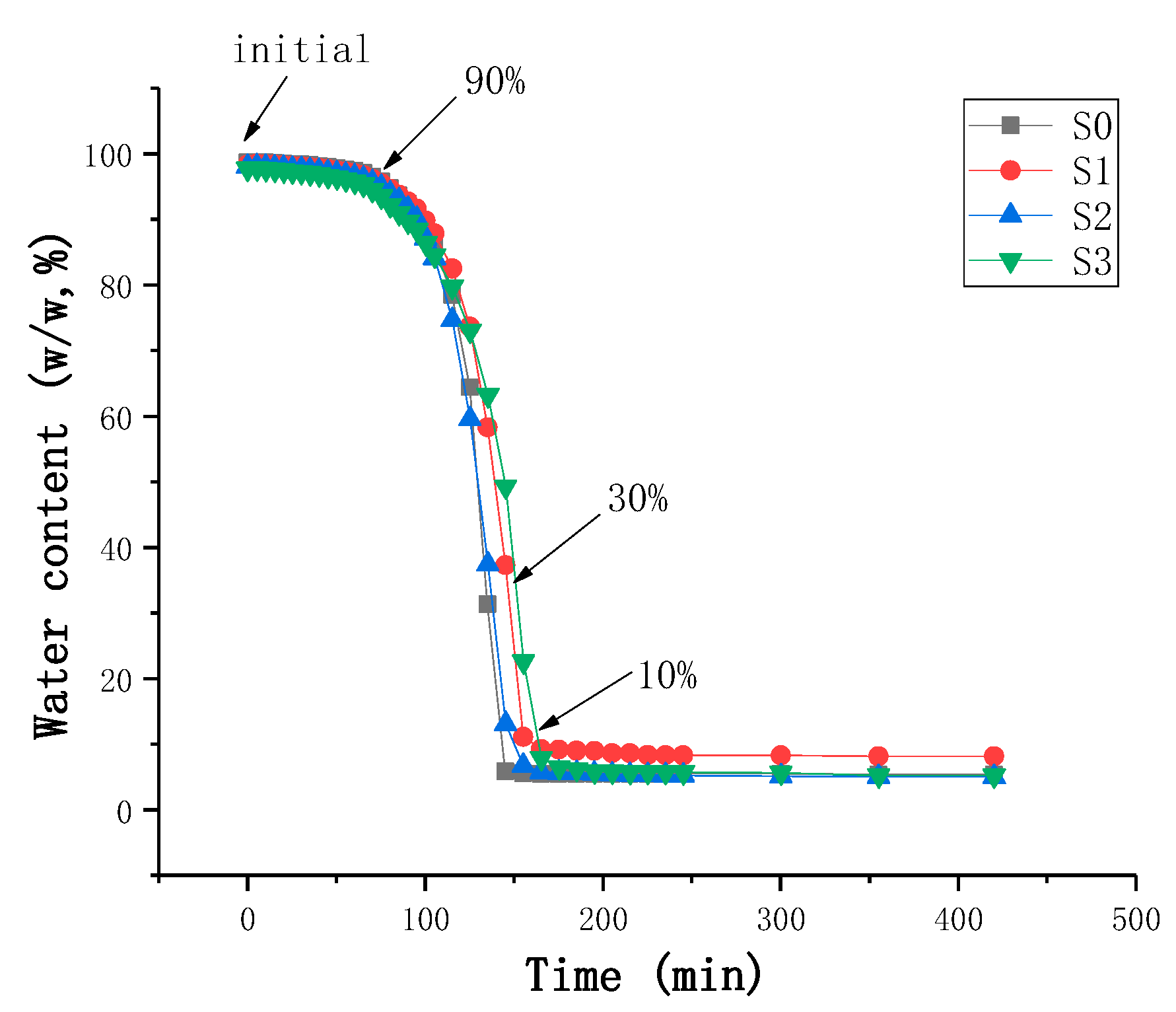


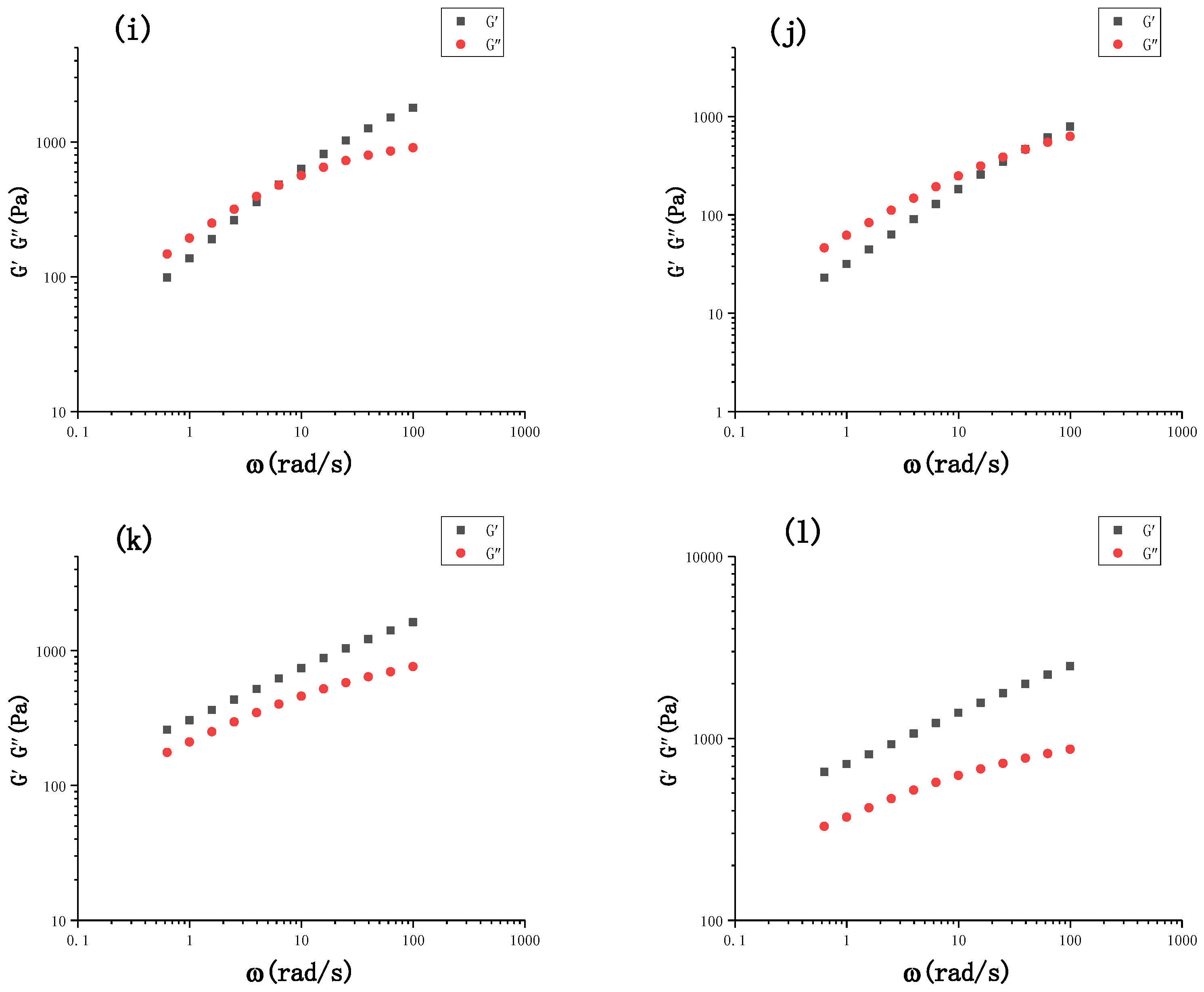

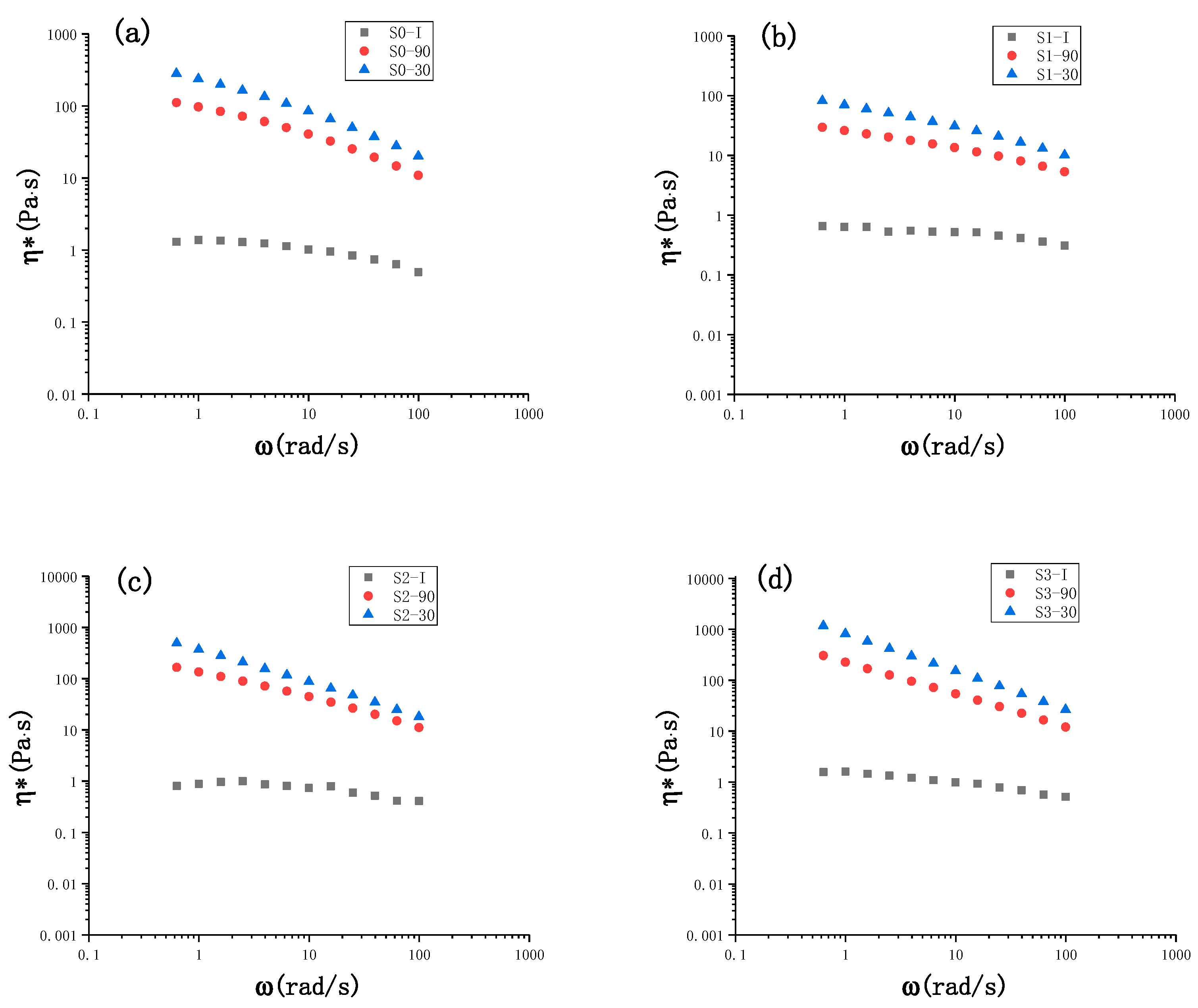




| Film-Forming Solutions | WCMC/g | WCET/g | Vwater/mL | Initial Water Content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 0.4 | 0 | 30 | 98.68 |
| S1 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 30 | 98.36 |
| S2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 30 | 98.04 |
| S3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 30 | 97.72 |
| Sn-I * | Sn-90 * | Sn-30 * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 1.49 | 160.00 | 562.75 |
| S1 | 0.64 | 27.74 | 84.60 |
| S2 | 1.00 | 280.35 | 911.58 |
| S3 | 1.56 | 1372.68 | 5339.03 |
| Film | Tensile Modulus (GPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (mm/mm)% |
|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 2.603 d ± 0.38 | 56.90 b ± 3.47 | 4.26 a ± 0.96 |
| S1 | 3.126 bc ± 0.30 | 57.18 b ± 10.13 | 3.68 b ± 1.04 |
| S2 | 4.037 ab ± 0.37 | 78.76 a ± 3.49 | 3.74 b ± 0.35 |
| S3 | 4.179 a ± 0.16 | 59.25 b ± 6.83 | 2.70 c ± 0.09 |
| Film | Tensile Modulus (GPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Thickness (μm) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMC/SPI film | 1.228 | 65.40 | 109.0 | Su et al. [37] |
| PVP/CMC hydrogel film | 1.423 | 20.93 | - | Roy et al. [38] |
| starch/CMC film | - | 16.11 | 80.0 | Ghanbarzadeh et al. [39] |
| Our work | 4.037 | 78.76 | 41.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Fu, Z.; Rao, J.; Xiong, J. Analysis of Correlation between Structure and Properties of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Film Loaded with Eu3+ and Tb3+ Fluorescence by Rheology at Different Drying Stages. Polymers 2022, 14, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091655
Ye J, Fu Z, Rao J, Xiong J. Analysis of Correlation between Structure and Properties of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Film Loaded with Eu3+ and Tb3+ Fluorescence by Rheology at Different Drying Stages. Polymers. 2022; 14(9):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091655
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Jun, Zichang Fu, Jiawei Rao, and Jian Xiong. 2022. "Analysis of Correlation between Structure and Properties of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Film Loaded with Eu3+ and Tb3+ Fluorescence by Rheology at Different Drying Stages" Polymers 14, no. 9: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091655
APA StyleYe, J., Fu, Z., Rao, J., & Xiong, J. (2022). Analysis of Correlation between Structure and Properties of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Film Loaded with Eu3+ and Tb3+ Fluorescence by Rheology at Different Drying Stages. Polymers, 14(9), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091655





