The Dependence of the Properties of Recycled PET Electrospun Mats on the Origin of the Material Used for Their Fabrication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization of Pristine Unprocessed Materials
2.2.1. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
2.2.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2.3. Surface Hydrophilicity
2.3. Optimization of PET Mats Electrospinning
2.4. Characterization of Fabricated Mats
2.4.1. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
2.4.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.4.4. Surface Hydrophilicity
2.4.5. Tensile Testing
2.5. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of Pristine Materials
3.2. Optimization of Electrospinning
3.3. Physico-Chemical and Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Fibrous Mats
3.4. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kijeński, J. Tworzywa polimerowe w zrównoważonym rozwoju—od potrzeby użycia do potrzeby zużycia. Cz. I. Nie ma odwrotu od “plastików”. Polimery 2019, 64, 725–738. [Google Scholar]
- Kijeński, J. Tworzywa polimerowe w zrównoważonym rozwoju—od potrzeby użycia do potrzeby zużycia. Cz. II. Powrót do monomerów. Polimery 2019, 64, 740–750. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, B.; Marfavi, Y.; AliAkbari, R.; Kowsari, E.; Borbor Ajdari, F.; Ramakrishna, S. Recent Studies on Recycled PET Fibers: Production and Applications: A Review. Mater. Circ. Econ. 2021, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, H.; Yalcin-Enis, I. Turning Plastic Wastes Into Textile Products. In Handbook of Solid Waste Management: Sustainability through Circular Economy; Baskar, C., Ramakrishna, S., Baskar, S., Sharma, R., Chinnappan, A., Sehrawat, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijeńska-Gawrońska, E.; Swieszkowski, W. General requirements of electrospun materials for tissue engineering. In Electrospun Materials for Tissue Engineering and Biomedical Applications: Research, Design and Commercialization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 3–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębski, T.; Kijeńska-Gawrońska, E.; Zołocińska, A.; Siennicka, K.; Słysz, A.; Paskal, W.; Włodarski, P.K.; Święszkowski; Pojda, Z.W. Bioactive Nanofiber-Based Conduits in a Peripheral Nerve Gap Management—An Animal Model Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan, E.; Karacelebi, Y.; Saatcioglu, E.; Ulag, S.; Sahin, A.; Aksu, B.; Croitoru, A.-M.; Codrea, C.I.; Ficai, D.; Gunduz, O.; et al. Fabrication of Electrospun Juglans regia (Juglone) Loaded Poly(lactic acid) Scaffolds as a Potential Wound Dressing Material. Polymers 2022, 14, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orudzhev, F.; Ramazanov, S.; Sobola, D.; Kaspar, P.; Trčka, T.; Částková, K.; Kastyl, J.; Zvereva, I.; Wang, C.; Selimov, D.; et al. Ultrasound and water flow driven piezophototronic effect in self-polarized flexible α-Fe2O3 containing PVDF nanofibers film for enhanced catalytic oxidation. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borojeni, I.A.; Gajewski, G.; Riahi, R.A. Application of Electrospun Nonwoven Fibers in Air Filters. Fibers 2022, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, K.; Zdarta, J.; Grzywaczyka, A.; Degórska, O.; Kijeńska-Gawrońska, E.; Pinelo, M.; Jesionowski, T. Horseradish peroxidase immobilised onto electrospun fibres and its application in decolourisation of dyes from model sea water. Process Biochem. 2020, 102, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijeńska-Gawrońska, E.; Bolek, T.; Bil, M.; Swieszkowski, W. Alignment and bioactive molecule enrichment of bio-composite scaffolds towards peripheral nerve tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4509–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A.; Simşek, M.; Dalkıranoğlu Aldemir, S.; Kazaroglu, N.; Gümüşderelioğlu, M. Honey-based PET or PET/chitosan fibrous wound dressings: Effect of honey on electrospinning process. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaki, M.; Yong, T.; He, W.; Ramakrishna, S. Surface engineering of electrospun polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibers towards development of a new material for blood vessel engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar]
- Bonfim, D.P.F.; Cruz, F.G.S.; Bretas, R.E.S.; Guerra, V.G.; Aguiar, M.L. A Sustainable Recycling Alternative: Electrospun PET-Membranes for Air Nanofiltration. Polymers 2021, 13, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, N.E.; Gillan, M.; Sweetser, D. Recycled PET Nanofibers for Water Filtration Applications. Polymers 2016, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strain, I.N.; Wu, Q.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Olsson, R.T.; Andersson, R.L. Electrospinning of recycled PET to generate tough mesomorphic fibre membranes for smoke filtration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 3, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Münchow, E.A.; Albuquerque, M.T.; Zero, B.; Kamocki, K.; Piva, E.; Gregory, R.L.; Bottino, M.C. Development and characterization of novel ZnO-loaded electrospun membranes for periodontal regeneration. Dent. Mater. Off. Publ. Acad. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1038–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; International Organization for Standarization. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- ISO 10993-12:2012; International Organization for Standarization. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- EFSA. Guidelines on submission of a dossier for safety evaluation by the EFSA of a recycling process to produce recycled plastics intended to be used for manufacture of materials and articles in contact with food—Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC). EFSA J. 2008, 6, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mejzler, D. Random degradation of chain polymers accompanied by partial dissolution of the degraded material. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Gen. Pap. 1964, 2, 1341–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.R.; Foreman, J.P. The response of aerospace composites to temperature and humidity. In Polymer Composites in the Aerospace Industry, 2nd ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Composites Science and Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Thorston, UK, 2020; pp. 253–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.P.; Silva, M.; Lima, É.P., Jr.; Paula, A.; Tommasini, F. Processing and Characterization of PET Composites Reinforced with Geopolymer Concrete Waste. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurusu, R.S.; Demarquette, N. Surface modification to control the water wettability of electrospun mats. Int. Mater. Rev. 2018, 64, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veleirinho, B.; Coelho, D.S.; Dias, P.F.; Maraschin, M.; Pinto, R.; Cargnin-Ferreira, E.; Peixoto, A.; Souza, J.A.; Ribeiro-do-Valle, R.M.; Lopes-da-Silva, J.A. Foreign body reaction associated with PET and PET/chitosan electrospun nanofibrous abdominal meshes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Additives for Mechanical Plastic Recycling. Available online: https://www.basf.com/ru/ru/media/news-releases/2013/07/p-13-307.html?fbclid=IwAR29d-CqHllifESijytqVwJsp6UXE9MXsag15QIrIuNzAO3nslsHdeg7kaE (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Liu, Y.; Park, M.; Ding, B.; Kim, J.; El-Newehy, M.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Kim, H.-Y. Facile electrospun Polyacrylonitrile/poly(acrylic acid) nanofibrous membranes for high efficiency particulate air filtration. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Wu, D.-Y.; Wang, S.-S. Bio-based polymer nanofiber with siliceous sponge spicules prepared by electrospinning: Preparation, characterisation, and functionalisation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 108, 110506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
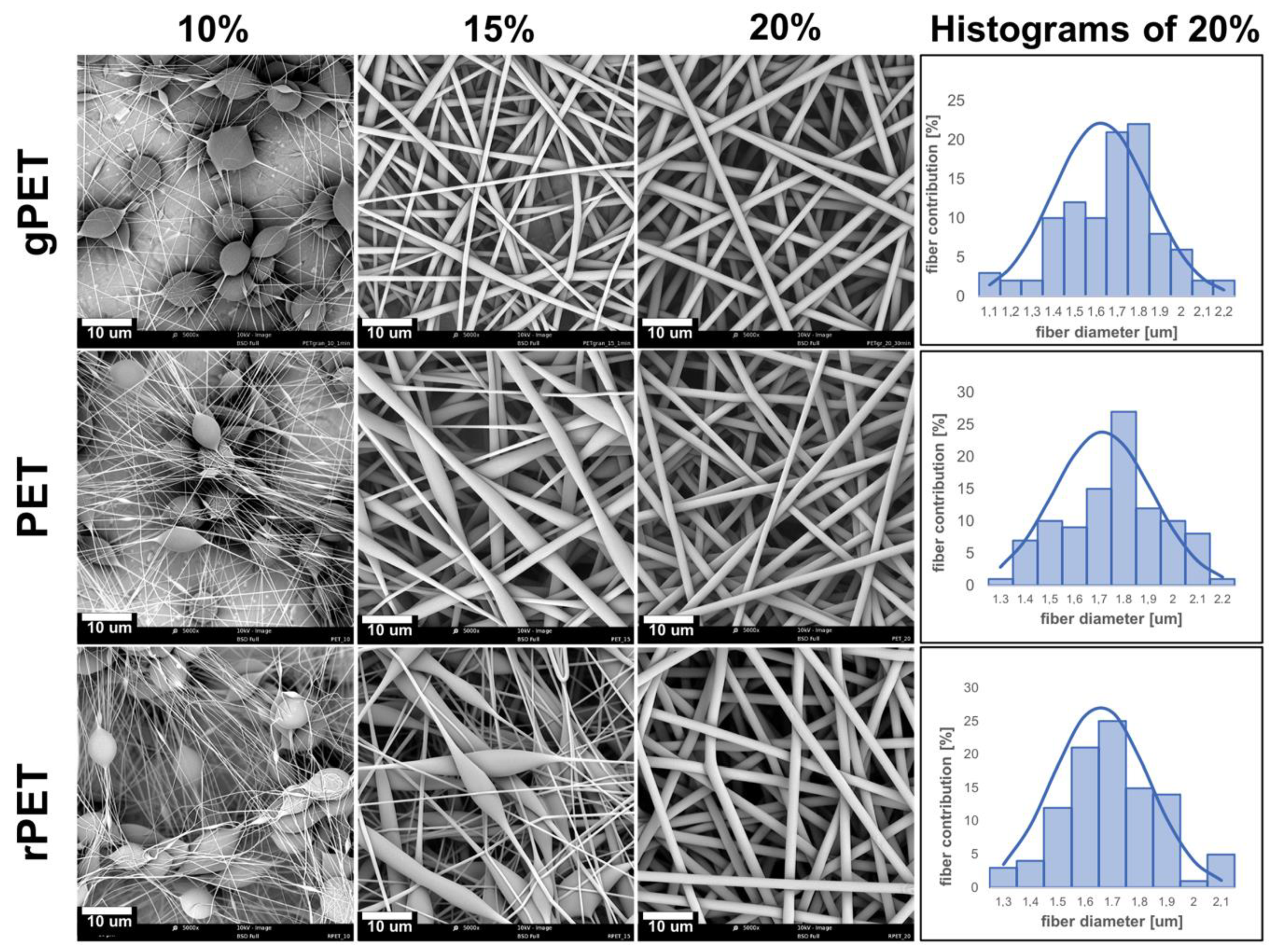
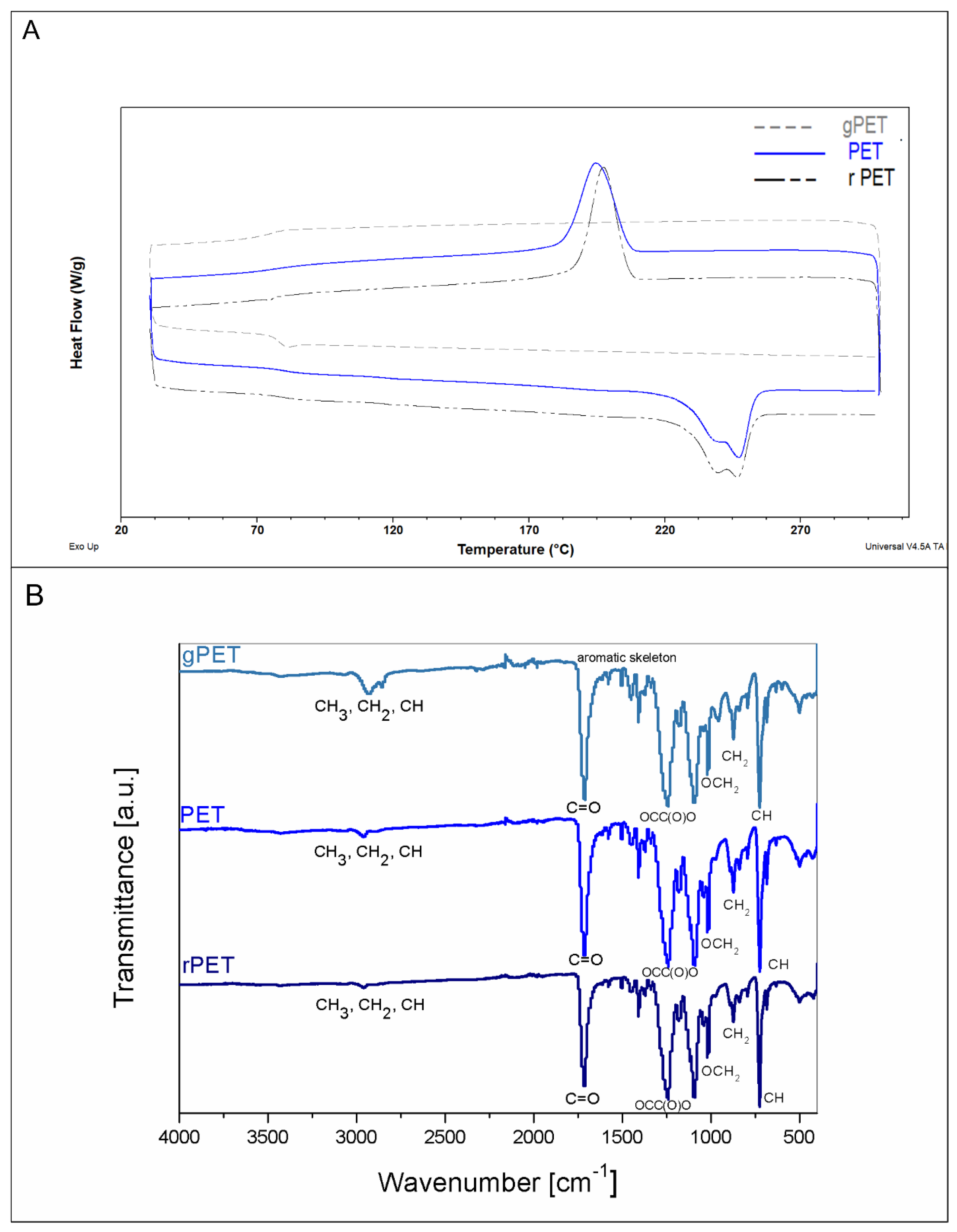


| PET Granulate | PET Bottles | Bottles from Recycled PET | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration [% (w/v)] | 10 | 15 | 20 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| Voltage [kV] | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Flow rate [mL/h] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Needle diameter [G] | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 |
| Needle to collector distance [cm] | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| Properties | PET Granulate | PET Bottles | Bottles from Recycled PET |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mw [g/mol] | 61,800 | 56,600 | 58,200 |
| Mn [g/mol] | 16,300 | 17,400 | 13,400 |
| PDI | 3.784 | 3.250 | 4.091 |
| Crystallinity [%] | 12 | 22 | 21.6 |
| Tg [°C] | 79.74 | 82.88 | 82.23 |
| Tm [°C] | 246.91 | 247.10 | 246.68 |
| Water contact angle [°] | 69 ± 7 | 81 ± 3 | 79 ± 7 |
| Properties | gPET | PET | rPET |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mw [g/mol] | 49,000 | 57,300 | 57,900 |
| Mn [g/mol] | 17,900 | 21,000 | 13,100 |
| PDI | 2.747 | 2.718 | 4.415 |
| Crystallinity [%] | - | 22.2 | 22.4 |
| Tg [°C] | 77.17 | 80.36 | 79.03 |
| Tc [°C] | - | 195.6 | 196.18 |
| Tm [°C] | - | 247.62 | 246.7 |
| ΔHm [J/g] | - | 31.1 | 31.39 |
| Water contact angle [°] | 138 ± 6 | 131 ± 3 | 132 ± 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kijeńska-Gawrońska, E.; Wiercińska, K.; Bil, M. The Dependence of the Properties of Recycled PET Electrospun Mats on the Origin of the Material Used for Their Fabrication. Polymers 2022, 14, 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142881
Kijeńska-Gawrońska E, Wiercińska K, Bil M. The Dependence of the Properties of Recycled PET Electrospun Mats on the Origin of the Material Used for Their Fabrication. Polymers. 2022; 14(14):2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142881
Chicago/Turabian StyleKijeńska-Gawrońska, Ewa, Katarzyna Wiercińska, and Monika Bil. 2022. "The Dependence of the Properties of Recycled PET Electrospun Mats on the Origin of the Material Used for Their Fabrication" Polymers 14, no. 14: 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142881
APA StyleKijeńska-Gawrońska, E., Wiercińska, K., & Bil, M. (2022). The Dependence of the Properties of Recycled PET Electrospun Mats on the Origin of the Material Used for Their Fabrication. Polymers, 14(14), 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142881








