Tough Hydrogels Based on Maleic Anhydride, Bulk Properties Study and Microfiber Formation by Electrospinning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the Hydrogels
2.3. Hydrogel Fibers Fabrication by Electrospinning
2.4. Materials Characterization
2.4.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Thermogravimetric Analyses (TGA)
2.4.2. Compressive Stress/Strain Study
2.4.3. Viscosity Measurements
2.4.4. Swelling Degree
2.4.5. Morphology of Hydrogel Nanofibers
3. Result and Discussion
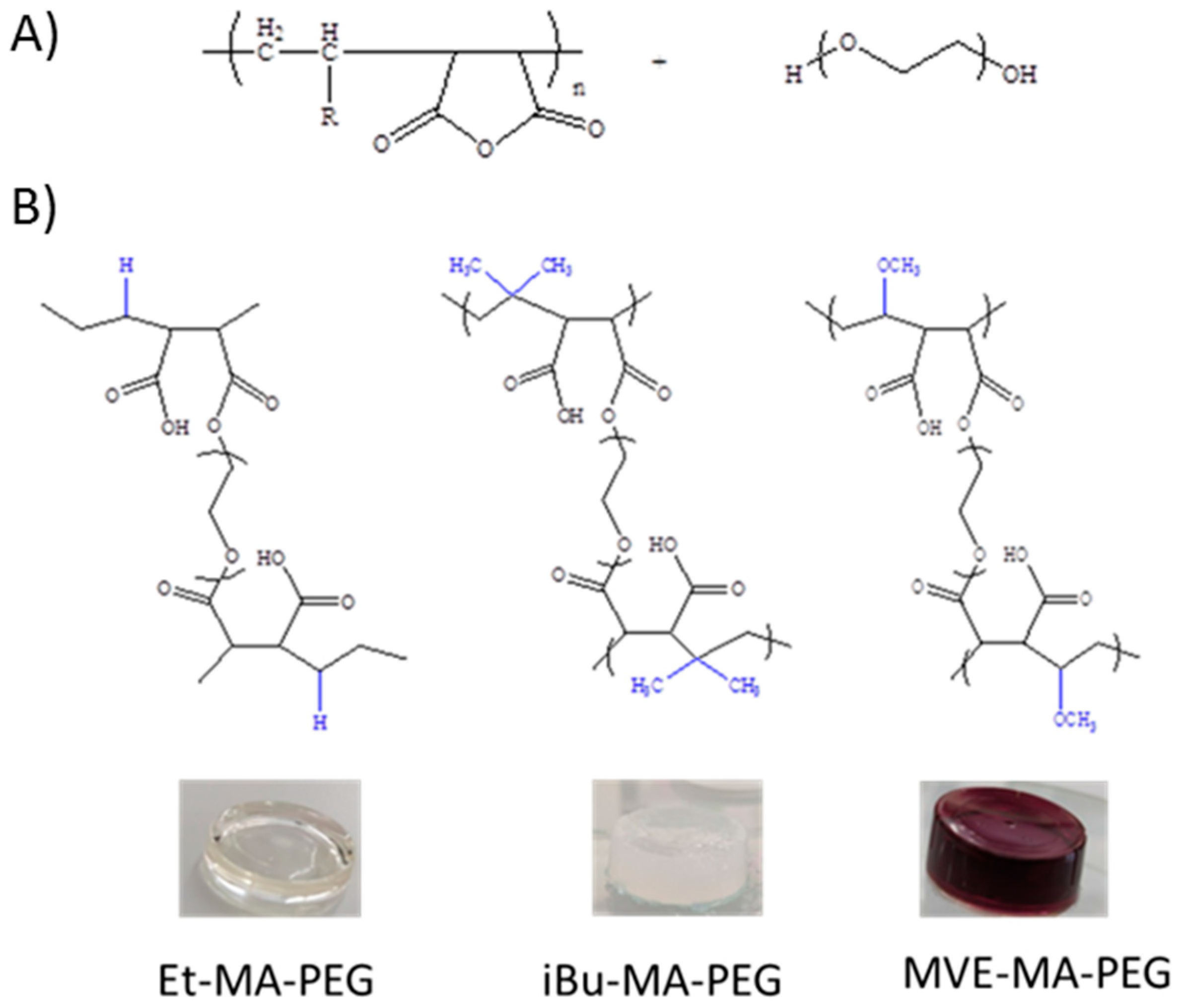
3.1. Maleic Anhydride-Based Hydrogels
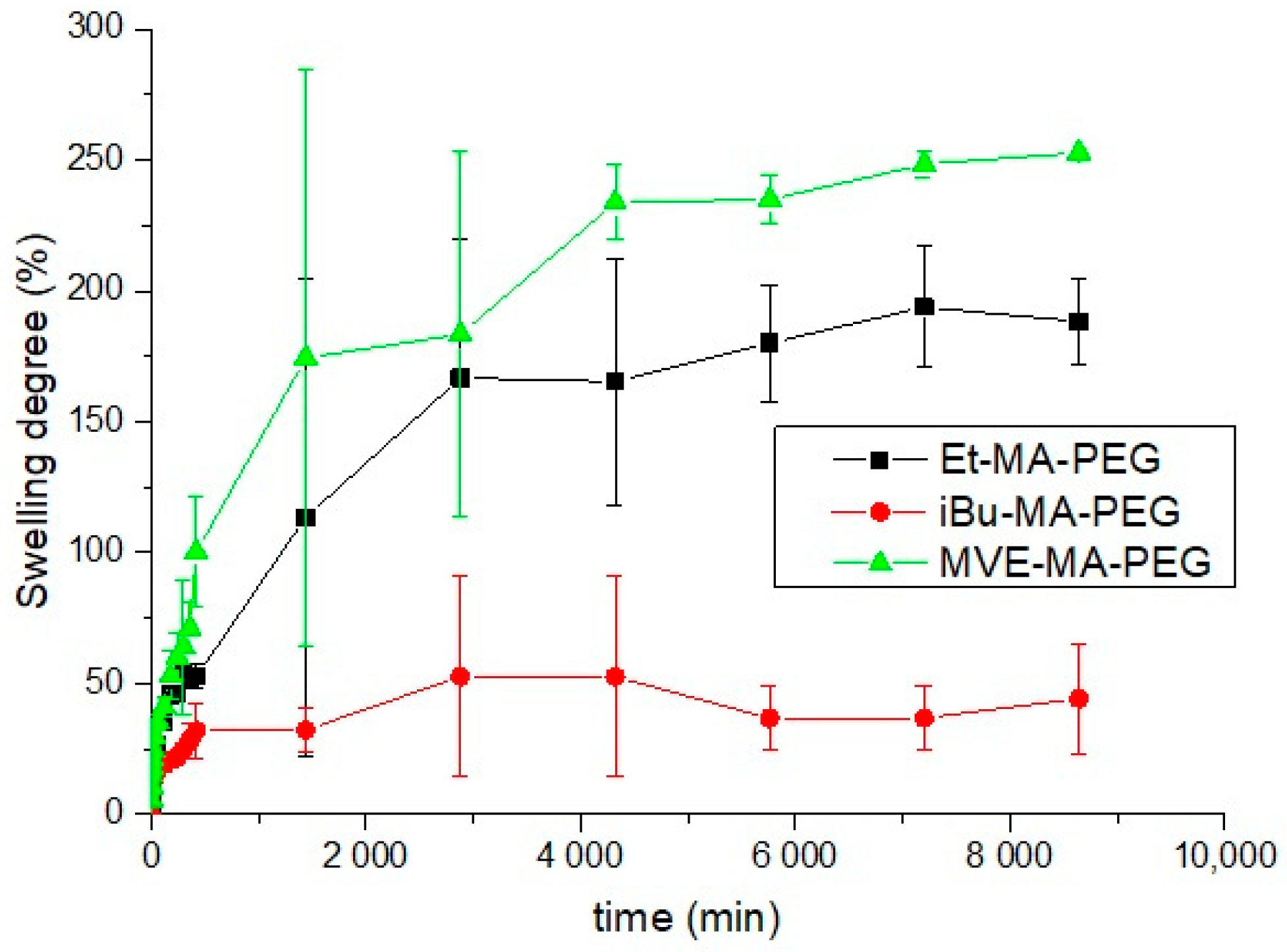
3.2. Swelling Ratio of Hydrogels
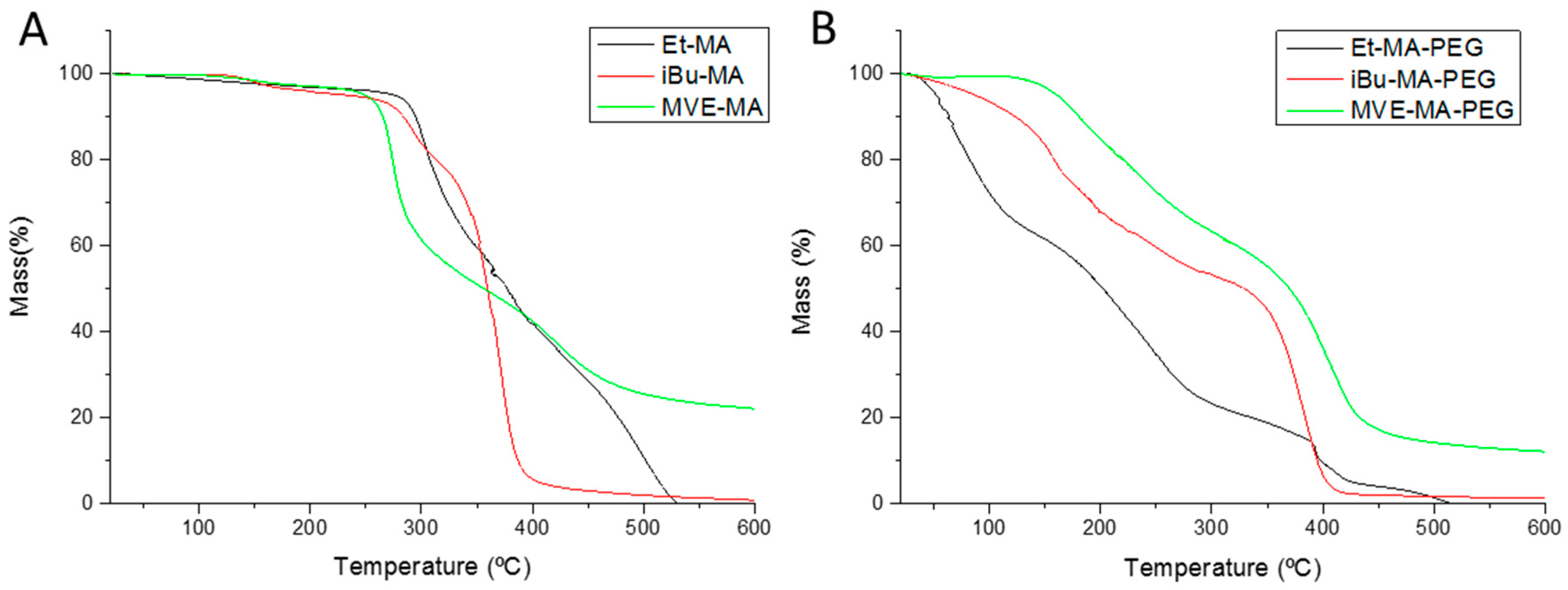
3.3. Thermal Stability of Hydrogels
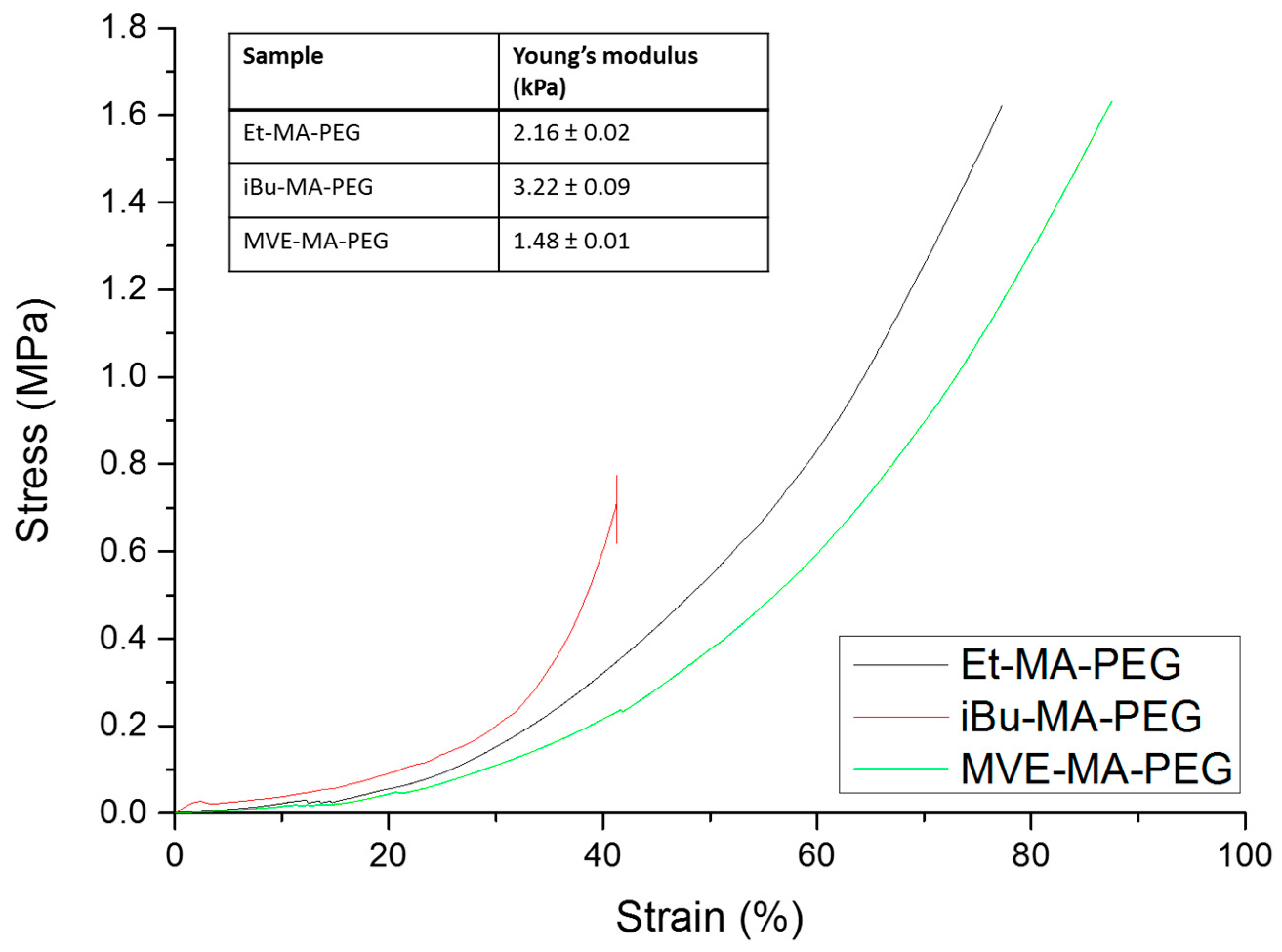
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Hydrogels
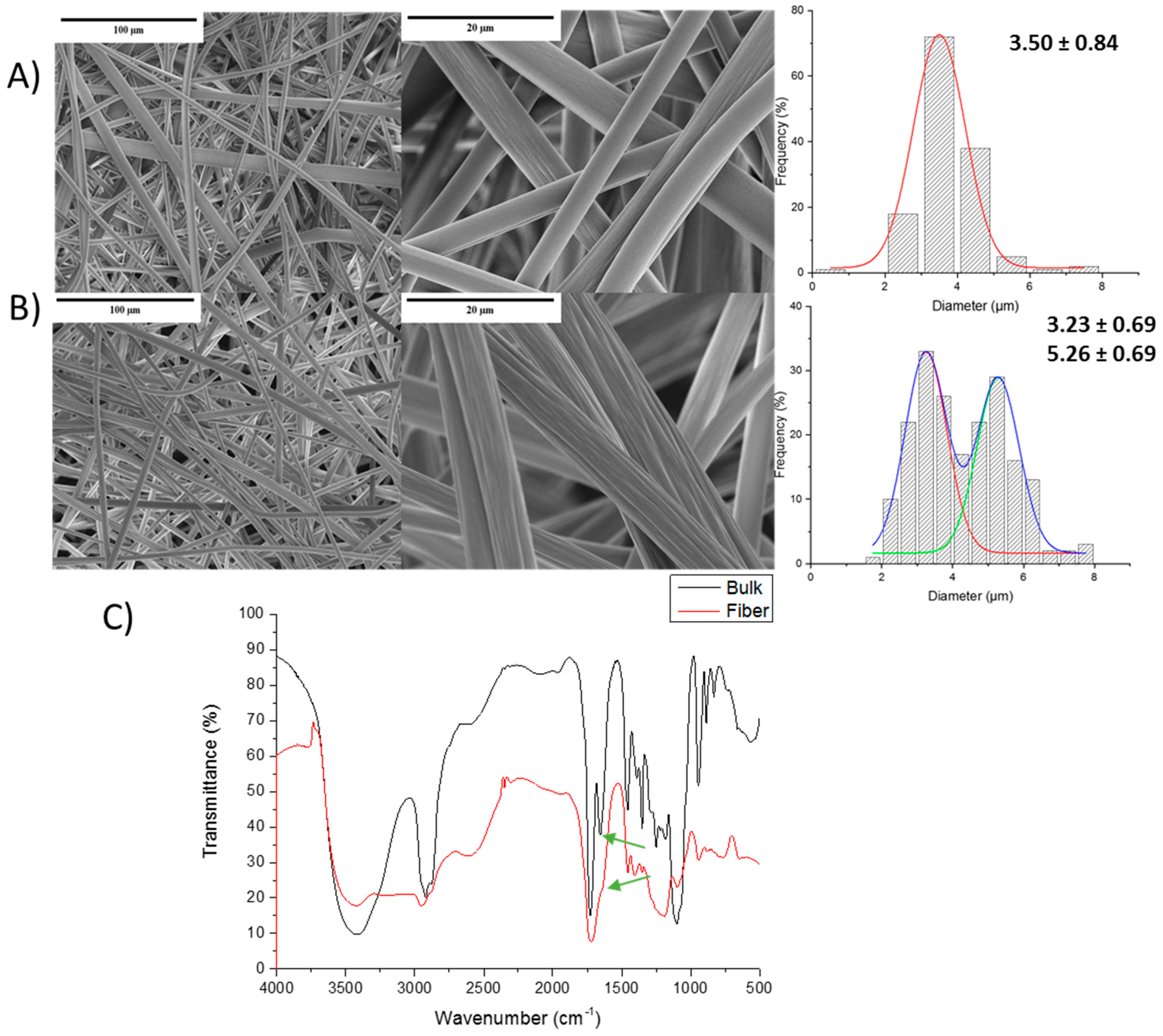
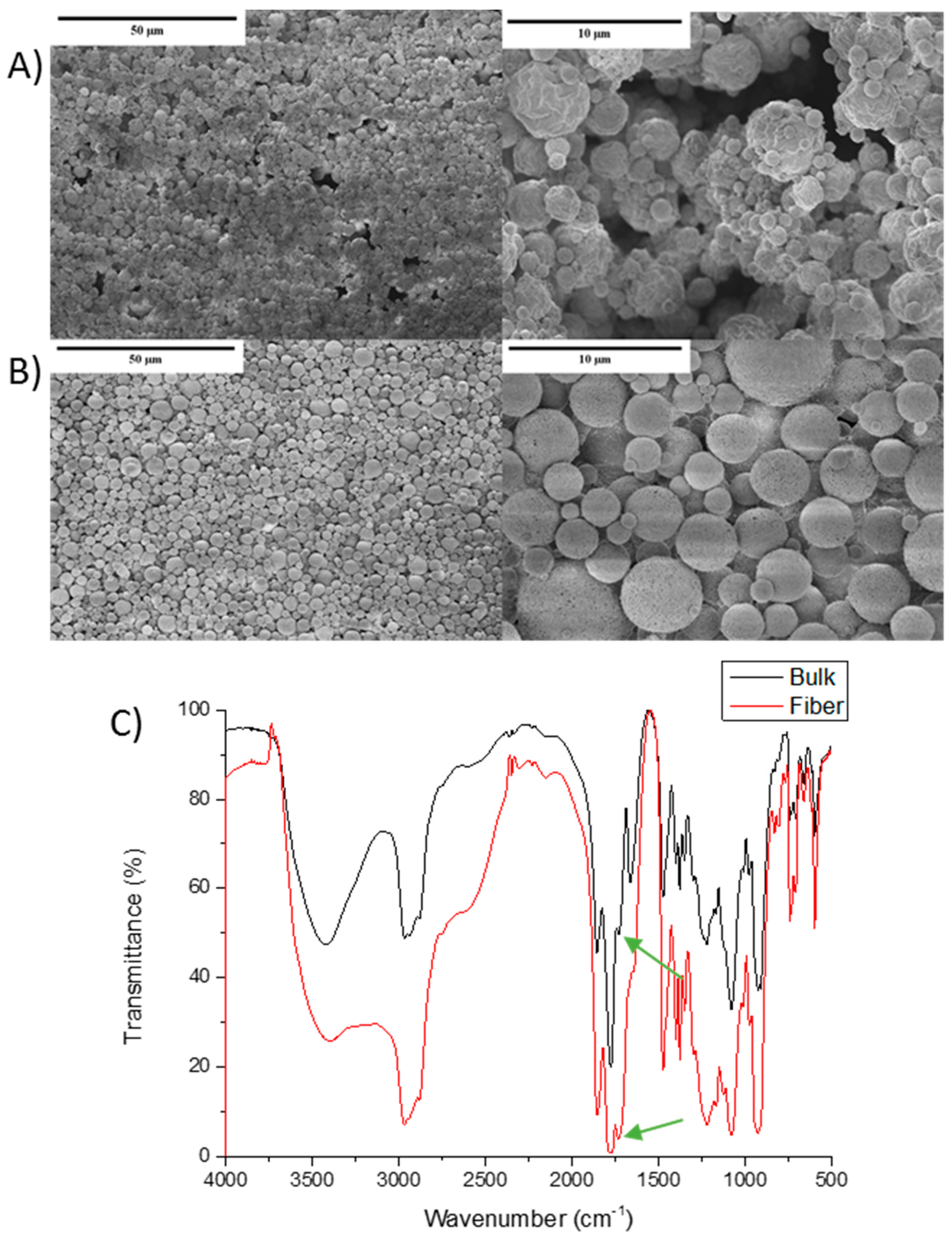
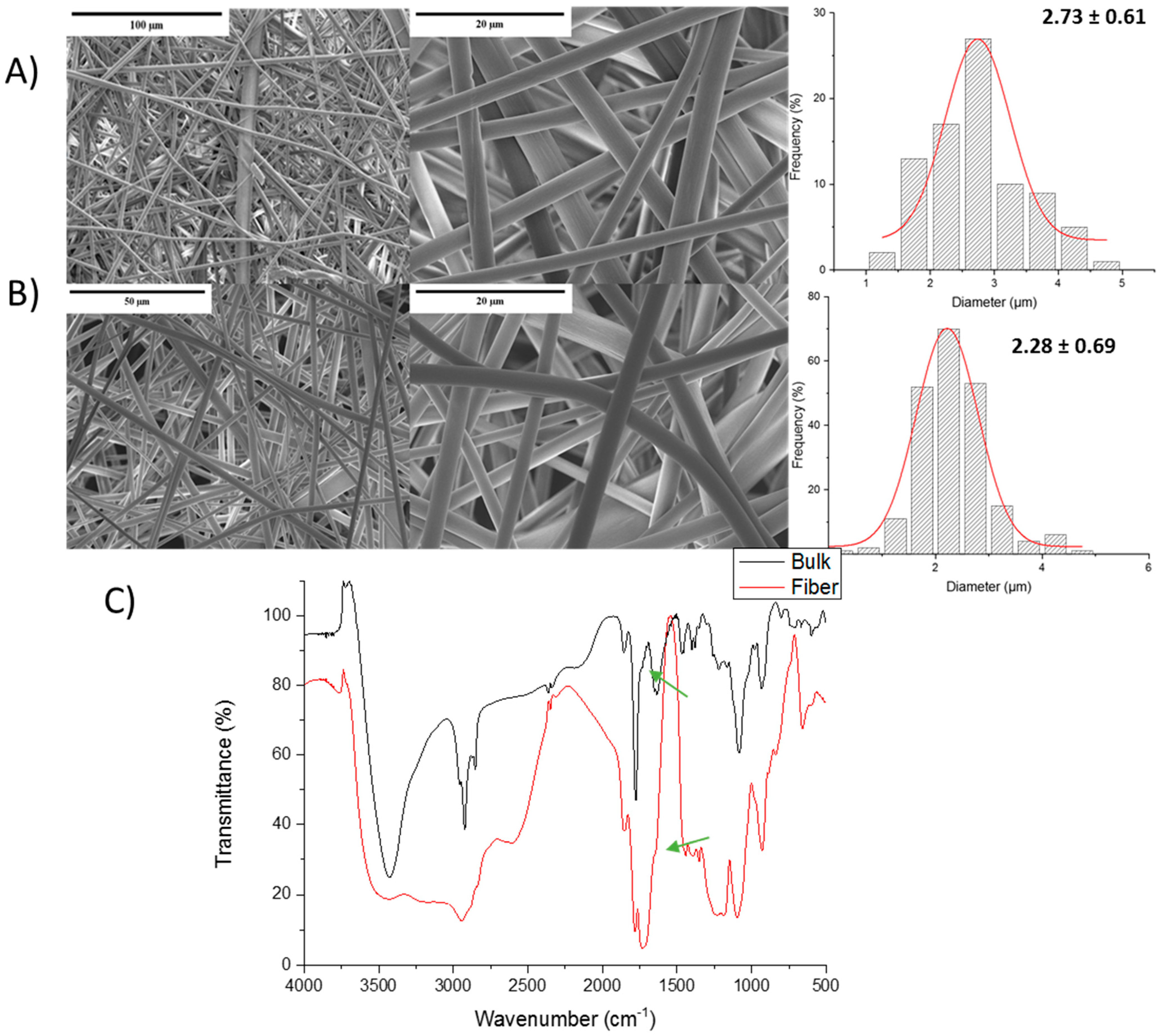
3.5. Maleic Anhydride-Based Hydrogel Fibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moghadam, P.N.; Azaryan, E.; Zeynizade, B. Investigation of poly(styrene-alt-maleic anhydride) copolymer for controlled drug delivery of ceftriaxone antibiotic. J. Macromol. Sci. Part. A Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 47, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, B.; Rameshbabu, A.P.; Ghosh, K.; Jha, P.K.; Jha, R.; Murugesan, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Dhara, S.; Mondal, K.C.; Basak, P.; et al. Impact of styrene maleic anhydride (SMA) based hydrogel on rat fallopian tube as contraceptive implant with selective antimicrobial property. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppas, N.A.; Hilt, J.Z.; Khademhosseini, A.; Langer, R. Hydrogels in Biology and Medicine: From Molecular Principles to Bionanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1869–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peak, C.W.; Wilker, J.J.; Schmidt, G. A review on tough and sticky hydrogels. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 2031–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.M.S.; Mano, J.F. Extremely strong and tough hydrogels as prospective candidates for tissue repair-A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 72, 344–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Han, C.R.; Duan, J.F.; Ma, M.G.; Zhang, X.M.; Xu, F.; Sun, R.C. Synthesis and characterization of mechanically flexible and tough cellulose nanocrystals-polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogels. Cellulose 2013, 20, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q. Tough and Self-Healable Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Repeatable Water Treatment. Polymers 2018, 10, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonoyama, T.; Gong, J.P. Double-network hydrogel and its potential biomedical application: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2015, 229, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, J. Fundamentals of double network hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 3654–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, X.; He, C.; Saricilar, S.; Wang, H. Mechanical properties of tough hydrogels synthesized with a facile simultaneous radiation polymerization and cross-linking method. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 106, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, P.A.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F.; Andrews, G.P.; Zawislak, A.; Price, J.H. Influence of plasticizer type and storage conditions on properties of poly(methyl vinyl ether-co-maleic anhydride) bioadhesive films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, L.; Foston, M.; Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K.; Ragauskas, A.J. Poly(methyl vinyl ether- co -maleic acid)−Polyethylene Glycol Nanocomposites Cross-Linked In Situ with Cellulose Nanowhiskers. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2660–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizondo, E.; Córdoba, A.; Sala, S.; Ventosa, N.; Veciana, J. Preparation of biodegradable poly (methyl vinyl ether-co-maleic anhydride) nanostructured microparticles by precipitation with a compressed antisolvent. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2010, 53, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj Singh, T.R.; McCarron, P.A.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Investigation of swelling and network parameters of poly(ethylene glycol)-crosslinked poly(methyl vinyl ether-co-maleic acid) hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, E.; De Barros, J.M.S.; Fernandez-Gutíerrez, M.; San Roman, J.; Ballamy, L.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Antimicrobial hydrogels based on autoclaved poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(methyl vinyl ether-alt- maleic anhydride) mixtures for wound care applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 55211–55219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, D.K.; Musa, O.M. Application of Maleic Anhydride-Based Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783319294544. [Google Scholar]
- Pompe, T.; Zschoche, S.; Herold, N.; Salchert, K.; Gouzy, M.F.; Sperling, C.; Werner, C. Maleic anhydride copolymers-A versatile platform for molecular biosurface engineering. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khil, M.-S.; Cha, D.-I.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, I.-S.; Bhattarai, N. Electrospun nanofibrous polyurethane membrane as wound dressing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003, 67B, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aklog, Y.F.; Nagae, T.; Izawa, H.; Morimoto, M.; Saimoto, H.; Ifuku, S. Preparation of chitin nanofibers by surface esterification of chitin with maleic anhydride and mechanical treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biber, E.; Gündüz, G.; Mavis, B.; Colak, U. Effects of electrospinning process parameters on nanofibers obtained from Nylon 6 and poly (ethylene-n-butyl acrylate-maleic anhydride) elastomer blends using Johnson SB statistical distribution function. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2010, 99, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, D.; Zhu, X.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Electrospun and photocrosslinked gelatin/dextran–maleic anhydride composite fibers for tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 113, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshosaz, J. Optimization of Poly (methyl vinyl ether-co-maleic acid) Electrospun Nanofibers as a Fast-Dissolving Drug Delivery System. Adv Biomed Res. 2018, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Meng, L.; Hong, Y.; Deng, H.; Bai, G.; Huang, X.; Hao, J.; Tang, B.Z. Poly[(maleic anhydride)-alt-(vinyl acetate)]: A pure oxygenic nonconjugated macromolecule with strong light emission and solvatochromic effect. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoncheva, K.; Lizarraga, E.; Irache, J.M. Pegylated nanoparticles based on poly(methyl vinyl ether-co-maleic anhydride): Preparation and evaluation of their bioadhesive properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 24, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, E.; Choo, E.S.G.; Tan, C.S.H.; Tang, X.; Sheng, Y.; Xue, J. Multifunctional PEGylated nanoclusters for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5994–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Yang, J.; Cui, Z.; Qin, S.; Qin, Q. The investigation of hydrophilic modification of membrane surface based on the mono-esterification between maleic anhydride and polyethylene glycol: Response surface methodology, reaction kinetics and performance analysis. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 112, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzarasa, G.; Osypova, A.; Consolati, G.; Quasso, F.; Soliveri, G.; Ribera, J.; Schwarze, F. Preparation of a Sepia Melanin and Poly(ethylene-alt-maleic Anhydride) Hybrid Material as an Adsorbent for Water Purification. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Al-Haddad, S.; Al-Rughaib, M.; Salman, M. Evaluation of hydrolyzed poly(isobutylene-alt-maleic anhydride) as a polyelectrolyte draw solution for forward osmosis desalination. Desalination 2016, 394, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaguchi, T.; Seno, M. Detailed mechanism and molecular weight dependence of thermal degradation of polyisobutylene. Polymer 1996, 37, 5607–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Vilas, J.L.; Rodríguez, M.; León, L.M. Thermal behaviour of H-bonded interpolymer complexes based on polymers with acrylamide or lactame groups and poly(acrylic acid): Influence of N-alkyl and α-methyl substitutions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 109, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-rubio, L.; Laza, J.M.; Pérez, L. Polymer–polymer complexes of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) and poly (N, N-diethylacrylamide) with poly (carboxylic acids): A comparative study. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Ikai, T.; Kurokawa, T.; King, D.R.; Gong, J.P. Double network hydrogels based on semi-rigid polyelectrolyte physical networks. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 6347–6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Peng, S.; Yang, C.; Qing, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, C. Covalent modification of graphene oxide by 4,4′-methylenebis(phenyl isocyanate) to enhance corrosion resistance of polystyrene coating. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2019, 297, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simha, N.K.; Carlson, C.S.; Lewis, J.L. Evaluation of fracture toughness of cartilage by micropenetration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirouz, A.; Chung, M.; Kwon, J.; Fortunato, G.; Radacsi, N. 2D and 3D electrospinning technologies for the fabrication of nanofibrous scaffolds for skin tissue engineering: A review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2020, 12, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.R.; Morsi, Y.; Zhu, T.; Ahmad, A.; Xie, X.; Yu, F.; Mo, X. Electrospinning: An emerging technology to construct polymer-based nanofibrous scaffolds for diabetic wound healing. Front. Mater. Sci. 2021, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Ma, X.; Hu, W.; Ren, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T. Effect of RGD content in poly(ethylene glycol)-crosslinked poly(methyl vinyl ether-alt-maleic acid) hydrogels on the expansion of ovarian cancer stem-like cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mira, A.; Mateo, C.R.; Mallavia, R.; Falco, A. Poly(methyl vinyl ether-alt-maleic acid) and ethyl monoester as building polymers for drug-loadable electrospun nanofibers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.; Banthia, A.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol-gelatin hydrogel membranes for biomedical applications. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oktay, B.; Baştürk, E.; Kayaman-Apohan, N.; Kahraman, M.V. Highly porous starch/poly(ethylene-alt-maleic anhydride) composite nanofiber mesh. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 1321–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bettahar, F.; Bekkar, F.; Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Ferahi, M.I.; Meghabar, R.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Ruiz-Rubio, L. Tough Hydrogels Based on Maleic Anhydride, Bulk Properties Study and Microfiber Formation by Electrospinning. Polymers 2021, 13, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060972
Bettahar F, Bekkar F, Pérez-Álvarez L, Ferahi MI, Meghabar R, Vilas-Vilela JL, Ruiz-Rubio L. Tough Hydrogels Based on Maleic Anhydride, Bulk Properties Study and Microfiber Formation by Electrospinning. Polymers. 2021; 13(6):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060972
Chicago/Turabian StyleBettahar, Faiza, Fadila Bekkar, Leyre Pérez-Álvarez, Mohammed Issam Ferahi, Rachid Meghabar, José Luis Vilas-Vilela, and Leire Ruiz-Rubio. 2021. "Tough Hydrogels Based on Maleic Anhydride, Bulk Properties Study and Microfiber Formation by Electrospinning" Polymers 13, no. 6: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060972
APA StyleBettahar, F., Bekkar, F., Pérez-Álvarez, L., Ferahi, M. I., Meghabar, R., Vilas-Vilela, J. L., & Ruiz-Rubio, L. (2021). Tough Hydrogels Based on Maleic Anhydride, Bulk Properties Study and Microfiber Formation by Electrospinning. Polymers, 13(6), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060972