Conductive GelMA–Collagen–AgNW Blended Hydrogel for Smart Actuator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Conductive GelMA–Collagen–AgNW Blended Hydrogel
2.2. Morphological Analysis of the Conductive Blended Hydrogel
2.3. Rheological Analysis of the Conductive Blended Hydrogel
2.4. Biocompatibility Analysis of the Conduvtive Blended Hydrogel
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Measurement of Electrical Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Conductive GelMA–Collagen–AgNW Blended Hydrogel Conditions
3.2. Analysis of Conductive GelMA–Collagen–AgNW Blended Hydrogel Properties
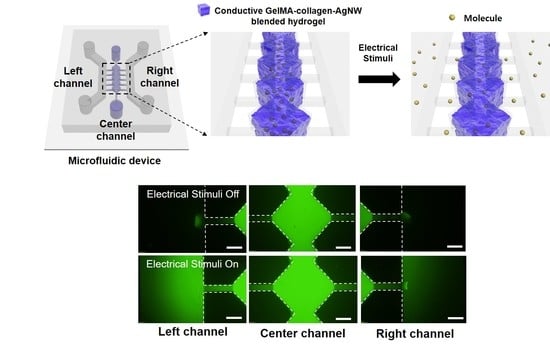
3.3. Conductive Smart Actuator of GelMA–Collagen–AgNW Hydrogel
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whittaker, R.H.; Feeny, P.P. Allelochemics: Chemical interactions between species. Science 1971, 171, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mooney, D.J. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.; Han, J.; Kim, Y.S. Nanocomposite hydrogel actuators hybridized with various dimensional nanomaterials for stimuli responsiveness enhancement. Nano Converg. 2019, 6, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.R.; Yong, K.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Cowie, A.C. Recent advances in photo-crosslinkable hydrogels for biomedical applications. BioTechniques 2019, 66, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascone, S.; Lamberti, G. Hydrogel-based commercial products for biomedical applications: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 573, 118803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C. Advances in biomimetic stimuli responsive soft grippers. Nano Converg. 2019, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.; Xian, C.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, G.; Wu, J. Natural Polymer—Based Hydrogels with Enhanced Mechanical Performances: Preparation, Structure, and Property. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, J.B.; Schmidt, C.E. Characterization of protein release from photocrosslinkable hyaluronic acid-polyethylene glycol hydrogel tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargeant, T.D.; Desai, A.P.; Banerjee, S.; Agawu, A.; Stopek, J.B. An in situ forming collagen–PEG hydrogel for tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D.; Mi, Y.; Li, X.; Fu, R.Z.; Duan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Feng, R.R. A novel human-like collagen hydrogel scaffold with porous structure and sponge-like properties. Polymers 2017, 9, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzewiecki, K.E.; Malavade, J.N.; Ahmed, I.; Lowe, C.J.; Shreiber, D.I. A thermoreversible, photocrosslinkable collagen bio-ink for free-form fabrication of scaffolds for regenerative medicine. Technology 2017, 5, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, T.R.; Kohane, D.S. Hydrogels in drug delivery: Progress and challenges. Polymer 2008, 49, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catoira, M.C.; Fusaro, L.; Di Francesco, D.; Ramella, M.; Boccafoschi, F. Overview of natural hydrogels for regenerative medicine applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Derakhshankhah, H.; Haghshenas, B.; Massoumi, B.; Abbasian, M.; Jaymand, M. A bio-inspired magnetic natural hydrogel containing gelatin and alginate as a drug delivery system for cancer chemotherapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lang, Q.; Yildirimer, L.; Lin, Z.Y.; Cui, W.; Annabi, N.; Ng, K.W.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M.; Khademhosseini, A. Photocrosslinkable gelatin hydrogel for epidermal tissue engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kankala, R.K.; Zhu, K.; Wang, S.-B.; Zhang, Y.S.; Chen, A.-Z. Coaxial extrusion of tubular tissue constructs using a gelatin/GelMA blend bioink. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 5514–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noshadi, I.; Hong, S.; Sullivan, K.E.; Sani, E.S.; Portillo-Lara, R.; Tamayol, A.; Shin, S.R.; Gao, A.E.; Stoppel, W.L.; Black III, L.D. In vitro and in vivo analysis of visible light crosslinkable gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 2093–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, H.; Zhang, D.; Yin, J.; Qian, J.; Wu, Z.L.; Fu, J. Interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels composed of chitosan and photocrosslinkable gelatin with enhanced mechanical properties for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldana, A.A.; Valente, F.; Dilley, R.; Doyle, B. Development of 3D bioprinted GelMA-alginate hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties. Bioprinting 2021, 21, e00105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Lee, H.; Lee, D.; Lee, Y. Highly conductive and flexible silver nanowire-based microelectrodes on biocompatible hydrogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18401–18407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Piao, X.; Yao, X.; Nie, E.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z. A facile method to prepare silver nanowire transparent conductive film for heaters. Mater. Lett. 2019, 249, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Daoud, W.A. Hybrid conductive hydrogels for washable human motion energy harvester and self-powered temperature-stress dual sensor. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, T. Recognition of different rough surface based highly sensitive silver nanowire-graphene flexible hydrogel skin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 21553–21561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Kang, W.S.; Lee, K.G.; Cho, H.-Y.; Conley, B.; Ahrberg, C.D.; Lim, J.H.; Mo, S.J.; Mun, S.G.; Kim, E.-J. Combinatorial biophysical cue sensor array for controlling neural stem cell fate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 156, 112125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Moon, J.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, S.W.; Ahrberg, C.D.; Chung, B.G. Conductive hydrogel/nanowire micropattern-based sensor for neural stem cell differentiation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Wang, X.-Y.; Mi, H.-Y.; Turng, L.-S. Stretchable gelatin/silver nanowires composite hydrogels for detecting human motion. Mater. Lett. 2019, 237, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.H.; Shin, H.H.; Choi, H.W.; Lim, J.H.; Mo, S.J.; Ahrberg, C.D.; Lee, J.M.; Chung, B.G. Electro-responsive hydrogel-based microfluidic actuator platform for photothermal therapy. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, A.; Vagin, M.; Khalaf, H.; Bertazzo, S.; Hodder, P.; Dånmark, S.; Bengtsson, T.; Altimiras, J.; Aili, D. Electroactive biomimetic collagen-silver nanowire composite scaffolds. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14146–14155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, M.R.; Cheong, I.W. Morphological Study on PNIPAAm Hydrogel Microspheres Prepared by Using SPG Membrane Emulsification and UV Photopolymerization. J. Adhes. Interface 2015, 16, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xie, M.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, H.; Nie, J.; Fu, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Shao, L.; Fu, J.; Chen, Z. Electro—Assisted Bioprinting of Low—Concentration GelMA Microdroplets. Small 2019, 15, 1804216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Alvarez, M.M.; Tamayol, A.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Ma, P.; Chen, M.; Dong, W. Long-chain branching hydrogel with ultrahigh tensibility and high strength by grafting via photo-induced polymerization. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 8650–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Dong, X.; Qi, M. Improved tunable range of the field-induced storage modulus by using flower-like particles as the active phase of magnetorheological elastomers. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 3504–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Heyer, P.; Kim, H.-J.; Song, J.-H.; Piao, L.; Kim, S.-H. Reversible macroscopic alignment of Ag nanowires. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3622–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liang, F.; Gou, J. Nanopaper enabled shape-memory nanocomposite with vertically aligned nickel nanostrand: Controlled synthesis and electrical actuation. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 7416–7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Shi, K.; Zhang, L.; Ju, X.-J.; Wang, W.; Xie, R.; Chu, L.-Y. Reduced graphene oxide-containing smart hydrogels with excellent electro-response and mechanical properties for soft actuators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15758–15767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, R.M.; Geddes, L.A. Conduction of electrical current to and through the human body: A review. Eplasty 2009, 9, 407–421. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Yang, B.; An, L.; Li, C.; Chan, Y. Water-driven programmable polyurethane shape memory polymer: Demonstration and mechanism. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J.; Du, S. Qualitative separation of the physical swelling effect on the recovery behavior of shape memory polymer. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ha, J.H.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Cho, H.-Y.; Jo, S.G.; Lee, S.H.; Eom, J.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Chung, B.G. Conductive GelMA–Collagen–AgNW Blended Hydrogel for Smart Actuator. Polymers 2021, 13, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081217
Ha JH, Lim JH, Kim JW, Cho H-Y, Jo SG, Lee SH, Eom JY, Lee JM, Chung BG. Conductive GelMA–Collagen–AgNW Blended Hydrogel for Smart Actuator. Polymers. 2021; 13(8):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081217
Chicago/Turabian StyleHa, Jang Ho, Jae Hyun Lim, Ji Woon Kim, Hyeon-Yeol Cho, Seok Geun Jo, Seung Hyun Lee, Jae Young Eom, Jong Min Lee, and Bong Geun Chung. 2021. "Conductive GelMA–Collagen–AgNW Blended Hydrogel for Smart Actuator" Polymers 13, no. 8: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081217
APA StyleHa, J. H., Lim, J. H., Kim, J. W., Cho, H.-Y., Jo, S. G., Lee, S. H., Eom, J. Y., Lee, J. M., & Chung, B. G. (2021). Conductive GelMA–Collagen–AgNW Blended Hydrogel for Smart Actuator. Polymers, 13(8), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081217