Enhancing the Antifungal Activity of Griseofulvin by Incorporation a Green Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Influence of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration on Germination and Inhibitory Concentration of Compounds Required for 50% Inhibition of Germinated Candida Strains
2.5. Evaluation of Anti-Biofilm Activity
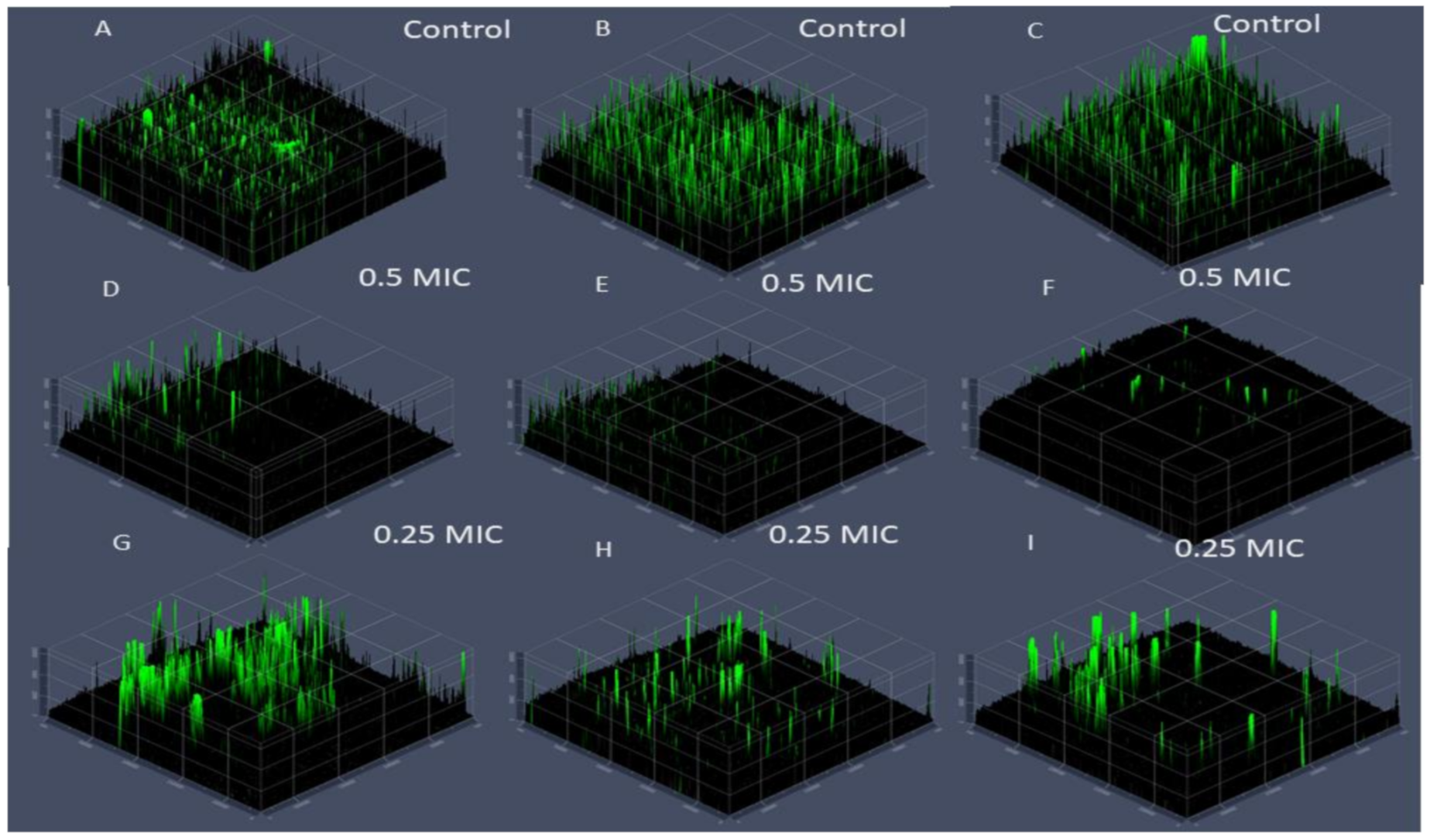
2.6. Visualization of Biofilm Inhibition by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
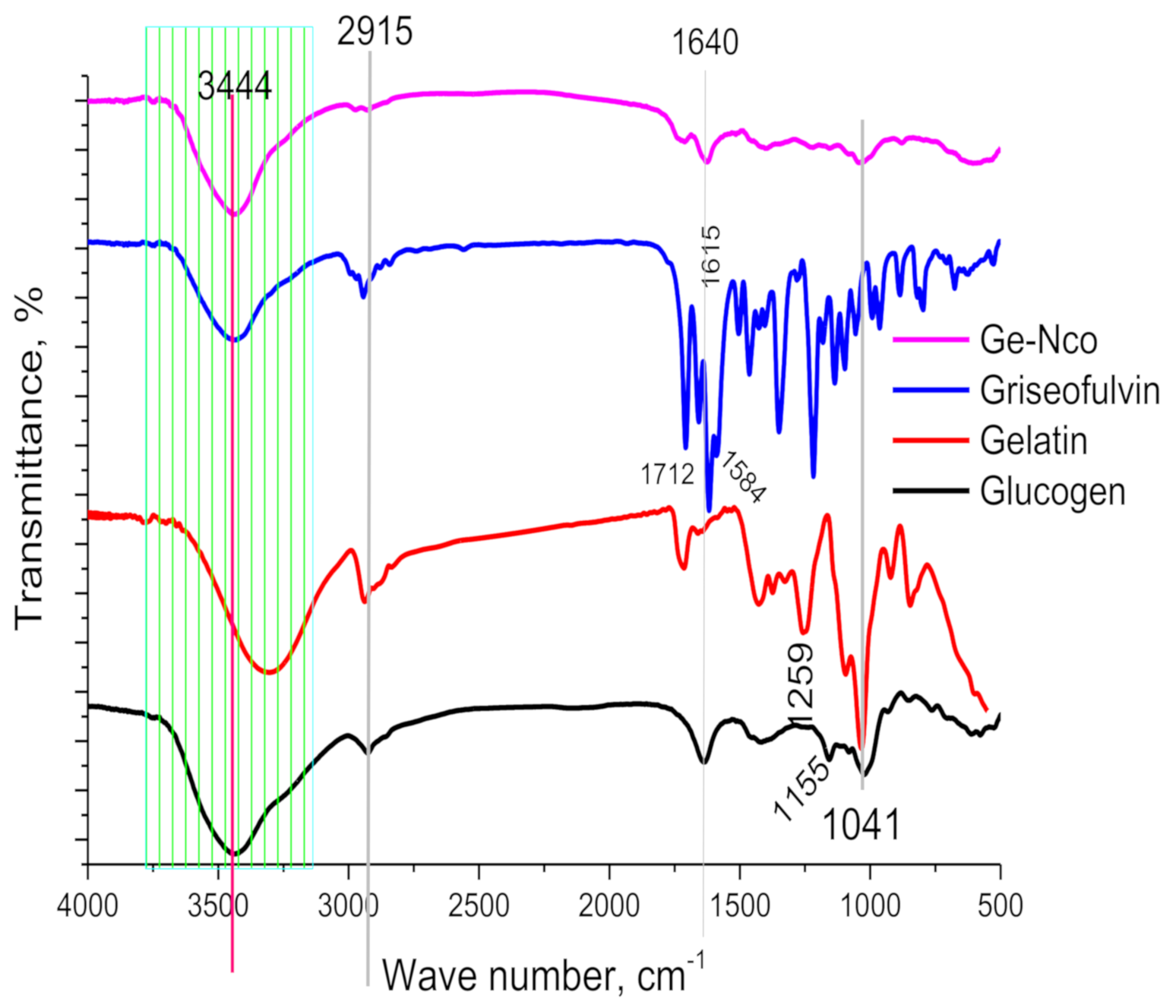
3.1.1. FT-IR
3.1.2. Crystallography
3.1.3. Topography Study
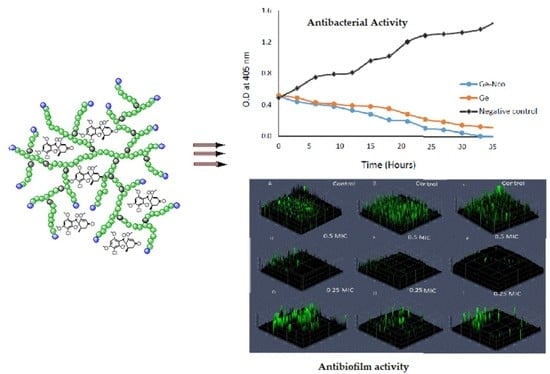
3.2. Anticandidal Susceptibility Testing
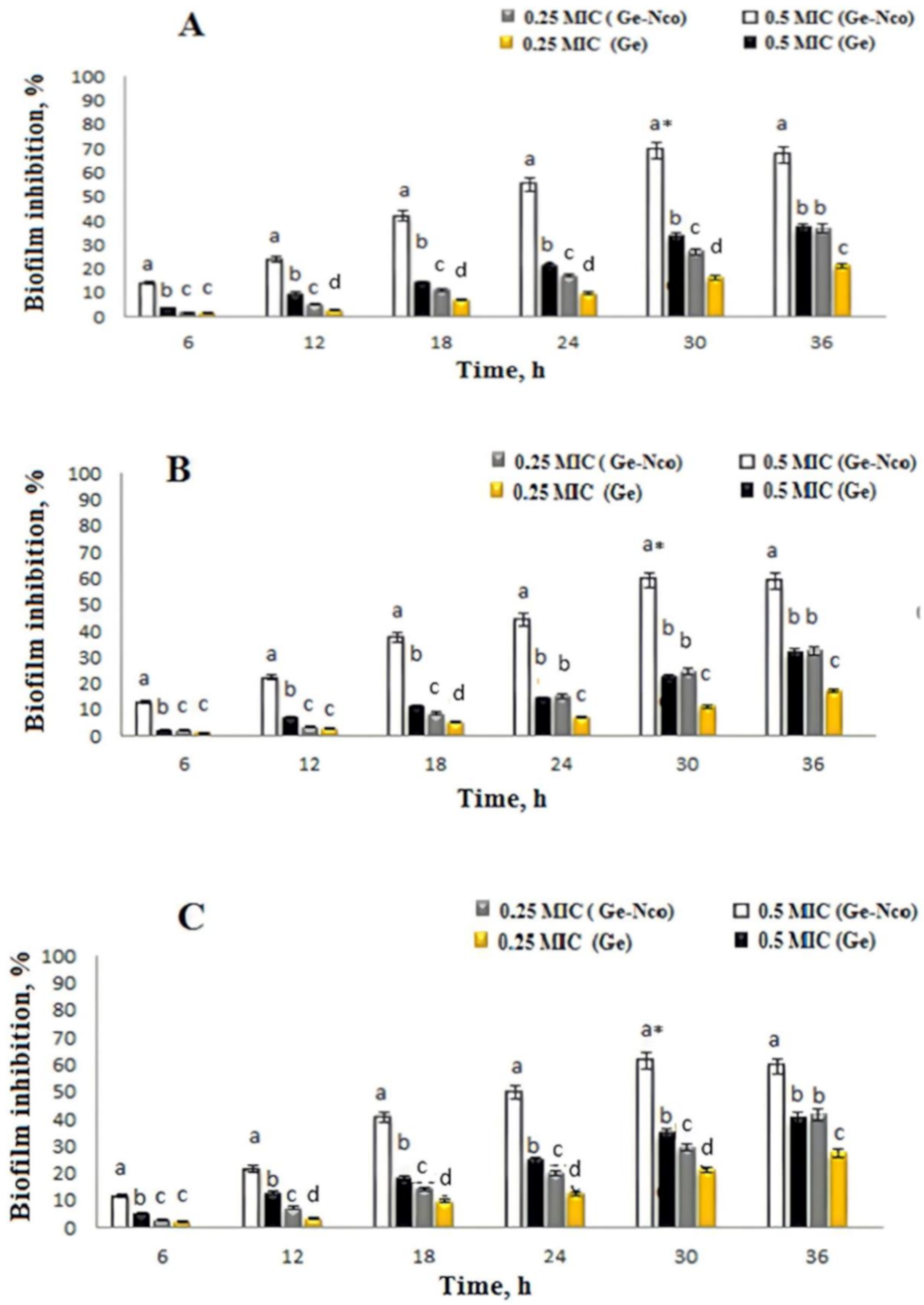
3.3. Inhibition of Fungal Biofilm by Green Nanocomposite-Based Biopolymers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, M.; Lass-Flörl, C. Changing epidemiology of systemic fungal infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Elghait, M.; Hasanin, M.; Hashem, A.H.; Salem, S.S. Ecofriendly novel synthesis of tertiary composite based on cellulose and myco-synthesized selenium nanoparticles: Characterization, antibiofilm and biocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucci, M.; Engelhardt, M.; Hamed, K.J.M. Mucormycosis in South America: A review of 143 reported cases. Mycoses 2019, 62, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, G.M. The Role of Bacterial Biofilm in Antibiotic Resistance and Food Contamination. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1705814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, E.; Krämer, R. Responses of microorganisms to osmotic stress. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adnan, M.; Patel, M.; Deshpande, S.; Alreshidi, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Reddy, M.N.; Emira, N.; De Feo, V. Effect of Adiantum philippense Extract on Biofilm Formation, Adhesion With Its Antibacterial Activities Against Foodborne Pathogens, and Characterization of Bioactive Metabolites: An in vitro-in silico Approach. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, M.; Ansari, M.A.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Ali, S.G.; Khan, H.M.; Almatroudi, A.; Siddiqui, M.I. Anticandidal activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles: Effect on growth, cell morphology, and key virulence attributes of Candida species. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndoricyimpaye, E.L.; Obed, T.; Claude, H.J.; d’Amour, M.J.; Denyse, N.; Reverien, R. Candida albicans infection among HIV positive and HIV negative women-Case study at Butare University Teaching Hospital (CHUB), Southern province of Rwanda. East Afr. Sci. 2020, 2, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraof, M.; Ibrahim, S.; Selim, M.A.; Hasanin, M. Immobilization of L-methionine γ-lyase on different cellulosicmaterialsand its potential application in green-selective synthesis of volatile sulfur compounds. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanin, M.S.; Moustafa, G.O. New potential green, bioactive and antimicrobial nanocomposites based on cellulose and amino acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.; Hasanin, M.; Hesemann, P. Synthesis and antimicrobial properties of new chitosan derivatives containing guanidinium groups. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraof, M.; Hasanin, M.S.; Farag, M.M.; Ahmed, H.Y. Green synthesis of bacterial cellulose/bioactive glass nanocomposites: Effect of glass nanoparticles on cellulose yield, biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabeldine, A.; Hasanin, M. Green synthesis of hydrolyzed starch–chitosan nano-composite as drug delivery system to gram negative bacteria. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 12, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadava, D.; Hillis, D.M.; Heller, H.C.; Berenbaum, M. Life: The Science of Biology, 9th ed.; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, S.; Elsayed, H.; Hasanin, M. Biodegradable, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Biofilm for Active Packaging Based on Extracted Gelatin and Lignocelluloses Biowastes. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 29, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Toxicology Program. National Toxicology Program Chemical Repository Database; Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health (NTP) USA: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Pulit-Prociak, J.; Staroń, A.; Staroń, P.; Chmielowiec-Korzeniowska, A.; Drabik, A.; Tymczyna, L.; Banach, M. Preparation and of PVA-based compositions with embedded silver, copper and zinc oxide nanoparticles and assessment of their antibacterial properties. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, Z.; Ghosh, R. Effect of zinc oxide addition on antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of hydroxyapatite: A potential nanocomposite for biomedical applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 21, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdiero, E.; Di Onofrio, V.; Maione, A.; Gambino, E.; Gesuele, R.; Menale, B.; Ciaravolo, M.; Carraturo, F.; Guida, M. Allium ursinum and Allium oschaninii against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Candida albicans Mono- and Polymicrobic Biofilms in In Vitro Static and Dynamic Models. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofiño-Rivera, A.; Ortega-Cuadros, M.; Galvis-Pareja, D.; Jiménez-Rios, H.; Merini, L.J.; Martínez-Pabón, M.C. Effect of Lippia alba and Cymbopogon citratus essential oils on biofilms of Streptococcus mutans and cytotoxicity in CHO cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.P.; Bui, C.K.; Nett, J.E.; Hartooni, N.; Mui, M.C.; Andes, D.R.; Nobile, C.J.; Johnson, A.D. An expanded regulatory network temporally controls C andida albicans biofilm formation. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 96, 1226–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehabeldine, A.M.; Ashour, R.M.; Okba, M.M.; Saber, F.R. Callistemon citrinus bioactive metabolites as new inhibitors of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 254, 112669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psaltis, A.J.; Ha, K.R.; Beule, A.G.; Tan, L.W.; Wormald, P.-J. Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy Evidence of Biofilms in Patients With Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Mal, D.; Singh, R.P. Synthesis, characterization and flocculation characteristics of cationic glycogen: A novel polymeric flocculant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 289, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanin, M.; El-Henawy, A.; Eisa, W.H.; El-Saied, H.; Sameeh, M. Nano-amino acid cellulose derivatives: Eco-synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachurek, I.; Pielichowski, K. Preparation and thermal characterization of poly (ethylene oxide)/griseofulvin solid dispersions for biomedical applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanaraju, M.D.; Kumaran, K.S.; Baskaran, T.; Moorthy, M.S.R. Enhancement of Bioavailability of Griseofulvin by Its Complexation with β-Cyclodextrin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1998, 24, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkordy, A.A.; Essa, E.A.; Dhuppad, S.; Jammigumpula, P. Liquisolid technique to enhance and to sustain griseofulvin dissolution: Effect of choice of non-volatile liquid vehicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 434, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božanić, D.K.; Dimitrijević-Branković, S.; Bibić, N.; Luyt, A.S.; Djoković, V. Silver nanoparticles encapsulated in glycogen biopolymer: Morphology, optical and antimicrobial properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izawa, H.; Nawaji, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Kadokawa, J.-i. Preparation of Glycogen-Based Polysaccharide Materials by Phosphorylase-Catalyzed Chain Elongation of Glycogen. Macromol. Biosci. 2009, 9, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Teng, X.; Li, G.; Rhim, J.-W. Preparation, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of gelatin/ZnO nanocomposite films. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.; Banthia, A.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol-gelatin hydrogel membranes for biomedical applications. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, E142–E146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Kulkarni, R.; Behme, R.J.; Kotiyan, P.N. Effect of the melt granulation technique on the dissolution characteristics of griseofulvin. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 329, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Guo, P.; Duan, J.; Cheng, Q.; Li, H. Comparative crystal structure determination of griseofulvin: Powder X-ray diffraction versus single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 3867–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahieu, A.; Willart, J.-F.; Guerain, M.; Derollez, P.; Danéde, F.; Descamps, M. Structure determination of phase II of the antifungal drug griseofulvin by powder X-ray diffraction. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2018, 74, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardi, J.; Scorzoni, L.; Bernardi, T.; Fusco-Almeida, A.; Giannini, M.M. Candida species: Current epidemiology, pathogenicity, biofilm formation, natural antifungal products and new therapeutic options. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megri, Y.; Arastehfar, A.; Boekhout, T.; Daneshnia, F.; Hörtnagl, C.; Sartori, B.; Hafez, A.; Pan, W.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Hamrioui, B. Candida tropicalis is the most prevalent yeast species causing candidemia in Algeria: The urgent need for antifungal stewardship and infection control measures. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.-X.; Zhou, C.-H. Recent Developments in Azole Compounds as Antibacterial and Antifungal Agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1963–2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, C.G.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. Candidiasis drug discovery and development: New approaches targeting virulence for discovering and identifying new drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| C. parapsilosis | C. tropicalis | C. albicans | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC | IC50 | MIC | IC50 | MIC | IC50 | |
| Griseofulvin | 49.9 ± 0.3 | 199.6 ± 0.3 | 99.8 ± 0.2 | 199.6 ± 0.2 | 49.92 ± 0.2 | 99.84 ± 0.2 |
| (Ge-Nco) | 6.24 ± 0.2 | 49.8 ± 0.2 | 12.48 ± 0.2 | 49.48 ± 0.2 | 12.48 ± 0.2 | 49.48 ± 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shehabeldine, A.; El-Hamshary, H.; Hasanin, M.; El-Faham, A.; Al-Sahly, M. Enhancing the Antifungal Activity of Griseofulvin by Incorporation a Green Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposite. Polymers 2021, 13, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040542
Shehabeldine A, El-Hamshary H, Hasanin M, El-Faham A, Al-Sahly M. Enhancing the Antifungal Activity of Griseofulvin by Incorporation a Green Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposite. Polymers. 2021; 13(4):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040542
Chicago/Turabian StyleShehabeldine, Amr, Hany El-Hamshary, Mohamed Hasanin, Ayman El-Faham, and Mosaed Al-Sahly. 2021. "Enhancing the Antifungal Activity of Griseofulvin by Incorporation a Green Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposite" Polymers 13, no. 4: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040542
APA StyleShehabeldine, A., El-Hamshary, H., Hasanin, M., El-Faham, A., & Al-Sahly, M. (2021). Enhancing the Antifungal Activity of Griseofulvin by Incorporation a Green Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposite. Polymers, 13(4), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040542