Cerium(III) Nitrate Containing Electrospun Wound Dressing for Mitigating Burn Severity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
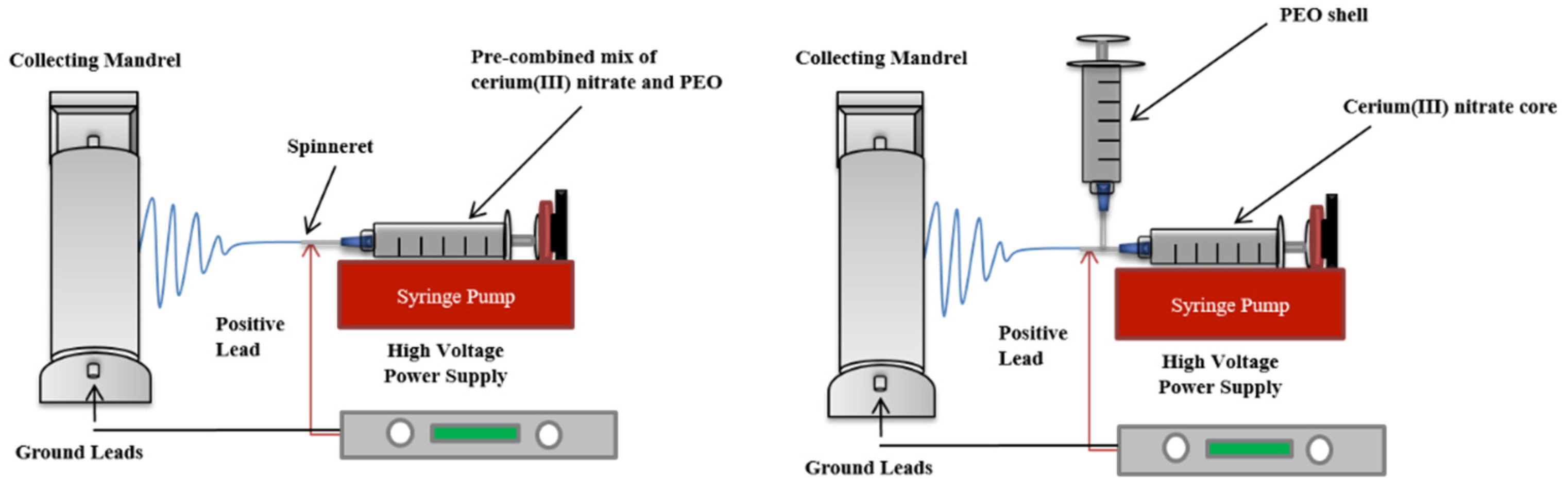
2.2. Preparation of Electrospun Cerium(III) Nitrate Containing Polyethylene Oxide Dressings
2.3. Dressing Characterization
2.4. In Vitro Dressing Degradation and Loading Potential
2.5. Cerium(III) Release Rate
2.6. In Vitro Cell Cytotoxicity
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of PEO/Ce(III) Solutions
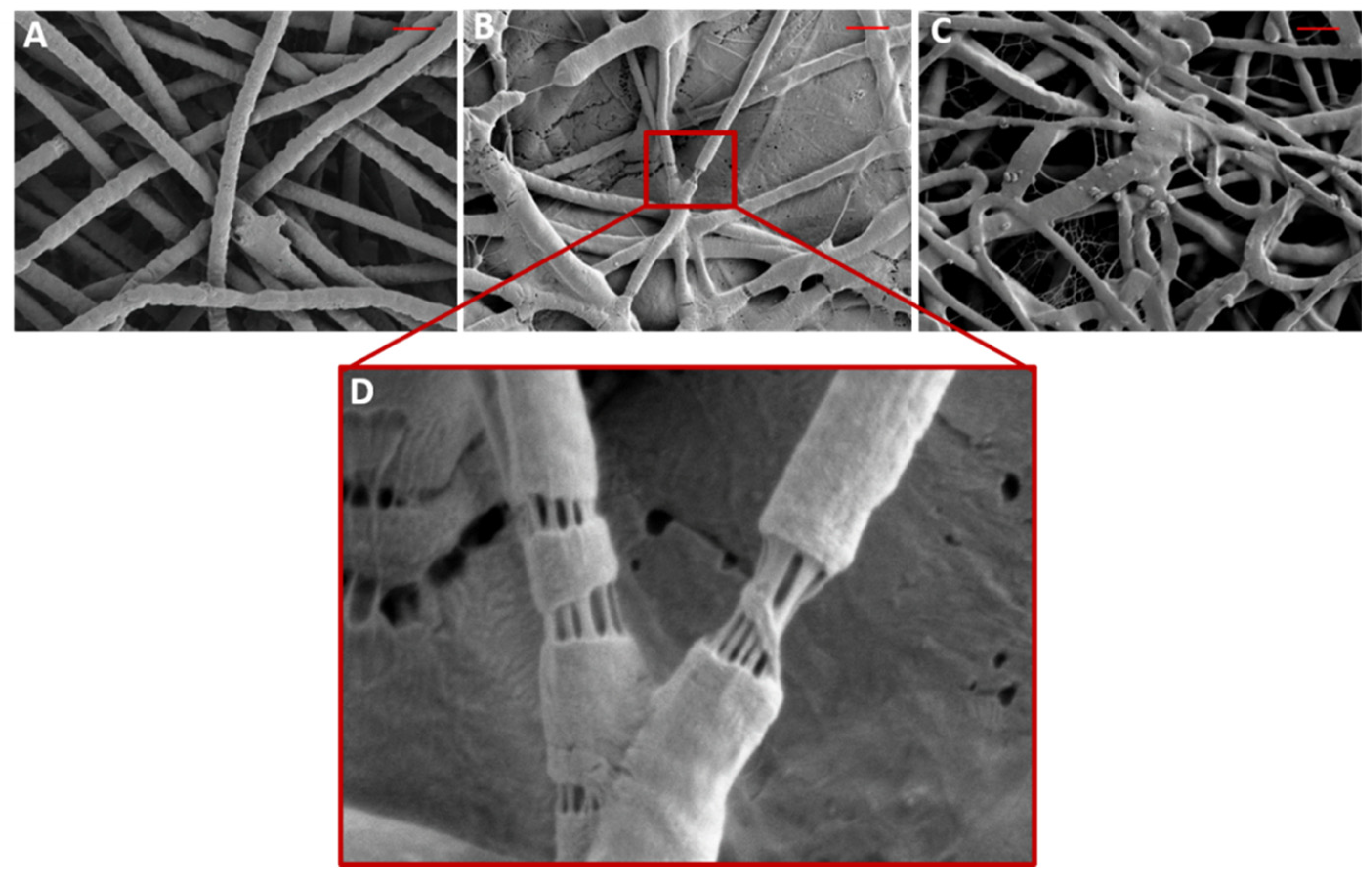
3.2. Morphology and Properties of PEO/Ce(III) Nanofibers
3.3. Dressing Chemical Composition
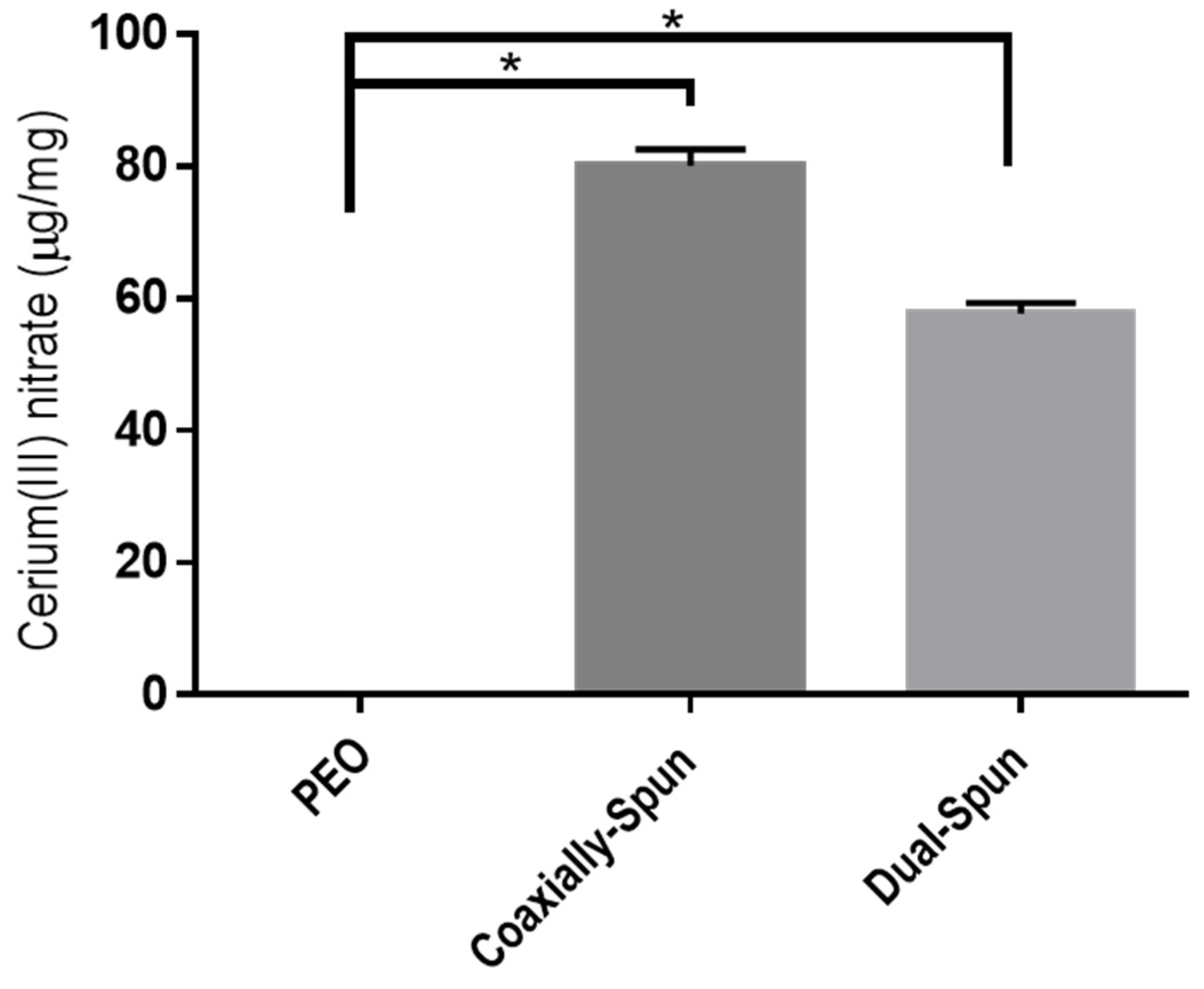
3.4. Cerium(III) Nitrate Loading Potential
3.5. Cerium(III) Release Rate
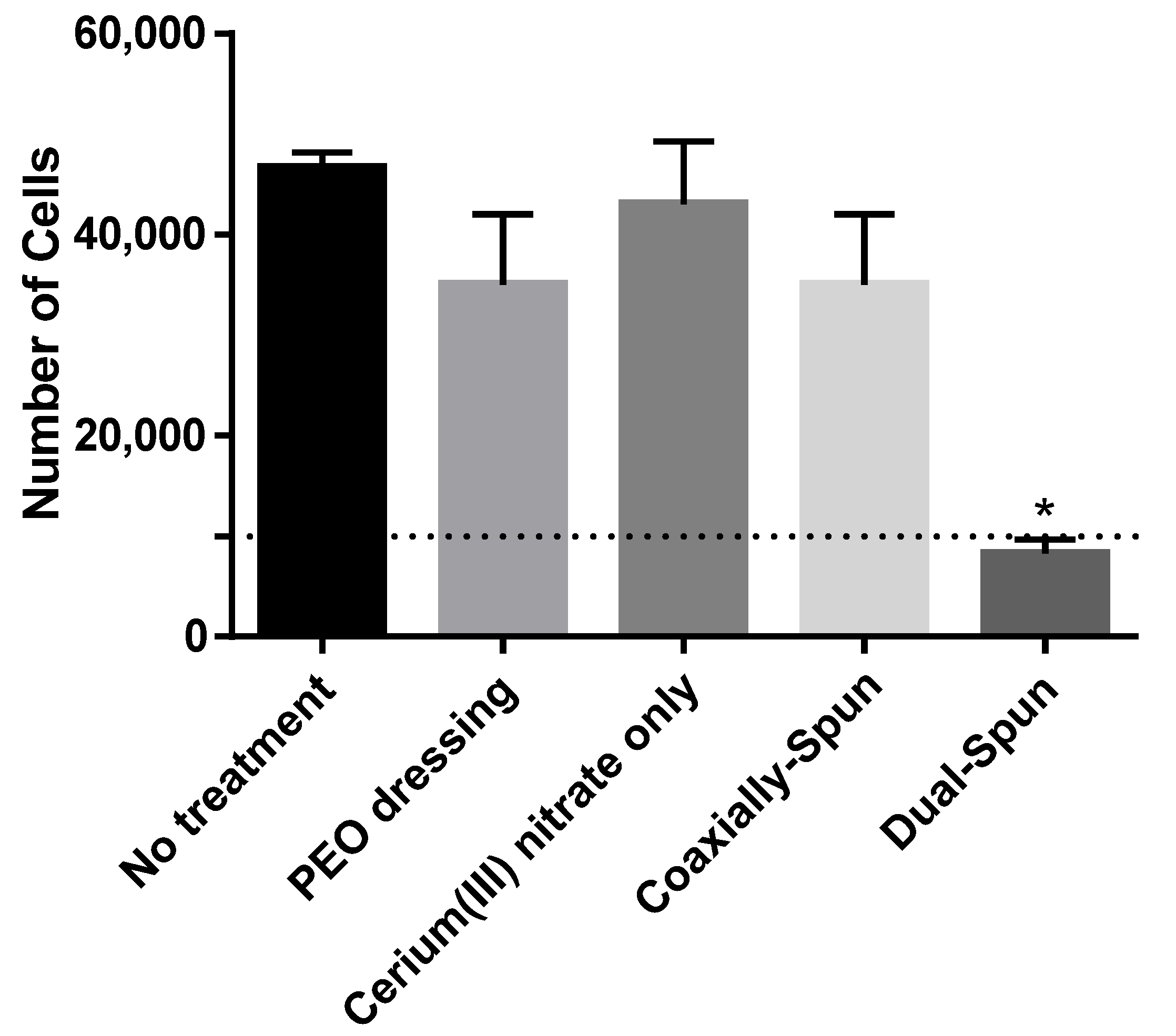
3.6. Viability of Human Dermal Fibroblasts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowan, M.P.; Cancio, L.C.; Elster, E.A.; Burmeister, D.M.; Rose, L.F.; Natesan, S.; Chan, R.K.; Christy, R.J.; Chung, K.K. Burn wound healing and treatment: Review and advancements. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavoni, V.; Gianesello, L.; Paparella, L.; Buoninsegni, L.T.; Barboni, E. Outcome predictors and quality of life of severe burn patients admitted to intensive care unit. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2010, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, R.K.; Aden, J.; Wu, J.; Hale, R.G.; Renz, E.M.; Wolf, S. Operative Utilization Following Severe Combat-Related Burns. J. Burn. Care Res. 2015, 36, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauvar, D.S.; Wolf, S.E.; Wade, C.E.; Cancio, L.C.; Renz, E.M.; Holcomb, J.B. Burns sustained in combat explosions in Operations Iraqi and Enduring Freedom (OIF/OEF explosion burns). Burns 2006, 32, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmauss, D.; Rezaeian, F.; Finck, T.; Machens, H.-G.; Wettstein, R.; Harder, Y. Treatment of Secondary Burn Wound Progression in Contact Burns—A Systematic Review of Experimental Approaches. J. Burn. Care Res. 2015, 36, e176–e189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin-Maghit, M.; Goudable, J.; Dalmas, E.; Steghens, J.P.; Bouchard, C.; Gueugniaud, P.Y.; Petit, P.; Delafosse, B. Time course of oxidative stress after major burns. Intensive Care Med. 2000, 26, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deveci, M.; Eski, M.; Sengezer, M.; Kisa, U. Effects of cerium nitrate bathing and prompt burn wound excision on IL-6 and TNF-α levels in burned rats. Burns 2000, 26, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten-Jaegers, S.M.H.J.; Nieuwenhuis, M.K.; Van Baar, M.E.; Niemeijer, A.S.; Hiddingh, J.; Beerthuizen, G.I.J.M. Epidemiology and Outcome of Patients with Burns Treated with Cerium Nitrate Silversulfadiazine. J. Burn. Care Res. 2017, 38, e432–e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, J.; Heppell, P. Cerium nitrate in the management of burns. Burns 2005, 31, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oen, I.M.M.H.; Van Baar, M.E.; Middelkoop, E.; Nieuwenhuis, M.K. Effectiveness of cerium nitrate–silver sulfadiazine in the treatment of facial burns: A multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 130, 274e–283e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheidegger, D.; Sparkes, B.; Lüscher, N.; Schoenenberger, G.; Allgöwer, M. Survival in major burn injuries treated by one bathing in cerium nitrate. Burns 1992, 18, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Huang, Y.; Tian, N.; Tong, Y.; Yin, R. Preparation and characterization of gelatin/cerium(III) film. J. Rare Earths 2010, 28, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Hasan, A.; Patan, N.K.; Dalvi, Y.B.; Varghese, R.; Antony, A.; Unni, R.N.; Sandhyarani, N.; Al Moustafa, A.-E. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticle Incorporated Electrospun Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Membranes for Diabetic Wound Healing Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.; Velez, A.; Wozniak, K.; Szydlowska, J.; Seal, S. Electron paramagnetic study on radical scavenging properties of ceria nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 442, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkbright, G.; West, T.; Woodward, C. Some spectrofluorimetric applications of the cerium(IV)-cerium(III) system. Anal. Chim. Acta 1966, 36, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, H.F.; Luqman, M.; Khalil, K.A.; Elnakady, Y.A.; Elkader, O.A.; Rady, A.M.; Alharthi, N.H.; Karim, M.R. Fabrication of core-shell structured nanofibers of poly (lactic acid) and poly (vinyl alcohol) by coaxial electrospinning for tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 98, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, B.; Carlson, M.A.; Gombart, A.F.; Reilly, D.A.; Xie, J. Recent advances in electrospun nanofibers for wound healing. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1335–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-F.; Carson, D.; Woodrow, K.A. Current strategies for sustaining drug release from electrospun nanofibers. J. Control. Release 2015, 220, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, M.; Amani-Tehran, M.; Latifi, M.; Mathur, S. Drug release profile in core–shell nanofibrous structures: A study on Peppas equation and artificial neural network modeling. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 113, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.; Kim, H.-W. Core–shell designed scaffolds for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2015, 21, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescignano, N.; Fortunati, E.; Montesano, S.; Emiliani, C.; Kenny, J.M.; Martino, S.; Armentano, I. PVA bio-nanocomposites: A new take-off using cellulose nanocrystals and PLGA nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, C.-H.; Lee, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chen, K.-Y. Novel bilayer wound dressing based on electrospun gelatin/keratin nanofibrous mats for skin wound repair. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G. Surface-functionalized electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Yang, C.; Chen, S.; Li, W.; Lou, J.; Wang, J. A facile approach to prepare shell/core nanofibers for drug controlled release. Mater. Lett. 2015, 150, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredenberg, S.; Wahlgren, M.; Reslow, M.; Axelsson, A. The mechanisms of drug release in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-based drug delivery systems—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Tzezana, R.; Zussman, E.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Venkatraman, S. Optimizing partition-controlled drug release from electrospun core–shell fibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 392, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Choi, S.H.; Yoo, H. Coaxial electrospun nanofibers for treatment of diabetic ulcers with binary release of multiple growth factors. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 5258–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, K.; Chen, W. A facile technique to prepare biodegradable coaxial electrospun nanofibers for controlled release of bioactive agents. J. Control. Release 2005, 108, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, K. Coaxial electrospinning for encapsulation and controlled release of fragile water-soluble bioactive agents. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Ghosh, C.; Hwang, S.-G.; Chanunpanich, N.; Park, J.S. Porous core/sheath composite nanofibers fabricated by coaxial electrospinning as a potential mat for drug release system. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 439, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Chung, O.H.; Park, J.S. Coaxial electrospun poly(lactic acid)/chitosan (core/shell) composite nanofibers and their antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Singh, S.; Das, S.; Kumar, A.; Self, W.T.; Seal, S. A facile synthesis of PLGA encapsulated cerium oxide nanoparticles: Release kinetics and biological activity. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakravan, M.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Ajji, A. A fundamental study of chitosan/PEO electrospinning. Polymer 2011, 52, 4813–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, X.; Xia, Y. Putting Electrospun Nanofibers to Work for Biomedical Research. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 1775–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angammana, C.J.; Jayaram, S.H. Analysis of the Effects of Solution Conductivity on Electrospinning Process and Fiber Morphology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Besenbacher, F. Electrospinning of uniform polystyrene fibers: The effect of solvent conductivity. Polymer 2008, 49, 5336–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

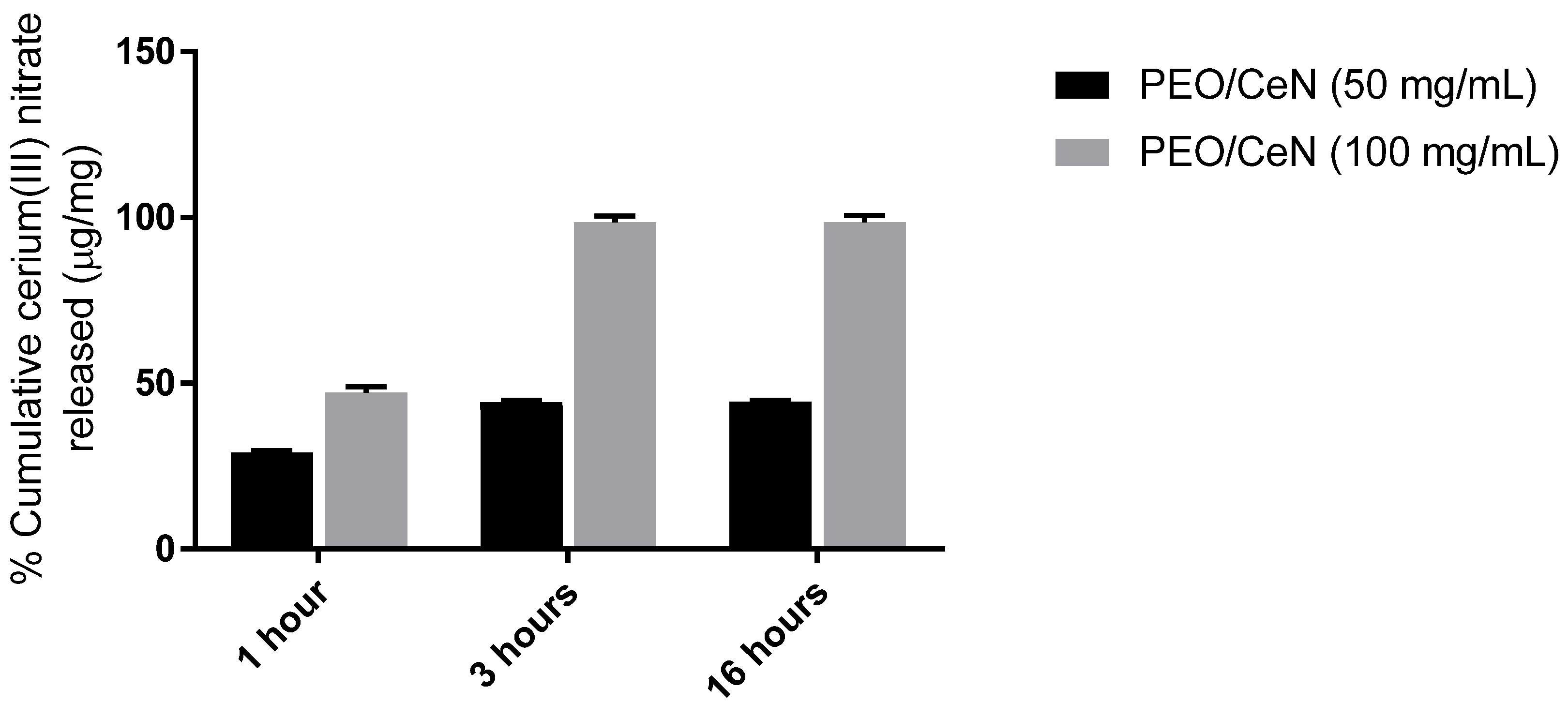
| Sample | Conductivity ± SD (ms/cm) * |
|---|---|
| 5% w/v PEO in 1:1 acetone, DCM | 0.00399 ± 0.000915 |
| 5% w/v Ce(III) nitrate in acetone | 2.12 ± 0.114 |
| 5% w/v PEO in 1:1 acetone, DCM + 5% w/v Ce(III) nitrate in acetone | 0.132 ± 0.00651 |
| Sample | Average Fiber Diameter ± SD (µm) | Average Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PEO, control | 1.80 ± 0.10 * | 56.6 ± 0.5 * |
| Dual-spun PEO/Ce(III) | 1.16 ± 0.21 | 49.0 ± 1.7 |
| Coaxially-spun PEO/Ce(III) | 1.09 ± 0.25 | 46.5 ± 2.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williams, C., III; Chambers-Wilson, R.; Roy, J.; Kowalczewski, C.; Jockheck-Clark, A.R.; Christy, R.; Martinez, L.A. Cerium(III) Nitrate Containing Electrospun Wound Dressing for Mitigating Burn Severity. Polymers 2021, 13, 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183174
Williams C III, Chambers-Wilson R, Roy J, Kowalczewski C, Jockheck-Clark AR, Christy R, Martinez LA. Cerium(III) Nitrate Containing Electrospun Wound Dressing for Mitigating Burn Severity. Polymers. 2021; 13(18):3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183174
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliams, Cortes, III, Ramanda Chambers-Wilson, Jahnabi Roy, Christine Kowalczewski, Angela R. Jockheck-Clark, Robert Christy, and Luis A. Martinez. 2021. "Cerium(III) Nitrate Containing Electrospun Wound Dressing for Mitigating Burn Severity" Polymers 13, no. 18: 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183174
APA StyleWilliams, C., III, Chambers-Wilson, R., Roy, J., Kowalczewski, C., Jockheck-Clark, A. R., Christy, R., & Martinez, L. A. (2021). Cerium(III) Nitrate Containing Electrospun Wound Dressing for Mitigating Burn Severity. Polymers, 13(18), 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183174






