Determination of Temperature-Dependent Coefficients of Viscosity and Surface Tension of Tamarind Seeds (Tamarindus indica L.) Polymer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Purification of Tamarind Seed Polymer
2.2. Temperature-Dependent Characterization of Tamarind Seed Polymer
3. Results and Discussion
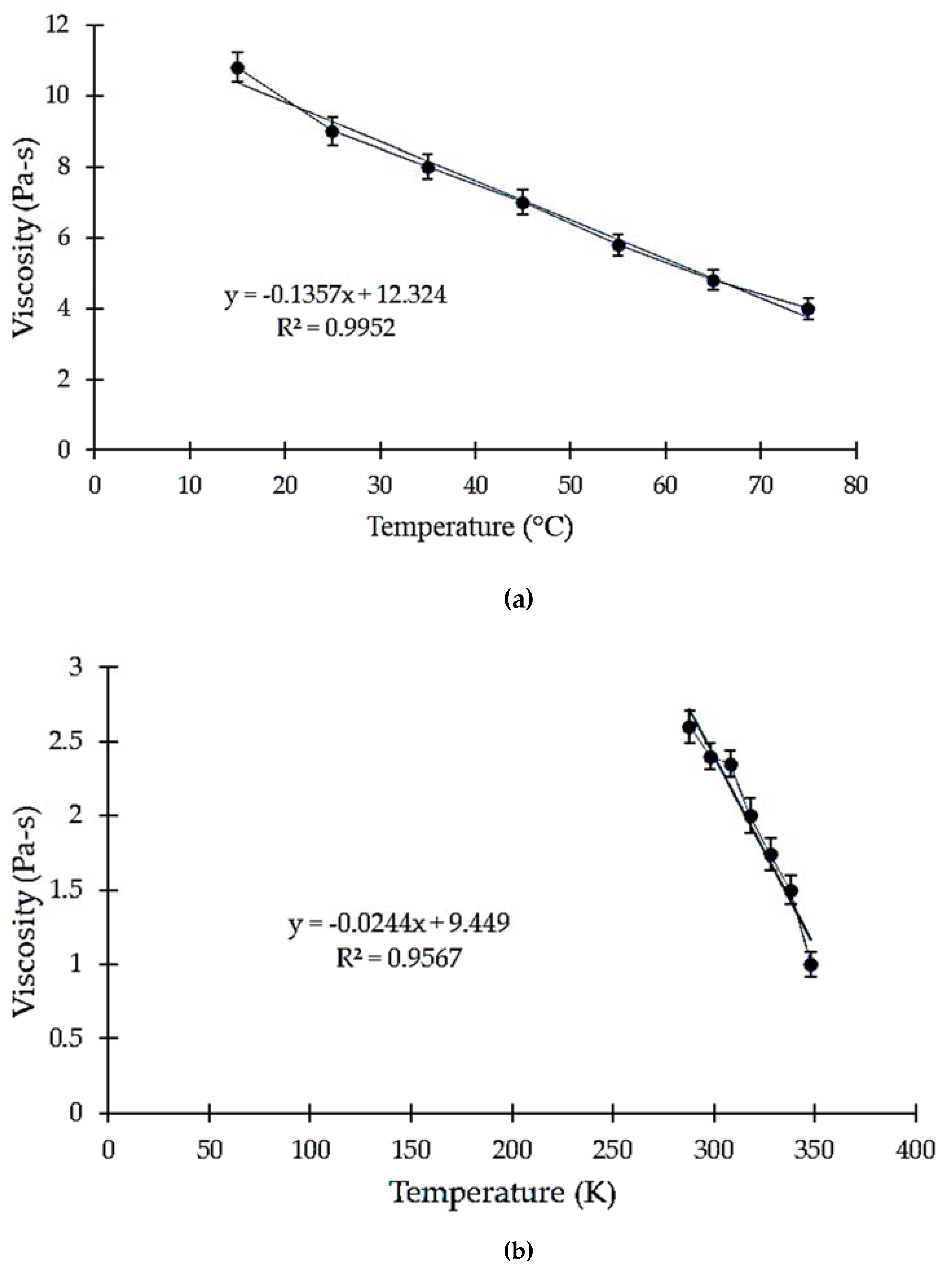
3.1. Effect of Temperature on Viscosity
3.2. Effect of Temperature on Surface Tension
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alonso-Sande, M.; Teijeiro, D.; Remunan-Lopez, C.; Alonso, M.J. Glucomannan a promising polysaccharide for biopharmaceutical purposes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satturwar, P.M.; Fulzele, S.V.; Dorle, A.K. Biodegradation and in vivo biocompatibility of rosin: A natural film-forming polymer. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2003, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmen Chifiriuc, M.; Mihai Grumezescu, A.; Grumezescu, V.; Bezirtzoglou, E.; Lazar, V.; Bolocan, A. Biomedical applications of natural polymers for drug delivery. Curr. Org. Chem. 2014, 18, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.; Zahedi, P.; Allen, C.J.; Piquette-Miller, M. Polymeric drug delivery systems for localized cancer chemotherapy. Drug Deliv. 2010, 17, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saettone, M.F.; Burgalassi, S.; Giannaccini, B.; Boldrini, E.; Bianchini, P.; Luciani, G. Ophthalmic Solutions Viscosified with Tamarind Seed Polysaccharide. U.S. Patent 6,056,950 A, 4 February 1997. [Google Scholar]
- El-Siddig, K.E.; Gunasena, H.P.M.; Prasad, B.A.; Pushpakumara, D.K.; Ramana, K.V.R.; Vijayanand, P. Tamarind: Tamarindus Indica; Southampton Centre for Underutilised Crops: Southampton, UK, 2006; pp. 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, R.A.; Martin, S.; Santos, G.L.; Valenga, F.; Buckeridge, M.S.; Reicher, F. Physico-chemical properties of seed xyloglucans from different sources. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Malviya, R.; Sharma, P.K. Extraction and characterization of tamarind seed polysaccharide as a pharmaceutical excipient. Pharmacogn. J. 2011, 3, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, R.; Srivastava, P.; Bansal, M.; Sharma, P.K. Formulation, evaluation and comparison of sustained release matrix tablets of diclofenac sodium using tamarind gum as release modifier. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2010, 3, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glicksman, M. Tamarind seed gum. In Food Hydrocoll; Glicksman, M., Ed.; CRC Press Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 191–202. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, P.; Malviya, R.; Gupta, S.; Sharma, P.K. Evaluation of various natural gums as release modifiers in tablet formulations. Phcog. J. 2010, 2, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.G. The Structure and Rheology of Complex Fluids; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rouillard, E.E.A. A Study of Boiling Parameters under Conditions of Laminar Non-Newtonian Flow with Particular Reference to Massecuite Boiling. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Natal, Durban, South Africa, October 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hapanowicz, J. Proposition of non-standard method useful for viscosity measurements of unstable two-phase systems coupled with examples of its application. Measurement 2020, 164, 108113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, R.S.; Peppas, N.A. Present and future applications of biomaterials in controlled drug delivery systems. Biomaterials. 1981, 2, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelardi, E.; Tavanti, A.; Celandroni, F.; Lupetti, A.; Blandizzi, C.; Boldrini, E.; Campa, M.; Senesi, S. Effect of a novel mucoadhesive polysaccharide obtained from tamarind seeds on the intraocular penetration of gentamicin and ofloxacin in rabbits. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, G. On the effect of the internal friction of fluids on the motion of pendulums. Trans. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1851, 8, 1–83. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A.K.; Bishnoi, R.S.; Kumar, M.; Fenin, V.; Jain, C.P. Applications of tamarind seeds polysaccharide-based copolymers in controlled drug delivery: An overview. Asian J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 4, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, R.; Sharma, P.K.; Dubey, S.K. Characterization of neem (Azadirachita indica) gum exudates using analytical tools and pharmaceutical approaches. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 15, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, N.; Malviya, R.; Sharma, P.K. Pharmaceutical applications and formulation based patents of Tamarindus indica seed polysaccharide and their modified derivatives. Adv. Biol. Res. 2014, 8, 274–281. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.; Bansal, J.; Kumar, N.; Malviya, R.; Sharma, P.K. Isolation and characterization studies of mucilage obtained from Trigonella foenum greacum l. seed and Tamarindus indica polysaccharide as a pharmaceutical excipient. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2014, 4, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawananorasest, K.; Saengtongdee, P.; Kaemchantuek, P. Extraction and characterization of tamarind (Tamarind indica L.) seed polysaccharides (TSP) from three difference sources. Molecules 2016, 21, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anema, S.G.; Lowe, E.K.; Li, Y. Effect of pH on the viscosity of heated reconstituted skim milk. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Ruths, M.; Israelachvili, J.N. Surface forces and nanorheology of molecularly thin films. In Nanotribology and Nanomechanics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 457–518. [Google Scholar]
- Malviya, R.; Sharma, P.K.; Dubey, S.K. Kheri (Acacia chundra, family: Mimosaceae) gum: Characterization using analytical, mathematical and pharmaceutical approaches. Polim. Med. 2017, 47, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, R.C.M.; Rodrigues, J.F. Composition and rheological properties of cashew tree gum, the exudates polysaccharide from Anacardium occidentale. Carbohydr. Polym. 1995, 26, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.G.; Rodrigues, J.F.; De Paula, R.C.M. Structure-property relationships in food biopolymer gels and solutions. Polimeros 1998, 2, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.R.R. Melt rheology of ethylene propylene diene rubber modified with propylene phosphorylated cashew nut shell liquid prepolymer. Iran. Polym. J. 2003, 12, 305–313. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, M.; Shafique, M.; Aggarwal, B.R.; Aeooqui, M.F. Density, viscosity and activation parameters of viscous flow for cetrimide in ethanol+water system at 301.5 K. Rasayan. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, S.V.; Oommen, Z.; Thomas, S. Melt elasticity and flow activation energy of nylon 6/polystyrene blends. Mater. Lett. 2002, 57, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameh, P.O. Physicochemical properties and rheological behaviour of Ficus glumosa gum in aqueous solution. Afr. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 7, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Eddy, N.O.; Udofia, I.; Uzairu, A.; Ongenyi, A.O.; Obadimu, C. Physiochemical, spectroscopic and rheological studies on Eucalyptus citriodora (ec) gum. J. Polym. Biopolym. Phys. Chem. 2014, 2, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, I.L.; Kartz, M. Viscosities and thermodynamics of various flows of some binary mixtures at different temperatures. Solut. Chem. 1990, 19, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, F.; Kashaninejad, M. Kinetics and thermodynamics of gum extraction from wild sage seed. Int. J. Food Eng. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruah, A.K.; Nath, L.K. Extraction, purification and physicochemical evaluation of mucilage of Chrysophyllum lanceolatum (blume) dc fruits: An investigation for bioadhesive property. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 8, 282–288. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, F.; Kashaninejad, M.; Tadayyon, A.; Arabameri, F. Modeling of extraction process of crude polysaccharides from basil seeds (Ocimum basilicum L.) as affected by process variables. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 5220–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, N.O.; Ameh, P.O.; Gimba, C.E.; Ebenso, E.E. Rheological modeling and characterization of Ficus platyphylla gum exudates. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, N. Note on the history of the reynolds number. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1990, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Tian, Y.; Wang, L.M. Glass transition and mixing thermodynamics of a binary eutectic system. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 3586–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjunath, M.; Gowda, D.V.; Kumar, P.; Srivastava, A.; Osmani, R.A.; Shinde, C.G. Guar gum and its pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2016, 8, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papon, P.; Leblond, J.; Meijer, P.H. Physics of Phase Transitions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 185–209. [Google Scholar]
- De Paula, R.C.M.; Santana, S.A.; Rodrigues, J.F. Composition and rheological properties of Albizia lebbeck gum exudate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 44, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, C.A.K.; Kumar, K.J. Formulation and optimization of pH sensitive drug releasing O/W emulsions using Albizia lebbeck L. seed polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wientjes, R.H.; Duits, M.H.; Jongschaap, R.J.; Mellema, J. Linear rheology of guar gum solutions. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 9594–9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| S.No. | Parameters | Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Activation energy | 20.46 ± 1.06 kJ/mol |
| 2. 3. 4. 5. | Change in entropy Change in enthalpy Entropy of fusion Gibb’s free energy | 23.66 ± 0.97 kJ/mol 0.10 ± 0.01 kJ/mol 0.86 ± 0.03 kJ mol−1 K−1 55.46 ± 1.69 kJ/mole |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malviya, R.; Jha, S.; Fuloria, N.K.; Subramaniyan, V.; Chakravarthi, S.; Sathasivam, K.; Kumari, U.; Meenakshi, D.U.; Porwal, O.; Sharma, A.; et al. Determination of Temperature-Dependent Coefficients of Viscosity and Surface Tension of Tamarind Seeds (Tamarindus indica L.) Polymer. Polymers 2021, 13, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040610
Malviya R, Jha S, Fuloria NK, Subramaniyan V, Chakravarthi S, Sathasivam K, Kumari U, Meenakshi DU, Porwal O, Sharma A, et al. Determination of Temperature-Dependent Coefficients of Viscosity and Surface Tension of Tamarind Seeds (Tamarindus indica L.) Polymer. Polymers. 2021; 13(4):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040610
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalviya, Rishabha, Sheetal Jha, Neeraj Kumar Fuloria, Vetriselvan Subramaniyan, Srikumar Chakravarthi, Kathiresan Sathasivam, Usha Kumari, Dhanalekshmi Unnikrishnan Meenakshi, Omji Porwal, Akanksha Sharma, and et al. 2021. "Determination of Temperature-Dependent Coefficients of Viscosity and Surface Tension of Tamarind Seeds (Tamarindus indica L.) Polymer" Polymers 13, no. 4: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040610
APA StyleMalviya, R., Jha, S., Fuloria, N. K., Subramaniyan, V., Chakravarthi, S., Sathasivam, K., Kumari, U., Meenakshi, D. U., Porwal, O., Sharma, A., Kumar, D. H., & Fuloria, S. (2021). Determination of Temperature-Dependent Coefficients of Viscosity and Surface Tension of Tamarind Seeds (Tamarindus indica L.) Polymer. Polymers, 13(4), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040610








